Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric vehicles for disabled
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicles (EVs), sourcing electric vehicles for disabled individuals poses unique challenges for B2B buyers. Despite the growing demand for eco-friendly transportation solutions, the market still grapples with significant barriers, including limited vehicle designs, inadequate charging infrastructure, and high initial costs. This guide is designed to navigate these complexities, providing comprehensive insights into the types of electric vehicles available, their applications, and the necessary adaptations to enhance accessibility.
We will explore various supplier vetting strategies to ensure that you partner with manufacturers committed to innovation and inclusivity. Additionally, cost analysis and financing options will be discussed to help you make informed purchasing decisions that align with your organization’s budget and mission. With a focus on the needs of international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including markets like Nigeria and Vietnam—this guide empowers stakeholders to champion accessible mobility solutions. By understanding the nuances of the electric vehicle market for disabled individuals, businesses can not only foster inclusivity but also tap into a growing segment that is poised for significant expansion in the coming years.
Understanding electric vehicles for disabled Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Wheelchair Accessible Vehicle (eWAV) | Designed for wheelchair users to travel in their wheelchair; includes a lowered floor and ramp for easy access. | Transportation services, mobility aid providers, and public transport systems. | Pros: Enhances independence for users; Cons: Limited options available due to design challenges. |
| Compact Electric Vehicles (CEVs) | Small, lightweight vehicles with adjustable ramps; designed for urban mobility without transfers. | Personal mobility, small fleet operations, and rental services. | Pros: Cost-effective and easy to maneuver; Cons: Limited speed and range compared to larger vehicles. |
| Adapted Electric Vehicles (AEVs) | Standard EVs modified with driving aids like hand controls and adjustable seating. | Fleet vehicles for disabled employees, taxi services, and personal use. | Pros: Customizable to specific needs; Cons: Adaptation costs can vary significantly. |
| Electric Multi-Purpose Vehicles (eMPVs) | Larger vehicles designed to transport multiple passengers, including those with disabilities. | Group transportation services, schools, and community transport. | Pros: Versatile for various mobility needs; Cons: Higher initial investment and operational costs. |
| Accessible Charging Solutions | Charging stations designed with accessible features, including ease of use for disabled drivers. | Infrastructure development for municipalities, fleet operators, and charging networks. | Pros: Expands access to EVs for disabled users; Cons: Still underdeveloped in many areas, leading to inconsistent availability. |
What Are Electric Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles (eWAVs) and Their B2B Relevance?
Electric Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles (eWAVs) are specifically engineered to allow wheelchair users to travel without transferring from their mobility device. They typically feature a lowered floor and a ramp for easy entry and exit. For B2B buyers in transportation services or public transport systems, investing in eWAVs can significantly enhance service offerings, ensuring compliance with accessibility regulations while meeting the growing demand for inclusive transport solutions.
How Do Compact Electric Vehicles (CEVs) Serve the Disabled Community?
Compact Electric Vehicles (CEVs) are designed for urban mobility, featuring adjustable ramps that allow wheelchair users to enter without assistance. Their small footprint makes them ideal for city driving and parking. B2B applications include personal mobility solutions and rental services targeting urban areas. Buyers should consider the balance between affordability and the vehicle’s operational limitations, such as speed and range.
What Are Adapted Electric Vehicles (AEVs) and Their Customization Potential?
Adapted Electric Vehicles (AEVs) are standard electric vehicles modified to accommodate various disabilities. Features may include hand controls, adjustable seating, and other assistive technologies. These vehicles are suitable for fleet operations aimed at providing accessible transport for employees or customers. B2B buyers should weigh the customization options against potential costs, ensuring that the modifications meet specific user needs while remaining within budget.
How Do Electric Multi-Purpose Vehicles (eMPVs) Address Group Transport Needs?
Electric Multi-Purpose Vehicles (eMPVs) are larger vehicles designed to transport multiple passengers, including those with disabilities. They offer versatility for various mobility needs, making them suitable for group transportation services, schools, and community transport initiatives. B2B buyers must consider the higher initial investment and operational costs associated with eMPVs but can benefit from their ability to serve diverse user groups effectively.
Why Are Accessible Charging Solutions Critical for Electric Vehicles?
Accessible charging solutions are essential for ensuring that disabled drivers can easily charge their electric vehicles. These stations are designed with features that facilitate use by individuals with mobility challenges. B2B applications include infrastructure development for municipalities and charging networks. While the expansion of accessible charging solutions is crucial for inclusivity, buyers should be aware of the current underdevelopment in many regions, which can limit their effectiveness.
Key Industrial Applications of electric vehicles for disabled
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric vehicles for disabled | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Transportation | Integration of electric wheelchair accessible vehicles (eWAVs) into public transit systems | Enhanced mobility options for disabled individuals, leading to increased ridership and customer satisfaction | Compliance with local regulations, availability of charging infrastructure, and vehicle adaptability to local conditions |
| Healthcare and Rehabilitation | Use of electric vehicles for patient transport and mobility services | Improved access to healthcare facilities for disabled patients, enhancing service offerings for healthcare providers | Need for specialized vehicles that accommodate medical equipment and ensure patient comfort during transport |
| Tourism and Hospitality | Offering electric vehicles for disabled tourists in rental and travel services | Attracting a broader customer base by providing inclusive travel options, boosting tourism revenue | Training for staff on vehicle operation and accessibility features, partnerships with local disability organizations |
| Logistics and Delivery | Deployment of electric vans designed for transporting goods and mobility aids | Cost-effective and eco-friendly delivery solutions that cater to businesses serving disabled customers | Customization options for cargo space to accommodate various mobility devices, charging station availability |
| Education and Training | Provision of electric vehicles for educational institutions supporting students with disabilities | Facilitating access to educational opportunities for disabled students, fostering inclusivity | Ensuring vehicles are equipped with necessary adaptations and training for drivers to assist students effectively |
How Can Electric Vehicles for Disabled Transform Public Transportation?
