Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric cargo l6e vehicle
In the face of increasing urbanization and a pressing need for sustainable logistics solutions, sourcing electric cargo L6e vehicles presents a pivotal challenge for businesses aiming to enhance their delivery capabilities. As cities grapple with congestion and environmental regulations, the demand for efficient, compact, and eco-friendly transportation options has never been greater. This guide delves deep into the global market for electric cargo L6e vehicles, offering insights into various types, applications, and the latest innovations transforming urban logistics.
International B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, will find this comprehensive resource invaluable. It covers essential aspects such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and the regulatory landscape surrounding electric vehicles. By equipping businesses with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions, this guide empowers them to not only comply with local regulations but also to leverage the operational advantages of electric cargo vehicles.
From refrigerated transport solutions to versatile delivery vans, electric cargo L6e vehicles offer remarkable flexibility for businesses involved in last-mile delivery. As you navigate this evolving market, the insights provided here will help you identify the best solutions tailored to your unique logistics needs, ensuring a sustainable and efficient future for your operations.
Understanding electric cargo l6e vehicle Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| J4-C Electric Cargo Car | EEC-certified, refrigeration capabilities, compact design | Last-mile delivery, perishable goods | Pros: Low emissions, versatile; Cons: Limited range for long distances. |
| J2-C Electric Mini Van | Good load capacity (330kg), cruising range of 100-200 km | Short-distance transportation, logistics | Pros: Economical for urban use; Cons: Less cargo space compared to larger models. |
| Y2-C Electric Cargo Car | Customizable cargo boxes, robust build, suitable for food delivery | Cold chain logistics, urban deliveries | Pros: Adaptable for various cargo types; Cons: Initial investment can be high. |
| L6e-BP Low-Speed Car | Low-speed operation (max 45 km/h), compact design | Urban mobility, light cargo transport | Pros: Cost-effective for local deliveries; Cons: Speed limitations may affect efficiency. |
| EEC Coc Electric Van | Versatile design, suitable for various cargo types | General logistics, food transport | Pros: Complies with regulations; Cons: May require specialized maintenance. |
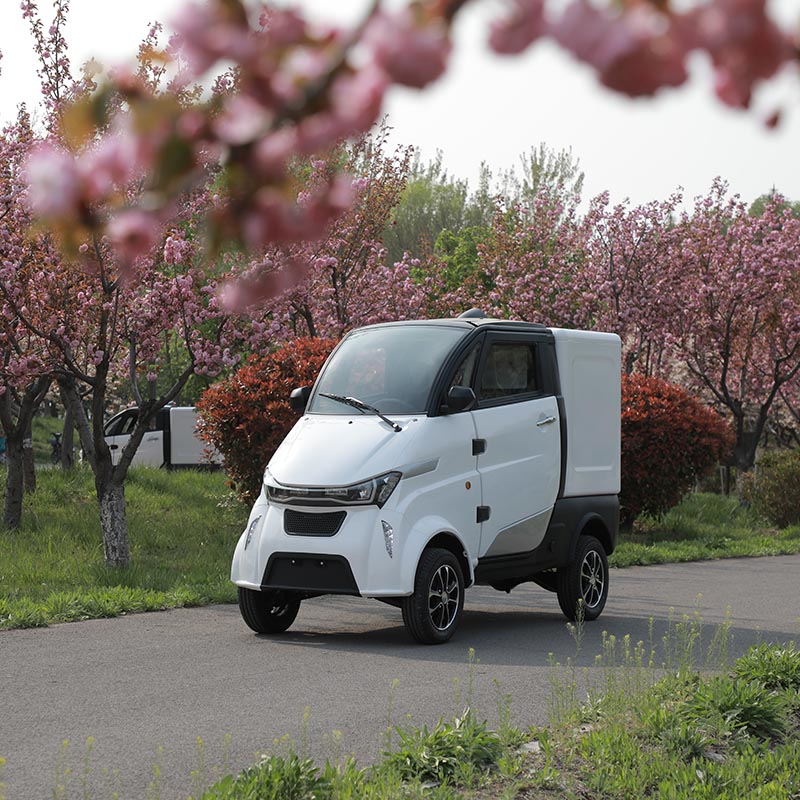
What are the Key Characteristics of the J4-C Electric Cargo Car?
The J4-C Electric Cargo Car is designed specifically for urban logistics, meeting EEC L6e standards for efficiency and sustainability. Its compact size allows for easy maneuverability in congested city environments, while the refrigeration capability makes it ideal for transporting perishable goods. B2B buyers should consider its suitability for last-mile delivery services, as it offers low operational costs and reduced emissions. However, the vehicle’s range may limit its use for longer deliveries.
