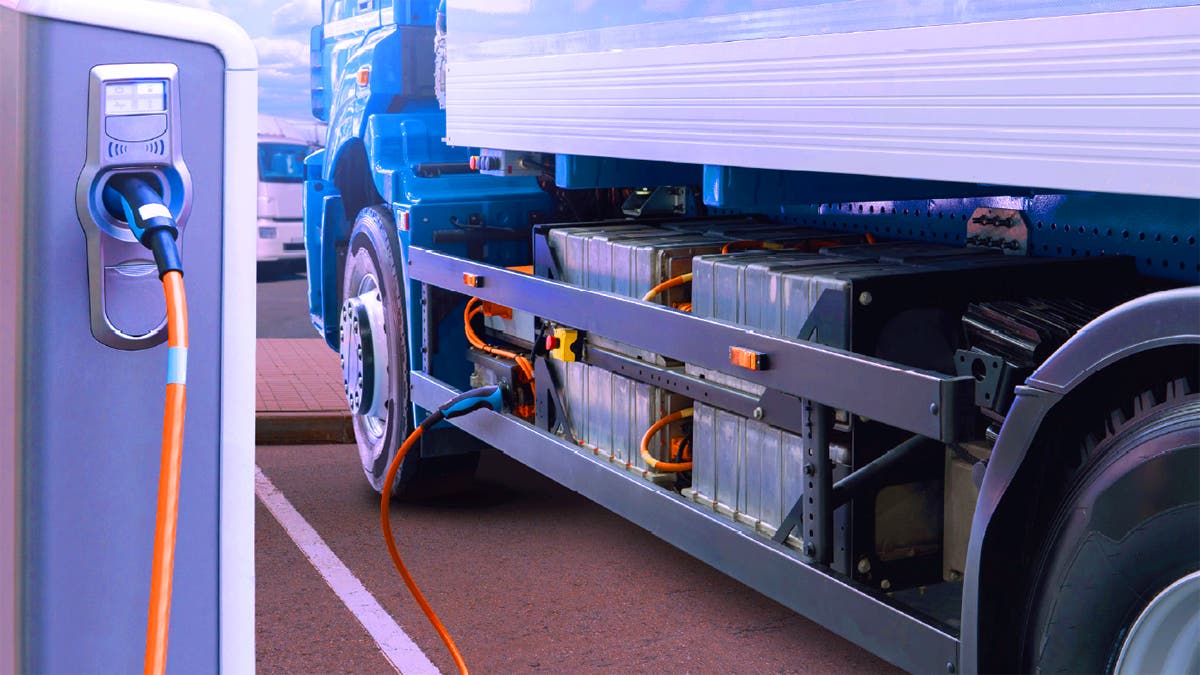
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for heavy duty electric car
In an era marked by rapid technological advancement and heightened environmental consciousness, sourcing heavy-duty electric cars has become a pressing challenge for international B2B buyers. The transition from traditional combustion engines to electric alternatives is not merely a trend; it’s a strategic shift that can significantly impact operational efficiency and sustainability. This comprehensive guide serves as a pivotal resource for businesses looking to navigate the complex landscape of heavy-duty electric vehicles, covering a wide array of topics including vehicle types, applications across various industries, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
Understanding the nuances of heavy-duty electric cars is essential for making informed purchasing decisions, particularly in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key players like Germany and Brazil. This guide empowers B2B buyers by providing actionable insights into the latest trends, technological innovations, and regulatory frameworks that influence the electric vehicle sector. By equipping businesses with the knowledge needed to identify suitable suppliers and evaluate total cost of ownership, this resource aims to streamline the decision-making process and facilitate a seamless transition to electric mobility. The future of transportation is electric, and this guide is your roadmap to successfully integrating heavy-duty electric cars into your fleet.
Understanding heavy duty electric car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Cargo Trucks | High payload capacity, designed for long-haul transport | Freight and logistics companies | Pros: Lower operating costs; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Electric Construction Trucks | Robust build, capable of heavy-duty tasks | Construction and infrastructure projects | Pros: Reduced emissions; Cons: Limited range in some models. |
| Electric Delivery Vans | Compact size, optimized for urban environments | Last-mile delivery services | Pros: Maneuverability in tight spaces; Cons: Limited payload compared to larger trucks. |
| Electric Buses | Designed for passenger transport with large capacity | Public transportation and shuttle services | Pros: Eco-friendly; Cons: High upfront costs and charging infrastructure needs. |
| Electric Refrigerated Trucks | Temperature-controlled, suitable for perishable goods | Food and pharmaceutical distribution | Pros: Maintains product integrity; Cons: Complex maintenance and higher costs. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Electric Cargo Trucks?
Electric cargo trucks are engineered for high payload capacities and long-haul transport, making them ideal for freight and logistics companies. These vehicles often come with advanced battery systems that provide extended ranges, allowing for efficient long-distance deliveries. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including fuel savings and potential government incentives, against the initial investment.
How Do Electric Construction Trucks Stand Out?
Electric construction trucks are built to endure the rigors of heavy-duty tasks on construction sites. They feature robust designs that accommodate high load capacities and provide excellent visibility for operators. B2B buyers in the construction sector should consider the operational benefits of reduced noise and emissions, which can enhance site safety and compliance with environmental regulations. However, potential limitations in range may require careful planning for charging infrastructure.
