Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for mini electric car eec coc
In today’s rapidly evolving automotive landscape, sourcing mini electric cars with EEC COC certification presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. As the demand for eco-friendly transportation solutions grows, businesses must navigate a complex web of regulations, quality standards, and supplier options to ensure they make informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the global market for mini electric cars, focusing on the EEC COC certification process, which is crucial for compliance in various regions, including Europe, Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
Throughout this guide, we explore the diverse types of mini electric vehicles available, their applications in urban mobility, and essential factors to consider when vetting suppliers. We also address pricing structures, logistical considerations, and the importance of after-sales support. By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and practical knowledge, this resource empowers them to identify reliable suppliers and make strategic investments that align with their sustainability goals and operational needs.
As the automotive industry shifts towards greener alternatives, understanding the nuances of mini electric cars with EEC COC certification is essential for businesses aiming to stay competitive and responsive to market demands. Whether you are looking to enhance your fleet or enter the electric vehicle market for the first time, this guide serves as your roadmap to success.
Understanding mini electric car eec coc Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Speed Electric Vehicle (LSEV) | Maximum speed of 45 km/h, compact design, suitable for urban use | Short-distance commuting, last-mile delivery services | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to park. Cons: Limited speed and range compared to higher-speed models. |
| Fully Enclosed Mini Electric Car | Enclosed body for safety, enhanced weather protection, spacious interior | Family use, urban mobility solutions | Pros: Comfort and safety features. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| EEC L7e Approved Mini Car | Higher speed capability (up to 90 km/h), spacious seating options | Second family car, rental services | Pros: Versatile usage, good for longer commutes. Cons: May require more extensive maintenance. |
| Electric Tricycles | Three-wheeled design, lower operating costs, easy maneuverability | Delivery services, urban transport | Pros: Lower cost, easy to navigate in traffic. Cons: Less stability than four-wheeled vehicles. |
| Compact Utility Electric Vehicle | Designed for both passenger and cargo transport, customizable configurations | Small business logistics, urban deliveries | Pros: Multi-functional, customizable. Cons: Limited passenger capacity compared to traditional vehicles. |
What are the Characteristics of Low-Speed Electric Vehicles (LSEVs)?
Low-Speed Electric Vehicles (LSEVs) are characterized by their compact size and maximum speed of 45 km/h, making them ideal for urban environments where traffic congestion is common. These vehicles are particularly suitable for short-distance commuting and serve as efficient last-mile delivery solutions. B2B buyers should consider their cost-effectiveness and ease of parking, though they may find limitations in speed and range compared to higher-capacity electric vehicles.
How do Fully Enclosed Mini Electric Cars Benefit Businesses?
Fully enclosed mini electric cars offer enhanced safety features and weather protection, making them an attractive option for families and urban mobility solutions. They typically provide a spacious interior, accommodating both passengers and cargo. For B2B buyers, the investment in these vehicles is justified by their comfort and safety features; however, the initial purchase price may be higher than less enclosed alternatives.
What Advantages Does EEC L7e Approval Offer for Mini Cars?
EEC L7e approved mini cars are designed for higher speeds, reaching up to 90 km/h, and often include spacious seating configurations. This makes them suitable for a variety of applications, including as second family cars or for rental services. When considering these vehicles, B2B buyers should weigh their versatility against potential maintenance needs, as the higher speed capabilities may lead to increased wear and tear.
Why Choose Electric Tricycles for Urban Delivery?
Electric tricycles are designed for maneuverability and cost efficiency, making them an excellent choice for urban delivery services. Their three-wheeled design allows for easy navigation in tight spaces, while their lower operating costs appeal to businesses looking to maximize profitability. However, B2B buyers should be aware of their stability limitations compared to four-wheeled vehicles, which may affect their suitability for certain applications.
What Makes Compact Utility Electric Vehicles a Smart Investment?
Compact utility electric vehicles are designed to transport both passengers and cargo, making them highly versatile for small business logistics and urban deliveries. Their customizable configurations allow businesses to tailor the vehicle to their specific needs. While they provide multi-functional benefits, B2B buyers should consider the limited passenger capacity compared to traditional vehicles, which may be a drawback for some applications.
Key Industrial Applications of mini electric car eec coc
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of mini electric car eec coc | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Mobility | Short-distance commuting and last-mile delivery | Reduces traffic congestion and pollution while ensuring efficient transport | Compliance with local regulations and EEC certification |
| Hospitality and Tourism | Guest transport within resorts and hotels | Enhances guest experience and promotes eco-friendly transportation | Customization options for branding and comfort features |
| Retail and E-commerce | In-store and warehouse logistics | Streamlines operations and reduces logistics costs | Battery capacity and range to meet operational needs |
| Healthcare | Patient transport in medical facilities | Provides a quick and efficient means of transport for patients | Safety features and reliability for sensitive transport |
| Educational Institutions | Campus transport for students and staff | Improves accessibility and reduces carbon footprint | Durability and maintenance support for continuous use |
How Are Mini Electric Cars Used in Urban Mobility?
