Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric vehicle license
Navigating the complexities of the global market for electric vehicle licenses can be daunting for international B2B buyers. With the rapid shift towards electrification in transportation, understanding the intricacies of acquiring an electric vehicle license is crucial for companies looking to invest in sustainable fleets. This guide aims to demystify the process by covering various types of electric vehicle licenses, their applications, and the associated costs. It also emphasizes the importance of thorough supplier vetting to ensure compliance with local regulations and standards.
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—countries like Nigeria and Vietnam—face unique challenges in this evolving landscape. Variations in licensing requirements, benefits, and fees can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This guide empowers B2B buyers by providing actionable insights, enabling them to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their sustainability goals and operational needs.
By the end of this guide, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of the electric vehicle license ecosystem, equipping them with the knowledge to navigate regulations, optimize costs, and leverage potential benefits. As the demand for electric vehicles continues to rise, staying informed will be key to gaining a competitive edge in the global market.
Understanding electric vehicle license Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) License | Designed for fully electric vehicles, often with unique identifiers like “E”. | Fleets, public transportation, delivery services. | Pros: Lower operating costs, access to incentives. Cons: Limited range compared to hybrids. |
| Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) License | For vehicles that combine electric and traditional fuel; must meet specific emissions standards. | Logistics companies, ride-sharing services. | Pros: Flexibility in fuel use, reduced emissions. Cons: Higher initial costs, complexity in managing fuel types. |
| Commercial EV License | Tailored for electric vehicles used in commercial applications, may include special regulations. | Cargo transport, service industries. | Pros: Possible tax incentives, fleet management benefits. Cons: Compliance requirements can vary by region. |
| Electric Taxi License | Specific to electric vehicles used as taxis, often includes operational perks like reduced fees. | Ride-hailing platforms, taxi companies. | Pros: Access to bus lanes, reduced congestion fees. Cons: Limited availability in some regions, potential for regulatory changes. |
| Specialized EV Fleet License | For businesses operating multiple EVs, may offer bulk registration benefits. | Large corporations, governmental fleets. | Pros: Streamlined registration, potential cost savings. Cons: May require significant initial investment in fleet. |
What Are the Characteristics of a Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) License?
The Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) License is specifically for vehicles that operate solely on electric power. This license often comes with unique identifiers, such as an “E” or “EV,” to signify its eco-friendly nature. B2B applications include fleet management for public transportation and delivery services. Businesses benefit from lower operating costs and various incentives, though the limited range compared to hybrids can be a drawback for some operational needs.
How Does a Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) License Differ?
A Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) License caters to vehicles that utilize both electric and traditional fuel sources. These vehicles must meet stringent emissions standards, making them suitable for logistics companies and ride-sharing services. The flexibility of using both electric and gasoline can be advantageous, allowing businesses to adapt to varying fuel costs. However, the initial investment is often higher, and managing fuel types can complicate operations.
What Are the Benefits of a Commercial EV License?
The Commercial EV License is tailored for electric vehicles utilized in commercial applications, which may include specific regulations and requirements. This license is ideal for cargo transport and service industries. Companies can take advantage of tax incentives and fleet management benefits, although compliance requirements can differ significantly by region. Understanding local regulations is crucial for maximizing the benefits of this license type.
What Makes an Electric Taxi License Unique?
Electric Taxi Licenses are specifically designed for electric vehicles operating as taxis. These licenses often provide operational perks, such as reduced fees or access to bus lanes, which are beneficial for ride-hailing platforms and taxi companies. While the advantages can be significant, the limited availability in certain regions and the potential for regulatory changes can pose challenges for businesses looking to adopt this model.
How Can a Specialized EV Fleet License Benefit Large Corporations?
The Specialized EV Fleet License is intended for businesses managing multiple electric vehicles, offering potential bulk registration benefits. This license is particularly advantageous for large corporations and governmental fleets looking to streamline their registration processes. While there may be cost savings associated with fleet management, companies must be prepared for the significant initial investment required to transition to an electric fleet.
Key Industrial Applications of electric vehicle license
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Electric Vehicle License | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transportation & Logistics | Fleet management for electric delivery vehicles | Reduced operational costs through fuel savings and incentives | Understanding local regulations and incentives available |
| Public Transport | Electrification of taxi and ride-sharing services | Enhanced brand reputation through sustainable practices | Compliance with local licensing requirements |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Production of EVs with specialized licensing requirements | Access to government incentives for electric vehicle production | Sourcing compliant materials and technology |
| Retail & E-commerce | Integration of electric delivery vehicles for logistics | Improved customer satisfaction with faster delivery options | Evaluating local EV infrastructure and charging stations |
| Municipal Services | Adoption of electric vehicles for public service fleets | Cost savings and reduced emissions, enhancing public image | Assessing regional support for EV initiatives |
How is Electric Vehicle License Utilized in Transportation & Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics sector, electric vehicle (EV) licenses play a crucial role in managing fleets of electric delivery vehicles. Businesses benefit from reduced operational costs due to fuel savings and government incentives for using low-emission vehicles. For international B2B buyers, understanding local regulations and the availability of incentives is essential to maximize financial benefits and ensure compliance.
