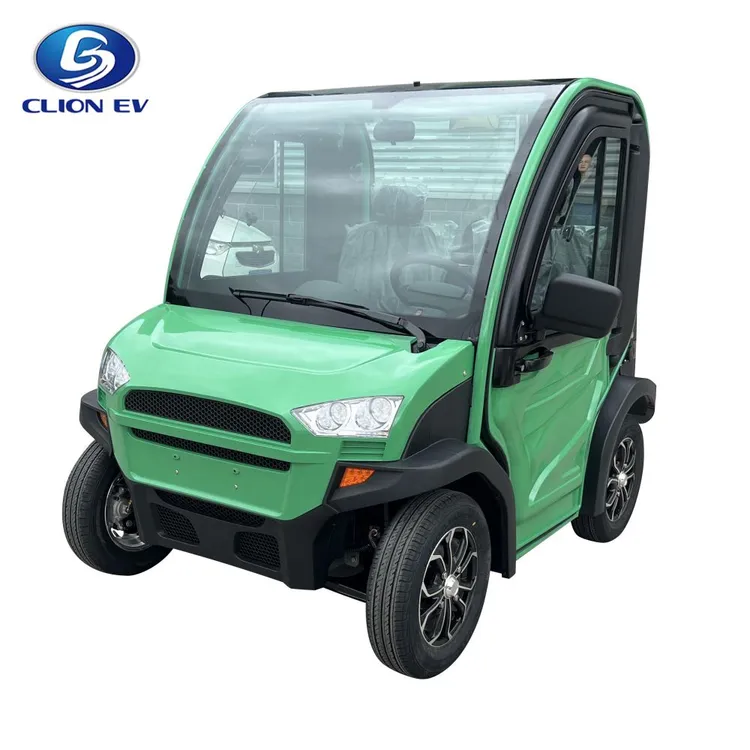
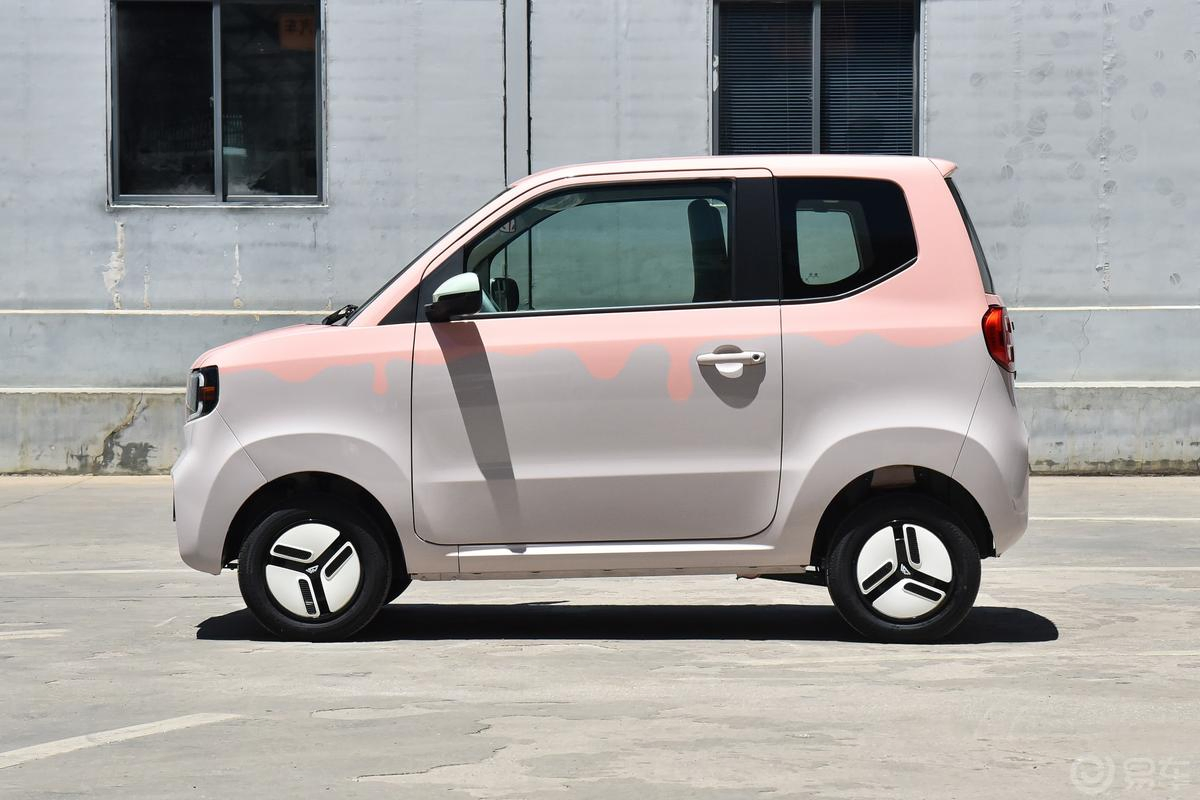
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for enclosed electric vehicle
In the rapidly evolving landscape of transportation, sourcing an enclosed electric vehicle (EEV) that meets diverse operational needs presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With increasing urbanization and a growing emphasis on sustainability, businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must navigate a complex market filled with various options, ranging from lightweight electric tricycles to compact electric cars. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of enclosed electric vehicles, covering essential types, innovative applications, supplier vetting criteria, and cost considerations.
