Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for street legal electric vehicle
The surge in demand for street legal electric vehicles (EVs) presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers looking to diversify their transportation offerings. However, navigating the complexities of this market can be daunting, especially when it comes to understanding the differences between various vehicle types, compliance with regional regulations, and identifying reliable suppliers. This guide aims to demystify the landscape of street legal electric vehicles by providing comprehensive insights into the different types of vehicles available, their applications in urban and suburban settings, and critical considerations for supplier vetting.
From low-speed neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs) to robust commercial electric fleets, we will explore the full spectrum of options tailored to meet diverse business needs. Key topics include understanding safety standards, assessing cost structures, and evaluating market trends that influence purchasing decisions. With a focus on international markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including Germany and Vietnam—this guide empowers buyers to make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and practical information, this resource will facilitate a smoother procurement process, enabling businesses to capitalize on the growing shift towards sustainable transportation solutions. Whether you are looking to enhance your fleet or introduce innovative electric mobility options, this guide serves as your essential roadmap in the evolving global market for street legal electric vehicles.
Understanding street legal electric vehicle Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) | Speed limit of 25 mph, safety features like seat belts, headlights | Urban transportation, tourism, campus shuttles | Pros: Cost-effective, environmentally friendly. Cons: Limited speed and range compared to conventional vehicles. |
| Neighborhood Electric Vehicles (NEVs) | Designed for short trips, stylish and social seating arrangements | Community outreach, short-distance logistics | Pros: Unique design, compliance with local regulations. Cons: Not suitable for high-speed roads. |
| Electric Carts | Open or enclosed designs, primarily for leisure or light transport | Golf courses, gated communities, resorts | Pros: Easy to maneuver, low maintenance. Cons: Limited cargo capacity and speed. |
| Electric Cargo Vehicles | Designed for transporting goods, higher payload capacity | Delivery services, small businesses | Pros: Zero emissions, cost-effective for last-mile delivery. Cons: Limited range compared to traditional trucks. |
| Electric Microcars | Compact design, road-legal with higher speeds up to 50 mph | Urban commuting, car-sharing services | Pros: Efficient for city driving, good range. Cons: Higher upfront costs compared to LSVs. |
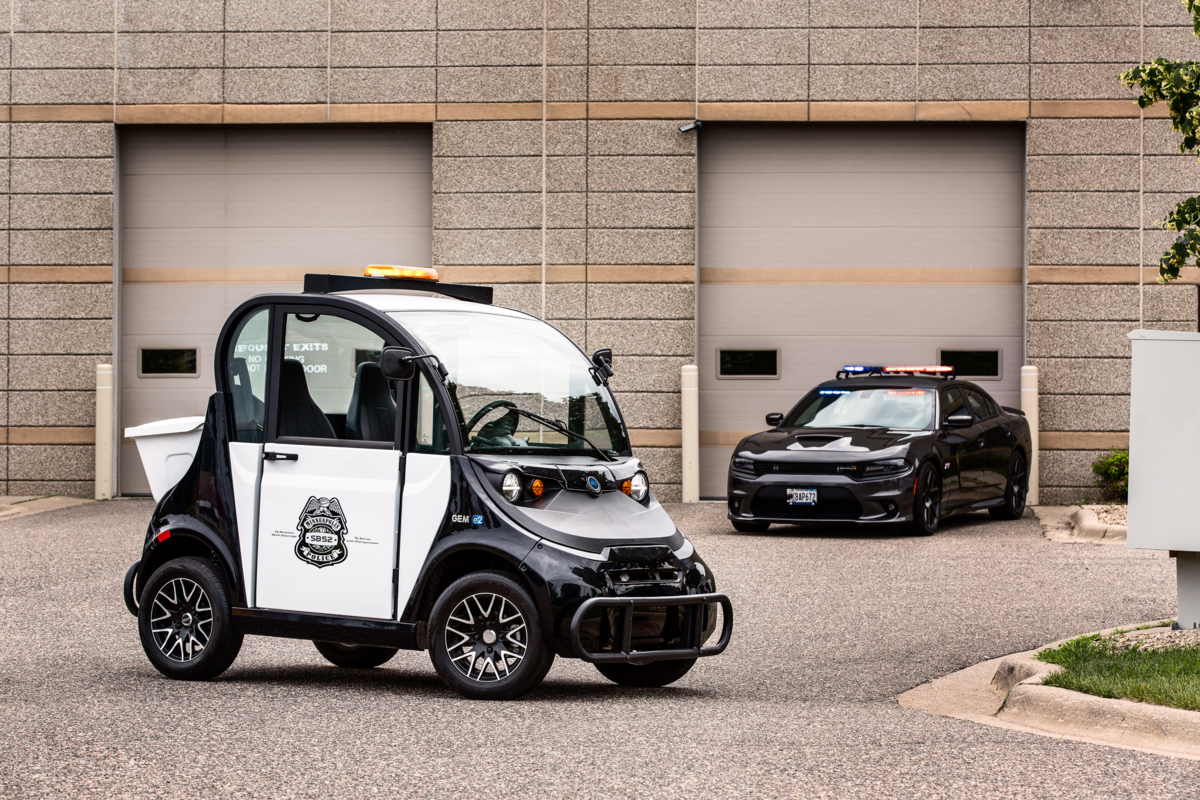
What Are Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) are electric vehicles that comply with safety standards and operate at a maximum speed of 25 mph. They are ideal for urban environments, offering a sustainable transportation solution for businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint. B2B buyers should consider factors such as local regulations, safety features, and the vehicle’s intended use when purchasing LSVs. Their versatility makes them suitable for applications ranging from campus shuttles to small-scale logistics.