Incorporating electric wheelchair accessible vehicles (eWAVs) into public transportation systems can significantly enhance mobility for disabled individuals. These vehicles allow for seamless entry and exit without the need for transfers, addressing a major barrier in public transit. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing these vehicles requires an understanding of local regulations and charging infrastructure to ensure compliance and accessibility.
What Benefits Do Electric Vehicles Offer Healthcare Providers?
Electric vehicles designed for patient transport can revolutionize mobility services within healthcare. They enable healthcare providers to offer improved access to facilities for disabled patients, thereby enhancing overall service quality. Buyers in the healthcare sector must prioritize vehicles that accommodate medical equipment and ensure patient comfort, necessitating thorough research on vehicle specifications and adaptability to local healthcare needs.
How Can the Tourism Sector Leverage Electric Vehicles for Disabled Guests?
The tourism and hospitality industry can greatly benefit from providing electric vehicles for disabled tourists. These inclusive travel options not only broaden the customer base but also enhance the overall experience for travelers with disabilities. B2B buyers in this sector should focus on partnerships with local disability organizations and ensure staff are trained in the operation and features of these vehicles to maximize customer satisfaction.
What Role Do Electric Vehicles Play in Logistics for Disabled Communities?
Logistics companies can utilize electric vehicles specifically designed for transporting goods and mobility aids, providing eco-friendly delivery solutions. This approach caters to businesses serving disabled customers, enhancing their service offerings while reducing carbon footprints. Buyers should consider customization options for cargo space and ensure the availability of charging stations to meet operational needs.
How Can Educational Institutions Benefit from Electric Vehicles for Disabled Students?
Educational institutions can enhance inclusivity by providing electric vehicles for students with disabilities. This initiative facilitates access to educational opportunities, fostering a more inclusive environment. Buyers in the education sector must ensure that vehicles come equipped with necessary adaptations and that drivers are trained to assist students effectively, creating a supportive atmosphere for learning.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric vehicles for disabled’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inadequate Charging Infrastructure for Disabled Drivers
The Problem: One of the significant challenges faced by B2B buyers in the electric vehicle (EV) market for disabled individuals is the inadequate charging infrastructure. Many disabled drivers rely on public charging stations, but existing facilities often lack accessibility features, such as ramps or appropriate signage. This situation is particularly concerning in regions where home charging options are limited, creating a barrier for disabled users who need to recharge their vehicles conveniently. The inconvenience can deter potential buyers from considering EVs altogether, ultimately affecting sales and market growth.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should advocate for partnerships with local governments and infrastructure developers to ensure that EV charging stations are designed with accessibility in mind. This includes compliance with the Electric Vehicles Accessible Charging Specification (PAS 1899). Buyers can collaborate with manufacturers to promote the installation of accessible charging points that feature lower charging connectors, wider parking spaces, and clear accessibility signage. Additionally, companies can invest in awareness campaigns to educate the public and stakeholders about the importance of inclusive charging facilities, thereby fostering a more supportive environment for disabled drivers.
Scenario 2: Limited Availability of Wheelchair Accessible Electric Vehicles (WAVs)
The Problem: Another pain point is the scarcity of electric vehicles specifically designed to accommodate wheelchair users. Many existing models do not provide the necessary adaptations, such as lowered floors or ramps, making them unsuitable for users who wish to remain in their wheelchairs while driving. This limitation can lead to frustration for B2B buyers seeking to fulfill the needs of their clients or employees with disabilities, as they are often left with few options that meet both accessibility and electric vehicle standards.
The Solution: B2B buyers should actively engage with EV manufacturers and conversion companies to advocate for the development of more Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles (WAVs). This can involve facilitating discussions between manufacturers and conversion specialists to explore innovative designs that incorporate electric drivetrains while still being wheelchair-friendly. Buyers can also consider forming or joining industry coalitions that focus on advancing accessible vehicle options, sharing best practices, and fostering collaborations. By emphasizing the importance of inclusivity in vehicle design, buyers can help drive demand for more WAVs in the electric vehicle market.
Scenario 3: High Initial Costs of Electric Vehicles for Disabled Users
The Problem: The upfront cost of electric vehicles can be a significant barrier for many potential buyers, especially for those with disabilities who may require additional adaptations. While running costs for EVs are generally lower than traditional vehicles, the initial investment remains a concern. This is particularly true in regions like Africa or South America, where the economic climate may not support such expenditures, thus limiting the accessibility of electric mobility solutions for disabled individuals.
The Solution: To combat the issue of high initial costs, B2B buyers can explore partnerships with financial institutions or government programs that provide incentives for purchasing electric vehicles. This could include promoting lease programs, subsidies, or grants specifically aimed at individuals with disabilities. Additionally, businesses can develop financing options that cater to the unique needs of disabled users, making EVs more financially accessible. Creating awareness about the long-term savings and environmental benefits of EVs can also help shift perceptions and encourage investments in electric mobility solutions. By working closely with stakeholders, B2B buyers can facilitate a more accessible pathway for disabled individuals to enter the electric vehicle market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric vehicles for disabled
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers?