By addressing critical questions around performance, safety, and environmental impact, this resource empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals and sustainability commitments. With insights tailored specifically for regions such as Nigeria and Vietnam, this guide provides actionable strategies to identify reliable suppliers and select vehicles that enhance efficiency and reduce total cost of ownership. As businesses strive to meet evolving consumer expectations and regulatory demands, understanding the dynamics of the EEV market becomes imperative.
Equip your organization with the knowledge to confidently invest in the future of transportation, leveraging enclosed electric vehicles to drive productivity and sustainability in your operations.
Understanding enclosed electric vehicle Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomous Balancing EV | Self-balancing technology, compact design, high efficiency | Urban commuting, delivery services, rental fleets | Pros: High stability, reduced operational costs. Cons: Limited cargo space compared to larger vehicles. |
| Low-Speed Electric Vehicle | Street-legal, designed for local travel, safety features | Campus transport, urban logistics, maintenance fleets | Pros: Cost-effective, eco-friendly. Cons: Limited speed and range compared to traditional vehicles. |
| Enclosed Electric Tricycle | Lightweight, weatherproof, pedal assist, compact for urban use | Last-mile delivery, urban commuting, shared mobility | Pros: Easy maneuverability, lower operating costs. Cons: Limited passenger capacity. |
| Electric Utility Vehicle | High payload capacity, built for durability, versatile design | Municipal services, maintenance, construction sites | Pros: Versatile, can handle heavy loads. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Electric Shuttle Vehicle | Spacious, designed for passenger transport, eco-friendly | Public transport, corporate shuttles, events | Pros: Comfortable for passengers, sustainable. Cons: Requires infrastructure for charging and maintenance. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Autonomous Balancing Electric Vehicles?
Autonomous balancing electric vehicles (ABEVs) combine the maneuverability of motorcycles with the safety of cars, featuring self-balancing technology. They are ideal for urban environments where space is limited, making them suitable for ride-sharing and delivery services. B2B buyers should consider the vehicle’s efficiency, operational costs, and safety features, as they can significantly impact long-term expenses and customer satisfaction.
How Do Low-Speed Electric Vehicles Fit into Urban Logistics?
Low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) are designed for local streets, offering safety features that exceed typical golf carts. They are perfect for applications like campus transport and urban logistics, where speed limits are low. B2B buyers should evaluate their operational needs, as LSEVs provide a cost-effective solution with lower maintenance and fuel costs, although they may not be suitable for longer distances.
What Advantages Do Enclosed Electric Tricycles Offer for Last-Mile Delivery?
Enclosed electric tricycles provide a blend of e-bike efficiency and car protection, making them ideal for last-mile delivery in urban areas. With features like weatherproofing and pedal assist, they are designed for comfort and convenience. For businesses, the lightweight design and lower operating costs are attractive, but the limited passenger capacity may restrict their use for larger deliveries.
Why Are Electric Utility Vehicles Essential for Municipal Services?
Electric utility vehicles (EUVs) are built for durability and can handle substantial payloads, making them essential for municipal services and maintenance operations. Their versatility allows them to perform various tasks, from waste collection to street maintenance. B2B buyers should weigh the initial investment against the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance, as these vehicles can significantly enhance operational efficiency.
How Can Electric Shuttle Vehicles Transform Public Transport?
Electric shuttle vehicles are spacious and designed for passenger transport, making them suitable for public transport, corporate shuttles, and events. They contribute to sustainability goals by reducing emissions and providing a comfortable travel experience. B2B buyers must consider the necessary infrastructure for charging and maintenance, as well as the overall cost-effectiveness compared to traditional shuttle options.
Key Industrial Applications of enclosed electric vehicle
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of enclosed electric vehicle | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Transport | Microtransit solutions for cities | Reduces congestion, lowers emissions, and enhances mobility | Compliance with local regulations, charging infrastructure |
| Logistics and Delivery | Last-mile delivery vehicles | Increases efficiency, reduces operational costs | Payload capacity, range, and serviceability in urban settings |
| Tourism and Hospitality | Shuttle services for resorts and urban attractions | Improves guest experience while promoting sustainability | Customization options, passenger capacity, and safety features |
| Education and Campus Transit | Campus shuttles for universities and colleges | Enhances accessibility and reduces carbon footprint | Safety certifications, range for campus size, and maintenance support |
| Emergency Services | Rapid response vehicles for local authorities | Ensures timely assistance and enhances public safety | Durability, all-weather capability, and quick charging options |
How Are Enclosed Electric Vehicles Used in Urban Transport?
Enclosed electric vehicles are increasingly utilized in microtransit solutions within urban environments, providing efficient and eco-friendly alternatives to traditional public transport. By reducing congestion and lowering emissions, these vehicles enhance mobility for residents and visitors alike. International buyers should consider local compliance requirements, charging infrastructure availability, and the vehicle’s adaptability to urban settings to ensure successful integration into existing transportation networks.
What Role Do Enclosed Electric Vehicles Play in Logistics and Delivery?
In the logistics sector, enclosed electric vehicles serve as last-mile delivery solutions, optimizing the transportation of goods in densely populated areas. Their compact size and eco-friendliness help businesses reduce operational costs while meeting consumer demand for sustainable practices. Buyers should prioritize payload capacity, range, and the vehicle’s ability to navigate urban landscapes effectively to maximize delivery efficiency.
