Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric car without driving licence home made cha
In an era where sustainable transportation solutions are rapidly evolving, the demand for electric cars without driving licenses, particularly homemade options, is gaining traction among international B2B buyers. This growing interest presents a unique challenge: how to effectively source and evaluate these innovative vehicles to meet diverse market needs. This guide aims to demystify the global market for electric cars without driving licenses, providing insights into the various types available, their applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting processes.
We delve into essential factors such as cost considerations, regulatory compliance, and technical specifications, equipping buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly Brazil and Germany—with the knowledge necessary for informed purchasing decisions. By highlighting best practices and offering actionable strategies, this comprehensive resource empowers businesses to navigate the complexities of sourcing electric vehicles that align with their operational goals while promoting eco-friendly transportation solutions.
Whether you are a retailer looking to expand your product lineup or a fleet manager aiming to reduce carbon footprints, understanding the landscape of electric cars without driving licenses is crucial. This guide will serve as your roadmap to making strategic investments in this burgeoning market, ensuring your business remains at the forefront of sustainable innovation.
Understanding electric car without driving licence home made cha Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Quadricycles | Small, lightweight, often limited speed (45 km/h) | Urban transportation, delivery services | Pros: Affordable, easy to maneuver; Cons: Limited range and speed. |
| DIY Electric Conversions | Custom-built from existing vehicles, versatile | Custom fleet solutions, specialized needs | Pros: Tailored to specific requirements; Cons: Labor-intensive, safety concerns. |
| Electric Mini-Vans | Compact, multi-passenger capacity, practical design | Family transport, small business use | Pros: Spacious, suitable for urban settings; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Electric Cargo Vehicles | Designed for transporting goods, larger battery | Logistics, e-commerce delivery | Pros: High load capacity, eco-friendly; Cons: Higher operational costs. |
| Electric Motorcycles | Two-wheeled, lightweight, agility in traffic | Delivery services, personal transport | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to park; Cons: Less stable than four-wheeled options. |
What Are Electric Quadricycles and Their B2B Suitability?
Electric quadricycles are compact vehicles designed for urban environments, typically limited to a maximum speed of 45 km/h. They are ideal for businesses looking to provide affordable and efficient transport solutions, especially in densely populated areas. Their lightweight design allows for easy navigation through traffic, making them suitable for delivery services and short-distance commuting. B2B buyers should consider the vehicle’s limited range and speed as potential drawbacks, especially for longer routes.
How Do DIY Electric Conversions Benefit Businesses?
DIY electric conversions involve repurposing existing vehicles by replacing internal combustion engines with electric motors. This approach allows businesses to customize vehicles according to specific operational needs, making it a viable option for those with unique requirements. However, the process can be labor-intensive and may raise safety concerns if not executed properly. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential costs and time involved in the conversion process.
What Features Make Electric Mini-Vans Attractive for B2B Buyers?
Electric mini-vans offer a practical solution for transporting multiple passengers or goods while maintaining a compact design. They are particularly useful for families or small businesses needing reliable transportation within urban settings. The spacious interior can accommodate various cargo, making them suitable for small business operations. However, the initial investment may be higher compared to other electric vehicles, which is a critical consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
Why Choose Electric Cargo Vehicles for Logistics?
Electric cargo vehicles are specifically designed for transporting goods, featuring larger batteries to support longer ranges and higher load capacities. They are increasingly popular in logistics and e-commerce, where eco-friendly transport solutions are in demand. Their ability to reduce operational costs through lower fuel expenses and maintenance makes them attractive to businesses focused on sustainability. However, buyers should be aware of the higher upfront costs associated with these vehicles.
How Do Electric Motorcycles Fit into the B2B Market?
Electric motorcycles are lightweight, agile vehicles ideal for navigating congested urban areas. Their cost-effectiveness and ease of parking make them an attractive option for delivery services and personal transport. They cater to businesses looking for economical solutions to urban mobility challenges. However, their two-wheeled design may present stability issues compared to four-wheeled vehicles, which buyers should consider when evaluating their suitability for specific applications.
