Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for low speed electric vehicle china
Navigating the global market for low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) from China presents unique challenges for international B2B buyers. Sourcing these affordable and efficient alternatives to traditional vehicles can be daunting, especially with the complexities of regulations, pricing, and supplier reliability. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the landscape of LSEVs, providing insights into various types, applications, and market dynamics.
From understanding the intricacies of battery technology to evaluating cost structures that can range from as low as $1,600 to over $3,000 for different models, this resource equips buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. The guide delves into the nuances of supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can identify trustworthy manufacturers capable of meeting their needs.
For B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging markets like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam—this guide serves as an invaluable tool. It empowers them to navigate the intricacies of the LSEV market, optimizing their sourcing strategies while addressing key challenges such as regulatory compliance and logistical considerations. By leveraging the insights provided, international buyers can confidently explore the potential of LSEVs as a sustainable transportation solution that aligns with their business objectives.
Understanding low speed electric vehicle china Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mini EV | Compact size, typically under 1.5 meters wide, speeds up to 70 KPH | Urban delivery, small businesses | Pros: Affordable, easy to park; Cons: Limited speed and range. |
| Ultra-Narrow EV | Less than 1.5 meters wide, no driver’s license required | Short-distance transport, child transport | Pros: Extremely maneuverable; Cons: Safety concerns, limited battery capacity. |
| Low-Speed Utility Vehicle (LSUV) | Designed for cargo transport, higher payload capacity | Logistics, agricultural support | Pros: Practical for rural applications; Cons: May require additional licensing. |
| Golf Cart-style EV | Similar to golf carts, often used for leisure and short trips | Resorts, campuses, gated communities | Pros: Comfortable for short distances; Cons: Not suitable for long commutes. |
| Lead-Acid Battery EV | Utilizes lead-acid batteries, lower initial cost | Budget-conscious buyers, rural areas | Pros: Low purchase price; Cons: Shorter lifespan and environmental concerns. |
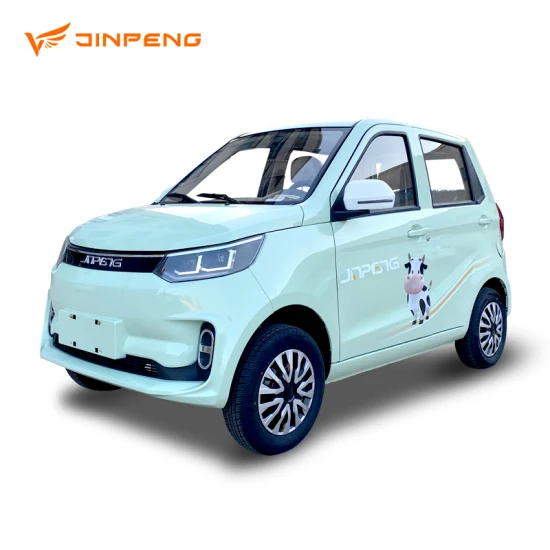
What Are the Key Characteristics of Mini EVs?
Mini EVs are compact electric vehicles designed for urban environments. They typically have a maximum speed of 70 KPH and are under 1.5 meters wide, making them highly maneuverable in congested areas. These vehicles are ideal for businesses focused on last-mile delivery or small-scale urban transport. When considering a Mini EV, buyers should evaluate the vehicle’s range, charging options, and local regulations regarding low-speed vehicles.
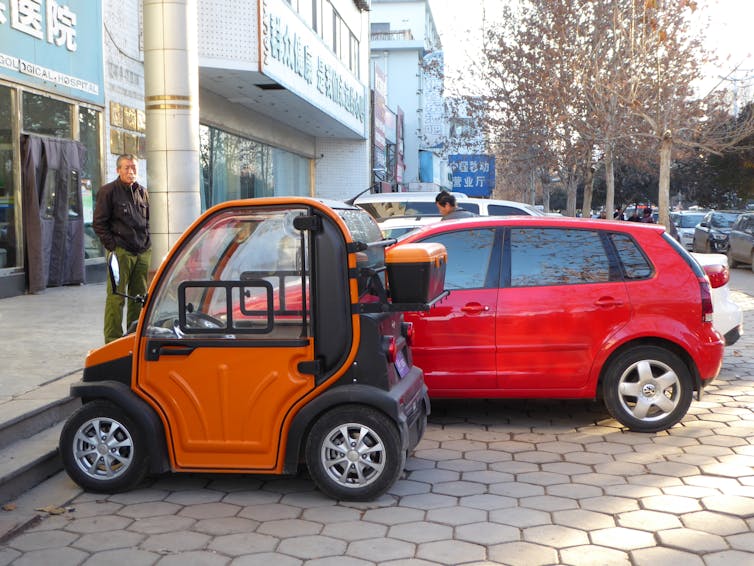
How Do Ultra-Narrow EVs Serve B2B Needs?
Ultra-Narrow EVs are designed to be less than 1.5 meters wide and can often be operated without a driver’s license. Their size allows them to navigate tight spaces, making them suitable for short-distance transport, especially in rural areas or densely populated cities. Businesses that cater to families, such as child transport services, may find these vehicles particularly useful. However, potential buyers should consider safety features and battery performance before purchasing.
