Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for minielectric car
In today’s rapidly evolving automotive landscape, sourcing the right minielectric car can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. As the demand for sustainable transportation solutions grows, businesses must navigate a complex array of options, specifications, and market dynamics. This guide delves deep into the minielectric car market, exploring various types, applications, and the benefits of integrating these vehicles into fleets. It addresses critical aspects such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and potential savings associated with electric vehicle ownership.
For businesses in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia—making informed purchasing decisions is essential. This comprehensive guide equips B2B buyers with actionable insights, enabling them to assess their needs effectively and select minielectric cars that align with their operational goals. By understanding the nuances of the market, buyers can capitalize on the benefits of electric mobility, such as reduced maintenance costs, tax incentives, and enhanced brand reputation through sustainable practices.
Ultimately, this guide serves as a vital resource for navigating the global market for minielectric cars, empowering businesses to make strategic decisions that drive efficiency and sustainability in their operations.
Understanding minielectric car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compact Electric Hatchbacks | Small size, agile handling, typically 4-5 seats | Urban deliveries, corporate fleets | Pros: Easy to park, lower operational costs. Cons: Limited cargo space. |
| Electric SUVs | Larger body, higher seating position, more cargo capacity | Family transport, employee shuttles | Pros: Versatile, comfortable for longer trips. Cons: Higher initial purchase price. |
| Electric Vans | Spacious interior, designed for transport and utility | Goods delivery, service vehicles | Pros: High cargo capacity, customizable interiors. Cons: May require larger charging infrastructure. |
| Performance Electric Vehicles | Enhanced power and acceleration, sporty design | Executive transport, marketing use | Pros: Impressive performance, brand prestige. Cons: Higher insurance and maintenance costs. |
| Multi-Purpose Electric Vehicles | Combination of passenger and cargo capabilities | Mixed-use fleets, logistics | Pros: Flexibility in usage, efficient for diverse operations. Cons: Complex maintenance if not designed well. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Compact Electric Hatchbacks for B2B Buyers?
Compact electric hatchbacks are characterized by their small footprint and agile handling, making them ideal for urban environments. With seating for 4-5 passengers, they are suitable for short-distance travel and urban deliveries. B2B buyers can leverage their lower operational costs and ease of parking, making them a cost-effective option for businesses with tight city logistics. However, the limited cargo space can be a drawback for companies needing to transport larger items.
How Do Electric SUVs Serve B2B Applications Effectively?
Electric SUVs offer a balance of size and utility, featuring higher seating positions and ample cargo capacity. They are particularly well-suited for family transport and employee shuttles, providing comfort during longer trips. B2B buyers appreciate their versatility and capability to accommodate various transport needs. Although the initial purchase price is typically higher than hatchbacks, the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance can justify the investment.
What Benefits Do Electric Vans Provide for Business Logistics?
Electric vans are designed for maximum utility, boasting spacious interiors that can be customized for various transport needs. They are ideal for goods delivery and service vehicles, providing high cargo capacity and the ability to accommodate larger items. B2B buyers must consider the need for a robust charging infrastructure, as the operational requirements may differ from smaller vehicles. The flexibility in design and use makes electric vans a valuable addition to any logistics fleet.
How Can Performance Electric Vehicles Enhance Corporate Image?
Performance electric vehicles are distinguished by their enhanced power and acceleration, appealing to businesses focused on brand prestige and executive transport. These vehicles not only provide a luxurious driving experience but also align with sustainability goals, showcasing a commitment to eco-friendly practices. While they may come with higher insurance and maintenance costs, the benefits of impressing clients and stakeholders can outweigh these expenses for many organizations.
What Advantages Do Multi-Purpose Electric Vehicles Offer to Diverse Fleets?
Multi-purpose electric vehicles combine passenger and cargo capabilities, making them incredibly versatile for businesses with varied transport needs. They are excellent for mixed-use fleets, allowing companies to maximize utility without needing multiple vehicle types. B2B buyers should evaluate the design and maintenance complexity, as poorly designed models can lead to increased upkeep costs. Overall, their flexibility makes them a smart choice for organizations looking to optimize their fleet operations.