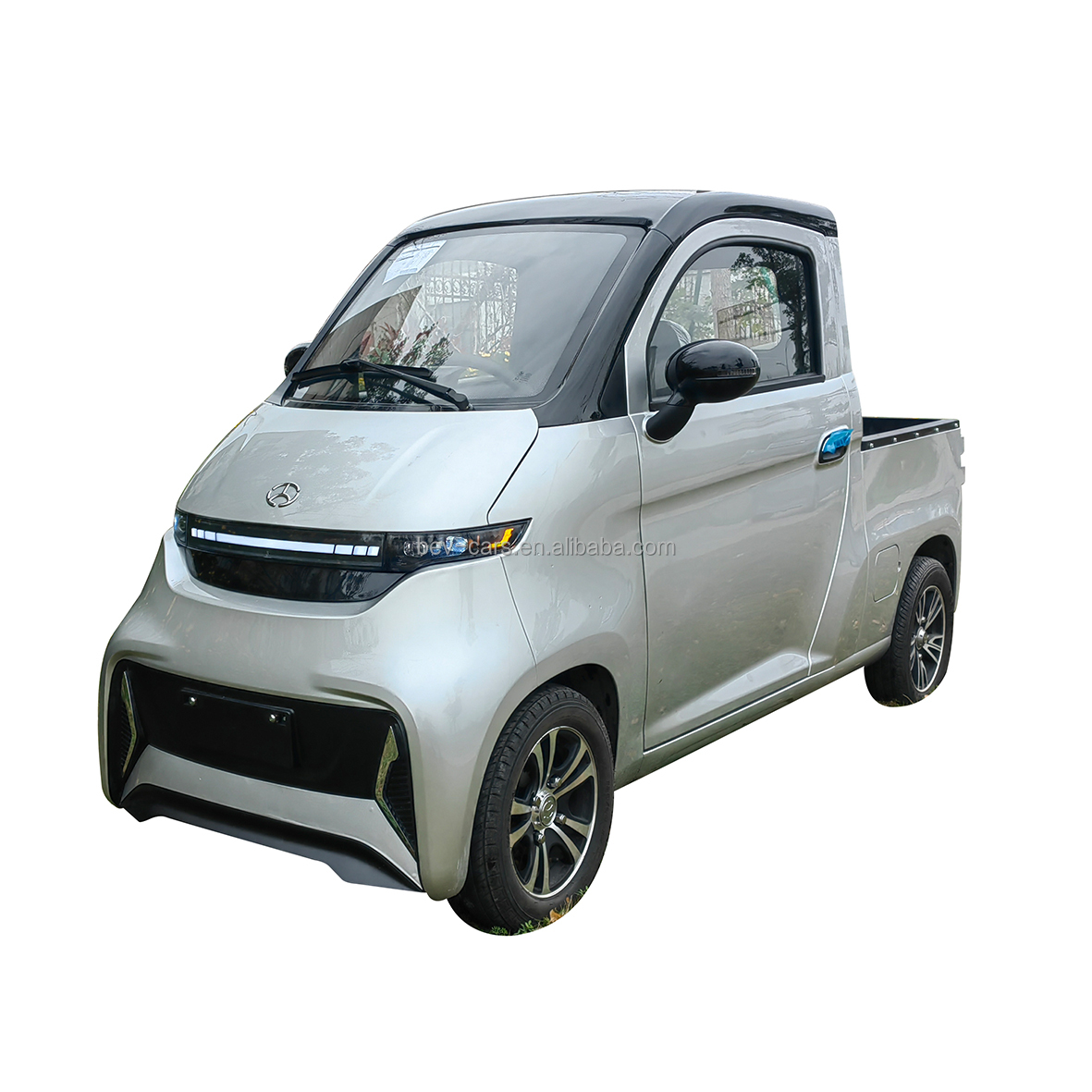
How Does the J2-C Electric Mini Van Stand Out in Urban Logistics?
The J2-C Electric Mini Van is a compact vehicle that excels in short-distance transport, boasting a load capacity of 330kg and a cruising range of 100-200 km. This makes it particularly suitable for urban delivery services, including logistics and cold chain applications. Buyers will appreciate its economical nature and low maintenance costs, although the smaller cargo space may be a drawback for businesses requiring larger transport solutions.
What Makes the Y2-C Electric Cargo Car Ideal for Cold Chain Logistics?
The Y2-C Electric Cargo Car offers a robust design with customizable cargo boxes, making it an excellent choice for cold chain logistics and food delivery. Its ability to accommodate both refrigeration and heating systems allows businesses to transport a variety of goods under optimal conditions. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of adaptability against the potential higher initial investment, which can be justified by the vehicle’s versatility and efficiency in urban settings.
Why is the L6e-BP Low-Speed Car a Cost-Effective Solution for Local Deliveries?
The L6e-BP Low-Speed Car is tailored for urban mobility with a maximum speed of 45 km/h, making it an economical choice for light cargo transport. Its compact design is ideal for navigating tight city streets, and it provides a cost-effective option for businesses focusing on local deliveries. However, buyers need to consider the speed limitations, which may impact delivery efficiency in certain scenarios.
How Does the EEC Coc Electric Van Offer Versatility for Businesses?
The EEC Coc Electric Van is designed to handle various cargo types, making it a versatile option for general logistics and food transport. Its compliance with EEC regulations ensures that it meets safety and environmental standards, which is crucial for international buyers. While it provides a reliable solution for businesses, potential buyers should be aware of the specialized maintenance that may be required to keep the vehicle in optimal condition.
Key Industrial Applications of electric cargo l6e vehicle
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric cargo l6e vehicle | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-commerce & Retail | Last-mile delivery solutions | Enhanced delivery efficiency and reduced operational costs | Vehicle range, load capacity, and adaptability for urban environments |
| Food & Beverage | Cold chain logistics for perishable goods | Maintains product quality and reduces spoilage | Temperature control systems and compliance with health regulations |
| Urban Logistics | Urban freight transport | Minimizes traffic congestion and lowers emissions | Maneuverability in crowded areas and local regulatory compliance |
| Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | Delivery of medical supplies | Ensures timely delivery of critical supplies | Reliability, temperature control for sensitive items, and service support |
| Waste Management | Collection and transportation of recyclables | Supports sustainability initiatives and reduces carbon footprint | Load capacity, vehicle durability, and local service availability |
How Are Electric Cargo L6e Vehicles Used in E-commerce & Retail?
