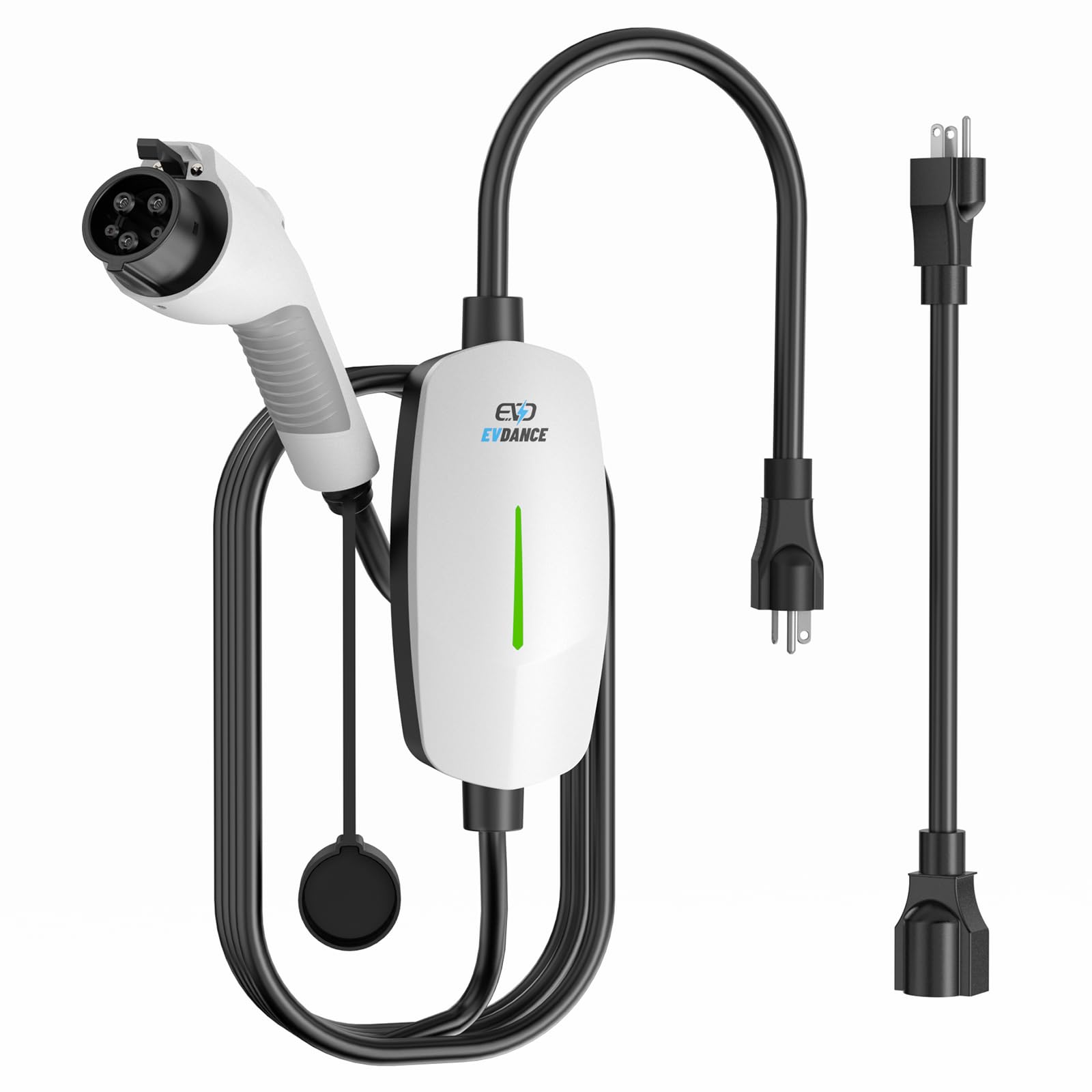
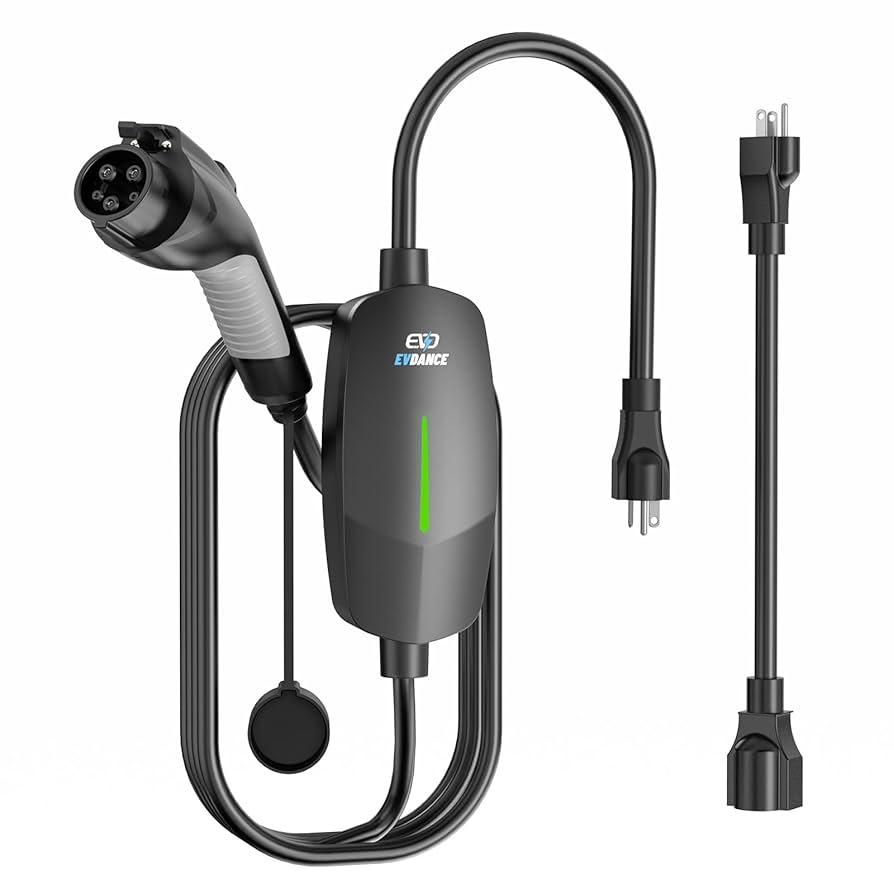
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger
Navigating the complexities of sourcing affordable and effective electric vehicle (EV) chargers can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets like Africa and South America. With the rapid growth of the EV market, understanding the diverse range of products available—from Level 1 to Level 3 chargers—has become essential. This guide delves into the various types of EV chargers, their applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting, providing actionable insights into cost considerations and installation requirements.