Why Are Electric Delivery Vans Essential for Urban Logistics?
Electric delivery vans are compact and specifically optimized for urban environments, making them perfect for last-mile delivery services. Their maneuverability allows for efficient navigation through congested city streets. Businesses should consider the advantages of reduced operating costs and lower emissions against the trade-off of limited payload capacities. The growing demand for sustainable logistics solutions makes these vehicles increasingly attractive.
What Makes Electric Buses a Viable Option for Public Transport?
Electric buses are designed for passenger transport, offering high capacity and zero emissions. They are becoming essential in public transportation systems worldwide, especially in urban areas striving to reduce air pollution. B2B buyers need to weigh the environmental benefits and potential long-term savings in fuel and maintenance against the high upfront costs and the need for robust charging infrastructure.
How Do Electric Refrigerated Trucks Benefit Perishable Goods Transport?
Electric refrigerated trucks are specialized vehicles designed to transport perishable goods while maintaining strict temperature controls. This feature is crucial for businesses in the food and pharmaceutical sectors. B2B buyers should consider the integrity of their products during transport, as well as the potential for lower operating costs. However, they must also be aware of the complexities involved in maintenance and higher initial costs associated with these specialized trucks.
Key Industrial Applications of heavy duty electric car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of heavy duty electric car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics and Transportation | Last-mile delivery in urban areas | Reduced operational costs and improved delivery efficiency | Range, battery capacity, and charging infrastructure availability |
| Construction | Heavy-duty electric trucks for construction sites | Lower emissions and reduced noise levels, enhancing site safety | Load capacity, terrain adaptability, and battery life |
| Waste Management | Electric refuse collection vehicles | Compliance with environmental regulations and cost savings | Vehicle durability, maintenance support, and local regulations |
| Agriculture | Electric tractors and transport vehicles | Sustainability and lower fuel costs, improving profit margins | Power requirements, compatibility with existing farm equipment |
| Mining | Electric haul trucks for mineral transport | Reduced carbon footprint and lower fuel expenses | Terrain capability, battery range, and charging solutions |
How Are Heavy Duty Electric Cars Transforming Logistics and Transportation?
In the logistics and transportation sector, heavy-duty electric cars are increasingly used for last-mile delivery in urban areas. These vehicles address the challenge of rising fuel costs and emissions regulations. Businesses benefit from reduced operational costs and improved delivery efficiency, as electric vehicles often have lower maintenance costs and can access urban zones with restrictions on fossil fuel vehicles. Buyers should consider factors like range, battery capacity, and the availability of charging infrastructure to ensure optimal performance in their operations.
What Role Do Heavy Duty Electric Cars Play in the Construction Industry?
In the construction industry, heavy-duty electric trucks are utilized on job sites for transporting materials and equipment. These vehicles help companies comply with stringent emissions regulations while minimizing noise pollution, which is crucial in urban settings. The reduced environmental impact enhances the company’s image and can lead to potential cost savings in fuel and maintenance. Buyers need to focus on load capacity, terrain adaptability, and battery life to meet the demanding requirements of construction projects effectively.
How Are Heavy Duty Electric Cars Enhancing Waste Management Practices?
Electric refuse collection vehicles are revolutionizing waste management by offering a cleaner alternative to traditional diesel trucks. These vehicles not only help companies comply with environmental regulations but also reduce operational costs associated with fuel and maintenance. The quiet operation of electric trucks improves the quality of life in residential areas during early morning collections. Key considerations for buyers include vehicle durability, maintenance support, and adherence to local regulations to ensure seamless integration into existing fleets.
In What Ways Are Heavy Duty Electric Cars Beneficial for Agriculture?
In agriculture, heavy-duty electric cars, particularly tractors and transport vehicles, are being adopted for their sustainability benefits. They help farmers reduce their carbon footprint while lowering fuel costs, ultimately improving profit margins. The ability to operate quietly also minimizes disturbances to livestock and wildlife. When sourcing electric agricultural vehicles, buyers should assess power requirements and compatibility with existing farm equipment to ensure a smooth transition to electric operations.
How Are Heavy Duty Electric Cars Impacting the Mining Industry?
Heavy-duty electric haul trucks are making significant inroads in the mining sector by transporting minerals more sustainably. These vehicles contribute to a reduced carbon footprint and lower fuel expenses, aligning with the industry’s shift toward greener practices. Their robust design is essential for navigating the challenging terrains of mining sites. When considering electric haul trucks, buyers must evaluate terrain capability, battery range, and available charging solutions to meet the unique demands of mining operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘heavy duty electric car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Addressing Range Anxiety in Heavy Duty Electric Vehicles
The Problem: One of the significant challenges for B2B buyers considering heavy-duty electric cars is range anxiety. Businesses in sectors like logistics and construction often operate on tight schedules and need to ensure their vehicles can cover long distances without frequent recharging. In regions like Africa and South America, where charging infrastructure may still be developing, the fear of running out of battery power during critical operations can be a major deterrent. This anxiety can lead to hesitation in making the transition to electric options, ultimately affecting operational efficiency and sustainability goals.