What Advantages Do Low-Speed Utility Vehicles Offer?
Low-Speed Utility Vehicles (LSUVs) are designed for practical applications, particularly in logistics and agricultural sectors. They have a higher payload capacity compared to standard low-speed vehicles, making them ideal for transporting goods in rural or semi-urban areas. When purchasing LSUVs, businesses should assess the vehicle’s cargo capacity, durability, and suitability for their specific operational needs.
Why Choose Golf Cart-style EVs for Short Trips?
Golf Cart-style EVs are popular for leisure use and short-distance travel, especially in resorts, campuses, and gated communities. Their design prioritizes comfort and ease of use, making them appealing for recreational applications. Businesses in hospitality or education may benefit from these vehicles, but they are not suitable for long commutes or heavy cargo transport. Buyers should consider the vehicle’s range and charging infrastructure in their operational areas.
What Should B2B Buyers Know About Lead-Acid Battery EVs?
Lead-Acid Battery EVs are among the most affordable options in the low-speed electric vehicle market. They are particularly appealing to budget-conscious buyers in rural areas, where cost efficiency is crucial. However, these vehicles come with drawbacks, including shorter battery lifespan and potential environmental issues associated with lead-acid technology. Businesses should weigh the initial cost against long-term operational efficiency and sustainability when considering these vehicles.
Key Industrial Applications of low speed electric vehicle china
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of low speed electric vehicle china | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Delivery Services | Last-mile delivery of goods within city limits | Reduces transportation costs and improves delivery efficiency | Look for vehicles with adequate cargo space and range; consider local regulations for LSEVs. |
| Tourism and Leisure | Shuttle services in tourist areas | Enhances customer experience and reduces carbon footprint | Ensure vehicles are comfortable and have a good aesthetic; check for charging infrastructure in tourist zones. |
| Agriculture | Transporting goods and personnel within farms | Cost-effective transportation solution for rural areas | Assess durability and terrain capability; consider battery life and charging options for remote locations. |
| Education | School transportation for children | Provides safe, affordable transport for students | Verify safety features and compliance with local regulations; consider ease of access for children. |
| Healthcare | Patient transport in rural areas | Improves access to healthcare services | Ensure vehicles are equipped for medical transport needs; consider range and charging facilities in rural settings. |
How Are Low-Speed Electric Vehicles Used in Urban Delivery Services?
In urban delivery services, low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) are increasingly utilized for last-mile delivery. These compact vehicles can navigate congested city streets, making them ideal for transporting goods quickly and efficiently. By adopting LSEVs, businesses can significantly reduce transportation costs and enhance delivery efficiency, especially in areas where larger vehicles may struggle. International buyers should consider local regulations regarding vehicle size and weight, as well as ensure the vehicles have adequate cargo space and battery range to meet operational needs.
What Role Do Low-Speed Electric Vehicles Play in Tourism and Leisure?
In the tourism sector, LSEVs serve as shuttle services in busy tourist areas, providing a unique and eco-friendly transportation option. These vehicles enhance the customer experience by offering convenient transport between attractions while contributing to a reduction in carbon emissions. For businesses, investing in aesthetically pleasing and comfortable LSEVs can attract more customers. Buyers should also evaluate the availability of charging infrastructure in tourist zones to maintain operational efficiency.
How Are Low-Speed Electric Vehicles Beneficial in Agriculture?
Agricultural businesses leverage LSEVs for transporting goods and personnel within farms. These vehicles provide a cost-effective solution for rural transportation, where larger vehicles may be impractical. By using LSEVs, farmers can optimize their operations and reduce reliance on fuel-based vehicles, leading to lower operational costs. Buyers in the agricultural sector should assess the durability of the vehicles and their capability to handle various terrains, as well as consider battery life and charging options in remote locations.
How Do Low-Speed Electric Vehicles Support Education?
In the education sector, LSEVs are employed for safe and affordable school transportation, particularly in rural areas. These vehicles provide a reliable means of transport for students, ensuring they can attend school consistently. For educational institutions, prioritizing safety features and compliance with local regulations is crucial. Buyers should also consider ease of access for children and the overall comfort of the vehicles to enhance the transportation experience.
What Advantages Do Low-Speed Electric Vehicles Offer in Healthcare?
LSEVs are increasingly used for patient transport in rural healthcare settings, improving access to medical services. These vehicles can navigate areas that may be difficult for larger ambulances, providing a vital link for patients in remote communities. Healthcare providers should ensure that the vehicles are equipped with necessary medical transport features and assess the range and charging facilities available in rural settings. This ensures that patient care is not compromised due to transportation challenges.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘low speed electric vehicle china’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Compliance with Local Regulations
The Problem: B2B buyers seeking to import low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) from China often face challenges navigating the complex landscape of local regulations. Different countries have varying laws regarding vehicle safety standards, emissions, and import tariffs, which can lead to significant delays and unexpected costs. Buyers may find themselves uncertain about which models comply with their local regulations, risking non-compliance and potential fines.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, it is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research on the regulatory environment in their target market before making purchasing decisions. Collaborating with local legal experts or compliance consultants can provide clarity on required standards. Additionally, buyers should seek manufacturers who offer detailed documentation on vehicle specifications, compliance certifications, and testing results. Establishing a clear communication channel with suppliers in China can also help ensure that the chosen vehicles meet local requirements, potentially saving time and resources during the import process.