What are the Benefits of Electric Vehicle Licenses for Public Transport?
Public transport systems increasingly adopt electric taxis and ride-sharing services, leveraging EV licenses to enhance their sustainability efforts. By transitioning to electric vehicles, companies improve their brand reputation and attract environmentally conscious customers. Buyers in this sector must navigate local licensing requirements to ensure their fleet meets regional standards while taking advantage of available incentives.
How Do Automotive Manufacturers Leverage Electric Vehicle Licenses?
Automotive manufacturers benefit from electric vehicle licenses by producing EVs that comply with specialized licensing requirements. This compliance opens doors to government incentives designed to promote electric vehicle production, ultimately reducing costs. Buyers must focus on sourcing compliant materials and technology to meet local regulations while ensuring their products remain competitive in the market.
Why is Electric Vehicle Licensing Important for Retail & E-commerce?
In the retail and e-commerce sectors, integrating electric delivery vehicles powered by EV licenses can significantly enhance logistics efficiency. Businesses can improve customer satisfaction through faster, eco-friendly delivery options, which can be a strong differentiator in a competitive market. Evaluating the local EV infrastructure and availability of charging stations is critical for buyers to ensure operational feasibility.
What Advantages Do Municipal Services Gain from Electric Vehicle Licenses?
Municipal services adopting electric vehicles for public service fleets can achieve substantial cost savings and reduced emissions, positively impacting their public image. Electric vehicle licenses facilitate this transition by providing access to incentives that support fleet electrification. Buyers in this sector should assess regional support for EV initiatives and ensure alignment with local sustainability goals.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric vehicle license’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Varied Regulations Across Regions
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly those managing fleets of electric vehicles (EVs), often encounter the challenge of navigating the diverse regulations related to EV licenses in different regions. For instance, a company operating in both Nigeria and Germany may find that the requirements for obtaining an EV license plate vary significantly. This can lead to confusion and potential non-compliance, resulting in fines or restrictions on fleet operations.
The Solution: To effectively manage this complexity, companies should invest in regulatory compliance software or platforms that specialize in automotive regulations. These tools can provide real-time updates on licensing requirements, helping businesses stay informed about the latest rules in different regions. Additionally, forming partnerships with local legal or compliance experts can provide invaluable insights and ensure that the organization adheres to all necessary regulations. Regular training sessions for fleet managers on these regulations will also enhance understanding and compliance across the organization.
Scenario 2: Limited Access to Charging Infrastructure
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the issue of inadequate charging infrastructure for electric vehicles, especially in regions like Africa and parts of South America. This limitation can hinder the operational efficiency of businesses that rely on electric vehicles for logistics or transportation. Without sufficient charging stations, vehicles may be left idle, leading to increased operational costs and reduced productivity.
The Solution: To mitigate this challenge, businesses should consider investing in the establishment of their own charging stations. This can be done in partnership with local governments or energy companies, who may be interested in expanding EV infrastructure. Additionally, companies can explore mobile charging solutions or portable charging units that can be deployed in strategic locations to facilitate charging. By developing a tailored charging strategy that includes partnerships and investments in infrastructure, businesses can ensure their fleets remain operational and efficient.
Scenario 3: High Initial Costs of EV License Plates
The Problem: The initial costs associated with obtaining electric vehicle license plates can be a barrier for many businesses, especially startups or small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). In regions where administrative fees and production costs can add up to significant amounts, these expenses can deter businesses from transitioning to electric vehicles.
The Solution: Companies should take a proactive approach to budget for these costs by exploring available subsidies and incentives offered by local governments for EV adoption. Many regions provide financial assistance to businesses that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, which can help offset the costs of EV licensing. Furthermore, businesses can consider forming cooperatives with other local companies to share the costs of obtaining licenses and establishing charging infrastructure. By collaborating and pooling resources, businesses can lower the financial burden and make the transition to electric vehicles more feasible.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric vehicle license
What Are the Key Materials for Electric Vehicle License Plates?
When considering the materials for electric vehicle (EV) license plates, several factors come into play, including durability, cost, manufacturing complexity, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the production of EV license plates, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Perform as a Material for EV License Plates?