In the fast-paced world of e-commerce, electric cargo L6e vehicles are increasingly utilized for last-mile delivery. These vehicles offer a compact design that allows for easy navigation through congested urban areas, enhancing delivery efficiency. By adopting electric cargo solutions, businesses can significantly reduce operational costs associated with fuel and maintenance while also addressing environmental concerns related to emissions. International buyers should consider the vehicle’s range and load capacity to ensure they meet the demands of their specific delivery routes.
What Role Do Electric Cargo L6e Vehicles Play in Food & Beverage Logistics?
Electric cargo L6e vehicles are particularly advantageous in the food and beverage sector, where they can be equipped with refrigeration units for cold chain logistics. This capability is essential for transporting perishable goods over short distances, maintaining product quality and reducing spoilage. Buyers in this sector should prioritize vehicles with reliable temperature control systems and ensure compliance with local health regulations to guarantee the safe delivery of food items.
How Are Electric Cargo L6e Vehicles Transforming Urban Logistics?
Urban logistics is undergoing a transformation with the introduction of electric cargo L6e vehicles, which are specifically designed for efficient freight transport in densely populated areas. These vehicles help alleviate traffic congestion and lower emissions, aligning with the sustainability goals of many cities. For international buyers, it is crucial to assess the vehicle’s maneuverability in urban settings and ensure it meets local regulatory standards for commercial vehicles.
Why Are Electric Cargo L6e Vehicles Important for Healthcare Deliveries?
In the healthcare sector, electric cargo L6e vehicles are vital for the timely delivery of medical supplies and pharmaceuticals. Their reliability ensures that critical items reach healthcare facilities without delay, which can be life-saving. Buyers should focus on vehicles that offer temperature control features for sensitive medical supplies and consider the availability of after-sales service to maintain operational efficiency.
How Do Electric Cargo L6e Vehicles Support Waste Management Initiatives?
Electric cargo L6e vehicles play a crucial role in waste management by facilitating the collection and transportation of recyclables. Their eco-friendly design supports sustainability initiatives, helping municipalities reduce their carbon footprint. When sourcing these vehicles, buyers should evaluate their load capacity and durability to withstand the demands of waste collection, as well as the availability of local service support to ensure ongoing operational effectiveness.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric cargo l6e vehicle’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance Challenges
The Problem: For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, understanding and complying with various regulatory requirements for electric cargo L6e vehicles can be daunting. Regulations can vary significantly between countries and even cities, impacting vehicle specifications, safety standards, and environmental compliance. This complexity can lead to potential delays in procurement, increased costs, and even legal penalties if regulations are not properly adhered to.
The Solution: To effectively navigate these regulatory landscapes, buyers should engage with local experts or consultants who specialize in electric vehicle (EV) compliance. It’s crucial to conduct thorough research on the specific EEC L6e standards applicable in your target market. Buyers should prioritize sourcing vehicles from manufacturers who provide detailed documentation regarding their compliance with local regulations. Additionally, establishing a relationship with government bodies or industry associations can provide valuable insights into upcoming regulatory changes. Regular training for procurement teams on compliance matters can also mitigate risks associated with regulatory non-compliance.
Scenario 2: Addressing Range Anxiety in Urban Deliveries
The Problem: One of the most significant concerns for businesses considering electric cargo L6e vehicles is range anxiety—worrying that the vehicle won’t have enough battery capacity to complete deliveries within urban settings. This is particularly pressing for logistics companies operating in cities where tight delivery windows are crucial. If vehicles run out of charge mid-delivery, it can lead to costly delays, dissatisfied customers, and a damaged reputation.
The Solution: To overcome range anxiety, businesses should carefully assess their operational routes and battery performance specifications before procurement. Opting for electric cargo vehicles with proven battery ranges, ideally above the typical distance required for daily operations, can ensure reliability. Additionally, integrating route optimization software can help in planning more efficient delivery paths that consider charging station locations. Investing in a robust charging infrastructure, including fast chargers at strategic depots, will also enhance operational efficiency and minimize downtime. Suppliers should offer guidance on the best practices for battery management to extend the lifespan and reliability of the vehicles.
Scenario 3: Managing Maintenance and Operational Costs
The Problem: While electric vehicles are generally associated with lower operating costs compared to traditional combustion engines, the actual maintenance and operational costs can still pose challenges. For businesses in regions with limited access to specialized EV maintenance services, sourcing spare parts and ensuring regular servicing can be a significant headache. This can lead to unexpected downtimes and increased operational expenses.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing electric cargo L6e vehicles from manufacturers who have established service networks and support infrastructure in their regions. It’s advisable to evaluate the availability of spare parts and the manufacturer’s commitment to after-sales support. Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule tailored to the specific electric vehicle model can also minimize unexpected repairs and prolong the vehicle’s lifespan. Furthermore, exploring partnerships with local service providers or training in-house staff on basic maintenance tasks can reduce reliance on external services, thereby cutting costs and ensuring vehicle uptime. By leveraging technology, such as telematics, companies can monitor vehicle performance and preemptively address maintenance issues before they escalate.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric cargo l6e vehicle
What Are the Key Materials for Electric Cargo L6e Vehicles?
Electric cargo L6e vehicles, such as the J4-C and J2-C, utilize a variety of materials that enhance their performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Understanding these materials is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of electric cargo L6e vehicles, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international compliance.