How Do Neighborhood Electric Vehicles (NEVs) Stand Out in the Market?
Neighborhood Electric Vehicles (NEVs) are designed for short-distance travel, typically featuring stylish designs and social seating arrangements. These vehicles are perfect for community outreach initiatives and can be employed in tourism or local transport services. B2B buyers should focus on their compliance with local regulations and the potential for brand visibility, as NEVs often serve as a mobile advertisement for businesses. However, their limited speed makes them unsuitable for high-speed road usage.
Why Choose Electric Carts for Specific B2B Applications?
Electric carts are versatile vehicles primarily used in leisure settings such as golf courses or gated communities. They can be configured as open or enclosed vehicles, catering to various needs. For B2B buyers, electric carts offer low maintenance and easy maneuverability, making them an attractive choice for recreational businesses or resorts. However, their limited cargo capacity and speed may restrict their use for more demanding transport applications.
What Advantages Do Electric Cargo Vehicles Offer for Businesses?
Electric cargo vehicles are specifically designed for transporting goods, featuring higher payload capacities than standard electric vehicles. They are an excellent choice for delivery services and small businesses looking to enhance their logistics while adhering to eco-friendly practices. When considering electric cargo vehicles, B2B buyers should evaluate their range and charging infrastructure. While they provide significant savings on fuel costs, their range may not match that of traditional trucks.
How Do Electric Microcars Fit into Urban Transportation Strategies?
Electric microcars are compact vehicles that can reach speeds of up to 50 mph, making them suitable for urban commuting and car-sharing services. Their efficiency in city driving and good range make them a viable option for businesses looking to implement sustainable transportation solutions. B2B buyers should assess the initial investment and the potential for operational cost savings over time. Despite their higher upfront costs, electric microcars can provide significant long-term value for urban mobility strategies.
Key Industrial Applications of street legal electric vehicle
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of street legal electric vehicle | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tourism and Hospitality | Shuttle services for resorts and attractions | Enhanced guest experience, reduced operational costs, eco-friendly transport | Compliance with local vehicle regulations, safety features, maintenance support |
| Urban Delivery Services | Last-mile delivery solutions | Increased efficiency in urban areas, lower emissions, cost savings on fuel | Battery range, payload capacity, charging infrastructure availability |
| Municipal Services | Maintenance and inspection vehicles | Cost-effective operation, reduced noise pollution, sustainability initiatives | Vehicle specifications for municipal compliance, serviceability, and warranty |
| Real Estate and Property Management | On-site transportation for large properties | Improved tenant satisfaction, reduced vehicle fleet costs, eco-friendly image | Customization options, safety standards, and local regulations |
| Healthcare and Emergency Services | Patient transport and mobile clinics | Quick response times, cost-effective operations, enhanced patient care | Compliance with health regulations, safety features, and vehicle reliability |
How Are Street Legal Electric Vehicles Used in the Tourism and Hospitality Industry?
Street legal electric vehicles (EVs) are increasingly utilized in the tourism and hospitality sector as shuttle services for resorts, hotels, and attractions. They provide a sustainable transport option that enhances the guest experience by offering comfortable rides to nearby points of interest. These vehicles help operators reduce fuel costs and meet eco-friendly initiatives, which are crucial for attracting environmentally conscious travelers. Buyers in this sector should consider local regulations regarding vehicle operation and safety standards, alongside the need for maintenance support and service reliability.
What Role Do Street Legal Electric Vehicles Play in Urban Delivery Services?
In urban delivery services, street legal electric vehicles serve as efficient last-mile delivery solutions. Their compact size and ability to navigate crowded city streets make them ideal for quick deliveries, significantly reducing operational costs associated with traditional fuel vehicles. Additionally, their zero-emission operation aligns with growing sustainability goals. International buyers should assess battery range, payload capacity, and the availability of charging infrastructure in their regions to ensure optimal performance.
How Are Municipal Services Benefiting from Street Legal Electric Vehicles?
Municipalities are leveraging street legal electric vehicles for maintenance and inspection tasks. These vehicles offer a cost-effective solution for city operations while minimizing noise pollution and emissions. By adopting electric vehicles, municipalities can enhance their sustainability initiatives and improve the quality of life for residents. Buyers must ensure that the vehicles comply with local regulations and standards, while also considering serviceability and warranty options for long-term use.
In What Ways Are Street Legal Electric Vehicles Used in Real Estate and Property Management?
In real estate and property management, street legal electric vehicles are used for on-site transportation within large properties, such as golf courses or residential complexes. They improve tenant satisfaction by providing easy access to amenities and facilities, while also reducing the overall costs associated with maintaining a vehicle fleet. Buyers should look for customization options that meet their property’s specific needs, and ensure that vehicles adhere to local safety standards and regulations.
How Are Street Legal Electric Vehicles Enhancing Healthcare and Emergency Services?
