Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for delivery electric car
As businesses around the globe seek to enhance operational efficiency and reduce their carbon footprint, the challenge of sourcing delivery electric cars has become increasingly pressing. In the face of rising fuel costs and stringent environmental regulations, international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including key markets such as Germany and Saudi Arabia), must navigate a complex landscape of vehicle options that align with their logistics needs. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for organizations looking to invest in electric delivery vehicles, covering various types, applications, and the intricacies of supplier vetting.
With a focus on empowering informed purchasing decisions, this guide delves into the specifics of electric delivery cars, including their operational advantages, cost considerations, and the latest technological advancements. Buyers will find detailed insights into different vehicle models tailored for diverse delivery scenarios, from last-mile logistics to urban freight solutions. Additionally, we provide actionable strategies for evaluating suppliers, assessing total cost of ownership, and understanding incentives that can mitigate initial investment barriers.
By leveraging the information within this guide, international businesses can confidently transition to electric delivery vehicles, thereby enhancing their sustainability initiatives while meeting customer demands for efficient and eco-friendly logistics solutions.
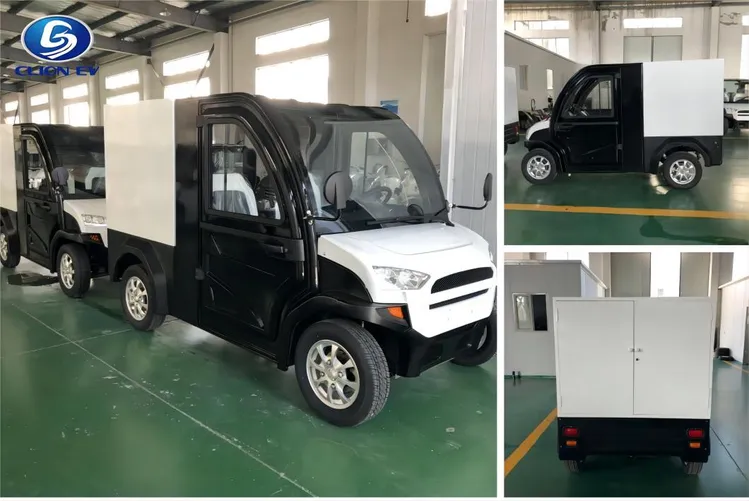
Understanding delivery electric car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Walk-In Delivery Vans | High cargo capacity, low step-in height, zero emissions | Last-mile delivery, logistics, e-commerce | Pros: Large cargo space, easy access; Cons: Higher upfront costs compared to ICE vans. |
| Cargo Electric Trucks | Robust construction, long-range capabilities | Freight transportation, bulk goods delivery | Pros: Strong payload capacity, suitable for long distances; Cons: May require specialized charging infrastructure. |
| Compact Delivery Vehicles | Smaller size, urban maneuverability | Urban deliveries, service vehicles | Pros: Easier parking, lower operational costs; Cons: Limited cargo space compared to larger vehicles. |
| Refrigerated Electric Vans | Temperature control, insulated cargo areas | Food and pharmaceutical distribution | Pros: Maintains product integrity; Cons: Higher maintenance costs due to refrigeration systems. |
| Multi-Purpose Electric Vehicles | Versatile configurations, adaptable design | Diverse delivery needs, service industries | Pros: Flexibility for various applications; Cons: Potentially higher initial investment for customization. |
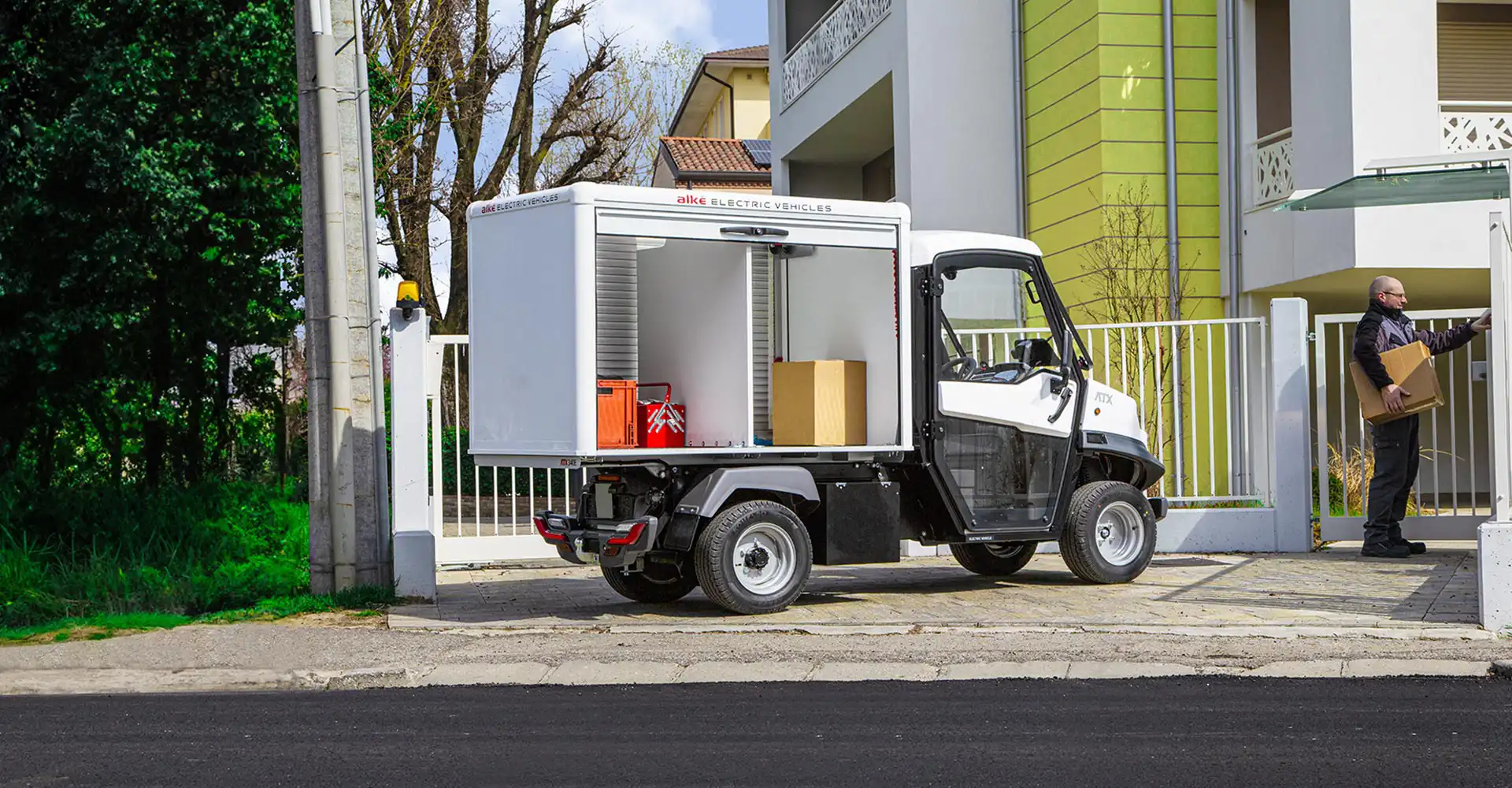
What Are the Characteristics of Walk-In Delivery Vans?
Walk-in delivery vans, such as the BrightDrop Zevo series, are designed for high cargo capacity, featuring a low step-in height for easy access. These vehicles are particularly suitable for last-mile delivery and logistics services, where efficient loading and unloading are crucial. B2B buyers should consider their operational needs, as these vans provide significant space and zero tailpipe emissions, making them ideal for urban environments. However, they come with a higher upfront cost compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vans.
How Do Cargo Electric Trucks Benefit Businesses?