Key Industrial Applications of minielectric car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of minielectric car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Delivery Services | Last-Mile Delivery Solutions | Reduced operational costs and environmental impact | Charging infrastructure availability and range capacity |
| Corporate Fleets | Employee Transportation | Lower fuel and maintenance costs, enhanced corporate image | Battery life and warranty options |
| Tourism and Hospitality | Eco-Friendly Transport Solutions | Attraction of eco-conscious customers, enhanced brand value | Comfort and range to cater to diverse tourist needs |
| Public Transportation | Shuttle Services for Urban Areas | Cost-effective, sustainable transit options | Compliance with local regulations and charging stations |
| Agriculture and Farming | Utility Vehicles for Farm Operations | Lower running costs and reduced emissions | Terrain adaptability and battery performance |
How Can Urban Delivery Services Benefit from minielectric Cars?
In urban delivery services, minielectric cars can serve as efficient last-mile delivery vehicles. Their compact size allows for easier navigation through congested city streets, reducing delivery times. Additionally, the lower operational costs associated with electric vehicles, including savings on fuel and maintenance, can significantly enhance profitability. Buyers in this sector must consider the availability of charging infrastructure and the vehicle’s range to ensure it meets daily operational needs.
What Advantages Do Corporate Fleets Gain from minielectric Cars?
For corporate fleets, adopting minielectric cars for employee transportation can yield substantial savings. The decreased costs related to fuel and maintenance, combined with the positive environmental impact, enhance the company’s image as a socially responsible entity. When sourcing these vehicles, businesses should prioritize battery life and warranty options to ensure long-term reliability and performance.
How Do minielectric Cars Enhance Tourism and Hospitality?
In the tourism and hospitality industry, minielectric cars can be utilized to provide eco-friendly transportation options for guests. This not only attracts environmentally conscious travelers but also boosts the establishment’s brand value. To cater to the diverse needs of tourists, buyers should focus on comfort features and the vehicle’s range, ensuring that it can accommodate longer trips without frequent recharging.
What Role Do minielectric Cars Play in Public Transportation?
Minielectric cars can be integrated into public transportation systems as shuttle services in urban areas. They offer a sustainable, cost-effective solution for cities looking to reduce emissions while providing reliable transit options. Key considerations for buyers in this sector include compliance with local regulations and the presence of sufficient charging stations to support operations.
How Are minielectric Cars Used in Agriculture and Farming?
In agriculture, minielectric cars can serve as utility vehicles for various farm operations. Their lower running costs and reduced emissions make them an attractive option for farmers looking to improve sustainability. Buyers should assess the vehicle’s adaptability to different terrains and its battery performance to ensure it meets the unique demands of agricultural tasks.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘minielectric car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Charging Infrastructure in Emerging Markets
The Problem: B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America often face significant challenges related to the availability of charging stations for electric vehicles. This scarcity can lead to range anxiety, where businesses worry that their fleets may not have adequate charging options during operations. Without sufficient charging infrastructure, the efficiency and effectiveness of using mini electric cars are compromised, limiting their appeal for businesses considering a transition to electric.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, B2B buyers should engage in strategic partnerships with local governments and private companies to advocate for the development of charging infrastructure. This could involve collaborating on initiatives that promote the installation of charging stations in high-traffic areas or within business premises. Furthermore, businesses can explore mobile charging solutions or invest in portable charging units that can be deployed to remote locations. By proactively addressing the charging infrastructure issue, companies can ensure their mini electric cars remain operational, thereby maximizing their investment.
Scenario 2: High Initial Costs vs. Long-Term Savings
The Problem: The upfront costs associated with purchasing mini electric cars can deter many businesses, particularly in developing economies where budget constraints are prevalent. Although electric vehicles typically offer lower operating costs over time, the initial financial outlay can create hesitation among B2B buyers who are accustomed to traditional gasoline vehicles. This situation can hinder the adoption of eco-friendly transportation options, which are crucial for meeting sustainability goals.
