Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for transportation vehicles
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, sourcing reliable transportation vehicles poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you’re operating in Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, or across Europe and South America, the need for versatile, efficient transport solutions is paramount. This comprehensive guide aims to equip businesses with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of purchasing transportation vehicles—ranging from passenger vans and shuttles to specialized cargo solutions.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into various types of transportation vehicles, their applications, and customization options that meet specific business needs. We will also provide insights into supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and the importance of compliance with local regulations. By addressing these critical areas, this resource empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they select the right vehicles to enhance operational efficiency and meet customer demands.
In an era where mobility and convenience are key drivers of success, understanding the global landscape of transportation vehicles will help your business stay ahead of the competition. With tailored insights and actionable strategies, this guide serves as a vital tool for organizations looking to optimize their transportation capabilities and drive growth in diverse markets.
Understanding transportation vehicles Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Passenger Vans | Seats up to 15, customizable configurations, ADA compliant | Corporate shuttles, hotels, tour operators | Pros: Versatile, comfortable; Cons: Limited cargo space |
| Minibuses | Capacity for 15+ passengers, often more compact than buses | Community transport, event shuttles | Pros: Economical, easier to maneuver; Cons: Less capacity than full-size buses |
| Cargo Vans | Designed for goods transport, various sizes and configurations | Delivery services, trades, logistics | Pros: High payload capacity, flexible interiors; Cons: Less passenger comfort |
| Luxury Transport Vans | Premium features, high-end finishes, spacious seating | Executive transport, high-end tourism | Pros: Enhanced comfort and style; Cons: Higher operational costs |
| Non-Emergency Medical Transport (NEMT) | Specialized for medical transport, ADA compliant | Healthcare facilities, senior care | Pros: Essential for patient transport; Cons: Specific regulations and compliance requirements |
What Are the Characteristics of Passenger Vans and Their Suitability for B2B Use?
Passenger vans are designed to comfortably seat up to 15 individuals, making them ideal for corporate shuttles, airport transport, and group outings. These vehicles can be customized with features such as wheelchair lifts and specialized seating arrangements, ensuring compliance with ADA regulations. When considering a purchase, businesses should evaluate their passenger volume needs, budget constraints, and potential for custom modifications to enhance functionality.
How Do Minibuses Differ and What Are Their Key B2B Applications?
Minibuses are compact vehicles that can carry over 15 passengers, making them a practical choice for community transport and event shuttles. They are often more economical than larger buses and easier to maneuver in urban environments. B2B buyers should consider the vehicle’s fuel efficiency, maintenance costs, and the specific needs of their transportation services to determine the best fit for their operations.
What Advantages Do Cargo Vans Offer for Commercial Use?
Cargo vans are specifically designed for transporting goods, featuring spacious interiors and various configurations to accommodate different types of cargo. They are essential for delivery services, trades, and logistics companies, providing high payload capacities and flexibility. When purchasing, businesses should assess the van’s payload limits, fuel efficiency, and the ability to customize the interior for specific cargo needs.
Why Choose Luxury Transport Vans for Executive Travel?
Luxury transport vans are equipped with high-end finishes and amenities, making them suitable for executive transport and high-end tourism. These vehicles provide spacious seating and premium features, enhancing the travel experience for clients. However, B2B buyers must weigh the higher operational costs against the potential for increased client satisfaction and brand reputation when considering this option.
What Are the Essential Features of Non-Emergency Medical Transport Vehicles?
Non-Emergency Medical Transport (NEMT) vehicles are tailored for patient transport, often featuring ADA compliance and specialized equipment for safely moving individuals with medical needs. These vehicles are critical for healthcare facilities and senior care organizations. Buyers should consider the specific regulatory requirements for medical transport, as well as the vehicle’s capacity for both ambulatory and wheelchair-bound passengers, to ensure compliance and safety.
Key Industrial Applications of transportation vehicles
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Transportation Vehicles | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitality | Airport Shuttle Services | Enhances guest experience and operational efficiency | Vehicle capacity, accessibility features, and comfort |
| Healthcare | Non-Emergency Medical Transportation (NEMT) | Facilitates patient mobility and compliance with regulations | ADA compliance, vehicle modifications, and reliability |
| Education | School Transportation Services | Ensures safe and reliable transport for students | Safety features, capacity, and maintenance support |
| Logistics and Delivery | Cargo Transport and Delivery Services | Streamlines supply chain operations and reduces delays | Load capacity, fuel efficiency, and custom configurations |
| Public Sector | Community Transport Services | Improves access to services for underserved populations | Accessibility options, vehicle customization, and cost |
How Are Transportation Vehicles Utilized in the Hospitality Sector?
