Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for street legal cheap electric vehicles
As businesses across the globe seek sustainable transportation solutions, the demand for street legal cheap electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly increasing. However, sourcing these vehicles can pose significant challenges, particularly for international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries such as Nigeria and Brazil. Navigating the complexities of regulations, safety standards, and varying market dynamics can be daunting. This guide aims to demystify the global market for street legal cheap electric vehicles, providing essential insights into different types of vehicles, their applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting.
In this comprehensive resource, buyers will find detailed analyses of low-speed vehicles (LSVs), electric micro-cars, and their specifications, ensuring they understand what qualifies as street legal in their respective regions. Additionally, we will cover critical factors such as pricing structures, cost-effectiveness, and long-term operational benefits, enabling businesses to make informed purchasing decisions. By leveraging the information provided, B2B buyers can confidently assess their options, align their procurement strategies with market trends, and ultimately enhance their operational efficiency while contributing to a greener future. This guide empowers international buyers to navigate the electric vehicle landscape with clarity and purpose, ensuring they stay ahead in a competitive marketplace.
Understanding street legal cheap electric vehicles Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) | Speed limit of 25 mph, enclosed cab, safety features (lights, seat belts) | Urban transport, campus mobility, delivery services | Pros: Cost-effective, eco-friendly; Cons: Limited speed and range. |
| Street-Legal Electric Carts | Designed for public road use, customizable, various passenger capacities | Resort transport, gated community transport | Pros: Versatile, user-friendly; Cons: May require licensing, speed restrictions. |
| Micro-Cars | Compact design, efficient for short trips, compliance with safety regulations | Last-mile delivery, urban commuting | Pros: Space-saving, affordable; Cons: Limited passenger capacity, less power. |
| Electric Cargo Vehicles | Designed for transporting goods, higher payload capacity | Logistics, small business deliveries | Pros: Zero emissions, cost-effective for short hauls; Cons: Higher upfront costs. |
| Solar-Powered Electric Vehicles | Equipped with solar panels for partial recharging, eco-friendly | Sustainable transport solutions, green initiatives | Pros: Reduces energy costs, eco-friendly; Cons: Initial investment can be high. |
What Are Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) and Their B2B Suitability?
Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) are designed for urban environments, typically limited to speeds of 25 mph. They are equipped with essential safety features such as seat belts and headlights, making them suitable for road use. B2B applications include urban transport services, campus mobility, and small delivery operations. Buyers should consider local regulations, as LSVs must meet specific safety standards to be street-legal. Their eco-friendly nature and lower operational costs make them attractive for businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint.
How Do Street-Legal Electric Carts Serve Businesses?
Street-legal electric carts are versatile vehicles that can be customized for various applications, including resort transport and gated community mobility. With the ability to carry multiple passengers and configurable features, they provide an efficient solution for businesses that require short-distance transportation. However, operators may need a driver’s license, and buyers should assess local regulations regarding their use on public roads. Their user-friendly design and cost-effectiveness make them appealing for businesses focused on enhancing customer experiences.
What Are the Advantages of Micro-Cars for Urban Commuting?
Micro-cars are compact electric vehicles ideal for short trips and urban commuting. Their small size allows for easy maneuverability in congested areas, making them suitable for last-mile delivery services and urban transport. While they are generally more affordable than larger vehicles, buyers should be aware of their limited passenger capacity and power. For businesses targeting urban markets, micro-cars can provide a practical and economical solution to meet growing demand for efficient transport.
Why Choose Electric Cargo Vehicles for Logistics?
Electric cargo vehicles are specifically designed to transport goods, offering higher payload capacities than standard passenger vehicles. They are particularly beneficial for logistics companies and small businesses involved in delivery services. While the initial investment may be higher, the long-term savings from reduced fuel costs and maintenance make them an attractive option. Businesses should evaluate their delivery routes and cargo needs to ensure these vehicles align with their operational goals.
What Are the Benefits of Solar-Powered Electric Vehicles?
Solar-powered electric vehicles integrate solar panels to harness renewable energy for partial recharging, making them an eco-friendly transport solution. They are ideal for businesses focused on sustainability and reducing energy costs. However, the initial investment can be considerable, and businesses must assess the feasibility of solar technology in their operational environment. For companies committed to green initiatives, these vehicles can enhance their brand image while contributing to environmental goals.
Key Industrial Applications of street legal cheap electric vehicles
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Street Legal Cheap Electric Vehicles | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tourism | Eco-friendly transportation for tours and excursions | Attracts eco-conscious travelers, reduces emissions | Compliance with local regulations, battery range, and maintenance options |
| Urban Delivery Services | Last-mile delivery solutions in urban environments | Reduces operational costs and carbon footprint | Cargo capacity, speed limitations, and charging infrastructure availability |
| Educational Institutions | Campus transportation for students and staff | Enhances campus mobility while promoting sustainability | Safety features, seating capacity, and total cost of ownership |
| Municipal Services | Community outreach and public service vehicles | Improves community engagement and reduces noise pollution | Compliance with municipal regulations, maintenance support, and durability |
| Real Estate Development | Shuttle services for residential and commercial developments | Increases property appeal and accessibility | Vehicle customization options, branding opportunities, and safety certifications |
How are Street Legal Cheap Electric Vehicles Used in the Tourism Industry?