How Can Enclosed Electric Vehicles Enhance Tourism and Hospitality Services?
Tourism and hospitality sectors are leveraging enclosed electric vehicles for shuttle services, enhancing guest experiences while promoting sustainability. These vehicles can efficiently transport guests between hotels and attractions, contributing to a greener image for resorts and urban destinations. When sourcing, businesses should focus on customization options, passenger capacity, and safety features to meet the diverse needs of travelers.
Why Are Enclosed Electric Vehicles Important for Educational Institutions?
In educational settings, enclosed electric vehicles can function as campus shuttles, providing accessible and sustainable transport for students and staff. This application not only enhances accessibility but also contributes to a reduced carbon footprint on campuses. Buyers in this sector must consider safety certifications, range capabilities suitable for campus size, and ongoing maintenance support to ensure reliable operation.
How Do Enclosed Electric Vehicles Support Emergency Services?
Enclosed electric vehicles are vital for emergency services, providing rapid response capabilities for local authorities. Their ability to navigate urban environments quickly ensures timely assistance during emergencies, enhancing public safety. When sourcing these vehicles, agencies should look for durability, all-weather capabilities, and quick charging options to maintain readiness and effectiveness in various scenarios.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘enclosed electric vehicle’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating the High Costs of Fleet Electrification
The Problem: For many businesses, transitioning to an enclosed electric vehicle (EEV) fleet presents significant upfront costs, including vehicle acquisition and infrastructure development for charging stations. This financial burden can deter companies from making the shift, especially in regions where budgets are tight, such as in parts of Africa and South America. Additionally, the potential for decreased operational efficiency during the transition phase adds to the hesitation.
The Solution: To mitigate these financial challenges, B2B buyers should consider a phased approach to electrification. Start by identifying key operations that could benefit most from EEVs, such as local deliveries or employee transportation. Look for vendors that offer financing options or leasing agreements to spread out the initial costs. Furthermore, explore partnerships with local governments or organizations that provide incentives or grants for electric vehicle adoption. Finally, consider retrofitting existing vehicles with electric drive systems as an alternative to full fleet replacement, allowing for gradual integration of EEVs while minimizing disruption.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Range Anxiety for Urban Deliveries
The Problem: A common concern among businesses considering enclosed electric vehicles is range anxiety—the fear that an EEV will not have sufficient battery life to complete a daily delivery route. This is particularly relevant in urban environments where frequent stops can drain batteries more quickly. Companies may worry about the reliability of EEVs for time-sensitive deliveries, potentially impacting customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
The Solution: B2B buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of delivery routes to understand the actual distance and frequency of stops. This data can help in selecting EEV models with a suitable range that exceeds the maximum daily distance traveled. Additionally, investing in advanced charging solutions, such as fast chargers at strategic locations along delivery routes, can alleviate range anxiety. Implementing a robust battery management system that monitors energy consumption and provides real-time updates on battery status can further enhance confidence in vehicle performance. Finally, consider integrating EEVs with route optimization software to improve efficiency and ensure that vehicles are always operating within their range capabilities.
Scenario 3: Addressing Safety and Compliance Concerns
The Problem: Safety and regulatory compliance are critical considerations for businesses looking to integrate enclosed electric vehicles into their operations. In many regions, especially in Europe and the Middle East, stringent safety standards must be met. B2B buyers may face challenges in ensuring that their EEVs are equipped with the necessary safety features, such as crash protection, visibility, and signaling devices, which can lead to liability issues and affect insurance costs.
The Solution: To address safety concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing EEVs that meet or exceed local safety regulations, including certifications from recognized authorities. Conducting thorough due diligence on manufacturers is essential—look for those with a strong track record of compliance and safety innovation. Implementing regular maintenance schedules and training programs for drivers on safe operation can further enhance safety outcomes. Additionally, consider investing in technology solutions such as collision avoidance systems and telematics that provide real-time data on vehicle performance and driver behavior. This proactive approach not only ensures compliance but also fosters a culture of safety within the organization, ultimately reducing risks and potential liabilities.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for enclosed electric vehicle
What Are the Key Materials for Enclosed Electric Vehicles?
When selecting materials for enclosed electric vehicles (EEVs), it’s essential to consider properties that influence performance, safety, and sustainability. This analysis focuses on four common materials: aluminum, high-strength steel, composite materials, and thermoplastics. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact the vehicle’s design, manufacturing process, and end-user experience.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Enclosed Electric Vehicles?
Aluminum is widely used in the automotive industry due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. With a density approximately one-third that of steel, aluminum contributes to a lighter overall vehicle weight, enhancing efficiency and range. It also has a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for structural components.
Pros: Aluminum is durable and resistant to rust, which is particularly advantageous in humid or coastal environments. Its recyclability also aligns with sustainability goals, appealing to environmentally conscious markets.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which can be higher than traditional steel. Additionally, the manufacturing processes, such as welding and forming, can be more complex and require specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it ideal for components exposed to moisture, such as body panels and frames. However, buyers should consider local availability and the potential need for specialized suppliers.
What Role Does High-Strength Steel Play in Vehicle Design?
High-strength steel (HSS) is another popular choice for EEVs, particularly for structural components that require superior strength and durability. HSS can withstand higher loads and impacts, ensuring passenger safety.