In the hospitality industry, transportation vehicles such as airport shuttles play a critical role in enhancing guest experience. Hotels and resorts leverage these vehicles to provide seamless transfers for guests arriving or departing from airports. This not only improves operational efficiency but also elevates the overall guest experience, encouraging repeat business. For international B2B buyers, considerations like vehicle capacity, accessibility features for disabled guests, and comfort level are paramount to ensure a positive experience.
What Role Do Transportation Vehicles Play in Healthcare?
Transportation vehicles in healthcare are essential for non-emergency medical transportation (NEMT), facilitating patient mobility to appointments and treatments. These vehicles are specially equipped to accommodate patients with varying mobility needs, ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations. For B2B buyers in this sector, key requirements include ADA compliance, custom modifications for medical equipment, and reliability to prevent delays in patient care. This investment not only supports patient health but also enhances the provider’s reputation.
How Are Transportation Vehicles Implemented in Education?
In the education sector, transportation vehicles are vital for school transportation services, ensuring safe and reliable transport for students. Schools and educational institutions utilize buses and vans to transport students to and from school, as well as for field trips and extracurricular activities. For buyers in this industry, safety features, vehicle capacity, and ongoing maintenance support are crucial factors. A well-managed school transport system not only ensures student safety but also fosters parental trust and satisfaction.
What Are the Applications of Transportation Vehicles in Logistics and Delivery?
In logistics and delivery, transportation vehicles are indispensable for cargo transport, enabling businesses to streamline their supply chain operations. Efficient transport reduces delays and enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring timely delivery of goods. For B2B buyers in this sector, important considerations include load capacity, fuel efficiency, and the ability to customize vehicles based on specific delivery needs. Investing in the right transportation solutions can significantly enhance operational efficiency and lower costs.
How Do Transportation Vehicles Benefit Public Sector Initiatives?
Transportation vehicles in the public sector are crucial for community transport services, improving access to essential services for underserved populations. These vehicles can be tailored to meet the needs of various community groups, including the elderly and disabled. For international buyers in this sector, key considerations include accessibility options, vehicle customization for specific community needs, and cost-effectiveness. By investing in suitable transportation solutions, public agencies can foster inclusivity and support community development initiatives.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘transportation vehicles’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Managing Diverse Passenger Needs in Transportation
The Problem:
B2B buyers in the transportation sector often face the challenge of accommodating a wide range of passenger needs. For instance, companies managing shuttle services for hotels or community centers may need to transport not only regular passengers but also individuals with mobility challenges. This dual requirement can complicate vehicle selection and fleet management, leading to potential service delays and customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution:
To address this issue, B2B buyers should consider investing in versatile transport vehicles that can be easily modified to accommodate various passenger needs. For example, selecting a vehicle like the Ford Transit or Mercedes-Benz Sprinter, which offers options for wheelchair lifts and customizable seating arrangements, can ensure that all passengers are comfortably accommodated. When sourcing these vehicles, it is crucial to engage with manufacturers or dealers who provide upfitting services, enabling buyers to tailor the vehicle to their specific operational demands. Additionally, implementing training programs for drivers on how to assist passengers with disabilities can enhance service quality and promote inclusivity.
Scenario 2: Cost Management and Operational Efficiency
The Problem:
Transportation companies often grapple with the rising costs of fuel, maintenance, and vehicle acquisition. In regions with fluctuating economic conditions, such as parts of Africa and South America, managing these expenses while maintaining a reliable service can feel overwhelming. Companies may find themselves stuck with underperforming vehicles that drain resources rather than support profitability.
The Solution:
To combat these financial challenges, B2B buyers should prioritize fuel-efficient and low-maintenance vehicles. When evaluating transportation options, consider models with advanced fuel economy ratings, such as the latest Ford Transit models equipped with EcoBoost engines. Furthermore, implementing a comprehensive fleet management system can provide valuable insights into vehicle performance and maintenance schedules, allowing for proactive decision-making. Buyers should also explore leasing options that can reduce upfront costs and offer flexibility as business needs evolve. By carefully analyzing total cost of ownership and utilizing data-driven insights, companies can enhance operational efficiency and reduce unnecessary expenditures.
Scenario 3: Regulatory Compliance and Safety Concerns
The Problem:
Navigating regulatory compliance and ensuring passenger safety can be daunting for transportation companies, especially in regions with stringent laws regarding vehicle standards and passenger transport. Issues like ADA compliance in the U.S. or local transportation regulations in the Middle East can pose significant challenges, leading to costly fines or operational shutdowns if not addressed properly.