As businesses across the globe pivot towards sustainability, the demand for cost-effective charging solutions is surging. Buyers will benefit from detailed analysis on features, pricing, and supplier reliability, enabling them to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. This guide specifically caters to the unique challenges faced by companies in regions like the Middle East and Europe, including Germany and Brazil, where varying infrastructure and regulatory landscapes can impact purchasing choices.
By equipping B2B buyers with essential knowledge about the EV charging market, this guide empowers them to identify the best products and suppliers that not only meet their cost criteria but also ensure performance and reliability. Embrace the transition to electric mobility with confidence, informed by the insights contained within this comprehensive resource.
Understanding cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 Charger | 120-volt, standard outlet, slow charging (1.4 kW) | Small businesses, home use, low-demand environments | Pros: Low cost, easy installation. Cons: Slow charge, not suitable for fast-paced operations. |
| Level 2 Charger | 240-volt, faster charging (up to 19 kW) | Commercial fleets, multi-unit residential, workplaces | Pros: Faster charging, versatile installation options. Cons: Higher initial cost, may require electrical upgrades. |
| DC Fast Charger | 400-800 volts, ultra-fast charging (up to 350 kW) | Public charging stations, fleet operations | Pros: Rapid charging, ideal for high-traffic areas. Cons: High installation and equipment costs. |
| Smart Charger | Load management, Wi-Fi connectivity, app-controlled | Commercial and residential use, energy management | Pros: Optimizes energy use, remote monitoring. Cons: Potentially higher upfront costs, reliance on internet connectivity. |
| Multi-vehicle Charger | Dual charging ports, simultaneous charging capability | Parking lots, commercial fleets, car rental services | Pros: Efficient for multiple vehicles, space-saving. Cons: Higher cost, may require robust electrical setup. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Level 1 Chargers for B2B Buyers?
Level 1 chargers utilize a standard 120-volt outlet, making them the most basic option for EV charging. They deliver a slow charge, typically around 1.4 kW, which is suitable for low-demand environments such as small businesses or home use. B2B buyers should consider the low installation costs and ease of use, but they must also be aware that the slow charging speed may not meet the needs of high-traffic operations or commercial fleets.
How Do Level 2 Chargers Benefit Businesses?
Level 2 chargers operate on a 240-volt supply and can deliver charging speeds of up to 19 kW, making them ideal for commercial fleets, multi-unit residential buildings, and workplaces. They offer a balance between cost and efficiency, allowing vehicles to charge overnight or during work hours. While the initial investment may be higher, the benefits of faster charging and versatility in installation make them a popular choice among B2B buyers.
Why Choose DC Fast Chargers for Public Applications?
DC Fast Chargers are designed for rapid charging, with outputs ranging from 50 to 350 kW. This type of charger is typically found in public charging stations or used by fleet operations that require quick turnaround times. Although the installation and equipment costs are significantly higher, the ability to charge vehicles in a matter of minutes makes them essential for businesses looking to serve high-traffic areas effectively.
What Are the Advantages of Smart Chargers for Energy Management?
Smart chargers integrate load management features and Wi-Fi connectivity, allowing users to control charging sessions via mobile applications. These chargers are suitable for both commercial and residential applications, particularly in settings where energy management is critical. While they may come with a higher upfront cost, the long-term savings from optimized energy usage and remote monitoring capabilities make them an attractive option for B2B buyers focused on sustainability.
How Do Multi-Vehicle Chargers Support Fleet Operations?
Multi-vehicle chargers feature dual charging ports, allowing simultaneous charging of multiple EVs. This is particularly beneficial for parking lots, commercial fleets, and car rental services where space and efficiency are paramount. While they require a more robust electrical setup and come with a higher price tag, the ability to service multiple vehicles at once makes them a valuable investment for businesses looking to optimize their charging infrastructure.