Cargo electric trucks are characterized by their robust construction and long-range capabilities, making them suitable for freight transportation and bulk goods delivery. These vehicles often have a strong payload capacity, which is essential for businesses that transport heavy goods over long distances. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should assess their need for specialized charging infrastructure, as these trucks may require dedicated charging solutions to maximize efficiency.
Why Choose Compact Delivery Vehicles for Urban Deliveries?
Compact delivery vehicles are designed for urban environments, offering smaller sizes that enhance maneuverability and ease of parking. They are ideal for businesses focused on urban deliveries and service applications, where space is limited. B2B buyers can benefit from lower operational costs and easier navigation in congested areas. However, the trade-off is a limited cargo space, which may not suit all delivery needs.
What Are the Advantages of Refrigerated Electric Vans?
Refrigerated electric vans are equipped with temperature control systems and insulated cargo areas, making them essential for food and pharmaceutical distribution. These vehicles ensure product integrity during transportation, which is critical for businesses in the perishable goods sector. While they provide significant benefits, B2B buyers should be aware of the higher maintenance costs associated with refrigeration systems.
How Do Multi-Purpose Electric Vehicles Enhance Delivery Flexibility?
Multi-purpose electric vehicles offer versatile configurations and adaptable designs, catering to diverse delivery needs across various industries. Their flexibility allows businesses to customize the vehicle based on specific operational requirements, making them suitable for everything from package delivery to service applications. However, B2B buyers must consider the potentially higher initial investment required for customization to meet their unique needs.
Key Industrial Applications of delivery electric car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Delivery Electric Car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-commerce | Last-Mile Delivery of Goods | Reduces operational costs and carbon footprint, enhancing brand reputation. | Range, cargo capacity, and charging infrastructure availability. |
| Food and Beverage | Distribution of Perishable Goods | Maintains product integrity while meeting tight delivery schedules. | Temperature control features and refrigeration options. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Delivery of Medical Supplies and Equipment | Ensures timely delivery of critical products, improving service reliability. | Compliance with regulatory standards and tracking capabilities. |
| Retail | Direct-to-Consumer Deliveries | Increases customer satisfaction with faster delivery times. | Vehicle durability for varying road conditions and urban settings. |
| Logistics and Warehousing | Fleet Operations for Bulk Deliveries | Streamlines operations and reduces total cost of ownership. | Fleet management software integration and maintenance support. |
How Are Delivery Electric Cars Utilized in E-commerce Logistics?
In the e-commerce sector, delivery electric cars are primarily used for last-mile delivery, transporting packages directly to consumers’ doorsteps. They provide a sustainable alternative to traditional delivery methods, significantly reducing operational costs and carbon emissions. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, considerations such as vehicle range and cargo capacity are critical to ensure efficient delivery operations in diverse urban landscapes.
What Role Do Delivery Electric Cars Play in Food and Beverage Distribution?
