Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for disabled car electric
In the quest for sourcing electric vehicles tailored for individuals with disabilities, international B2B buyers face a myriad of challenges. The global market for disabled car electric solutions is burgeoning, yet it remains fraught with complexities such as accessibility features, regulatory compliance, and varying infrastructure across regions. This guide provides an in-depth exploration of the landscape, encompassing various types of accessible electric vehicles, innovative adaptations, and the latest advancements in technology.
Buyers will find valuable insights into how to vet suppliers effectively, ensuring they choose partners who prioritize quality and inclusivity. Additionally, this resource outlines the cost considerations involved, providing a clear framework for budgeting and investment. By addressing the specific needs of markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria—this guide empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance mobility solutions for disabled individuals.
As the demand for sustainable and accessible transportation grows, understanding the nuances of the disabled car electric market is crucial for fostering independence and mobility for all. This comprehensive guide equips B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to navigate this evolving sector with confidence.
Understanding disabled car electric Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
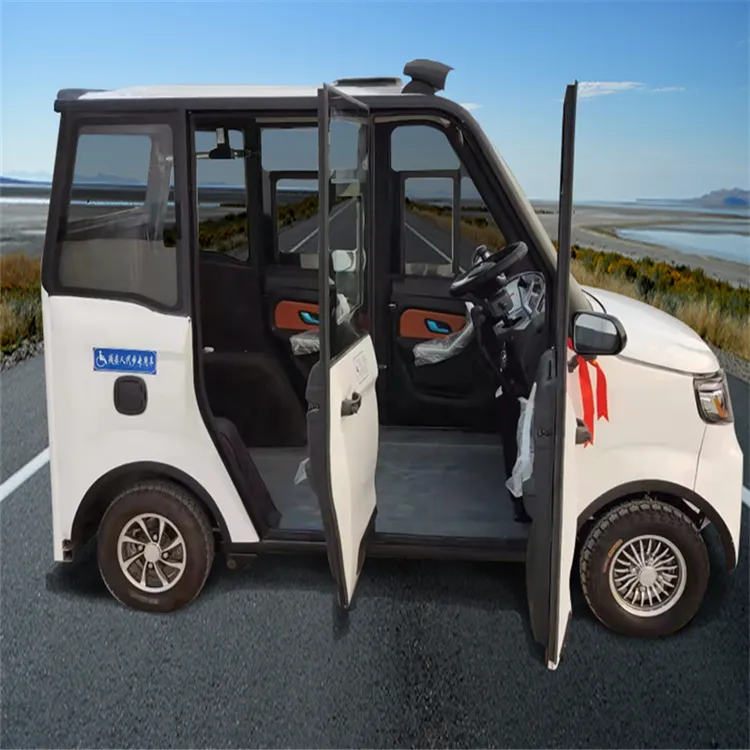
| Electric Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles (eWAVs) | Designed to allow wheelchair users to ride while seated in their wheelchair; often includes ramps and lowered floors. | Fleet services for disability transport, rental agencies focusing on accessible vehicles. | Pros: Direct access for wheelchair users; promotes independence. Cons: Limited models available; potentially higher upfront costs. |
| Compact Electric Mobility Cars | Smaller electric vehicles with features like adjustable ramps and minimal transfer requirements for easy access. | Dealerships targeting urban mobility solutions, mobility aid providers. | Pros: Cost-effective; easy to maneuver in urban settings. Cons: Limited space for larger mobility devices. |
| Adaptable Electric Vehicles | Vehicles that can be modified with driving aids, such as hand controls and swivel seats, to accommodate various disabilities. | Custom vehicle converters, adaptive equipment suppliers. | Pros: High customization potential; versatile for different needs. Cons: Modification costs can add up; may require specialized knowledge for adaptations. |
| Electric Vans for Mobility | Larger vehicles equipped to transport multiple passengers or larger mobility equipment, often with ramp access. | Public transport services, community mobility programs. | Pros: Capacity for multiple passengers; suitable for group transport. Cons: Higher operational costs; may require specialized drivers. |
| Electric Vehicle Charging Solutions | Infrastructure designed to provide accessible charging options for disabled drivers, including adapted charging stations. | Charging station manufacturers, municipal planning departments. | Pros: Essential for supporting the EV ecosystem; promotes inclusivity. Cons: Implementation can be slow; requires collaboration between stakeholders. |
What Are Electric Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles (eWAVs) and Their B2B Relevance?
Electric Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles (eWAVs) are specifically designed to accommodate wheelchair users, allowing them to travel while remaining in their wheelchairs. These vehicles typically feature ramps and lowered floors for easy access. For B2B buyers, eWAVs are critical in fleet services catering to individuals with disabilities, enabling transportation companies to offer inclusive services. However, the limited availability of models and potentially high initial costs can be a challenge when considering procurement.
How Do Compact Electric Mobility Cars Enhance Urban Mobility?
Compact electric mobility cars are designed for easy maneuverability in urban environments, often equipped with adjustable ramps that allow wheelchair users to enter without transfers. These vehicles are particularly appealing to dealerships focusing on urban mobility solutions, as they offer an affordable and efficient option for city dwellers. While they promote independence, their limited space may restrict the transport of larger mobility devices, which should be considered during the purchasing process.