The Solution:
B2B buyers must prioritize sourcing vehicles that meet all applicable safety and compliance standards. For instance, selecting transportation vehicles that are ADA-compliant ensures that companies can legally and safely transport individuals with disabilities. Engaging with manufacturers who specialize in compliant vehicles, such as those offering wheelchair-accessible options, is essential. Additionally, staying informed about local and international regulations through industry associations or consulting services can help transportation companies remain compliant. Regular training sessions for drivers and staff on safety protocols and compliance updates can further mitigate risks and enhance overall service quality. By adopting a proactive approach to compliance and safety, transportation businesses can build a reputation for reliability and responsibility, ultimately leading to increased customer trust and loyalty.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for transportation vehicles
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Transportation Vehicles?
When selecting materials for transportation vehicles, understanding the key properties that affect performance is crucial. Common materials include steel, aluminum, composites, and plastics. Each material presents unique characteristics that influence durability, cost, and suitability for specific applications.
How Does Steel Perform in Transportation Vehicle Applications?
Steel is renowned for its strength and durability, making it a popular choice in vehicle manufacturing. It has a high tensile strength, excellent impact resistance, and can withstand high temperatures and pressures. However, steel is susceptible to corrosion, which can be a significant drawback in humid or coastal environments.
Pros: Steel’s durability and cost-effectiveness make it suitable for structural components and chassis. It is widely available and can be easily welded and formed into complex shapes.
Cons: The main limitations of steel include its weight, which can impact fuel efficiency, and the need for protective coatings to prevent rust, particularly in regions with high humidity or exposure to saltwater.
For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel is essential. In regions like Africa and South America, where infrastructure may be less developed, sourcing high-quality steel can be a challenge.
Why Is Aluminum Preferred for Lightweight Vehicle Designs?
Aluminum is increasingly favored in the transportation sector due to its lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. It has a lower density than steel, which contributes to improved fuel efficiency and handling. Aluminum also has good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its ability to reduce overall vehicle weight, leading to enhanced performance and fuel economy. It is also resistant to corrosion, which is vital for vehicles operating in harsh environments.
Cons: The main drawback is its higher cost compared to steel and its lower strength-to-weight ratio, which may necessitate thicker sections in some applications.
For international buyers, understanding local recycling capabilities is crucial, as aluminum is highly recyclable. Compliance with standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions is also important, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where environmental regulations are stringent.
How Do Composites Enhance Performance in Transportation Vehicles?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, are becoming more prevalent in vehicle manufacturing due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. Composites can be engineered to provide specific performance characteristics, making them suitable for various applications.
Pros: Composites are lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, offering design flexibility. They also provide superior resistance to environmental factors, making them ideal for vehicles exposed to extreme conditions.
Cons: The primary limitations include higher manufacturing costs and complexity in production. Additionally, repair processes for composite materials can be more challenging than for metals.
International buyers should consider the availability of skilled labor for composite manufacturing and repair. Compliance with standards like ASTM D3039 for tensile properties of composites is also essential, particularly in regions with advanced automotive industries.
What Role Do Plastics Play in Transportation Vehicle Design?
Plastics are widely used in transportation vehicles for components such as dashboards, interior trims, and fuel tanks. They offer versatility, lightweight characteristics, and resistance to corrosion and chemicals.
Pros: The main advantages of plastics include their low weight, cost-effectiveness, and ease of molding into various shapes. They can also provide excellent insulation properties.
Cons: However, plastics may not offer the same level of strength and durability as metals, which can be a concern for structural components. Additionally, some plastics may degrade under UV exposure unless treated.
For international buyers, understanding the specific plastic grades and their compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for tensile properties is important. In regions like the Middle East, where temperatures can be extreme, selecting UV-resistant plastics is crucial.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Transportation Vehicles
| Material | Typical Use Case for transportation vehicles | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Chassis, structural components | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Body panels, frames | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, lower strength-to-weight ratio | High |
| Composites | Body panels, structural components | High strength-to-weight ratio, design flexibility | Higher manufacturing costs, complex repairs | High |
| Plastics | Interior components, fuel tanks | Lightweight, cost-effective, versatile | Lower strength, potential UV degradation | Low |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of common materials used in transportation vehicles, focusing on their properties, advantages, and considerations for international buyers. Understanding these factors is essential for making informed procurement decisions that align with regional requirements and standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for transportation vehicles
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Transportation Vehicles?
Manufacturing transportation vehicles involves a series of well-defined stages that ensure quality and efficiency. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage employs specific techniques to optimize production and meet the evolving demands of the market.
Material Preparation: How Is Material Sourced and Prepped?