Key Industrial Applications of electric car without driving licence home made cha
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric car without driving licence home made cha | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Mobility Solutions | Last-mile delivery services using lightweight electric vehicles | Reduces transportation costs, enhances delivery speed, and lowers emissions | Availability of local parts, compliance with local regulations |
| Tourism and Leisure | Eco-friendly shuttle services for tourists | Attracts environmentally conscious tourists and enhances brand reputation | Battery capacity, vehicle range, and safety features |
| Agriculture | Utility vehicles for agricultural tasks (e.g., transporting goods) | Increases efficiency in operations and reduces fuel costs | Durability, off-road capability, and maintenance support |
| Education | Campus transport solutions for students and staff | Promotes sustainable transport and reduces traffic congestion | Customization options, safety measures, and charging infrastructure |
| Logistics and Warehousing | In-house transportation for moving goods within facilities | Streamlines operations and reduces reliance on fossil fuels | Weight capacity, battery life, and ease of maintenance |
How Can Electric Cars Without a Driving Licence Enhance Urban Mobility Solutions?
In urban areas, last-mile delivery services are increasingly turning to lightweight electric cars that do not require a driving licence. These vehicles can navigate congested city streets, allowing businesses to deliver goods quickly and efficiently. The benefits include lower operational costs and reduced carbon footprints, which are particularly appealing in regions prioritizing sustainability. Buyers must consider local regulations regarding vehicle specifications and ensure the availability of spare parts for maintenance.
What Role Do Electric Cars Play in the Tourism and Leisure Industry?
Electric cars without a driving licence can serve as eco-friendly shuttle services for tourists in urban or scenic locations. This application not only appeals to environmentally conscious travelers but also enhances the brand image of tourism operators. By providing a unique and sustainable transport option, businesses can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty. Key considerations for sourcing include vehicle aesthetics, battery range, and safety features to ensure passenger comfort and security.
How Can Agriculture Benefit from Electric Cars Without a Driving Licence?
In the agricultural sector, utility vehicles converted from traditional cars into electric models can be used for transporting goods across farms. This application enhances operational efficiency by reducing fuel costs and minimizing emissions. Buyers in agriculture should focus on the vehicle’s durability, off-road capabilities, and ease of maintenance, as these factors are crucial for rural environments where access to service centers may be limited.
Why Are Electric Cars Important for Educational Institutions?
Educational institutions can utilize electric cars without a driving licence for campus transport solutions, providing safe and sustainable travel for students and staff. This not only promotes a green initiative but also helps alleviate parking and traffic congestion on campuses. Buyers should consider customization options to meet specific campus needs, along with safety measures and the availability of charging infrastructure to support the fleet.
How Do Electric Cars Improve Logistics and Warehousing Operations?
In logistics and warehousing, electric cars can facilitate the movement of goods within facilities, optimizing workflow and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This application streamlines operations and contributes to a company’s sustainability goals. When sourcing these vehicles, businesses should prioritize weight capacity, battery life, and ease of maintenance to ensure they meet the demands of a fast-paced logistics environment.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric car without driving licence home made cha’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance for Homemade Electric Cars
The Problem:
B2B buyers in the electric car sector, particularly those interested in homemade electric vehicles (EVs) without a driving license, often struggle to navigate the complex regulatory landscape. Different countries have varying laws governing vehicle registration, safety standards, and licensing requirements. For businesses in regions like Africa or South America, the lack of clear guidelines can lead to significant delays in product development and market entry, as buyers may face fines or legal challenges if their vehicles do not comply with local regulations.
The Solution:
To effectively manage regulatory compliance, businesses should invest in a comprehensive understanding of local and international automotive regulations. This includes engaging legal consultants who specialize in automotive law and establishing relationships with local regulatory bodies to ensure that homemade electric cars meet safety and performance standards. Additionally, businesses should implement a robust documentation process that includes detailed design specifications, safety tests, and proof of compliance with emission standards. By proactively addressing regulatory requirements, companies can minimize delays and avoid penalties, ultimately streamlining their path to market.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Battery Efficiency and Longevity
The Problem:
Another significant pain point for B2B buyers in the homemade electric car segment is the challenge of sourcing efficient, reliable batteries that offer longevity and performance. In regions where access to quality components may be limited, businesses risk building vehicles that either underperform or require frequent battery replacements, which can lead to increased operational costs and customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution:
B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with reputable battery suppliers who specialize in electric vehicle technology. Conducting thorough research to identify suppliers that offer high-capacity lithium-ion batteries, known for their efficiency and longevity, is crucial. Additionally, implementing a battery management system (BMS) can help monitor battery health and optimize charging cycles, thereby extending battery life. Training teams on best practices for battery care and maintenance will also enhance performance, ensuring that the vehicles remain competitive in the market. This proactive approach not only improves product reliability but also enhances customer trust in the brand.
Scenario 3: Addressing Consumer Education and Market Awareness
The Problem:
Many potential customers in regions such as the Middle East and Europe remain unaware of the benefits of electric cars without a driving license, often perceiving them as inferior options. This lack of understanding can hinder sales and market penetration, making it a crucial challenge for B2B buyers looking to promote homemade electric vehicles effectively.