Scenario 2: Limited Knowledge of Battery Technology and Maintenance
The Problem: One of the critical pain points for buyers is understanding the battery technology used in low-speed electric vehicles, particularly those that rely on lead-acid batteries. Many prospective buyers may not be aware of the implications of using lead-acid batteries, such as their shorter lifespan, lower energy efficiency, and environmental concerns. This lack of knowledge can lead to poor decision-making regarding vehicle selection and maintenance, resulting in higher long-term costs and operational inefficiencies.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing vehicles equipped with advanced lithium-ion battery technology, which offers better performance, longevity, and environmental sustainability. Engaging with manufacturers who provide comprehensive training on battery care and maintenance is crucial. This training should cover best practices for charging, storage, and recycling of batteries. Additionally, implementing a structured maintenance schedule can help maximize the lifespan of the vehicles and reduce unexpected costs related to battery failures. Buyers can also leverage online forums and industry publications to stay updated on the latest advancements in battery technology and maintenance strategies.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Scaling Up Fleet Operations
The Problem: For B2B buyers looking to establish or expand a fleet of low-speed electric vehicles, scaling operations can pose significant challenges. Issues such as supply chain disruptions, inconsistent quality from manufacturers, and difficulties in securing financing for larger orders can hinder growth. This can lead to delays in deployment and reduced competitiveness in their respective markets.
The Solution: To effectively scale operations, buyers should develop strategic partnerships with reliable manufacturers that have a proven track record of consistent quality and delivery. Conducting site visits to production facilities in China can help buyers assess manufacturing capabilities firsthand. Additionally, diversifying suppliers can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions. Buyers should also consider exploring financing options such as leasing or partnerships with local financial institutions to ease the burden of large upfront investments. By creating a robust logistical and financial plan, buyers can streamline their scaling efforts and enhance their market position.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for low speed electric vehicle china
What Are the Common Materials Used in Low-Speed Electric Vehicles in China?
Low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) in China are gaining traction due to their affordability and practicality. Understanding the materials used in their construction is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to source components or entire vehicles. Here, we analyze four common materials used in LSEVs: steel, aluminum, plastic composites, and lead-acid batteries.
How Does Steel Contribute to the Durability of Low-Speed Electric Vehicles?
Steel is a primary material for the chassis and structural components of LSEVs. It offers excellent strength and durability, which is essential for vehicle safety and longevity. Key properties include high tensile strength and resistance to deformation under stress, making it suitable for handling the rigors of daily use.
Pros: Steel is relatively inexpensive and widely available, which reduces manufacturing costs. It also has excellent weldability, allowing for complex shapes and designs.
Cons: The main drawback is its weight, which can affect the overall efficiency of electric vehicles by reducing range. Additionally, steel is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various coatings and treatments can enhance its corrosion resistance, making it suitable for diverse environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding vehicle safety standards, which often reference ASTM and ISO standards.
Why Is Aluminum Preferred for Lightweight Components in LSEVs?
Aluminum is increasingly used in low-speed electric vehicles for components like body panels and frames. Its lightweight nature helps improve energy efficiency and range.
Pros: Aluminum is corrosion-resistant and has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for applications where weight savings are critical.
Cons: The primary disadvantage is its higher cost compared to steel, which may impact the overall pricing of LSEVs. Additionally, aluminum requires specialized welding techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s lightweight properties significantly enhance vehicle performance, particularly in urban environments where agility and maneuverability are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the differences in aluminum grades and ensure that they meet relevant international standards, such as JIS or DIN.
How Do Plastic Composites Enhance Design Flexibility in Low-Speed Electric Vehicles?
Plastic composites are often used for interior components and non-structural parts in LSEVs. They offer design flexibility and can be molded into complex shapes.
Pros: These materials are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be produced in various colors and finishes, enhancing aesthetic appeal.
Cons: Plastic composites may not provide the same level of durability as metals, especially in high-stress applications. They can also be more expensive to recycle.
Impact on Application: The use of plastic composites can reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, improving efficiency while allowing for innovative design options.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that plastic composites comply with local environmental regulations, especially concerning recyclability and sustainability.
What Role Do Lead-Acid Batteries Play in Low-Speed Electric Vehicles?
Lead-acid batteries are commonly used in LSEVs due to their affordability and ease of manufacturing. They provide sufficient power for the low-speed applications typical of these vehicles.
Pros: Lead-acid batteries are cost-effective and have a well-established recycling infrastructure, making them a practical choice for budget-conscious buyers.
Cons: They have a lower energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries, resulting in shorter ranges and longer charging times. Additionally, they can be heavy, which may affect vehicle performance.