The manufacturing process begins with sourcing high-quality materials, which may include steel, aluminum, composites, and plastics. Suppliers are often evaluated based on their ability to deliver materials that meet industry standards and specifications. Once sourced, materials undergo preparation, which may involve cutting, shaping, and treating to enhance durability. For instance, steel may be galvanized to prevent corrosion, which is crucial for vehicles operating in diverse climates, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Vehicle Manufacturing?
After materials are prepared, they are subjected to forming techniques that shape them into parts and components. Common forming processes include stamping, bending, and extrusion. For example, sheet metal stamping is widely used to create body panels, while extrusion is often used for aluminum components. Advanced manufacturing technologies, such as CNC machining and 3D printing, are increasingly being integrated into the forming process to achieve precise specifications and reduce waste.
How Is the Assembly Process Structured for Transportation Vehicles?
The assembly stage is where individual parts come together to form the complete vehicle. This process typically follows a sequential workflow, often on an assembly line. Key components, such as the chassis, engine, and transmission, are assembled first, followed by the installation of interior features and exterior panels. Automated systems, including robotics, play a significant role in enhancing assembly speed and accuracy, reducing the potential for human error. For B2B buyers, understanding the assembly process can provide insights into lead times and customization options.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Vehicle Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of transportation vehicles to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with international standards. Implementing robust QA measures not only improves product quality but also enhances brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards, such as ISO 9001, provide a framework for quality management systems that manufacturers must adhere to. ISO 9001 focuses on process improvement, customer satisfaction, and regulatory compliance. Additionally, industry-specific standards, such as CE marking in Europe and API standards in oil and gas applications, ensure that vehicles meet regional safety and performance requirements. B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers are certified to these standards, as compliance indicates a commitment to quality.
What Are the Key Checkpoints in the Quality Control Process?
Quality control (QC) involves systematic checks at various stages of the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage assesses raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections occur during the production process to identify and rectify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection verifies that the completed vehicle meets all quality standards before shipment.
These checkpoints help identify issues early in the process, reducing the risk of non-compliance and ensuring that only high-quality vehicles reach the market.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Ensure Vehicle Quality?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality and performance of transportation vehicles. Common testing methods include:
- Static and Dynamic Load Testing: Ensures that components can withstand operational stresses.
- Crash Testing: Evaluates vehicle safety under collision conditions, crucial for meeting regulatory standards.
- Environmental Testing: Assesses vehicle performance under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures and humidity, which is particularly relevant for markets in Africa and the Middle East.
- Emissions Testing: Verifies compliance with environmental regulations, particularly in Europe and South America.
These tests are critical in ensuring vehicles are safe, reliable, and environmentally friendly, ultimately influencing purchasing decisions for B2B buyers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control measures implemented by their suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits allows buyers to assess compliance with quality standards firsthand.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s QC processes and performance metrics.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing process and product quality.
These strategies are essential for mitigating risks associated with purchasing transportation vehicles, particularly when sourcing from international suppliers.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate specific nuances in quality control, including:
- Cultural Differences: Variations in business practices and quality expectations may exist between regions, necessitating clear communication and alignment on standards.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have distinct regulatory requirements that must be adhered to, which can complicate the QC process.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Issues: Transportation and logistics can impact product quality, particularly if vehicles are not stored or transported under optimal conditions.
Understanding these nuances is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure they receive products that meet their specific requirements and comply with local regulations.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for transportation vehicles are intricate and multifaceted. By understanding the main stages of manufacturing, quality control checkpoints, testing methods, and the nuances that come with international sourcing, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and standards. This knowledge is particularly valuable in regions with diverse market demands, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring that buyers select reliable partners in the transportation vehicle supply chain.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘transportation vehicles’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, sourcing the right transportation vehicles is crucial for operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. This guide provides a practical checklist to help international buyers make informed decisions when procuring vehicles for diverse transportation needs, from passenger shuttles to cargo vans.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your vehicle requirements. Consider factors such as passenger capacity, cargo space, accessibility features, and specific configurations needed for your operations. This clarity will streamline your search and help suppliers understand your needs more accurately.
- Passenger Capacity: Determine the maximum number of passengers you need to transport comfortably.
- Accessibility Features: Identify if you require wheelchair lifts or ramps to comply with regulations and cater to all users.
Step 2: Research Potential Vehicle Types
Explore the various types of transportation vehicles available in the market. Common options include passenger vans, minibuses, and cargo vans, each serving different purposes. Understanding the options allows you to choose the most suitable vehicle type for your business needs.
- Passenger Vans: Ideal for shuttling groups to events or airports.
