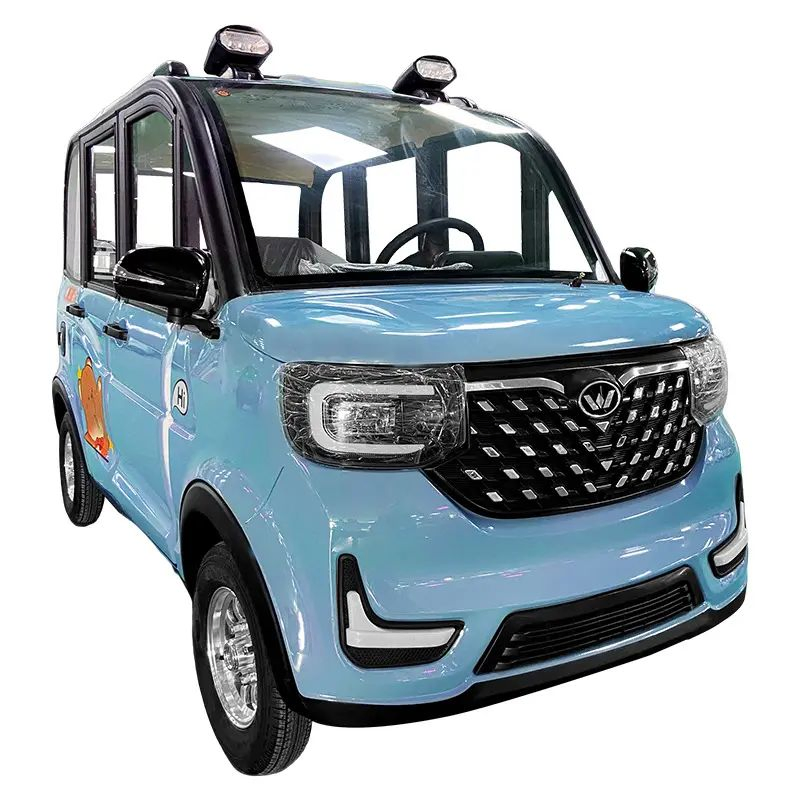
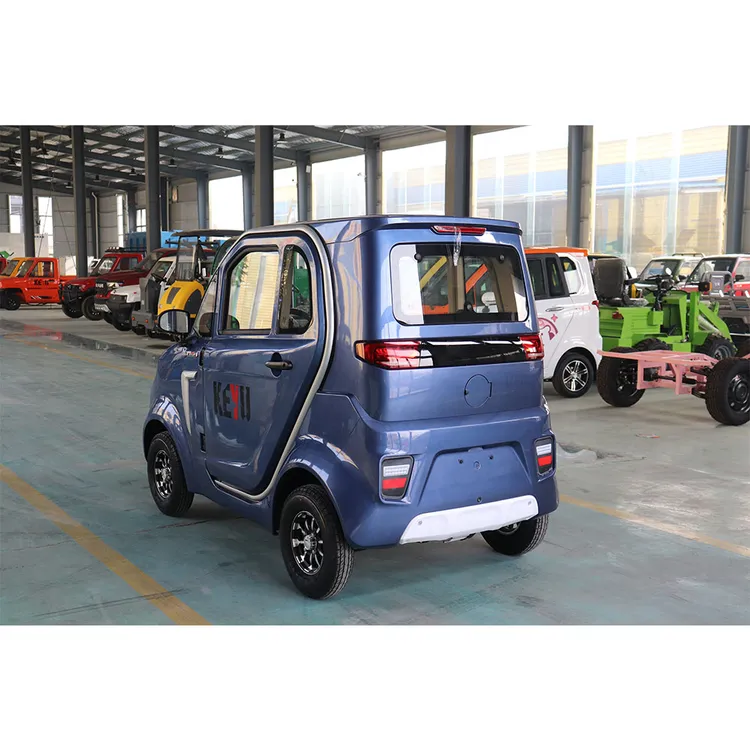
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 4 wheel electric car
In an era where sustainable transportation is a growing priority, navigating the global market for four-wheel electric cars presents unique challenges for B2B buyers. Sourcing the right electric vehicles that meet both operational needs and regional demands, particularly in markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, requires a strategic approach. This comprehensive guide delves into various types of four-wheel electric cars, their applications across diverse sectors, and the critical factors for supplier vetting. It also addresses cost considerations, charging infrastructure, and technological advancements that influence purchasing decisions.
As international B2B buyers face the pressing need for reliable electric vehicles that can withstand varying terrains and climates, this guide equips them with actionable insights. By understanding the capabilities of leading models, assessing their specifications, and evaluating supplier credentials, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their sustainability goals and operational requirements. From rugged off-road capabilities to urban-friendly designs, the four-wheel electric car market offers a wealth of options that can enhance fleet efficiency while minimizing environmental impact. This guide serves as a vital resource, empowering buyers to navigate the complexities of the electric vehicle landscape and ultimately drive their businesses forward in a greener direction.