Impact on Application: While lead-acid batteries are suitable for low-speed applications, their limitations may affect the vehicle’s operational range and efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the environmental impact of lead-acid battery disposal and ensure compliance with local regulations regarding battery recycling and safety standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Low-Speed Electric Vehicles
| Material | Typical Use Case for Low-Speed Electric Vehicle China | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Chassis and structural components | High strength and durability | Heavy and prone to corrosion | Low |
| Aluminum | Body panels and frames | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and complex welding | Med |
| Plastic Composites | Interior components and non-structural parts | Design flexibility and aesthetic appeal | Lower durability in high-stress areas | Med |
| Lead-Acid Batteries | Power source for LSEVs | Cost-effective and recyclable | Lower energy density and heavy | Low |
This guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions about material selection in low-speed electric vehicles. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials is essential for ensuring compliance with regional standards and meeting market demands.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for low speed electric vehicle china
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Low-Speed Electric Vehicles in China?
The manufacturing of low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) in China involves several critical stages that ensure efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
In this initial stage, raw materials such as steel, aluminum, and plastic are sourced and prepared for production. Suppliers are often selected based on their ability to meet specific quality standards and delivery timelines. The selection of materials is crucial as it affects the vehicle’s durability, performance, and weight. Additionally, battery components are procured, with lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries being the most common choices for LSEVs. Manufacturers may choose suppliers who can provide materials that comply with international safety and environmental standards.
Forming
The forming stage involves shaping the raw materials into parts that will comprise the vehicle. This typically includes processes like stamping, bending, and molding. Advanced manufacturing techniques such as CNC machining and robotic welding are increasingly utilized to enhance precision and efficiency. The use of automation helps reduce human error and speeds up production, which is vital given the growing demand for LSEVs.
Assembly
Once the parts are formed, they move to the assembly line, where skilled workers and automated systems come together to construct the vehicle. This phase includes the installation of the electrical system, battery pack, and various components like wheels, doors, and interior fittings. Assembly lines are designed for flexibility, allowing for different models to be produced without significant downtime. Quality control measures are integrated into the assembly process to ensure that each component meets the required specifications.
Finishing
The finishing stage focuses on the vehicle’s aesthetics and final quality checks. This may involve painting, polishing, and applying protective coatings to enhance durability and appearance. After finishing, vehicles undergo a final inspection to ensure they meet both domestic and international standards before leaving the factory.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Low-Speed Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of LSEV manufacturing, particularly for international B2B buyers who require compliance with various standards. Several internationally recognized and industry-specific standards guide the quality assurance processes.
What International Standards Are Relevant for LSEV Manufacturing?
Manufacturers often adhere to ISO 9001, which outlines the criteria for a quality management system. This standard ensures that companies consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, CE marking is crucial for products sold in Europe, as it indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection legislation. Other relevant certifications may include API standards for automotive components.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify issues early on. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage assesses the quality of raw materials and components received from suppliers. It ensures that only materials meeting specified standards are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During assembly, IPQC measures are taken to monitor the manufacturing process. This includes regular inspections and tests to ensure that each stage meets quality criteria.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, FQC involves comprehensive testing of the completed vehicles. This may include performance tests, safety checks, and compliance verifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
Manufacturers employ various testing methods to ensure product quality. Common methods include:
-
Electrical Testing: To verify the functionality and safety of electrical systems and battery performance.
-
Durability Testing: Simulating real-world conditions to assess the vehicle’s resilience and longevity.
-
Safety Testing: Ensuring compliance with safety standards, which may involve crash tests and evaluations of braking systems.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential to mitigate risks and ensure product reliability. Several strategies can be employed:
What Are the Best Practices for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Conducting thorough supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess quality control practices. Buyers should evaluate:
-
Quality Management Systems: Review documentation related to ISO certifications and internal quality processes.
-
Production Capabilities: Inspect manufacturing facilities to understand their capacity and technology used.
-
Past Performance: Analyze reports on product recalls, defects, and customer feedback to gauge reliability.
How Can Buyers Leverage Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of supplier practices. These inspections can include:
-
Pre-shipment Inspections: Ensuring that products meet specifications before they are shipped.
-
Random Sampling: Assessing a sample of goods from a production batch to verify quality.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for B2B Buyers in Specific Regions?
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances in quality certification and compliance. For instance:
-
Regional Regulations: Different countries may have unique regulations governing vehicle safety and emissions. Understanding these can help buyers avoid compliance issues.
-
Import Tariffs and Duties: Buyers should consider how tariffs may affect the overall cost of procurement. This is particularly relevant for vehicles imported from China, as different countries have varying import duties.
-
Cultural Considerations: Building strong relationships with suppliers is essential in many cultures, impacting communication and negotiation processes.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for low-speed electric vehicles in China are complex but vital for meeting international standards and buyer expectations. By understanding these processes and implementing robust verification strategies, B2B buyers can ensure they source high-quality, reliable vehicles for their markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘low speed electric vehicle china’
This guide serves as a practical resource for international B2B buyers seeking to procure low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) from China. With the increasing demand for affordable and efficient transportation solutions, understanding the sourcing process is crucial. Below is a step-by-step checklist to facilitate your procurement journey.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical specifications for the LSEVs you intend to purchase. Consider factors such as vehicle size, battery type (lead-acid vs. lithium-ion), and maximum speed. This ensures that the vehicles meet your operational needs and comply with local regulations in your target market.