Key Industrial Applications of cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Transportation | Charging stations for electric buses and taxis | Reduces operational costs and enhances sustainability efforts | Availability of fast chargers, compatibility with vehicle types, and installation requirements |
| Logistics and Delivery | Depot charging solutions for electric delivery vehicles | Increases fleet efficiency and lowers fuel costs | Power output, scalability for future growth, and charging speed are critical considerations |
| Hospitality | Charging stations at hotels and resorts | Attracts eco-conscious guests and enhances guest experience | Location suitability, integration with existing infrastructure, and user-friendly interfaces |
| Retail | EV charging points at shopping centers | Encourages longer customer stays and boosts foot traffic | Number of charging ports, payment integration, and visibility for customers |
| Manufacturing | Employee charging stations at manufacturing facilities | Improves employee satisfaction and supports corporate sustainability goals | Power capacity, safety certifications, and ease of access for employees |
How Can Cheap Electric Vehicle Chargers Benefit Public Transportation?
In the public transportation sector, cheap good price electric vehicle (EV) chargers can be deployed at bus depots and taxi ranks to facilitate the charging of electric buses and taxis. This not only reduces operational costs due to lower energy prices compared to fossil fuels but also aligns with sustainability initiatives. Buyers in this sector must consider the compatibility of chargers with various vehicle types and the availability of fast chargers to minimize downtime.
What Are the Advantages of Cheap EV Chargers in Logistics and Delivery?
For logistics and delivery companies, installing charging solutions for electric delivery vehicles at depots can significantly enhance fleet efficiency. These chargers enable vehicles to be charged overnight or during breaks, leading to lower fuel costs and a reduced carbon footprint. Key sourcing considerations include the power output of chargers to accommodate multiple vehicles and the scalability of the charging infrastructure to meet future growth.
How Do EV Chargers Enhance the Hospitality Industry?
In the hospitality sector, hotels and resorts can install cheap good price EV chargers to provide charging facilities for guests. This amenity attracts eco-conscious travelers and enhances their overall experience, potentially increasing customer loyalty. When sourcing chargers, businesses should evaluate the integration of charging stations with existing infrastructure and ensure user-friendly interfaces for guests.
What Benefits Do Retailers Gain from EV Charging Stations?
Retailers can install EV charging points at shopping centers to encourage longer customer stays and boost foot traffic. By offering charging facilities, businesses can differentiate themselves and attract a growing demographic of electric vehicle owners. Retailers should consider the number of charging ports needed, payment integration options, and the visibility of charging stations to maximize customer engagement.
How Can Manufacturing Facilities Leverage EV Chargers?
Manufacturing facilities can enhance employee satisfaction by providing charging stations for electric vehicles. This initiative supports corporate sustainability goals and can improve employee retention. Buyers in this sector should focus on the power capacity of chargers, safety certifications, and ease of access to ensure a seamless charging experience for employees.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Budget Constraints for EV Chargers
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly small to mid-sized businesses in regions like Africa and South America, face significant budget constraints when it comes to acquiring electric vehicle (EV) chargers. While the transition to electric vehicles is essential for sustainability and operational efficiency, the upfront costs of chargers can be prohibitive, especially when considering installation and infrastructure upgrades. This financial strain can delay the adoption of EV technology, hindering potential growth and competitive advantage.
The Solution: To mitigate these budgetary challenges, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing affordable yet reliable EV chargers that offer essential features without unnecessary frills. Buyers can look for options such as the Emporia EV Charger, which is priced competitively while providing robust functionalities like smart charging capabilities and load management. Additionally, leveraging government incentives and grants for EV infrastructure can significantly offset costs. Businesses should engage with local authorities or industry associations to explore available subsidies or tax credits. Lastly, negotiating bulk purchase agreements with manufacturers or suppliers can further reduce per-unit costs, making the transition to electric vehicle fleets more financially viable.
Scenario 2: Compatibility Issues with Diverse EV Models
The Problem: B2B buyers in the transportation and logistics sectors often manage a diverse fleet of electric vehicles, which may include different brands and models. This diversity can lead to compatibility issues with charging equipment, creating operational inefficiencies and downtime. For instance, chargers that only support specific connector types can limit the usability of the charging stations, frustrating drivers and increasing costs associated with maintaining multiple charging solutions.
The Solution: To address compatibility challenges, businesses should invest in versatile EV chargers that support multiple connector types, such as the J1772 and Tesla NACS standards. Chargers like the ChargePoint Home Flex, which come equipped with universal connectors, can cater to a variety of vehicle models, ensuring that the entire fleet can charge effectively without the need for multiple charging stations. Additionally, conducting a thorough assessment of the fleet’s vehicle types prior to purchasing chargers can help businesses select the most suitable equipment. Implementing a standard connector type across the fleet can also simplify the charging infrastructure, enhancing efficiency and reducing operational complexities.
Scenario 3: High Installation and Infrastructure Costs
The Problem: The costs associated with installing EV chargers can escalate quickly, especially for businesses operating in older facilities that require significant electrical upgrades. Many B2B buyers underestimate these costs, leading to budget overruns and project delays. This issue is particularly pronounced in regions with less developed electrical infrastructure, where the need for extensive modifications can deter businesses from investing in EV charging solutions altogether.