How Does Steel Contribute to the Durability of Electric Cargo Vehicles?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for structural components of electric cargo vehicles. It typically has excellent corrosion resistance when treated with protective coatings.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its strength and ability to withstand high stress, which is vital for vehicle safety. However, steel can be heavy, which may impact the vehicle’s overall weight and efficiency. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex, leading to higher production costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is critical for the chassis and frame of electric cargo vehicles, ensuring they can handle the rigors of urban delivery. Its compatibility with various coatings allows for improved corrosion resistance, essential for vehicles operating in diverse climates.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the steel used complies with international standards such as ASTM or DIN. In regions like Africa and South America, where road conditions can vary, the use of high-quality steel is crucial for longevity and performance.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Electric Cargo Vehicle Design?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice for vehicle bodies and components. It can withstand a range of temperatures and is recyclable, which adds to its sustainability profile.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which enhances energy efficiency and increases the vehicle’s range. However, aluminum can be more expensive than steel and may require specialized welding techniques, complicating the manufacturing process.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in body panels and structural components, contributing to the vehicle’s overall efficiency. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for vehicles that operate in coastal or humid environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying costs of aluminum in different regions and ensure compliance with local recycling regulations. In Europe, for instance, there are stringent standards for materials used in vehicle construction.
How Do Composites Enhance Performance in Electric Cargo Vehicles?
Key Properties: Composite materials, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent resistance to environmental factors. They can also be molded into complex shapes, providing design flexibility.
Pros & Cons: Composites are lightweight and can significantly reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, improving efficiency. However, they can be costly and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which could increase lead times.
Impact on Application: Composites are often used in non-structural components, such as interior panels and cargo boxes. Their ability to be customized makes them ideal for specific applications, such as refrigerated cargo transport.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of composite materials in their region and ensure that suppliers meet international quality standards. In markets like Brazil, where cost sensitivity is high, the price of composites may be a limiting factor.
What Is the Importance of Lithium-Ion Batteries in Electric Cargo Vehicles?
Key Properties: Lithium-ion batteries are known for their high energy density, long cycle life, and relatively low self-discharge rates. They perform well across a wide range of temperatures, making them suitable for various climates.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of lithium-ion batteries is their efficiency and ability to provide sufficient power for electric cargo vehicles. However, they can be expensive and require careful handling and disposal due to environmental concerns.
Impact on Application: These batteries are essential for the electric drivetrain, impacting the vehicle’s range and performance. Their lightweight nature contributes to overall vehicle efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure compliance with international safety standards for battery manufacturing and disposal. In regions like the Middle East, where temperatures can be extreme, battery performance and warranty terms should be carefully evaluated.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Cargo L6e Vehicles
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric cargo l6e vehicle | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Chassis and structural components | High strength and durability | Heavy, complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Aluminum | Body panels and structural components | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, specialized welding | High |
| Composites | Interior panels and specialized cargo boxes | High strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive, complex manufacturing | High |
| Lithium-Ion Battery | Electric drivetrain and power storage | High energy density, long cycle life | Expensive, environmental concerns | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric cargo l6e vehicle
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electric Cargo L6e Vehicles?
The manufacturing of electric cargo L6e vehicles is a complex process that involves multiple stages, ensuring that the vehicles meet the high standards expected by international B2B buyers. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves sourcing high-quality materials such as steel for the frame, lithium iron phosphate batteries, and ABS resin for the body. Manufacturers often establish relationships with certified suppliers to ensure consistency and reliability. Material testing is crucial here, with checks for durability, weight, and compatibility with electric vehicle standards.
-
Forming: In this stage, the prepared materials are shaped into components of the vehicle. Techniques such as stamping, welding, and molding are commonly employed. For instance, the chassis is often fabricated using advanced robotic welding techniques to ensure precision and strength. The forming process must comply with specific industry standards to guarantee safety and performance.
-
Assembly: This critical phase brings together all the components, including the drivetrain, battery systems, and cargo area. Assembly lines are typically organized to optimize workflow, with stations dedicated to specific tasks such as installation of the electric motor and battery management systems. Quality checks are integrated throughout the assembly process to catch any discrepancies early.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves painting, detailing, and preparing the vehicle for delivery. This includes applying protective coatings, ensuring the electrical systems are functional, and performing aesthetic checks. The finishing process must also adhere to environmental regulations, particularly concerning emissions from painting processes.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Electric Cargo L6e Vehicle Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of electric cargo L6e vehicles to ensure they meet international standards and customer expectations. This involves adherence to both international standards like ISO 9001 and industry-specific certifications such as CE and API.
-
International Standards: Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers have a robust quality management system in place. This standard emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction, which is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage in international markets.
-
Industry-Specific Certifications: Certifications like CE (European Conformity) and EEC (European Economic Community) are essential for electric vehicles sold in Europe. These certifications confirm that the vehicles meet safety and environmental regulations. In regions like Africa and South America, manufacturers may need to comply with local regulations that reflect similar standards.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Electric Cargo L6e Vehicle Production?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each vehicle meets the required specifications. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. It ensures that all materials meet predefined standards before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC is conducted at various assembly stations. Technicians perform checks to verify that each component is correctly assembled and functions as intended. This might include testing electrical connections and ensuring that the vehicle’s weight distribution is optimal.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the vehicle is delivered, a comprehensive final inspection is conducted. This includes road testing to assess performance metrics such as speed, range, and braking systems. Additionally, aesthetic checks for paint quality and interior finishes are performed to ensure the vehicle meets market expectations.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Electric Cargo L6e Vehicles?