The Solution:
To combat this issue, businesses should develop targeted marketing campaigns that educate consumers about the advantages of electric vehicles, including cost savings, environmental benefits, and ease of use. Collaborating with local influencers and hosting community events can help increase visibility and foster trust among potential buyers. Additionally, creating informative content such as webinars, tutorials, and social media posts can engage consumers and clarify misconceptions about homemade electric cars. By effectively communicating the value proposition and addressing consumer concerns, businesses can create a more informed customer base, driving demand and facilitating market growth.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric car without driving licence home made cha
When selecting materials for a homemade electric car designed for use without a driving license, it’s crucial to consider factors such as performance, cost, and regional compliance. Below, we analyze four common materials that are suitable for various components of such vehicles.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in Electric Car Manufacturing?
Aluminum is a lightweight metal known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it an ideal choice for electric car frames and body panels. It has a high corrosion resistance, especially when treated, which is essential for vehicles exposed to diverse environmental conditions. Aluminum can withstand temperatures up to 660°C, making it suitable for various applications, including battery enclosures.
Pros: The primary advantages of aluminum include its lightweight nature, which enhances vehicle efficiency and range, and its recyclability, which aligns with sustainability goals. Additionally, it is relatively easy to manufacture and weld.
Cons: However, aluminum can be more expensive than steel, and its manufacturing processes may require specialized equipment, which could increase initial costs for small-scale producers.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with electrical components makes it suitable for housing batteries and electrical systems, ensuring safety and performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local sourcing options to reduce costs. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is critical, especially for safety and performance certifications.
Why Is Steel a Preferred Material for Structural Components?
Steel is another commonly used material, particularly for structural components like the chassis. It offers high tensile strength and durability, making it capable of withstanding significant loads and impacts.
Pros: Steel is relatively inexpensive and widely available, making it a cost-effective choice for many manufacturers. Its robustness ensures long-lasting performance, which is essential for vehicle safety.
Cons: The primary drawback is its weight, which can negatively impact the vehicle’s efficiency and range. Steel also has a lower corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, necessitating protective coatings.
Impact on Application: Steel is particularly effective in areas requiring high strength and rigidity, such as the vehicle’s frame and suspension components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding vehicle safety standards, which may vary significantly across regions like Europe and the Middle East.
How Does Composite Material Enhance Performance in Electric Cars?
Composite materials, particularly carbon fiber and fiberglass, are increasingly popular in electric vehicle manufacturing due to their lightweight and high-strength properties. These materials can significantly reduce overall vehicle weight, improving efficiency.
Pros: Composites offer excellent corrosion resistance and can be molded into complex shapes, providing design flexibility. They also contribute to better energy efficiency due to their lightweight nature.
Cons: The primary limitation is the high cost of raw materials and the complexity of manufacturing processes, which may not be feasible for small-scale producers.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly suitable for body panels and interior components, where weight reduction is critical for performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific manufacturing capabilities available in their region, as composite production may require advanced technology and expertise.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Electric Car Design?
Plastics, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polycarbonate, are used in various applications, including dashboards, battery casings, and interior components. These materials are lightweight and can be produced in various colors and finishes.
Pros: Plastics are cost-effective and can be easily molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs. They also provide good insulation properties, which is crucial for electrical components.
Cons: However, plastics may have lower structural integrity compared to metals and can degrade under UV exposure unless treated.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for non-structural components, contributing to overall vehicle weight reduction while providing aesthetic flexibility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations regarding plastic use and disposal is essential, especially in regions with strict waste management policies.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric car without driving licence home made cha | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Frame, body panels, battery enclosures | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, requires specialized manufacturing | Medium |
| Steel | Chassis, structural components | High strength and durability | Heavier, lower corrosion resistance | Low |
| Composite | Body panels, interior components | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | High cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Plastic | Dashboards, battery casings, interior components | Cost-effective and design flexibility | Lower structural integrity, UV degradation | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers looking to innovate in the electric vehicle market, particularly in regions with diverse requirements and preferences.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric car without driving licence home made cha
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electric Cars Without Driving Licenses?
The manufacturing process for electric cars, especially those designed for use without a driving license, is a meticulous endeavor that involves multiple stages. These stages can be broken down into material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Electric Car Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the foundation of the manufacturing process. Manufacturers typically source lightweight materials such as aluminum and composites to ensure the vehicle remains nimble and energy-efficient. The initial step involves selecting high-quality batteries, electric motors, and structural components. Ensuring that all materials meet international standards is crucial, particularly for B2B buyers looking to maintain quality and compliance. Suppliers may be required to provide material certifications, which can be verified through audits or quality assurance reports.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used?