Understanding 4 wheel electric car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| All-Wheel Drive SUVs | Enhanced traction and stability; raised ground clearance | Transportation services, fleet management | Pros: Better handling in adverse conditions; versatile. Cons: May have reduced range compared to 2WD models. |
| Off-Road Capable Electric Vehicles | Robust design; advanced off-road features; high ground clearance | Adventure tourism, utility services | Pros: Superior off-road performance; durable. Cons: Higher purchase price; may require specialized maintenance. |
| Compact Electric Crossovers | Smaller size; efficient space utilization; urban-friendly | Urban deliveries, small business fleets | Pros: Maneuverable in city traffic; lower operational costs. Cons: Limited cargo space; range may vary with load. |
| Luxury Electric 4x4s | Premium features; high performance; advanced technology | Executive transport, luxury rental services | Pros: Exceptional comfort and technology; strong brand appeal. Cons: High cost; may not be practical for all businesses. |
| Electric Pickups | Versatile cargo capacity; rugged design; towing capabilities | Logistics, agricultural applications | Pros: Excellent utility; strong towing capacity. Cons: Limited market availability; may have higher initial investment. |
What Are the Characteristics of All-Wheel Drive SUVs?
All-wheel drive (AWD) SUVs are designed to provide enhanced traction and stability, making them suitable for various driving conditions. These vehicles typically feature raised ground clearance and a robust chassis, allowing them to handle rough terrains and adverse weather effectively. B2B buyers in sectors like transportation services and fleet management find AWD SUVs appealing for their versatility and reliability, especially in regions with unpredictable climates. However, it’s essential to consider that opting for AWD may result in a slight reduction in range compared to two-wheel drive models.
How Do Off-Road Capable Electric Vehicles Stand Out?
Off-road capable electric vehicles are engineered for rugged environments, featuring advanced technologies that enhance their off-road performance. Key characteristics include high ground clearance, durable construction, and specialized driving modes for different terrains. These vehicles are particularly beneficial for businesses in adventure tourism and utility services, where off-road capabilities are essential. While they provide exceptional durability and performance, buyers should be aware of their higher purchase price and potential maintenance complexities.
What Makes Compact Electric Crossovers Ideal for Urban Applications?
Compact electric crossovers are designed for efficiency and maneuverability, making them well-suited for urban environments. Their smaller size allows for easy navigation through city traffic, while their electric powertrains contribute to lower operational costs. B2B applications include urban deliveries and small business fleets, where space optimization and cost-effectiveness are critical. However, buyers should consider the limited cargo space and the potential variability in range when carrying heavier loads.
Why Choose Luxury Electric 4x4s for Executive Transport?
Luxury electric 4x4s combine high performance with premium features, making them an attractive option for executive transport and luxury rental services. These vehicles often come equipped with advanced technology, superior comfort, and strong brand recognition, appealing to businesses that prioritize client experience. While they offer exceptional driving comfort and status, the high initial cost and practicality for everyday use are factors buyers must weigh.
What Are the Advantages of Electric Pickups for Logistics?
Electric pickups are designed for versatility, offering robust cargo capacity and towing capabilities that cater to various logistical needs. They are particularly valuable in sectors like logistics and agriculture, where transporting goods and equipment is essential. Buyers should appreciate the utility these vehicles provide; however, limited market availability and potentially higher initial investments may pose challenges for some businesses.
Key Industrial Applications of 4 wheel electric car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 4 wheel electric car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics & Transportation | Last-Mile Delivery Solutions | Enhanced efficiency and reduced operational costs through electric mobility. | Range capabilities, charging infrastructure, and maintenance support. |
| Agriculture | Off-Road Utility Vehicles | Ability to navigate rugged terrains, improving productivity in crop management. | Ground clearance, battery life in rural settings, and adaptability to various terrains. |
| Tourism & Hospitality | Eco-Friendly Transport Services | Attracts eco-conscious customers and reduces carbon footprint. | Vehicle comfort, range for tours, and local charging options. |
| Construction | Site Transportation | Provides reliable transport for workers and materials in challenging environments. | Durability, off-road capabilities, and compliance with local regulations. |
| Emergency Services | Rapid Response Vehicles | Quick access to remote areas during emergencies, ensuring timely assistance. | Reliability under extreme conditions and availability of service support. |
How Can 4 Wheel Electric Cars Transform the Logistics and Transportation Sector?
In the logistics and transportation sector, four-wheel electric cars are increasingly being utilized for last-mile delivery solutions. Their ability to navigate urban environments while providing zero-emission transport aligns with global sustainability goals. Businesses benefit from reduced fuel costs and lower maintenance expenses compared to traditional vehicles. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, considerations include the vehicle’s range capabilities and the availability of charging infrastructure in urban centers.
What Role Do 4 Wheel Electric Cars Play in Agriculture?
In agriculture, four-wheel electric cars serve as versatile off-road utility vehicles, essential for operations in rugged terrain. They can assist in transporting equipment, supplies, and personnel, significantly improving productivity in crop management. Buyers from rural areas, particularly in regions like Nigeria and Brazil, should focus on ground clearance and battery life, ensuring the vehicles can handle uneven surfaces and long workdays without frequent recharging.
How Are 4 Wheel Electric Cars Beneficial for the Tourism and Hospitality Industry?