In the tourism sector, street legal cheap electric vehicles serve as eco-friendly transportation options for guided tours and excursions. These vehicles enhance the visitor experience by offering a quiet, sustainable mode of transport that aligns with the growing trend of eco-conscious tourism. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing vehicles that comply with local regulations and have robust battery life is critical to ensure uninterrupted service during peak tourist seasons.
What Role Do Electric Vehicles Play in Urban Delivery Services?
Street legal cheap electric vehicles are increasingly being adopted for last-mile delivery solutions in urban areas. They provide businesses with a cost-effective alternative for transporting goods while minimizing their environmental impact. Buyers in this sector should consider the cargo capacity and speed limitations of the vehicles, as well as the availability of charging infrastructure to support daily operations, especially in densely populated cities in the Middle East and Europe.
How Are Educational Institutions Utilizing Electric Vehicles?
Educational institutions are leveraging street legal cheap electric vehicles for campus transportation, facilitating easy movement for students and staff. This application not only enhances campus mobility but also reflects the institution’s commitment to sustainability. Buyers from educational sectors must focus on safety features, seating capacity, and the total cost of ownership to ensure the vehicles meet the needs of a diverse student population, particularly in developing regions.
Why Are Municipal Services Interested in Electric Vehicles?
Municipal services are utilizing street legal cheap electric vehicles for community outreach and public service tasks. These vehicles enhance community engagement while reducing noise pollution and emissions. When sourcing vehicles, municipalities should prioritize compliance with local regulations, maintenance support, and durability to withstand various environmental conditions, especially in regions prone to extreme weather.
What Benefits Do Real Estate Developers Gain from Electric Vehicles?
Real estate developers are incorporating street legal cheap electric vehicles into their projects as shuttle services to improve accessibility for residents and visitors. This strategy increases property appeal and can even enhance the marketability of developments. Buyers in this sector should look for vehicles that offer customization options for branding, as well as safety certifications to ensure compliance with local laws and standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘street legal cheap electric vehicles’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Local Regulations for Street-Legal Electric Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the daunting task of understanding and complying with various local regulations regarding street-legal electric vehicles. For example, a company in Nigeria looking to introduce a fleet of electric delivery vehicles may find that the vehicle requirements differ significantly from one state or municipality to another. This inconsistency can lead to confusion, potential fines, and delays in getting their vehicles on the road, ultimately affecting their bottom line.
The Solution: To effectively navigate these regulatory challenges, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on local laws before making any purchases. This includes consulting with local transportation authorities, legal experts, and industry associations that specialize in electric vehicle regulations. Additionally, investing in vehicles that come with a comprehensive compliance guarantee can mitigate risks. Buyers should request documentation that outlines how specific models meet both national and local safety standards. Using a checklist to ensure that all safety features, such as seat belts, lights, and mirrors, are included can also streamline the compliance process. Building relationships with local dealers who are well-versed in these regulations can provide ongoing support and updates about any changes in the law.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Vehicle Safety and Reliability for Business Operations
The Problem: One of the primary concerns for B2B buyers is ensuring that the street-legal electric vehicles they acquire are safe and reliable for daily operations. For instance, a small logistics company in Brazil may be interested in cheap electric vehicles but worry about the lack of safety features like robust brakes and emergency systems. A vehicle malfunction could lead to serious accidents, liability issues, and damage to the company’s reputation.
The Solution: To address safety concerns, buyers should prioritize vehicles that are certified as Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) and come equipped with standard safety features. Conducting a thorough evaluation of the vehicles’ safety ratings, crash test results, and customer reviews can provide insights into reliability. Buyers should also inquire about the availability of service and maintenance support from the manufacturer or dealer. Establishing a regular maintenance schedule can help ensure the vehicles remain in optimal condition and reduce the likelihood of breakdowns. Additionally, opting for models with advanced safety technologies, such as anti-lock braking systems and collision detection, can enhance overall safety and protect both drivers and cargo.
Scenario 3: Maximizing Cost-Effectiveness While Meeting Operational Needs
The Problem: Budget constraints can severely limit options for B2B buyers interested in street-legal electric vehicles. Companies in regions like the Middle East may find that while some vehicles are marketed as affordable, the total cost of ownership—factoring in maintenance, insurance, and charging infrastructure—can be significantly higher than expected. This discrepancy can lead to financial strain and affect the overall feasibility of adopting electric vehicles.
The Solution: To maximize cost-effectiveness, buyers should conduct a comprehensive total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis before making a purchase. This analysis should include not only the upfront costs but also long-term expenses such as charging infrastructure, insurance, and maintenance. Buyers should explore bulk purchase discounts or financing options that can alleviate immediate financial burdens. Partnering with local energy providers for incentives or rebates on charging stations can also reduce initial costs. Additionally, considering the lifecycle of the vehicle—including battery lifespan and resale value—can provide a clearer picture of long-term viability. Engaging with manufacturers that offer warranties and service packages can also mitigate future expenses, ensuring that the investment remains sustainable.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for street legal cheap electric vehicles
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Street Legal Cheap Electric Vehicles?