- Cargo Vans: Suitable for transporting goods and equipment, especially for logistics companies.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Thoroughly assess potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your specifications and provide quality vehicles. Request detailed information on their vehicle models, customization options, and after-sales support.
- Customization Options: Ensure the supplier can accommodate specific modifications to suit your operational needs.
- After-Sales Support: Inquire about warranty terms, maintenance services, and parts availability to support long-term vehicle use.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
It is essential to ensure that the vehicles comply with local laws and regulations in your target market. This includes safety standards, emissions regulations, and accessibility requirements.
- Safety Certifications: Check if the vehicles have passed necessary safety tests and certifications.
- Emissions Standards: Ensure the vehicles meet the environmental regulations of the countries you operate in.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes. Compare pricing not only based on the initial cost but also consider the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, fuel efficiency, and expected lifespan.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Analyze long-term costs versus initial purchase price to make a financially sound decision.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about discounts for bulk purchases, which can significantly affect overall pricing.
Step 6: Arrange Test Drives and Inspections
Before finalizing your purchase, arrange for test drives and inspections of the vehicles. This step allows you to assess the comfort, handling, and overall quality of the vehicles firsthand.
- Comfort and Usability: Evaluate how the vehicle meets your needs for passenger comfort and cargo capacity.
- Quality Check: Inspect the vehicle for build quality and available features to ensure it aligns with your expectations.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Once you are satisfied with your choice, finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure that all terms, including delivery timelines, payment conditions, and warranties, are clearly outlined and agreed upon.
- Clear Terms: Make sure both parties understand the obligations and responsibilities to avoid future disputes.
- Delivery and Setup: Confirm the logistics of vehicle delivery and any necessary setup or training for your team.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing transportation vehicles effectively, ensuring they choose the right solutions for their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for transportation vehicles Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Transportation Vehicles?
When sourcing transportation vehicles, understanding the cost structure is critical for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: This encompasses the raw materials used in vehicle production, such as steel, aluminum, plastics, and specialized components like engines and electronics. Fluctuations in material prices can significantly impact overall costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs include wages for workers involved in vehicle assembly, engineering, and design. Regions with higher labor costs may lead to increased vehicle prices, making it essential to consider labor markets when sourcing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. These overhead costs are often distributed across all units produced, affecting the pricing structure.
-
Tooling: Tooling refers to the costs associated with the equipment and machinery needed for production. Custom tooling for specialized vehicles can elevate initial costs, which may be amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures is crucial for maintaining vehicle safety and performance standards. While this may add to costs, it enhances the vehicle’s reliability and brand reputation.
-
Logistics: Transportation of the finished vehicles to the buyer’s location involves significant logistics costs. This includes shipping fees, handling charges, and potential tariffs, especially for international transactions.
-
Margin: Finally, the supplier’s profit margin will impact the final pricing. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can help buyers gauge if they are getting a fair deal.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Transportation Vehicle Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of transportation vehicles, notably:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often qualify for bulk pricing discounts, significantly reducing the per-unit cost. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to optimize their purchasing strategy.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specific configurations can increase vehicle costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, ADA compliance) can lead to increased costs but often result in better durability and safety. Buyers should weigh the benefits of investing in higher quality against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and financial stability can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their reliability and service quality, while newer entrants might offer competitive pricing to build market share.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can affect the total cost of ownership. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who bears shipping costs and risks, impacting the final price.
What Negotiation Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency for Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can leverage several strategies to enhance cost efficiency:
-
Conduct Thorough Market Research: Understanding market pricing and competitor offerings can empower buyers during negotiations. It allows them to benchmark prices and ensure they are not overpaying.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, TCO includes maintenance, fuel efficiency, and potential resale value. Evaluating TCO can reveal long-term savings opportunities.
-
Negotiate Payment Terms: Flexible payment terms, such as extended payment periods or financing options, can alleviate upfront cost pressures and improve cash flow.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, terms, and priority service. Regular communication and engagement can foster trust and loyalty.
-
Explore Alternative Suppliers: Diversifying supplier options can create competitive pricing dynamics. It is beneficial to engage multiple suppliers to compare offers and service levels.
Disclaimer on Pricing
It is essential to note that vehicle prices can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions, location, and customization options. Buyers should seek formal quotes and conduct due diligence before finalizing any transactions to ensure they have the most accurate and current pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing transportation vehicles With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Transportation Vehicles
In the dynamic landscape of logistics and passenger transport, businesses often seek solutions that best meet their operational needs. While transportation vehicles, such as vans and shuttles, are commonly utilized, alternative methods exist that may offer distinct advantages depending on specific circumstances. This section explores viable alternatives to transportation vehicles, providing B2B buyers with insights to make informed decisions.