Why Are Adaptable Electric Vehicles Essential for Diverse Needs?
Adaptable electric vehicles can be fitted with driving aids, such as hand controls and swivel seats, to meet various mobility requirements. These vehicles are beneficial for custom vehicle converters and adaptive equipment suppliers targeting diverse customer needs. The high level of customization allows these vehicles to cater to a wide range of disabilities, but B2B buyers should be aware that modification costs can accumulate, requiring careful budgeting.
What Advantages Do Electric Vans for Mobility Offer?
Electric vans designed for mobility are larger vehicles that can transport multiple passengers or accommodate larger mobility equipment. They are ideal for public transport services and community mobility programs looking to enhance accessibility. While their capacity for group transport is a significant advantage, buyers must consider the higher operational costs and potential need for specialized drivers, which can impact overall profitability.
How Do Electric Vehicle Charging Solutions Support Accessibility?
Electric vehicle charging solutions are crucial for ensuring that disabled drivers can access charging stations. These solutions include adapted charging stations that cater to the needs of disabled users. For B2B buyers involved in manufacturing charging infrastructure or municipal planning, investing in accessible charging solutions is essential for fostering an inclusive EV ecosystem. However, the slow pace of implementation and the necessity for collaboration between various stakeholders can pose challenges.
Key Industrial Applications of disabled car electric
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of disabled car electric | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Transportation | Integration of electric vehicles in accessible transit systems | Enhances inclusivity and access for disabled individuals, increasing ridership | Compliance with accessibility standards, partnerships with local governments |
| Healthcare Services | Mobile clinics using electric vehicles for patient transport | Reduces carbon footprint while providing essential healthcare access | Vehicle customization for medical equipment, charging infrastructure |
| Tourism and Hospitality | Accessible electric shuttles for tourist attractions | Attracts a broader audience, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty | Fleet management solutions, partnerships with local attractions |
| Logistics and Delivery | Electric vehicles for last-mile delivery of accessible goods | Expands market reach while showcasing commitment to sustainability | Adaptations for loading and unloading mobility devices, route planning software |
| Automotive Retail | Showroom models for electric vehicles designed for disabled drivers | Differentiates offerings, tapping into a growing market segment | Collaboration with manufacturers for accessible features, training for sales staff |
How Can Public Transportation Benefit from Disabled Car Electric Solutions?
Public transportation systems can integrate disabled car electric vehicles to enhance accessibility for individuals with mobility challenges. By providing electric options, these systems can reduce environmental impact while promoting inclusivity. Key requirements for international buyers in regions like Africa or the Middle East include compliance with local accessibility standards and the establishment of partnerships with local governments to ensure funding and support.
What Role Do Electric Vehicles Play in Healthcare Services?
Electric vehicles can serve as mobile clinics, providing essential healthcare services directly to patients, particularly in underserved areas. This application addresses the challenge of transportation barriers faced by individuals with disabilities. Buyers in the healthcare sector should consider vehicle customization to accommodate medical equipment and ensure access to charging infrastructure for effective operation.
How Can the Tourism Industry Leverage Accessible Electric Vehicles?
Tourism and hospitality sectors can utilize electric shuttles designed for accessibility to cater to a wider audience, including disabled tourists. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also demonstrates a commitment to sustainability. B2B buyers must focus on fleet management solutions and partnerships with local attractions to create seamless experiences for tourists.
What Are the Logistics Benefits of Electric Vehicles for Last-Mile Delivery?
In logistics, electric vehicles can facilitate last-mile delivery of accessible goods, ensuring that individuals with disabilities receive products and services tailored to their needs. This approach expands market reach while showcasing a commitment to sustainability. Buyers should prioritize adaptations for loading mobility devices and invest in route planning software to optimize delivery efficiency.
How Can Automotive Retailers Differentiate Their Offerings with Disabled Car Electric Models?
Automotive retailers can differentiate themselves by showcasing electric vehicles designed specifically for disabled drivers. This taps into a growing market segment seeking more inclusive transportation options. Key sourcing considerations include collaboration with manufacturers to ensure accessible features are included and training sales staff to effectively communicate these benefits to potential buyers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘disabled car electric’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Availability of Wheelchair Accessible Electric Vehicles (WAVs)
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter significant challenges when trying to source wheelchair accessible electric vehicles (WAVs). The current market has a limited selection of WAVs, primarily due to the design constraints associated with electric vehicle batteries, which are typically placed beneath the vehicle floor. This positioning complicates the necessary modifications for creating a low entry point for wheelchair users. Consequently, businesses aiming to provide inclusive transportation options find themselves struggling to meet the needs of their clients, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where accessible transportation is crucial.
The Solution: To overcome this limitation, B2B buyers should actively engage with manufacturers and conversion specialists who specialize in adaptive vehicle technology. Establishing partnerships with these entities can facilitate the development of custom solutions that meet specific accessibility standards while ensuring compliance with local regulations. Buyers should also advocate for collaborative efforts between electric vehicle manufacturers and WAV converters to expand the availability of electric WAVs. Additionally, participating in industry expos and forums can provide insights into upcoming models and innovations that may not yet be widely known, helping businesses to stay ahead of the curve.