In the urban mobility sector, mini electric cars certified under EEC COC are increasingly utilized for short-distance commuting and last-mile delivery solutions. These vehicles address the growing challenges of traffic congestion and urban pollution by providing an eco-friendly alternative to traditional vehicles. Businesses looking to enhance their transportation offerings must consider the local regulatory landscape to ensure compliance with EEC certification standards, which can vary significantly across regions in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Role Do Mini Electric Cars Play in Hospitality and Tourism?
In the hospitality and tourism industry, mini electric cars serve as an effective means of guest transport within resorts and hotels. They significantly enhance the guest experience by offering convenient and eco-friendly transportation options. For B2B buyers in this sector, customization options for branding and comfort features are vital to align the vehicles with the establishment’s image. Additionally, these cars can be a selling point for eco-conscious travelers, providing a competitive edge in the market.
How Are Mini Electric Cars Revolutionizing Retail and E-commerce?
Retail and e-commerce businesses are leveraging mini electric cars for efficient in-store and warehouse logistics. By streamlining operations, these vehicles help reduce logistics costs while also being environmentally friendly. For international buyers, it is crucial to assess the battery capacity and range of these vehicles to ensure they meet the demands of their operational needs. The ability to navigate tight spaces and make quick deliveries makes them an attractive option for retailers.
What Benefits Do Mini Electric Cars Provide to Healthcare?
In the healthcare sector, mini electric cars are essential for patient transport within medical facilities. They offer a quick and efficient means of moving patients, particularly in busy hospitals where time is critical. Buyers in this field must prioritize safety features and the reliability of these vehicles, as patient transport requires adherence to strict safety standards. Additionally, the vehicles should be easy to maintain to ensure uninterrupted service.
How Are Educational Institutions Utilizing Mini Electric Cars?
Educational institutions are adopting mini electric cars for campus transport, facilitating movement for students and staff. These vehicles improve accessibility across large campuses and contribute to a reduced carbon footprint. For B2B buyers in education, durability and maintenance support are key considerations, as these vehicles are expected to withstand frequent use in diverse weather conditions. Investing in reliable mini electric cars can significantly enhance campus life and promote sustainability initiatives.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘mini electric car eec coc’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance Challenges with EEC COC
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant hurdles when it comes to understanding and navigating the regulatory landscape surrounding mini electric cars, particularly in obtaining the European Economic Community (EEC) Certificate of Conformity (COC). This certification is crucial for ensuring that vehicles meet EU safety, environmental, and performance standards. Buyers may struggle with the complex documentation process or become overwhelmed by the varying requirements across different countries, leading to delays in market entry and increased operational costs.
The Solution: To effectively navigate regulatory compliance, it is essential for buyers to establish a clear understanding of the specific EEC COC requirements relevant to their target markets. This begins with thorough research into local regulations, as these can vary significantly across regions such as Africa, South America, and Europe. Engaging with experienced consultants or legal advisors who specialize in automotive compliance can provide invaluable insights and streamline the certification process. Additionally, collaborating closely with manufacturers who are well-versed in EEC standards can facilitate smoother documentation and ensure that the vehicles meet all necessary compliance criteria from the outset. Buyers should also consider joining industry associations that focus on electric vehicles, as these organizations often provide resources and guidance on regulatory matters.
Scenario 2: Addressing Concerns about Vehicle Performance and Reliability
The Problem: Many B2B buyers worry about the performance and reliability of mini electric cars, especially regarding their range and ability to handle various terrains. Concerns may arise from the perceived limitations of electric vehicles, such as battery life and charging time, which can impact operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Buyers may fear that investing in these vehicles could lead to higher maintenance costs or a negative user experience, especially in regions with challenging road conditions.
The Solution: To mitigate performance concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing mini electric cars from reputable manufacturers that provide detailed specifications and performance metrics. It’s essential to conduct comprehensive product testing and request performance guarantees that align with the operating environment of the target market. Buyers can also benefit from leveraging technology that enhances vehicle performance, such as advanced battery management systems that optimize energy usage and increase overall range. Additionally, offering training programs for drivers on how to maximize vehicle efficiency and maintenance can further enhance reliability and user satisfaction. Building strong relationships with suppliers for ongoing support and service can also ensure that any issues are promptly addressed.
Scenario 3: Tackling Cost Concerns and Return on Investment (ROI)
The Problem: Cost remains a significant concern for B2B buyers when considering the purchase of mini electric cars. Buyers often grapple with the initial investment versus long-term savings, questioning whether these vehicles will deliver a satisfactory return on investment. Factors such as upfront costs, maintenance expenses, and potential tax incentives or subsidies can complicate this decision-making process, particularly in diverse markets with varying economic conditions.