When selecting materials for street legal cheap electric vehicles, it is crucial to consider their properties, costs, and suitability for various applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of these vehicles.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Electric Vehicle Construction?
Aluminum is widely utilized in electric vehicle construction due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. With a temperature rating that can withstand significant variations, aluminum is ideal for vehicle bodies and structural components. It offers a high strength-to-weight ratio, which enhances vehicle efficiency by reducing overall weight and improving battery range.
Pros: Aluminum is durable and lightweight, contributing to better fuel efficiency. Its corrosion resistance minimizes maintenance costs over time.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex and costly compared to other materials like steel. Additionally, aluminum may not provide the same level of impact resistance as heavier metals.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for various media, including exposure to moisture and harsh environmental conditions, making it ideal for regions with high humidity or rainfall.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential when sourcing aluminum. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local availability and cost fluctuations.
What Role Does Steel Play in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Steel, particularly high-strength steel, is another common material used in electric vehicles. Known for its robustness and impact resistance, steel is often used in the chassis and structural components of vehicles. It has a high temperature rating and excellent tensile strength, which is critical for safety in collision scenarios.
Pros: Steel is cost-effective and widely available, making it a popular choice among manufacturers. Its strength provides enhanced safety features.
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact battery efficiency and overall vehicle performance. Additionally, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various coatings and treatments can enhance its resistance to environmental factors, making it suitable for diverse climates.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the steel used meets local standards for safety and performance. In regions like the Middle East, where temperatures can soar, selecting treated steel can prevent premature degradation.
Why Is Plastic Important in Electric Vehicle Design?
Plastics, especially engineering-grade thermoplastics, are increasingly used in electric vehicles for components like dashboards, interior panels, and even some exterior parts. They offer excellent temperature resistance and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative design.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight, which helps improve vehicle efficiency. They are also resistant to corrosion and can be produced at a lower cost compared to metals.
Cons: While durable, plastics may not withstand high-impact scenarios as well as metals. They can also degrade under UV exposure unless treated.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for various interior applications and can be designed to withstand moisture and temperature variations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with environmental regulations regarding plastic use is crucial. Buyers in Europe, for instance, must adhere to stringent regulations concerning the recyclability of materials.
How Do Composites Enhance Electric Vehicle Performance?
Composite materials, often a combination of fibers and resins, are gaining traction in electric vehicle manufacturing. They provide a high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for both structural and aesthetic applications.
Pros: Composites are lightweight and can be engineered for specific performance characteristics, enhancing vehicle efficiency.
Cons: The cost of composite materials can be high, and their manufacturing processes may require specialized techniques and equipment.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly effective in applications exposed to harsh conditions, such as battery enclosures and body panels.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should assess the availability of composite manufacturing capabilities in their regions. Compliance with international standards is also critical, especially in markets like Europe where regulations are stringent.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Street Legal Cheap Electric Vehicles
| Material | Typical Use Case for street legal cheap electric vehicles | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Vehicle body and structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Steel | Chassis and structural components | Cost-effective and strong | Heavier, prone to corrosion | Low |
| Plastic | Interior panels and dashboards | Lightweight and moldable | Less impact resistance | Low |
| Composites | Battery enclosures and body panels | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers looking to enhance their offerings in the street legal cheap electric vehicle market. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials can significantly influence manufacturing decisions and product performance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for street legal cheap electric vehicles
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Street Legal Cheap Electric Vehicles?
The manufacturing process of street legal cheap electric vehicles (EVs) involves several critical stages that ensure quality, safety, and compliance with regulations. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing vehicles.
Material Preparation: How Is the Quality of Raw Materials Ensured?
The first stage in manufacturing involves the careful selection and preparation of raw materials. Manufacturers often utilize high-strength steel, lightweight composites, and eco-friendly materials to enhance performance and sustainability. Quality assurance starts here, with incoming quality control (IQC) checks to verify the specifications and integrity of materials. Suppliers should provide certificates of conformity and test reports to ensure materials meet international standards.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape the Vehicle Components?
The forming stage includes processes such as stamping, molding, and machining. Advanced techniques like Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining are frequently employed to ensure precision in part production. For example, the chassis and body components are often stamped from high-strength steel to achieve both durability and weight savings. B2B buyers should inquire about the machinery used and whether manufacturers follow best practices in forming to maintain dimensional accuracy and reduce waste.
Assembly: How Are Components Integrated into a Complete Vehicle?
The assembly stage is where various components come together to form a complete vehicle. This phase can include manual and automated processes. Robotics may be utilized for tasks like welding and painting, which enhances consistency and reduces human error. During assembly, in-process quality control (IPQC) checkpoints are vital. These checkpoints ensure that components are correctly installed and that electrical systems meet safety standards. Buyers should verify that the assembly facility is equipped with modern technology and trained personnel.
Finishing: What Is Involved in the Final Touches of Production?