Scenario 2: Challenges with Charging Infrastructure for Disabled Electric Vehicle Users
The Problem: A significant pain point for B2B buyers is the inadequate charging infrastructure tailored for disabled electric vehicle users. Research indicates that many public charging stations lack accessible features, such as dropped kerbs or designated parking spaces, making it difficult for disabled drivers to charge their vehicles. This lack of accessibility not only hampers user experience but also raises concerns for businesses seeking to promote electric mobility solutions to their clients in regions like the Middle East and Europe, where public charging is essential.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should advocate for the adoption of the Electric Vehicles Accessible Charging Specification (PAS 1899) in their local regions. Engaging with local government and infrastructure development agencies to push for accessible charging stations is critical. Buyers can also partner with charging network providers to ensure that new installations are compliant with accessibility standards. Additionally, businesses can consider providing educational resources for their clients on locating accessible charging stations, thus enhancing the overall user experience and confidence in electric vehicle adoption.
Scenario 3: High Initial Costs and Financial Accessibility Concerns
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of high initial costs associated with electric vehicles, which can deter businesses from investing in disabled car electric options. The upfront price of these vehicles, especially new models, often exceeds that of traditional petrol or diesel cars. This financial barrier is particularly pronounced in markets where budgets are tight, such as in emerging economies in Africa and South America. Moreover, the absence of adequate financing options can make it difficult for businesses to justify these investments, despite the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance.
The Solution: To alleviate these financial concerns, B2B buyers should explore available government incentives and subsidies for electric vehicle purchases in their regions. Many countries offer financial assistance programs specifically designed for businesses that invest in accessible transportation solutions. Furthermore, buyers should consider forming alliances with financial institutions to create tailored financing options that cater to the unique needs of their clientele. By providing information on leasing programs, such as those offered through the Motability Scheme in Europe, businesses can help clients manage costs more effectively while promoting the adoption of electric vehicles.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for disabled car electric
What Are the Key Materials Used in Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers?
When selecting materials for electric vehicles designed for disabled drivers, several factors must be considered, including performance properties, manufacturing complexity, and cost-effectiveness. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the production of accessible electric vehicles, focusing on their suitability for B2B applications.
Aluminum: A Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant Option
Key Properties: Aluminum is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity. It typically performs well under a range of temperatures, making it suitable for various climates.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum contributes to improved vehicle efficiency and range, which is crucial for electric vehicles. However, it can be more expensive than steel and may require specialized welding techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly beneficial for components like the vehicle frame and body panels, where weight reduction can lead to better performance. Its corrosion resistance is vital in humid or coastal environments, making it a preferred choice in regions like the Middle East and coastal areas of South America.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions such as Africa and Europe should ensure that aluminum components comply with relevant standards like ASTM B209 or EN 573. Understanding local sourcing options can also help mitigate costs.
Steel: The Traditional Choice with Strength and Durability
Key Properties: Steel is renowned for its high tensile strength and durability, making it a common choice for structural components. It has a high melting point and excellent impact resistance.
Pros & Cons: While steel is generally less expensive than aluminum and offers superior strength, it is heavier, which can negatively impact the vehicle’s range and efficiency. Additionally, steel is prone to corrosion unless treated with protective coatings.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used in the chassis and other structural components of electric vehicles. Its durability makes it suitable for vehicles that may encounter rough terrain, particularly in regions with less developed infrastructure.
International Considerations: B2B buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM A36 and EN 10025 for structural steel. In regions like Nigeria, where road conditions may be challenging, the durability of steel can be a significant advantage.
Composite Materials: Innovative and Versatile
Key Properties: Composites, often made from a combination of plastic and fiber materials, offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. They can be engineered to meet specific performance requirements.
Pros & Cons: Composites can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs. However, they can be more expensive to produce and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can complicate supply chains.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for interior components, such as seating and panels, where weight reduction and design flexibility are essential. Their resistance to corrosion is particularly beneficial in humid environments.
International Considerations: Buyers should look for compliance with standards like ASTM D3039 for composite materials. In regions like Europe, where sustainability is a priority, composites can also contribute to the vehicle’s overall eco-friendliness.
Thermoplastics: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Key Properties: Thermoplastics are lightweight, easy to mold, and can be recycled. They have good impact resistance and can withstand a range of temperatures.
Pros & Cons: The low cost and ease of manufacturing make thermoplastics an attractive option for many components. However, they may not offer the same level of durability as metals, particularly in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Thermoplastics are often used in non-structural components, such as dashboards and trim. Their lightweight nature can help improve overall vehicle efficiency.
International Considerations: Compliance with standards such as ASTM D638 for plastics is essential for international buyers. In regions with high temperatures, like parts of Africa and the Middle East, thermal stability should be a key consideration.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for disabled car electric | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Vehicle frame and body panels | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Steel | Chassis and structural components | High strength and durability | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Composite | Interior components (seating, panels) | Design flexibility and lightweight | Higher production costs | High |
| Thermoplastics | Non-structural components (dashboards) | Low cost and ease of manufacturing | Less durable than metals | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with valuable insights into the materials available for electric vehicles designed for disabled drivers, helping them make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for disabled car electric
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers?