The Solution: To address cost concerns effectively, buyers should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis that incorporates both direct and indirect costs associated with mini electric cars. This analysis should include potential savings from lower fuel costs, reduced maintenance expenses, and any available governmental incentives for electric vehicle purchases. Additionally, engaging in negotiations with manufacturers for bulk purchasing discounts or financing options can help alleviate financial strain. Buyers should also explore partnerships with local governments or organizations focused on sustainability, which may provide additional financial support or incentives. Finally, implementing a robust tracking system to monitor the performance and cost savings of the fleet over time can help substantiate the ROI, making it easier to justify future investments in electric vehicles.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for mini electric car eec coc
What Are the Key Materials for Mini Electric Cars with EEC COC Certification?
When selecting materials for mini electric cars, particularly those with EEC COC certification, it is essential to consider properties that enhance performance, durability, and compliance with international standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of these vehicles: aluminum, high-strength steel, ABS plastic, and lithium-ion batteries.
Aluminum: A Lightweight Champion
Key Properties: Aluminum is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. It can withstand a temperature range from -200°C to 600°C, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which contributes to improved energy efficiency and range in electric vehicles. However, it can be more expensive than steel and may require specialized manufacturing techniques, increasing production complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in the vehicle frame and body panels, enhancing performance by reducing overall weight. This is particularly beneficial for urban environments where agility and speed are crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure that the aluminum used meets standards such as ASTM B221 or EN 573. Additionally, the cost implications of sourcing aluminum versus steel should be carefully evaluated.
High-Strength Steel: The Durability Factor
Key Properties: High-strength steel offers excellent tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for structural components. It can handle high-pressure environments and is often treated for corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: While high-strength steel is generally less expensive than aluminum, it is heavier, which can negatively impact the vehicle’s range. However, its durability makes it suitable for safety-critical components, such as the chassis and crash structures.
Impact on Application: This material is typically used in areas requiring robust structural integrity, ensuring passenger safety. Its ability to absorb energy during collisions is a significant advantage.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A992 and EN 10025 is crucial for buyers in Europe and North America. In regions like Africa and South America, the availability of high-quality steel may vary, impacting sourcing decisions.
ABS Plastic: Versatility and Safety
Key Properties: Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a thermoplastic known for its impact resistance and toughness. It can withstand temperatures up to 80°C and is resistant to many chemicals.
Pros & Cons: ABS is lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, making it suitable for interior components and body panels. However, it may not be as durable as metals and can degrade under UV exposure unless treated.
Impact on Application: ABS is commonly used for dashboard components, trims, and other interior features, contributing to the overall aesthetics and comfort of the vehicle.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that ABS meets relevant standards like ISO 105-A02 for colorfastness and ASTM D638 for tensile strength. In regions with high UV exposure, UV-resistant grades may be preferred.
Lithium-Ion Batteries: Powering the Future
Key Properties: Lithium-ion batteries offer high energy density, lightweight, and low self-discharge rates. They can operate efficiently within a temperature range of -20°C to 60°C.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of lithium-ion batteries is their ability to provide significant range with relatively low weight. However, they can be expensive and require careful handling due to safety concerns.
Impact on Application: These batteries are integral to the vehicle’s powertrain, affecting range, charging time, and overall performance. Their efficiency is critical for urban mobility solutions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international safety standards such as UN 38.3 for transport and IEC 62133 for performance is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of charging infrastructure in their regions.
Summary of Material Selection for Mini Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for mini electric car eec coc | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Vehicle frame and body panels | Lightweight, enhances energy efficiency | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| High-Strength Steel | Chassis and crash structures | Excellent durability and impact resistance | Heavier, may reduce range | Medium |
| ABS Plastic | Interior components and body panels | Lightweight, moldable | Less durable, UV degradation risk | Low |
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | Powertrain and energy storage | High energy density, lightweight | Expensive, safety handling required | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of materials relevant to the mini electric car market, particularly for international B2B buyers. Understanding these materials will facilitate informed decision-making and enhance product performance in diverse markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for mini electric car eec coc
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Mini Electric Cars with EEC COC?
The manufacturing process of mini electric cars compliant with the EEC Certificate of Conformity (COC) involves several crucial stages. Each stage is designed to ensure that the final product meets both safety and performance standards.
Material Preparation: Sourcing and Quality Control
The first step in manufacturing involves sourcing high-quality materials. Manufacturers typically use materials like high-strength ABS and PP plastics for the body, aluminum for the wheels, and lead-acid or lithium batteries for power. Suppliers are evaluated based on their ability to meet international standards such as ISO 9001, which ensures quality management systems are in place. Manufacturers should maintain an approved supplier list and conduct regular audits to ensure that materials meet specifications.
Forming: Advanced Techniques for Precision Parts
The forming stage encompasses various techniques, including injection molding for plastic components and die-casting for metal parts. Advanced machinery ensures precision in creating parts that fit together seamlessly. This stage also includes the fabrication of the vehicle’s chassis, which must be robust enough to support both the weight of the vehicle and the passengers. Laser cutting and CNC machining are often employed to enhance accuracy and reduce waste.