The finishing stage involves painting, coating, and final inspections. A durable, weather-resistant paint is often applied to protect the vehicle from environmental factors. Additionally, manufacturers may employ anti-corrosion treatments to enhance longevity. Final quality control (FQC) checks are performed to assess the overall aesthetics and functionality of the vehicle. Buyers should request documentation of the finishing processes, including any certifications for environmental compliance.
What International Standards Apply to Manufacturing and Quality Assurance?
B2B buyers should be aware of the various international standards that apply to the manufacturing and quality assurance of street legal cheap electric vehicles. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system and is crucial for ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes.
- ISO 14001: Focused on environmental management, this standard helps manufacturers minimize their environmental impact.
- CE Marking: For vehicles sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- SAE Standards: In the U.S., various Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) standards apply to vehicle safety and performance.
Understanding these standards can help B2B buyers assess the credibility and reliability of potential suppliers.
What Quality Control Checkpoints Should Be Considered?
Quality control checkpoints are essential throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that vehicles meet safety and performance standards. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verifying raw materials upon arrival.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring assembly processes to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished vehicle, including functional tests and safety inspections.
Buyers should engage with suppliers about their specific QC processes and ask for detailed reports on these checkpoints.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Street Legal Electric Vehicles?
Testing methods play a crucial role in validating the safety and performance of street legal cheap electric vehicles. Common methods include:
- Electrical Testing: Ensures that the vehicle’s electrical systems function correctly and safely.
- Crash Testing: Simulates various accident scenarios to assess the vehicle’s safety features.
- Environmental Testing: Examines how the vehicle performs under different weather conditions.
B2B buyers should request documentation of these tests to verify compliance with safety standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that a supplier adheres to high-quality standards, B2B buyers can take several steps:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control measures.
- Reports: Requesting quality reports and testing certifications to verify compliance with international standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors to evaluate the quality of the manufacturing processes and finished vehicles.
This due diligence is particularly important for buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, where regulatory environments may vary.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing street legal cheap electric vehicles internationally, buyers must consider various nuances, including:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have specific regulations regarding vehicle safety and emissions. Understanding these can prevent costly mistakes.
- Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices can vary, impacting negotiations and quality expectations.
- Logistics Challenges: Import/export regulations and logistics can affect lead times and delivery schedules. Buyers should work closely with suppliers to ensure smooth processes.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Ensure They Source Quality Street Legal Cheap Electric Vehicles?
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in place for street legal cheap electric vehicles, B2B buyers can make informed decisions. Engaging with suppliers about their quality control practices, verifying compliance with international standards, and conducting thorough audits will help ensure that the vehicles meet safety and performance requirements. This proactive approach will enhance the buyer’s confidence in their sourcing decisions and ultimately contribute to successful business outcomes.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘street legal cheap electric vehicles’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure street-legal cheap electric vehicles (EVs). With the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions across international markets, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s essential to navigate the procurement process effectively. This guide outlines critical steps to ensure you select the right vehicles that meet your operational needs and comply with local regulations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital for ensuring that the electric vehicles you source align with your operational requirements. Consider factors such as maximum speed, range, capacity, and safety features.
– Speed Requirements: Ensure the vehicles can legally operate in your intended markets, typically needing to exceed 20 mph (32 km/h) for street-legal status.
– Safety Features: Verify that the vehicles include necessary safety components like seat belts, headlights, and turn signals.
Step 2: Research Local Regulations
Understanding local regulations is crucial to ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues. Different regions have varying laws regarding street-legal vehicles.
– Licensing Requirements: Check if drivers need to have a specific license to operate these vehicles.
– Road Use Regulations: Investigate any restrictions on where these vehicles can be driven, particularly in urban areas with specific zoning laws.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, thorough evaluation is necessary to mitigate risks. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from existing clients, especially those in similar markets.
– Reputation and Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in providing street-legal electric vehicles.
– After-Sales Support: Assess the level of after-sales service and support offered, including warranty terms and maintenance options.
Step 4: Assess Vehicle Features and Performance
Examine the features and performance metrics of the vehicles you’re considering. This includes battery life, charging time, and overall reliability.
– Battery Type: Opt for vehicles equipped with high-quality, durable batteries that offer longer life and better performance.
– Performance Metrics: Evaluate the vehicle’s ability to handle various terrains, especially if it will be used in diverse environments.
Step 5: Request and Compare Quotes
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers and vehicles, request detailed quotes. This will help you understand the pricing structures and any additional costs involved.
– Cost Breakdown: Ensure quotes include all relevant costs such as shipping, taxes, and potential customization fees.
– Volume Discounts: Inquire about discounts for bulk purchases, as this can significantly impact your overall budget.
Step 6: Conduct a Pilot Test
Before finalizing your order, conducting a pilot test can provide valuable insights into the vehicle’s performance in real-world conditions.
– User Feedback: Gather feedback from the end-users regarding comfort, usability, and any operational challenges faced.
– Performance Evaluation: Analyze the vehicle’s performance metrics during the pilot to ensure they meet your expectations.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Agreements
Once you have completed all evaluations and tests, it’s time to finalize contracts with your chosen supplier. Ensure that all terms, conditions, and warranties are clearly outlined.