Once materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves shaping and cutting materials into the required components. Techniques such as stamping, laser cutting, and CNC machining are widely utilized to achieve precision in parts like chassis, body panels, and battery enclosures. These techniques help ensure that parts fit together seamlessly during assembly, which is critical for performance and safety.
How Is the Assembly Process Conducted?
The assembly process is where the individual components come together to form the electric vehicle. This stage usually includes several steps:
-
Sub-assembly of Major Components: Key components such as the electric motor and battery systems are assembled separately before being integrated into the main chassis.
-
Integration of Electrical Systems: Wiring harnesses, control units, and safety systems are installed to ensure proper functionality and compliance with safety standards.
-
Final Assembly: The main components are brought together, and the vehicle is built according to specific design and engineering requirements. This phase often involves multiple teams working concurrently to streamline the assembly process.
What Finishing Techniques Are Essential in Electric Car Manufacturing?
Finishing processes are crucial for both aesthetics and functionality. They include painting, surface treatment, and final inspections. The finishing stage not only enhances the vehicle’s visual appeal but also protects against corrosion and wear. Manufacturers often apply eco-friendly paints and coatings to align with sustainability goals, which is increasingly important for international buyers.
What Quality Control Standards Should Be Followed?
Quality assurance is a critical component of the manufacturing process. International standards such as ISO 9001 ensure that manufacturers maintain a high level of quality throughout their operations. This standard emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction, which is vital for B2B relationships.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Established?
To implement effective quality control, manufacturers typically establish several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet predefined specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, random checks are conducted to ensure that all procedures are followed correctly and that any issues are addressed immediately.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the vehicles are dispatched, a final inspection is performed to ensure that each unit meets quality and safety standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the integrity and performance of electric vehicles. Common tests include:
-
Functional Testing: Ensures that all electrical systems operate correctly.
-
Durability Testing: Simulates real-world conditions to assess how well the vehicle performs over time.
-
Safety Testing: Evaluates the vehicle’s compliance with safety regulations, including crash tests and battery safety assessments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are some strategies:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the production processes and adherence to quality standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed reports that outline their quality control measures, test results, and compliance with international standards.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of verification, ensuring that products meet the necessary specifications before shipment.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various regulatory landscapes. Understanding local compliance requirements is crucial. For instance, European markets may require CE marking to indicate conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Additionally, buyers should be aware of the logistical challenges that may arise during international shipments. Ensuring that quality control processes are upheld throughout the supply chain can mitigate risks associated with delays or non-compliance.
Conclusion: The Importance of Quality Assurance in Electric Car Manufacturing
In summary, the manufacturing process for electric cars designed for use without a driving license encompasses several critical stages, from material preparation to finishing. Emphasizing quality control through established standards and rigorous testing methods is essential for maintaining product integrity. For international B2B buyers, verifying supplier practices through audits and quality reports is key to ensuring that their investments are sound and compliant with local regulations. By prioritizing these aspects, businesses can foster successful partnerships and contribute to the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric car without driving licence home made cha’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring or creating electric cars without a driving license, often referred to as “voiturettes” or quadricycles. These vehicles have gained traction in various markets due to their affordability and accessibility, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By following this checklist, you can make informed decisions about sourcing or manufacturing these electric vehicles, ensuring compliance with local regulations and market demands.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical specifications for the electric vehicle you intend to source or build. This includes considerations such as size, weight, battery capacity, and range. Understanding these parameters will help you align your procurement strategy with customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
- Battery Type: Decide between lithium-ion or lead-acid batteries based on cost and performance.
- Range Requirements: Consider the average distance users will travel to ensure the vehicle meets their needs.
Step 2: Research Regulatory Compliance
Investigate local regulations regarding electric vehicles, particularly those that pertain to vehicles that do not require a driving license. Compliance with safety, emissions, and operational standards is essential to avoid legal complications.
- Safety Standards: Ensure that the vehicle meets crash safety requirements.
- Licensing Exemptions: Understand the specific criteria that allow vehicles to be driven without a license in your target markets.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to conduct thorough evaluations. Request company profiles, past project case studies, and references from other buyers in similar sectors or regions.
- Supplier Reputation: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in manufacturing or supplying electric vehicles.
- Quality Certifications: Verify if the supplier holds relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) that demonstrate adherence to quality standards.