Assembly: Bringing Components Together
Once the parts are formed, the assembly process begins. This stage typically involves multiple assembly lines where skilled technicians install components such as the electric motor, battery, and electronic control systems. Quality checks are integrated into the assembly line, with checkpoints to verify that each component is installed correctly and functions as intended. This is crucial for ensuring the vehicle operates safely and efficiently.
Finishing: Quality Assurance and Aesthetic Appeal
The finishing stage includes painting, interior assembly, and the installation of safety features like seat belts and airbags. Manufacturers often employ robotic painting systems for a consistent finish that meets aesthetic and durability standards. Additionally, this stage involves rigorous quality control testing, including visual inspections and functional tests to ensure that all systems are operational.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Mini Electric Cars?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for mini electric cars, particularly for B2B buyers looking to ensure reliability and safety in their purchases.
What International Standards Should Be Considered?
Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management, CE marking for safety, and EEC regulations for environmental considerations is essential. Manufacturers must document their compliance processes and maintain certifications to facilitate smoother transactions with international buyers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established at various stages of production:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves checking raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet predefined specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): QC personnel monitor the production process to identify any deviations from standards. This may involve testing components during assembly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished product is conducted before it leaves the manufacturing facility. This includes testing vehicle performance, safety features, and compliance with regulatory standards.
How Are Testing Methods Used to Ensure Quality?
Common testing methods for mini electric cars include:
- Functional Testing: Evaluates the operational performance of all vehicle systems, including braking, acceleration, and electronic controls.
- Safety Testing: Ensures that all safety features, such as seat belts and airbags, function correctly. Crash tests may also be conducted to assess passenger safety in the event of an accident.
- Environmental Testing: Assesses the vehicle’s performance under various weather conditions and terrains to ensure reliability in diverse environments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insight into the supplier’s QC practices. This includes reviewing documentation related to quality management systems and compliance with international standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Buyers should request detailed quality reports that outline the results of various testing methods and any corrective actions taken in response to identified issues.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturer’s processes and the quality of the final product.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of QC and certification is vital. Different regions may have specific regulations and compliance requirements. For example, the European market may demand stricter adherence to CE marking and EEC certification compared to other regions. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations to ensure that the vehicles they import meet all necessary legal requirements.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing process of mini electric cars with EEC COC involves meticulous attention to detail at every stage, from material preparation to finishing. Quality assurance measures, grounded in international standards, play a pivotal role in ensuring that these vehicles are safe, reliable, and compliant with regulations. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes and implementing thorough verification methods will enhance their purchasing decisions and foster long-term business relationships.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘mini electric car eec coc’
Introduction
This guide provides a structured approach for B2B buyers looking to procure mini electric cars with an EEC Certificate of Conformity (COC). Given the growing demand for eco-friendly transportation solutions, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of sourcing these vehicles is critical. This checklist will help streamline the procurement process, ensuring quality, compliance, and cost-effectiveness.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider factors such as maximum speed, battery type, range, seating capacity, and safety features. This step is vital as it helps you communicate your needs effectively and ensures that suppliers can meet your expectations.
- Key Specifications to Consider:
- Motor power (e.g., 3kW, 1.5kW)
- Battery capacity (e.g., 60V, 80Ah Lead-acid or Lithium)
- Maximum speed and range
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Start by conducting thorough research to identify reputable manufacturers and suppliers of mini electric cars. Look for companies with a proven track record in producing EEC-certified vehicles. This step is crucial for establishing a shortlist of suppliers who can provide the quality and specifications you need.
- Where to Look:
- Industry trade shows and exhibitions
- Online B2B marketplaces
- Manufacturer directories
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications, including the EEC Certificate of Conformity. This certification guarantees that the vehicles comply with European safety and environmental standards. Verification is essential to avoid compliance issues that could arise later in the procurement process.
- What to Check:
- Validity of the EEC COC
- Additional certifications (e.g., ISO, CE)
Step 4: Request Product Samples and Specifications
Request samples or detailed product specifications from shortlisted suppliers. Evaluating samples allows you to assess the quality and functionality of the mini electric cars. This step is important to confirm that the vehicles meet your defined specifications and quality standards.
- What to Examine:
- Build quality and materials used
- Performance metrics (speed, range, battery life)
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in negotiations with your selected suppliers to determine pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. This step is crucial for ensuring that you receive the best possible deal while maintaining quality standards. Be prepared to discuss bulk order discounts or long-term partnership arrangements.
- Considerations:
- Payment methods (e.g., T/T, L/C)
- Minimum order quantities and lead times
Step 6: Evaluate After-Sales Support and Warranty
Assess the after-sales support and warranty options provided by the suppliers. Reliable after-sales service can significantly impact your overall experience and satisfaction with the purchase. This step ensures that you have recourse in case of defects or issues with the vehicles.