Delivery electric cars are essential for the food and beverage industry, particularly for the distribution of perishable goods. These vehicles can be equipped with temperature control features to maintain product integrity during transit. This capability is vital for businesses aiming to meet strict delivery schedules while ensuring the quality of their products. Buyers should prioritize vehicles that offer reliable refrigeration options and can handle the unique challenges of food delivery.
How Are Delivery Electric Cars Beneficial for Pharmaceuticals?
The pharmaceutical industry relies heavily on timely deliveries of medical supplies and equipment, where delivery electric cars play a crucial role. These vehicles help ensure that critical products reach healthcare providers without delays, thereby enhancing service reliability. For B2B buyers in this sector, compliance with regulatory standards and the ability to track shipments in real-time are essential features to consider when sourcing electric delivery vehicles.
In What Ways Do Delivery Electric Cars Enhance Retail Operations?
In retail, delivery electric cars facilitate direct-to-consumer deliveries, which is increasingly important in a competitive market. By utilizing these vehicles, retailers can improve customer satisfaction through faster delivery times while also enhancing their sustainability efforts. Buyers should evaluate the durability of vehicles to ensure they can withstand varying road conditions, especially in regions with less developed infrastructure.
How Do Delivery Electric Cars Streamline Logistics and Warehousing?
For logistics and warehousing, delivery electric cars are integrated into fleet operations for bulk deliveries. This integration streamlines operations and significantly reduces the total cost of ownership compared to traditional fuel-powered vehicles. Buyers must consider the compatibility of these vehicles with fleet management software and the availability of maintenance support to maximize their operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘delivery electric car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Managing Range Anxiety in Urban Deliveries
The Problem:
B2B buyers often grapple with range anxiety, particularly in urban environments where delivery schedules can be tight and routes unpredictable. This concern is heightened when operating electric delivery vehicles in regions with limited charging infrastructure. Buyers worry about whether their fleet can cover the required distances without running out of battery, especially during peak hours when charging stations may be occupied or difficult to access.
The Solution:
To mitigate range anxiety, B2B buyers should prioritize electric delivery vehicles that offer extended battery ranges and rapid charging capabilities. Models like the BrightDrop Zevo 600, which boasts an estimated combined range of up to 272 miles, can accommodate most urban delivery routes without the need for frequent recharges. Buyers should also analyze their delivery patterns to determine average distances and identify high-demand areas for charging stations. Collaborating with local charging network providers to establish dedicated charging points can further enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, implementing route optimization software can help drivers maximize their vehicle’s range by choosing paths that minimize energy consumption, ensuring that deliveries are completed smoothly and on time.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Driver Safety and Comfort
The Problem:
Another significant challenge for B2B buyers is ensuring the safety and comfort of drivers operating electric delivery vehicles. With the shift to electric fleets, there may be concerns about how these vehicles perform in adverse weather conditions or during long delivery shifts. Moreover, inadequate safety features could lead to accidents, resulting in injuries and increased liability for the company.
The Solution:
Investing in electric delivery vehicles equipped with advanced safety features is crucial. Models like the Rivian Commercial Van come with 360-degree cameras and enhanced driver assistance systems that provide comprehensive visibility and aid in collision avoidance. Buyers should conduct thorough evaluations of available models, focusing on safety ratings and driver feedback regarding comfort features like climate control and seating ergonomics. Additionally, providing ongoing safety training for drivers and ensuring vehicles are regularly maintained will further enhance safety and comfort on the road. Establishing a feedback loop where drivers can report issues or suggest improvements can help continuously refine safety protocols and vehicle configurations.
Scenario 3: Navigating Cost and Financing Challenges
The Problem:
B2B buyers may face significant financial hurdles when transitioning to an electric delivery fleet, including higher upfront costs and uncertainties regarding long-term savings. While electric vehicles often promise lower operational costs through reduced fuel and maintenance expenses, the initial investment can be daunting, especially for companies operating on tight budgets.
The Solution:
To navigate these financial challenges, buyers should explore various financing options such as leasing, which can lower initial costs while providing flexibility as business needs evolve. Companies like GM Envolve offer tailored leasing programs that allow businesses to access electric vehicles without a hefty upfront investment. Furthermore, buyers should stay informed about government incentives and tax credits available for electric vehicle purchases, which can significantly offset costs. Conducting a total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis will help buyers understand the long-term savings from reduced fuel costs and maintenance, making a compelling case for the transition to electric delivery vehicles. Finally, engaging with fleet management consultants can provide insights into cost-effective strategies for integrating electric vehicles into existing operations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for delivery electric car
What Are the Key Materials for Delivery Electric Cars?
When selecting materials for delivery electric cars, several factors come into play, including performance, durability, cost, and international compliance. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of delivery electric vehicles, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Enhance Delivery Electric Cars?
Aluminum is widely utilized in the manufacturing of delivery electric cars due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio. It typically withstands temperatures up to 600°F and exhibits good corrosion resistance, making it ideal for various environmental conditions.
Pros and Cons: Aluminum is lightweight, which contributes to improved energy efficiency and range. However, it can be more expensive than traditional steel and may require specialized welding techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Its lightweight nature improves vehicle dynamics and battery efficiency, while its corrosion resistance ensures longevity, especially in humid or coastal regions.
International Considerations: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East must ensure compliance with local standards, such as DIN and ASTM, which may dictate specific grades of aluminum for automotive applications.
What Role Does Steel Play in Delivery Electric Vehicles?