Step 4: Assess Manufacturing Capabilities
If considering a homemade or custom-built electric vehicle, assess the manufacturing capabilities of your team or partners. This includes evaluating tools, technologies, and expertise required for assembly and modification.
- Machining and Fabrication: Ensure access to facilities that can produce necessary components like adapter plates and couplers.
- Technical Expertise: Confirm that your team possesses the necessary skills for electrical and mechanical assembly.
Step 5: Gather Cost Estimates
Request detailed cost estimates from potential suppliers or manufacturers. This should include the cost of materials, labor, and any additional fees associated with compliance and shipping.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not only the purchase price but also the long-term operational costs, such as maintenance and energy consumption.
- Budget Planning: Ensure your budget aligns with projected costs to avoid financial shortfalls during the project.
Step 6: Pilot Testing and Feedback
Once you have sourced or constructed a prototype, conduct pilot testing to gather user feedback. This step is vital for identifying potential improvements and ensuring the vehicle meets market expectations.
- User Experience: Collect data on performance, comfort, and usability.
- Iterative Improvements: Use feedback to refine the vehicle design or sourcing strategy before full-scale production.
Step 7: Develop a Marketing Strategy
Finally, formulate a marketing strategy to promote your electric vehicle. Highlight its benefits, such as affordability, ease of use, and compliance with local regulations.
- Target Audience: Identify your primary customer segments, such as urban commuters or delivery services.
- Sales Channels: Consider both online and offline sales channels to reach a wider audience.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing or building electric cars without a driving license, ensuring a successful entry into this growing market.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric car without driving licence home made cha Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Building a Homemade Electric Car Without a Driving License?
When considering the cost structure for sourcing components for a homemade electric car designed for users without a driving license, several critical cost components come into play. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The primary materials will include an electric motor, batteries, an adapter plate, and various electronic components. The selection of batteries, such as lead-acid versus lithium-ion, significantly impacts overall costs. Additionally, sourcing lightweight materials for the body can reduce energy consumption and improve efficiency.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the complexity of the build and the expertise required. For businesses, employing skilled technicians for assembly and installation will incur higher labor costs. Alternatively, businesses might consider training existing employees, which could be a cost-effective strategy over time.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. For small-scale operations or home-based workshops, overhead might be lower, but as production scales, these costs will need to be accounted for in pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial investments in tooling and equipment (e.g., welding tools, machining equipment) are crucial. These costs can be amortized over multiple builds, making them more manageable for ongoing production.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing a robust QC process ensures that the final product meets safety and performance standards, which is particularly important for vehicles. This adds an additional layer of cost but is necessary to avoid liabilities and enhance customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Costs associated with sourcing components, shipping, and handling must also be factored in. Businesses should consider local suppliers to minimize logistics costs and lead times.
-
Margin: Finally, determining an appropriate profit margin is essential. This margin should reflect the risks involved and the competitive landscape, particularly in international markets.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Homemade Electric Cars?
Several factors influence the pricing of homemade electric cars without a driving license, impacting both the total cost and the final price point.
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing of components can lead to significant cost savings. Businesses should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) with suppliers to take advantage of economies of scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Tailoring components to meet specific requirements can increase costs. Offering customization options may appeal to niche markets but should be balanced against cost-effectiveness.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly influences pricing. Higher-quality, certified materials may command a premium but can enhance the vehicle’s durability and safety, which is critical in maintaining a good reputation.
-
Quality and Certifications: Compliance with international safety and environmental regulations can add to costs but is essential for market acceptance, particularly in Europe and North America.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can impact both cost and quality. Establishing strong relationships can lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international commercial terms (Incoterms) is vital for managing logistics and cost responsibilities in cross-border transactions. Buyers must be clear on who bears costs at each stage of shipping and delivery.
What Buyer Tips Can Optimize Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Electric Cars?
International B2B buyers should consider several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency when sourcing components for electric cars.
-
Negotiation Strategies: Cultivating strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better terms and pricing. Regular communication and long-term agreements can lead to improved rates.
-
Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluating the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just upfront costs is crucial. This includes considering maintenance, energy consumption, and resale value, which can significantly affect overall profitability.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America may face unique challenges, including currency fluctuations and import tariffs. Understanding local market dynamics is essential for effective budgeting.