Street legal electric vehicles are increasingly used in healthcare for patient transport and mobile clinics. Their quiet operation and eco-friendly design make them suitable for urban environments, allowing for quick response times in emergencies. This capability not only enhances patient care but also reduces operational costs. Buyers in the healthcare sector must consider compliance with health regulations, safety features, and the reliability of the vehicles to ensure they meet the demands of patient transport services.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘street legal electric vehicle’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance for Street Legal Electric Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers in regions such as Africa and South America often face the challenge of navigating complex and varying regulations regarding street legal electric vehicles (EVs). Many countries have different requirements for vehicle safety, emissions, and licensing, which can lead to confusion and potential legal issues. A company looking to introduce street legal EVs into its fleet may struggle to understand whether their vehicles meet local standards, resulting in delays and unforeseen costs.
The Solution: To effectively address regulatory compliance, it is essential for buyers to engage with local automotive regulatory bodies and legal experts who specialize in transportation laws. Conduct thorough research on the specific regulations applicable in your region, focusing on safety standards like those set by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the U.S. or similar organizations in your country. Additionally, consider collaborating with manufacturers that provide detailed documentation on compliance with both local and international standards. This proactive approach will not only streamline the vehicle acquisition process but also mitigate risks associated with non-compliance, ensuring that the fleet operates within legal parameters.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Adequate Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles
The Problem: A common pain point for businesses adopting street legal electric vehicles is the lack of adequate charging infrastructure. In many developing regions, the availability of charging stations is limited, making it challenging to operate a fleet of electric vehicles efficiently. Without sufficient charging options, companies may face operational downtimes, affecting productivity and customer service.
The Solution: To overcome the challenge of inadequate charging infrastructure, B2B buyers should conduct a comprehensive assessment of their operational areas to identify potential charging locations. This includes partnering with local governments or private entities to establish charging stations. Additionally, investing in portable charging solutions or onsite charging facilities can provide more flexibility. Businesses can also explore partnerships with energy providers to create a network of charging stations that supports their operations. By ensuring that charging infrastructure is in place before deploying electric vehicles, companies can maintain seamless operations and enhance the overall efficiency of their fleet.
Scenario 3: Addressing Range Anxiety with Electric Vehicles
The Problem: Range anxiety is a significant concern for businesses considering the switch to street legal electric vehicles. B2B buyers may worry that the limited range of electric vehicles will hinder their operations, particularly in regions where long-distance travel is common or where charging stations are sparse. This fear can lead to hesitance in adopting electric vehicles, impacting sustainability goals and operational efficiency.
The Solution: To alleviate range anxiety, it is crucial for businesses to choose street legal electric vehicles that offer competitive ranges and robust battery technology. Buyers should focus on models that incorporate advanced lithium-ion batteries, which provide longer ranges and faster charging capabilities. Additionally, businesses can implement fleet management systems to monitor vehicle usage and optimize routes, ensuring that vehicles remain within their operational range. Educating drivers about efficient driving practices that maximize battery life can also help. Finally, consider developing a strategy for gradual fleet electrification, starting with shorter routes to build confidence in electric vehicle performance before expanding to longer distances. This approach not only mitigates range anxiety but also demonstrates a commitment to sustainable practices.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for street legal electric vehicle
What Are the Key Materials for Street Legal Electric Vehicles?
When selecting materials for street legal electric vehicles (EVs), various factors must be considered, including performance, cost, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of street legal EVs, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
How Do Metals Like Aluminum Benefit Street Legal Electric Vehicles?
Aluminum is widely utilized in the manufacturing of street legal EVs due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating up to 400°F (204°C) and can withstand moderate pressure, making it suitable for various structural components.
Pros: Aluminum’s low density contributes to better energy efficiency and range for electric vehicles. Additionally, it is relatively easy to fabricate, which can reduce manufacturing complexity.
Cons: The primary drawback is the cost, as aluminum can be more expensive than other metals. Furthermore, while it offers good strength, it may not be as durable as steel under certain conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly compatible with electric vehicle components that require weight reduction without sacrificing structural integrity, such as frames and body panels.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM and EN for aluminum alloys, which may vary in specifications.
What Role Does Steel Play in the Construction of Street Legal Electric Vehicles?
Steel is another common material used in street legal EVs, particularly for structural components due to its high strength and durability. It generally has a temperature rating exceeding 800°F (427°C) and offers excellent resistance to various environmental conditions.
Pros: Steel is cost-effective and provides superior impact resistance, making it ideal for safety-critical components like chassis and frames.
Cons: The major downside is its weight, which can negatively affect the vehicle’s range and efficiency. Additionally, steel is prone to corrosion unless treated or coated.
Impact on Application: Steel is well-suited for components that require high strength and durability, such as the vehicle’s undercarriage and safety structures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with international standards like DIN and JIS for steel grades, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where local regulations may vary.
How Does Plastic Contribute to the Design of Street Legal Electric Vehicles?
Plastics, including composites and thermoplastics, are increasingly used in street legal EVs for components like dashboards, body panels, and trim. They generally offer good temperature resistance up to 200°F (93°C) and are lightweight.
Pros: Plastics are versatile, cost-effective, and can be molded into complex shapes, reducing manufacturing complexity. They also provide good thermal and electrical insulation.
Cons: The main limitation is their lower strength compared to metals, which may not be suitable for high-stress applications. Additionally, some plastics can degrade under UV exposure unless treated.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for non-structural components, enhancing aesthetic appeal while contributing to weight savings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with standards such as ASTM D638 for plastics, especially in markets like Germany and Vietnam, where environmental regulations may be stringent.