- Support Services to Inquire About:
- Warranty duration and coverage
- Availability of spare parts and maintenance services
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Once you are satisfied with the terms and conditions, finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure that all details, including specifications, pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty clauses, are clearly documented. This step is critical to protecting your investment and ensuring a smooth transaction.
- Key Components to Include:
- Detailed product specifications
- Payment terms and delivery schedules
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing mini electric cars with EEC certification, ensuring a successful procurement process.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for mini electric car eec coc Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Mini Electric Cars with EEC COC?
When sourcing mini electric cars that comply with EEC COC standards, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and price negotiation. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
-
Materials: The selection of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-quality components like lithium batteries, aluminum wheels, and durable plastics can increase initial costs but may enhance performance and longevity, thus reducing total cost of ownership (TCO). For instance, opting for a high-capacity lithium battery may raise upfront costs but can provide a longer range and better efficiency.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the production location. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing; however, they might compromise on quality. B2B buyers should consider the skill level of the workforce and whether it aligns with their quality expectations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead and Tooling: Overhead costs include utilities, rent, and administrative expenses, while tooling costs relate to the machinery and equipment used in manufacturing. Efficient production processes can help minimize these costs. Buyers should inquire about the supplier’s production capacity and technology to gauge potential savings.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes can prevent defects and ensure compliance with safety and regulatory standards, thereby protecting the buyer’s investment. Buyers should look for suppliers that emphasize quality assurance, as this can reduce long-term costs associated with recalls or repairs.
-
Logistics: Transporting mini electric cars from the manufacturer to the destination can incur significant costs. Factors such as shipping method (e.g., RoRo or container shipping), distance, and local tariffs play a role. Buyers should evaluate Incoterms to clarify responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance.
-
Margin: Supplier margins will vary based on market conditions and competition. Buyers should understand the typical markup in the industry to negotiate effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Mini Electric Cars?
Several factors influence the pricing of mini electric cars, and understanding these can lead to more favorable purchasing decisions.
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their current and future needs to negotiate better pricing based on anticipated order quantities.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized vehicles tailored to specific market needs can attract higher costs due to additional design and production requirements. Buyers should balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as EEC compliance) can increase initial costs but may enhance safety and reliability, making them worthwhile investments in the long run.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can significantly affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge a premium, but they also reduce risks associated with poor performance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of trade can impact total costs. Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) dictate who bears the costs and risks at various stages of the shipping process, which can affect the final price.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers of Mini Electric Cars?
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough market research to understand prevailing prices and identify multiple suppliers. This knowledge provides leverage during negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership: Emphasize TCO rather than just upfront costs. Highlight the benefits of higher-quality options that may have lower maintenance and operational costs over time.
-
Be Clear About Requirements: Clearly outline specifications and expectations to avoid misunderstandings that could lead to additional costs later.
-
Establish Long-term Relationships: Building a strong partnership with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms in the future. Loyal customers often receive preferential treatment.
-
Utilize Payment Terms to Your Advantage: Negotiate favorable payment terms, such as extended payment periods or discounts for upfront payments, to improve cash flow.
Final Note on Pricing
While indicative prices can provide a baseline for negotiations, actual costs will vary based on the specific configurations, order sizes, and market conditions. B2B buyers should approach sourcing with flexibility and a clear understanding of their requirements to achieve optimal results.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing mini electric car eec coc With Other Solutions
Introduction
In an era where sustainable transportation solutions are increasingly prioritized, mini electric cars with EEC COC certification represent a compelling option for urban mobility. However, several alternatives exist that also cater to the needs of businesses and consumers seeking efficient, eco-friendly vehicles. This analysis compares the mini electric car EEC COC with two viable alternatives: electric scooters and traditional combustion engine vehicles. Each alternative offers unique advantages and disadvantages that can significantly impact purchasing decisions for B2B buyers in diverse regions.
| Comparison Aspect | Mini Electric Car EEC COC | Electric Scooter | Traditional Combustion Engine Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Max speed: 45 km/h; Range: up to 90 km | Max speed: 25-60 km/h; Range: up to 80 km | Max speed: 120 km/h; Range: 600 km |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; Low running cost | Lower initial cost; Low running cost | Higher initial cost; Higher running cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires space for parking and charging | Highly portable; easy to park | Requires more space and infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; periodic battery checks | Very low maintenance; fewer parts | Higher maintenance; more frequent servicing |
| Best Use Case | Short city commutes; family use | Individual urban transport; last-mile delivery | Long-distance travel; varied applications |
Detailed Breakdown
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Scooters?
Electric scooters present a cost-effective and highly portable alternative for urban mobility. They are particularly advantageous for short distances and can easily navigate congested city streets. With lower initial costs and minimal maintenance requirements, electric scooters are appealing to budget-conscious buyers. However, their limited speed and range may not suffice for longer commutes or family transport needs. Additionally, safety concerns in heavy traffic and weather conditions can deter some users.