Testing methods are essential for validating the performance and safety of electric cargo L6e vehicles. Common approaches include:
-
Performance Testing: This assesses the vehicle’s capabilities under various conditions, including load capacity, range, and acceleration. Manufacturers often use dynamometers to simulate real-world driving conditions.
-
Safety Testing: Compliance with safety standards involves crash testing and evaluating braking systems. Manufacturers might engage third-party testing facilities to ensure unbiased results.
-
Environmental Testing: This ensures that the vehicle operates effectively in diverse climates. Tests may include exposure to extreme temperatures and humidity levels to gauge battery performance and material durability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is crucial to ensuring that they are investing in reliable products. Here are several strategies:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of the manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the QC processes in place. Audits can be performed by the buyers themselves or through third-party services to ensure an objective assessment.
-
Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline their QC processes, testing methodologies, and results. These documents should include metrics related to defect rates and compliance with international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspection: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an additional layer of assurance. These services can conduct independent evaluations of the manufacturing processes and final products before shipment.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Understanding the nuances of QC and certifications is critical for international B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Buyers must be aware of:
-
Regional Regulations: Different regions may have specific regulations regarding electric vehicles. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are compliant with local laws to avoid potential legal issues.
-
Certification Validity: It’s essential to verify the authenticity of certifications provided by suppliers. This can often be done by checking with issuing bodies or regulatory authorities.
-
Cultural Considerations: Different regions may place varying levels of importance on certain certifications and quality standards. Understanding these cultural nuances can help buyers navigate supplier relationships more effectively.
By focusing on these aspects of manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electric cargo L6e vehicles, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric cargo l6e vehicle’
When considering the procurement of electric cargo L6e vehicles, a structured approach can significantly enhance the decision-making process. This guide offers a step-by-step checklist tailored to B2B buyers, ensuring that you secure a vehicle that meets your operational needs and aligns with sustainability goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical before initiating the sourcing process. Consider the vehicle’s size, load capacity, range, and any specialized features, such as refrigeration for perishable goods. Knowing your requirements will help filter options and prevent costly mismatches.
Step 2: Research Regulatory Compliance
Ensure that the vehicles you are considering meet relevant regulatory standards, such as EEC L6e certification. Compliance with these standards not only guarantees safety and performance but also avoids potential legal issues in your operational regions. Verify the certification documents directly from the manufacturer or authorized dealers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, it is essential to thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from previous clients, particularly those in similar industries or regions. Assess their ability to provide after-sales support and spare parts, which are crucial for long-term operational efficiency.
- Look for:
- Years of experience in the electric vehicle market.
- Customer testimonials and case studies demonstrating successful deployments.
Step 4: Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Calculating the total cost of ownership is vital to understanding the financial implications of your purchase. This includes not just the initial vehicle cost, but also maintenance, insurance, energy consumption, and potential tax incentives for electric vehicles. A thorough TCO analysis will help ensure that the investment aligns with your budget and financial goals.
Step 5: Request and Analyze Quotes
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline all costs associated with the vehicle, including delivery, taxes, and any additional features. Compare these quotes not only on price but also on value-added services such as warranty terms and service agreements. This analysis will help you identify the best overall deal.
Step 6: Conduct a Pilot Test
If feasible, arrange for a pilot test of the vehicle to evaluate its performance in real-world conditions. This trial period allows you to assess aspects such as maneuverability, range under various loads, and overall reliability. Feedback from your team can provide invaluable insights into whether the vehicle meets your operational needs.
Step 7: Finalize Contract Terms and Conditions
Before concluding the procurement process, ensure that all contract terms and conditions are clear and favorable. Pay attention to warranty coverage, service agreements, and any penalties for non-compliance. A well-defined contract protects your interests and sets clear expectations for both parties.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing electric cargo L6e vehicles effectively, ensuring that their investment supports their operational and sustainability objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric cargo l6e vehicle Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Electric Cargo L6e Vehicles?
When sourcing electric cargo L6e vehicles, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The materials used in electric cargo vehicles, such as the chassis, battery systems, and body components, significantly impact the overall cost. High-quality materials can enhance durability and performance but may raise initial expenses. For instance, lithium iron phosphate batteries are more expensive than traditional lead-acid batteries, yet they offer longer life and efficiency.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and are influenced by local wage rates and the complexity of manufacturing processes. Skilled labor is often necessary for assembly and quality control, particularly in regions with advanced manufacturing capabilities.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses associated with the production facility. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead, ultimately reducing the vehicle’s cost.
-
Tooling: Initial investments in tooling and machinery can be substantial, especially for custom or specialized vehicles. However, these costs can be amortized over higher production volumes, which is a critical consideration for B2B buyers.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures that the vehicles meet industry standards and specifications, which is vital for safety and performance. While this adds to the cost, it can prevent costly recalls and enhance the vehicle’s market reputation.
-
Logistics: Shipping and transportation costs should not be overlooked. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties can significantly affect the final price. Understanding local regulations and logistics networks is crucial for international buyers.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions, competition, and perceived value.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Electric Cargo L6e Vehicles?