Steel remains a staple in the automotive industry, including electric delivery vehicles, due to its high tensile strength and cost-effectiveness. It can handle high-pressure environments and is often treated for corrosion resistance.
Pros and Cons: Steel is durable and less expensive than aluminum, making it a popular choice for structural components. However, it is heavier, which can negatively impact the vehicle’s range and efficiency. Additionally, it may be prone to rust if not adequately treated.
Impact on Application: Steel’s robustness makes it suitable for high-impact areas, such as the chassis and frame, but its weight can lead to increased energy consumption.
International Considerations: B2B buyers should be aware of compliance with regional standards like JIS in Japan and ASTM in the U.S., which may affect the choice of steel grades for safety and performance.
How Does Composite Material Benefit Delivery Electric Cars?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP), are gaining traction in electric vehicle design due to their lightweight and high-strength properties. They can withstand significant stress and offer excellent temperature resistance.
Pros and Cons: Composites are lighter than metals, which enhances energy efficiency and performance. However, they are typically more expensive and may require specialized manufacturing processes that can complicate production.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for non-structural components, such as body panels, where weight savings are critical without compromising safety.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider the availability of composite materials and the associated manufacturing capabilities, as these may vary significantly.
Why Is Plastic Used in Delivery Electric Vehicle Components?
Plastics are increasingly used in electric delivery vehicles for various components, including interior fittings and electronic housings. They are lightweight, versatile, and can be engineered to provide specific properties, such as UV resistance.
Pros and Cons: Plastics are cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, offering design flexibility. However, they may not provide the same level of durability as metals and can degrade under extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for non-load-bearing applications, contributing to overall weight reduction and cost savings.
International Considerations: Compliance with environmental regulations regarding plastic use, such as those in the EU, is crucial for international buyers, particularly concerning recyclability and sustainability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Delivery Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for delivery electric car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, structural components | Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Steel | Chassis, frame | Durable, cost-effective | Heavier, prone to rust | Medium |
| Composite | Body panels, non-structural components | Lightweight, high strength | Expensive, specialized manufacturing | High |
| Plastic | Interior fittings, electronic housings | Cost-effective, design flexibility | Less durable, can degrade under stress | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with critical insights into the materials used in delivery electric cars, enabling informed decisions that align with performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for delivery electric car
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electric Delivery Vehicles?
The manufacturing process for electric delivery vehicles (EDVs) involves several key stages, each designed to ensure efficiency, sustainability, and high quality. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing these vehicles.
1. Material Preparation
Material preparation is the first stage in the manufacturing process, where raw materials such as aluminum, steel, and composite materials are sourced and processed. Advanced materials are chosen for their lightweight properties, which contribute to improved energy efficiency and vehicle performance. Suppliers must adhere to international standards for material quality, ensuring that they are free from defects and suitable for automotive applications. Buyers should verify the provenance and quality certifications of materials used, as this can significantly impact the vehicle’s performance and longevity.
2. Forming and Fabrication Techniques
Following material preparation, the forming stage involves techniques such as stamping, molding, and machining to create the various components of the vehicle. For instance, the body panels are often stamped from sheets of metal, while electric motor components may be machined for precision.
Innovative techniques, such as additive manufacturing (3D printing), are increasingly being utilized for producing complex components with less waste. This not only streamlines production but also allows for customization, which can be crucial for businesses looking for tailored solutions. Buyers should assess whether suppliers are leveraging modern manufacturing technologies to enhance efficiency and reduce lead times.
3. Assembly Process
The assembly process is where all the individual components come together to form a complete vehicle. This stage involves multiple sub-assemblies, such as the chassis, powertrain, and electrical systems. Automation plays a significant role in this phase, with robotics being used for tasks like welding and component placement.
Quality control checkpoints are critical during assembly, where each vehicle is systematically inspected to ensure that it meets design specifications and safety standards. B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly practices employed by manufacturers, including the use of lean manufacturing techniques to minimize waste and optimize productivity.
4. Finishing Touches
The finishing stage includes painting, interior fitting, and final inspections. Electrocoating and powder coating are commonly used for corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Additionally, this stage ensures that all safety features and electronic systems are functioning correctly.
Buyers should evaluate the environmental standards that manufacturers adhere to in this phase, particularly regarding waste management and emissions during painting and finishing processes. Sustainable practices can enhance a company’s corporate social responsibility profile, which is increasingly important in global markets.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Electric Delivery Vehicle Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of electric delivery vehicles, ensuring that every unit produced meets stringent safety and performance standards.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Electric Delivery Vehicles?
Manufacturers often adhere to various international standards, such as ISO 9001, which provides a framework for quality management systems. This certification ensures that organizations consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (for European markets) and API standards (for components like batteries) are crucial. These certifications provide assurance that the vehicles meet safety and environmental regulations, which is vital for international buyers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control in electric vehicle manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints throughout the production process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage assesses the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the manufacturing process. Effective IQC can prevent defects from propagating through production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC involves monitoring production processes to catch defects early. This might include checks after critical operations like welding and assembly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, FQC ensures that the finished vehicle meets all specifications and safety requirements. This may include dynamic testing of the vehicle’s systems and thorough inspections of all safety features.