– Legal Review: Have legal counsel review contracts to safeguard your interests.
– Payment Terms: Clarify payment schedules and conditions to avoid any misunderstandings later on.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement process for street-legal cheap electric vehicles with confidence, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for street legal cheap electric vehicles Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Street-Legal Cheap Electric Vehicles?
When sourcing street-legal cheap electric vehicles (EVs), understanding the cost structure is critical for B2B buyers. The primary cost components typically include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. High-quality batteries, lightweight materials for the body, and durable components for safety features can increase initial costs but may enhance longevity and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and manufacturing practices. Countries with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing; however, quality assurance should not be compromised. Skilled labor is essential for assembling complex electrical systems and safety features.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the operational costs associated with the production facility, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling is significant, particularly for custom designs or modifications. Buyers should consider the tooling costs associated with their specific requirements when negotiating prices.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous quality control processes ensures that vehicles meet safety and performance standards. While QC adds to the overall cost, it is essential for minimizing defects and ensuring compliance with local regulations.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping, customs duties, and warehousing, can add significant expenses. Buyers should factor in the logistics involved in importing vehicles, especially for international transactions.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which varies based on the competitive landscape and market demand. Understanding the average margins in the industry can provide leverage during negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors influence the pricing of street-legal cheap electric vehicles:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often lead to bulk discounts, making it more cost-effective for buyers looking to source multiple units.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized vehicles with additional features or specifications will generally incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and necessary quality certifications can influence pricing. Compliance with local regulations may require additional testing and certification, impacting overall costs.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and their own cost structures will affect pricing. Establishing relationships with reputable suppliers can lead to better terms and pricing.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can influence the final cost. Understanding who bears the risk and cost during transportation can help in budgeting accurately.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency?
International B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiation: Engage in thorough negotiations with suppliers, leveraging volume orders or long-term contracts to secure better pricing. Be prepared to discuss and understand the cost components to argue effectively.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, insurance, and operational costs over the vehicle’s lifespan. A slightly higher initial investment may lead to lower TCO through better energy efficiency and durability.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and regional market conditions that can affect pricing. Ensure that all cost factors are transparent and included in the negotiations.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Always request detailed quotations from suppliers, as prices can vary widely based on specifications, order size, and market conditions. Indicative prices may not reflect the final cost, so clarity in communication is essential.
By understanding these components and influencers, B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that balance cost with quality and compliance, ultimately leading to successful procurement of street-legal cheap electric vehicles.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing street legal cheap electric vehicles With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Street Legal Cheap Electric Vehicles
When evaluating transportation solutions for urban mobility, it’s essential to consider a range of alternatives to street legal cheap electric vehicles (EVs). These alternatives can offer distinct advantages depending on the specific needs of businesses and consumers in various markets. Below, we compare street legal cheap electric vehicles with two viable alternatives: traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and public transportation systems.
| Comparison Aspect | Street Legal Cheap Electric Vehicles | Traditional Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles | Public Transportation Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Speed: Up to 25 mph (40 km/h) | Speed: Varies, typically 30-100 mph (48-160 km/h) | Speed: Varies, generally slower in urban areas |
| Cost | Approx. $10,000 – $25,000 | Typically $15,000 – $40,000 (excluding fuel) | Low-cost per trip, monthly passes available |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires local regulations approval | Established infrastructure, less regulatory complexity | Dependent on government infrastructure investment |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, battery-based | Higher maintenance due to mechanical components | Minimal personal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Short urban commutes, eco-friendly transport | Long-distance travel, diverse driving conditions | High-density urban areas, budget-conscious commuters |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Traditional Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles?
Traditional internal combustion engine vehicles remain a popular choice for many businesses due to their established infrastructure and wide availability. They generally offer greater performance in terms of speed and distance, making them suitable for longer journeys or varied terrains. However, they come with higher fuel and maintenance costs, as well as environmental concerns related to emissions. In regions with limited charging infrastructure for electric vehicles, ICE vehicles may be more practical despite their higher operational costs.
How Does Public Transportation Compare as an Alternative?
Public transportation systems provide an economical alternative for urban mobility, especially in densely populated areas. They can significantly reduce individual transportation costs and environmental impact per passenger. However, public transport relies heavily on government investment and infrastructure, which can be lacking in certain regions. Additionally, public transport may not offer the convenience or flexibility that personal vehicles provide, often requiring users to adhere to fixed schedules and routes.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Transportation Solution?
For B2B buyers, the decision to invest in street legal cheap electric vehicles versus alternatives hinges on several factors, including operational costs, the target market, and local infrastructure. Buyers should assess the specific use case for their transportation needs—whether it be short urban commutes, long-distance travel, or mass transit solutions. By evaluating performance, cost-effectiveness, and ease of implementation, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals and sustainability objectives. Understanding local regulations and market conditions will further aid in selecting the most suitable transportation solution for their specific context.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for street legal cheap electric vehicles
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Street Legal Cheap Electric Vehicles?