Several factors can influence pricing when sourcing electric cargo L6e vehicles:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Understanding minimum order quantities (MOQ) can help buyers leverage better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses while ensuring the vehicles meet operational requirements.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Vehicles that comply with specific quality standards or certifications, such as EEC homologation, may carry a premium price. However, these certifications can enhance resale value and operational reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers play a significant role. Established manufacturers may charge more but offer better after-sales support and warranties.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of sale, including who is responsible for shipping and customs duties, can significantly affect total costs. Buyers should negotiate terms that minimize their risk and exposure to unexpected costs.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating Prices and Ensuring Cost Efficiency?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the following tips can enhance negotiation strategies:
-
Conduct Thorough Market Research: Understanding market prices and supplier offerings can empower buyers during negotiations. Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to create a competitive landscape.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential resale value. A higher initial investment may be justified by lower operating costs.
-
Be Flexible with Specifications: If possible, consider standard specifications instead of custom features to reduce costs. Customization can lead to longer lead times and higher prices.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Long-term partnerships often yield favorable conditions.
-
Stay Informed on Regulatory Changes: Changes in regulations can impact costs, especially in regions with strict environmental standards. Keeping abreast of these changes can help buyers anticipate price fluctuations.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices and cost components discussed in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific vehicle configurations. It is essential for buyers to conduct due diligence and obtain tailored quotes to ensure accurate budgeting for their sourcing needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric cargo l6e vehicle With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives in Urban Logistics
As the demand for efficient and sustainable urban logistics solutions grows, businesses are increasingly exploring various alternatives to traditional cargo transport methods. The electric cargo L6E vehicle, with its innovative design and eco-friendly attributes, presents a compelling option. However, it is essential for B2B buyers to consider other viable solutions that may better align with their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and environmental goals. This analysis compares the electric cargo L6E vehicle with two notable alternatives: electric bicycles and conventional diesel vans.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Cargo L6E Vehicle | Electric Bicycle | Conventional Diesel Van |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Max speed: 45 km/h, range: 80-200 km | Max speed: 25-28 km/h, range: 40-100 km | Max speed: 90-120 km/h, range: 500-800 km |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower running costs | Lower initial cost, minimal running costs | Lower initial cost, high fuel and maintenance costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure, regulatory compliance | Minimal infrastructure needed, easy to deploy | Requires fuel stations, more complex regulations |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to electric drivetrain | Very low maintenance | Higher maintenance due to engine and parts |
| Best Use Case | Urban deliveries, short to medium distances, perishable goods | Last-mile delivery, small packages | Long-distance transport, larger loads |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Bicycle
Electric bicycles (e-bikes) have gained traction as a practical alternative for urban logistics, especially for last-mile delivery. They offer a lower initial investment compared to electric cargo vehicles and boast minimal running costs, primarily limited to battery charging and occasional maintenance. However, their performance is restricted by lower speeds and range, making them less suitable for larger or bulk deliveries. E-bikes excel in congested urban areas where maneuverability is critical, but their limited cargo capacity can be a drawback for businesses needing to transport heavier or larger items.
Conventional Diesel Van
Conventional diesel vans have been the backbone of urban logistics for decades, providing robust performance for long-distance transport. They can handle larger loads and travel longer distances without the need for frequent refueling stops. However, the initial cost of diesel vans can be lower than electric vehicles, but ongoing fuel and maintenance expenses can accumulate significantly over time. Furthermore, diesel vans contribute to higher emissions, which can be a critical factor for businesses aiming to enhance their sustainability credentials. Regulatory pressure regarding emissions is also increasing, making diesel solutions less viable in the long run.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Selecting the right transport solution for urban logistics hinges on a thorough understanding of your operational requirements, budget, and sustainability goals. The electric cargo L6E vehicle stands out as a forward-thinking option, particularly for businesses focused on reducing emissions and enhancing delivery efficiency. However, electric bicycles may offer a cost-effective solution for last-mile deliveries, while conventional diesel vans remain suitable for longer distances and heavier loads. B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their specific needs, including delivery range, load capacity, and environmental considerations, to make an informed decision that aligns with their business strategy.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric cargo l6e vehicle
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Cargo L6e Vehicles?
When considering electric cargo L6e vehicles, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties that influence performance, cost-effectiveness, and operational suitability.
-
EEC Certification
The European Economic Community (EEC) certification is a regulatory requirement for electric vehicles, ensuring they meet safety, environmental, and operational standards. For B2B buyers, this certification not only enhances the vehicle’s marketability but also assures compliance with local regulations, reducing the risk of legal issues and enhancing brand reputation. -
Battery Type and Capacity
Most electric cargo L6e vehicles utilize lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries due to their longevity and safety. A common specification is a 60V battery with capacities ranging from 80Ah to 105Ah. Battery capacity directly influences the vehicle’s range (typically between 80 to 200 km), which is critical for logistics operations. Selecting a vehicle with an appropriate battery capacity can optimize delivery routes and reduce operational costs. -
Load Capacity
The load capacity, often specified in kilograms, indicates how much weight the vehicle can safely transport. For example, many L6e vehicles have a load capacity ranging from 300 to 500 kg. Understanding this metric helps businesses assess whether the vehicle can handle their specific delivery needs, particularly in sectors like food distribution or cold chain logistics. -
Cruising Range
The cruising range of an electric cargo vehicle refers to the maximum distance it can travel on a single charge. This specification is vital for urban logistics, where efficient route planning is essential. A typical range for L6e vehicles varies from 80 km to 200 km, allowing businesses to determine if the vehicle can meet their delivery schedules without frequent recharging. -
Charging Time
Charging time is a critical consideration for fleet operations. Most electric cargo L6e vehicles can be fully charged in 2 to 8 hours, depending on the battery type and charger specifications. Knowing the charging duration helps businesses plan their logistics and minimizes downtime, ensuring more efficient use of the vehicle. -
Brake System
The brake system’s design, whether hydraulic or electronic, plays a significant role in safety and maintenance. Vehicles equipped with advanced braking systems often provide better stopping power and reliability. Understanding the brake system’s specifications can help buyers evaluate long-term maintenance needs and safety standards.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Electric Cargo Vehicle Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are several key terms to understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of electric cargo vehicles, OEMs are critical for sourcing high-quality components, ensuring reliability and performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs helps buyers manage their inventory and budget effectively while ensuring they meet the supplier’s requirements. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing, terms, and conditions for specific products. This process is essential for comparing offers and making informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps businesses understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving it. In the electric vehicle industry, understanding lead times is crucial for planning and ensuring that vehicles are available when needed. -
Cold Chain Logistics
This term describes the supply chain process of transporting temperature-sensitive products, such as food and pharmaceuticals. Vehicles designed for cold chain logistics often feature specialized insulation and refrigeration systems, making them essential for certain industries.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms not only empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions but also enhances their negotiating power and operational efficiency in the electric cargo vehicle market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric cargo l6e vehicle Sector
What Are the Global Drivers and Key Trends Impacting the Electric Cargo L6e Vehicle Market?