When selecting materials for electric vehicles (EVs) designed for disabled drivers, several factors come into play, including performance, durability, cost, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these vehicles: aluminum, high-strength steel, composites, and thermoplastics.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers?
Aluminum is a popular choice in the automotive industry due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for components like frames and body panels. The reduced weight contributes to improved energy efficiency and range in electric vehicles, which is particularly advantageous for models designed for disabled drivers who may require additional mobility aids.
Pros: Aluminum is durable and resistant to rust, which is essential for vehicles exposed to various climates, especially in regions like Africa and South America. Its lightweight properties enhance vehicle performance.
Cons: The primary drawback of aluminum is its higher cost compared to traditional steel. Additionally, manufacturing processes for aluminum can be more complex, requiring specialized techniques like welding and extrusion.
Impact on Application: Aluminum components can withstand various media, including moisture and road salts, making them suitable for diverse environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like the Middle East and Europe should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B209 for aluminum sheet and plate. The higher initial cost may be offset by long-term savings in fuel efficiency.
What Role Does High-Strength Steel Play in Electric Vehicle Design?
High-strength steel is another material frequently used in the automotive sector, particularly for structural components. Its strength allows for thinner sections, which can save weight while maintaining safety standards.
Pros: The material is cost-effective and readily available, making it a practical choice for manufacturers. High-strength steel also offers excellent crashworthiness, which is crucial for the safety of all drivers, including those with disabilities.
Cons: While it is durable, high-strength steel is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact the vehicle’s range and efficiency. Corrosion resistance is also lower unless treated.
Impact on Application: High-strength steel is compatible with various media and can endure harsh environmental conditions, making it suitable for diverse markets.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A572 is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of local suppliers to minimize costs.
How Do Composites Enhance Accessibility in Electric Vehicles?
Composites, including carbon fiber and fiberglass, are increasingly being used in the automotive industry for their lightweight and high-strength properties. These materials are particularly beneficial for components that require intricate designs, such as custom seating systems for disabled drivers.
Pros: Composites are lightweight, which can improve vehicle efficiency. They also offer excellent design flexibility and can be molded into complex shapes, enhancing accessibility features.
Cons: The primary limitation is the high cost of composite materials and the complexity of their manufacturing processes. Repairing composite components can also be more challenging than metal.
Impact on Application: Composites can withstand various environmental conditions, including moisture and UV exposure, making them suitable for outdoor use.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM D3039 for composite materials. The high initial investment may be justified by the long-term benefits of reduced weight and increased efficiency.
Why Are Thermoplastics Important in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Thermoplastics are increasingly being utilized in electric vehicles due to their versatility and ease of manufacturing. They can be used for interior components, panels, and even some structural elements.
Pros: Thermoplastics are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be easily molded into complex shapes. They are also cost-effective and can be recycled, aligning with sustainability goals.
Cons: While durable, thermoplastics may not offer the same level of strength as metals, which can limit their use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Thermoplastics are compatible with various environments, making them suitable for different climates and conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM D638 is crucial. Buyers should also consider local recycling capabilities to maximize sustainability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers
| Material | Typical Use Case for Electric Vehicles for Disabled | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, frames | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| High-Strength Steel | Structural components | Cost-effective, excellent crashworthiness | Heavier, lower corrosion resistance | Medium |
| Composites | Custom seating systems, intricate designs | Lightweight, design flexibility | High cost, challenging repairs | High |
| Thermoplastics | Interior components, panels | Lightweight, recyclable | Lower strength compared to metals | Medium |
This guide serves as a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions regarding material selection for electric vehicles designed for disabled drivers. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials will facilitate better procurement strategies and enhance product development.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric vehicles for disabled
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers?
The manufacturing of electric vehicles (EVs) tailored for disabled drivers involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets the unique needs of this demographic.
Material Preparation: Sourcing and Selection
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves selecting high-quality materials that are both lightweight and durable, which is essential for enhancing vehicle performance while ensuring the safety of disabled passengers. Manufacturers often opt for advanced composite materials and high-strength steel to achieve a balance between weight and structural integrity.
In addition to traditional materials, specialized components such as accessible ramps, swivel seats, and automated loading systems are sourced from trusted suppliers. Collaborations with specialized firms that focus on assistive technologies can enhance the vehicle’s functionality.
Forming: Shaping Components for Accessibility
The forming stage is where the raw materials are shaped into components. Techniques such as stamping, bending, and extrusion are commonly used to create the vehicle’s body and structural parts. For EVs designed for disabled drivers, this stage requires particular attention to dimensions that accommodate wheelchair access, such as ensuring sufficient interior height and width.
Moreover, forming includes the customization of parts like battery enclosures and seating systems. Manufacturers may utilize advanced computer-aided design (CAD) software to simulate and optimize designs that enhance accessibility without compromising aesthetics.
Assembly: Integrating Accessibility Features
During the assembly phase, various components are brought together. This stage is critical for integrating features specifically designed for disabled drivers, such as adjustable seating, powered tailgates, and user-friendly controls.
Assembly lines may employ automated processes for standard components, while specialized teams handle the installation of accessibility features. This hybrid approach ensures efficiency while maintaining high-quality standards. Manufacturers should also ensure that assembly workers are trained to understand the importance of these adaptations, as improper installation can lead to safety issues.