Pros: It offers excellent structural integrity and is generally more cost-effective than aluminum. HSS also allows for thinner sections, which can lead to weight savings.
Cons: While HSS is strong, it is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact vehicle range and efficiency. Additionally, it is susceptible to corrosion unless adequately treated.
Impact on Application: HSS is ideal for chassis and safety-related components. Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards, such as ASTM or JIS, to meet safety regulations.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Performance?
Composite materials, often made from a combination of fibers and resins, are gaining traction in EEV design due to their lightweight and high-strength properties. They can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Pros: Composites offer excellent corrosion resistance and can be tailored for specific performance characteristics. Their lightweight nature enhances vehicle efficiency.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be more complex and costly, requiring specialized techniques like resin transfer molding. Additionally, composites may have lower impact resistance compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for body panels and interior components where weight savings are crucial. Buyers must consider the availability of skilled labor and technology in their regions.
What Advantages Do Thermoplastics Offer for Enclosed Electric Vehicles?
Thermoplastics are increasingly being used in EEVs for various applications, including interior panels and some structural components. They are lightweight and can be easily molded into complex shapes.
Pros: Thermoplastics are cost-effective and can be recycled, making them an attractive option for sustainable vehicle design. They also have good impact resistance and can be produced in various colors and finishes.
Cons: While they offer flexibility, thermoplastics may not provide the same level of strength as metals or composites, which can limit their use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Thermoplastics are ideal for non-structural components and interior finishes. International buyers should ensure that selected materials meet local regulations for safety and environmental compliance.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Enclosed Electric Vehicles
| Material | Typical Use Case for enclosed electric vehicle | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, frames | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| High-Strength Steel | Chassis, safety components | Excellent strength and cost-effective | Heavier and corrosion-prone | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Body panels, interior components | Lightweight and customizable | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| Thermoplastics | Interior panels, non-structural components | Cost-effective and recyclable | Lower strength compared to metals | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the materials that can enhance the performance and sustainability of enclosed electric vehicles, catering to the needs of international B2B buyers across diverse markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for enclosed electric vehicle
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Enclosed Electric Vehicles?
The manufacturing process of enclosed electric vehicles (EEVs) involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets safety, performance, and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess potential suppliers and their capabilities.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Commonly Used?
The first stage in manufacturing EEVs is material preparation. Key materials typically include high-strength steel or aluminum for the chassis, composite materials for body panels, and various plastics for interior components. The selection of materials is crucial for balancing weight, safety, and cost. Advanced materials like carbon fiber may also be employed to enhance performance and durability, particularly in high-end models.
Forming: How Are Components Shaped and Molded?
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This involves processes such as stamping, bending, and molding to create the vehicle’s structural components. Techniques like hydroforming and 3D printing are becoming increasingly popular, allowing for complex shapes that traditional methods may struggle to achieve. The use of automated machinery enhances precision and reduces the risk of defects, which is vital for maintaining quality.
Assembly: What Is the Process for Bringing Components Together?
The assembly stage is where components come together to form the complete vehicle. This process typically follows a lean manufacturing approach, which minimizes waste and maximizes efficiency. Key assembly techniques include robotic welding, which ensures consistent quality, and manual assembly for intricate parts that require human oversight. Integration of electrical systems and battery packs is also performed during this stage, emphasizing the need for skilled labor and robust training programs.
Finishing: How Is the Vehicle Prepared for Market?
The final stage, finishing, encompasses painting, coating, and final inspections. This stage not only improves the vehicle’s aesthetics but also provides protection against corrosion and wear. Techniques such as powder coating and electrostatic painting are commonly used for their durability and environmental benefits. Quality assurance checks are performed throughout the finishing process to ensure compliance with safety and performance standards.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Enclosed Electric Vehicles?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of enclosed electric vehicles, ensuring that products meet international safety and performance standards. B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with key QA standards that affect their purchasing decisions.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
One of the most recognized international standards is ISO 9001, which outlines the requirements for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has effective processes in place to ensure consistent quality. Additionally, European buyers should consider CE marking, which certifies that a product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
What Industry-Specific Certifications Are Important?
For enclosed electric vehicles, industry-specific certifications such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) for electrical safety and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) standards in the U.S. are essential. These certifications ensure that vehicles are safe for public use and meet regulatory requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in EEV Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process. B2B buyers should understand these checkpoints to evaluate potential suppliers effectively.
What Are the Main QC Checkpoints?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint ensures that raw materials meet specified standards before they enter the production line. Suppliers should provide certificates of compliance or test reports for incoming materials.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC checks are performed at various stages to monitor production processes. This includes inspections of formed parts and assembly stages to identify defects early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the vehicles leave the factory, FQC involves comprehensive inspections and testing, ensuring that the finished product meets all performance and safety standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. Here are some effective strategies:
What Methods Can Be Used for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess quality control practices. Buyers should request audits that focus on the supplier’s adherence to international standards and internal QC processes. Third-party audits can also provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s capabilities.
What Documentation Should Be Requested?
Buyers should request documentation such as quality management system manuals, QC reports, and certificates of compliance for materials used. These documents provide insights into a supplier’s commitment to quality and regulatory compliance.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For buyers operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several unique QC considerations should be taken into account.
How Do Regulatory Differences Affect Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements that impact product certifications. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are compliant with local regulations, such as those set by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the U.S. or the European Union’s REACH regulations for chemical safety. Understanding these differences is crucial for avoiding compliance issues and ensuring market readiness.