Understanding the essential technical specifications of street-legal cheap electric vehicles (EVs) is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those looking to make informed decisions for fleet management or retail purposes. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
1. Top Speed and Power Output
Street-legal cheap electric vehicles typically have a maximum speed of 20-25 mph (32-40 km/h). This speed is significant because it aligns with regulations governing low-speed vehicles (LSVs) in many jurisdictions. Buyers should ensure that the vehicle can perform adequately in urban settings where such speed limits apply, making it suitable for short commutes and localized transport.
2. Battery Capacity and Range
Battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), determines the distance an EV can travel on a single charge. Common capacities for street-legal electric vehicles range from 10 kWh to 20 kWh, offering a range of approximately 40 to 80 miles (64 to 128 km). For B2B buyers, understanding battery technology is crucial to assess lifecycle costs, charging infrastructure needs, and potential downtime due to charging.
3. Safety Features
Safety features in street-legal EVs include seat belts, headlights, turn signals, and occupant protection systems (OPS) that meet federal safety standards. Compliance with these standards not only ensures the safety of passengers but also protects businesses from liability issues. Buyers should prioritize vehicles that exceed basic safety requirements, particularly in regions where regulatory scrutiny is higher.
4. Material Composition
The materials used in the construction of street-legal electric vehicles impact durability, weight, and overall performance. Common materials include high-strength steel and lightweight composites. Understanding material specifications is vital for B2B buyers as it affects vehicle longevity, maintenance costs, and operational efficiency. Lightweight vehicles can enhance range and performance, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
5. Charging Time and Compatibility
Charging time is a critical consideration, with most street-legal EVs taking anywhere from 4 to 8 hours for a full charge using standard home chargers. Compatibility with various charging systems (Level 1 and Level 2) can influence operational logistics and convenience. B2B buyers should evaluate the charging infrastructure available in their regions to ensure efficient fleet operations.
6. Payload Capacity
Payload capacity indicates how much weight the vehicle can carry, which is particularly important for businesses needing to transport goods or multiple passengers. Many street-legal EVs have a payload capacity ranging from 1,000 to 1,500 pounds (450 to 680 kg). Buyers should assess their specific transportation needs to select vehicles that can handle their operational requirements.
What Are Common Trade Terminologies Used in the Street Legal Electric Vehicle Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and facilitate smoother transactions for B2B buyers. Here are some essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components or vehicles that are sold under another company’s brand name. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers looking to source parts or collaborate on vehicle modifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ signifies the smallest order quantity that a supplier is willing to accept. For buyers, knowing the MOQ helps in budgeting and planning inventory levels, especially when dealing with vehicle fleets.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price proposals from suppliers. Buyers should prepare detailed RFQs to ensure they receive accurate pricing and terms from manufacturers, which can aid in budget planning and supplier selection.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international shipping terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the transportation of goods. Understanding these terms helps buyers navigate logistics and ensure compliance with international trade regulations.
5. Homologation
Homologation refers to the certification process that ensures a vehicle meets local regulatory standards. Buyers should verify that the vehicles they intend to purchase have undergone proper homologation to avoid legal issues and ensure roadworthiness.
6. Aftermarket
This term relates to products and services available after the initial sale of a vehicle, such as accessories or parts. Understanding the aftermarket landscape can provide buyers with options for vehicle customization and maintenance, enhancing the longevity and functionality of their investments.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, optimizing their investment in street-legal cheap electric vehicles.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the street legal cheap electric vehicles Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Street Legal Cheap Electric Vehicles Sector?
The street legal cheap electric vehicles (EVs) sector is witnessing significant growth driven by increasing urbanization, rising fuel prices, and a global shift towards sustainability. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are keenly exploring the potential of low-speed vehicles (LSVs) as an alternative to traditional vehicles. The demand for cost-effective transportation solutions is escalating, with micro-EVs emerging as a viable choice for last-mile connectivity and urban commuting.
Key trends include the integration of advanced technologies such as smart connectivity features, which enhance user experience and vehicle efficiency. Buyers are increasingly looking for vehicles equipped with IoT capabilities that allow for fleet management and real-time monitoring, thus improving operational efficiency. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on safety regulations is leading manufacturers to prioritize compliance with international standards, which is crucial for B2B buyers looking to ensure product reliability and customer satisfaction.
The market is also influenced by governmental incentives aimed at promoting electric mobility. Countries in Africa and South America are beginning to implement tax breaks and subsidies for electric vehicles, creating a more favorable purchasing environment for B2B buyers. As the market evolves, it is essential for businesses to stay informed about local regulations and incentives to make informed sourcing decisions.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Street Legal Cheap Electric Vehicles Industry?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the street legal cheap electric vehicles sector, as stakeholders increasingly prioritize eco-friendly practices in their operations. The environmental impact of electric vehicles is significantly lower than that of traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, particularly when considering the lifecycle emissions associated with manufacturing and end-of-life disposal. For international B2B buyers, aligning with manufacturers that prioritize sustainable practices can enhance brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Ethical sourcing is equally critical, especially in regions where supply chains may be challenged by labor issues or environmental concerns. Buyers should seek suppliers that demonstrate transparency in their sourcing practices and adhere to established ethical standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade certifications can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices.
Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials, such as recycled plastics and sustainably sourced metals, is becoming increasingly prevalent in the manufacturing of street legal EVs. By choosing suppliers that utilize these materials, B2B buyers can contribute to a circular economy while also meeting regulatory requirements for sustainability.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Street Legal Cheap Electric Vehicles?
The evolution of street legal cheap electric vehicles can be traced back to the late 1990s, when low-speed vehicles began to gain traction in the U.S. market as an eco-friendly alternative for short-distance travel. Initially, these vehicles catered primarily to niche markets, such as golf courses and gated communities. However, advancements in battery technology and growing environmental awareness have propelled their adoption into broader urban settings.
By the early 2000s, manufacturers began to innovate, producing electric carts that met federal safety standards, allowing them to be classified as street legal. This marked a significant turning point, as electric vehicles transitioned from being perceived as mere novelty items to becoming integral components of urban transportation solutions. In recent years, the market has expanded globally, with manufacturers targeting emerging markets in Africa and South America, where affordable and sustainable transportation solutions are in high demand.
As the industry continues to evolve, the focus on technological integration and sustainability will shape its future, presenting new opportunities for B2B buyers looking to invest in innovative transportation solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of street legal cheap electric vehicles
-
How do I ensure the street-legal status of an electric vehicle before purchase?
To verify the street-legal status of an electric vehicle, you should review the manufacturer’s compliance with local regulations and federal safety standards specific to low-speed vehicles (LSVs). Look for certifications that demonstrate adherence to safety features such as seat belts, headlights, and speed limits. It’s also wise to consult local transportation authorities or legal experts in the region where you intend to operate the vehicle. Conducting thorough due diligence can prevent potential legal issues and ensure that the vehicle meets your operational requirements. -
What is the best type of street-legal electric vehicle for urban environments?
For urban settings, compact electric vehicles (EVs) or low-speed vehicles (LSVs) are ideal due to their maneuverability and ability to navigate congested areas. Models like GEM or Eli ZERO, which are designed for short trips and have a maximum speed of around 25 mph, are well-suited for city driving. Additionally, consider vehicles that offer features such as enclosed cabs and efficient energy usage, as these enhance comfort and sustainability in densely populated environments. -
What customization options are typically available for street-legal electric vehicles?
Customization options for street-legal electric vehicles can vary by manufacturer but often include features like upgraded seating, additional safety equipment, and aesthetic modifications such as color choices. Some manufacturers also offer technology enhancements, such as GPS navigation, solar panel installations, and climate control systems. It’s beneficial to discuss customization possibilities with suppliers upfront to ensure your vehicle meets specific operational needs and branding requirements. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for purchasing street-legal electric vehicles?
Minimum order quantities can differ significantly among manufacturers and suppliers. Typically, MOQs may range from one unit for small-scale buyers to larger quantities for wholesale purchases. For international buyers, negotiating MOQs is often possible, especially if you are considering a long-term partnership. Always confirm with suppliers about any potential discounts for bulk orders, as this can lead to significant cost savings. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing street-legal electric vehicles?
Payment terms for purchasing street-legal electric vehicles can vary widely based on the supplier and the size of the order. Common arrangements include full upfront payment, partial deposits with the remainder due upon delivery, or installment plans. It’s crucial to clarify payment methods, currency, and any potential fees associated with international transactions. Additionally, consider negotiating terms that offer buyer protection, such as escrow services, to safeguard your investment. -
How can I effectively vet suppliers of street-legal electric vehicles?
To vet suppliers, start by conducting thorough research on their industry reputation, years in business, and customer reviews. Request references from previous clients and assess their responsiveness and willingness to provide detailed product information. Additionally, verify their compliance with international standards and regulations governing street-legal vehicles. A visit to their manufacturing facility, if feasible, can also provide insights into their production processes and quality control measures. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international shipping of electric vehicles?
When planning for international shipping of electric vehicles, consider factors such as shipping methods (containerized vs. roll-on/roll-off), customs regulations, and import duties that may apply in your country. Partnering with logistics companies experienced in handling automotive shipments can streamline the process. Also, ensure that your vehicles are adequately insured during transit and that you have all necessary documentation, including bills of lading and import permits, to facilitate a smooth delivery. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for when sourcing street-legal electric vehicles?