Aluminum is a popular choice for license plates due to its lightweight nature and corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 150°C and can withstand moderate pressure. The primary advantage of aluminum is its durability and resistance to environmental factors, making it suitable for outdoor use. However, aluminum plates can be more expensive than alternatives like plastic, and they may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can increase costs.
For international buyers, aluminum license plates must comply with various standards, such as ASTM for material properties and DIN for manufacturing processes. In regions like Africa and South America, where cost sensitivity is high, the initial investment in aluminum may be a deterrent despite its long-term benefits.
What Role Does Polycarbonate Play in EV License Plates?
Polycarbonate is another viable option for EV license plates, known for its high impact resistance and flexibility. It can endure temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C, making it suitable for diverse climates. The key advantage of polycarbonate is its lightweight nature and lower production cost compared to metals. However, it may not offer the same level of UV resistance as aluminum, leading to potential discoloration over time.
For buyers in the Middle East and Africa, polycarbonate plates may be appealing due to their lower cost and ease of manufacturing. However, compliance with local standards for durability and weather resistance is essential to ensure that the plates perform well in harsh conditions.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material for EV License Plates?
Steel, particularly stainless steel, is another material used for EV license plates. Known for its strength and corrosion resistance, stainless steel can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various environments. The primary advantage of steel is its longevity and resistance to wear and tear. However, it is heavier than aluminum and polycarbonate, which can be a drawback in terms of ease of handling and installation.
International buyers should consider the compliance requirements for steel plates, especially in Europe, where regulations regarding recycling and material sourcing are stringent. The higher cost of stainless steel may also be a concern for budget-conscious buyers in regions like South America.
What About Plastic as a Material for EV License Plates?
Plastic, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is a cost-effective option for EV license plates. It is lightweight, resistant to chemicals, and can withstand temperatures up to 80°C. The main advantage of plastic is its low cost and ease of production, making it accessible for various markets. However, its lower durability compared to metals can lead to a shorter lifespan, especially in extreme weather conditions.
For international B2B buyers, plastic plates must meet specific standards for durability and UV resistance. In regions like Africa and the Middle East, where environmental conditions can be harsh, ensuring compliance with local regulations is crucial to avoid issues related to plate degradation.
Summary Table of Material Selection for EV License Plates
| Material | Typical Use Case for Electric Vehicle License | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Long-lasting, outdoor license plates | Corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Polycarbonate | Lightweight, flexible license plates | Lower production cost | Potential UV degradation | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Durable, heavy-duty license plates | Exceptional strength | Heavier, higher cost | High |
| Plastic | Cost-effective, lightweight license plates | Low cost, easy to produce | Lower durability | Low |
In conclusion, selecting the right material for electric vehicle license plates involves balancing cost, durability, and compliance with regional standards. International buyers must assess their specific needs and local regulations to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric vehicle license
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Electric Vehicle License Plates?
The manufacturing process of electric vehicle (EV) license plates involves several critical stages to ensure durability, functionality, and compliance with regulatory standards. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source high-quality license plates.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used for EV License Plates?
The first step in manufacturing EV license plates is selecting the right materials. Common materials include aluminum and polycarbonate, which are chosen for their lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and durable properties.
- Aluminum: Often used for its strength and resistance to environmental factors, making it ideal for outdoor use.
- Polycarbonate: This plastic material is also popular due to its impact resistance and flexibility.
Once the materials are selected, they undergo a series of pre-processing techniques such as cutting and surface treatment to prepare them for forming.
2. How Are EV License Plates Formed?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the desired license plate dimensions. This can be accomplished through techniques like stamping or injection molding.
- Stamping: For aluminum plates, stamping machines apply high pressure to cut and shape the material. This method ensures precise dimensions and clean edges.
- Injection Molding: For polycarbonate plates, melted plastic is injected into molds to create the plate shape. This technique allows for complex designs and is often used for plates with embedded technology.
What Are the Assembly and Finishing Processes for EV License Plates?
Following the forming stage, assembly and finishing processes are crucial for enhancing the functionality and aesthetics of the license plates.
3. Assembly: What Components Are Included?
The assembly stage typically involves adding various components to the license plates, such as:
- Reflective Sheeting: This is applied to improve visibility, especially at night.
- Barcodes or QR Codes: These are often integrated for electronic identification and tracking.
- Fastening Features: Holes for screws or other fastening mechanisms may also be included.
4. Finishing: How Is Quality Enhanced?
Finishing processes include surface treatments such as anodizing for aluminum plates or applying UV-resistant coatings for polycarbonate plates. These enhancements not only improve durability but also provide weather resistance and increase the lifespan of the plates.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in EV License Plate Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process for EV license plates, ensuring that the final products meet international standards and customer expectations.