What Are the Challenges in Cross-Border Quality Control?
Cross-border quality control can present challenges such as language barriers and differing standards. Buyers should establish clear communication channels and consider hiring local representatives to facilitate the QC process. Engaging with third-party inspection agencies familiar with local regulations can also mitigate risks.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Ensure Quality in Enclosed Electric Vehicles?
B2B buyers of enclosed electric vehicles must be diligent in assessing manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. By understanding the key stages of manufacturing, relevant international standards, and effective QC checkpoints, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market requirements. Engaging in thorough supplier evaluations, requesting necessary documentation, and being mindful of regional regulations will ultimately lead to better purchasing outcomes and enhanced product reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘enclosed electric vehicle’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure enclosed electric vehicles (EEVs). The growing demand for sustainable and efficient transportation solutions makes it imperative to approach this procurement strategically. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they select the right vehicle to meet their operational needs while aligning with environmental goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific requirements is crucial before initiating the sourcing process. Determine the intended use of the enclosed electric vehicle, such as urban commuting, delivery services, or utility work.
– Considerations may include:
– Range: How far the vehicle needs to travel on a single charge.
– Payload capacity: The weight the vehicle must carry.
– Speed: Compliance with local regulations for low-speed vehicles.
Step 2: Research Available Models
Familiarize yourself with the various models of enclosed electric vehicles on the market. Different manufacturers offer distinct features and technologies that can impact performance and cost.
– Key features to compare:
– Safety features: Look for vehicles with advanced safety certifications.
– Efficiency: Assess energy consumption rates and total cost of ownership.
– Comfort: Evaluate seating arrangements and weather protection.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct thorough due diligence. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies that demonstrate their experience in the enclosed electric vehicle sector.
– What to look for:
– Customer reviews and testimonials from clients in similar markets.
– Warranty offerings and after-sales support options.
– Availability of replacement parts and service capabilities.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the enclosed electric vehicles comply with local transportation regulations and safety standards. This is particularly important in regions with specific requirements for electric vehicles.
– Check for:
– Certifications like NHTSA compliance for safety standards.
– Emission standards and sustainability certifications.
– Any necessary permits for operation in your area.
Step 5: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers and models, request detailed quotes that include all associated costs. Comparing pricing will help you identify the most cost-effective options.
– Important elements to compare:
– Initial purchase price versus long-term operational costs.
– Maintenance costs and availability of incentives or rebates for electric vehicles.
– Financing options and leasing arrangements that may be available.
Step 6: Conduct a Test Drive
If possible, arrange for a test drive of the enclosed electric vehicle to assess its performance and comfort firsthand. This step is vital to ensure the vehicle meets your expectations in real-world conditions.
– Pay attention to:
– Handling and responsiveness during the drive.
– Comfort features such as seating and cabin space.
– Noise levels and ride quality, particularly in urban settings.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Establish Terms
Once you’ve made your decision, finalize the purchase by establishing clear terms with the supplier. This includes delivery timelines, payment terms, and any service agreements.
– Ensure clarity on:
– Warranty coverage and service support.
– Training for your staff on vehicle operation and maintenance.
– Return policies or satisfaction guarantees in case the vehicle does not meet expectations.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing enclosed electric vehicles, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and sustainability in their organizations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for enclosed electric vehicle Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Enclosed Electric Vehicle Sourcing?
When analyzing the cost structure of enclosed electric vehicles (EEVs), several components play a critical role. The major cost elements include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Lightweight composites and high-grade metals may enhance performance and durability but at a higher cost. Conversely, using cheaper materials could reduce upfront costs but may lead to increased maintenance and lower longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on region and skill level. Skilled labor in manufacturing EEVs can command higher wages, particularly in developed markets. This is especially relevant for intricate assembly processes requiring expertise in electric systems and vehicle safety standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these expenses, making it crucial for manufacturers to invest in automation and lean production techniques.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for customized or specialized vehicles. Buyers should consider the amortization of these costs over the expected production volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures product reliability and compliance with safety regulations. While this adds to the cost, it mitigates risks associated with product failures in the market.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can fluctuate based on the geographical location of the supplier and the buyer. International shipping, tariffs, and customs duties can significantly influence the final cost.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically apply a margin that reflects their business model, market demand, and competitive landscape. Understanding margin structures can provide buyers leverage in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Sourcing of Enclosed Electric Vehicles?
Several factors influence the pricing of enclosed electric vehicles. These include volume or minimum order quantity (MOQ), specifications and customization, materials used, quality certifications, supplier factors, and Incoterms.
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to significant discounts. Buyers should negotiate terms that take advantage of economies of scale, particularly when sourcing for fleets.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary modifications that can inflate prices.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: The choice of materials and the presence of certifications (e.g., safety, environmental standards) can affect both cost and pricing. Opting for certified suppliers may incur higher initial costs but can lead to savings in compliance and liability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge a premium but offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) affects the distribution of costs and responsibilities between buyer and seller. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage shipping and logistics costs effectively.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Enclosed Electric Vehicles?
To maximize value when sourcing enclosed electric vehicles, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing and terms. Be prepared to leverage competing offers to secure better deals.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider factors like maintenance, energy costs, and potential resale value.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Understand the economic context of your region. For instance, in markets like Africa and South America, local supply chains and currency fluctuations can significantly impact pricing.