-
Market Trends and Innovations: Keeping abreast of the latest trends in electric vehicle technology can provide insights into potential cost-saving innovations or alternative components that enhance value.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure, price influencers, and strategic purchasing practices will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions in the emerging market for homemade electric cars designed for users without driving licenses.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric car without driving licence home made cha With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Electric Cars Without Driving Licence Home Made Cha
In the evolving landscape of electric mobility, it’s crucial for B2B buyers to consider various solutions that meet their specific operational needs. The concept of electric cars that can be operated without a driving license, particularly homemade versions, presents a unique opportunity. However, there are several alternative options worth evaluating, including commercially available electric vehicles, electric scooters, and bicycle conversion kits. Below is a comparative analysis of these alternatives.
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Car Without Driving Licence Home Made Cha | Commercially Available Electric Cars | Electric Scooters | Bicycle Conversion Kits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate speed, limited range | High performance, long range | Moderate speed, short range | Varies, generally low-speed |
| Cost | Low initial investment (DIY) | Higher upfront cost | Lower than cars, varies | Moderate, depending on components |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires DIY skills, tools, and knowledge | Plug-and-play, minimal setup | Ready to use | Requires some mechanical skills |
| Maintenance | DIY maintenance, potentially high time investment | Professional servicing recommended | Low maintenance | DIY maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Local commuting, budget-conscious users | Business fleets, longer distances | Urban commuting, short trips | Fitness, eco-friendly transport |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Commercially Available Electric Cars
Commercially available electric cars offer a comprehensive solution for businesses needing reliable transportation. They are designed for optimal performance, providing longer ranges and faster speeds than homemade electric cars. However, the upfront investment is significantly higher. While maintenance is typically lower than traditional vehicles, professional servicing is often required, adding to ongoing costs. This option is best suited for businesses that prioritize reliability and performance over initial cost.
Electric Scooters
Electric scooters are an increasingly popular alternative for urban environments, offering a quick and efficient means of transport. They are generally more affordable than both homemade electric cars and commercial electric vehicles. The ease of use and low maintenance make them attractive, particularly for short commutes. However, their limited range and speed may not meet the needs of businesses requiring longer travel distances. They are ideal for urban commuting and short-distance travel, especially in crowded city settings.
Bicycle Conversion Kits
Bicycle conversion kits transform traditional bicycles into electric models, providing an eco-friendly transportation option. These kits are relatively affordable and allow for a customized approach to mobility. While they require some mechanical skills for installation and maintenance, they are a low-cost solution for businesses promoting sustainability and fitness. However, the speed and range are generally lower compared to other electric vehicle options, making them less suitable for longer commutes.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business
When selecting the right transportation solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific needs, including budget constraints, range requirements, and ease of implementation. Electric cars without driving licenses, especially homemade versions, can be an excellent option for local commuting at a low cost, but may lack the performance and reliability of commercially available electric vehicles. Electric scooters offer a practical alternative for urban commuting, while bicycle conversion kits provide a sustainable option for fitness-oriented businesses. Evaluating these factors will help businesses make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and customer needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric car without driving licence home made cha
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Electric Cars Without Driving Licenses?
When considering the procurement of electric cars designed for use without a driving license, understanding the technical properties is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are some key specifications that are particularly relevant:
-
Battery Capacity (kWh)
– Definition: The total energy storage capacity of the battery, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
– Importance: A higher capacity allows for greater range and longer usage periods between charges, which is vital for commercial applications, especially in regions with limited charging infrastructure. -
Range (km)
– Definition: The distance the vehicle can travel on a full charge, typically expressed in kilometers (km).
– Importance: Knowing the range helps businesses assess the vehicle’s suitability for specific applications, such as urban deliveries or personal transport in rural areas. -
Charging Time (hours)
– Definition: The time required to fully charge the vehicle’s battery from a depleted state.
– Importance: Shorter charging times enhance operational efficiency, allowing for quicker turnaround between uses, which is critical for fleet operators. -
Maximum Load Capacity (kg)
– Definition: The maximum weight the vehicle can safely carry, including passengers and cargo, expressed in kilograms (kg).
– Importance: Understanding load capacity is essential for businesses that require transporting goods or multiple passengers, ensuring compliance with safety regulations. -
Motor Power (kW)
– Definition: The output power of the electric motor, measured in kilowatts (kW).
– Importance: Higher motor power generally translates to better acceleration and performance, which can be a key selling point for customers looking for efficiency in urban environments.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Electric Cars Without Driving Licenses?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some important terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships helps businesses identify reliable suppliers for components and ensure quality standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budget planning and inventory management, particularly for businesses looking to scale operations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services.
– Importance: Issuing RFQs allows businesses to compare pricing and terms from various suppliers, ensuring they get the best deal. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps businesses understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, which is vital for international transactions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time from when an order is placed until it is fulfilled.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is essential for inventory management and planning, particularly for businesses that rely on timely delivery of electric vehicles for operations. -
Warranty Period
– Definition: The duration of time during which the manufacturer will repair or replace defective parts.