The Solution: To alleviate range anxiety, B2B buyers should focus on selecting heavy-duty electric vehicles with superior battery technology and extended range capabilities. Research models that offer advanced battery management systems, which optimize power usage and extend the driving range. Additionally, businesses can conduct a thorough assessment of their operational routes to determine the optimal vehicle specifications. Partnering with manufacturers that provide detailed insights into real-world performance metrics can also help. Establishing a reliable charging strategy is essential; this could involve investing in fast-charging stations at key locations along frequent routes or utilizing mobile charging solutions. Collaborating with local governments or private companies to improve charging infrastructure can further enhance confidence in transitioning to electric vehicles.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Initial Cost Barriers for Heavy Duty Electric Cars
The Problem: The initial purchase price of heavy-duty electric vehicles often presents a significant barrier for B2B buyers. Many companies, especially small to medium enterprises, may find it challenging to justify the upfront investment compared to traditional fossil fuel vehicles. This is particularly acute in regions like the Middle East and South America, where budget constraints can limit options. The lack of awareness about total cost of ownership (TCO) savings, including maintenance and fuel costs, can lead to reluctance in switching to electric vehicles.
The Solution: B2B buyers should conduct a comprehensive analysis of the total cost of ownership over the vehicle’s lifespan. This includes not only the purchase price but also maintenance, fuel savings, and potential government incentives or rebates for electric vehicle purchases. Manufacturers often offer financing options or leasing programs that can make initial costs more manageable. Buyers can also explore grants or subsidies available in their region aimed at promoting electric vehicle adoption. Engaging with a financial advisor who specializes in fleet management can provide insights into the long-term savings and help create a robust financial plan that supports the transition to electric heavy-duty vehicles.
Scenario 3: Navigating Charging Infrastructure Challenges for Heavy Duty Electric Vehicles
The Problem: Another critical pain point for B2B buyers is the availability and accessibility of charging infrastructure. In many parts of Europe and developing regions in Africa and South America, the existing charging stations may not support the heavy-duty vehicles required for commercial use, leading to operational delays and inefficiencies. The lack of a comprehensive charging network can deter businesses from transitioning to electric solutions, fearing that their operations will be hampered by insufficient charging options.
The Solution: To navigate these challenges, businesses should take a proactive approach in developing a charging infrastructure strategy tailored to their operations. This could involve conducting an audit of existing charging stations and identifying gaps in coverage. Investing in on-site charging solutions can also be beneficial, allowing businesses to charge their fleet overnight or during off-peak hours. Collaborating with local utilities or charging network providers to establish partnerships can help expand charging options tailored to heavy-duty electric vehicles. Moreover, engaging with industry peers to share best practices and experiences regarding charging infrastructure can provide valuable insights and foster a community approach to overcoming these challenges.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for heavy duty electric car
What Are the Key Materials for Heavy Duty Electric Cars?
When selecting materials for heavy-duty electric vehicles (EVs), several factors come into play, including performance, durability, cost, and regional compliance. This analysis focuses on four common materials: aluminum, steel, composite materials, and lithium-ion batteries, highlighting their properties, advantages, limitations, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Heavy Duty Electric Cars?
Aluminum is widely used in the automotive industry due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 600°C and excellent fatigue resistance, making it suitable for various components, including chassis and body panels.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its weight reduction capability, which enhances energy efficiency and range. Additionally, its resistance to corrosion prolongs the lifespan of components, reducing maintenance costs.
Cons: However, aluminum can be more expensive than traditional steel and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and oil, but care must be taken to prevent galvanic corrosion when paired with dissimilar metals.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like Europe and North America, compliance with standards such as ASTM and EN is essential. Buyers from Africa and South America may also need to consider local availability and cost fluctuations.
What Role Does Steel Play in Heavy Duty Electric Vehicles?
Steel remains a popular choice for heavy-duty electric cars, particularly for structural components. It offers high strength and can withstand significant stress, with a temperature rating often exceeding 800°C.
Pros: The primary advantage of steel is its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. It provides excellent durability and crash resistance, making it ideal for safety-critical components.
Cons: On the downside, steel is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact the vehicle’s range and efficiency. It is also prone to corrosion unless treated, adding to maintenance costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various fluids and can handle high-pressure applications, making it suitable for components like frames and suspension systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as DIN and JIS is crucial, especially in Europe and Asia. Buyers in emerging markets should assess the local supply chain for steel availability and pricing.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Heavy Duty Electric Cars?
Composite materials, including carbon fiber and fiberglass, are increasingly used in heavy-duty electric vehicles due to their unique properties. They offer high strength-to-weight ratios and can withstand high temperatures, often rated above 200°C.
Pros: The lightweight nature of composites significantly improves energy efficiency and overall performance. They also provide excellent corrosion resistance and can be molded into complex shapes.
Cons: However, composites can be expensive and may require specialized manufacturing techniques, which can complicate production and increase lead times.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for various applications, including body panels and interior components, but they may not be compatible with all types of fluids, necessitating careful selection.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying standards for composites in different regions. In Europe, compliance with EN standards is essential, while buyers in Africa and South America should consider local manufacturing capabilities.
What Is the Importance of Lithium-Ion Batteries in Heavy Duty Electric Cars?