The manufacturing of electric vehicles (EVs) designed specifically for disabled drivers involves several critical stages, each aimed at ensuring the highest quality and accessibility standards. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
In this initial stage, manufacturers select high-quality materials that meet both safety and accessibility requirements. Common materials include lightweight metals such as aluminum and high-strength steel for the frame, along with durable plastics and composites for interior components. The selection process is crucial as it impacts the vehicle’s overall weight, safety, and energy efficiency.
Forming: How Are Vehicle Components Shaped?
Once materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes such as stamping, molding, and extrusion. These techniques shape the various components of the vehicle, including the body panels, chassis, and structural reinforcements. Advanced techniques like hydroforming may also be utilized to create complex shapes that enhance structural integrity while reducing weight, which is particularly beneficial for electric vehicle performance.
Assembly: What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
The assembly stage involves integrating all components into a cohesive unit. This includes installing the electric drivetrain, battery packs, and accessibility features such as ramps and swivel seats. Automation plays a significant role in this phase, with robotic systems used for precision tasks. Manual assembly is also vital, especially for specialized adaptations that cater to the unique needs of disabled users.
Finishing: How Is the Final Product Prepared for Market?
The finishing stage encompasses painting, quality checks, and final adjustments. This is where the vehicle is given its exterior color and protective coatings. Quality assurance checks are performed to ensure all components function correctly, and any necessary adjustments are made. This stage is essential for delivering a product that meets both aesthetic and functional standards.
What Quality Control Standards Are Relevant for Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers?
Quality control (QC) is critical in the manufacturing of electric vehicles, especially those designed for disabled individuals. Adhering to relevant international standards ensures that products are safe, reliable, and meet the specific needs of users.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
ISO 9001 is a globally recognized standard that outlines quality management system requirements. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers have a robust quality framework in place. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking in Europe and API specifications may apply, depending on the components used (e.g., electrical systems).
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing stages help identify and rectify defects early in the process.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive assessment of the finished product ensures that it meets all safety and functional specifications before it is delivered to the market.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Manufacturers utilize a variety of testing methods to ensure that electric vehicles for disabled drivers are safe and reliable. These methods may include:
- Crash Testing: Evaluating the vehicle’s structural integrity and safety features under simulated crash conditions.
- Electrical Testing: Assessing the performance and safety of electrical components, including battery systems and wiring.
- Accessibility Testing: Ensuring that features such as ramps and seating arrangements meet the required standards for usability by disabled individuals.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure product reliability. Here are several strategies to consider:
What Should Buyers Look for in Audits and Reports?
Buyers should request documentation of quality audits, including results from internal and external assessments. Regular audits by third-party organizations can provide an unbiased view of the supplier’s quality management practices.
Are Third-Party Inspections Necessary?
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. These independent entities can evaluate the manufacturing process and ensure compliance with relevant standards, providing buyers with peace of mind.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in ensuring quality control in their supply chain.
How Can Cultural and Regulatory Differences Impact QC?
Cultural differences and varying regulatory environments can influence manufacturing practices and standards. Buyers should be aware of local regulations related to vehicle accessibility and safety, as well as any certifications required in their target markets.
What Role Does Compliance Play in International Transactions?
Compliance with international standards not only affects product quality but also impacts marketability. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are compliant with both local and international standards to avoid potential legal issues and ensure product acceptance in their respective markets.
Conclusion: Why Is Understanding Manufacturing Processes and Quality Control Critical for B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers in the electric vehicle sector, particularly those focused on accessible vehicles for disabled drivers, a thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and quality control measures is essential. By prioritizing quality assurance, buyers can ensure that the products they offer meet the highest standards of safety, functionality, and accessibility, ultimately leading to improved customer satisfaction and business success.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘disabled car electric’
In today’s evolving automotive landscape, sourcing electric vehicles for individuals with disabilities is critical for ensuring accessibility and independence. This guide provides a structured checklist for B2B buyers to effectively procure ‘disabled car electric’ options that meet the diverse needs of users while maintaining high standards of quality and functionality.
Step 1: Identify User Requirements
Understanding the specific needs of your target demographic is paramount. Evaluate factors such as wheelchair accessibility, seating arrangements, and driving aids. This will ensure that the vehicles you consider can accommodate various mobility challenges and preferences.
- Considerations:
- Assess the type of mobility devices users will be transporting.
- Determine the driving conditions (urban vs. rural) to inform vehicle specifications.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the electric vehicles you wish to procure. This includes battery range, charging capabilities, and the physical dimensions of the vehicle.
- Key Factors:
- Battery life should be sufficient for daily use without frequent recharging.
- Charging infrastructure compatibility is essential, especially in regions with limited access to charging stations.
Step 3: Research and Evaluate Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Look for manufacturers who specialize in accessible electric vehicles and have a proven track record in the industry.
- What to Look For:
- Supplier certifications and compliance with international standards for accessibility.
- Customer testimonials and case studies that highlight their reliability and customer service.
Step 4: Assess Vehicle Adaptability and Features
Evaluate the adaptability of the electric vehicles for different user needs. Features like powered tailgates, adjustable seating, and easy-access ramps can significantly enhance usability.