Quality assurance measures can include certifications from recognized automotive safety organizations and adherence to international manufacturing standards. Review the supplier’s quality control processes, including inspections during production and pre-shipment checks. Request information on warranty terms and after-sales support, as these factors can significantly impact the overall value and reliability of the vehicles. Establishing clear quality expectations upfront can help ensure that the vehicles meet your operational standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 3 Street Legal Cheap Electric Vehicles Manufacturers & Suppliers List
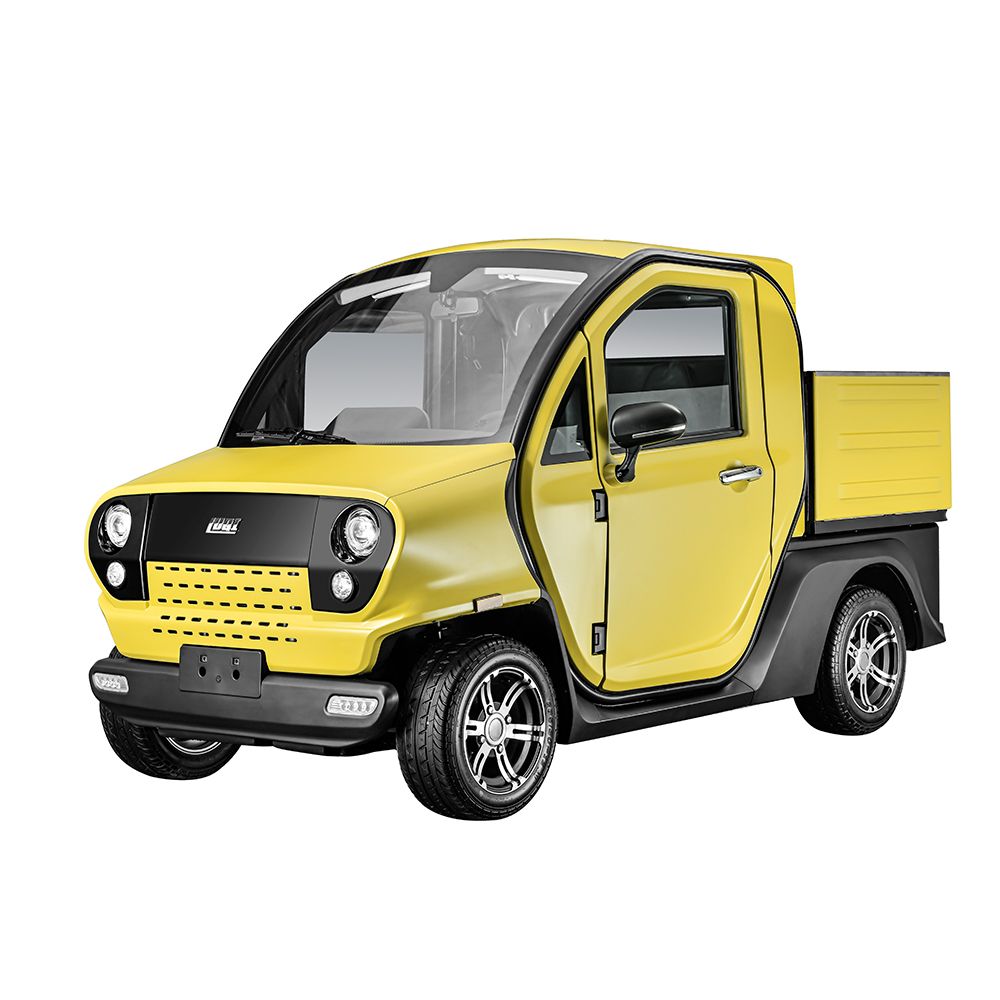
1. Gemcar – Street-Legal Electric Carts
Domain: gemcar.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Street-Legal Electric Carts are designed for on-road driving with a speed of up to 25 mph (40 km/h). They include features such as:
– Occupant protection system (OPS) certified to SAE J2358 standards
– Optional full doors for a fully enclosed cab
– Standard safety features: 3-point seat belts, headlights, tail lights, brake lights, parking brake, turn signals, backup camera, horn, reflectors, m…
2. Eli Zero – All-Electric Two-Seater
Domain: electrek.co
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Eli Zero: All-electric two-seater, expected in US market soon, designed as LSV, compliant with Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards and CARB requirements, pre-order program launching, pricing not announced but costs around €14,000 (approx. US $15,000) in Europe. Wink Motors: Four models homologated for street-legal use in US, budget models Sprout and Sprout Solar under US $10,000, premium models…
3. Dach – Apollo, Falcon 2+2; Tomberlin – Shadowhawk
Domain: southjerseyev.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: 2025 Dach Apollo – $12,995
2025 Dach Falcon 2+2 – $9,995
2025 Tomberlin Shadowhawk – $23,995
Electric and gas-powered golf carts
Gas-powered utility task vehicles (UTVs)
Industrial and commercial vehicles
Custom and reconditioned vehicles
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for street legal cheap electric vehicles
As the demand for eco-friendly transportation solutions grows globally, the strategic sourcing of street-legal cheap electric vehicles presents significant opportunities for B2B buyers. These vehicles, designed for urban environments and compliant with safety regulations, provide an affordable alternative to traditional vehicles, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key takeaways include the importance of ensuring compliance with local regulations, understanding the unique features that differentiate street-legal electric vehicles from low-speed vehicles, and recognizing the potential for cost savings through bulk purchasing and local partnerships.
Investing in these innovative vehicles not only aligns with sustainability goals but also addresses the increasing urban mobility challenges faced by many communities. As international markets continue to embrace electric mobility, B2B buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize safety, efficiency, and affordability in their designs.
Looking ahead, the landscape for street-legal electric vehicles is poised for expansion, with growing consumer interest and government incentives likely to drive demand. Now is the time for international buyers to engage with suppliers and capitalize on this transformative shift in transportation. Together, we can pave the way for a greener future and unlock new avenues for business growth.