5. Which International Standards Should Be Followed?
For B2B buyers, it is essential to ensure that suppliers adhere to recognized international quality standards such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that products consistently meet customer requirements and regulatory standards.
- ISO 14001: Relevant for environmental management, this standard ensures that the manufacturing processes minimize environmental impact.
In addition to these, industry-specific certifications like CE marking (for products sold in the European Economic Area) may also apply.
6. What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
The quality control (QC) process should include several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular inspections during the manufacturing process help identify and rectify issues before final assembly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product is conducted to ensure it meets all specifications and standards before shipping.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers. Here are some actionable insights:
7. What Verification Methods Are Available?
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing facilities can provide insights into their quality control processes. This includes examining their adherence to ISO standards and reviewing their QC documentation.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports that outline the results of various QC tests performed at different stages of production.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality assurance processes.
8. Are There QC Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and market expectations is vital.
- Regional Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulations concerning environmental impact, safety, and product quality. It is crucial to ensure that the license plates comply with these local standards.
- Cultural Considerations: Building relationships with suppliers in diverse regions requires an understanding of local business practices and cultural nuances, which can impact negotiations and quality expectations.
Conclusion: Why Is Understanding Manufacturing and Quality Assurance Critical for B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers in the electric vehicle sector, comprehending the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures of EV license plates is essential for making informed sourcing decisions. By focusing on the right materials, manufacturing techniques, and rigorous quality control standards, businesses can ensure they are obtaining high-quality products that enhance their operational efficiency and contribute to sustainable practices. Understanding these elements not only aids in supplier selection but also promotes long-term partnerships that can adapt to the evolving needs of the electric vehicle market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric vehicle license’
In today’s rapidly evolving automotive landscape, securing an electric vehicle (EV) license is essential for businesses aiming to capitalize on the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions. This step-by-step checklist is designed to guide international B2B buyers through the procurement process of obtaining an electric vehicle license. Follow these actionable steps to ensure a smooth and efficient application.
Step 1: Understand Local Regulations
Before initiating the licensing process, familiarize yourself with the specific regulations governing electric vehicles in your target market. Each region may have distinct requirements, benefits, and eligibility criteria for EV licenses. Understanding these nuances will help you navigate the application process and optimize the advantages available to your business.
- Research Local Authorities: Identify the relevant government agencies responsible for EV licensing in your area.
- Review Policy Changes: Stay updated on any recent legislative changes that may affect licensing requirements or benefits.
Step 2: Identify Eligible Vehicles
Not all vehicles qualify for an electric vehicle license, so it’s critical to determine which models meet the necessary criteria. This step ensures that your investment aligns with local regulations and maximizes potential benefits.
- Review Vehicle Classifications: Confirm that your vehicles fall under eligible categories such as Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs), or qualifying Plug-in Hybrids (PHEVs).
- Check Emission Standards: Ensure that the vehicles meet local emissions standards, which can vary significantly by region.
Step 3: Gather Required Documentation
Proper documentation is essential for a successful application. Compile all necessary paperwork to avoid delays in processing your EV license.
- Ownership Proof: Collect vehicle registration documents and ownership papers.
- Insurance Information: Ensure that you have a valid insurance certificate that covers the vehicle type.
- Compliance Verification: Be prepared to provide any technical compliance documentation if required by local authorities.
Step 4: Choose Your Application Method
Decide whether to apply for the EV license in person or online, based on the options available in your region. This choice can affect the speed and efficiency of your application process.
- In-Person Applications: Visit local vehicle registration offices if online options are not available. Bring all required documents to facilitate the process.
- Online Applications: If available, utilize digital platforms to submit your application. This may include filling out forms and uploading documents electronically.
Step 5: Assess Costs and Fees
Understanding the financial implications of obtaining an EV license is crucial for budget planning. Evaluate all associated costs to avoid unexpected expenses.
- Application Fees: Be aware of administrative fees, which can vary by region, typically ranging from $30 to $60.
- Additional Costs: Factor in any costs related to license plate production and potential ongoing fees for maintaining the license.
Step 6: Monitor Application Status
After submission, keep track of your application status to ensure timely processing. This proactive approach can help you address any issues that may arise.
- Follow-Up Communication: Maintain contact with the licensing authority to inquire about your application status.
- Prepare for Additional Requests: Be ready to provide any additional documentation or information if requested by the authorities.
Step 7: Leverage License Benefits
Once you receive your EV license, take full advantage of the benefits it offers. These may include free parking, access to bus lanes, and exemptions from certain fees.