How Do Traditional Combustion Engine Vehicles Compare?
Traditional combustion engine vehicles provide superior performance in terms of speed and range, making them suitable for long-distance travel and varied applications. They are often preferred for businesses requiring transportation of goods or larger groups of people. However, the higher initial and ongoing costs associated with fuel, maintenance, and environmental impact are significant drawbacks. Furthermore, as cities worldwide push for greener transportation solutions, reliance on combustion engines may become increasingly untenable.
Conclusion
When selecting the right transportation solution, B2B buyers must carefully consider their specific needs, including distance, cost, and vehicle usage. The mini electric car EEC COC stands out for its balance of performance, affordability, and eco-friendliness, making it ideal for urban commuting and short family trips. Meanwhile, electric scooters may offer a more economical choice for individual users, while traditional combustion vehicles remain valuable for businesses requiring extensive travel capabilities. Ultimately, the decision should align with the operational goals, budgetary constraints, and sustainability objectives of the buyer’s organization.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for mini electric car eec coc
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Mini Electric Cars with EEC COC?
When considering the procurement of mini electric cars, particularly those compliant with the European Economic Community Certificate of Conformity (EEC COC), understanding the technical specifications is crucial. Here are some critical properties that buyers should evaluate:
-
Motor Power (kW)
The motor power typically ranges from 1.5 kW to 3 kW for mini electric cars. This specification directly affects the vehicle’s performance, including acceleration and the ability to navigate various terrains. A higher power rating often translates to better performance, making it essential for B2B buyers to align motor specifications with intended use cases, such as urban commuting or leisure driving. -
Battery Capacity (Ah)
Battery capacity is measured in Amp-hours (Ah) and dictates how long the vehicle can operate before needing a recharge. Common configurations include 60V with capacities ranging from 58Ah to 105Ah. Understanding battery capacity is vital for estimating range and operational efficiency, helping businesses plan their logistics and operational costs effectively. -
Maximum Speed (km/h)
The maximum speed is typically capped at 45 km/h for EEC L6e and L7e classifications. This limitation is important for ensuring compliance with regulations and understanding the vehicle’s suitability for urban environments. Buyers need to evaluate whether the speed aligns with their transportation needs, particularly in densely populated areas. -
Range (km)
The range of a mini electric car, often between 40 km to 115 km on a single charge, is a critical metric for B2B buyers. This specification influences operational planning, including charging infrastructure requirements and the potential for longer trips without interruptions. Buyers should consider their specific use cases and the distances typically traveled. -
Weight and Load Capacity (kg)
The curb weight and load capacity (often 190 kg for mini cars) determine how many passengers and goods can be transported. This factor is crucial for businesses that may need to transport cargo or multiple passengers, impacting vehicle selection and operational efficiency. -
Safety Features
Safety features such as hydraulic disc brakes, LED lighting, and advanced dashboard systems enhance the vehicle’s reliability. Understanding these features helps buyers assess the vehicle’s compliance with safety regulations and its suitability for diverse operational environments.
Which Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know When Purchasing Mini Electric Cars?
Navigating the procurement process for mini electric cars involves understanding specific trade jargon that can influence negotiations and operational outcomes. Here are essential terms to be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that manufactures products that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of mini electric cars, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality assurance practices and potential customization options. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for budget planning and inventory management, particularly for businesses looking to scale their operations or test market demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request pricing from suppliers for specific products. Utilizing RFQs allows businesses to compare offers and negotiate better terms, ensuring they secure the best deal for their needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping costs and risk management. Familiarity with these terms is vital for B2B buyers to understand their liabilities and ensure smooth logistics. -
EEC COC (European Economic Community Certificate of Conformity)
This certification confirms that a vehicle meets EU regulations. Understanding its importance can help buyers ensure compliance, avoid legal issues, and enhance their marketability in regions that require such certification. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration between placing an order and receiving the product. Knowing the lead time is essential for effective supply chain management and operational planning, especially for businesses with tight deadlines.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market strategies.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the mini electric car eec coc Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Shaping the Mini Electric Car EEC COC Market?
The mini electric car market, especially those compliant with EEC COC standards, is witnessing significant growth driven by various global factors. Increasing urbanization, coupled with the rising demand for eco-friendly transport solutions, is steering the focus towards electric vehicles (EVs). B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly interested in these vehicles as they offer a practical solution for short-distance travel and urban commuting.
Emerging trends include the integration of advanced technologies such as smart dashboards, enhanced battery management systems, and improved safety features. The shift towards electric mobility is also being propelled by government incentives aimed at reducing carbon footprints and promoting sustainable transport. Countries in Europe, like Germany, are investing heavily in EV infrastructure, while regions in Africa and South America are exploring electric mobility as a means to address urban congestion and pollution.