Comparison of Transportation Vehicles and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Transportation Vehicles | Ride-Sharing Platforms | Public Transit Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High capacity, customizable for various needs | Flexible, on-demand service | Fixed routes, limited flexibility |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; ongoing maintenance costs | Variable pricing based on demand | Generally low cost, subsidized by governments |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires fleet management and training | Easy to adopt; minimal setup | Requires coordination with local transit authorities |
| Maintenance | Regular servicing and upkeep needed | Minimal; managed by service provider | Typically maintained by government entities |
| Best Use Case | Corporate transport, events, medical transport | Short-distance travel, urban areas | Commuting in metropolitan areas |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Ride-Sharing Platforms
Ride-sharing services, such as Uber or Lyft, provide a flexible transport solution that adapts to the needs of businesses requiring on-demand transportation. These platforms allow users to book rides via mobile apps, offering convenience and immediate service without the overhead of managing a fleet. However, while they are cost-effective for short trips, ride-sharing can become expensive during peak demand times, making it less viable for large groups or frequent travel.
Public Transit Systems
Public transit systems, including buses and trains, offer a low-cost transportation option that can effectively serve urban populations. These systems are usually subsidized by government entities, allowing for affordable fares and widespread access. However, the fixed routes and schedules can limit flexibility, making them less suitable for businesses needing tailored transport solutions. Additionally, the quality of service can vary significantly based on the location and level of investment in infrastructure.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Transportation Solution for Your Business Needs
Selecting the ideal transportation solution requires a thorough understanding of your business’s specific needs, budget, and operational requirements. Transportation vehicles offer a high level of customization and capacity for corporate and medical transport, while alternatives like ride-sharing platforms and public transit systems provide flexibility and cost-efficiency for short-distance travel. B2B buyers should evaluate their unique scenarios, considering factors such as passenger volume, frequency of use, and budget constraints, to determine the most effective transportation strategy. By aligning the chosen solution with organizational goals, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and service quality.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for transportation vehicles
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Transportation Vehicles?
Understanding the technical properties of transportation vehicles is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications that should be considered:
1. Seating Capacity
Seating capacity refers to the number of passengers a vehicle can accommodate, including the driver. This specification is crucial for businesses like hotels, shuttle services, or event organizers that require efficient transport solutions. A higher seating capacity can enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction, particularly in high-demand scenarios.
2. Payload Capacity
Payload capacity indicates the maximum weight a vehicle can safely carry, including passengers, cargo, and equipment. For B2B buyers, this property is vital as it directly affects the vehicle’s performance and compliance with safety regulations. Businesses must choose vehicles that can handle their specific load requirements without compromising safety or efficiency.
3. Engine Specifications
The engine specifications, including type (e.g., gasoline or diesel), horsepower, and torque, influence a vehicle’s performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions. For companies operating in regions with strict environmental regulations, selecting vehicles with low emissions and high fuel efficiency can lead to significant cost savings and compliance with local laws.
4. Vehicle Dimensions
Vehicle dimensions, such as length, width, height, and wheelbase, play a significant role in maneuverability and storage. Understanding these dimensions is crucial for businesses that operate in urban environments or have specific parking constraints. Proper dimensions can enhance the vehicle’s versatility in various operational contexts.
5. Safety Features
Safety features, including airbags, anti-lock braking systems, and electronic stability control, are paramount for any transportation vehicle. B2B buyers must prioritize vehicles equipped with advanced safety technologies to protect passengers and cargo. Investing in safety can also reduce liability and insurance costs for businesses.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in the Transportation Vehicle Industry?
Familiarity with industry-specific jargon can significantly enhance communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the transportation vehicle sector, understanding OEM relationships is crucial for ensuring quality and compatibility when sourcing replacement parts or customizing vehicles.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory planning. It can also influence the decision to source from different suppliers based on their production capabilities.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. In the transportation vehicle market, submitting RFQs can help buyers compare prices, specifications, and lead times, ultimately leading to more informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers involved in cross-border vehicle procurement, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thus minimizing misunderstandings.
5. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with acquiring and operating a vehicle over its lifespan, including purchase price, maintenance, insurance, fuel, and depreciation. Understanding TCO allows B2B buyers to evaluate the long-term financial implications of their vehicle choices, leading to better strategic decisions.
In summary, grasping both the technical properties and trade terminology associated with transportation vehicles is essential for B2B buyers. These insights empower decision-makers to make informed choices that align with their operational needs and business goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the transportation vehicles Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting Transportation Vehicles?