- Stay Informed on Local Incentives: Regularly check for updates on new benefits or changes to existing regulations that could enhance your business operations.
- Promote Sustainability: Utilize your EV license to enhance your brand’s image as a sustainable and eco-friendly business, which can attract more customers and partnerships.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of obtaining an electric vehicle license more effectively, positioning themselves to succeed in a sustainable future.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric vehicle license Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Electric Vehicle License Sourcing?
When evaluating the costs associated with electric vehicle (EV) licenses, several components contribute to the overall expenditure. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control, logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The primary materials used in the production of license plates include metal or plastic substrates, inks for printing, and any additional coatings or finishes that enhance durability and visibility. The choice of materials can significantly affect the cost, especially when opting for environmentally friendly options.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of workers involved in the design, production, and quality assurance of the license plates. In regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, this can represent a significant portion of the overall price.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these overheads.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for molds and production equipment can be substantial, particularly for customized or large-volume orders. Buyers should consider whether their order size justifies these tooling expenses.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that the license plates meet regulatory standards involves rigorous testing and inspection processes. These quality assurance measures, while adding to costs, are crucial for compliance and customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the destination and chosen Incoterms. International shipping may involve customs duties and tariffs, which can further inflate the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin that varies based on market competition, demand, and perceived value. Understanding the competitive landscape can provide buyers with leverage during negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Electric Vehicle License Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of EV licenses that buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities can significantly affect pricing. Bulk purchases often lead to lower per-unit costs, making it advantageous for companies with a larger fleet or extensive operations.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom license plates with specific designs or identifiers may incur additional costs. Buyers should assess whether the benefits of customization justify the extra expense.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials not only impacts the price but also the quality certifications required. Higher quality materials may come with a higher initial cost but can lead to reduced long-term maintenance and replacement expenses.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and geographical location of the supplier can influence pricing. Suppliers closer to the buyer may offer lower logistics costs, while established suppliers with proven track records might command higher prices due to perceived quality.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms can help buyers minimize unexpected costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in EV License Procurement?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can adopt several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engaging suppliers in negotiations can yield favorable pricing. Presenting bulk order intentions or long-term partnership opportunities may convince suppliers to lower costs.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the TCO beyond the initial purchase price. Factors such as longevity, maintenance costs, and potential savings from incentives (like free parking or toll exemptions) can make a seemingly higher-priced option more economical in the long run.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing dynamics, including government incentives for EVs and fluctuating material costs. This knowledge can provide leverage in negotiations and help anticipate changes in pricing.
-
Research Local Regulations: Local regulations may influence the costs associated with obtaining EV licenses. Understanding these regulations can help buyers navigate the complexities of compliance and avoid unexpected expenses.
Disclaimer
The prices and costs mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, regulatory changes, and supplier-specific factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric vehicle license With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Electric Vehicle Licenses
As businesses and municipalities worldwide seek sustainable transportation solutions, the electric vehicle (EV) license has emerged as a key component in promoting the adoption of low-emission vehicles. However, various alternatives can also contribute to achieving similar sustainability goals. This section compares the electric vehicle license with alternative solutions such as fleet electrification initiatives and public transportation enhancements.
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Vehicle License | Fleet Electrification Initiatives | Public Transportation Enhancements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Provides direct benefits to EV owners, such as access to HOV lanes and reduced fees. | Offers a comprehensive reduction in emissions through a complete fleet transition to electric vehicles. | Increases accessibility and reduces congestion by providing efficient transport options. |
| Cost | Low initial cost (around $50-$60); potential savings from reduced parking and toll fees. | Higher upfront investment for fleet conversion, but long-term savings on fuel and maintenance. | Moderate cost for infrastructure improvements; potential for government subsidies. |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple application process; varies by region. | Requires careful planning, budgeting, and possible fleet downtime during transition. | Can be complex, needing public engagement and coordination with local governments. |
| Maintenance | Standard vehicle maintenance; EVs often have lower maintenance needs. | Requires ongoing fleet management and regular updates to technology. | Maintenance of public transport vehicles and infrastructure can be resource-intensive. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for individual businesses or drivers looking to capitalize on EV benefits. | Best suited for companies with large vehicle fleets looking to reduce overall emissions. | Effective for urban areas seeking to enhance public transit and reduce traffic congestion. |
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Fleet Electrification Initiatives?