The Solution: To manage installation costs effectively, businesses should conduct a comprehensive energy audit of their facilities before purchasing EV chargers. This audit helps identify existing electrical capacity and any necessary upgrades, allowing for better planning and budgeting. Additionally, opting for Level 2 chargers, which require less intensive installation compared to DC fast chargers, can be a more economical choice for businesses that do not require rapid charging. It’s advisable to work with experienced electricians who can provide insights into cost-effective installation practices and potential alternatives, such as load management systems that optimize energy use without requiring extensive upgrades. By proactively addressing installation challenges, businesses can implement EV charging solutions without incurring excessive costs, paving the way for a smoother transition to electric mobility.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Electric Vehicle (EV) Chargers?
When selecting materials for cheap, good-price electric vehicle (EV) chargers, it’s essential to consider properties that influence performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of EV chargers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Plastic Impact the Performance of EV Chargers?
Key Properties: Plastic materials, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polycarbonate, offer excellent insulation properties and resistance to corrosion. They can withstand temperatures ranging from -40°C to 100°C, making them suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons: Plastics are lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to mold into complex shapes, which simplifies manufacturing. However, they may not be as durable as metals and can degrade under prolonged exposure to UV light unless treated.
Impact on Application: Plastic housings are often used for lightweight, portable EV chargers. They are compatible with various media, including moisture and dust, but may not withstand extreme mechanical stress.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO is crucial. Buyers should ensure that the plastic used is UL-certified for safety, especially in regions with stringent regulations, such as Europe.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in EV Charger Construction?
Key Properties: Aluminum is known for its lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity, with a melting point of around 660°C. Its corrosion resistance can be enhanced through anodization.
Pros & Cons: Aluminum is durable and can withstand outdoor conditions, making it ideal for permanent installations. However, it is more expensive than plastics and requires more complex manufacturing processes, including machining and welding.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used for the structural components of EV chargers, providing strength without adding excessive weight. It is compatible with various environmental conditions, making it suitable for outdoor installations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Aluminum must meet specific standards, such as DIN and JIS, especially in regions like Germany and Japan. Buyers should also consider the availability of aluminum in their local markets to avoid supply chain issues.
How Does Steel Compare in Terms of Durability for EV Chargers?
Key Properties: Steel, particularly stainless steel, offers high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. It can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, with a melting point exceeding 1,500°C.
Pros & Cons: Steel is highly durable and provides excellent protection for internal components. However, it is heavier and more expensive than both plastic and aluminum, and its manufacturing process can be more complex due to welding and finishing requirements.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used in the enclosures of EV chargers, providing robust protection against physical damage and environmental factors. Its compatibility with various media makes it suitable for outdoor and industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards, such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel, is vital. Buyers should also consider the local availability of steel and the associated costs of transportation.
What Advantages Does Copper Offer for Electrical Components in EV Chargers?
Key Properties: Copper is an excellent conductor of electricity, with a conductivity rating of approximately 59.6 x 10^6 S/m. It also has good thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
Pros & Cons: Copper is essential for the wiring and connectors in EV chargers, ensuring efficient energy transfer. However, it is more expensive than aluminum and can be prone to oxidation if not properly coated.
Impact on Application: Copper is used in the internal wiring and connectors of EV chargers, ensuring reliable performance and safety. Its compatibility with electrical media makes it indispensable for high-performance applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that copper components comply with international electrical standards, such as IEC 60228, to guarantee safety and performance in various markets.
Summary Table of Material Selection for EV Chargers
| Material | Typical Use Case for cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic | Housings for portable chargers | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable, UV degradation | Low |
| Aluminum | Structural components for permanent installations | Durable and corrosion-resistant | More expensive and complex to manufacture | Medium |
| Steel | Enclosures for robust protection | High strength and durability | Heavier and more expensive | High |
| Copper | Wiring and connectors for efficient energy transfer | Excellent electrical conductivity | Expensive and prone to oxidation | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with critical insights into the materials used in EV chargers, ensuring informed decisions that align with performance, cost, and compliance requirements in their respective markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Affordable Electric Vehicle Chargers?
The manufacturing of inexpensive electric vehicle (EV) chargers involves several critical stages, each designed to optimize efficiency and quality while keeping costs low. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation: Sourcing Cost-Effective Components
The first stage is material preparation, where manufacturers source raw materials such as metals, plastics, and electrical components. The goal here is to balance cost and quality. Key considerations include:
- Supplier Relationships: Manufacturers often establish long-term relationships with suppliers to secure bulk pricing on high-quality components. This can lead to significant cost savings, which can be passed on to buyers.
- Material Specifications: Standard specifications for materials used in EV chargers often include copper for wiring due to its excellent conductivity, and durable plastics for enclosures to withstand environmental factors.
- Sustainability: As the demand for eco-friendly products grows, many manufacturers are prioritizing sustainable sourcing practices.
How Are EV Chargers Formed and Assembled?