- Vehicle Type: Determine if you need mini EVs, ultra-narrow vehicles, or specific models tailored for certain applications.
- Performance Requirements: Assess the maximum speed and range based on the intended use, whether for urban commuting or rural transport.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Research the current market landscape for LSEVs in China. This includes identifying key manufacturers, pricing trends, and regulatory environments that might affect your purchase.
- Competitor Analysis: Look into other international buyers’ experiences and preferences, especially those from similar regions like Africa and the Middle East.
- Regulatory Insights: Understand local regulations regarding LSEV usage in your market to ensure compliance.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your needs. Request comprehensive company profiles, product catalogs, and references from previous clients.
- Supplier Reputation: Investigate their market presence, years of operation, and customer feedback.
- Product Quality Assurance: Ask for details on quality control processes and compliance with international standards.
Step 4: Request Samples and Test Vehicles
Before making a large order, request samples or arrange for test vehicles. This allows you to evaluate the quality, performance, and user-friendliness of the vehicles.
- Hands-On Assessment: Check the build quality, comfort, and ease of operation to ensure it meets your expectations.
- Performance Testing: Assess the vehicle’s speed, battery life, and handling under different conditions.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you’ve selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize pricing and terms. This includes understanding the FOB price, payment terms, and delivery timelines.
- Cost Breakdown: Ensure transparency in pricing, including any hidden costs such as tariffs or shipping fees.
- Payment Security: Choose secure payment methods and clarify terms to protect your investment.
Step 6: Verify Compliance with International Standards
Confirm that the LSEVs comply with international safety and environmental standards. This is particularly important for markets in Europe and other regions with stringent regulations.
- Certifications: Request documentation for certifications such as ISO, CE, or local compliance.
- Sustainability Practices: Evaluate the supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices, especially regarding battery disposal and emissions.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and After-Sales Support
Finally, develop a logistics plan for transporting the vehicles from China to your location. Ensure that the supplier offers after-sales support and warranty options.
- Shipping Arrangements: Decide whether to use your own freight forwarder or the supplier’s services, considering cost and reliability.
- Support Services: Inquire about training, spare parts availability, and customer support to ensure smooth operation post-purchase.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your procurement process for low-speed electric vehicles from China, ensuring that you make informed decisions that align with your business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for low speed electric vehicle china Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Low-Speed Electric Vehicle Sourcing from China?
When sourcing low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) from China, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. LSEVs are often made with less expensive components like lead-acid batteries, which are cheaper but may have higher replacement costs over time compared to lithium-ion alternatives. Buyers should assess whether investing in higher-quality materials might yield better long-term performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs in China can vary based on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. While labor is generally less expensive than in many Western countries, suppliers in more developed areas may charge higher rates due to better infrastructure and skilled labor availability.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, maintenance, and administrative costs. It’s essential for buyers to inquire about these overhead costs, as they can influence the final pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific vehicle designs or features can add to initial costs. Buyers looking for specialized LSEVs should consider these upfront expenses in their budget, as they may significantly affect unit prices.
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust QC processes are essential to ensure product reliability and compliance with international standards. Buyers should evaluate the QC practices of potential suppliers, as enhanced quality assurance can lead to higher initial costs but can save money in the long run by reducing defects and warranty claims.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on the chosen Incoterms, destination, and freight methods. For example, Full Container Load (FCL) shipping can range from $2,290 to $6,870 depending on the destination. Buyers must factor in these logistics costs when calculating the total cost of ownership.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on market conditions and the supplier’s reputation. Buyers should research multiple suppliers to understand the typical margin range and negotiate accordingly.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Low-Speed Electric Vehicles?
Several factors can influence the pricing of LSEVs, making it critical for buyers to understand these nuances:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to reduced per-unit costs. Buyers should determine the minimum order quantity (MOQ) and consider pooling orders with other businesses to achieve cost efficiencies.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can increase costs significantly. Buyers should clearly define their needs upfront to avoid unexpected price increases later.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications can drive up costs but may be necessary for compliance with regulations in the buyer’s home country. Understanding local regulatory requirements can help buyers make informed decisions about material selection.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can also affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better service and quality assurance, which can lead to lower total costs over time.
-
Incoterms: Different shipping terms can affect the total cost. For instance, choosing FOB (Free on Board) means that buyers are responsible for shipping costs once the goods are loaded, while CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) includes shipping in the supplier’s price.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help International Buyers Secure Better Pricing?
For B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can lead to significant savings:
-
Establish Clear Requirements: Clearly outlining specifications and quality standards can minimize misunderstandings and additional costs.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building a rapport with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Long-term relationships often yield favorable negotiation outcomes.