Lithium-ion batteries are the cornerstone of electric vehicle technology, providing the necessary energy storage for electric propulsion. They typically operate efficiently within a temperature range of -20°C to 60°C.
Pros: The primary advantage of lithium-ion batteries is their high energy density, allowing for longer ranges and faster charging times. They are also lightweight compared to other battery technologies.
Cons: However, lithium-ion batteries can be expensive and are sensitive to temperature extremes, which may affect performance and lifespan.
Impact on Application: These batteries are compatible with electric drive systems and regenerative braking, essential for heavy-duty applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international safety standards, such as UN 38.3 for transport, is crucial. Buyers should also consider regional regulations on battery recycling and disposal.
Summary of Material Selection for Heavy Duty Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for heavy duty electric car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Chassis, body panels | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Steel | Frames, suspension systems | Cost-effective, durable | Heavier, prone to corrosion | Low |
| Composite Materials | Body panels, interior components | High strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive, specialized manufacturing | High |
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | Energy storage for propulsion | High energy density, lightweight | Expensive, temperature-sensitive | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of materials essential for heavy-duty electric vehicles, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional compliance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for heavy duty electric car
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Heavy Duty Electric Cars?
The manufacturing process for heavy duty electric cars involves several crucial stages, each designed to ensure the vehicle meets stringent performance and safety standards.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The first stage in manufacturing begins with material selection and preparation. Heavy duty electric vehicles (EVs) typically utilize advanced materials such as high-strength steel, aluminum, and composite materials to optimize weight and performance. These materials are subjected to rigorous testing to ensure they can withstand the stresses of heavy-duty applications.
The sourcing of these materials often involves partnerships with suppliers who are compliant with international standards, ensuring that the quality of materials is consistent. For international B2B buyers, verifying the material specifications and certifications can be crucial to ensure compliance with local regulations.
How Is the Forming Process Conducted?
The forming process involves shaping the prepared materials into components that will make up the vehicle. Techniques such as stamping, forging, and extrusion are commonly used.
For heavy duty electric vehicles, components like the chassis and body panels require precision forming to guarantee structural integrity and safety. Manufacturers often employ advanced technologies such as robotic arms and CNC machines to achieve high levels of accuracy, which is essential for the assembly stage that follows.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
Assembly is a critical phase where all components come together to form the complete vehicle. This stage typically involves the integration of the electric powertrain, battery systems, and various electronic components.
Robotic automation plays a significant role in this phase, enhancing efficiency and reducing the likelihood of human error. Quality assurance checkpoints are integrated throughout the assembly line to monitor for defects and ensure that each vehicle meets predefined specifications.
How Is Finishing Done to Ensure Quality?
The finishing stage includes painting, surface treatment, and the installation of interior components. This stage is vital not only for aesthetics but also for protecting the vehicle against environmental factors.
Techniques such as electrocoating and powder coating are often employed to enhance durability. Additionally, manufacturers may employ advanced testing methods like corrosion resistance testing and UV exposure tests to ensure the longevity of the vehicle’s exterior.
What International Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant?
Quality assurance is a fundamental component of the manufacturing process for heavy duty electric cars. Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers maintain a consistent level of quality in their processes and products.
In addition, industry-specific standards like CE marking in Europe and API standards for components are crucial for compliance and market acceptance. These standards help B2B buyers confirm that the vehicles meet regulatory requirements in their respective regions.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints Throughout the Process?
Quality control (QC) is integrated at various stages of the manufacturing process through several checkpoints, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is the initial inspection stage where incoming materials and components are checked against specifications to ensure compliance before they enter production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the assembly process, various checkpoints are established to monitor and verify that the assembly is proceeding according to established standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the finished vehicles undergo comprehensive testing, including functionality tests, safety checks, and performance evaluations.
Each of these QC checkpoints is crucial for identifying and rectifying issues early in the manufacturing process, thereby minimizing defects and ensuring that the final product meets quality standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Heavy Duty Electric Cars?
Testing methods for heavy duty electric cars include:
-
Durability Testing: Vehicles are subjected to rigorous stress tests to ensure they can withstand real-world conditions, such as extreme temperatures and heavy loads.
-
Battery Testing: Given the importance of battery performance in electric vehicles, manufacturers conduct extensive tests on battery life, charging cycles, and thermal management.
-
Safety Testing: This includes crash tests and safety feature evaluations to ensure that vehicles comply with safety regulations.
-
Environmental Testing: Manufacturers assess how vehicles perform under various environmental conditions, which is particularly relevant for international markets with diverse climates.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several strategies:
-
Conducting Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards.
-
Reviewing Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide comprehensive quality reports that detail their QC processes, testing methods, and outcomes.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s compliance with international standards and industry practices.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various quality control nuances.
Different countries may have unique regulations regarding vehicle emissions, safety standards, and materials used. Therefore, it is crucial for buyers to understand these regulations and ensure that their suppliers are compliant. Additionally, language barriers and differences in business practices can complicate the verification process.