The transportation vehicles sector is experiencing transformative changes driven by globalization, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. One of the primary global drivers is the rising demand for efficient and reliable transportation solutions across various industries, particularly in emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia are witnessing rapid urbanization, which increases the need for versatile transport solutions such as passenger vans and shuttles.
Emerging technologies such as telematics and fleet management software are revolutionizing how businesses operate within this sector. These tools provide real-time data on vehicle performance, helping companies optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption, and enhance overall operational efficiency. Additionally, the trend towards electric and hybrid vehicles is gaining momentum, influenced by both regulatory measures and a growing awareness of environmental concerns.
International B2B buyers are increasingly looking for vehicles that not only meet their transportation needs but also align with sustainability goals. This shift is prompting manufacturers to innovate and offer customizable options that cater to specific business requirements, such as wheelchair accessibility and cargo configurations. As a result, understanding regional market dynamics and sourcing strategies is crucial for businesses looking to invest in transportation vehicles.
How Is Sustainability Impacting B2B Sourcing for Transportation Vehicles?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of B2B sourcing strategies in the transportation vehicles sector. The environmental impact of traditional fossil-fuel-powered vehicles has led companies to seek greener alternatives. This shift is particularly relevant for international buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where regulatory frameworks are evolving to prioritize sustainability.
Ethical sourcing is not just about reducing emissions; it also encompasses the entire supply chain. B2B buyers are increasingly demanding transparency from manufacturers regarding their sourcing practices and the environmental impact of their operations. This includes utilizing ‘green’ certifications and sustainable materials in vehicle production. Manufacturers that prioritize ethical supply chains are often viewed more favorably, gaining a competitive edge in the market.
Furthermore, the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant trend, with many governments offering incentives for businesses to transition to greener fleets. As a result, international buyers should focus on suppliers who are committed to sustainability and can demonstrate compliance with environmental standards.
What Is the Historical Context of Transportation Vehicles in the B2B Market?
The evolution of transportation vehicles has been marked by significant advancements in technology and design. Initially, the sector was dominated by basic utility vehicles that served specific functions. Over the decades, the introduction of features such as improved safety mechanisms, fuel efficiency, and customizable options has transformed transportation vehicles into sophisticated tools for businesses.
In recent years, the shift towards passenger comfort and luxury has become evident, with manufacturers offering high-end features like advanced climate control and connectivity options. This evolution is particularly important for B2B buyers in sectors such as tourism and corporate travel, where the experience of end-users is paramount.
As the market continues to evolve, understanding this historical context allows buyers to make informed decisions about their investments in transportation vehicles, ensuring they align with current trends and future needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of transportation vehicles
-
How do I choose the right transportation vehicle for my business needs?
Selecting the ideal transportation vehicle involves assessing your specific operational requirements, such as passenger capacity, cargo space, and accessibility features. Consider the type of services you intend to offer, whether it’s shuttle services, non-emergency medical transport, or luxury travel. Evaluate the vehicle’s customization options to ensure it meets your branding and functional needs. It’s also advisable to review fuel efficiency, maintenance costs, and the reputation of the manufacturer for reliability and support. -
What are the key features to look for in a commercial transport van?
When sourcing a commercial transport van, prioritize features such as seating capacity, safety specifications, and adaptability for various passenger needs (e.g., wheelchair accessibility). Look for vehicles equipped with modern technology, such as GPS navigation, rear-view cameras, and climate control systems. Additionally, consider the availability of custom modifications to enhance comfort and branding opportunities. Ensuring the vehicle complies with local regulations and international safety standards is also crucial. -
How can I vet suppliers of transportation vehicles?
To vet suppliers effectively, start by researching their industry reputation through online reviews and customer testimonials. Check their experience in international trade and their ability to meet specific regional requirements, especially if you are sourcing from different continents. Request references from previous clients and inquire about their after-sales support and warranty policies. It’s also beneficial to visit the supplier’s facility if possible or engage in virtual tours to assess their manufacturing capabilities and quality control processes. -
What are the typical payment terms when purchasing transportation vehicles?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier and the value of the transaction. Common arrangements include a deposit upon order confirmation, followed by a balance payment upon delivery or a net 30/60/90 days term after receipt of the vehicle. Be sure to discuss and negotiate these terms upfront, considering factors such as financing options, letters of credit, and any potential for discounts on early payments. Understanding the currency implications and exchange rates is also essential in international transactions. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for transportation vehicles?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the type of vehicle. Some suppliers may allow single-unit purchases, while others might have MOQs of five or more units, especially for customized vehicles. Discussing your specific needs with suppliers is crucial, as they may offer flexibility in order quantities for new buyers or larger orders. Additionally, consider the logistics of importing multiple vehicles versus a single unit, which can impact costs and lead times. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing vehicles internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, establish clear specifications and standards with your supplier before production begins. Request detailed information about their QA processes, including inspections at various stages of manufacturing. It’s advisable to conduct third-party inspections or audits during production and pre-shipment to verify compliance with your standards. Additionally, familiarize yourself with international certifications that the vehicles must meet, such as ISO or local safety regulations, to ensure product reliability. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing vehicles?