Additionally, the availability of diverse financing options, including leasing and pay-per-use models, is making mini electric cars more accessible to businesses. As the market matures, international B2B buyers are likely to seek partnerships with manufacturers who can provide customized solutions tailored to local regulations and consumer preferences.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Mini Electric Car Sector?
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it is a core component of business strategy in the mini electric car sector. The environmental impact of sourcing materials, particularly for batteries, is a critical consideration. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as sourcing conflict-free minerals and utilizing recyclable materials in vehicle production.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated, especially as consumers become more conscious of the environmental and social implications of their purchases. Businesses are now looking for suppliers who can provide certifications that validate the sustainability of their products, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and EEC COC for compliance with European standards. Additionally, innovations in battery technology, such as lithium-ion alternatives that reduce reliance on scarce resources, are becoming a focal point for manufacturers.
Incorporating ‘green’ certifications and materials into the supply chain not only enhances a company’s brand image but also aligns with the growing regulatory frameworks aimed at reducing carbon emissions. This shift towards ethical sourcing is likely to influence purchasing decisions, with B2B buyers increasingly favoring manufacturers who can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the Mini Electric Car Market?
The mini electric car market has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from niche products to mainstream vehicles. Initially, electric vehicles were often perceived as impractical due to limited range and performance. However, technological advancements have led to significant improvements in battery efficiency and vehicle design, making mini electric cars more appealing to a broader audience.
The introduction of EEC COC certifications has further enhanced the credibility of these vehicles in international markets. This certification ensures that vehicles meet safety and environmental standards, which is crucial for B2B buyers looking to mitigate risks associated with compliance and liability. As urban mobility solutions gain traction worldwide, mini electric cars are positioned to play a vital role in the future of transportation, especially in densely populated urban areas.
Overall, the market dynamics for mini electric cars are shaped by a combination of technological innovation, sustainability considerations, and evolving consumer preferences, making it a compelling sector for B2B engagement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of mini electric car eec coc
-
How do I ensure the quality of mini electric cars when sourcing from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, start by vetting suppliers through certifications such as EEC COC and ISO standards. Request samples to evaluate the build quality, performance, and safety features firsthand. Additionally, conduct background checks and seek references from other businesses that have previously engaged with the supplier. Establish clear communication regarding quality expectations and inspection processes, and consider using third-party quality assurance services to verify compliance before shipment. -
What are the key specifications to consider when selecting a mini electric car for urban use?
When selecting a mini electric car for urban use, prioritize specifications such as maximum speed (ideally around 45 km/h), battery capacity (look for at least 60V 80Ah), and range (aim for a minimum of 90 km). Other important factors include interior space, safety features (like disc brakes and a robust body), and comfort elements (ergonomic seats, air conditioning). Ensure the vehicle meets local regulations, especially in terms of emissions and safety standards. -
What customization options are typically available for mini electric cars?
Customization options for mini electric cars can include color choices, interior finishes, and additional features like multimedia systems or enhanced safety equipment. Some manufacturers may offer tailored specifications such as battery upgrades or motor power adjustments based on your market needs. Discuss your requirements upfront with the supplier to understand the extent of customization they can provide, as well as any associated costs and lead times. -
What are the common payment terms for purchasing mini electric cars from international suppliers?
Common payment terms include options like T/T (telegraphic transfer), L/C (letter of credit), or even escrow services for larger orders. Typically, a 30% deposit is required upfront, with the remaining balance due before shipment. Be sure to clarify the payment schedule and any additional fees related to currency conversion or bank charges. Understanding these terms upfront will help mitigate financial risks and ensure a smoother transaction process. -
How can I effectively manage logistics when importing mini electric cars?
To manage logistics effectively, partner with a reliable freight forwarder experienced in automotive imports. They can assist with shipping methods (like RoRo or container shipping) and help navigate customs regulations in your country. Ensure you have all necessary documentation, including the EEC COC, to facilitate a smooth customs clearance process. Planning for potential delays and understanding the shipping timeline will also help you manage inventory more effectively. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for mini electric cars from manufacturers?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among manufacturers, typically ranging from 1 to 50 units or more. Some suppliers may offer lower MOQs for first-time buyers or samples. It’s essential to negotiate MOQs based on your business needs and to understand any implications on pricing, lead times, and shipping costs. Always confirm the MOQ during initial discussions to align expectations and ensure that your order fits your budget and operational capacity. -
What safety features should I look for in a mini electric car for commercial use?
For commercial use, prioritize safety features such as robust braking systems (preferably disc brakes), seatbelts, and a sturdy chassis that meets EEC safety standards. Look for additional safety technology, including LED lights for visibility, rearview cameras, and anti-lock braking systems (ABS). Ensure that the vehicle has passed relevant crash tests and adheres to local safety regulations to protect your drivers and minimize liability. -
How do I handle after-sales support and warranty issues for imported mini electric cars?