The tourism and hospitality industry can leverage four-wheel electric cars to offer eco-friendly transport services to guests. This not only attracts environmentally-conscious travelers but also aligns with the growing demand for sustainable tourism practices. Businesses must consider vehicle comfort and range for tours, as well as the availability of local charging options to ensure seamless guest experiences. This is particularly relevant in tourist-heavy regions across Europe and the Middle East.
In What Ways Do 4 Wheel Electric Cars Enhance Construction Operations?
In construction, four-wheel electric cars provide reliable transportation for workers and materials on job sites, particularly in challenging environments. Their off-road capabilities allow them to navigate rough terrain, which is crucial for construction projects in remote locations. Companies should prioritize durability and compliance with local regulations when sourcing these vehicles, ensuring they can withstand the rigors of the job site while adhering to safety standards.
How Do 4 Wheel Electric Cars Support Emergency Services?
Emergency services can utilize four-wheel electric cars as rapid response vehicles, ensuring quick access to remote areas during critical situations. These vehicles enhance the ability to provide timely assistance, which is vital in emergencies. For international buyers, reliability under extreme conditions and the availability of service support are essential factors to consider, particularly in regions prone to natural disasters or with limited infrastructure.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘4 wheel electric car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Charging Infrastructure in Emerging Markets
The Problem: B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America often face significant challenges due to inadequate charging infrastructure for electric vehicles. The lack of accessible and reliable charging stations can deter companies from investing in 4-wheel electric cars, as fleet management becomes complicated. Companies worry about the potential downtime and operational disruptions if vehicles run out of charge during critical missions, especially in remote areas where charging options may be limited.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should consider investing in partnerships with local governments and charging network providers to expand the charging infrastructure in their operational areas. Additionally, companies can explore the feasibility of installing their own charging stations, particularly at central fleet depots. When sourcing 4-wheel electric cars, buyers should prioritize models that offer fast-charging capabilities and longer ranges. This not only mitigates the risk of running out of power but also ensures that vehicles can be quickly recharged during operational hours. Furthermore, organizations can implement route planning software that integrates real-time data on charging station locations and availability, optimizing routes to reduce the risk of downtime.
Scenario 2: Performance and Range Anxiety in Off-Road Conditions
The Problem: Buyers are often concerned about the performance of 4-wheel electric cars in off-road conditions, particularly regarding range and battery life. In regions with challenging terrains, such as rural areas in Brazil or the rugged landscapes of the Middle East, the fear of battery depletion during critical tasks can lead to hesitancy in adopting these vehicles. This anxiety is exacerbated when potential buyers are uncertain about the vehicle’s ability to handle various environmental conditions, including mud, snow, and steep inclines.
The Solution: To alleviate these concerns, B2B buyers should conduct thorough assessments of the specific electric models that perform well in off-road conditions. When evaluating vehicles, focus on those equipped with advanced all-wheel drive systems and robust battery management technologies that enhance performance in challenging terrains. It is also beneficial to request detailed performance metrics from manufacturers, such as power distribution efficiency and real-world range under varying load conditions. Buyers can further mitigate range anxiety by investing in a mixed fleet that includes both electric and traditional vehicles, allowing for flexibility during peak operational demands while the electric models gain traction in performance and range reliability over time.
Scenario 3: High Initial Costs and Total Cost of Ownership Concerns
The Problem: The upfront costs of purchasing 4-wheel electric cars can be a significant barrier for B2B buyers, particularly in cost-sensitive markets. Many organizations fear that the initial investment outweighs the potential savings in fuel and maintenance costs. This is especially pertinent for companies operating in regions like Nigeria, where budget constraints are a common issue. Additionally, the uncertainty surrounding resale value and battery life can complicate financial forecasting and investment decisions.
The Solution: B2B buyers should conduct a comprehensive Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis that includes not only the purchase price but also potential savings on fuel, maintenance, and tax incentives for electric vehicle adoption. Engaging with manufacturers and industry experts to obtain detailed TCO projections can provide clarity on long-term financial benefits. Furthermore, exploring financing options such as leasing or fleet financing can reduce the burden of upfront costs. Buyers should also investigate government incentives and subsidies available for electric vehicle purchases in their respective regions, which can significantly lower the effective cost. Finally, fostering relationships with suppliers who offer robust warranties and support can further enhance the value proposition of investing in 4-wheel electric cars, ensuring long-term reliability and operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 4 wheel electric car
What Are the Key Materials Used in Four-Wheel Electric Cars?
In the rapidly evolving market for four-wheel electric vehicles (EVs), the selection of materials plays a crucial role in determining performance, durability, and overall vehicle efficiency. Below, we analyze several common materials used in the construction of these vehicles, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Electric Vehicle Design?
Aluminum is widely used in the automotive industry due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. With a density approximately one-third that of steel, aluminum significantly reduces vehicle weight, which enhances energy efficiency and extends battery range. The material can withstand temperatures up to 600°C and has good fatigue resistance, making it suitable for structural components.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight nature leads to improved fuel efficiency. It is also recyclable, aligning with sustainability goals.
Cons: The initial cost of aluminum is higher than traditional steel, and manufacturing processes can be more complex, often requiring specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it ideal for components exposed to harsh environments, particularly in regions with high humidity or saline conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America may need to consider local availability and cost implications of sourcing aluminum.