When importing vehicles, consider shipping methods (container shipping vs. roll-on/roll-off), customs regulations, and documentation requirements in your destination country. Engage a freight forwarder experienced in vehicle logistics to navigate the complexities of international shipping, including tariffs and taxes. Plan for potential delays in shipping and customs clearance, and ensure you have appropriate insurance coverage during transit. Understanding the total landed cost, including shipping, duties, and fees, will help you budget effectively. -
What customization options are available for transportation vehicles?
Customization options for transportation vehicles can include modifications for seating arrangements, accessibility features, and branding elements like custom graphics. Suppliers often provide choices for interior finishes, climate control systems, and entertainment features tailored to your needs. For specific applications, such as medical transport, vehicles can be fitted with specialized equipment like wheelchair lifts or storage for medical supplies. Discuss your requirements with the manufacturer to explore all available options and ensure the final product aligns with your business objectives.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Transportation Vehicles Manufacturers & Suppliers List
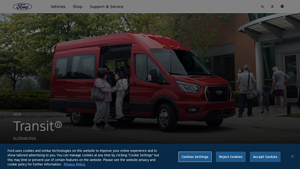
1. Ford – 2025 Transit® Van
Domain: ford.com
Registered: 1988 (37 years)
Introduction: 2025 Ford Transit® Van offers seating for up to 15 passengers, available all-wheel drive (AWD), and two engine options: a 3.5L PFDi V6 and a 3.5L EcoBoost® V6. It features a versatile interior suitable for various hauling needs, with three height and two length options. Key features include a honeycomb mesh grille, power-adjusting manual-folding mirrors, 50/50 hinged rear doors, adaptive cruise co…
2. iStock – Transportation Vehicles Stock Photos
Domain: istockphoto.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: This company, iStock – Transportation Vehicles Stock Photos, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Central Dispatch – Auto Transportation Marketplace
Domain: centraldispatch.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Central Dispatch is America’s largest self-managed auto transportation marketplace, connecting thousands of shippers and carriers. Key features include:
– Mobile app for carriers to execute moves, complete inspections, and streamline communication.
– Digital dispatches for fast shipment management with a single dashboard for tracking vehicles and jobs.
– A rating system for users to rate partne…
4. Enchanted Learning – Vehicles and Transportation Word List
Domain: enchantedlearning.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Vehicles and Transportation Word List from Enchanted Learning includes an A-to-Z list of various vehicles and modes of transportation, ideal for expanding vocabulary for students, teachers, and transportation enthusiasts. The list features terms such as aerial tramway, aircraft, ambulance, bicycle, bus, ferry, helicopter, jet ski, limousine, motorcycle, rocket, sailboat, subway, and many more, cov…
5. Daniel’s Training – Transport Vehicle Essentials
Domain: danielstraining.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: A transport vehicle is defined as a cargo-carrying vehicle such as an automobile, van, tractor, truck, semitrailer, tank car, or rail car used for the transportation of cargo by any mode. Each cargo-carrying body (trailer, rail car, etc.) is considered a separate transport vehicle. The definition excludes aircraft and vessels from being classified as transport vehicles, despite the term ‘by any mo…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for transportation vehicles
In the evolving landscape of transportation vehicles, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical element for businesses looking to optimize their operations. By leveraging a diverse range of options—from passenger vans to specialized transport vehicles—companies can tailor their fleets to meet specific needs, whether for luxury travel, community outreach, or medical transport. This customization not only enhances operational efficiency but also improves passenger experience, positioning businesses for success in competitive markets.
B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize understanding the unique features and compliance standards of various vehicle models. By doing so, they can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives and regulatory requirements. Additionally, considering the benefits of upfitting vehicles for accessibility and comfort can significantly expand market reach and customer satisfaction.
As we look to the future, the demand for versatile and reliable transportation solutions will only grow. International buyers are encouraged to engage with manufacturers and suppliers to explore innovative solutions that can drive efficiency and profitability in their operations. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your fleet and elevate your business to new heights.