After materials are prepared, the next step involves forming and assembling the components. This process typically includes:
- Forming Techniques: Techniques such as injection molding for plastic parts and stamping for metal enclosures are commonly used. These methods allow for rapid production while maintaining dimensional accuracy.
- Component Assembly: The assembly line is a critical area where components are put together. Automated systems are increasingly used to enhance precision and speed. For instance, robotic arms may be employed for soldering circuit boards.
- Integration of Smart Features: Many affordable EV chargers now include smart technology for remote monitoring and control. Integrating these features during assembly can streamline functionality and reduce costs.
What Finishing Processes Enhance Product Quality?
Finishing processes are essential for ensuring that the chargers meet both aesthetic and functional requirements. This stage may involve:
- Surface Treatments: Techniques such as powder coating or anodizing are employed to improve corrosion resistance and enhance visual appeal. These treatments can also help in meeting environmental compliance standards.
- Quality Control Inspections: Before moving to the next stage, products often undergo initial quality checks to identify defects early, saving time and costs associated with rework later.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are in Place for EV Chargers?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of EV chargers, especially for B2B transactions where reliability is critical. Various international and industry-specific standards guide these processes.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for EV Charger Manufacturing?
Manufacturers often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, ensuring consistent product quality. Other pertinent standards include:
- CE Marking: This certification indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards within the European Economic Area, essential for products sold in Europe.
- API Standards: While more commonly associated with the petroleum industry, API standards can also apply to specific components used in EV chargers, especially those related to electrical safety.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in the manufacturing of EV chargers is typically structured around several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor production efficiency and product quality. This includes real-time measurements and adjustments.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final stage of quality control involves comprehensive testing of the finished product. This can include electrical safety tests, performance checks, and environmental resilience assessments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is crucial for mitigating risks.
What Auditing Processes Should Buyers Consider?
Conducting audits of potential suppliers is an effective way to assess their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. This can include:
- On-Site Audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to observe the production process firsthand, assess equipment quality, and review documentation.
- Supplier Certifications: Buyers should request documentation of certifications such as ISO 9001 and CE compliance to ensure that the supplier adheres to established quality standards.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Confidence?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These services can include:
- Product Testing: Third-party labs can conduct rigorous testing on samples to ensure they meet international standards and specifications.
- Compliance Verification: These inspections can also verify compliance with local regulations, which is particularly important for buyers in regions with strict import standards.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware Of?
When sourcing EV chargers from international suppliers, buyers should be aware of specific nuances that could impact their purchasing decisions:
- Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding electrical safety and environmental compliance. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these requirements to avoid potential legal issues.
- Logistical Considerations: Importing products from overseas may involve complex logistics, including customs clearance and tariffs. Understanding these factors can help in calculating the total cost of ownership.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Building strong relationships with suppliers may require an understanding of cultural differences in business practices and communication styles, especially when dealing with suppliers from diverse regions.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing affordable electric vehicle chargers, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger’
In today’s rapidly evolving electric vehicle (EV) market, sourcing a cost-effective EV charger is essential for businesses looking to enhance their sustainability efforts and meet growing consumer demand. This guide provides a comprehensive checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process for affordable yet reliable electric vehicle chargers.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific needs is the foundation of a successful sourcing strategy. Determine the type of EV chargers required, whether Level 1 or Level 2, based on your charging speed and usage frequency. Consider factors such as:
– Charging capacity: Look for chargers with outputs that meet your fleet or facility’s requirements.
– Connector types: Ensure compatibility with the EV models you intend to charge (e.g., J1772 or Tesla NACS).
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Before diving into supplier negotiations, perform thorough market research to identify available products and pricing structures. This step is crucial for comparing options and ensuring you’re getting a good deal. Focus on:
– Competitor analysis: Investigate what similar businesses are using and their satisfaction levels.
– Pricing benchmarks: Gather data on price ranges for the chargers you are considering to ensure you are making a competitive purchase.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This evaluation helps ensure you partner with a reliable provider. Key considerations include:
– Reputation: Look for reviews and testimonials that highlight the supplier’s reliability and customer service.
– Experience: Choose suppliers with a proven track record in the EV charging market.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensuring that your supplier meets industry standards and certifications is vital for quality assurance. Certifications like UL, CE, or ISO indicate compliance with safety and performance standards. This step protects your investment by ensuring:
– Product safety: Certified chargers are more likely to meet safety requirements, reducing liability risks.
– Quality assurance: Suppliers with recognized certifications often provide better product reliability.
Step 5: Assess Installation and Maintenance Services
Consider whether the supplier offers installation and ongoing maintenance services. Proper installation is critical to the optimal performance of EV chargers. Look for:
– Installation expertise: Ensure the supplier has qualified technicians who can install the chargers safely.
– Maintenance support: Inquire about warranties and service agreements to keep chargers operational and efficient over time.
Step 6: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you’ve identified potential suppliers, it’s time to negotiate pricing and terms. Leverage the information gathered during your research to secure the best possible deal. Pay attention to:
– Volume discounts: If purchasing multiple chargers, ask about bulk pricing options.
– Payment terms: Understand the payment structure and any financing options that may be available.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Plan for Implementation
After selecting a supplier and agreeing on terms, finalize your purchase by reviewing contracts carefully. Ensure all specifications and services are clearly documented. Additionally, develop an implementation plan that includes:
– Timeline: Set clear milestones for delivery and installation.