-
Local Incentives: Research available government incentives for electric vehicles. These can lower the effective cost and improve ROI.
-
Supplier Relationships: Build long-term relationships with suppliers to enhance collaboration, secure better pricing, and ensure consistent quality.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for enclosed electric vehicles vary widely based on specifications, supplier, and market conditions. The information provided here is intended as a guideline and should be verified with suppliers for current pricing and terms. Always conduct thorough market research before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing enclosed electric vehicle With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Enclosed Electric Vehicles
In the evolving landscape of urban transportation, businesses are increasingly exploring various options to meet their mobility needs. Enclosed electric vehicles (EEVs) present a unique blend of safety, efficiency, and comfort. However, alternative solutions like electric motorcycles and low-speed electric utility vehicles (EVs) also offer compelling benefits. This section provides a comparative analysis of EEVs against these alternatives, focusing on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Enclosed Electric Vehicle | Electric Motorcycle | Low-Speed Electric Utility Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Max speed: 50 km/h; range: 150-200 km | Max speed: 160 km/h; range: 250 km | Max speed: 40 km/h; range: 80-113 km |
| Cost | $20,000 – $30,000 | $10,000 – $25,000 | $15,000 – $25,000 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure; minimal training needed | Requires basic motorcycle training; charging stations needed | Generally easy to implement; compatible with standard outlets |
| Maintenance | Moderate (battery replacement, parts availability) | Low (fewer moving parts) | Low to moderate (simple design, parts availability) |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting, delivery services in all weather | Long-distance travel, thrill-seeking riders | Short-distance transport in urban settings, microtransit solutions |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Motorcycles?
Electric motorcycles are a lightweight and agile alternative, ideal for riders who prioritize speed and range. With maximum speeds reaching up to 160 km/h and a range of 250 km, they cater well to long-distance travel. However, they require motorcycle training for safe operation, which may present a barrier for some users. Additionally, while they have lower initial costs compared to EEVs, they lack the enclosed safety features and storage capacity that enclosed vehicles offer.
How Do Low-Speed Electric Utility Vehicles Compare?
Low-speed electric utility vehicles, such as those from GEM, are specifically designed for urban environments, offering speeds up to 40 km/h and a range of 80-113 km. They excel in short-distance transport and are often used for campus, resort, or municipal purposes. The cost is competitive, and they are easy to implement due to their compatibility with existing infrastructure. However, their limited speed and range may not make them suitable for longer commutes or deliveries, potentially restricting their use cases compared to enclosed electric vehicles.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Selecting the right transportation solution depends heavily on specific business needs and operational contexts. For organizations focused on all-weather safety and comfort, enclosed electric vehicles provide unparalleled protection and efficiency. Conversely, businesses prioritizing speed and lower costs may find electric motorcycles suitable, while those needing a flexible solution for local transport might opt for low-speed electric utility vehicles. Ultimately, evaluating factors like budget, intended use, and operational requirements will guide B2B buyers to the most appropriate vehicle for their unique circumstances.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for enclosed electric vehicle
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Enclosed Electric Vehicles?
Understanding the technical specifications of enclosed electric vehicles (EEVs) is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed procurement decisions. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade: The materials used in the construction of EEVs significantly impact durability, weight, and cost. Common materials include high-strength steel, aluminum, and composites. Each material offers varying levels of strength-to-weight ratios, which are essential for achieving efficiency and safety in electric vehicles. For example, aluminum provides a lightweight solution while maintaining structural integrity, which is vital for maximizing battery efficiency and overall performance.
-
Battery Capacity (kWh): Battery capacity directly affects the range and performance of an EEV. Measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), this specification indicates how much energy the battery can store. A higher capacity allows for longer ranges between charges, which is particularly important for commercial applications where downtime must be minimized. When sourcing EEVs, understanding the battery technology and its lifespan can lead to better lifecycle cost management.
-
Payload Capacity: This specification defines the maximum weight an EEV can carry, including passengers and cargo. For businesses, knowing the payload capacity is critical for ensuring that the vehicle meets operational needs without risking safety or performance. It’s essential to consider how payload affects efficiency and battery consumption, especially in logistics and delivery applications.
-
Charging Time: The time it takes to fully charge the vehicle is a key operational factor. Quick charging options can significantly reduce downtime, making EEVs more attractive for businesses that rely on continuous use. Understanding the charging infrastructure available in your region, including fast-charging capabilities, is essential for effective fleet management.
-
Safety Features: Safety is paramount in vehicle design, especially for enclosed electric vehicles. Features such as advanced braking systems, stability controls, and crash protection mechanisms are vital. These specifications not only comply with regulatory standards but also enhance driver and passenger safety, which can reduce liability for businesses.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Enclosed Electric Vehicle Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are some key terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of EEVs, OEMs are crucial for ensuring that the vehicle components meet quality and performance standards. Businesses should consider sourcing from reputable OEMs to maintain consistency and reliability in their fleet.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ indicates the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, particularly for businesses looking to scale their fleet quickly. It can also influence negotiation strategies when engaging with suppliers.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing for specific products or services. In the EEV market, submitting an RFQ can help businesses compare costs and features across different suppliers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps businesses understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, which is vital when importing EEVs or their components.