Establishing clear communication channels and utilizing technology for real-time updates on manufacturing processes can help mitigate these challenges.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in the production of heavy duty electric cars is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, alongside robust quality control practices, buyers can ensure they source reliable and high-quality vehicles that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘heavy duty electric car’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in navigating the procurement process for heavy-duty electric vehicles (EVs). With the shift towards sustainable transport solutions, understanding the critical steps in sourcing these vehicles can lead to better investment decisions, optimized fleet management, and alignment with environmental goals.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your procurement process. Consider the vehicle’s intended use, payload capacity, range requirements, and any industry-specific regulations. For instance, if operating in urban environments, a truck with a smaller footprint may be more advantageous.
- Payload Capacity: Identify the weight limits essential for your operations.
- Range Requirements: Determine the distance your vehicles will need to travel on a single charge.
2. Research Available Models and Features
Conduct thorough research on the various models available in the market. Different manufacturers offer unique features such as advanced safety systems, battery technology, and customization options. Understanding these features will help you select a vehicle that aligns with your operational needs.
- Battery Technology: Look for models that offer fast charging capabilities and longer battery life.
- Safety Features: Evaluate the inclusion of systems like automatic braking, lane-keeping assistance, and visibility enhancements.
3. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your business needs. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from businesses in similar industries or regions. This step helps you gauge the supplier’s reliability and product quality.
- Supplier Reputation: Look for reviews and feedback from other customers.
- Experience: Consider how long the supplier has been in the electric vehicle market.
4. Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Understanding the total cost of ownership is crucial for making informed decisions. This includes not only the purchase price but also operational costs such as maintenance, insurance, and charging infrastructure. A lower initial price might lead to higher long-term costs.
- Operational Costs: Calculate costs related to electricity consumption and maintenance schedules.
- Incentives and Subsidies: Research available government incentives that can offset initial costs.
5. Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and comply with local and international regulations. This verification protects your investment and helps avoid legal complications later on.
- Quality Certifications: Look for ISO certifications or industry-specific standards.
- Regulatory Compliance: Confirm adherence to environmental regulations and safety standards.
6. Plan for Charging Infrastructure
Develop a comprehensive plan for charging infrastructure to ensure your fleet can operate efficiently. Assess the availability of charging stations in your operational areas and consider whether you will need to invest in your own charging solutions.
- Charging Options: Investigate the types of chargers compatible with your vehicles.
- Installation Requirements: Consider the logistics and costs associated with installing charging stations at your facilities.
7. Implement a Pilot Program
Before full-scale deployment, consider implementing a pilot program to test the selected vehicles in real-world conditions. This allows you to evaluate performance, assess driver feedback, and identify any operational challenges.
- Performance Metrics: Track fuel efficiency, maintenance needs, and user satisfaction.
- Feedback Loop: Use insights from the pilot to make adjustments before scaling up your fleet.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed and strategic decisions when sourcing heavy-duty electric vehicles, ensuring alignment with their operational goals and sustainability objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for heavy duty electric car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Heavy Duty Electric Car Sourcing?
When sourcing heavy-duty electric vehicles (EVs), understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and financial planning. The primary components of the cost structure include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is significant, particularly for batteries, which are often the most expensive components in EVs. High-quality lithium-ion batteries, for instance, can represent a substantial portion of the overall vehicle cost. Other materials include lightweight metals for chassis and body, which can enhance efficiency.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in manufacturing, assembling, and testing the vehicles. This varies based on geographic location, with regions offering lower labor costs providing a competitive advantage.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate overhead costs, impacting overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Investment in specialized tooling and machinery is necessary for the production of heavy-duty EVs. This is a one-time cost that can be amortized over the production volume, affecting the unit cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that vehicles meet stringent quality and safety standards incurs costs related to inspections and testing. This is particularly important for international markets, where compliance with local regulations is mandatory.
-
Logistics: Transportation of components and finished vehicles adds to the total cost. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and tariffs can significantly influence logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Heavy Duty Electric Car Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of heavy-duty electric vehicles:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to discounts. Understanding the supplier’s pricing structure and negotiating for better rates based on anticipated volumes can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications/Customization: Tailoring vehicles to specific needs—such as enhanced battery capacity or specialized features—can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against its impact on the overall budget.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly affects costs. Premium materials may enhance vehicle performance and longevity but will also increase the purchase price.
-
Quality/Certifications: Vehicles that meet higher safety and environmental standards may come at a premium. However, investing in certified vehicles can reduce long-term operational costs and enhance brand reputation.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and location can all impact pricing. Buyers should conduct thorough research and consider potential partnerships with established manufacturers.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is vital for calculating total costs. Different Incoterms can affect who bears the costs and risks during transportation, impacting the final price.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the following tips can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing and payment terms. Establishing a good rapport with suppliers can lead to better deals and terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the TCO rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors such as maintenance, energy costs, and potential incentives or rebates for electric vehicles.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local economic conditions, tariffs, and taxes. Familiarizing yourself with these nuances can aid in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Leverage Incentives: Many governments offer incentives for electric vehicle purchases. Research available rebates and tax credits in your region to reduce overall costs.