– Training: Arrange for staff training on using the chargers effectively.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for affordable electric vehicle chargers, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational and sustainability goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Affordable Electric Vehicle (EV) Chargers?
When sourcing cheap and competitively priced electric vehicle (EV) chargers, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. High-quality components such as copper wiring, durable enclosures, and advanced semiconductor technology are critical for charger efficiency and safety. However, opting for less expensive alternatives may reduce initial costs but compromise performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on geographical location and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Regions with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing, but this may affect quality. It’s crucial to evaluate the skill level of the workforce and the implications for the final product.
-
Manufacturing Overhead and Tooling: This includes costs associated with factory operations, machinery, and equipment. Efficient production processes can lower overhead costs, while specialized tooling for unique charger designs may increase initial investments but can lead to better margins over time.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes ensures product reliability and compliance with international safety standards. While this may add to upfront costs, it ultimately reduces the risk of recalls and enhances brand reputation.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on the destination, mode of transport, and packaging requirements. B2B buyers should consider these factors when calculating total costs, especially for international transactions.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically mark up their costs to maintain a profit margin. This margin can vary based on market demand, competitive landscape, and the perceived value of the product.
What Influences the Pricing of Electric Vehicle Chargers?
Several factors can influence the pricing of electric vehicle chargers, particularly in international B2B transactions:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers may offer lower per-unit costs for larger orders, which is crucial for businesses planning to resell or deploy chargers at scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized chargers that meet specific requirements (e.g., faster charging capabilities, unique connector types) typically come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the added costs.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Chargers that meet higher quality standards or come with certifications (like UL or CE) often command higher prices. These certifications can be critical for ensuring compliance with local regulations.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and production capacity of suppliers can impact pricing. Long-term relationships with trusted suppliers may yield better pricing and service agreements.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for B2B buyers. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can greatly affect overall costs.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help B2B Buyers Secure Better Pricing?
-
Leverage Volume: Buyers should emphasize their purchasing power when negotiating. Committing to larger orders can provide leverage for better pricing and terms.
-
Explore Total Cost of Ownership: Instead of focusing solely on the purchase price, consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes installation, maintenance, and operational costs. Highlighting TCO can help justify investments in higher-quality chargers that may offer better long-term savings.
-
Investigate Pricing Nuances for Different Regions: Understanding regional market dynamics can provide insights into pricing strategies. For instance, suppliers in Europe may have different pricing structures compared to those in Africa or South America due to varying import tariffs, labor costs, and demand levels.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority in order fulfillment, and additional support services.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for electric vehicle chargers can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and raw material costs. The figures discussed herein are indicative and may vary significantly based on specific order requirements, regional factors, and the evolving nature of the EV market. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives for Electric Vehicle Charging Solutions
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure, choosing the right charging solution is crucial for businesses looking to invest in sustainable technology. While a “cheap good price electric vehicle (EV) charger” offers an affordable entry point, several alternative solutions may provide different benefits that could align better with specific business needs. This analysis compares the budget-friendly EV charger against other viable alternatives to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Cheap Good Price Electric Vehicle (EV) Charger | Alternative 1: DC Fast Charger | Alternative 2: Solar-Powered Charger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate charging speed (Level 2, 6-19 kW) | High-speed (50-350 kW) | Variable speed (depends on sunlight) |
| Cost | $400 – $700 for equipment | $10,000 – $50,000 | $5,000 – $20,000 (installation varies) |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple installation, often plug-and-play | Complex installation, requires permits | Moderate complexity, requires solar setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, occasional checks required | Moderate maintenance due to high usage | Low maintenance; solar panels may need cleaning |
| Best Use Case | Home or small business charging needs | High-traffic commercial areas | Off-grid locations or eco-conscious businesses |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of DC Fast Chargers?
DC Fast Chargers are designed for rapid charging, making them suitable for commercial applications where time is a priority. They can significantly reduce downtime for electric vehicles, providing up to 350 kW of power, which can charge a vehicle from 10% to 80% in about 30 minutes. However, the initial investment is considerably higher, often ranging from $10,000 to $50,000, depending on the setup and location. Additionally, their complexity requires professional installation and adherence to local regulations, making them less accessible for smaller businesses or those with limited budgets.
How Do Solar-Powered Chargers Compare in Terms of Cost and Functionality?
Solar-powered chargers present an innovative and sustainable alternative for businesses committed to reducing their carbon footprint. They harness solar energy to charge EVs, making them particularly effective in regions with abundant sunlight. The costs for solar charging setups can vary significantly, typically ranging from $5,000 to $20,000, depending on installation and capacity. While the maintenance is generally low, the charging speed can be inconsistent, relying on weather conditions. This solution is best suited for off-grid locations or businesses looking to enhance their green credentials.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right EV Charging Solution for Your Business
When selecting the most appropriate EV charging solution, B2B buyers should carefully consider their unique operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term sustainability goals. A cheap good price electric vehicle charger may offer a cost-effective solution for home or small-scale applications. However, for businesses with high traffic volumes or a commitment to sustainability, investing in DC Fast Chargers or solar-powered options could yield better returns in terms of performance and environmental impact. Ultimately, understanding the specific context and requirements of your business will guide you in making the most strategic choice for your EV charging infrastructure.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Cheap Good Price Electric Vehicle (EV) Chargers?