The Solution: B2B buyers should conduct a thorough total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis to clearly illustrate the long-term savings associated with mini electric cars. This analysis should consider factors such as fuel savings, reduced maintenance costs, and potential tax incentives available in their region. Additionally, buyers can explore financing options, such as leasing or government grants, which can spread the initial investment over time. By presenting a compelling business case that outlines both the immediate and long-term financial benefits, companies can overcome budgetary concerns and facilitate the transition to electric vehicles.
Scenario 3: Employee Training and Adaptation to Electric Vehicle Technology
The Problem: Transitioning to mini electric cars requires a shift in mindset and operational practices for many businesses. Employees may be unfamiliar with the technology and features of electric vehicles, leading to inefficiencies in usage and maintenance. This gap in knowledge can result in resistance to change, affecting productivity and the overall success of the electric vehicle initiative.
The Solution: To ease this transition, B2B buyers should implement comprehensive training programs that educate employees about the benefits and functionality of mini electric cars. Training sessions can cover topics such as optimal charging practices, understanding vehicle range, and utilizing any integrated technology like navigation apps that locate charging stations. Additionally, creating a feedback loop where employees can share their experiences and challenges can foster a culture of continuous improvement. By investing in employee education and engagement, businesses can ensure a smoother transition to electric vehicles, enhancing both employee satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for minielectric car
What Are the Key Materials Used in Minielectric Cars?
When selecting materials for minielectric cars, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with international standards. The following analysis focuses on four common materials: aluminum, carbon fiber, steel, and plastics.
How Does Aluminum Enhance Performance in Minielectric Cars?
Aluminum is widely used in the automotive industry due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 600°F (315°C) and can withstand significant pressure, making it ideal for structural applications in minielectric vehicles.
Pros and Cons: Aluminum’s lightweight characteristic contributes to improved energy efficiency and range, essential for electric vehicles. However, it can be more expensive than traditional steel and may require specialized manufacturing processes, such as welding or extrusion, which can increase production complexity.
Impact on Application: In minielectric cars, aluminum is often used for the chassis and body panels, significantly reducing overall vehicle weight and enhancing performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: B2B buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should be aware of local sourcing capabilities and compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. The higher cost of aluminum may also be a consideration in markets sensitive to pricing.
What Role Does Carbon Fiber Play in Minielectric Vehicle Design?
Carbon fiber is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and rigidity, making it an attractive option for high-performance applications. It can withstand temperatures up to 400°F (204°C) and is resistant to corrosion.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of carbon fiber is its exceptional strength, which allows for thinner, lighter components without sacrificing durability. However, it comes with a high manufacturing cost and requires specialized techniques for processing, which can limit its use in mass production.
Impact on Application: Carbon fiber is often used in high-performance components such as body panels and internal structures, where weight savings can lead to significant efficiency improvements.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and South America should consider the availability of carbon fiber suppliers and the need for compliance with local regulations regarding material safety and performance standards.
How Does Steel Remain Relevant in Minielectric Cars?
Steel is still a fundamental material in automotive manufacturing due to its strength and cost-effectiveness. It can handle high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various applications within minielectric vehicles.
Pros and Cons: The durability and lower cost of steel make it a popular choice for many structural components. However, its heavier weight can negatively impact the vehicle’s range and efficiency compared to lighter materials like aluminum or carbon fiber.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used in the frame and safety structures of minielectric cars, providing essential crash protection and rigidity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Steel standards vary by region, and buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations and certifications. In markets like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, the cost-effectiveness of steel may appeal to budget-conscious buyers.
What Advantages Do Plastics Offer for Minielectric Cars?
Plastics are increasingly used in automotive applications due to their versatility and lightweight properties. They can withstand a range of temperatures, depending on the type, and offer excellent corrosion resistance.
Pros and Cons: The main advantage of plastics is their low weight and ease of molding into complex shapes, which can lead to design flexibility. However, they may not be as durable as metals and can be sensitive to UV exposure and temperature extremes.
Impact on Application: Plastics are often used in interior components, dashboards, and non-structural body parts, where weight savings and design flexibility are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the environmental regulations regarding plastic use and recycling in their respective regions, especially in Europe, where sustainability is a significant concern.