What Role Does Steel Play in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Steel remains a fundamental material in vehicle manufacturing, especially for the chassis and structural components. High-strength steel variants provide excellent durability and impact resistance, essential for safety. Steel can withstand significant loads and offers good temperature resilience.
Pros: Steel is relatively low-cost and widely available, making it a cost-effective choice for manufacturers. Its strength-to-weight ratio can be optimized with advanced high-strength steel (AHSS).
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact the overall weight of the vehicle and reduce energy efficiency.
Impact on Application: Steel is suitable for components requiring high strength and rigidity, such as the vehicle frame and crash structures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding steel grades and their compliance with international standards. In regions like Europe, stringent regulations may influence material selection.
How Does Carbon Fiber Enhance Performance in Electric Vehicles?
Carbon fiber is increasingly being used in high-performance electric vehicles due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and rigidity. It can endure high stress and is resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for components that require lightweight yet robust materials.
Pros: The use of carbon fiber can lead to significant weight savings, enhancing vehicle performance and range. It also provides a premium feel, which can be a selling point for luxury EVs.
Cons: Carbon fiber is considerably more expensive than both aluminum and steel. Its manufacturing processes are complex and time-consuming, which can lead to higher production costs.
Impact on Application: Carbon fiber is particularly beneficial for components like body panels and interior structures where weight reduction is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of carbon fiber manufacturing capabilities in their regions. Compliance with international standards for quality and safety is also crucial.
What Are the Benefits of Using Composites in Electric Vehicles?
Composite materials, often a combination of plastic and reinforcing fibers, are gaining traction in the automotive sector. They offer excellent weight reduction, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility, making them suitable for various applications in electric vehicles.
Pros: Composites can be molded into complex shapes, reducing the need for multiple parts and assembly processes. They are also lightweight, which enhances vehicle efficiency.
Cons: The cost of composites can be high, and their recycling is more challenging than metals. Additionally, they may not offer the same level of impact resistance as metals.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for non-structural components, such as interior panels and trim, where weight savings and design flexibility are priorities.
Considerations for International Buyers: Understanding the local market for composite materials and ensuring compliance with relevant standards is essential, especially in regions with developing automotive industries.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Four-Wheel Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for 4 Wheel Electric Car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, structural components | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher initial cost, complex mfg | High |
| Steel | Chassis, crash structures | Low-cost, widely available | Heavier than aluminum, less efficient | Medium |
| Carbon Fiber | Body panels, performance components | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Very high cost, complex mfg | High |
| Composites | Interior panels, non-structural components | Lightweight, design flexibility | High cost, challenging recycling | Medium to High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers in the electric vehicle sector, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 4 wheel electric car
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a 4-Wheel Electric Car?
The manufacturing process of a 4-wheel electric car is intricate and involves several key stages, each designed to ensure high-quality production and optimal performance. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Electric Vehicle Production?
Material preparation is the foundational stage where raw materials are sourced and processed. Electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers prioritize lightweight materials such as aluminum and high-strength steel to enhance efficiency and performance. Advanced composites may also be utilized in specific components to reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity.
In addition to selecting appropriate materials, suppliers often perform rigorous testing to ensure they meet industry standards. This includes assessing the electrical conductivity of materials used in battery production, as well as the thermal properties of components exposed to high heat. Materials are also checked for environmental compliance, ensuring they align with international regulations such as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals).
What Techniques Are Employed in the Forming Stage?
The forming stage involves transforming raw materials into components through various techniques. Common methods include stamping, extrusion, and molding. For instance, the chassis may be produced using stamping techniques that create complex shapes from sheet metal, while battery housings might be formed through injection molding of advanced polymers.
In the context of electric vehicles, manufacturers increasingly employ automated technologies like robotics to enhance precision and efficiency. Automation reduces human error and increases production speed, allowing for the consistent manufacture of high-quality parts that meet stringent specifications.
How Is the Assembly Process Structured for Electric Cars?
The assembly process is where individual components are brought together to form the complete vehicle. This stage requires meticulous planning to ensure that each part fits seamlessly with others, particularly in an electric vehicle where components such as the battery, electric motors, and drive systems must be integrated effectively.
Typically, the assembly line is organized in a way that allows for a logical flow of parts, minimizing handling and potential damage. Advanced tracking systems are often implemented to monitor the assembly process, ensuring that each vehicle is built to the exact specifications. This includes the use of torque wrenches and other specialized tools to ensure that all fasteners are tightened to the required standards.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used to Ensure Quality?
Finishing is the final stage of manufacturing, where the vehicle undergoes surface treatments, painting, and quality checks. This stage not only enhances the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal but also provides protective coatings that can prolong the lifespan of the car.
In the context of electric vehicles, special attention is given to the insulation of electrical components to prevent corrosion and ensure safety. Manufacturers may employ techniques such as powder coating or electrocoating to achieve a durable finish that meets both aesthetic and functional requirements.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Essential for Electric Vehicles?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of 4-wheel electric cars, ensuring that every vehicle meets safety and performance standards. International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, emphasizing continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
Which Industry-Specific Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
In addition to general quality standards, B2B buyers must also consider industry-specific certifications. For electric vehicles, compliance with standards such as CE marking for safety, and UL certification for electrical components, is essential. These certifications signal that the vehicle meets necessary regulatory requirements and is safe for use in different markets.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Structured?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure compliance with specifications. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage checks the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the manufacturing process.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular inspections during production help identify issues that may arise during assembly, allowing for immediate corrective action.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This stage involves thorough testing of the finished vehicle, including performance tests, safety inspections, and compliance checks to ensure the product meets all necessary standards before delivery.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the performance and safety of electric vehicles. Common practices include:
- Electrical Testing: Ensures that battery systems operate efficiently and safely under different conditions.