The electric cargo L6e vehicle market is witnessing significant growth driven by urbanization, rising e-commerce demands, and stringent environmental regulations. As cities expand, the need for efficient last-mile delivery solutions has intensified. Electric vehicles (EVs), particularly L6e models, cater to this demand by offering maneuverability in congested urban areas while minimizing emissions. The trend towards electrification is further bolstered by government incentives aimed at reducing carbon footprints, especially in regions like Europe and parts of Africa and South America.
Emerging B2B technology trends include the integration of IoT for fleet management, which enables real-time tracking and data analysis, enhancing operational efficiency. Additionally, advancements in battery technology are extending the range and reducing charging times, making electric cargo vehicles more viable for businesses. In markets such as Nigeria and Brazil, where logistics infrastructure is still developing, the adoption of electric cargo vehicles is also influenced by local manufacturing initiatives, which aim to reduce import costs and stimulate job creation.
International buyers should be aware of the varying regulatory environments across regions. For instance, the European Union has established stringent standards for vehicle emissions and safety, which influence sourcing decisions. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers looking to invest in electric cargo L6e vehicles that comply with local regulations while meeting their logistics needs.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence the Electric Cargo L6e Vehicle Sector?
Sustainability is a core consideration in the electric cargo L6e vehicle market, with businesses increasingly prioritizing environmentally friendly practices. The environmental impact of logistics operations is under scrutiny, prompting companies to seek greener alternatives. Electric cargo vehicles offer a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional fuel-powered vehicles, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Ethical sourcing practices are equally important, as buyers are encouraged to engage with manufacturers who prioritize responsible supply chains. This includes sourcing materials that are recyclable or produced with minimal environmental impact. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and adherence to EEC standards for electric vehicles signify a commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. B2B buyers are advised to consider these certifications when selecting suppliers, as they reflect a manufacturer’s dedication to reducing their ecological footprint.
Furthermore, utilizing environmentally friendly materials in vehicle construction and promoting recycling initiatives can enhance a company’s brand image and attract eco-conscious consumers. As global markets evolve, businesses that integrate sustainability into their operations are likely to gain a competitive edge.
What Is the Evolution of Electric Cargo L6e Vehicles and Its Relevance for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of electric cargo L6e vehicles has been marked by technological advancements and shifting market demands. Initially, electric vehicles were limited in range and functionality, making them less appealing for commercial use. However, with improvements in battery technology and electric drivetrains, modern L6e vehicles now offer enhanced performance and versatility, making them suitable for various applications, including last-mile delivery and cold chain logistics.
As urban logistics challenges grow, particularly in densely populated regions, the demand for compact, efficient delivery solutions has surged. The introduction of models like the J4-C and J2-C highlights the industry’s response to these challenges, offering features tailored for urban environments, such as refrigeration capabilities and low maintenance costs.
For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Engaging with manufacturers who are at the forefront of these developments ensures access to the latest technology and compliance with emerging regulations, thus enhancing operational efficiency and sustainability in logistics operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric cargo l6e vehicle
-
How can I ensure compliance with EEC L6e regulations for electric cargo vehicles?
To ensure compliance with EEC L6e regulations, it’s essential to partner with manufacturers who have EEC certification for their vehicles. Request documentation proving compliance and familiarize yourself with the specific regulatory requirements in your country. Additionally, consider engaging local legal or trade experts who can assist in understanding any additional local regulations that may apply, ensuring that the vehicles you import meet all necessary standards for safety and performance. -
What are the most suitable applications for electric cargo L6e vehicles?
Electric cargo L6e vehicles are ideal for urban logistics, especially for short-distance deliveries. They are particularly effective in food delivery and cold chain logistics due to their ability to accommodate refrigeration units. Businesses in sectors like e-commerce, retail, and food distribution can leverage these vehicles to enhance their delivery efficiency while also contributing to sustainability goals by reducing carbon emissions in urban areas. -
What customization options are available for electric cargo L6e vehicles?
Most manufacturers offer a range of customization options for electric cargo L6e vehicles, including cargo box designs, refrigeration systems, and interior configurations. You can tailor the vehicle to fit specific business needs, such as enhanced storage for perishable goods or specialized equipment for particular industries. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore all available customization options that can optimize operational efficiency. -
What are the common payment terms when sourcing electric cargo L6e vehicles?