B2B buyers should request detailed quality reports from manufacturers, as these documents provide insights into the efficacy of their quality assurance processes.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers looking to ensure the quality of electric delivery vehicles should consider several verification methods:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of manufacturing facilities allows buyers to assess the quality management systems in place. This includes reviewing compliance with international standards and evaluating the overall production environment.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting documentation that outlines quality control procedures, including testing results and defect rates, can help buyers gauge the reliability of the supplier.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturer’s quality control processes. This is especially important for international buyers who may not be able to visit production facilities.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is crucial. Different regions may have varying standards and regulations that impact vehicle compliance. For example, European markets have strict emissions and safety standards that must be met for vehicles to be sold.
Additionally, buyers should be aware of the logistics involved in importing vehicles, including customs regulations and documentation requirements. Establishing a clear line of communication with suppliers regarding quality expectations and compliance can mitigate potential issues.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for electric delivery vehicles are complex and multifaceted. B2B buyers must thoroughly evaluate potential suppliers based on their manufacturing capabilities, adherence to quality standards, and commitment to sustainability. This diligence will ensure that they make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals and market requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘delivery electric car’
In today’s rapidly evolving logistics landscape, sourcing electric delivery vehicles (EDVs) is essential for businesses aiming to enhance efficiency and sustainability. This guide provides a structured approach for B2B buyers looking to procure delivery electric cars, focusing on key considerations that can streamline the sourcing process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical requirements for your delivery electric vehicles. Consider factors such as cargo capacity, range, battery specifications, and specific features necessary for your operations.
– Cargo Volume: Assess the volume of goods typically transported to ensure the vehicle meets your needs.
– Range: Evaluate the distance your deliveries cover to select a vehicle with an adequate range to avoid downtime.
Step 2: Assess Regulatory Compliance
Ensure that the vehicles you are considering comply with local and international regulations. Different regions may have specific emissions standards and safety requirements that must be met.
– Certification: Check for compliance certificates from relevant authorities.
– Incentives: Investigate potential government incentives for electric vehicles, which can significantly reduce overall costs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from businesses similar to yours.
– Track Record: Look for suppliers with a proven history of delivering electric vehicles to businesses in your sector.
– Support Services: Evaluate the level of post-purchase support and maintenance services offered by the supplier.
Step 4: Analyze Total Cost of Ownership
Calculate the total cost of ownership (TCO) for the electric delivery vehicles, not just the initial purchase price. TCO includes maintenance, charging infrastructure, insurance, and potential tax benefits.
– Long-Term Savings: Assess fuel savings compared to traditional vehicles and potential maintenance savings due to fewer moving parts.
– Financing Options: Explore financing options that may be available through suppliers or third-party financial institutions.
Step 5: Test Drive and Evaluate Performance
Arrange for test drives of shortlisted vehicles to evaluate their performance in real-world conditions. Pay attention to driving comfort, technology features, and operational efficiency.
– Driver Feedback: Involve your drivers in the evaluation process to gain insights into comfort and usability.
– Performance Metrics: Look for features that enhance driver safety and operational efficiency, such as advanced navigation and telematics systems.
Step 6: Consider Upfitting and Customization Options
Identify if the vehicles require any customizations or upfitting to suit your operational needs. Many suppliers offer modular designs that can be tailored to specific delivery requirements.
– Modular Features: Explore options for shelving, cargo management systems, or specialized equipment based on your logistics needs.
– Future Scalability: Ensure that the customization options can accommodate future growth or changes in your business model.
Step 7: Finalize Purchase and Delivery Logistics
Once you’ve selected the right vehicle, finalize the purchase agreement, ensuring all terms are clear. Discuss delivery logistics to ensure a smooth transition to your fleet.
– Delivery Schedule: Set a realistic timeline for delivery and any training sessions for your drivers.
– Documentation: Ensure all necessary paperwork, warranties, and service agreements are finalized prior to delivery.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing delivery electric cars, aligning with their operational goals while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for delivery electric car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Delivery Electric Car Sourcing?
When sourcing delivery electric vehicles (EVs), it’s crucial to understand the various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing structure. These include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as batteries, electric drivetrains, and lightweight materials, significantly influences the final price. Battery costs are particularly high and are subject to market fluctuations.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct and indirect labor involved in the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is essential for assembling complex electric systems, which may lead to higher wages compared to traditional vehicle assembly.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with production facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. As manufacturers invest in advanced technologies for EV production, these overhead costs may rise.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized tooling for electric vehicle production can be substantial. This upfront cost is often amortized over the production volume, influencing unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Given the critical safety and performance standards for delivery EVs, robust QC processes are necessary. The costs associated with testing and ensuring compliance with international standards can add to the overall expense.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs must be considered, especially for international buyers. The complexity of transporting EVs, which may require special handling due to battery regulations, can increase logistics costs.
-
Margin: Finally, the manufacturer’s profit margin is included in the price. This margin can vary significantly based on market competition, brand reputation, and the unique features of the vehicle.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Delivery Electric Car Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of delivery electric cars, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Manufacturers often have tiered pricing structures that favor larger orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as enhanced battery capacity or specialized cargo solutions, can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials affects both cost and vehicle performance. High-quality materials may lead to higher initial costs but can result in lower maintenance and operational costs over time.
-
Quality and Certifications: Vehicles that meet higher safety and environmental standards may come with a premium price. Ensure that any certifications are recognized in your target market to avoid compliance issues.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established manufacturers may charge more, but they often provide better warranties and service support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is essential for determining who bears the cost and risk at different stages of the shipping process. This knowledge can help in negotiating better terms with suppliers.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Delivery Electric Car Prices?