-
Lifecycle Cost: This term refers to the total cost of ownership over the life of the vehicle, including purchase price, maintenance, fuel, and disposal. Understanding lifecycle costs is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to optimize their investments and achieve long-term savings.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the enclosed electric vehicle market more effectively, ensuring they make strategic decisions that align with their operational goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the enclosed electric vehicle Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Enclosed Electric Vehicle Market?
The enclosed electric vehicle (EEV) sector is witnessing significant growth, driven by multiple global trends. Urbanization is accelerating, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, and parts of Europe, leading to increased demand for sustainable, efficient transportation solutions. Innovations in battery technology are enhancing vehicle performance, with ranges improving to meet the needs of urban commuters. Furthermore, regulatory support for electric vehicles is strengthening, with governments offering incentives for low-emission vehicles.
International B2B buyers are also focusing on the cost-effectiveness of EEVs, as these vehicles typically boast lower operational costs compared to traditional vehicles. Emerging technologies such as autonomous driving capabilities and smart connectivity are becoming essential features that enhance the appeal of EEVs. Additionally, trends towards shared mobility solutions are reshaping the market, with businesses looking to integrate EEVs into their fleets for ride-sharing and micro-transit services.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Relationships in the EEV Sector?
Sustainability is a critical concern for B2B buyers in the enclosed electric vehicle market. The environmental impact of sourcing materials and manufacturing processes can significantly influence purchasing decisions. Businesses are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, which include using recycled materials, minimizing waste, and implementing energy-efficient production methods.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as companies strive to ensure that their supply chains are free from exploitation and environmental degradation. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to local labor laws are becoming standard requirements for suppliers. B2B buyers are encouraged to seek partners who can provide transparency in their sourcing practices, showcasing their commitment to sustainability. This not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
What Is the Historical Context of Enclosed Electric Vehicles?
The evolution of enclosed electric vehicles can be traced back to the early 21st century when advancements in electric propulsion technology began to gain traction. Initially, electric vehicles were largely limited to compact cars and scooters, but the need for more versatile and comfortable urban transportation solutions led to the development of enclosed models.
As cities became congested and air quality concerns intensified, the demand for EEVs surged. Manufacturers began to innovate with designs that combined the benefits of traditional vehicles with the efficiency of electric powertrains. Today, the market features a diverse range of options, including electric motorcycles, tricycles, and compact utility vehicles, all designed to meet the unique needs of urban environments. The ongoing focus on sustainability and technological advancements continues to shape the future of the EEV sector, making it a compelling area for international B2B buyers to explore.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of enclosed electric vehicle
-
How do I choose the right enclosed electric vehicle for my business needs?
Selecting the right enclosed electric vehicle (EEV) involves assessing your specific operational requirements. Consider factors like payload capacity, range, speed, and intended use—whether for transportation, delivery, or utility tasks. Evaluate the vehicle’s energy efficiency and maintenance costs, as these will significantly impact your total cost of ownership. Additionally, analyze the vehicle’s safety features, especially if it will be used in urban areas. Finally, consult with suppliers to understand customization options that can cater to your unique business needs. -
What are the advantages of investing in enclosed electric vehicles for my fleet?
Enclosed electric vehicles offer numerous benefits, including reduced operational costs due to lower energy consumption compared to traditional vehicles. They are environmentally friendly, aligning with sustainability goals by producing zero emissions. Additionally, EEVs provide comfort and safety for drivers and passengers, ensuring a reliable transport solution in various weather conditions. Investing in EEVs can also enhance your brand image as a forward-thinking, eco-conscious organization, potentially attracting customers who prioritize sustainability. -
What customization options are available for enclosed electric vehicles?
Customization options for enclosed electric vehicles can vary by manufacturer but typically include modifications to size, color, and interior layout. You may also request specific features such as enhanced battery packs for extended range, cargo management systems, or advanced safety technologies. Some manufacturers offer specialized designs tailored for particular industries, such as healthcare or logistics. It’s crucial to discuss your requirements with potential suppliers early in the sourcing process to ensure they can meet your specifications. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) when sourcing enclosed electric vehicles?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the specific model of the enclosed electric vehicle. Some manufacturers may have an MOQ of as few as 5-10 units, while others might require larger orders to optimize production efficiency and pricing. For B2B buyers, it’s essential to communicate your needs upfront and inquire about potential bulk discounts, as larger orders can often yield more favorable pricing and terms. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing enclosed electric vehicles internationally?
Payment terms can differ based on the supplier and the nature of your business relationship. Common practices include a deposit upfront (typically 20-30%) with the remaining balance due upon delivery or prior to shipping. Some suppliers may offer financing options or installment plans for larger orders. It’s advisable to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, letter of credit) and ensure compliance with international trade regulations to avoid any financial discrepancies. -
How can I vet suppliers of enclosed electric vehicles for reliability?
To vet suppliers effectively, start by reviewing their industry experience and reputation. Look for certifications and compliance with international safety and quality standards. Request references from previous clients to gauge customer satisfaction and reliability. Additionally, consider visiting the manufacturing facilities if feasible, or conducting virtual audits to assess their production capabilities. Engaging in trade shows or industry events can also provide insights into potential suppliers’ reputations and product offerings. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from enclosed electric vehicle suppliers?