What Advantages Do Advanced Composites Offer for Street Legal Electric Vehicles?
Advanced composites, including carbon fiber and fiberglass, are gaining traction in the EV sector due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. They can withstand temperatures up to 300°F (149°C) and offer excellent corrosion resistance.
Pros: Composites are lightweight and can significantly improve vehicle performance and efficiency. They also allow for innovative design possibilities.
Cons: The primary disadvantage is the high cost and complexity of manufacturing, which can limit their widespread use in budget-sensitive markets.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly suitable for high-performance applications, such as body panels and structural reinforcements, where weight savings are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards for composites, such as ASTM D3039, is essential, particularly for buyers in regions with advanced automotive markets like Europe.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Street Legal Electric Vehicles
| Material | Typical Use Case for street legal electric vehicle | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Frames, body panels | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and lower durability | High |
| Steel | Chassis, safety structures | High strength and cost-effective | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Plastic | Dashboards, body panels, trim | Versatile and cost-effective | Lower strength and UV degradation | Low |
| Advanced Composites | Body panels, structural reinforcements | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
This material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers in the street legal electric vehicle market, enabling informed decisions that align with performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for street legal electric vehicle
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Street-Legal Electric Vehicles?
The manufacturing process for street-legal electric vehicles (EVs) involves several key stages, each designed to ensure both performance and safety. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Street-Legal Electric Vehicles?
Material preparation is the first crucial step in manufacturing street-legal EVs. This phase involves sourcing high-quality materials such as lightweight metals, composites, and plastics, which are essential for creating efficient and durable vehicle components. Suppliers must adhere to stringent standards for material quality, as this directly impacts the vehicle’s performance and safety. Additionally, materials are often pre-treated to enhance their properties, such as corrosion resistance and weight reduction.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in the Production of Electric Vehicles?
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes. Techniques such as stamping, bending, and molding are commonly used to shape metal and plastic components. Advanced methods like hydroforming can be employed for creating complex shapes that enhance aerodynamics and reduce weight. The choice of technique often depends on the component being manufactured; for instance, the chassis may require stamping, while the body panels might be molded.
How Are Components Assembled in Street-Legal Electric Vehicles?
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form the complete vehicle. This process typically involves automated assembly lines that utilize robotics for precision and efficiency. Key components such as the electric drivetrain, battery systems, and safety features must be installed with utmost care to ensure compliance with safety standards. Quality control checkpoints are integrated into the assembly line to monitor each step, ensuring that every vehicle meets predefined specifications.
What Finishing Processes Are Essential for Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Finishing processes, including painting, coating, and detailing, are crucial for enhancing both aesthetics and durability. These processes protect the vehicle from environmental factors, such as UV exposure and corrosion, while also providing a polished appearance. Additionally, the application of anti-scratch coatings and rust inhibitors can significantly extend the vehicle’s lifespan. The finishing stage is often the last opportunity for manufacturers to ensure quality before the vehicle is dispatched.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Relevant for Street-Legal Electric Vehicles?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of street-legal electric vehicles to ensure safety and performance. Various international standards, such as ISO 9001, play a critical role in establishing quality management systems within manufacturing operations. Compliance with these standards indicates that manufacturers have implemented effective processes for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
How Are International Standards Applied in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
For street-legal electric vehicles, adherence to international standards such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) is mandatory, especially for markets in Europe and North America. These standards cover essential safety features, emissions regulations, and performance benchmarks. Manufacturers must ensure that their products undergo rigorous testing and certification to meet these requirements before they can be marketed.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, typically involving several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of raw materials and components before they enter production. Proper documentation and supplier audits are essential to verify material quality.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the assembly process, IPQC monitors the quality of the work being performed. This includes checks on the installation of critical safety components and adherence to assembly specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the vehicle is fully assembled, FQC involves a comprehensive inspection of the finished product. This may include road testing, safety feature verification, and compliance checks against regulatory standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Street-Legal Electric Vehicles?
Testing methods for street-legal electric vehicles are diverse and tailored to ensure safety, durability, and performance. Common testing protocols include:
-
Crash Testing: Vehicles undergo simulated crash scenarios to evaluate their safety features, including occupant protection systems. Compliance with NHTSA and SAE crash test standards is essential.
-
Battery Testing: Given the reliance on electric power, battery performance testing is critical. This includes assessments of charge cycles, discharge rates, and thermal management under various conditions.
-
Performance Testing: Road tests are conducted to evaluate acceleration, braking, and handling characteristics. These tests ensure that the vehicle meets performance benchmarks required for street legality.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
B2B buyers must conduct thorough due diligence to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers. Key strategies include:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of manufacturing facilities allows buyers to assess compliance with quality standards and production capabilities directly. This provides insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request comprehensive quality reports that detail the supplier’s QC processes, testing results, and certifications. This documentation can reveal the supplier’s adherence to international standards.
-
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s manufacturing processes. These inspectors can conduct random checks and assessments to ensure compliance with quality requirements.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in quality assurance. Regulatory compliance may vary significantly across regions, necessitating a thorough understanding of local laws and standards. Buyers should also consider logistical factors such as shipping and customs regulations that may impact product quality during transit.