- Essential Features:
- Ensure vehicles can accommodate various mobility aids.
- Look for advancements in assistive technology that improve driving safety and comfort.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Accessibility Standards
Ensure that the vehicles meet local and international accessibility standards. This includes compliance with regulations such as the Electric Vehicles Accessible Charging Specification (PAS 1899).
- Compliance Checks:
- Review documentation and certifications that demonstrate adherence to accessibility guidelines.
- Investigate the availability of accessible charging stations to support user convenience.
Step 6: Consider Total Cost of Ownership
Analyze the total cost of ownership, including initial purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. While electric vehicles may have higher upfront costs, they often result in lower long-term expenses.
- Cost Considerations:
- Look into available financing options or grants for acquiring electric vehicles for disabled users.
- Factor in the potential savings from lower fuel and maintenance costs.
Step 7: Build Relationships with Key Stakeholders
Establish connections with relevant stakeholders, including disability advocacy groups, local governments, and community organizations. These relationships can provide valuable insights and support in your procurement process.
- Networking Opportunities:
- Attend industry expos and conferences focused on mobility solutions.
- Collaborate with organizations to understand best practices and emerging trends in accessible transportation.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure they are well-equipped to procure electric vehicles that not only fulfill technical specifications but also genuinely enhance the mobility and independence of individuals with disabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for disabled car electric Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers?
When sourcing electric vehicles designed for disabled drivers, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the overall cost. Lightweight materials like aluminum and advanced composites are preferred for their durability and efficiency, but they often come at a premium. Additionally, sourcing environmentally friendly materials can add to costs but may appeal to eco-conscious markets.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of the vehicle design. Skilled labor is essential for assembling specialized adaptations that cater to disabled users, such as modified seating and ramp systems. Countries with higher labor costs may see increased pricing, while regions with lower wages may offer more competitive rates.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead costs encompass utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs, impacting the final pricing of the vehicle.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized vehicle adaptations can be a significant upfront cost. Buyers should consider whether the supplier has the necessary tooling in place or if new investments will be required, as this affects both pricing and lead times.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that vehicles meet safety and accessibility standards involves rigorous QC processes. The costs associated with these checks can vary based on the certifications required in different markets, influencing the overall pricing strategy.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for sourcing components and delivering finished vehicles are crucial. International shipping can add complexity and cost, particularly for buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where logistics infrastructure may be less developed.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a profit margin into their pricing. Understanding the standard margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers?
Several factors can influence the pricing of electric vehicles designed for disabled drivers.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes generally lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQ terms to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features tailored to specific needs can significantly increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses during production.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The use of high-quality materials and compliance with international standards can raise costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to perceived quality and service levels.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms can help buyers manage costs effectively. Different Incoterms can dictate who bears the cost of shipping and insurance, influencing the overall price.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Cost-Efficiency in Electric Vehicle Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage volume purchases and long-term relationships to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers may be more willing to offer discounts for committed buyers.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the ongoing operational costs, such as maintenance and energy consumption. Electric vehicles typically have lower running costs compared to traditional combustion engines.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of market trends and pricing strategies specific to your region. Currency fluctuations and import duties can affect the final cost significantly.
-
Research Local Regulations: Compliance with local regulations can incur additional costs. Familiarize yourself with these to avoid surprises.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for electric vehicles designed for disabled drivers can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned above. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and consult with multiple suppliers to obtain accurate quotes tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing disabled car electric With Other Solutions
Exploring Viable Alternatives to Disabled Car Electric Solutions
In the rapidly evolving landscape of mobility solutions for individuals with disabilities, it is essential to assess the available options critically. While electric vehicles designed for disabled drivers present innovative advantages, various alternatives exist that can also enhance mobility and accessibility. This analysis compares ‘disabled car electric’ solutions with two alternatives: traditional wheelchair-accessible vehicles (WAVs) and ride-sharing services tailored for individuals with mobility challenges.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Disabled Car Electric | Traditional Wheelchair-Accessible Vehicle (WAV) | Ride-Sharing Services for Disabled Users |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Limited to urban areas; speeds up to 25 mph | Versatile for various terrains; can offer higher speeds | Flexible travel options; varied vehicle types |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower running costs | Moderate initial cost; ongoing maintenance required | Pay-per-ride; potentially more expensive over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized manufacturing and infrastructure | Readily available; established market | Easy to use through apps; no vehicle ownership |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized service for electric components | Standard maintenance practices for vehicles | No maintenance required; service provider’s responsibility |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for independent mobility in urban settings | Suitable for diverse travel needs, including long-distance | Great for spontaneous travel without vehicle ownership |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Traditional Wheelchair-Accessible Vehicles (WAVs)
Traditional WAVs are modified vehicles that allow wheelchair users to enter and exit while remaining in their wheelchairs. These vehicles typically feature lowered floors and ramps, providing ease of access. The primary advantage of WAVs is their versatility; they can accommodate a broader range of mobility devices and offer higher speeds than electric models designed for disabled use. However, the ongoing maintenance costs and potential for breakdowns can be a disadvantage, particularly for businesses looking to maintain a reliable fleet.