Summary of Material Selection for Minielectric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for Minielectric Car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Chassis and body panels | Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Carbon Fiber | High-performance components | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost, specialized processing required | High |
| Steel | Frame and safety structures | Cost-effective, durable | Heavier weight can impact efficiency | Low |
| Plastics | Interior components, non-structural parts | Lightweight, design flexibility | Less durable, sensitive to UV and temperature | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in minielectric cars, enabling informed decisions that align with both performance and market requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for minielectric car
What are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Mini Electric Car?
The manufacturing process for a mini electric car involves several critical stages, each designed to optimize efficiency, safety, and product quality. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: How are Components Sourced and Prepared?
Material preparation is foundational to the manufacturing process. Manufacturers source a variety of materials, including high-strength steel for the chassis, lightweight aluminum for the body panels, and advanced polymer composites for interior components. Sourcing these materials often involves rigorous supplier selection processes, ensuring that they meet international standards for quality and sustainability.
Once materials are acquired, they undergo preparation processes such as cutting, bending, and machining. This stage is crucial for ensuring that components fit together seamlessly in later stages. Quality checks are performed to confirm that materials meet specifications before they proceed to the next phase.
Forming: What Techniques are Used to Shape Components?
The forming stage utilizes advanced techniques such as stamping, extrusion, and casting to shape the materials into the necessary parts for the mini electric car. For example, the chassis may be stamped from sheets of high-strength steel, while components like battery enclosures may be cast from aluminum.
Robotic automation is increasingly employed in this phase to enhance precision and efficiency. This not only speeds up production but also minimizes human error, ensuring that each component is produced to exact specifications.
Assembly: How are the Components Brought Together?
During the assembly stage, components are brought together in a systematic manner. This includes the installation of the electric powertrain, battery systems, and electronic control units. The assembly line is designed for efficiency, often utilizing modular assembly techniques that allow workers to focus on specific tasks.
Quality control checkpoints are integrated into the assembly process. For instance, inspections are conducted at critical points (often referred to as In-Process Quality Control, or IPQC) to ensure that each assembly step meets quality standards. Any discrepancies are addressed immediately to prevent defects from propagating through the production line.
Finishing: What Steps are Taken to Ensure Quality and Aesthetics?
The finishing stage involves several processes, including painting, surface treatment, and final inspections. The painting process not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the mini electric car but also provides a protective layer against environmental factors.
Final Quality Control (FQC) checks are performed at this stage to ensure that the vehicle meets all specifications and is free from defects. This may involve functional testing of electrical systems, battery performance assessments, and safety checks.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of mini electric cars, with various international and industry-specific standards guiding the process. Understanding these standards is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those in diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Which International Standards are Relevant for Quality Assurance?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized international standard for quality management systems (QMS). It emphasizes a process-oriented approach and requires manufacturers to demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Compliance with ISO 9001 can enhance a manufacturer’s credibility in international markets.
Other relevant standards may include CE marking for compliance with European health and safety requirements, and API specifications for parts that involve oil and gas components. These certifications provide assurance that products are manufactured to high standards and are safe for use.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product integrity. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to verify compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous checks during production to identify and rectify issues immediately.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing and inspection of finished vehicles before they are shipped to buyers.
These checkpoints help ensure that potential defects are identified early, reducing the risk of costly recalls or customer dissatisfaction.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers looking to ensure the quality of their suppliers, several methods can be employed.
What Methods Can Be Used to Audit and Verify Suppliers?
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits of manufacturing facilities allows buyers to assess quality control processes directly. This includes reviewing documentation related to compliance with international standards, inspecting equipment, and observing production practices.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting regular quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their performance over time. These reports should detail metrics such as defect rates, customer complaints, and corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These organizations often have expertise in specific industries and can offer detailed evaluations.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various certification requirements and quality assurance practices that may differ by region.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Quality Assurance?
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and standards is crucial. For example, while CE marking may be essential for products sold in Europe, other regions may have different certifications.