When selecting a cost-effective electric vehicle (EV) charger, several technical properties are crucial to ensure compatibility, efficiency, and safety. Understanding these specifications can help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
1. Charging Level and Output
EV chargers are categorized into three charging levels, with Level 2 being the most common for home use. Level 2 chargers typically operate on 240 volts, providing an output ranging from 6 to 19 kilowatts, which can charge a vehicle overnight. For businesses, the charging output is vital for assessing how quickly vehicles can be charged and ensuring they can meet fleet demands without significant downtime.
2. Connector Types
There are two primary connector types for EV chargers: J1772 and Tesla’s North American Charging Standard (NACS). Understanding the connector type is essential for compatibility with various EV models. B2B buyers should consider the flexibility of chargers that offer interchangeable connectors or adapters, which can cater to a diverse fleet or customer base.
3. Load Management Capability
Load management features allow chargers to adjust their power output based on the home or facility’s overall energy usage. This is particularly important for businesses with existing electrical infrastructure limitations. By optimizing charging times and rates, companies can avoid costly electrical panel upgrades and manage energy costs effectively.
4. Safety Certifications
Safety is paramount when dealing with electrical equipment. EV chargers should have certifications such as UL2594 or Energy Star. These certifications indicate that the products meet specific safety and efficiency standards, reducing liability risks for businesses and ensuring reliable operation.
5. Weather Resistance
Many chargers are designed for outdoor use and come with weatherproof enclosures (e.g., NEMA Type 4). This feature is essential for businesses operating in varying climates, ensuring that the charger remains functional and safe regardless of environmental conditions.
6. Smart Features
Modern EV chargers often include smart technology, allowing users to control charging sessions remotely through mobile applications. Features such as scheduling, real-time monitoring, and usage reports can provide valuable insights for fleet management and operational efficiency.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon in the EV Charger Industry?
Understanding industry jargon is critical for navigating the B2B landscape of EV chargers. Here are several essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the EV charger industry, working with OEMs can provide buyers with reliable products that meet specific quality standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. It can also impact the scalability of purchasing decisions.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and other details for a specific quantity of goods. This process is vital for B2B transactions, enabling buyers to compare costs and terms effectively.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which is essential for international transactions in the EV charger market.
5. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO refers to the comprehensive assessment of all costs associated with acquiring and operating a product over its lifecycle. For EV chargers, TCO includes initial purchase price, installation, maintenance, and energy costs, helping businesses understand the long-term financial implications.
6. Warranty Period
The warranty period is the time during which the manufacturer guarantees the product’s performance and will repair or replace defective units. A longer warranty can be indicative of product quality and reliability, making it a critical factor for B2B buyers.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed purchasing decisions in the growing electric vehicle charger market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Cheap Electric Vehicle (EV) Charger Market?
The electric vehicle (EV) charger market is experiencing robust growth driven by a confluence of factors. Globally, the transition towards renewable energy sources and the need to reduce carbon emissions are compelling governments and businesses to invest heavily in EV infrastructure. This shift is particularly pronounced in regions such as Africa and South America, where EV adoption is rapidly increasing, albeit from a lower base. Furthermore, European countries, including Germany, are leading the charge with stringent regulations aimed at reducing fossil fuel dependence, thereby creating a ripe environment for affordable EV charger solutions.
Emerging technologies are also shaping the market dynamics. The integration of smart technologies, such as load management systems and mobile app connectivity, is becoming increasingly standard in affordable chargers. These innovations not only enhance user experience but also optimize energy consumption, making them attractive to B2B buyers looking for cost-effective solutions. Additionally, the trend towards modular and scalable charging solutions allows businesses to adapt their infrastructure as demand grows, which is vital in rapidly evolving markets.
As international B2B buyers, understanding these trends is crucial. The ability to source low-cost, high-quality EV chargers can significantly enhance your competitive edge in regions where infrastructure is still developing. By aligning with manufacturers that prioritize efficiency and innovation, businesses can position themselves favorably in the market.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Your B2B Sourcing Strategy for EV Chargers?
Sustainability is no longer an option but a necessity for businesses operating in the EV charger sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing and sourcing practices must be carefully considered, especially as consumers and corporations alike are increasingly scrutinizing the ecological footprint of their purchases. For B2B buyers, this means prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing waste during production.
Ethical sourcing also plays a significant role in the decision-making process. Buyers should seek manufacturers who are transparent about their supply chains and who actively work to ensure fair labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Fair Trade can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. Furthermore, opting for products that are certified ‘green’ not only enhances your brand reputation but may also qualify your business for tax incentives and grants aimed at promoting sustainable practices.
By integrating sustainability and ethical sourcing into your procurement strategy, you can help foster a more responsible industry while ensuring compliance with increasingly stringent regulations. This approach not only appeals to environmentally conscious consumers but also positions your business as a leader in the transition to a greener economy.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Cheap EV Charger Market?