To mitigate risks, it is advisable for buyers to establish clear communication channels with suppliers and conduct regular follow-ups regarding quality assurance practices. This proactive approach ensures that expectations are aligned and that any potential quality issues are addressed promptly.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for street-legal electric vehicles are intricate and multifaceted. For B2B buyers, understanding these processes is crucial for making informed decisions when selecting suppliers. By focusing on manufacturing stages, quality standards, testing methods, and verification strategies, buyers can ensure they partner with reliable manufacturers who prioritize quality and compliance in their production of street-legal electric vehicles.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘street legal electric vehicle’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring street-legal electric vehicles (EVs). With the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions, understanding the nuances of sourcing these vehicles is crucial. This checklist will help you navigate the procurement process effectively, ensuring you choose the right vehicle for your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it’s essential to outline the technical specifications required for your street-legal electric vehicles. Consider factors such as maximum speed, passenger capacity, and safety features. This clarity will enable you to communicate your needs effectively to potential suppliers and ensure they can meet your requirements.
- Key Specifications to Consider:
- Maximum speed (typically 20-25 mph)
- Enclosure options (full doors, weather protection)
- Safety standards compliance (e.g., NHTSA, SAE J2358)
Step 2: Research Local Regulations
Understanding local laws regarding street-legal electric vehicles is critical, as regulations can vary significantly by region. Familiarize yourself with speed limits, vehicle classification, and any specific requirements for operating these vehicles on public roads. This knowledge will help you avoid legal issues post-purchase and ensure smooth operations.
- Important Points to Check:
- Maximum allowable speed on public roads
- Licensing requirements for drivers
- Restrictions on vehicle types in urban areas
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can deliver quality street-legal electric vehicles. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from other businesses in similar sectors. This evaluation is crucial to establishing trust and ensuring that the supplier has a track record of reliability.
- Questions to Ask Suppliers:
- What certifications do you hold for your vehicles?
- Can you provide examples of successful deployments in my region?
- What after-sales support and warranty do you offer?
Step 4: Assess Safety Features
Safety is paramount in the selection of street-legal electric vehicles. Ensure that the vehicles you are considering include essential safety features such as seat belts, headlights, turn signals, and mirrors. Compliance with established safety standards not only protects passengers but also mitigates liability for your business.
- Safety Features to Look For:
- Occupant protection systems
- Weather-resistant structures
- Visibility enhancements (reflectors, lights)
Step 5: Consider Cost and Financing Options
Budgeting for the procurement of street-legal electric vehicles involves more than just the initial purchase price. Explore financing options that could ease the financial burden, such as leasing or installment plans. Understanding total cost of ownership—including maintenance, insurance, and charging infrastructure—is also critical for long-term financial planning.
- Cost Factors to Analyze:
- Initial purchase price vs. leasing options
- Expected maintenance costs
- Energy consumption and charging expenses
Step 6: Test Drive and Demonstrate Vehicles
Before finalizing your purchase, arrange for test drives and demonstrations of the vehicles under consideration. This hands-on experience allows you to evaluate comfort, handling, and overall performance. It also provides an opportunity to assess how well the vehicle meets your operational needs.
- Things to Evaluate During the Test Drive:
- Comfort and ergonomics for drivers and passengers
- Acceleration and braking performance
- Ease of use for various driving conditions
Step 7: Finalize Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier and vehicle, carefully review and negotiate the purchase agreement. Ensure that all agreed-upon specifications, delivery timelines, and warranty details are clearly documented. This step is vital to protect your investment and ensure that both parties have a mutual understanding of the terms.
- Key Elements to Confirm:
- Payment terms and conditions
- Delivery schedules and logistics
- Warranty coverage and service agreements
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing street-legal electric vehicles, ensuring a well-informed and successful procurement process.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for street legal electric vehicle Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Street Legal Electric Vehicles?
When sourcing street legal electric vehicles (EVs), understanding the cost structure is vital for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials such as batteries, electric motors, chassis, and safety features can vary significantly based on quality and availability. Lithium-ion batteries, which are crucial for EV performance, often represent the largest material cost. Buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers who offer bulk purchasing options to reduce costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled workers involved in assembly, testing, and quality assurance. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, manufacturers may provide competitive pricing. However, ensure that labor standards meet international safety and quality regulations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and administrative expenses related to production facilities. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate overhead costs, impacting the overall pricing of vehicles.
-
Tooling: Customization often requires specialized tooling, which can be a significant upfront investment. Buyers should discuss tooling costs with suppliers, particularly if they require unique designs or features.
-
Quality Control (QC): Compliance with safety and performance standards is non-negotiable in the EV market. The costs associated with QC processes ensure that vehicles meet local regulations, which can vary by region.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can be substantial, especially for international buyers. Understanding Incoterms and negotiating favorable shipping conditions can help minimize these expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding industry standards for margins can help in negotiating better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Street Legal Electric Vehicles?
Several factors influence the pricing of street legal electric vehicles beyond the basic cost structure:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in larger quantities can significantly reduce per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their operational needs to take advantage of volume discounts.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features and specifications can drive up costs. Standard models often offer better pricing, so consider if customizations are essential for your market.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, SAE) can increase upfront costs but may result in lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) through enhanced durability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality and service may charge a premium, but their products often justify the investment.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Purchasing Electric Vehicles?
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage in discussions with multiple suppliers to understand market pricing. Leverage quotes to negotiate better terms and pricing.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership: Consider the long-term operational costs of vehicles, including maintenance, energy consumption, and resale value, rather than just the initial purchase price.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Different regions may have specific taxes, tariffs, and regulations that affect pricing. For example, buyers in Europe may face stricter emissions regulations that could influence vehicle specifications and costs.