Fleet electrification initiatives involve transitioning an entire vehicle fleet to electric models, which can lead to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. The advantages include lower operating costs over time due to reduced fuel consumption and maintenance expenses, as electric vehicles generally require less upkeep than traditional combustion engine vehicles. However, the initial investment can be substantial, requiring businesses to assess their budgetary constraints carefully. Moreover, the transition can involve logistical challenges, such as ensuring that charging infrastructure is in place and training staff on new technologies.
How Do Public Transportation Enhancements Serve as an Alternative?
Public transportation enhancements focus on improving existing transit systems to make them more efficient and accessible. This can include adding electric buses, improving service frequency, and integrating smart technologies for real-time tracking. The primary advantage of this approach is that it can reduce the number of individual vehicles on the road, thereby decreasing overall emissions and traffic congestion. However, implementation can be complex and may face resistance from the public or local authorities. Additionally, while costs can be mitigated through government funding, the ongoing maintenance of public transport infrastructure can be a significant burden.
Conclusion: Which Solution is Best for Your Business Needs?
When considering alternatives to the electric vehicle license, businesses must evaluate their unique needs and objectives. An electric vehicle license can be a cost-effective solution for individual drivers or small fleets aiming to reduce operational costs while enjoying specific local benefits. In contrast, fleet electrification is more suited for larger enterprises committed to sustainability and capable of managing the associated transition costs. Public transportation enhancements are ideal for urban businesses looking to contribute to broader societal goals of reducing congestion and improving air quality. Ultimately, the right choice depends on a thorough analysis of operational capabilities, financial resources, and long-term sustainability goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric vehicle license
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Electric Vehicle Licenses?
When engaging in the electric vehicle (EV) licensing sector, understanding the critical technical properties is vital for B2B buyers. Here are some essential specifications that influence the licensing process and operational efficiency:
-
Eligibility Criteria for Vehicles
Vehicles eligible for an EV license plate typically include Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs), and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs). Each category has specific requirements, such as a minimum all-electric range or CO2 emissions thresholds. For B2B operations, knowing these criteria ensures compliance with local regulations, facilitating smoother registration processes and avoiding potential fines. -
Cost of Registration
The total cost for obtaining an EV license plate often includes administration fees and production costs, which can range from $50 to $60 in various regions. For businesses, understanding these costs is crucial for budgeting, especially when scaling fleets or integrating EVs into existing operations. It also aids in assessing the return on investment, particularly when considering long-term savings from reduced fuel costs and tax incentives. -
Renewal and Validity Period
Most EV licenses have a defined validity period, after which renewal is necessary. This period can vary by region but is typically one to three years. For fleet managers, keeping track of renewal dates is essential to maintain compliance and avoid operational interruptions. Automating reminders can help in managing large fleets efficiently. -
Regulatory Compliance Documentation
When applying for an EV license, businesses need to submit specific documentation, including proof of vehicle registration, insurance certificates, and sometimes technical compliance verification. Understanding the required documents streamlines the application process, reducing delays and ensuring that vehicles are roadworthy and compliant with local laws. -
Digital Registration Options
Some regions are transitioning to digital vehicle registration systems, allowing for quicker approvals and reduced paperwork. B2B buyers should be aware of these technological advancements, as they can significantly enhance efficiency in managing vehicle licenses, especially for businesses operating across multiple jurisdictions.
Which Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know in the Electric Vehicle License Sector?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the EV licensing landscape. Here are key terms to understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce components or vehicles sold under another company’s brand. In the context of EVs, knowing the OEM can help businesses ensure they are sourcing parts from reliable manufacturers, which is crucial for maintaining fleet quality and compliance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is critical for B2B buyers when sourcing vehicles or components, as it affects inventory management and costs. Negotiating lower MOQs can help smaller businesses enter the EV market more effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. For companies looking to acquire EV licenses or vehicles, issuing an RFQ can streamline the procurement process, ensuring competitive pricing and favorable terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of predefined commercial terms used in international trade that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in global procurement of EV components, as they dictate shipping, insurance, and liability during transit. -
ZEV (Zero Emission Vehicle)
ZEVs are vehicles that produce no tailpipe emissions. Recognizing this term is essential for businesses focusing on sustainability initiatives and understanding regulatory incentives tied to environmentally friendly vehicles. -
LEZ (Low Emission Zone)
This term refers to areas where access is restricted for vehicles that do not meet specific emissions standards. B2B buyers should be aware of LEZ regulations, especially if they operate in urban areas, as it can impact operational routes and costs associated with compliance.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies will empower B2B buyers to navigate the electric vehicle licensing landscape effectively, ensuring compliance, optimizing costs, and enhancing operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric vehicle license Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing the Electric Vehicle License Sector?