Moreover, buyers should consider the implications of local sourcing laws, environmental regulations, and import/export tariffs, which can influence both quality and cost. Establishing clear communication with suppliers regarding these requirements can facilitate smoother transactions and compliance.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for mini electric cars are complex but essential for ensuring product reliability and safety. B2B buyers should be proactive in verifying supplier capabilities and compliance with international standards to secure high-quality products that meet market demands.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘minielectric car’
Introduction
This sourcing guide is designed to assist international B2B buyers in procuring mini electric cars efficiently and effectively. As the demand for electric vehicles rises globally, especially in markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the procurement process is critical. This checklist will guide you through essential steps to ensure you make informed purchasing decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical specifications that align with your operational needs and market conditions. Consider factors such as battery capacity, range, and performance metrics that are crucial for your intended use, whether for urban commuting or longer journeys.
– Key Considerations:
– Maximum range per charge (look for models offering 200+ miles for flexibility).
– Battery charging time and type (DC fast charging can significantly reduce downtime).
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Regulations
Stay informed about the latest trends in the electric vehicle market, including local regulations and incentives that may affect your purchase. Understanding the market can help you identify potential advantages and challenges in your region.
– Key Considerations:
– Availability of government incentives for electric vehicle purchases.
– Compliance with local emission regulations and environmental standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your requirements. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from previous clients, particularly those in similar industries or geographic areas.
– Key Considerations:
– Look for suppliers with a proven track record in electric vehicle sales.
– Check for certifications and partnerships with recognized automotive standards organizations.
Step 4: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Review the after-sales support offered by suppliers, including warranty terms and maintenance services. A robust after-sales program can save your business time and money in the long run.
– Key Considerations:
– Look for warranties that cover at least 8 years or 100,000 miles for the battery.
– Ensure that the supplier provides accessible maintenance services and support networks.
Step 5: Analyze Total Cost of Ownership
Calculate the total cost of ownership (TCO) of the mini electric car, factoring in purchase price, maintenance, insurance, and charging costs over time. This analysis is essential for determining the economic viability of your investment.
– Key Considerations:
– Compare fuel savings against traditional vehicles, as electric cars typically incur lower operating costs.
– Include potential tax incentives and rebates in your financial calculations.
Step 6: Test Drive and Evaluate Performance
Arrange for test drives to assess the performance and comfort of the mini electric cars you are considering. This firsthand experience can help you gauge the vehicle’s suitability for your specific needs.
– Key Considerations:
– Pay attention to handling, acceleration, and overall driving experience.
– Evaluate the ease of use of onboard technology and navigation systems.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier and vehicle, negotiate and finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure all terms, including payment schedules, delivery timelines, and service agreements, are clearly outlined.
– Key Considerations:
– Look for flexibility in financing options, such as leasing or purchasing.
– Confirm that all warranties and service agreements are documented in the contract.
Following this checklist will enable B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of sourcing mini electric cars, ensuring a strategic and informed purchase decision.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for minielectric car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Mini Electric Cars?
When considering the sourcing of mini electric cars, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials for mini electric cars can vary significantly depending on the specifications and quality required. Key components such as batteries, electric motors, and vehicle chassis materials (e.g., aluminum, steel, or composites) represent major cost drivers. As battery technology advances, buyers may also encounter fluctuating prices for lithium, cobalt, and nickel.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the geographic location of production. Regions with higher wage standards may yield higher labor costs, impacting overall pricing. However, automation and technology integration in manufacturing can mitigate some of these expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, including facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes and economies of scale can help reduce these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The cost of tooling refers to the equipment and machinery required for manufacturing the vehicles. Initial tooling investments can be high, but they are critical for ensuring production efficiency and quality.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that mini electric cars meet safety and performance standards incurs costs related to testing and certification. Investing in robust QC processes is essential for maintaining brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can significantly affect the total cost, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as distance, transport mode, and customs duties must be carefully considered.