Reputable suppliers should have a comprehensive quality assurance (QA) process in place, including inspections at various stages of production. Look for suppliers that provide documentation on their QA protocols, such as ISO certifications or adherence to specific automotive safety standards. It’s also beneficial to inquire about warranties and after-sales support, as these can reflect the supplier’s confidence in their product quality and commitment to customer satisfaction. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing enclosed electric vehicles?
When importing enclosed electric vehicles, consider shipping methods, costs, and estimated delivery times. Work with logistics partners familiar with automotive imports to navigate customs regulations effectively. Ensure that all necessary documentation, such as import permits and compliance certifications, is prepared in advance to prevent delays. Additionally, evaluate the total landed cost, including duties, taxes, and handling fees, to accurately assess your budget for the purchase.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Enclosed Electric Vehicle Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. GemCar – Automotive Software Solution
Domain: gemcar.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: GemCar is a comprehensive software solution designed for the automotive industry, offering features such as inventory management, customer relationship management (CRM), point of sale (POS), and reporting tools. It aims to streamline operations for car dealerships and service centers, enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction.
2. Veemo – Lightweight Electric Vehicle
Domain: veemo.ca
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Veemo is a lightweight, fully-enclosed electric vehicle designed for urban travel, combining the efficiency of an e-bike with the comfort of a car. Key specifications include: Max Speed: 32 KM/H (20MPH), Range: 30 – 100 KM (19 – 62 miles), Payload Capacity: 159 KG (350 lbs), Weight: 61 KG (135 lbs), Max Power: 750W / 500W / 250W (software limited). Features include all-weather resilience, user-cen…
3. Moto Electric Vehicles – Customizable Small Electric Utility Vehicles
Domain: motoelectricvehicles.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Moto Electric Vehicles offers a range of small electric utility vehicles designed for commercial work applications. Key features include:
– Customizable options such as special seating, custom paint jobs, enhanced rims & wheels, industrial designs, security accessories, optional light kits, premium audio, wheelchair ramps, cargo boxes, hydraulic dump beds, weather enclosures, and back-up cameras….
4. ZEV – T3-1 Micro Enclosed Trike
Domain: zelectricvehicle.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: ZEV T3-1 Micro Enclosed Trike
– Type: Motorcycle-sized vehicle, legal to drive on the street
– Dimensions: 2380 mm L x 1200 mm W x 1585 mm H
– Wheelbase: 1620 mm
– Weight: 390 Kg (863 lbs) empty, 615 Kg (1359 lbs) gross vehicle weight
– Payload Capacity: 225 Kg (496 lbs)
– Rear Cargo Area: 1300 mm L x 900 mm W (35 inches L x 35 inches W), weight capacity 194 Kg (360 lbs)
– Seating: 2-3 adults, 35-…
5. GIO – All-Season Enclosed Mobility Scooter
Domain: giomobility.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: {‘name’: ‘GIO All-Season Enclosed Mobility Scooter’, ‘color’: ‘Blue’, ‘price’: ‘$5,795 USD’, ‘shipping’: ‘Free shipping, no USA sales tax, no tariffs’, ‘top_speed’: ‘Up to 18mph’, ‘range’: ’30 miles’, ‘full_recharge_time’: ‘8-10 hours’, ‘weight_capacity’: ‘500 lbs’, ‘weight’: ‘670 lbs’, ‘dimensions’: {‘exterior’: {‘length’: ’79 inches’, ‘width’: ’53 inches’, ‘height’: ’62 inches’}, ‘interior’: {‘l…
6. Matrix EV – Electric Car
Domain: ridethewindebikes.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Electric Car by Matrix EV features a sleek design, advanced electric drivetrain, spacious interior, and eco-friendly performance. It is equipped with state-of-the-art technology, including a digital dashboard, regenerative braking, and a long-range battery. The car offers a comfortable ride with ample cargo space and safety features such as airbags and stability control. Ideal for urban commuting …
7. Facebook – Self-Balancing Electric Motorcycle
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: self-balancing, fully-enclosed electric motorcycle
8. ScooterCarZ – Electric Low Speed Vehicles
Domain: scootercarz.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: ScooterCarZ offers a range of Electric Low Speed Vehicles (LSVs) designed for economical and fun transportation. Key features include: headlights, taillights, blinkers, 4-way flashers, low speed vehicle light, keyless entry, backup camera, windshield wipers, lithium batteries, and a stereo/MP3 player. The vehicles can be charged using a standard 110 outlet and can be outfitted with a photovoltaic …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for enclosed electric vehicle
In the rapidly evolving landscape of enclosed electric vehicles (EEVs), strategic sourcing emerges as a vital component for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the diverse offerings—ranging from self-balancing two-wheelers like Lit Motors’ AEV to compact utility vehicles from GEM and the versatile Veemo e-trikes—allows businesses to tailor their fleets to meet specific operational needs.
Key takeaways include the importance of sustainability and cost-efficiency, as these vehicles often present lower total ownership costs and reduce carbon footprints. Additionally, the emphasis on safety features and regulatory compliance is crucial for ensuring consumer confidence and operational legality in various regions.
As the demand for eco-friendly transportation solutions grows, investing in EEVs not only supports environmental goals but also positions businesses to capitalize on emerging trends in urban mobility. Now is the time for international buyers to engage with manufacturers and suppliers, exploring innovative solutions that will drive the future of transport. Embrace this opportunity to lead in sustainability and efficiency—your journey towards a greener, more profitable future begins today.