– Importance: A robust warranty period can enhance buyer confidence and reduce long-term operational costs, making it a critical consideration in procurement decisions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals in the electric vehicle market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric car without driving licence home made cha Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Electric Car Without Driving License Sector?
The electric car sector is experiencing a notable transformation, driven by the rising demand for sustainable transportation solutions. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the market for electric cars without a driving license—often referred to as quadricycles or voiturettes—is gaining traction. Key drivers include increasing urbanization, the push for reduced emissions, and the growing popularity of alternative mobility solutions among younger demographics. In Europe, for instance, these vehicles are becoming an attractive option for teenagers seeking safer, more affordable transportation alternatives to scooters.
Emerging B2B sourcing trends reflect a shift towards modularity and customization. Companies are increasingly focusing on sourcing parts that can be easily integrated into home-built electric vehicles, such as lightweight chassis and high-efficiency electric motors. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers looking to enter markets with cost-sensitive consumers. Furthermore, technological advancements in battery technology and electric drivetrains are allowing manufacturers to offer enhanced performance at competitive prices, making these vehicles more appealing.
International B2B buyers should also be aware of regulatory frameworks that govern electric vehicle production and sales. For example, the European Union has established stringent regulations aimed at promoting low-emission vehicles, which can influence sourcing decisions. Understanding these regulations is essential for navigating the market effectively and ensuring compliance.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Electric Car Without Driving License Sector?
Sustainability is a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the electric car sector, particularly in the context of electric vehicles without driving licenses. The environmental impact of sourcing materials and components must be assessed, as the industry grapples with issues related to battery production and disposal. The extraction of raw materials, such as lithium and cobalt, raises concerns about environmental degradation and social implications in mining regions.
Buyers can mitigate these risks by prioritizing ethical sourcing practices and partnering with suppliers committed to sustainability. This includes sourcing batteries and components that have been certified for their environmental impact, as well as exploring materials that are recyclable or derived from sustainable sources. Additionally, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and various green labels can provide assurance of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Incorporating sustainability into the supply chain not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products. As international markets continue to evolve, buyers who prioritize ethical sourcing will be better positioned to meet consumer expectations and regulatory requirements.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Electric Cars Without a Driving License?
The concept of electric cars without a driving license has its roots in the broader evolution of personal transportation. Initially, these vehicles were designed to meet the needs of individuals who required an accessible and cost-effective mobility solution, particularly in densely populated urban areas. The introduction of lightweight electric vehicles, often classified as quadricycles, provided a practical alternative for those who either could not obtain a traditional driving license or preferred a simpler mode of transport.
Over the past decade, advancements in electric vehicle technology have significantly improved the performance and affordability of these cars. The rise of DIY electric vehicle kits and home-built conversions has democratized access to electric mobility, allowing enthusiasts and entrepreneurs to innovate within this space. This shift is particularly relevant in emerging markets, where cost-effective transportation solutions are crucial for economic development. As the sector continues to grow, it presents unique opportunities for B2B buyers to engage with a diverse array of products and suppliers, catering to a wide range of consumer needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric car without driving licence home made cha
-
How do I ensure the quality of electric cars without a driving license when sourcing from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, it’s crucial to conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Request certifications, quality assurance processes, and product samples. It’s advisable to visit the manufacturing facility if possible or use third-party inspection services to verify the quality of the vehicles before making a bulk purchase. Additionally, establishing clear quality standards and expectations in the contract can help mitigate risks. -
What are the key features to consider when selecting an electric car without a driving license?
When selecting a license-free electric car, consider factors such as range, battery capacity, charging time, and safety features. Evaluate the vehicle’s size and weight, as these impact performance and efficiency. Additionally, assess the availability of parts and service options in your region to ensure long-term support and maintenance. It’s also beneficial to understand local regulations regarding license-free vehicles. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for electric cars without a driving license?
The MOQ can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific model of the electric car. Generally, manufacturers may require a MOQ ranging from 10 to 50 units for customized orders. It’s essential to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to find a suitable arrangement. Some suppliers may also offer flexibility for first-time buyers or during promotional periods. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted for international purchases of electric vehicles?
Payment terms vary by supplier but typically include options such as upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. Common methods include bank transfers, letters of credit, and escrow services. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that align with your financial capabilities while ensuring security for both parties. Always document the agreed terms in the contract to avoid disputes. -
How can I customize electric cars without a driving license for my market?