- Durability Testing: Simulates real-world driving conditions to assess the vehicle’s performance over time.
- Crash Testing: Evaluates the vehicle’s safety features and structural integrity under impact.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. This can include:
- Conducting Audits: Regular on-site inspections can provide insights into the manufacturing and quality assurance practices of suppliers.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control processes, certifications, and testing results.
- Utilizing Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent agencies to assess manufacturing practices can ensure compliance with international standards and provide an unbiased evaluation of quality.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is crucial. Different regions may have varying regulations and standards, impacting the importation and sale of electric vehicles.
Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulatory requirements and ensure that their suppliers can meet these standards. Additionally, understanding the implications of certifications like ISO, CE, and UL can aid in navigating the complexities of international trade, ensuring that products are compliant and safe for the target market.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for 4-wheel electric cars are pivotal to delivering high-quality, safe vehicles to the market. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring they partner with manufacturers who prioritize quality and compliance. Emphasizing rigorous quality control and adherence to international standards will ultimately lead to better products and customer satisfaction in the rapidly evolving electric vehicle industry.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘4 wheel electric car’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring four-wheel electric cars (4WECs). As the demand for electric vehicles continues to rise globally, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the key steps in the sourcing process is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This checklist will help buyers navigate through the complexities of specifications, supplier evaluations, and compliance requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, it’s crucial to outline your specific technical requirements. This includes determining the desired range, battery capacity, and off-road capabilities of the electric vehicle.
– Considerations: Identify whether you need features such as all-wheel drive for enhanced traction or advanced battery technology for extended range, especially in regions with challenging terrains.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Regulatory Requirements
Understanding the current market landscape and regulatory frameworks is vital for successful procurement.
– Actionable Insights: Analyze trends in electric vehicle adoption within your target region, including government incentives, emission regulations, and infrastructure readiness. This will inform your decision-making process and ensure compliance with local laws.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ascertain their reliability and product quality.
– Key Actions: Request detailed company profiles, including years in operation, production capacity, and past project case studies. Look for references from other buyers in similar markets or industries to gauge supplier performance and credibility.
Step 4: Assess Vehicle Performance and Features
Conduct a comprehensive assessment of the vehicle models you are considering.
– Important Factors: Evaluate performance metrics such as acceleration, terrain handling, and energy efficiency. Additionally, examine the technological features offered, such as regenerative braking and advanced driver-assistance systems, which can enhance the vehicle’s usability.
Step 5: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the vehicles meet international safety and environmental standards.
– Certification Details: Check for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems, and any local certifications required for electric vehicles in your target market. Compliance with these standards is crucial for legal and operational reasons.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you’ve narrowed down your list of suppliers, engage in negotiations to secure favorable terms.
– Negotiation Tips: Discuss not only pricing but also warranty terms, after-sales support, and delivery timelines. Understanding the total cost of ownership—including maintenance and charging infrastructure—can influence your final decision.
Step 7: Plan for After-Sales Support and Maintenance
Consider the long-term relationship with your supplier by assessing their after-sales service capabilities.
– Service Considerations: Investigate the availability of spare parts, technical support, and maintenance services. A reliable after-sales support system is essential for minimizing downtime and ensuring the longevity of your fleet.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing four-wheel electric cars, ultimately leading to successful procurement and operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 4 wheel electric car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing 4-Wheel Electric Cars?
When sourcing four-wheel electric cars, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, including metals, batteries, and electronics, is a significant portion of the total cost. Battery technology, particularly lithium-ion batteries, plays a pivotal role in determining the overall price. As advancements in battery technology continue, prices may fluctuate based on material availability and sourcing strategies.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled workers, engineers, and assembly line staff. In regions where labor is more affordable, sourcing can be cost-effective. However, skilled labor is crucial for the assembly of complex electric vehicles, impacting the overall cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs, making it vital to assess the supplier’s operational efficiency.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for molds, dies, and specialized equipment can be substantial. These costs are often amortized over the production run, so higher volume orders can lead to lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that vehicles meet safety and performance standards incurs costs related to testing and inspections. Suppliers with robust QC processes might charge a premium, but this can lead to long-term savings by reducing warranty claims and recalls.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing expenses are critical, particularly for international buyers. The choice of Incoterms can significantly affect logistics costs, impacting the total cost of ownership.
-
Margin: The supplier’s profit margin will vary based on market conditions, competition, and perceived value. Understanding the pricing model of suppliers helps in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of 4-Wheel Electric Cars?
Several factors influence the pricing of four-wheel electric cars, particularly for international B2B buyers.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders usually benefit from economies of scale, leading to lower per-unit costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features or specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly outline their needs to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials: The choice of materials, particularly in battery components and body construction, can dramatically influence costs. Higher-quality materials often come with a higher price tag but may offer better performance and longevity.