Payment terms can vary by supplier but typically include options like a deposit followed by payment upon delivery or completion of manufacturing. Common arrangements include 30% upfront and the remaining balance upon shipment. Always clarify payment terms before proceeding with an order, and consider using secure payment methods that offer buyer protection, especially for international transactions. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for electric cargo L6e vehicles?
The minimum order quantity for electric cargo L6e vehicles can vary significantly between manufacturers. Some suppliers may accept orders as low as one unit, while others may require a minimum of five to ten units. When negotiating with suppliers, inquire about their MOQ and whether they can accommodate smaller orders, particularly if you’re testing the market or starting a new delivery service. -
How can I vet suppliers of electric cargo L6e vehicles effectively?
To vet suppliers effectively, conduct thorough research into their reputation, product quality, and customer service. Request references from other B2B clients and check reviews or testimonials. It’s also beneficial to visit their manufacturing facilities if possible or request product samples. Ensure they have the necessary certifications, such as EEC approval, and verify their after-sales support capabilities, including maintenance and warranty services. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing electric cargo L6e vehicles?
Logistics considerations for importing electric cargo L6e vehicles include understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties specific to your country. Coordinate with your supplier to determine the best shipping options and ensure all documentation, such as bills of lading and customs declarations, is in order. Additionally, consider working with a logistics partner experienced in handling vehicle imports to streamline the process and mitigate potential delays. -
What quality assurance processes should I expect from manufacturers of electric cargo L6e vehicles?
Reputable manufacturers should have established quality assurance (QA) processes that include rigorous testing of vehicles for safety, performance, and compliance with regulatory standards. Inquire about their QA protocols, such as pre-shipment inspections and warranty policies. It’s also advisable to request detailed documentation of their QA procedures and to understand their approach to handling defects or issues that may arise post-purchase.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Electric Cargo L6E Vehicle Manufacturers & Suppliers List
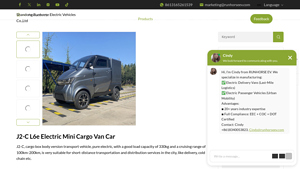
1. RunHorse – J2-C L6e Electric Mini Cargo Van
Domain: runhorseev.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Product Name: J2-C L6e Electric Mini Cargo Van Car
Product Code: 8613165261539
Type: Electric Mini Cargo Van
Load Capacity: 330 kg
Cruising Range: 100 km – 200 km
Max Speed: 45 km/h
Seating Capacity: 1
Battery: 105Ah/206Ah LiFePO4 with BMS system (fast charging)
Motor: 60V/3000W – 60V/4000W AC asynchronous motor
Charging Time: 2-3 hours (fast charging)
Brakes: Front disc brake & rear drum brake
Ty…
2. Yunlong – Y2-C Electric Vehicle
Domain: bev-cars.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Brand: Yunlong
Model: Y2-C
Operation Philosophy: Ideal solution for food delivery and cold chain logistics & transportation in cities.
Certificate: EEC L6e
Supply Ability: 1000 units/month
MOQ: 1 unit
Port: Qindao
Delivery terms: 20-40 days after receiving deposit
Payment terms: TT/LC
Loading Capacity: 2 units for 1*20′ GP, 8 units for 1*40 HQ
Skylight: Designed for fresh air
Seat: Genuine Leather…
3. Runhorse – EEC Coc L6e Four Wheel Mobility Mini Electric Cargo Van
Domain: marathitrade.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Product Name: EEC Coc L6e Four Wheel Mobility Mini Electric Cargo Van Car
Model: Runhorse J2-C
Certification: EEC L6E
Purpose: Last mile solution for city delivery & logistics, express, city logistics, and supermarket goods transportation
Battery: 100AH or 200AH Lithium iron phosphate battery with fast charger
Charging Time: 2-3 hours
Power Consumption: Less than $0.5 per 100 km
Motor: AC motor wi…
4. EEC – L6e Electric Cargo Truck
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: EEC L6e electric cargo box truck car equipped with 105Ah LiFePo4 Battery with BMS & Fast charging system, 3 Kw Motor, Rated Load 300-500kg, Max. Speed 45Km/h.
5. ScrapingDog – Instagram Data Solutions
Domain: instagram.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Contact us at [email protected] for scraping Instagram. Let us know how many pages you want to scrape per month.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric cargo l6e vehicle
In the dynamic world of urban logistics, the adoption of electric cargo L6e vehicles presents an exceptional opportunity for businesses aiming to enhance their delivery capabilities while minimizing their environmental footprint. The recent innovations, such as the J4-C and J2-C models, demonstrate the versatility and efficiency of electric cargo solutions, catering specifically to last-mile delivery and cold chain logistics. These vehicles, compliant with EEC standards, not only ensure regulatory adherence but also offer features like refrigeration capabilities and low maintenance costs, making them ideal for urban environments.
Strategic sourcing of these vehicles can significantly impact operational efficiency and sustainability. For international buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this is an opportune moment to explore partnerships with manufacturers and dealers. Investing in electric cargo L6e vehicles can lead to cost savings, enhanced delivery performance, and a stronger commitment to environmental responsibility.
As urban areas increasingly embrace greener transport solutions, now is the time for businesses to act. Engage with manufacturers to assess how electric cargo vehicles can be integrated into your logistics framework, paving the way for a more sustainable and efficient future in urban delivery services.