-
Analyze Total Cost of Ownership: When evaluating options, consider not just the purchase price but also maintenance, operation, and potential resale value. A more expensive vehicle may offer better longevity and lower total costs.
-
Stay Informed: Understanding market trends and supplier capabilities can provide leverage during negotiations. Buyers should stay updated on industry standards and pricing trends.
-
Be Prepared to Walk Away: Knowing your limits and being willing to explore other suppliers can strengthen your negotiating position.
By understanding the cost components, price influencers, and negotiation strategies, international buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing low-speed electric vehicles from China, ultimately leading to more favorable outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing low speed electric vehicle china With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternative Transportation Solutions
As businesses and municipalities explore sustainable transportation options, comparing various solutions becomes critical for informed decision-making. Low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) from China have gained traction due to their affordability and practicality, especially in emerging markets. However, other alternatives exist that may better suit specific needs based on performance, cost, and operational efficiency. This analysis will evaluate LSEVs against two viable alternatives: electric bicycles (e-bikes) and compact gasoline vehicles.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Low Speed Electric Vehicle China | Electric Bicycle (E-Bike) | Compact Gasoline Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Max speed ~70 KPH | Max speed ~28-32 KPH | Max speed ~180 KPH |
| Cost | ~$3,000 | ~$500 – $2,000 | ~$15,000 – $25,000 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires basic infrastructure for charging | Minimal infrastructure needed | Requires gas stations and maintenance services |
| Maintenance | Moderate; battery replacements needed | Low; general upkeep | High; regular servicing required |
| Best Use Case | Urban short-distance travel | Commuting in congested areas | Longer-distance travel and highway use |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Bicycle (E-Bike)
E-bikes offer a cost-effective and efficient alternative for urban commuting. With a lower price point, they are accessible to a broader audience and require less infrastructure for charging. Their lightweight design allows for easy maneuverability in congested areas. However, e-bikes have limited speed and range, making them less suitable for longer trips. They also lack the enclosed protection that LSEVs provide, which can be a disadvantage in inclement weather.
Compact Gasoline Vehicle
Compact gasoline vehicles are a traditional option that offers superior performance and speed compared to LSEVs. They are well-suited for longer distances and can easily navigate highways. However, the higher purchase price and ongoing fuel costs can be significant drawbacks, especially in regions where fuel prices are volatile. Additionally, gasoline vehicles require regular maintenance, which can increase operational costs over time. Environmental concerns also arise due to emissions, making them a less sustainable choice.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Transportation Solution
When choosing between low-speed electric vehicles and their alternatives, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational requirements and regional context. Factors such as budget constraints, intended use case, and infrastructure availability will significantly influence the decision. While LSEVs provide an excellent balance of affordability and utility for short urban trips, e-bikes may serve well for individual commuters in congested areas. Conversely, compact gasoline vehicles offer speed and versatility for longer journeys but come with higher costs and environmental implications. A thorough assessment of these factors will empower buyers to select the most appropriate transportation solution for their needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for low speed electric vehicle china
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Low-Speed Electric Vehicles in China?
Low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) have gained popularity in China due to their affordability, practicality, and unique specifications. Understanding the essential technical properties can help B2B buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Battery Type and Capacity
Most LSEVs in China utilize lead-acid batteries, although lithium-ion options are becoming more prevalent. The battery capacity, often measured in amp-hours (Ah), directly affects the vehicle’s range and performance. For example, a 48V, 100Ah battery might provide a range of 80-100 kilometers per charge. For B2B buyers, selecting the right battery type is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency and meeting the specific needs of the target market.
2. Maximum Speed
LSEVs typically have a maximum speed limit of 70 km/h (43 mph), which categorizes them under low-speed vehicles. This specification is vital for compliance with local regulations in various markets, particularly in urban areas where speed limits are strictly enforced. Buyers must consider local regulations to ensure that the vehicles they import meet safety and legal standards.
3. Vehicle Dimensions
LSEVs are generally designed to be compact, often measuring less than 1.5 meters in width. This dimension not only facilitates easier parking in crowded urban settings but also allows for maneuverability in tight spaces. For B2B buyers, understanding vehicle dimensions is important for logistics and distribution strategies, as it can impact shipping costs and storage requirements.
4. Weight Capacity
The weight capacity of LSEVs is a critical parameter, typically ranging from 300 kg to 800 kg. This includes both the vehicle’s weight and its payload. Knowing the weight capacity is essential for businesses aiming to transport goods or passengers, as it directly influences operational efficiency and safety.
5. Material Composition
The materials used in constructing LSEVs, such as steel or high-strength plastic, affect durability, weight, and cost. A vehicle that is too heavy may be less efficient, while one made from low-quality materials may have a shorter lifespan. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that provide detailed material specifications to ensure product longevity and reliability.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Relevant to Low-Speed Electric Vehicles?