-
Quality/Certifications: Vehicles that meet specific international standards or certifications may come at a premium. Certifications ensure compliance with safety and environmental regulations, which can be crucial for markets in Europe and North America.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a history of quality may charge higher prices, but they often provide better support and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs and risk, which can influence the total landed cost of the vehicle.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Negotiating 4-Wheel Electric Car Prices?
For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, negotiation and cost-efficiency strategies are crucial.
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume orders to negotiate better prices. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to more favorable terms over time.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. Sometimes a higher upfront cost can result in long-term savings through better efficiency and lower maintenance.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. Exchange rates, tariffs, and local market conditions can affect the final pricing. Buyers should conduct thorough market research to understand these dynamics.
-
Due Diligence: Always vet suppliers for their financial stability, production capacity, and compliance with international standards to minimize risks.
In conclusion, understanding the intricate cost structure and pricing influencers is essential for successful sourcing of four-wheel electric cars. By leveraging the insights provided, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market conditions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 4 wheel electric car With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to 4 Wheel Electric Cars
As the demand for sustainable and efficient transportation solutions rises, businesses are increasingly considering various options to meet their mobility needs. While four-wheel electric cars offer significant advantages in performance and environmental impact, alternative solutions may also provide compelling benefits depending on specific operational requirements. This section delves into a comparative analysis of four-wheel electric cars against hybrid vehicles and traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | 4 Wheel Electric Car | Hybrid Vehicle | Internal Combustion Engine Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Instant torque, high efficiency, and all-terrain capability | Good balance of power and fuel efficiency | Established performance, with a broad range of power outputs |
| Cost | Higher initial investment but lower long-term operating costs | Moderate initial cost, variable fuel economy | Lower initial cost but higher fuel and maintenance costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure, may need fleet adjustments | Easier to integrate with existing infrastructure | Minimal changes required; widely available and understood |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance due to fewer moving parts | Moderate maintenance; hybrid components require oversight | Higher maintenance due to complex mechanical systems |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for businesses focused on sustainability and off-road capabilities | Suitable for companies needing versatility and moderate eco-friendliness | Best for operations in areas lacking charging infrastructure or requiring high mileage |
Understanding Hybrid Vehicles as an Alternative
Hybrid vehicles combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor, offering a middle ground between traditional fuel and electric solutions. They provide good fuel efficiency and lower emissions than ICE vehicles, making them an appealing choice for businesses that require flexibility. However, hybrids can still be dependent on fossil fuels, which may not align with corporate sustainability goals. Additionally, while they offer reduced maintenance compared to traditional vehicles, they still require more upkeep than fully electric models due to their dual powertrains.
Examining Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles
Internal combustion engine vehicles have long been the standard in transportation, offering a wide range of models and performance options. They can be less expensive upfront and are readily available in most markets, making them an easy choice for many businesses. However, ICE vehicles are increasingly criticized for their environmental impact and long-term operating costs, which include fuel and maintenance. As many regions implement stricter emissions regulations, reliance on these vehicles may pose a risk for businesses looking to future-proof their fleets.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When selecting the most suitable vehicle solution, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and long-term sustainability goals. While four-wheel electric cars offer robust performance and lower operating costs, hybrid vehicles can serve as a versatile alternative for businesses transitioning to greener practices. Conversely, traditional ICE vehicles may still be appropriate for operations in areas with limited charging infrastructure. By considering these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 4 wheel electric car
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Four-Wheel Electric Cars?
Understanding the essential technical properties of four-wheel electric cars (4×4 EVs) is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here are some key specifications that you should consider:
1. Electric Range
The electric range refers to the maximum distance a vehicle can travel on a single charge. For B2B buyers, a longer range is essential as it influences the vehicle’s usability in various geographical conditions, particularly in regions with limited charging infrastructure. A typical range for 4×4 EVs can vary from 250 to over 350 miles, impacting fleet operations and customer satisfaction.
2. Charging Speed
Charging speed, measured in kilowatts (kW), indicates how quickly the vehicle can recharge its battery. This is particularly vital for businesses that require quick turnaround times for their fleets. Fast-charging capabilities (often 150 kW and above) allow for 80% charge in under 30 minutes, making it feasible to maintain operational efficiency, especially in remote areas.
3. All-Wheel Drive (AWD) System
The AWD system in 4×4 electric cars enhances traction and stability by distributing power to all four wheels. This feature is critical in markets prone to adverse weather conditions or rough terrains. B2B buyers should assess the sophistication of the AWD system, such as whether it uses traditional mechanical components or advanced electric motors for improved performance.
4. Battery Capacity
Battery capacity, usually measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), determines how much energy the battery can store. A higher capacity translates to longer range and better performance. For businesses, selecting vehicles with adequate battery capacity ensures that they can meet operational demands without frequent recharging, thereby reducing downtime.
5. Ground Clearance
Ground clearance is the distance between the vehicle’s undercarriage and the ground. This specification is particularly relevant for off-road capabilities and navigating uneven terrains. B2B buyers should consider models with adjustable ground clearance to enhance versatility across various environments.