Ride-Sharing Services for Disabled Users
Ride-sharing services tailored for individuals with disabilities provide an accessible and flexible transportation option. These services allow users to book rides via mobile applications, offering various vehicle types based on the user’s needs. The convenience of not owning a vehicle and the ability to use the service on-demand are significant benefits. However, costs can accumulate quickly, especially for frequent users, and the availability of accessible vehicles may vary by region, potentially leading to inconsistencies in service quality.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Mobility Solution
When selecting the most suitable mobility solution, B2B buyers must consider various factors such as performance requirements, cost implications, and specific use cases. For organizations focused on providing independence and convenience for disabled individuals, a disabled car electric may offer innovative features that enhance user experience, particularly in urban environments. Conversely, WAVs may be more appropriate for businesses needing versatile transportation options across different terrains. Ride-sharing services provide an excellent alternative for those prioritizing flexibility and minimal upfront investment. Ultimately, understanding the unique needs of the end-users and the operational context will guide buyers in making an informed decision that best supports their mobility objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for disabled car electric
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Cars for Disabled Drivers?
When evaluating electric vehicles (EVs) designed for disabled drivers, several technical properties are crucial for ensuring performance, accessibility, and user satisfaction. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Ramp Weight Capacity
This specification refers to the maximum weight the vehicle’s ramp can support when loading or unloading a wheelchair. A higher weight capacity ensures that a broader range of mobility devices can be accommodated. For B2B buyers, understanding this specification is critical for meeting diverse customer needs, especially in markets with varying user requirements. -
Battery Range
The distance an electric vehicle can travel on a single charge is fundamental for usability. Vehicles designed for disabled drivers should ideally have a battery range of at least 100-150 miles to ensure sufficient travel distance without frequent recharging. For business buyers, this impacts customer satisfaction and operational efficiency, particularly in regions with limited charging infrastructure. -
Accessibility Features
This encompasses design elements such as swivel seats, powered tailgates, and adjustable seat heights. These features are vital for enhancing user experience and independence. Buyers should prioritize vehicles that integrate these accessibility options, as they can significantly influence purchase decisions among end-users. -
Charging Time
The duration required to fully charge an electric vehicle can vary significantly. Vehicles with fast-charging capabilities—often achieving an 80% charge in under an hour—are particularly beneficial for users who require quick turnaround times. For B2B purchasers, this can enhance the vehicle’s attractiveness to potential clients who prioritize efficiency. -
Safety Standards
Compliance with safety regulations is paramount, especially for vehicles catering to disabled drivers. This includes features such as advanced braking systems and stability control. B2B buyers must ensure that the vehicles meet local and international safety standards, as this can affect liability and insurance considerations. -
Material Composition
The materials used in constructing the vehicle, such as lightweight alloys and high-strength composites, can influence performance and durability. Understanding the material specifications helps buyers assess the vehicle’s longevity and maintenance costs, which are critical factors in B2B purchasing decisions.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Disabled Electric Vehicle Market?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication in the B2B environment. Here are some commonly used terms relevant to the disabled electric vehicle sector:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of electric vehicles, knowing the OEM can help buyers ensure they are sourcing high-quality components for vehicle adaptations. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, understanding MOQ is crucial for inventory management and budgeting, especially when dealing with specialized vehicles that may have higher production costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process where a buyer requests a quote from suppliers for specific products or services. This is particularly relevant for buyers looking to acquire custom adaptations or bulk purchases of electric vehicles designed for disabled individuals. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers involved in cross-border purchases, as they clarify shipping responsibilities, risk, and costs. -
WAV (Wheelchair Accessible Vehicle)
A WAV is a vehicle modified to allow wheelchair users to travel while remaining in their wheelchair. Understanding this term is critical for businesses focused on providing solutions tailored to the needs of disabled customers. -
eWAV (Electric Wheelchair Accessible Vehicle)
This term refers to electric vehicles specifically designed or adapted to accommodate wheelchair users. As the market for accessible electric vehicles grows, recognizing this term helps buyers identify suitable models for their clientele.
By equipping themselves with knowledge of these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with the needs of their customers in the growing market for electric vehicles tailored for disabled drivers.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the disabled car electric Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Disabled Car Electric Market?
The disabled car electric market is experiencing a paradigm shift driven by several global trends. Increased demand for electric vehicles (EVs) aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability and reduced emissions, compelling manufacturers to innovate in accessibility features. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the push for inclusivity in mobility solutions is becoming critical. This includes the rise of wheelchair-accessible electric vehicles (eWAVs) and adaptations that cater to a diverse range of mobility needs.
Emerging technologies such as smart vehicle systems, assistive driving aids, and adaptive seating options are pivotal in enhancing user experience. Companies are leveraging Internet of Things (IoT) technologies to create vehicles that can communicate with smart infrastructure, thereby improving accessibility for disabled drivers. Furthermore, the demand for electric vehicles is expected to surge as governments worldwide set targets to phase out fossil-fuel vehicles, creating opportunities for B2B partnerships in the supply chain of electric mobility solutions.