-
Understand Local Market Dynamics: In regions like Africa and South America, local demand, infrastructure, and government incentives can affect pricing and availability. Buyers should stay informed about local market conditions.
-
Consider Payment Terms and Financing Options: Some suppliers may offer financing or extended payment terms, which can ease cash flow while allowing for a larger upfront purchase.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices for street legal electric vehicles can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. The information provided is indicative, and actual costs should be confirmed with suppliers for accurate quotations tailored to specific needs and circumstances.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing street legal electric vehicle With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Street Legal Electric Vehicles
In the quest for sustainable urban mobility solutions, businesses often explore various alternatives to street legal electric vehicles (EVs). Understanding the differences between these options is crucial for making informed decisions that align with operational needs and financial constraints. This analysis compares street legal electric vehicles with two viable alternatives: traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and bicycles, focusing on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Street Legal Electric Vehicle | Internal Combustion Engine Vehicle | Bicycle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Up to 25 mph (40 km/h) | Typically 30-120 mph (48-193 km/h) | Up to 20 mph (32 km/h) |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; lower operational costs | Lower initial cost; higher fuel and maintenance costs | Low initial cost; minimal operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure and regulatory compliance | Widely available fuel infrastructure; less regulation | Easy to implement; no fuel infrastructure needed |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance; fewer moving parts | Higher maintenance due to complex mechanics | Minimal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting and short trips | Longer distances and varied terrains | Short commutes and eco-friendly transport |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles?
Internal combustion engine vehicles are a well-established alternative, offering a broad range of performance capabilities. With speeds typically ranging from 30 to 120 mph, they are suitable for longer trips and varied terrains. However, they come with higher operational costs due to fuel consumption and regular maintenance needs, such as oil changes and engine repairs. Additionally, businesses must navigate increasing regulatory pressures related to emissions, which may impact their long-term viability.
How Do Bicycles Compare as a Transportation Solution?
Bicycles represent the most sustainable and cost-effective alternative for urban mobility. With minimal initial investment and virtually no fuel costs, they are ideal for short commutes and encourage healthier lifestyles. Bicycles also require less infrastructure, making them easy to implement in various settings. However, their performance is limited, and they may not be suitable for longer distances or in adverse weather conditions, potentially necessitating alternative transportation for those scenarios.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When selecting the most appropriate transportation solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific requirements, including operational costs, environmental impact, and regulatory compliance. Street legal electric vehicles are excellent for urban environments where low-speed travel is common, and sustainability is a priority. In contrast, internal combustion engine vehicles may still serve businesses needing versatility for longer distances. Bicycles, while limited in range and speed, offer an eco-friendly option that encourages employee wellness and reduces urban congestion. By carefully evaluating these alternatives, businesses can choose the solution that best aligns with their operational goals and sustainability initiatives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for street legal electric vehicle
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Street Legal Electric Vehicles?
Street legal electric vehicles (EVs) are designed to meet specific technical standards and regulations, which can significantly influence their marketability and usability in various regions. Understanding these properties is vital for B2B buyers looking to invest in or distribute these vehicles.
1. Maximum Speed and Power Output
Street legal electric vehicles typically have a maximum speed ranging from 20 mph (32 km/h) to 25 mph (40 km/h). This speed classification is essential because it determines where the vehicle can be legally operated. In many regions, vehicles exceeding these limits may require additional certifications or may not be permitted on public roads. For B2B buyers, understanding speed specifications can help ensure compliance with local regulations, thus avoiding potential legal issues.
2. Weight Capacity and Dimensions
The maximum loaded weight of street legal electric vehicles usually does not exceed 3,000 lbs (1,361 kg). This includes both the vehicle’s weight and its payload. Buyers need to consider weight limits as they can affect transportation, storage, and the vehicle’s overall performance. Furthermore, vehicle dimensions play a crucial role in urban environments where space is limited, making it necessary for B2B buyers to choose models that fit their operational needs.
3. Battery Type and Range
Most street legal electric vehicles utilize lithium-ion batteries, known for their efficiency and longevity. The range of these vehicles—how far they can travel on a single charge—varies significantly, typically from 30 to 100 miles (48 to 161 km). Understanding battery specifications is critical for B2B buyers, as it directly impacts operational costs, charging infrastructure requirements, and customer satisfaction.
4. Safety Features
Street legal electric vehicles are required to meet specific safety standards, including features like seat belts, headlights, tail lights, turn signals, and reflectors. Compliance with these safety regulations is non-negotiable for B2B buyers, as vehicles that do not meet safety standards can face restrictions in sale and usage. Buyers should prioritize vehicles with comprehensive safety features to enhance user protection and legal compliance.
5. Charging Infrastructure Compatibility
Compatibility with existing charging infrastructure is another essential property. Street legal electric vehicles typically require Level 2 charging stations for efficient charging. B2B buyers must consider the availability of charging stations in their target markets and the associated installation costs. Understanding this infrastructure can greatly influence the operational efficiency of electric vehicle fleets.
What Are the Common Trade Terminologies Related to Street Legal Electric Vehicles?