6. Torque and Horsepower
Torque and horsepower figures indicate the vehicle’s performance capabilities. Torque is particularly important in electric vehicles as it provides instantaneous power for acceleration. Understanding these figures helps businesses evaluate whether the vehicle meets their operational performance requirements, such as load capacity and speed.
What Are Common Trade Terminologies Related to Four-Wheel Electric Cars?
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication in the B2B sector. Here are some common terms you should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that manufactures parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of 4×4 EVs, understanding OEM relationships is essential for sourcing quality components and ensuring compatibility with vehicle systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ can help in budgeting and inventory planning. This is particularly significant for fleet purchases, where bulk orders may be required to achieve cost savings.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a business process in which a company solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to compare pricing and features of different 4×4 EV models, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms helps B2B buyers navigate shipping costs, delivery timelines, and risk management, which are crucial for importing 4×4 EVs from different markets.
5. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with purchasing and operating a vehicle over its lifetime, including purchase price, maintenance, fuel, and depreciation. B2B buyers should evaluate TCO when considering 4×4 EVs to ensure they are making financially sound decisions.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of acquiring four-wheel electric cars more effectively, ensuring that their investments align with operational needs and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 4 wheel electric car Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the 4 Wheel Electric Car Sector?
The global market for four-wheel electric cars is experiencing a significant transformation driven by increasing demand for sustainable transport solutions, the rise of electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure, and regulatory pressures aimed at reducing carbon emissions. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers are witnessing a surge in interest toward electric SUVs and 4×4 vehicles that combine performance with eco-friendliness. Key trends include the integration of advanced technology, such as all-wheel drive systems that enhance traction and stability, making these vehicles suitable for various terrains and climates. This is particularly relevant for markets with diverse geographical challenges, like Nigeria and Brazil, where consumers seek reliability in adverse weather conditions.
Moreover, manufacturers are adopting modular designs that facilitate the production of multiple variants from a single platform, streamlining sourcing processes for B2B buyers. The growing emphasis on local production also presents opportunities for international partnerships, enabling buyers to tap into regional manufacturing capabilities while reducing logistics costs. As electric vehicles become more mainstream, the competition among OEMs is fostering innovation, leading to improved battery technology and charging solutions that cater to the needs of international markets.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing in the 4 Wheel Electric Car Sector?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of the four-wheel electric car sector, shaping not only product offerings but also sourcing strategies for B2B buyers. The environmental impact of traditional manufacturing practices has prompted a shift towards ethical supply chains, emphasizing the use of recycled materials and sustainably sourced components. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, which often includes obtaining ‘green’ certifications that validate their environmental practices.
Moreover, the push for transparency in supply chains is gaining traction, with stakeholders demanding greater accountability regarding the sourcing of raw materials, especially critical minerals like lithium and cobalt used in batteries. B2B buyers can leverage this trend by collaborating with suppliers that adhere to ethical mining practices and offer traceability in their supply chains. Not only does this enhance brand reputation, but it also aligns with growing consumer preferences for environmentally friendly products, thus driving sales in emerging markets.
How Has the 4 Wheel Electric Car Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the four-wheel electric car sector has been marked by technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences. Initially, electric vehicles were seen as niche products with limited range and performance, but the demand for sustainable transportation has spurred innovation. Over the past decade, manufacturers have focused on enhancing battery technology and developing all-wheel drive systems that rival traditional combustion engines in performance.
This shift is particularly relevant in regions where rugged terrains and adverse weather conditions challenge vehicle performance. The introduction of models like the electric Mercedes G-Class and the Subaru Solterra exemplifies the industry’s response to these needs, showcasing that electric vehicles can be both capable and environmentally friendly. As the sector continues to mature, B2B buyers can expect even more versatile and sustainable offerings that cater to diverse market demands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 4 wheel electric car
-
How do I evaluate the quality and performance of a 4-wheel electric car?
To assess the quality and performance of a 4-wheel electric car, consider several key metrics: range, charging speed, and drivetrain technology. Look for models with robust battery life that match the driving needs of your market. Review specifications for all-wheel-drive systems to ensure they provide adequate traction and stability in various terrains. Additionally, seek out independent reviews and test drives to gather real-world performance data. Engaging with existing users in your region can also provide valuable insights into durability and maintenance. -
What is the best 4-wheel electric car for off-road conditions?
For off-road conditions, models like the Mercedes G580 with EQ Technology and the Kia EV9 stand out. The G580 offers exceptional off-road capability with advanced features and a strong powertrain, making it ideal for rugged terrains. Alternatively, the Kia EV9 provides a Terrain Mode Select for enhanced traction in mud, sand, or snow. Evaluate your specific needs, including terrain type and expected usage, to determine the best fit for your operations. -
What are the common customization options available for electric vehicles?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for electric vehicles, including battery size, drivetrain configurations, and interior features. Additional options may include specialized off-road packages, technology upgrades, and bespoke exterior colors or finishes. When engaging with suppliers, inquire about the extent of customization available and any associated costs or lead times, as these can significantly impact delivery schedules and overall project budgets. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for 4-wheel electric cars?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for 4-wheel electric cars vary by manufacturer and region. Typically, MOQs can range from a handful of units to several dozen, depending on the supplier’s production capabilities and inventory levels. It’s advisable to negotiate MOQs based on your business needs and market demand. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also provide flexibility in order sizes, especially if you plan for future orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electric cars internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include deposits of 20-30% upfront with the balance due upon delivery or before shipping. Some manufacturers may offer financing options or extended payment plans for large orders. Always ensure clarity on payment methods, currency, and any potential fees associated with international transactions. Establishing a letter of credit can also enhance security for both parties in international trade. -
How can I ensure compliance with international trade regulations when importing electric cars?