For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, negotiating effectively can lead to significant cost savings:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also long-term costs, including maintenance, charging infrastructure, and potential government incentives for electric vehicles.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can result in better pricing and terms. Regular communication can lead to favorable negotiations in future purchases.
-
Be Transparent About Requirements: Clearly communicate your needs and expectations to suppliers. This transparency can lead to more accurate quotes and reduce the risk of unexpected costs.
-
Explore Financing Options: Investigate various financing options that may be available for electric vehicle purchases. Some manufacturers offer leasing programs that can improve cash flow while acquiring new vehicles.
Conclusion
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing influences when sourcing delivery electric cars is vital for making informed purchasing decisions. By considering the various cost components, price influencers, and employing strategic negotiation techniques, international B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing strategy and potentially reduce overall expenses. Always remember to conduct thorough due diligence and seek indicative prices tailored to your specific requirements to ensure a successful procurement process.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing delivery electric car With Other Solutions
In the rapidly evolving landscape of logistics and delivery, businesses must consider various solutions to optimize their operations. While delivery electric cars are gaining traction for their sustainability and efficiency, there are other viable alternatives that also serve to enhance last-mile delivery. This section explores the comparative merits of delivery electric cars against alternative solutions like traditional delivery vans and cargo bikes.
| Comparison Aspect | Delivery Electric Car | Traditional Delivery Van | Cargo Bike |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Up to 272 miles range | Varies (10-400 miles) | Limited to 15-30 miles |
| Cost | $45,225 – $46,925 | $30,000 – $50,000 | $2,000 – $5,000 |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate (charging infrastructure needed) | High (existing infrastructure) | Low (minimal setup required) |
| Maintenance | Lower (fewer moving parts) | Moderate (routine maintenance needed) | Very low (minimal mechanical parts) |
| Best Use Case | Urban and suburban delivery | General delivery in varied terrains | Urban areas with heavy traffic |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Traditional Delivery Vans?
Traditional delivery vans, powered by internal combustion engines, have been a staple in logistics for years. They offer a broader range, making them suitable for longer routes and diverse terrains. However, their operational costs can be higher due to fuel and maintenance requirements. Additionally, the environmental impact is significant, as these vehicles contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. For businesses operating in areas with stringent emissions regulations, the transition to electric vehicles may be more favorable.
How Do Cargo Bikes Compare to Delivery Electric Cars?
Cargo bikes represent a sustainable alternative, especially in congested urban settings. They are cost-effective and have lower maintenance needs, making them appealing for small businesses or those focused on last-mile delivery. The limited range is a significant drawback; cargo bikes are best suited for short distances. Furthermore, they may not be suitable for transporting larger or heavier packages, which limits their application in certain logistics scenarios.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Delivery Solution?
For B2B buyers considering delivery solutions, the choice between a delivery electric car, traditional delivery van, or cargo bike depends on several factors. These include the operational range required, budget constraints, and sustainability goals. Companies focused on reducing their carbon footprint may lean towards electric vehicles, while those needing to navigate longer distances or varied terrains might opt for traditional vans. On the other hand, businesses operating in dense urban environments may find cargo bikes to be the most efficient and cost-effective option. Ultimately, assessing specific logistical needs and environmental objectives will guide buyers in selecting the most appropriate solution for their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for delivery electric car
What are the Key Technical Properties of Delivery Electric Cars?
When considering delivery electric vehicles (EVs) for fleet operations, understanding key technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications that B2B buyers should evaluate:
-
Battery Capacity (kWh)
Battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), indicates how much energy the vehicle can store. A higher capacity typically allows for longer ranges, which is crucial for delivery operations that may involve long routes. For instance, vehicles like the BrightDrop Zevo 600 offer up to 272 miles of range, significantly reducing the need for frequent recharging during busy delivery schedules. -
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR)
GVWR is the maximum weight a vehicle is rated to safely carry, including its own weight plus cargo. This measurement is vital for fleet managers to ensure compliance with local regulations and to maintain vehicle safety. For example, the Zevo models have a GVWR of up to 11,000 lbs, allowing for substantial cargo loads without compromising performance. -
Cargo Volume (cu. ft.)
Cargo volume refers to the space available for transporting goods, measured in cubic feet (cu. ft.). A larger cargo volume means more goods can be transported per trip, enhancing operational efficiency. The BrightDrop Zevo 600 provides up to 614.7 cu. ft. of cargo space, making it suitable for various delivery needs. -
Charging Rate (miles per hour)
The charging rate, expressed in miles per hour, indicates how quickly the vehicle can be recharged at a charging station. Fast charging capabilities minimize downtime, which is crucial for fleet operations. The Zevo models feature a max charging rate of 160 miles per hour, allowing for quick turnarounds during busy delivery periods. -
Payload Capacity (lbs.)
Payload capacity refers to the maximum weight the vehicle can safely carry, excluding its own weight. This specification is critical for ensuring that delivery operations remain efficient and within legal limits. For instance, the Zevo 600 has a maximum payload capacity of 3,180 lbs, accommodating a wide variety of delivery types.
What are Common Trade Terms in the Delivery Electric Car Industry?