Familiarizing oneself with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B electric vehicle market.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of street legal electric vehicles, knowing the OEM can help buyers assess quality, reliability, and warranty support. This is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, understanding MOQ can aid in budget planning and inventory management. It also influences negotiation strategies when establishing relationships with manufacturers or suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price offers from suppliers for specific products. For street legal electric vehicles, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare prices and terms, facilitating a more strategic purchasing process.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B buyers, as they clarify shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation, which are crucial for effective import and export operations.
5. LSV (Low-Speed Vehicle)
LSV is a classification for vehicles that meet specific federal safety standards and have a maximum speed of 25 mph (40 km/h). Understanding this classification is vital for B2B buyers to ensure compliance with local regulations and to accurately market their products.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions in the growing market of street legal electric vehicles, ensuring compliance and optimizing their investment strategies.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the street legal electric vehicle Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Street Legal Electric Vehicle Market?
The street legal electric vehicle (EV) sector is experiencing significant transformation, driven by various global factors. The increasing focus on sustainable transportation solutions, urban congestion, and the need for affordable mobility options are primary drivers. International B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are observing a surge in demand for low-speed vehicles (LSVs) as cities adopt stricter emissions regulations and promote green transport initiatives.
Emerging technologies, such as advanced battery systems and smart connectivity features, are enhancing vehicle performance and user experience. This trend is leading to the integration of IoT capabilities in street legal EVs, enabling fleet management systems that optimize route planning and reduce operational costs. Buyers should be aware of the potential for collaborative partnerships with technology providers to leverage these advancements.
Market dynamics are also influenced by changing consumer preferences. The rising popularity of “last-mile” transportation solutions, particularly in urban areas, is pushing manufacturers to innovate in design and functionality. As buyers navigate this landscape, they should prioritize suppliers who offer customizable vehicles tailored to specific market needs, ensuring they remain competitive in their respective regions.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Street Legal Electric Vehicle Industry?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the street legal electric vehicle market, influencing sourcing strategies and supplier selection for B2B buyers. The environmental impact of traditional vehicles has prompted a shift toward electric options, which are inherently more sustainable due to their zero-emission operation. However, the sustainability narrative extends beyond just the vehicle’s end use; it encompasses the entire supply chain.
Buyers should seek partners committed to ethical sourcing practices. This includes the use of sustainable materials, such as recycled metals and eco-friendly composites, and adherence to environmental regulations throughout the manufacturing process. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, as consumer awareness regarding environmental issues grows, businesses that prioritize “green” certifications and materials in their offerings will likely see increased demand. This trend is particularly relevant in regions like Europe, where consumers are increasingly inclined to support brands that demonstrate corporate social responsibility.
What Is the Brief History of Street Legal Electric Vehicles?
The evolution of street legal electric vehicles dates back to the late 20th century, primarily driven by the need for cleaner urban transport solutions. Initially, these vehicles were perceived as niche products, largely limited to low-speed applications in resorts and gated communities. However, as urban areas faced increasing congestion and pollution, the concept of electric vehicles began to gain traction.
In the early 2000s, advancements in battery technology and government incentives spurred interest in electric mobility. The development of stringent safety standards for low-speed vehicles enabled manufacturers to innovate and create more robust options suitable for public roads. Today, street legal electric vehicles are not only recognized for their environmental benefits but are also being integrated into broader transportation networks, offering a viable alternative to traditional automobiles. This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers, as it informs current market opportunities and future growth potential in the sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of street legal electric vehicle
-
1. How do I determine if a street-legal electric vehicle (EV) meets my country’s regulations?
To ensure compliance with local regulations, start by researching the specific laws governing low-speed vehicles (LSVs) or neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs) in your target market. Each region may have different requirements regarding speed limits, safety features, and vehicle classifications. Engaging with local automotive regulatory bodies or industry associations can provide essential insights. Additionally, verify whether the manufacturer’s vehicles are certified for sale in your country, focusing on necessary documentation and compliance standards. -
2. What is the best street-legal electric vehicle for urban transport solutions?
For urban transport, consider vehicles that combine efficiency, speed, and safety features. Look for street-legal electric vehicles designed for low-speed urban environments, with a maximum speed of 25 mph (40 km/h) and features like enclosed cabs, safety belts, and headlights. Models that offer customizable options for passenger capacity and cargo space can also enhance their utility. Evaluate the vehicle’s range, charging time, and maintenance requirements to ensure it aligns with your operational needs. -
3. How can I vet suppliers of street-legal electric vehicles?
To vet suppliers, start by assessing their industry reputation through reviews, testimonials, and case studies from previous clients. Check for certifications and compliance with international safety standards, such as FMVSS and SAE J2358. Request detailed product specifications, warranty information, and after-sales support terms. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers can also provide insight into their responsiveness and willingness to meet your specific needs. Lastly, consider visiting their manufacturing facilities if feasible. -
4. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for street-legal electric vehicles?