Finishing: Quality and Aesthetics
The finishing stage involves applying coatings, paints, and surface treatments to enhance the vehicle’s durability and aesthetic appeal. This is especially important for electric vehicles, which often serve as a statement of environmental consciousness and style.
Additionally, quality checks are critical at this stage. Manufacturers may apply protective coatings that also assist in the vehicle’s longevity and ease of maintenance, which is essential for users who may rely on their vehicles for daily transportation.
How Do Quality Assurance Processes Ensure the Safety of Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers?
Quality assurance (QA) in the manufacturing of electric vehicles for disabled drivers is paramount. It ensures that vehicles not only meet regulatory standards but also fulfill the specific needs of users with disabilities.
What International Standards Guide Quality Assurance in EV Manufacturing?
Manufacturers typically adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which provides a framework for quality management systems. Compliance with these standards assures B2B buyers of consistent product quality and an effective operational process.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) are crucial. These certifications ensure that the vehicle meets safety and performance criteria set by regulatory bodies, particularly in regions like Europe and North America.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous checks during assembly help identify defects early in the production cycle, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished vehicle ensures that all specifications, including accessibility features, are met before delivery.
These checkpoints are complemented by rigorous testing methods, including functional tests for accessibility features, crash tests, and environmental simulations to validate the vehicle’s performance under various conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial for ensuring reliable partnerships.
What Are Effective Strategies for Supplier Audits and Inspections?
One of the most effective ways to assess a supplier’s QC processes is through regular audits. Buyers can request to conduct on-site inspections to evaluate the manufacturing facility, observe QC procedures in action, and review documentation related to certifications and compliance with international standards.
Additionally, requesting third-party inspection reports provides an unbiased view of the supplier’s quality management systems. Buyers should also consider asking for historical data on defect rates and customer feedback to gauge the supplier’s reliability over time.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
International buyers must be aware of the nuances in quality control that may vary by region. For instance, some countries may have different safety regulations and certification requirements. Understanding these variations is essential for ensuring compliance and avoiding costly delays.
Moreover, language barriers and cultural differences can impact communication regarding quality expectations. Establishing clear, documented quality standards and expectations from the outset can mitigate misunderstandings and foster a more productive partnership.
Conclusion
As the electric vehicle market continues to evolve, the need for accessible solutions for disabled drivers becomes increasingly critical. Manufacturers play a vital role in this evolution through meticulous attention to the manufacturing process and stringent quality assurance practices. For B2B buyers, understanding these processes and the associated quality control measures is key to sourcing vehicles that meet the high standards necessary for safety and usability. By leveraging international standards and thorough verification methods, businesses can ensure they are investing in reliable, accessible electric vehicles that serve the needs of disabled drivers worldwide.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric vehicles for disabled’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed for B2B buyers looking to procure electric vehicles (EVs) specifically adapted for individuals with disabilities. As the demand for inclusive and sustainable transportation solutions grows, understanding how to navigate the complexities of this market is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This checklist will help ensure that you select the right vehicles that meet both functional needs and regulatory requirements.
Step 1: Identify Your Target Market and User Needs
Understanding the specific requirements of your target demographic is crucial. Assess the mobility needs of disabled individuals in your market, including wheelchair users, those requiring driving adaptations, and the elderly. This step ensures that the vehicles you consider will provide the necessary accessibility features, such as ramp access and adequate storage for mobility devices.
Step 2: Define Technical Specifications and Compliance Standards
Establish clear technical specifications for the vehicles you intend to source. This includes compliance with international standards like PAS 1899 for accessible charging infrastructure and guidelines for wheelchair accessibility. Ensure that the vehicles can accommodate necessary adaptations, such as hand controls and swivel seats, to enhance usability for disabled drivers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough evaluations. Request company profiles, product specifications, and references from previous buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to inclusive design and innovation in their electric vehicle offerings, as this will be crucial for long-term partnerships.
Step 4: Assess Adaptation and Customization Options
Consider the ability of suppliers to provide vehicle adaptations tailored to specific user needs. Evaluate options for modifications such as powered tailgates, parking assistance, and in-car voice assistance. The availability of these adaptations not only enhances usability but also expands your customer base by catering to diverse mobility requirements.
Step 5: Examine Charging Infrastructure Compatibility
Investigate the compatibility of the electric vehicles with existing and future charging infrastructure. Look for vehicles that are designed to work seamlessly with accessible charging points, ensuring that disabled users can charge their vehicles without barriers. This is particularly important in regions where public charging facilities may be limited.
Step 6: Review Pricing Models and Financial Assistance Programs
Understand the pricing structures associated with the vehicles and explore financial assistance programs available for disabled drivers, such as the Motability Scheme. Assess whether your procurement strategy can incorporate these financial models to make electric vehicles more accessible to your target market.
Step 7: Implement Feedback Mechanisms for Continuous Improvement
After procurement, establish a system for gathering feedback from end-users regarding vehicle performance and accessibility features. This feedback loop will be invaluable for future sourcing decisions and can help you refine your product offerings to better meet the needs of disabled drivers.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure they are making informed and strategic decisions when sourcing electric vehicles for disabled individuals, ultimately fostering a more inclusive transportation landscape.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric vehicles for disabled Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Electric Vehicles Designed for Disabled Drivers?