-
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing and support over time, enhancing overall procurement efficiency.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for heavy-duty electric vehicles can fluctuate based on market conditions, currency exchange rates, and other factors. Therefore, it’s advisable to consult with suppliers for the most accurate and up-to-date pricing information tailored to specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing heavy duty electric car With Other Solutions
In the rapidly evolving landscape of commercial transportation, B2B buyers are faced with various options to meet their heavy-duty needs. Understanding the alternatives to heavy-duty electric cars is essential for making informed decisions that align with operational goals and sustainability objectives. This analysis compares heavy-duty electric vehicles against two viable alternatives: diesel-powered trucks and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
| Comparison Aspect | Heavy Duty Electric Car | Diesel-Powered Truck | Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque, instant power delivery; suitable for urban and regional hauling | Proven performance, high load capacity; longer range | Comparable to diesel in power; shorter range than diesel, longer refueling times |
| Cost | Higher upfront costs; lower operating costs due to reduced fuel and maintenance | Lower initial investment; fluctuating fuel prices and higher maintenance costs | Higher initial investment; operational costs depend on hydrogen price stability |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure; limited by range for long-haul | Established infrastructure; easy to implement with existing fleets | Requires specialized refueling stations; still developing infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Generally lower due to fewer moving parts; battery replacement cost must be considered | Higher maintenance needs due to engine complexity | Regular maintenance for fuel cells; fewer moving parts than diesel |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for urban deliveries, short-haul routes; suitable for companies focusing on sustainability | Versatile for long-haul and varied applications; well-suited for traditional logistics | Suitable for heavy-duty applications requiring fast refueling; potential for long-haul transport |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Diesel-Powered Trucks?
Diesel-powered trucks have long been the backbone of the transportation industry. They offer a lower upfront cost compared to electric vehicles, which is appealing for companies with tight budgets. Their established infrastructure means that logistics companies can easily integrate them into existing operations. However, diesel trucks are subject to fluctuating fuel prices and have higher maintenance costs due to complex engine systems. Additionally, environmental regulations are tightening, which could lead to increased costs for compliance.
How Do Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles Compare?
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles present a promising alternative with the potential for zero emissions and fast refueling times. They are capable of delivering performance levels comparable to diesel trucks and can be suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is still developing, which poses a significant challenge for widespread adoption. Moreover, the high initial investment and operational costs are contingent on the stability of hydrogen prices, making this option less predictable than electric or diesel solutions.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the best heavy-duty vehicle solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and sustainability goals. Heavy-duty electric cars are ideal for businesses prioritizing eco-friendliness and operating in urban environments with charging infrastructure. Diesel trucks remain a reliable choice for long-haul operations due to their established use and infrastructure. Meanwhile, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles could be a game-changer for companies that require rapid refueling and are willing to invest in emerging technology. By evaluating these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for heavy duty electric car
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Heavy Duty Electric Cars?
When considering heavy-duty electric vehicles (EVs), several technical specifications are crucial for B2B buyers to understand. These properties directly influence vehicle performance, operational costs, and suitability for specific business needs.
1. Battery Capacity (kWh)
Battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), determines the total energy stored in the vehicle’s battery. A higher capacity allows for longer ranges, which is critical for heavy-duty applications involving long hauls or extensive urban deliveries. For businesses, understanding battery capacity helps in estimating operational range and planning charging schedules, ultimately impacting logistics and efficiency.
2. Payload Capacity (kg or tons)
Payload capacity indicates the maximum weight a vehicle can safely carry, including cargo and passengers. This specification is vital for businesses in industries such as logistics, construction, and waste management, where the vehicle’s ability to handle heavy loads directly affects profitability and operational efficiency. Buyers should ensure that the payload capacity aligns with their operational requirements.
3. Charging Time (hours)
Charging time is the duration required to fully charge the vehicle’s battery from a depleted state. Fast charging capabilities can significantly reduce downtime, allowing businesses to maintain productivity. Understanding charging time is essential for fleet management, as it influences scheduling and operational efficiency, particularly in sectors where quick turnaround is crucial.
4. Range (km)
The range of a heavy-duty electric vehicle is the distance it can travel on a single charge. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions with varying infrastructure, range is a critical factor in assessing the vehicle’s suitability for specific routes and applications. A longer range reduces the need for frequent charging stops, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
5. Motor Power (kW)
Motor power, expressed in kilowatts (kW), affects the vehicle’s acceleration and ability to handle steep gradients or heavy loads. For B2B buyers, understanding motor power is essential for selecting vehicles that can meet the demands of specific tasks, ensuring that performance expectations align with operational needs.
6. Vehicle Weight (kg)
The vehicle’s weight impacts its efficiency, handling, and compliance with local regulations regarding road usage. A lighter vehicle can offer better energy efficiency and payload capacity, while a heavier vehicle may be more robust and suitable for tough terrains. B2B buyers must consider vehicle weight in relation to their operational context to optimize performance and cost.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicle Industry?
Understanding industry terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common trade terms relevant to heavy-duty electric vehicles:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces components or products that are used in another company’s end product. In the context of heavy-duty electric vehicles, OEMs are responsible for manufacturing vehicle parts or entire vehicles. For B2B buyers, partnering with reputable OEMs ensures quality and reliability in vehicle performance.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. For heavy-duty electric vehicles, understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to assess the feasibility of bulk purchasing and negotiating better pricing. It can also impact inventory management and cash flow.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price offers from suppliers for specific goods or services. When considering heavy-duty electric vehicles, businesses should prepare detailed RFQs to ensure they receive accurate and competitive bids, facilitating better decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international trade rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities associated with importing heavy-duty electric vehicles.
5. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with owning and operating a vehicle over its lifespan, including purchase price, maintenance, fuel (or electricity), and depreciation. For B2B buyers, calculating TCO is vital for evaluating the long-term financial implications of investing in heavy-duty electric vehicles.
6. EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment)
EVSE refers to the infrastructure used to deliver electricity to electric vehicles for charging. Understanding EVSE options is important for B2B buyers to ensure they have the necessary charging facilities to support their fleet of heavy-duty electric vehicles.
By grasping these technical specifications and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the heavy duty electric car Sector
What Are the Global Drivers and Key Trends Influencing the Heavy-Duty Electric Car Market?
The heavy-duty electric vehicle (EV) market is undergoing a transformative phase, driven by several global factors. A growing emphasis on sustainability and carbon neutrality has prompted governments and businesses to invest heavily in electric mobility solutions. In regions like Europe, South America, and parts of Africa, regulatory frameworks are increasingly mandating the adoption of low-emission vehicles, creating an urgent demand for heavy-duty electric cars.
Emerging technologies are also reshaping the market landscape. Innovations in battery technology, including solid-state batteries and improved charging infrastructure, are enhancing the operational efficiency and range of heavy-duty electric vehicles. For B2B buyers, particularly in markets such as Germany and Brazil, understanding these technological advancements is critical for making informed purchasing decisions. Furthermore, the rise of telematics and fleet management software allows businesses to optimize logistics, reduce costs, and enhance overall productivity.
Market dynamics are influenced by supply chain complexities, particularly regarding the sourcing of critical components like batteries and electric drivetrains. Buyers are encouraged to establish partnerships with manufacturers that prioritize local sourcing to mitigate risks associated with global supply chain disruptions. As electric vehicles become more mainstream, the competitive landscape is also evolving, with traditional automakers and new entrants vying for market share, making it essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about brand reputation and reliability.
How Do Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Decisions in the Heavy-Duty Electric Car Sector?
Sustainability is no longer a niche consideration but a core aspect of business strategy, particularly in the heavy-duty electric vehicle sector. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing products that minimize environmental impact, as consumers and stakeholders demand greater corporate responsibility. Heavy-duty electric cars significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to their fossil-fuel counterparts, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Ethical sourcing has become equally important. Buyers should seek suppliers that adhere to responsible sourcing practices, ensuring that materials used in vehicle manufacturing, such as lithium and cobalt for batteries, are obtained without compromising human rights or environmental integrity. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and the Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) code of conduct can guide buyers in selecting suppliers committed to ethical practices.
Furthermore, companies that invest in sustainable supply chains are often rewarded with improved brand loyalty and market differentiation. B2B buyers in regions such as the Middle East and Africa must recognize the long-term value of partnering with manufacturers that prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing, as these practices not only enhance corporate reputation but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Heavy-Duty Electric Car Market?
The heavy-duty electric vehicle market has evolved dramatically over the past two decades. Initially, electric vehicles were seen primarily as personal transportation solutions, but advancements in technology have expanded their application to commercial vehicles. Early models struggled with range and performance, limiting their adoption for heavy-duty tasks. However, with substantial investments in battery technology and charging infrastructure, manufacturers are now producing vehicles capable of meeting the rigorous demands of industries like logistics, construction, and public transport.
The market has also witnessed a shift in consumer perception, as businesses increasingly recognize the long-term cost savings and environmental benefits associated with electric fleets. This evolution is further accelerated by government incentives and funding programs aimed at promoting electric vehicle adoption. As a result, the heavy-duty electric vehicle segment is poised for significant growth, offering B2B buyers a range of innovative and sustainable options to support their operational needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of heavy duty electric car
-
How do I solve range anxiety when sourcing heavy-duty electric cars?
Range anxiety is a common concern for businesses transitioning to electric vehicles. To address this, assess the specific range requirements based on your operational routes. Research various models and their range capabilities, ensuring they align with your daily needs. Additionally, consider investing in charging infrastructure at strategic locations to minimize downtime. Collaborating with suppliers who offer comprehensive support, including route planning and charging solutions, can also enhance your operational efficiency and alleviate concerns regarding vehicle range. -
What is the best heavy-duty electric vehicle for regional transport?
The ideal heavy-duty electric vehicle for regional transport often combines range, payload capacity, and charging efficiency. Models such as the Volvo FH Electric and Ram 1500 REV are designed for regional-haul applications, offering robust performance and reliability. Evaluate the vehicle specifications against your operational requirements, including typical distances traveled and load capacities. Consulting with manufacturers and industry experts can provide insights into the most suitable models for your business needs. -
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for heavy-duty electric vehicles?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the electric vehicle market, product quality, and customer support. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in heavy-duty electric vehicles and positive customer testimonials. Assess their supply chain reliability and after-sales service, including maintenance support and warranty options. Additionally, ensure they comply with international standards and regulations, particularly if you’re sourcing from different regions, such as Africa or South America. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for heavy-duty electric vehicles?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between manufacturers and depend on factors like production capabilities and customization options. Generally, larger orders may qualify for better pricing and terms, while smaller orders could incur higher per-unit costs. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies. Some manufacturers may offer flexibility for initial orders, especially for businesses looking to pilot electric vehicles in their fleets. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing heavy-duty electric vehicles?