The evolution of the electric vehicle charger market can be traced back to the early 2000s, when the first generation of EVs was introduced. Initially, chargers were basic and lacked the technological sophistication that is now common. As EV adoption gained momentum, particularly in the last decade, the demand for more efficient and user-friendly charging solutions surged.
Technological advancements, such as the development of Level 2 chargers, have enabled faster charging times, making EV ownership more convenient. The introduction of smart chargers that integrate with mobile apps and home energy management systems reflects a significant shift toward user-centric designs. Today, the market is characterized by a diverse range of products catering to different consumer needs, from home charging solutions to commercial installations.
This evolution has been particularly impactful in regions like Europe and North America, where regulatory frameworks have encouraged investment in charging infrastructure. As the market continues to mature, B2B buyers must stay informed about the latest trends and technologies to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their business goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger
-
How can I ensure the quality of cheap electric vehicle chargers when sourcing?
To ensure quality, request certifications from suppliers, such as UL, CE, or ISO standards, which indicate compliance with safety and performance regulations. Additionally, ask for product samples to evaluate the build quality and performance. Consider third-party testing reports and customer reviews to gauge reliability. Engaging in factory audits or using reputable sourcing agents can also help verify supplier credibility and product integrity. -
What are the best electric vehicle chargers for budget-conscious businesses?
For budget-conscious businesses, the Emporia EV Charger and ChargePoint Home Flex are highly recommended due to their cost-effectiveness and robust features. The Emporia charger, priced around $429, offers smart charging capabilities and is suitable for various EV models. The ChargePoint Home Flex, while slightly higher in price at around $600, provides excellent user interface features and performance, making it a worthwhile investment for reliable charging solutions. -
What customization options are available for electric vehicle chargers?
Many manufacturers offer customization options, including branding, color schemes, and specific features tailored to business needs. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements with suppliers upfront. Customization may also extend to the charging power output and connector types to accommodate different vehicle models. Be sure to inquire about lead times and minimum order quantities (MOQs) for customized products to ensure they align with your project timelines. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for electric vehicle chargers?
MOQs for electric vehicle chargers can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the charger model. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to 500 units for bulk orders. Some manufacturers may offer lower MOQs for first-time buyers or for less customized products. It’s essential to clarify MOQs before finalizing any agreements to ensure they meet your purchasing needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electric vehicle chargers internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region but typically include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or payment on delivery. Many suppliers may request a deposit (often 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Ensure you negotiate favorable terms that mitigate risks, especially when dealing with international transactions. It’s also wise to confirm the currency used for transactions and any associated fees. -
How can I efficiently manage logistics for sourcing electric vehicle chargers from international suppliers?
Effective logistics management involves choosing the right shipping methods and partners. Consider using freight forwarders who specialize in international shipping and can navigate customs regulations. Always calculate total landed costs, including duties, taxes, and shipping fees, to understand your overall expenditure. Establish clear timelines for delivery and communicate with suppliers to ensure timely dispatch of your orders. -
What quality assurance measures should I implement when sourcing EV chargers?
Implementing quality assurance measures involves establishing a rigorous inspection process at various stages of the supply chain. Request pre-shipment inspections and ensure that products meet specified standards. Collaborate with suppliers who provide detailed quality control documentation, such as test reports and certifications. Additionally, consider maintaining a return policy for defective units to safeguard your investment. -
Are there specific regulations I need to be aware of when importing electric vehicle chargers?
Yes, regulations can vary by country and may include safety standards, environmental regulations, and import tariffs. Familiarize yourself with the specific electrical safety standards applicable in your market, such as CE in Europe or IEC standards globally. Consult with customs brokers or legal experts to ensure compliance with local regulations and avoid potential fines or shipment delays.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 2 Cheap Good Price Electric Vehicle (Ev) Charger Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Lectron – Vehicle to Load (V2L) Adapter
Domain: bestbuy.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Electric Car Chargers available at Best Buy include various models and features. Key products include: 1. Lectron – Vehicle to Load (V2L) Adapter Compatible with Hyundai Ioniq 5 – Black, Rating: 0 out of 5 stars (not yet reviewed). 2. Lectron – CCS1 to NACS Adapter for Tesla Model S, 3, X, Y – up to 500A (500V) – Black, Rating: 0 out of 5 stars (not yet reviewed). 3. Lectron – Tesla to J1772 EV Ch…
2. Facebook – Charging Solutions
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Charging Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cheap good price electric vehicle (ev) charger
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of affordable electric vehicle (EV) chargers presents an invaluable opportunity for international B2B buyers. By understanding the diverse range of charging solutions available, including Level 2 chargers like the Emporia Classic and Pro models, businesses can meet the growing demand for efficient and cost-effective EV infrastructure. Key considerations include evaluating installation costs, connector compatibility, and the long-term benefits of smart charging technology that optimizes energy consumption.
Investing in quality EV chargers not only enhances operational efficiency but also aligns with global sustainability goals, making it a smart choice for forward-thinking companies in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As the EV market continues to expand, the need for reliable and economical charging solutions will only intensify.
Now is the time for B2B buyers to act decisively. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, you can secure the best pricing and features, ensuring your organization is well-positioned in the evolving landscape of electric mobility. Embrace the future of transportation and invest in affordable EV charging solutions that drive both profitability and sustainability.