Understanding the cost structure of electric vehicles (EVs) tailored for disabled drivers is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the overall cost. High-strength lightweight materials are often used to enhance vehicle performance and range, but they can be more expensive. Additionally, specialized adaptations such as ramps or automated loading systems for mobility devices can add to material costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for the assembly and adaptation of EVs. Labor costs may vary based on the region, with countries in Europe generally experiencing higher wage rates compared to those in Africa or South America. This disparity can impact the final price for international buyers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Overhead can fluctuate based on production volume; higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for adaptations specific to disabled drivers can be a significant upfront expense. For instance, modifications for wheelchair accessibility require specialized molds and machinery, which can drive costs up.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring the vehicle meets safety and accessibility standards necessitates rigorous QC processes. The expenses associated with testing and certification can be substantial, but they are crucial for compliance and consumer trust.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, which include transportation and customs duties, can vary widely based on the destination. Buyers in remote areas may face higher logistics costs, impacting the total landed cost of the vehicle.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a margin to cover business risks and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on market competition and perceived value.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions for Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers?
Several factors influence pricing, which B2B buyers must consider to optimize their sourcing strategies.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Pricing often improves with larger orders due to bulk purchasing discounts. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that allow for cost-effective procurement while meeting their operational needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as specialized seating or driving aids, can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses during the customization process.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The quality of materials used directly affects the vehicle’s durability and performance. Buyers should prioritize certified materials that comply with international standards to ensure safety and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their proven track record, while new entrants might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk, which can significantly impact total costs.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers?
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, particularly for larger orders. Leverage competitive bids to negotiate favorable terms, including payment plans and warranty options.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the TCO, which includes maintenance, insurance, and energy costs. Electric vehicles generally have lower running costs, making them a more economical choice over time.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and regional market conditions that can affect pricing. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should factor these variables into their budgets.
-
Long-Term Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved service, and access to new products. Consider establishing contracts that include performance incentives for suppliers.
-
Research and Development Collaboration: Engage in discussions with manufacturers about potential joint ventures or collaborations for R&D. This can lead to innovative solutions tailored to the specific needs of disabled drivers, enhancing market competitiveness.
In conclusion, understanding the intricate cost structures and pricing influences is crucial for B2B buyers in the electric vehicle market for disabled individuals. By leveraging this knowledge, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational and financial goals.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric vehicles for disabled With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Electric Vehicles for Disabled Individuals
In the quest for accessible transportation solutions, electric vehicles (EVs) tailored for disabled users offer significant advantages, but they are not the only option available. Organizations and individuals must consider various alternatives that can meet mobility needs while taking into account factors such as performance, cost, and ease of implementation. Below, we compare electric vehicles for disabled individuals against two viable alternatives: traditional wheelchair accessible vehicles (WAVs) and public transport systems equipped with accessibility features.
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Vehicles For Disabled | Traditional Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles (WAVs) | Public Transport with Accessibility Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High; suitable for urban and suburban driving with low emissions | Moderate; often limited to specific routes and operating hours | Variable; depends on service availability and frequency |
| Cost | Higher initial cost; lower running costs; incentives available | Moderate to high initial cost; maintenance costs vary | Generally lower cost; subsidized fares in some regions |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires adaptations for specific needs; charging infrastructure is limited | Ready-made options available; minimal adaptations needed | Dependent on local service; may require planning |
| Maintenance | Generally low; fewer moving parts compared to combustion engines | Moderate; depends on vehicle age and condition | Variable; often includes maintenance of transit vehicles |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for independent mobility; suitable for urban environments | Best for users needing consistent access without reliance on public transport | Suitable for those who do not require immediate access and can plan trips |
Traditional Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles (WAVs)
Traditional WAVs have been a staple in accessible transportation for years. These vehicles are specifically modified to accommodate wheelchair users, featuring ramps and lowered floors. The primary advantage is their availability; many manufacturers provide ready-made options that can be purchased or leased. However, they often operate on fossil fuels, which can lead to higher emissions and running costs compared to electric alternatives. Additionally, while WAVs can offer reliable access, they may not always align with the increasing demand for environmentally friendly solutions.
Public Transport with Accessibility Features
Public transport systems are increasingly incorporating accessibility features, such as low-floor buses and designated seating for disabled passengers. This alternative offers a cost-effective means of transportation for individuals who do not need immediate access to a vehicle. The primary benefits include lower fares and the potential for social interaction during travel. However, the limitations include dependence on schedules and routes, which may not always align with personal needs. Additionally, the quality of accessible features can vary significantly between regions, which can impact user experience.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the most appropriate transportation solution for disabled individuals, B2B buyers should carefully evaluate their specific requirements, such as the frequency of use, budget constraints, and environmental considerations. Electric vehicles for disabled users offer a modern, eco-friendly option that promotes independence but may require significant investment and infrastructure development. In contrast, traditional WAVs provide immediate access without the need for extensive modifications, while public transport offers a lower-cost solution but may lack the flexibility needed for spontaneous travel. By weighing these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their organizational goals and the needs of the individuals they serve.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric vehicles for disabled
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Vehicles for Disabled Individuals?
Understanding the technical specifications of electric vehicles (EVs) designed for disabled drivers is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are several essential properties that should be considered:
1. Accessibility Features
Accessibility features encompass adaptations like swivel seats, powered ramps, and in-car voice assistance. These elements are vital for ensuring ease of entry and exit for wheelchair users. B2B buyers must prioritize vehicles that integrate these features seamlessly, as they enhance user independence and satisfaction.