The electric vehicle (EV) license sector is witnessing substantial growth driven by global sustainability initiatives and regulatory changes aimed at reducing carbon emissions. As countries ramp up their efforts to transition to greener transportation, the demand for EV-specific licenses is increasing, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This growth is propelled by the rising number of electric vehicles on the road, incentivized by local governments through tax breaks, free parking, and exemptions from congestion charges. For international B2B buyers, this represents an opportunity to align with governmental policies that favor sustainable practices, enhancing their corporate social responsibility profiles.
In terms of technology, the integration of digital platforms for license applications is becoming more common, streamlining the process for businesses and individual users alike. Countries like Germany and New York City are pioneering online registration systems, which not only reduce administrative burdens but also improve compliance tracking for EVs. Furthermore, the trend towards smart city initiatives is influencing market dynamics, as cities seek to integrate EV infrastructure with urban planning, thus creating opportunities for businesses to invest in charging stations and related services.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Electric Vehicle License Supply Chain?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the electric vehicle license sector, influencing both sourcing and operational practices. The environmental impact of traditional vehicles has led to a heightened focus on green certifications and sustainable materials in the production of EVs and their components, including license plates. Companies that prioritize ethical sourcing can differentiate themselves in a competitive market, appealing to environmentally-conscious consumers and businesses.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Stakeholders are increasingly scrutinizing the sourcing of materials used in EV production, from metals to plastics, and companies must ensure that their supply chains are transparent and environmentally responsible. This not only enhances brand reputation but also mitigates risks associated with potential regulatory penalties for non-compliance with environmental standards. B2B buyers should look for partnerships with suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, as this will be crucial in meeting the evolving demands of consumers and regulators alike.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Electric Vehicle License Sector?
The electric vehicle license sector has evolved significantly over the past decade. Initially, EV licenses were introduced primarily as a means to promote the adoption of electric vehicles through incentives such as reduced registration fees and access to exclusive parking. As the environmental benefits of EVs became more widely recognized, many governments began to implement more comprehensive policies, including dedicated license plates that identify electric vehicles and provide additional perks.
In recent years, the shift toward urban electrification and smart city initiatives has further transformed the landscape. Regions across Europe, Africa, and South America are now developing tailored programs to support EV adoption, reflecting a broader commitment to sustainable urban development. As this sector continues to grow, international B2B buyers must stay informed about regulatory changes and technological advancements to effectively navigate the market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric vehicle license
-
How do I solve the challenges of acquiring an electric vehicle license in multiple countries?
Navigating the regulatory landscape for electric vehicle licenses can be complex due to varying local laws. Start by conducting thorough research on each target market’s requirements, including eligibility criteria, application processes, and associated costs. Engaging with local legal experts or consultants can provide insights and facilitate compliance. Additionally, consider leveraging technology solutions for streamlined documentation management and communication with local authorities to expedite the licensing process. -
What is the best strategy for sourcing electric vehicle licenses internationally?
The best strategy involves identifying reliable local partners or agents who have a deep understanding of the regulatory framework in each target country. Conduct due diligence to vet these suppliers, checking their reputation, experience, and client references. Additionally, attending industry trade shows or networking events can help establish connections with key stakeholders. Collaborating with local automotive associations can also provide valuable insights and facilitate smoother sourcing. -
What are the key benefits of having an electric vehicle license for businesses?
Obtaining an electric vehicle license offers businesses several advantages, including access to incentives such as tax breaks, reduced fees, and exclusive parking privileges. These benefits can significantly lower operational costs and enhance the company’s sustainability profile. Furthermore, having an electric vehicle license may improve public perception and customer loyalty, as consumers increasingly favor environmentally responsible companies. This can lead to a competitive edge in the market. -
What are the typical costs associated with acquiring an electric vehicle license?
The costs can vary widely depending on the region and specific regulations. Generally, you can expect to pay administrative fees ranging from $20 to $30, with additional charges for plate production. Total costs may range from $50 to $60. However, these expenses are often offset by long-term savings such as reduced parking fees and exemptions from congestion charges. It’s crucial to budget accordingly and factor in potential fluctuations in local regulations. -
What documents are required to apply for an electric vehicle license?
To apply for an electric vehicle license, businesses typically need to provide several key documents. These include proof of vehicle ownership, an insurance certificate, and a government-issued ID. Some jurisdictions may also require technical compliance verification for the vehicle. Ensure that all documentation is accurate and complete to avoid delays in the application process. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in the electric vehicle license application process?
Quality assurance can be maintained by establishing a clear protocol for document preparation and submission. Regularly train your team on the latest regulatory changes and best practices in the application process. Additionally, consider employing a dedicated compliance officer or consultant who can oversee the process and ensure all requirements are met. Implementing a checklist for all necessary documents can also help minimize errors. -
What are the logistics considerations for transporting electric vehicles after obtaining a license?