Understanding industry jargon is vital for effective communication in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms related to the low-speed electric vehicle market in China.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the LSEV context, buyers often work with OEMs to customize vehicles to meet specific market demands. This relationship can lead to tailored solutions that enhance competitiveness.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For LSEVs, MOQs can vary significantly among manufacturers. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory levels and cash flow effectively, ensuring they do not overcommit resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ for LSEVs can facilitate comparison among suppliers, leading to better pricing and terms. It streamlines the procurement process and ensures transparency.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to avoid unexpected costs and ensure smooth logistics.
5. FOB (Free On Board)
FOB is a shipping term indicating that the seller is responsible for transportation costs until the goods are loaded on the shipping vessel. After that, the buyer assumes responsibility. Understanding FOB terms is vital for budgeting logistics costs and negotiating contracts effectively.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the low-speed electric vehicle market in China more effectively, ensuring successful transactions and operational success.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the low speed electric vehicle china Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Low-Speed Electric Vehicle Sector in China?
The low-speed electric vehicle (LSEV) market in China has witnessed exponential growth, driven by several global trends. As urbanization accelerates in developing regions, including Africa, South America, and the Middle East, the demand for affordable, efficient transportation solutions is surging. LSEVs, often priced at a fraction of conventional electric vehicles (EVs), cater to this need, making them appealing to budget-conscious consumers. Furthermore, the rising fuel prices and stringent emissions regulations are prompting a shift from gasoline-powered vehicles to electric alternatives, positioning LSEVs as a practical choice for first-time buyers.
Emerging B2B trends indicate a growing interest in vehicle customization and localization, particularly for international markets. Manufacturers are focusing on adapting their offerings to meet specific regional needs, such as climate considerations and regulatory compliance. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam, where local market conditions may dictate specific vehicle features. Additionally, there is an increasing emphasis on technological integration, with features such as smart connectivity and enhanced battery management systems becoming standard in new models.
International B2B buyers should also be aware of the evolving regulatory landscape. The Chinese government is considering stricter regulations for LSEVs, which could impact sourcing strategies. Buyers must remain agile, adapting to these changes while ensuring they select suppliers who are compliant with both local and international standards.
How Important is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Low-Speed Electric Vehicle Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations for B2B buyers in the LSEV sector. As global environmental concerns rise, consumers and businesses alike are increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly products. LSEVs, which produce zero tailpipe emissions, contribute positively to urban air quality, particularly in densely populated areas. However, the environmental impact of the production processes and the materials used in these vehicles must also be considered.
Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adopt sustainable practices, including the use of recyclable materials and responsible sourcing of components. Ethical supply chains not only enhance a brand’s reputation but also align with the growing consumer demand for transparency. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the choice of battery technology is crucial. While many LSEVs utilize lead-acid batteries, which pose environmental challenges, manufacturers are increasingly exploring lithium-ion alternatives that offer better performance and recyclability. B2B buyers should advocate for suppliers who are investing in greener technologies, as this will not only meet consumer expectations but also ensure compliance with emerging regulatory frameworks focused on sustainability.
What Is the Evolution and History of the Low-Speed Electric Vehicle Market in China?
The LSEV market in China has evolved significantly over the past decade. Initially emerging as a solution for rural transport, these vehicles have gained traction in urban settings, where their compact size and affordability appeal to consumers seeking alternatives to larger, more expensive vehicles. The introduction of LSEVs coincided with China’s broader push towards electrification in transportation, aligning with national goals to reduce urban pollution and dependence on fossil fuels.
By 2018, the LSEV fleet in China had grown to approximately 4 million vehicles, representing about 2% of the country’s total passenger cars. This rapid growth was fueled by advancements in battery technology and manufacturing efficiencies, enabling manufacturers to offer vehicles at competitive prices. As the market matures, international B2B buyers are presented with unique opportunities to source these vehicles for diverse applications, from personal use to last-mile delivery solutions.
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of the LSEV market in China is essential for international buyers. By recognizing the key trends, prioritizing sustainability, and acknowledging the sector’s evolution, businesses can make informed sourcing decisions that align with both market demands and ethical considerations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of low speed electric vehicle china
-
How do I solve issues related to low-speed electric vehicle (LSEV) regulations in my country?
Navigating LSEV regulations can be complex, as they vary by region. It’s essential to research local laws regarding vehicle classifications, safety standards, and registration processes. Consult with local automotive authorities or legal experts to ensure compliance. Additionally, partner with suppliers who are knowledgeable about export regulations and can provide documentation to facilitate smooth importation into your country. -
What is the best sourcing strategy for low-speed electric vehicles from China?
To effectively source LSEVs, consider a multi-faceted strategy that includes attending trade shows, using B2B marketplaces, and leveraging industry contacts. Establish relationships with reputable manufacturers that offer quality assurance and after-sales support. Conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers, including checking references and reviewing their production capabilities, to ensure they can meet your specific needs. -
How can I customize low-speed electric vehicles for my market?
Customization options for LSEVs can include branding, color selections, and modifications to meet local standards. Engage directly with manufacturers to discuss your requirements and inquire about their flexibility in production. Consider providing detailed specifications and examples of desired features to facilitate effective communication. A written agreement outlining customization details can help avoid misunderstandings. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for low-speed electric vehicles?