2. Battery Placement and Weight Distribution
The placement of the battery in EVs is a critical factor. Typically located beneath the vehicle floor, battery positioning affects the vehicle’s center of gravity, which in turn impacts stability and handling. For Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles (WAVs), the design must accommodate both the battery and the necessary modifications for wheelchair access. Buyers should ensure that manufacturers address these considerations to avoid compromising safety or usability.
3. Charging Infrastructure Compatibility
Electric vehicles for disabled users must be compatible with accessible charging infrastructure. This includes evaluating the weight and ease of use of charging cables, as well as the physical accessibility of charging stations. It’s essential for B2B buyers to engage with suppliers that prioritize compliance with accessible charging standards, such as PAS 1899, to ensure their clients can easily recharge their vehicles.
4. Material Grade and Durability
The materials used in the construction of EVs should be of high-grade quality to ensure durability and longevity, especially in vehicles designed for disabled users who may require additional adaptations. High-quality materials not only enhance safety but also reduce the frequency of repairs, thus lowering total cost of ownership. Buyers should inquire about the material specifications and warranties offered by manufacturers.
5. Adaptation Compatibility
The ability to integrate various driving aids—like hand controls and pedal adaptations—into the vehicle is another critical property. B2B buyers should focus on vehicles that allow for easy customization to meet individual mobility needs. This adaptability can significantly enhance the marketability of the vehicle to a broader range of disabled users.
6. Safety Features and Standards Compliance
Safety is paramount in any vehicle, and for electric vehicles catering to disabled drivers, it becomes even more crucial. Features such as automatic emergency braking, traction control, and advanced airbag systems should meet or exceed industry safety standards. B2B buyers must confirm that the vehicles comply with relevant safety regulations to minimize liability and ensure user safety.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in the Electric Vehicle Industry for Disabled Users?
Navigating the landscape of electric vehicles for disabled users also requires familiarity with specific trade terminology. Here are some key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of EVs, OEMs are critical as they provide the core components that must be compatible with accessibility adaptations. Buyers should build relationships with reliable OEMs to ensure quality and support.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory effectively and negotiate better terms with manufacturers. This can impact pricing and availability, especially for specialized vehicles.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that an organization submits to suppliers to request pricing, terms, and conditions for a specific product or service. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to obtain competitive pricing and assess suppliers’ capabilities, particularly for customized electric vehicles.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping and insurance. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to mitigate risks and clarify obligations related to the delivery of electric vehicles for disabled users.
5. WAV (Wheelchair Accessible Vehicle)
WAVs are specifically designed to accommodate wheelchair users, allowing them to enter and exit the vehicle without transferring from their wheelchair. This term is essential for buyers focused on accessibility and inclusivity in their vehicle offerings.
6. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with owning and operating a vehicle over its lifetime, including purchase price, maintenance, fuel, and insurance. B2B buyers should evaluate TCO to assess the long-term value of electric vehicles for disabled individuals, ensuring they meet budgetary constraints and operational needs.
By understanding these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electric vehicles tailored for disabled users, ultimately enhancing their offerings and market reach.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric vehicles for disabled Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics in the Electric Vehicles for Disabled Sector?
The electric vehicles (EV) market for disabled individuals is witnessing significant growth, driven by a confluence of factors including increasing environmental awareness, technological advancements, and evolving regulatory frameworks. Globally, the push towards sustainable mobility solutions is reshaping the automotive landscape. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for accessible and environmentally friendly transportation solutions is rising. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for products that not only meet the mobility needs of disabled individuals but also align with broader sustainability goals.
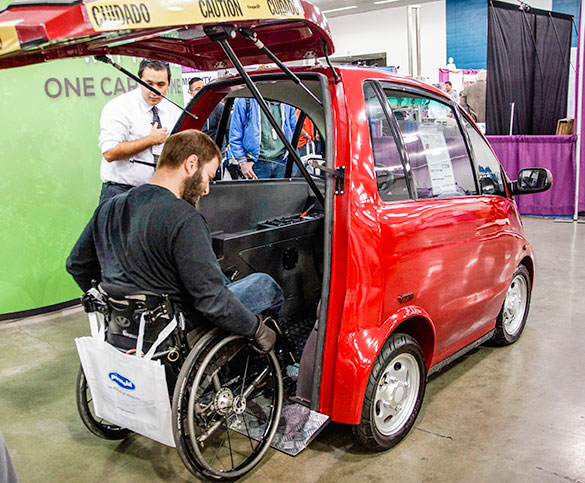
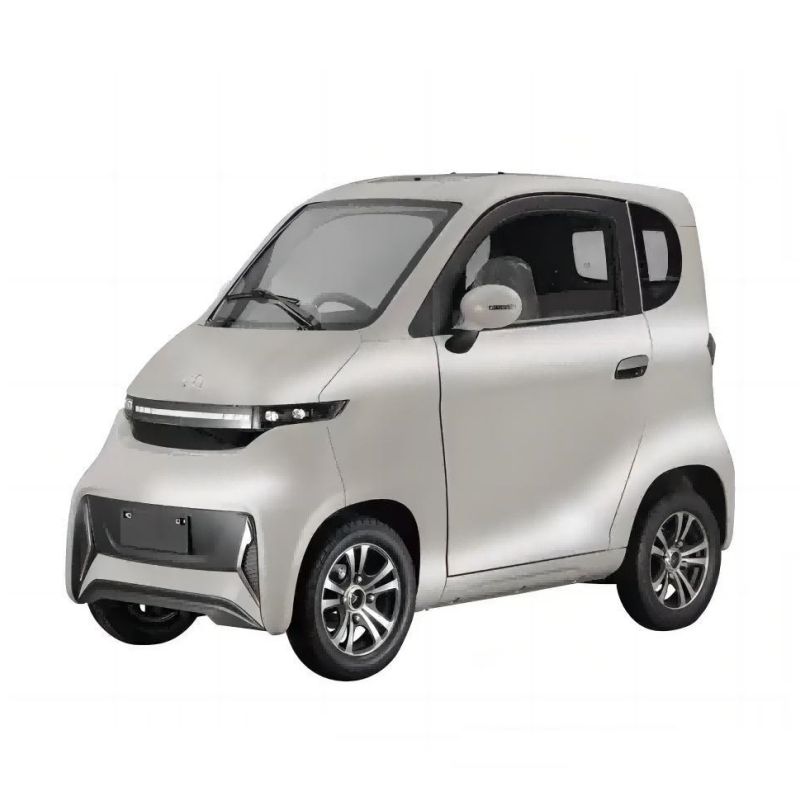
Key trends include the development of specialized vehicle adaptations, such as driving aids and accessible charging solutions, which are essential for enhancing usability for disabled drivers. Manufacturers are beginning to collaborate with assistive technology firms to create vehicles equipped with features like powered tailgates, adjustable seats, and automated loading systems. Furthermore, the push for more wheelchair-accessible electric vehicles (eWAVs) is gaining momentum, as seen with new models like the Eco M and Kia PV5 WAV, which cater specifically to the needs of wheelchair users.