Payment terms for heavy-duty electric vehicles typically include a deposit at the time of order, with the balance due upon delivery or within a specified period after receipt. Terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your business relationship. It’s essential to negotiate favorable terms that align with your cash flow needs. Additionally, consider discussing financing options that may be available, as many manufacturers offer tailored financing solutions for B2B buyers. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for heavy-duty electric vehicles?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and compliance certifications from your suppliers. Conduct thorough due diligence by reviewing production processes and quality control measures in place at the manufacturing facility. If possible, arrange for inspections or audits before finalizing your purchase. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and the process for addressing any potential defects or issues post-purchase to safeguard your investment. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing heavy-duty electric vehicles?
Logistics for importing heavy-duty electric vehicles involve multiple factors, including shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Engage with a logistics provider experienced in transporting vehicles internationally to navigate potential challenges. Ensure compliance with local regulations, including emissions standards and import duties. Planning for proper handling during transit and securing adequate insurance coverage will also mitigate risks associated with shipping high-value assets. -
How can I customize heavy-duty electric vehicles to meet my business needs?
Customization options for heavy-duty electric vehicles often include modifications to payload capacity, battery configurations, and specialized equipment. Engage with manufacturers early in the procurement process to discuss your specific requirements. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions to enhance vehicle performance for particular industries, such as construction or logistics. Assess the additional costs and timelines associated with customization to ensure they align with your operational goals and budget.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 4 Heavy Duty Electric Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Ram Brand – Key Electric Trucks and Vans
Domain: ramtrucks.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Ram Brand electric trucks and vans include the Ram 1500 REV, projected availability in 2026, and the Ram ProMaster® EV, available to order now with a cargo van model coming in 2025. The lineup emphasizes affordability, charging convenience, range and battery capabilities, and business benefits. Key features include cutting-edge technology, exceptional capability, and a focus on performance and eff…
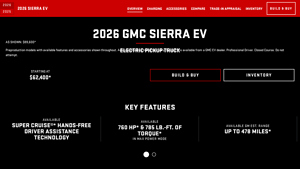
2. GMC – 2026 Sierra EV Electric Pickup Truck
Domain: gmc.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Model: 2026 GMC Sierra EV Electric Pickup Truck
Starting Price: $62,400 (Elevation), $79,300 (AT4), $69,700 (Denali)
As Shown Price: $89,600
EPA-Estimated Range: Up to 460 miles (390 miles as shown), Extended Range battery up to 410 miles, Max Range battery up to 478 miles
Power: 760 HP in Max Power Mode, 605 HP standard
Torque: 785 lb-ft in Max Power Mode
Charging: 800V public DC fast charging of…
3. TFL Car – Heavy Duty Electric Pickup Trucks
Domain: tflcar.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: 1. Heavy Duty Electric Pickup Trucks: Discussion on the feasibility of heavy duty electric pickup trucks, with a focus on the potential for plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) like the Ram Ramcharger. Mention of Ford possibly developing a Super Duty EREV (Extended Range Electric Vehicle) with a 5.0L V8 range extender. 2. Honda’s Next EV: Honda’s upcoming 0 (Zero) EV series is expected to repl…
4. ScienceDirect – Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicles
Domain: sciencedirect.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: {“title”: “Heavy-Duty Electric Vehicles: From Concept to Reality”, “authors”: [“Shashank Arora”, “Alireza Tashakori Abkenar”, “Kari Tammi”], “published_year”: 2021, “ISBN”: “978-0-12-818126-3”, “language”: “English”, “publisher”: “Elsevier Inc.”, “imprint”: “Butterworth-Heinemann”, “DOI”: “https://doi.org/10.1016/C2018-0-02433-0”, “description”: “This book presents a step-by-step design and develo…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for heavy duty electric car
Why is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Heavy Duty Electric Vehicles?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of heavy-duty electric vehicles (EVs), strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for B2B buyers. By prioritizing partnerships with manufacturers like Ram and Volvo, businesses can leverage cutting-edge technology, enhanced operational efficiency, and substantial cost savings. The financial incentives available for electric vehicles further amplify the value proposition, making it essential for international buyers to stay informed about local and global market trends.
What Future Trends Should International Buyers Anticipate?
As the demand for sustainable transport solutions grows, the heavy-duty electric vehicle market is expected to expand significantly. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prepare for innovations in battery technology and charging infrastructure that will enhance vehicle performance and reduce operational costs. The shift towards electrification is not just a trend; it represents a fundamental change in how goods are transported globally.
How Can B2B Buyers Position Themselves for Success?
Now is the time for international B2B buyers to act strategically. Engage with manufacturers to explore tailored solutions that meet specific business needs, and consider the long-term benefits of adopting electric fleets. By investing in heavy-duty electric vehicles today, companies can not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also position themselves competitively in a market that is increasingly favoring green technologies. Embrace the future of transportation—make the strategic switch to electric today.