Market dynamics are also influenced by the need for robust charging infrastructure tailored to the disabled community. Research indicates that less than 3% of public charging stations are accessible, highlighting a significant gap that presents opportunities for B2B collaborations in developing inclusive charging solutions. As the market matures, the integration of ethical sourcing and sustainability into supply chains will be paramount, influencing purchasing decisions among B2B buyers.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Disabled Car Electric Sector?
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it’s a business imperative in the disabled car electric sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing electric vehicles is substantial, and international buyers are increasingly focused on sourcing from companies that prioritize eco-friendly practices. This includes utilizing sustainable materials in vehicle production and ensuring that the supply chain adheres to ethical labor standards.
The push for ‘green’ certifications is gaining traction, with buyers seeking manufacturers who can demonstrate compliance with recognized environmental standards. This can include certifications for low emissions, sustainable sourcing of materials, and responsible waste management practices. For B2B buyers, aligning with suppliers who value sustainability not only enhances brand reputation but also meets the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
Moreover, the integration of renewable energy sources in the charging infrastructure for electric vehicles is essential. Buyers must consider how their sourcing decisions can contribute to a holistic approach to sustainability, including partnerships with companies that provide green energy solutions for charging stations. As ethical sourcing becomes a competitive differentiator, B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who can showcase transparency in their supply chains and commitment to reducing their carbon footprint.
What Is the Evolution of the Disabled Car Electric Market?
The evolution of the disabled car electric market reflects a broader transformation in the automotive industry. Initially, electric vehicles focused primarily on performance and efficiency, with little consideration for accessibility. However, as awareness of the needs of disabled individuals has grown, manufacturers have begun to innovate solutions that cater specifically to this demographic.
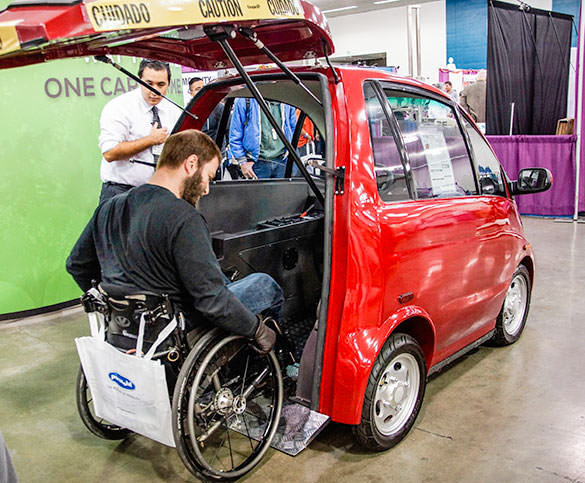
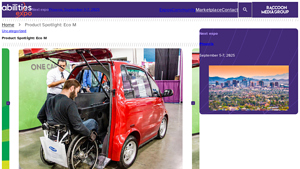
The introduction of models like the Eco M signifies a turning point, where functionality meets inclusive design. This vehicle allows wheelchair users to drive without the need for transfers, showcasing how advancements in technology can create a more accessible transportation landscape. The collaboration between manufacturers and adaptation specialists is crucial to overcoming existing barriers, such as the challenges associated with integrating battery systems in wheelchair-accessible designs.
As the market continues to evolve, it is essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about emerging trends, technologies, and regulatory changes that can impact their sourcing strategies. By understanding the historical context and current dynamics, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business goals while contributing to a more inclusive and sustainable future in mobility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of disabled car electric
-
How do I choose the right electric vehicle for disabled users?
When selecting an electric vehicle (EV) for disabled users, consider factors like accessibility features, ease of entry and exit, and the vehicle’s ability to accommodate mobility devices. Look for models that offer adjustable ramps, ample interior space, and adaptive technologies such as powered seats and hand controls. Additionally, assess the vehicle’s range and charging options to ensure it meets the specific needs of your target market, especially in regions with varying infrastructure. -
What are the key features to look for in electric cars designed for disabled drivers?
Key features include wheelchair accessibility, adjustable seating, and advanced safety technologies. Electric cars should have a low floor for easy access, sufficient space for mobility devices, and customizable driving aids. Evaluate the vehicle’s integration of assistive technologies, such as voice control and parking assistance, which enhance usability for disabled drivers. Furthermore, ensure the vehicle complies with local regulations and standards regarding accessibility. -
What are the typical payment terms when sourcing electric vehicles for disabled drivers?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and the scale of your order. Most suppliers offer flexible terms, including upfront payments, installment plans, or leasing options. For bulk orders, consider negotiating discounts or extended payment schedules. It’s crucial to clarify terms related to warranty coverage, delivery timelines, and return policies to mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
How can I vet suppliers of electric vehicles for disabled individuals?
To vet suppliers, start by checking their industry reputation through reviews and testimonials from other B2B buyers. Verify their certifications, quality control processes, and compliance with international safety standards. It’s also beneficial to request samples or demonstrations of the vehicles to assess their accessibility features firsthand. Networking within industry trade shows or forums can provide insights into reliable suppliers and their product offerings. -
What customization options are available for electric vehicles catering to disabled users?
Customization options may include modifications such as wheelchair lifts, hand controls, and personalized seating arrangements. Suppliers often provide the ability to tailor vehicles to meet specific needs, including interior layout and technology integration. When sourcing, inquire about the extent of customization available and the associated costs. Collaborating with specialized vehicle converters can also enhance the range of adaptations offered. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for electric vehicles designed for disabled drivers?