Additionally, the market is influenced by consumer expectations for inclusivity and accessibility. Companies that prioritize these aspects in their product offerings are likely to gain a competitive edge. As the market matures, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to stay informed about these dynamics to make strategic sourcing decisions that enhance their product portfolios.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Electric Vehicles for Disabled Sector?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the electric vehicle sector, particularly in the context of sourcing materials and manufacturing processes. The environmental impact of traditional vehicles has led to increased scrutiny of supply chains, prompting manufacturers to adopt more sustainable practices. This is especially relevant for B2B buyers who are seeking to align with environmentally responsible suppliers.
Ethical sourcing of materials—such as lithium for batteries—has become a critical focus area. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to sustainable mining practices and demonstrate a commitment to minimizing environmental degradation. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Responsible Minerals Initiative can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on using recycled materials in vehicle production, which not only reduces waste but also lowers the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing new components. B2B buyers should actively seek partnerships with manufacturers that utilize ‘green’ certifications and materials, as these can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
What Has Been the Evolution of Electric Vehicles for Disabled Individuals?
The evolution of electric vehicles tailored for disabled individuals has been gradual, marked by increasing awareness of the need for inclusivity in transportation. Historically, the automotive industry has overlooked the specific needs of disabled drivers, leading to a limited selection of accessible vehicles. However, recent advancements in technology and design have begun to address these gaps.
The introduction of adaptable features and the development of specialized models, like wheelchair-accessible vehicles, reflect a significant shift in the market. Early electric vehicles primarily focused on general consumer needs, but as the demand for inclusivity has grown, manufacturers are now prioritizing features that enhance accessibility. This transformation has been fueled by advocacy from disability rights organizations and a broader societal push for equal mobility solutions.
As the industry continues to innovate, the future looks promising for electric vehicles designed for disabled individuals. Manufacturers are increasingly recognizing the importance of this segment, paving the way for a more inclusive and sustainable automotive landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric vehicles for disabled
-
How do I solve accessibility issues when sourcing electric vehicles for disabled individuals?
To address accessibility issues in electric vehicles (EVs) for disabled individuals, focus on collaborating with manufacturers that prioritize inclusive design. Look for features such as adjustable seating, powered ramps, and accessible charging solutions. Engaging with local disability advocacy groups can also provide insights into specific needs and preferences. Additionally, consider forming partnerships with vehicle adaptation companies to enhance the usability of EVs for different mobility requirements. -
What is the best electric vehicle for wheelchair users?
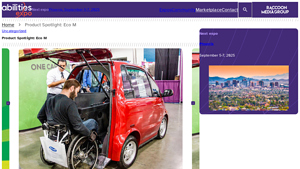
The best electric vehicle for wheelchair users typically combines accessibility with performance and comfort. Vehicles like the Eco M offer an adjustable rear ramp and allow users to drive without transferring from their wheelchair. When assessing options, prioritize models that provide ample interior space, easy access, and advanced assistive technologies. Always evaluate user feedback and consult experts in the mobility sector to identify the most suitable models for your target market. -
What customization options are available for electric vehicles aimed at disabled drivers?
Customization options for electric vehicles targeting disabled drivers can include adaptations like hand controls, swivel seats, and boot hoists for easy storage of mobility devices. Many manufacturers also offer tailored modifications to meet specific needs, such as lowering the vehicle floor for wheelchair access. When sourcing, ensure your suppliers can provide detailed customization capabilities and inquire about their experience in working with assistive technology to enhance vehicle usability. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for electric vehicles for disabled drivers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for electric vehicles can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and model. Some manufacturers may have MOQs as low as one vehicle, especially for specialized adaptations, while others may require larger bulk orders to ensure cost-effectiveness. It is advisable to negotiate MOQs based on your market demand and to explore the possibility of pilot programs or trial runs to assess vehicle performance and customer interest before committing to larger orders. -
How do I vet suppliers of electric vehicles for disabled individuals?