To ensure compliance with international trade regulations, familiarize yourself with the import laws of your country and the exporting country. This includes understanding tariffs, taxes, and any specific vehicle standards or certifications required. Working with a customs broker can streamline the process, helping you navigate documentation and compliance issues. Additionally, always verify that your supplier adheres to international quality standards and has the necessary certifications for their vehicles. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric cars?
Logistics considerations for importing electric cars include shipping methods, transit times, and handling of specialized equipment like charging stations. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in automotive imports to manage the logistics process. Additionally, account for potential delays in customs clearance and ensure that the vehicles are insured during transit. Planning for local transportation and storage upon arrival is also crucial to minimize downtime. -
How do I vet suppliers of 4-wheel electric cars effectively?
To effectively vet suppliers of 4-wheel electric cars, start by researching their reputation and customer reviews. Request references and case studies from previous clients to assess their reliability and product quality. Evaluate their production capabilities, certifications, and compliance with international standards. Conducting factory visits or audits can provide deeper insights into their operations. Finally, consider their responsiveness and communication skills, as these are key indicators of a long-term partnership.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 4 Wheel Electric Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Subaru – Solterra, Mercedes – G 580 EQ
Domain: drivingelectric.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: 1. Subaru Solterra: Prices from £52,495, Maximum WLTP combined range: 289 miles, Features: four-wheel drive, off-road-oriented features, X-MODE, Grip Control, 150kW charging capability.
2. Mercedes G 580 with EQ Technology: Prices from £180,860, Maximum WLTP combined range: 285 miles, Power: 579bhp, Torque: 1,164Nm, 0-62mph in 4.7 seconds, 112kWh battery, 200kW peak charging speed.
3. Kia EV9: Pri…
2. BMW – 2025 iX
Domain: cars.usnews.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Best All-Wheel-Drive Electric Cars in 2025:
1. **2025 BMW iX**
– Price: $87,250
– U.S. News Overall Score: 8.9/10
– Battery: 111.5-kWh
– Horsepower: 516 or 610 (depending on trim)
– Features: 12.3-inch digital instrument cluster, heated steering wheel, quad-zone automatic climate control.
2. **2025 Rivian R1S**
– Price: $75,900
– U.S. News Overall Score: 8.9/10…
3. Volvo – XC40 Recharge
Domain: volvocarstampa.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: {“Volvo XC40 Recharge”: {“Range”: “254 miles”, “MPGe (Combined)”: “98 MPGe”, “Horsepower”: “402 hp”, “Seats”: “5”, “Warranty”: “8 yrs / 100K miles on battery”}, “Volkswagen ID.4”: {“Range”: “263 miles”, “MPGe (Combined)”: “102 MPGe”, “Horsepower”: “335 hp”, “Seats”: “5”, “Warranty”: “8 yrs / 100K miles on battery”}, “Ford Mustang Mach-E”: {“Range”: “260-270 miles”, “MPGe (Combined)”: “82-84 MPGe”,…
4. Hyundai – 2026 Ioniq 9
Domain: truecar.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {“model”:”2026 Hyundai Ioniq 9″,”starting_price”:”$67,920″,”electric_range”:”311 – 335 mi”,”seating_capacity”:”up to 7 passengers”,”trim_levels”:”6 trim levels”,”powertrain_options”:”single-motor rear-wheel-drive or dual-motor all-wheel-drive”,”performance_version_horsepower”:”422 horsepower”,”charging_time”:”10% to 80% in about 25 minutes on DC fast charger”,”production_start”:”Spring 2025″,”key_…
5. Eli – Electric Micro Car
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Eli launches an electric micro ‘car’ priced at $11,900 in the US.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 4 wheel electric car
In navigating the evolving landscape of four-wheel electric vehicles (EVs), international B2B buyers must focus on strategic sourcing to capitalize on this burgeoning market. The increasing demand for 4×4 electric cars is driven by their enhanced traction, stability, and off-road capabilities—attributes highly valued in diverse environments, from the rugged terrains of Nigeria to the urban landscapes of Brazil. Sourcing partnerships with manufacturers that prioritize innovation, sustainability, and reliability will be crucial in ensuring a competitive edge.
Furthermore, as advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure continue to emerge, buyers should seek models that balance range with efficient charging solutions. Understanding regional preferences and market dynamics will enable businesses to tailor offerings that resonate with local consumers, fostering long-term growth.
As we look to the future, the potential of four-wheel electric cars is immense. By embracing strategic sourcing practices, B2B buyers can position themselves as leaders in the electric vehicle market. Now is the time to act—engage with manufacturers and suppliers who can provide the latest technologies and insights, paving the way for a sustainable and profitable future in the electric automotive sector.