Customization options often include modifications to design, battery specifications, and added features like infotainment systems or safety enhancements. Discuss your specific requirements with the manufacturer early in the negotiation process to ensure they can accommodate your needs. Be aware that extensive customization may affect lead times and costs, so it’s important to balance your desires with practicality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric cars?
Logistics for importing electric cars involve assessing shipping methods, customs regulations, and local import duties. It’s crucial to partner with a logistics provider experienced in handling vehicles to ensure compliance and timely delivery. Additionally, consider warehousing options and local transportation needs upon arrival. Proper planning can help avoid delays and unexpected costs. -
What are the common challenges when sourcing electric cars without a driving license internationally?
Common challenges include navigating varying regulations across countries, ensuring quality control, and managing shipping logistics. Language barriers and cultural differences can also complicate negotiations. It’s essential to establish clear communication channels and consider working with local agents or partners who understand the market dynamics. Building strong relationships with suppliers can help overcome these obstacles. -
How do I evaluate the reputation of a supplier for electric cars without a driving license?
Evaluating a supplier’s reputation involves researching their history, customer reviews, and industry standing. Look for testimonials from previous clients and check for any complaints or issues reported online. Engaging with industry associations or trade groups can provide additional insights. Conducting background checks and requesting references can further validate their credibility and reliability as a supplier.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
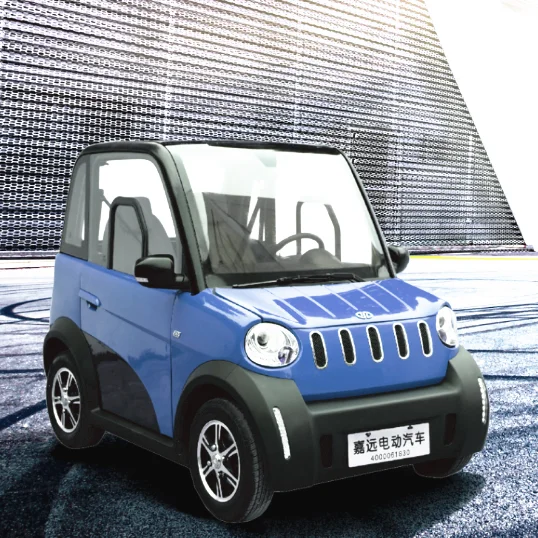
Top 3 Electric Car Without Driving Licence Home Made Cha Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Instructables – Electric Car Conversion Guide
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Build your own electric car by converting a gasoline vehicle. Key steps include:
1. **Get a Car**: Look for a lightweight car with no power features. Example: Geo Metro for $500.
2. **Remove Gasoline Components**: Take out the gas tank, engine, exhaust, radiator, etc. This can save weight and allow for selling parts to offset costs.
3. **Adapter Plate**: Create an adapter plate from aluminum to co…
2. Reddit – EV Charging Solutions
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The user plans to purchase a used electric vehicle (EV) but cannot charge it at home due to parental restrictions. They are exploring public charging options, specifically free Level 2 charging stations located far from their home. The user expresses a desire for independence and the ability to travel without relying on their ebike or parents for rides. They mention that their father is considerin…
3. Citroën – Ami 100% Electric Quadricycle
Domain: citroen.co.uk
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Citroën Ami 100% Electric Quadricycle
– Price: From £7,695 OTR for standard model, £8,095 OTR for colour versions
– Electric: 100% electric vehicle
– Range: Up to 46 miles (WMTC)
– Top Speed: 28 mph
– Charging Time: 0% to 100% in 4 hours
– Dimensions: 2.41m long, 1.39m wide, 1.52m high
– Turning Circle: 7.2m
– Interior Storage: 63L to 200L (if passenger seat used for storage)
– Warranty: 2-year ma…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric car without driving licence home made cha
The growing interest in electric cars without a driving license presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As manufacturers pivot towards more sustainable solutions, the demand for homemade electric vehicles is on the rise. Strategic sourcing of components, such as lightweight materials and efficient battery systems, can significantly reduce costs while enhancing vehicle performance.
Investing in the development and assembly of electric vehicles that cater to local needs not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also taps into a burgeoning market of consumers seeking affordable and eco-friendly transportation alternatives.
As we look to the future, it’s crucial for businesses to engage with local suppliers and innovators to cultivate a robust ecosystem that supports the production of electric cars without a driving license. By fostering partnerships and leveraging local expertise, companies can position themselves at the forefront of this transformative industry. We encourage B2B buyers to explore these opportunities, invest in sustainable technologies, and contribute to the evolution of transportation in their regions.