MOQs for LSEVs can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and specific vehicle models. Typically, manufacturers may set MOQs between 10 to 50 units to ensure cost-effectiveness. It’s advisable to discuss your purchasing plans with suppliers early in negotiations to determine their willingness to accommodate smaller orders or offer flexible terms, especially if you’re testing the market. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing low-speed electric vehicles from China?
Payment terms can vary by supplier, but common practices include a deposit of 30-50% upfront, with the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer favorable terms for larger orders or established buyers. Always clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., T/T, L/C) and ensure that terms are documented in the sales agreement to avoid potential disputes. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for low-speed electric vehicles sourced from China?
To ensure quality, consider implementing a comprehensive quality assurance (QA) plan that includes on-site inspections during production, third-party testing, and pre-shipment inspections. Collaborate with suppliers that have established QA processes and certifications. Additionally, specify quality standards in your contract to hold manufacturers accountable for delivering vehicles that meet your specifications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing LSEVs?
Logistics are critical when importing LSEVs. Assess shipping options, including FOB (Free on Board) terms, and factor in costs for tariffs and customs clearance. Determine the best mode of transport based on your timelines and budget. Collaborating with experienced freight forwarders can streamline the logistics process, ensuring timely delivery while managing compliance with international shipping regulations. -
How do I handle after-sales support and warranty claims for low-speed electric vehicles?
Establish clear communication channels with your supplier for after-sales support, including warranty terms and repair services. Discuss the process for handling warranty claims upfront and ensure that it is documented in your agreement. Providing training for your local team on basic maintenance and troubleshooting can also enhance customer satisfaction and reduce the frequency of claims.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Low Speed Electric Vehicle China Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. KEYU – New Electric Car Low Speed
Domain: marketplace.china-crunch.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “KEYU New Electric Car Low Speed”, “Fuel Type”: “BEV”, “Body Type”: “Mini EV”, “Steering Options”: [“LHD”, “RHD”], “Price”: “2,990 USD”, “FOB Price”: “2,990 USD”, “Location”: “Shandong, China”, “Lead Time”: “~2 weeks after full T/T payment received”, “Dimensions”: {“Length”: “3050 mm”, “Width”: “1550 mm”, “Height”: “1600 mm”}, “Wheel Tread”: {“Front”: “1270 mm”, “Rear”: “1300 mm”}…
2. Hezonev – Low-Speed Electric Vehicles
Domain: hezonev.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) designed for urban and suburban environments, offering eco-friendly transportation solutions. Features include a compact design, energy-efficient electric motors, and customizable options for various applications. Ideal for short-distance travel, these vehicles provide a sustainable alternative to traditional gas-powered cars.
3. Research in China – LSEV Industry Report 2020-2026
Domain: researchinchina.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: China Low-speed Electric Vehicle (LSEV) Industry Report, 2020-2026; Hard Copy Price: $3,400; Single User License (PDF Unprintable) Price: $3,200; Enterprise-wide License (PDF Printable & Editable) Price: $4,800; Hard Copy + Single User License Price: $3,600; Pages: 220; Definition: LSEV includes passenger or freight electric vehicles driven by motor with max speed < 70km/h; Types: Electric bicycle…
4. Seneca ESG – Mini LSEVs
Domain: senecaesg.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: This company, Seneca ESG – Mini LSEVs, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. AliExpress – Low-Speed Electric Vehicle
Domain: aliexpress.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: This company, AliExpress – Low-Speed Electric Vehicle, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. The Conversation – Low-Speed Electric Vehicles
Domain: theconversation.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) in China have a top speed of 60 km/h, are compact resembling three-wheeled utility vehicles or golf buggies, and have an average price of £4,000. They are now eligible for license plates, which were previously not available, and are positioned as a low-emission alternative to traditional cars, aiding in urbanization and addressing parking issues.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for low speed electric vehicle china
What Are the Key Insights for International B2B Buyers in the Low-Speed Electric Vehicle Market?
The low-speed electric vehicle (LSEV) market in China presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. With prices starting as low as $1,600, these vehicles offer an affordable alternative for consumers who are transitioning from two-wheelers to four-wheelers, particularly in rural and urban areas where traditional vehicles may be financially out of reach. The strategic sourcing of LSEVs can provide significant cost savings and a competitive edge, allowing businesses to cater to a growing demographic that prioritizes budget-friendly transportation.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business Operations?
Leveraging strategic sourcing in the LSEV sector not only ensures access to quality products but also opens doors to innovative solutions that align with regional consumer needs. By partnering with reputable manufacturers in China, buyers can secure favorable pricing, timely deliveries, and adaptable product features that meet local regulations and preferences.
What Does the Future Hold for the Low-Speed Electric Vehicle Market?
As global demand for sustainable transport solutions rises, the LSEV market is poised for substantial growth. Now is the time for international buyers to engage with this evolving landscape. By investing in low-speed electric vehicles, businesses can not only contribute to reducing carbon footprints but also tap into a lucrative market that is redefining mobility. Reach out to reliable suppliers today to explore partnership opportunities and position your business at the forefront of this exciting industry.