Understanding industry terminology is equally important for navigating the B2B landscape effectively. Here are several common terms that buyers should be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that manufactures vehicles or components that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of delivery electric cars, OEMs play a crucial role in ensuring the quality and reliability of the vehicles purchased. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for fleet buyers as it impacts inventory management and purchasing strategies. Understanding MOQs can help buyers negotiate better terms and plan their budgets more effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where a buyer requests pricing and terms from suppliers for specific quantities of goods. In the context of electric delivery vehicles, issuing an RFQ allows businesses to compare offers from multiple manufacturers, ensuring competitive pricing and terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping costs, risks, and delivery points. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers negotiate better shipping agreements and understand their liabilities. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO is a financial estimate that helps buyers assess the overall cost of owning a vehicle over its lifetime, including purchase price, maintenance, fuel, and depreciation. Understanding TCO is crucial for B2B decision-makers as it provides a comprehensive view of the economic viability of electric delivery vehicles. -
Fleet Management Software
This refers to software solutions designed to help businesses manage their vehicle fleets efficiently. Features often include route optimization, real-time tracking, and maintenance scheduling. Utilizing fleet management software can enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs for businesses utilizing electric delivery vehicles.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the delivery electric car Sector
What Are the Global Drivers and Key Trends Shaping the Delivery Electric Car Market?
The delivery electric car sector is experiencing a transformative phase, driven by several global factors. The urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions has led governments across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to implement stringent regulations and provide incentives for electric vehicle (EV) adoption. For instance, the European Union aims for a significant reduction in carbon emissions by 2030, promoting the transition to electric delivery fleets. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce and the demand for last-mile delivery solutions are pushing businesses to consider electric vans that can efficiently navigate urban environments while minimizing their carbon footprint.
Emerging technologies are also reshaping the sourcing landscape. Innovations in battery technology, such as GM’s advanced battery platform for the BrightDrop Zevo series, are enhancing range and efficiency, making electric delivery vehicles more viable for long-distance logistics. Furthermore, connectivity features like fleet management systems enable real-time tracking and optimization, offering significant operational benefits. As international buyers seek to capitalize on these advancements, they are increasingly focusing on sourcing vehicles that align with their sustainability goals while also providing cost-effective solutions.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Delivery Electric Car Sector?
Sustainability is not just a buzzword but a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the delivery electric car sector. The environmental impact of traditional combustion engines has led many companies to seek electric alternatives that produce zero tailpipe emissions. By transitioning to electric fleets, businesses can reduce their operational greenhouse gas emissions by up to 50%, aligning with global sustainability initiatives and enhancing their brand reputation.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is becoming increasingly important as buyers are more conscious of the supply chain’s environmental and social impacts. Companies are now prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and ensuring fair labor practices. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED for green building are essential indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. By partnering with manufacturers that prioritize ethical sourcing and sustainability, businesses can enhance their operational resilience and comply with evolving regulations.
How Has the Delivery Electric Car Market Evolved Over Time?
The delivery electric car market has evolved significantly over the last decade, transitioning from niche products to mainstream solutions. Initially, electric vehicles were primarily seen as consumer products, but advancements in technology and a growing awareness of climate change have shifted perceptions. Major automotive players like General Motors and Rivian have entered the market, developing purpose-built electric vans designed for logistics and delivery.
The introduction of government incentives and the establishment of charging infrastructure have further accelerated adoption. As more businesses recognize the operational and environmental benefits of electric fleets, the market is poised for exponential growth. This evolution reflects a broader trend towards electrification across various sectors, emphasizing the necessity for B2B buyers to stay informed and proactive in their sourcing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of delivery electric car
-
How do I solve the challenge of sourcing electric delivery vehicles for my business?
To effectively source electric delivery vehicles, start by identifying your specific operational needs, such as cargo capacity, range, and budget. Research manufacturers that specialize in electric delivery vehicles and evaluate their offerings based on performance, safety features, and after-sales support. Engage with suppliers for product demonstrations and detailed specifications. Additionally, consider joining industry trade shows or forums to connect with potential suppliers and gain insights into market trends. Always verify suppliers’ credibility through reviews, references, and certifications to ensure a reliable partnership. -
What is the best electric delivery vehicle for last-mile logistics?
The ideal electric delivery vehicle for last-mile logistics should balance range, payload capacity, and maneuverability. Options like the BrightDrop Zevo 600, which offers up to 272 miles of range and a cargo volume of 614.7 cu. ft., are designed specifically for this purpose. Rivian’s Commercial Van is another contender, featuring advanced safety technology and energy-efficient design. Assess your specific delivery routes and volume needs to determine which vehicle provides the best operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness for your fleet. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting suppliers of electric delivery vehicles?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry reputation, production capabilities, and customer service. Evaluate their experience in the electric vehicle market and ask for case studies or testimonials from similar businesses. It’s also essential to assess their warranty and support services, including maintenance and repairs. Additionally, consider their compliance with international standards and regulations, especially if you’re importing vehicles to regions with specific requirements, such as Europe or the Middle East. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for electric delivery vehicles?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and region. Many manufacturers may set an MOQ of 10 to 50 vehicles for fleet orders to ensure cost-effectiveness and efficient production runs. However, some suppliers may offer flexibility for smaller businesses or first-time buyers. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that align with your business strategy and budget constraints. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing electric delivery vehicles?