The MOQ for electric vehicles can differ based on the manufacturer or supplier’s production capabilities. Generally, larger orders may qualify for better pricing and favorable terms. For small businesses or startups, it’s advisable to discuss potential for lower MOQs or trial orders to gauge market demand without significant upfront investment. Establishing a relationship with the supplier may also lead to more flexible ordering options. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing electric vehicles for disabled users?
Logistics considerations include shipping costs, import duties, and compliance with local regulations. Ensure the vehicles meet the necessary safety and emissions standards for the destination country. Collaborate with experienced logistics providers who understand the complexities of transporting vehicles internationally, including customs clearance and handling of specialized equipment. Planning for potential delays and understanding the shipping timeline is essential for maintaining supply chain efficiency. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for electric vehicles sourced for disabled individuals?
Quality assurance can be achieved through a multi-step process that includes pre-shipment inspections, obtaining certifications from recognized authorities, and reviewing the supplier’s production practices. Request documentation that outlines the vehicle’s compliance with international safety standards. Establish clear criteria for quality checks upon delivery, and consider implementing a feedback loop with end-users to continuously improve the product offering based on their experiences.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Disabled Car Electric Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. EcoCentre – Eco M
Domain: abilities.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Eco M
Manufacturer: EcoCentre
Type: Accessible Electric Vehicle
Launch Date: Second quarter of 2025
Key Features:
– Small footprint with a big impact
– Designed for wheelchair users with an adjustable rear ramp
– No transfers required; users can roll in, lock down, and drive off
– Speed capability: Up to 25 mph
– Aimed at providing independence and freedom for people with disabiliti…
2. Energy Saving Trust – Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers
Domain: energysavingtrust.org.uk
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Electric vehicles (EVs) offer several benefits for disabled drivers, including lower running costs (approximately £760 cheaper per year compared to petrol or diesel), reduced maintenance costs (around £200 cheaper annually), and a smoother driving experience due to automatic transmissions. EVs can be more expensive upfront, especially for modified or wheelchair accessible vehicles (WAVs). Financia…
3. BraunAbility – Electric Vehicle Adaptations
Domain: braunability.eu
Introduction: BraunAbility offers adaptations for electric vehicles, focusing on two categories: hybrids/electric cars built on fossil fuel platforms and fully electric cars. Key considerations include:
1. **Hybrids and Electric Cars Built on Fossil Fuel Platforms**:
– **Examples**: Peugeot e-208, Volkswagen Golf GTE, Ford Kuga.
– **Pros**: Easier to adapt due to standardized 12V power for electric fu…
4. Electric Vans – VW ID Buzz, Hyundai Staria, Toyota Commuter
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Wheelchair accessible vehicles, specifically electric vans like the VW ID Buzz, Hyundai Staria, and Toyota Commuter. The VW ID Buzz is newly released, but there are challenges in finding EV wheelchair accessible vans due to specific dimension regulations (1.5×1.5×0.8 meters). The Kia PV5 WAV is mentioned as a potential future option, along with the Geely Fazion Vans. The minimum allocated space fo…
5. MG – MG4 EV
Domain: drivingelectric.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: 1. MG4 EV: Advance payment: £0 (SE) to £649 (Trophy Long Range), Range: 200 miles (base), 281 miles (SE Long Range). 2. Hyundai Kona Electric: Advance payment: £99 (48kWh Advance) to £3,599 (65kWh Ultimate w/ Lux Pack), Range: circa 215 miles (base), over 300 miles (top-spec). 3. Skoda Enyaq: Advance payment: £0 (60) to £2,099 (85x SportLine Plus), Range: well over 300 miles (top models). 4. Renau…
6. CyberSwitching – Commercial Dual EV Charging Stations
Domain: cyberswitching.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Electric Vehicle Chargers Commercial Dual EV Charging station with Cable management, Dual CSE1 Level-2, 48A, RFID $ 3,290.00 – $ 3,890.00; Electric Vehicle Chargers Commercial Dual 48A EV Charging station with Cable management, Dual CSE3 Level-2 with display, RFID, CTEP $ 3,490.00 – $ 4,090.00; Electric Vehicle Chargers Commercial Dual EV Charging station, Dual CSE1 Level-2, 48A, RFID $ 2,890.00 O…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for disabled car electric
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicles tailored for individuals with disabilities, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in meeting growing demands across global markets. The introduction of innovative models like the Eco M exemplifies the potential for accessible electric cars to enhance independence and mobility for users. However, significant barriers remain, including design limitations, inadequate charging infrastructure, and the high cost of initial investments.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there lies an opportunity to advocate for and invest in solutions that address these challenges. Collaborating with manufacturers to develop wheelchair-accessible electric vehicles and ensuring compliance with accessibility standards can foster a more inclusive market.
As the transition to electric mobility accelerates, businesses that prioritize accessibility will not only meet regulatory requirements but also tap into a growing customer base. By embracing strategic sourcing, companies can position themselves at the forefront of this essential movement. Now is the time to act—engage with manufacturers and stakeholders to build a more inclusive future for electric vehicles that cater to all.