Vetting suppliers of electric vehicles for disabled individuals involves assessing their reputation, product quality, and compliance with industry standards. Check for certifications related to accessibility and safety, as well as customer testimonials and case studies. It’s also valuable to visit manufacturing facilities if possible, to evaluate their production processes. Additionally, engage in discussions about their experience with assistive technology and modifications to ensure they can meet the specific needs of disabled drivers. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electric vehicles internationally?
When sourcing electric vehicles internationally, payment terms can vary widely. Common arrangements include upfront payments, letters of credit, or staggered payments based on delivery milestones. It’s essential to clarify terms during negotiations to align with your cash flow and financial strategy. Ensure that you are aware of any import duties or taxes that may affect the overall cost and discuss any financing options that may be available through manufacturers or third-party financial institutions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in electric vehicles for disabled drivers?
To ensure quality assurance in electric vehicles for disabled drivers, implement a robust QA process that includes rigorous testing of vehicles for accessibility features and performance standards. Collaborate with suppliers that have established QA protocols and certifications. Regular audits and inspections during the production phase can help maintain high standards. Additionally, gathering feedback from end-users can inform ongoing improvements and adaptations necessary for future vehicle designs. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric vehicles?
When importing electric vehicles, logistics considerations include compliance with local regulations, customs clearance, and transportation methods. Evaluate the best shipping options based on cost and delivery time, and ensure that vehicles are adequately protected during transit. Additionally, be aware of potential delays in customs and have a plan for dealing with them. Establish relationships with logistics partners experienced in handling automotive imports to streamline the process and minimize risks.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Electric Vehicles For Disabled Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. EcoCentre – Eco M
Domain: abilities.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Eco M
Manufacturer: EcoCentre
Type: Accessible Vehicle
Launch Date: Second quarter of 2025
Features:
– Small footprint with a big impact
– Designed for wheelchair users with an adjustable rear ramp
– No transfers required; users can roll in, lock down, and drive off
– Speed capability: up to 25 mph
– Aimed at providing independence and freedom for people with disabilities
– Target a…
2. BraunAbility – Electric Car Adaptations
Domain: braunability.eu
Introduction: BraunAbility offers adaptations for electric cars, categorized into hybrids/electric cars built on fossil fuel platforms and fully electric cars. Key considerations include:
1. **Hybrids and Fossil Fuel Platforms**:
– **Examples**: Peugeot e-208, Volkswagen Golf GTE, Ford Kuga.
– **Pros**: Easier adaptation due to standardized 12V power for electric functions and shared mechanical design…
3. Energy Saving Trust – Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers
Domain: energysavingtrust.org.uk
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Electric vehicles (EVs) for disabled drivers offer several benefits, including lower running costs (around £760 cheaper per year compared to petrol/diesel), reduced maintenance costs (approximately £200 cheaper annually), and a smoother driving experience due to automatic transmissions. EVs can be adapted for accessibility, though they may have higher upfront costs, especially for modified or whee…
4. Volkswagen – ID Buzz
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Currently, there are limited options for wheelchair accessible electric vehicles (EVs) due to the placement of batteries typically under the vehicle, making it difficult to modify the floor for wheelchair access. The Volkswagen ID Buzz is mentioned as a potential accessible EV. Users express concerns about the lack of accessible charging stations for EVs, which impacts their purchasing decisions.
5. CyberSwitching – Dual EV Charging Stations
Domain: cyberswitching.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Electric Vehicle Chargers Commercial Dual EV Charging station with Cable management, Dual CSE1 Level-2, 48A, RFID $3,290.00 – $3,890.00; Electric Vehicle Chargers Commercial Dual 48A EV Charging station with Cable management, Dual CSE3 Level-2 with display, RFID, CTEP $3,490.00 – $4,090.00; Electric Vehicle Chargers Commercial Dual EV Charging station, Dual CSE1 Level-2, 48A, RFID $2,890.00 Origin…
6. Business Insider – EV Accessibility Challenges
Domain: businessinsider.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Electric vehicles (EVs) currently lack fully accessible options for wheelchair users in the US. Key challenges include:
1. **Battery Placement**: EV batteries are located under the floor, complicating accessibility modifications.
2. **Cost of Accessibility**: Converting a vehicle to be fully accessible can cost around $30,000, on top of the vehicle’s price.
3. **Size Requirements**: Accessible …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric vehicles for disabled
In the evolving landscape of electric vehicles (EVs) tailored for disabled individuals, strategic sourcing becomes pivotal for international B2B buyers. The current market presents significant opportunities, yet it also poses challenges such as design limitations, inadequate charging infrastructure, and a scarcity of wheelchair-accessible vehicle options. Businesses must prioritize collaborations with manufacturers and adaptation specialists to create vehicles that genuinely meet the diverse needs of disabled drivers.
Moreover, as the demand for eco-friendly solutions rises, sourcing accessible EVs can position companies as leaders in inclusivity and sustainability. Emphasizing the importance of adhering to standards like the Electric Vehicles Accessible Charging Specification (PAS 1899) is crucial for fostering a supportive environment for disabled motorists.
Looking ahead, the integration of innovative technologies and adaptive designs will be key drivers in expanding the market for electric vehicles for the disabled. International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are encouraged to leverage these insights and invest in partnerships that enhance mobility solutions. By doing so, they not only cater to a growing demographic but also contribute to a more inclusive and sustainable future.