Payment terms for electric delivery vehicles typically include options such as full upfront payment, financing, or leasing arrangements. Many suppliers may require a deposit upon order confirmation, followed by the balance before delivery. It’s crucial to clarify terms regarding installment payments, interest rates, and any potential tax incentives that may apply to your purchase. Always review the contract details carefully to avoid unexpected fees and ensure compliance with local regulations. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing electric delivery vehicles?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications, certifications, and compliance documents from your supplier. Conduct thorough inspections of the vehicles upon delivery, checking for defects and functionality. Establish a clear communication channel with the supplier for reporting issues and obtaining support. Additionally, consider implementing a trial period where you can test the vehicles in real operational conditions before fully committing to larger orders. -
What logistics considerations are important when importing electric delivery vehicles?
Logistics for importing electric delivery vehicles involve several critical factors, including transportation methods, customs regulations, and local compliance standards. Choose a reliable logistics partner experienced in handling vehicle imports. Ensure that all necessary documentation, such as bills of lading, customs declarations, and import permits, is prepared in advance to avoid delays. Additionally, consider the impact of local infrastructure on the delivery process, such as charging station availability and road conditions. -
How can I customize electric delivery vehicles to meet my business needs?
Customization options for electric delivery vehicles often include modifications like shelving, cargo management systems, and branding decals. Many manufacturers provide upfit solutions tailored to specific operational requirements. Discuss your customization needs during the ordering process with your supplier to explore available options. Additionally, inquire about the potential for future upgrades or modifications, ensuring that your investment can adapt to evolving business needs over time.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Delivery Electric Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
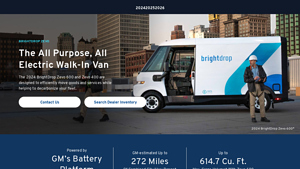
1. BrightDrop – Zevo 600 & Zevo 400
Domain: gmenvolve.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: 2024 BrightDrop Zevo 600 and Zevo 400
– Type: All Electric Walk-In Van
– Purpose: Efficiently move goods and services, decarbonize fleet
– Power: GM’s Battery Platform
– Estimated Range: Up to 272 miles (combined city/highway)
– Cargo Volume: Zevo 600 – 614.7 cu. ft.; Zevo 400 – 412.1 cu. ft.
– Lease Offer: $599/month for 36 months, $2,999 due at signing
– Starting Prices: Zevo 400 – $45,425; Zevo…
2. Rivian – Electric Commercial Vans
Domain: rivian.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Rivian Fleet offers electric work and commercial vans starting at $79,900. The Rivian Commercial Van is designed for sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and safety, featuring 360-degree cameras and patented energy-saving microclimate seats. It aims to reduce operational GHG emissions by 50% or more compared to internal combustion vehicles. Key dimensions include a length of 248.5 inches, height of…
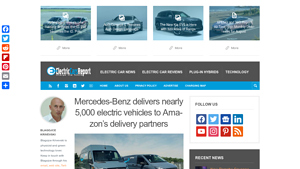
3. Mercedes-Benz – eVito and eSprinter Electric Vans
Domain: electriccarsreport.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Mercedes-Benz is delivering nearly 5,000 fully electric eVito and eSprinter vehicles to Amazon’s Delivery Service Partners (DSP) in Europe. This order marks the largest single order for Mercedes-Benz electric vehicles. The eVito is available with battery capacities of 90 kWh or 60 kWh, featuring a range of up to 480 kilometers (WLTP) and is ideal for urban environments. The eSprinter offers a rang…
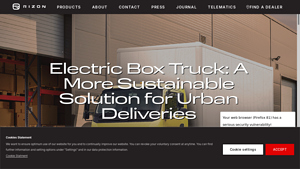
4. RIZON Trucks – Electric Box Truck
Domain: rizontruck.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Electric box truck, also known as electric delivery van or last-mile delivery vehicle, is part of RIZON Trucks, a Daimler Truck brand. It is designed for urban logistics with benefits including reduced CO2 emissions, lower operating costs, quiet operation, instant torque, and suitability for short distances and return-to-base operations. Key features include fewer moving parts leading to lower mai…
5. USPS – Electric Vehicle Initiative
Domain: about.usps.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: USPS intends to deploy over 66,000 electric vehicles by 2028, as part of a plan to acquire a total of 106,000 vehicles. This includes at least 60,000 Next Generation Delivery Vehicles (NGDV), with a minimum of 45,000 being battery electric. An additional 21,000 battery electric delivery vehicles are expected to be purchased, which will include commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) vehicles. The total in…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for delivery electric car
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of electric delivery vehicles is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency while achieving sustainability goals. The BrightDrop Zevo and Rivian Commercial Van exemplify the trend towards electrification, offering significant advantages such as reduced operational costs, lower carbon emissions, and advanced safety features. By investing in these vehicles, companies can not only contribute to global decarbonization efforts but also align with the increasing demand for eco-friendly logistics solutions.
As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe consider their fleet options, the importance of thorough supplier evaluation and partnership development cannot be overstated. Leveraging strategic sourcing practices will enable businesses to select the right electric vehicle solutions tailored to their unique logistical needs, ensuring a competitive edge in the evolving marketplace.
Looking ahead, the transition to electric delivery vehicles is not just a trend; it’s a necessity. Companies are encouraged to act now by engaging with suppliers, exploring financing options, and integrating electric vehicles into their operations. By doing so, they can position themselves as leaders in sustainability and innovation in the delivery sector.