Transporting electric vehicles requires careful planning, especially regarding charging infrastructure and route optimization. Ensure that logistics partners are equipped to handle electric vehicles, including access to charging stations during transit. Additionally, familiarize yourself with local regulations regarding vehicle transport, as they can differ significantly between countries. Planning for contingencies, such as unexpected delays or charging needs, is also essential for smooth logistics operations. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with suppliers for electric vehicle licenses?
When negotiating payment terms, aim for flexibility that suits your business cash flow. Common terms include net 30 or net 60 days, allowing time for processing and sales. Additionally, consider requesting discounts for early payments or bulk applications. It’s also advisable to clarify any penalties for late payments to avoid unexpected costs. Establishing a transparent and mutually beneficial payment agreement can foster a stronger relationship with your suppliers.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Electric Vehicle License Manufacturers & Suppliers List
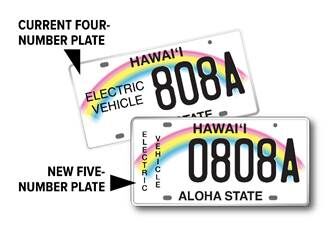
1. Wheelfront – EV License Plate
Domain: wheelfront.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: EV License Plate: A special license plate for Electric Vehicles (EVs) and plug-in hybrids featuring identifiers like ‘E’ or ‘EV’. Benefits include free or discounted parking, bus lane access, and exemptions from driving restrictions. Costs range from $50 to $60, including administration and production fees. Eligible vehicles include Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FC…
2. Rivian – Truck License Plates in Illinois
Domain: rivianforums.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: In Illinois, there is a sliding fee scale for truck license plates based on total weight. Class B allows for a total weight of 8,000 lbs, while Class D allows for 12,000 lbs. It is mandatory to have “EL” plates for electric vehicles (EVs) in Illinois, which incurs an extra fee. The discussion also touches on the importance of having the correct plates to avoid issues with law enforcement.
3. McCarthy Auto Group – 101 Funny EV License Plate Ideas
Domain: blog.mccarthyautogroup.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: The blog post provides a list of over 101 funny and clever personalized license plate ideas specifically for electric vehicles (EVs). It includes various creative suggestions such as “GAS XAUST”, “CH4RG3D”, “GOELEC”, and model-specific ideas for cars like the Chevy Bolt, Chevy Silverado EV, Hyundai IONIQ, Nissan LEAF, and Subaru Solterra. Additionally, it discusses the character limits for persona…
4. Mache Forum – Electric Vehicle License Plate
Domain: macheforum.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Colorado law (HOUSE BILL 21-1141) requires all hybrid and electric vehicles to display the new Electric Vehicle License Plate. If the vehicle has a Specialty Plate, it must also display an EV Decal in the upper right corner of the front windshield. The purpose of this law is to easily identify Electric Vehicles and potentially influence more purchases of electric vehicles. The EV license plate is …
5. Cobb EMC – Electric Vehicle Benefits
Domain: cobbemc.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: 1. Tax Savings: Potential federal tax credit of up to $7,500 for purchasing a new electric vehicle (EV). 2. Maintenance Savings: No need for oil changes, fuel filters, spark plugs, or yearly emissions tests, leading to reduced maintenance costs. 3. Fuel Savings: Cost to operate an EV is approximately 3-5 cents per mile compared to 10-15 cents per mile for gas vehicles. 4. HOV Lane Access: EVs can …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric vehicle license
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of electric vehicle (EV) licenses presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The adoption of EV-specific license plates not only enhances brand visibility but also aligns with global sustainability goals. Buyers can leverage the various benefits associated with these licenses, including access to exclusive parking, exemptions from congestion fees, and even eligibility for government incentives aimed at promoting low-emission vehicles.
As regulations and incentives evolve, understanding local market dynamics becomes crucial. Businesses should remain agile, adapting to changing policies that can impact operational costs and customer engagement. The benefits of investing in EV licenses extend beyond immediate financial advantages; they signal a commitment to environmental responsibility, enhancing corporate reputation in increasingly eco-conscious markets.
Looking ahead, companies are encouraged to proactively engage with local authorities and industry stakeholders to stay informed about upcoming changes and opportunities. By prioritizing strategic sourcing of EV licenses, businesses can position themselves as leaders in the transition to a sustainable future, driving both profitability and positive environmental impact. Take action now to integrate these insights into your sourcing strategy and capitalize on the growing demand for electric vehicles.