MOQs for street-legal electric vehicles can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the specific model. Generally, you may encounter MOQs ranging from 5 to 50 units, especially for customizable vehicles. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to understand their flexibility on MOQs, especially if you are a smaller buyer or looking to test the market. Some manufacturers may offer pilot programs or trial orders to facilitate initial purchases. -
5. What payment terms are common in international trade for street-legal electric vehicles?
Common payment terms include a deposit of 30% to 50% upfront, with the remaining balance due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or payment plans, especially for larger orders. It’s essential to clarify payment methods, such as bank transfers or letters of credit, to minimize risk. Discussing payment terms early in negotiations can also help establish trust and ensure that both parties are aligned. -
6. What quality assurance (QA) practices should I expect from manufacturers?
Reputable manufacturers should implement rigorous QA practices, including regular inspections throughout the production process and compliance with international safety standards. Look for certifications like ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Suppliers should provide documentation outlining their QA processes, including testing for safety features, performance, and durability. Additionally, inquire about warranty policies and support for any defects or issues post-purchase. -
7. How do logistics and delivery timelines work for importing street-legal electric vehicles?
Logistics for importing street-legal electric vehicles involve several steps, including shipping, customs clearance, and local delivery. Delivery timelines can vary based on the origin of the vehicle, shipping methods, and customs procedures. Typically, expect a lead time of 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the distance and shipping terms agreed upon. It’s crucial to work with logistics providers experienced in automotive imports to ensure smooth handling and compliance with local regulations. -
8. Are there customization options available for street-legal electric vehicles?
Most manufacturers offer a range of customization options for street-legal electric vehicles, including seating configurations, color choices, and additional safety features. Customization can also extend to technological enhancements, such as advanced navigation systems or upgraded battery options for extended range. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities and the costs associated with different customization options, ensuring that the final product aligns with your business objectives.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Street Legal Electric Vehicle Manufacturers & Suppliers List
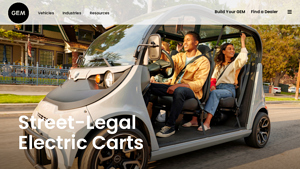
1. Gemcar – Street-Legal Electric Carts
Domain: gemcar.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Street-Legal Electric Carts are designed for on-road driving and are classified as Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs). Key features include:
– Speed: Up to 25 mph (40 km/h)
– Seating Capacity: Up to 6 forward-facing passengers
– Safety Features: Occupant protection system (OPS) certified to SAE J2358, standard safety features including 3-point seat belts, headlights, tail lights, brake lights, parking bra…
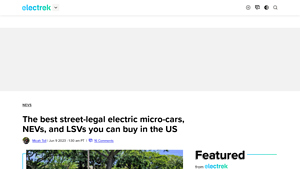
2. Eli Zero – All-Electric Two-Seater
Domain: electrek.co
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Eli Zero: All-electric two-seater, expected in US market soon, pre-order program launching, designed to meet LSV safety standards, estimated price around $15,000. Wink Motors: Four models (Sprout, Sprout Solar, Mark 1, Mark 2 Solar), prices under $10,000 for budget models, around $12,000 for premium models, four-seaters, fireproof LiFePO4 batteries, air conditioning, solar versions add 5 miles of …
3. MotoEV – Deluxe Street Legal Golf Cart & Electro Bubble Buddy LSV
Domain: motoelectricvehicles.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: This company, MotoEV – Deluxe Street Legal Golf Cart & Electro Bubble Buddy LSV, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
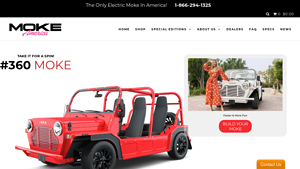
4. Moke™ – All-Electric Vehicle
Domain: mokeamerica.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Official Moke™ | The Only Electric Moke In America!\n- All-electric, zero-emission Electric Vehicle\n- 75-mile range lithium battery\n- Top speed up to 45 MPH\n- Built in Sarasota, Florida with a majority of American parts\n- 6-hour full charge with a standard household outlet\n- 6-month manufacturer’s warranty; 8-year lithium battery warranty\n- Designed for coastal communities, resort towns, and…
5. Reddit – Medium Speed Electric Vehicle
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Small, durable, relatively comfortable, inexpensive electric vehicle; capable of reaching speeds up to 35 mph; ideally seats 4; classified as medium speed vehicles (MSV); currently limited options available.
6. South Jersey EV – Street Legal Golf Carts
Domain: southjerseyev.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Street Legal Golf Carts for Sale in New Jersey, including:
– 2025 Dach Apollo: $12,995
– 2025 Dach Falcon 2+2: $9,995
– 2025 Tomberlin Shadowhawk: $23,995
Additional offerings include:
– Electric and gas-powered golf carts
– Gas-powered utility task vehicles (UTVs)
– Industrial and commercial vehicles
– Custom and reconditioned vehicles
Locations:
– 1322 Doughty Rd, Egg Harbor Township, NJ
– 106…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for street legal electric vehicle
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in the Street-Legal Electric Vehicle Market?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of street-legal electric vehicles (EVs), strategic sourcing offers significant advantages for B2B buyers. Understanding the distinctions between low-speed vehicles (LSVs) and traditional electric carts is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Street-legal electric vehicles like GEM and Club Car’s CRU not only comply with stringent safety standards but also provide a versatile transportation solution suitable for urban environments and recreational use.
The demand for sustainable transportation solutions is rising, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where urbanization is accelerating. By leveraging strategic sourcing, businesses can tap into emerging markets, align with local regulations, and ensure that they are equipped with vehicles that meet both safety and environmental standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Prepare for the Future of Electric Mobility?
As the global push for sustainability continues, investing in street-legal electric vehicles positions companies at the forefront of this transition. B2B buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships with reputable manufacturers that offer innovative solutions tailored to local market needs. Embracing this forward-thinking approach will not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to a greener future. Now is the time to act—seize the opportunity to integrate street-legal electric vehicles into your fleet and drive your business towards sustainable growth.