To handle after-sales support effectively, confirm the warranty terms with the supplier before purchase, including coverage duration and what it entails. Establish clear communication channels for reporting issues and seek suppliers who provide accessible technical support and spare parts. Consider entering into a service agreement for routine maintenance and repairs, ensuring that your fleet remains operational and compliant with local regulations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Mini Electric Car Eec Coc Manufacturers & Suppliers List
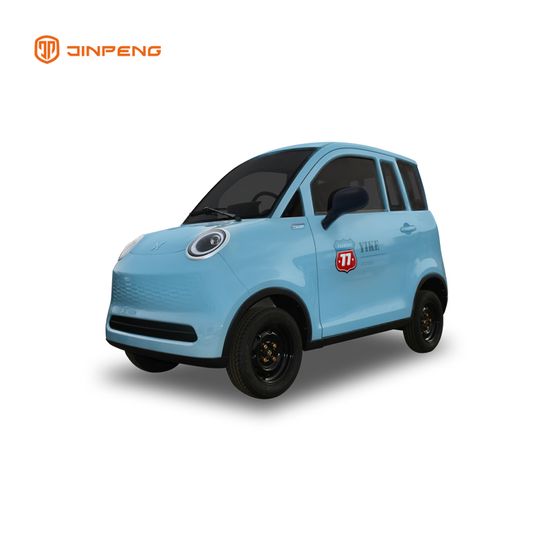
1. Fodauto – FWD-QH4 Electric Passenger Vehicle
Domain: fodauto.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: {“Model”:”FWD-QH4″,”Driving Type”:”Electric”,”Use For”:”Passenger”,”Body Type”:”Closed”,”Certification”:”EEC”,”Dimension (L*W*H)”:”2605*1295*1610MM”,”Net Weight”:”341kg (Without batteries weight)”,”Maximum Speed”:”25-45km/h”,”Max Load”:”225kg”,”Driving Range”:”60km”,”Motor”:”brushless 60V 2200W”,”Battery”:”60V 58AH”,”Charging Time”:”8-10 hours”,”Tyre”:”125/65-12*4″,”Passenger”:”2-3 (2 doors, 3 sea…
2. Mini Cooper Electric – 2024 Model Insights
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 2024 Mini Cooper Electric, range of 114 miles, suitable for short commutes (less than 5 miles), concerns about resale value and future battery improvements.
3. Yunlong – Mini Electric Vehicle Panda
Domain: bev-cars.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Mini Electric Vehicle
Manufacturer: Yunlong
Model: Panda
Approval: EEC L7e
Max Speed: 90 km/h
Seating Capacity: 2 front seats or 4 seats
Battery: 60V 58AH Lead-Acid Battery
Endurance Mileage: 80 km
Motor: 1500W high-speed motor, rear-wheel drive
Brake System: Four Wheel Disc Brakes with safety lock
Shock Absorption: Hydraulic shock absorption
Lighting: Full ligh…
4. Facebook – Mini Electric Car
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: mini electric car, top China manufacturer, EEC/L7e/COC certification, OEM/ODM
5. Chongqing Forward Auto Tech – New Energy Mini Electric Car
Domain: automaticelectriccar.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: EEC COC Certificate, 2200W motor, fully enclosed vehicles, new energy mini electric car, quality manufacturer: Chongqing Forward Auto Tech Co.,Ltd.
6. EEC – Mini Electric Auto Rickshaw
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: EEC COC Mini electric auto rickshaw, electric car for adults, made in China. Certified as EEC L1e-L7e. Features include a 105Ah LiFePo4 Battery with BMS, fast charging capability, and a 3 Kw motor.
7. Accio – Small Electric Car Options for 2025
Domain: accio.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Small Electric Car Street Legal: Best Options for 2025\nKey considerations:\n- Unit Price: $37 – $15,113\n- Product attributes: \n – Lithium-ion battery\n – 100km range\n – 25km/h max speed\n – Regenerative braking\n – LED headlights\n – ABS brakes\n – Air conditioning\n – Touchscreen display\n – Rearview camera\n – Bluetooth connectivity\n- Select by: Best Selling, MOQ < 5, Verified Sup…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for mini electric car eec coc
As the global market for mini electric cars continues to expand, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing becomes paramount for businesses looking to capitalize on this trend. The EEC COC certification ensures that these vehicles meet essential safety and environmental standards, which is a critical factor for international buyers. Key takeaways for B2B purchasers include the importance of selecting reliable suppliers who can offer customized solutions and competitive pricing, as well as understanding the regulatory landscape that varies by region.
Investing in mini electric vehicles not only enhances urban mobility but also aligns with global sustainability goals. The growing emphasis on eco-friendly transportation solutions presents a significant opportunity for businesses to differentiate themselves in the market.
Looking ahead, international buyers are encouraged to leverage strategic partnerships with manufacturers that prioritize quality and innovation. By doing so, they can ensure a steady supply of vehicles that meet evolving consumer demands. Engage with suppliers today to explore how mini electric cars can transform your business operations and contribute to a greener future.