-
Margin: The profit margin added by manufacturers and suppliers varies based on market conditions and competitive landscape. Understanding the margin expectations can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Mini Electric Car Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of mini electric cars, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can affect pricing. Bulk purchases generally lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should leverage their purchasing power to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications will typically increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and certifications required (e.g., safety, environmental) can influence costs. Higher-quality materials may result in a higher upfront investment but can lead to lower maintenance costs over time.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can impact both pricing and the overall sourcing experience. Buyers should conduct thorough research and assessments of potential suppliers.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is critical for international transactions. They define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly influence the total landed cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Maximize Cost Efficiency?
-
Negotiation: Buyers should be prepared to negotiate pricing and terms. Establishing a relationship with suppliers can lead to better deals and collaborative opportunities.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assessing TCO rather than just the upfront cost is crucial. Consider long-term savings from lower maintenance, fuel costs, and potential tax incentives for electric vehicles.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: When sourcing from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, trade regulations, and local market dynamics. Collaborating with local agents or partners can provide valuable insights.
-
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices: Buyers should always be cautious about relying solely on indicative prices. Costs can vary based on market conditions, and obtaining formal quotes from suppliers is essential for accurate budgeting.
By understanding these cost components, price influencers, and practical tips, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing mini electric cars, ultimately leading to better value and efficiency in their procurement processes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing minielectric car With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to the Minielectric Car for B2B Buyers
As businesses consider the adoption of electric vehicles, particularly the minielectric car, it’s essential to explore viable alternatives that may align better with specific operational needs and budgets. This analysis compares the minielectric car against two significant alternatives: conventional gasoline vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). Each option presents distinct advantages and challenges that can impact the decision-making process for B2B buyers.
| Comparison Aspect | Minielectric Car | Conventional Gasoline Vehicle | Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Quick acceleration, up to 212 miles range | Moderate acceleration, range varies significantly | Good acceleration, combined range of gas and electric |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost, lower operating costs due to savings on fuel and maintenance | Lower initial purchase price, higher fuel and maintenance costs | Moderate upfront cost, moderate fuel savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure, suitable for urban settings | Widely available infrastructure, minimal setup required | Requires some charging infrastructure, but can run on gasoline alone |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance needs (no oil changes) | Higher maintenance due to engine complexity | Moderate maintenance, as it combines both systems |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting, eco-conscious businesses | Long-distance travel, traditional fleets | Versatile for both city and highway driving |
What are the Pros and Cons of Conventional Gasoline Vehicles?
Conventional gasoline vehicles have long been the standard for transportation in many industries. Their primary advantage lies in their established infrastructure, making refueling quick and convenient. They typically have a lower purchase price compared to electric vehicles, making them more accessible for businesses with tight budgets. However, ongoing fuel costs and higher maintenance needs, including oil changes and engine repairs, can accumulate over time, leading to higher total cost of ownership. Furthermore, the environmental impact is a significant drawback, as these vehicles contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
How Do Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs) Compare?
Hybrid electric vehicles offer a middle ground between traditional gasoline vehicles and fully electric cars. They combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor, which can lead to improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions compared to gasoline-only vehicles. The initial purchase price is generally lower than that of fully electric vehicles, making them a more affordable option for some businesses. However, they still require maintenance for both the electric and gasoline components, which can complicate service needs. Additionally, while HEVs can operate on gasoline alone, they do not provide the same level of environmental benefits as fully electric options.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Vehicle Solution for Your Business
In determining the best vehicle solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and sustainability goals. The minielectric car excels in urban environments where charging infrastructure is available and can provide significant long-term savings. In contrast, conventional gasoline vehicles may be more suitable for businesses prioritizing lower initial costs and established refueling infrastructure. Hybrid electric vehicles can serve as a versatile option, offering benefits of both gasoline and electric systems, but may not deliver the full environmental advantages of a fully electric solution. Each alternative presents unique advantages, and careful evaluation will help businesses align their fleet choices with their strategic objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for minielectric car
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Minielectric Car?
When considering the procurement of minielectric cars, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for making informed decisions. Here are some of the essential properties that B2B buyers should focus on:
-
Battery Capacity (kWh)
– Definition: The battery capacity measures the amount of energy the battery can store, expressed in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
– B2B Importance: A higher battery capacity generally translates to a longer driving range. For businesses that rely on electric vehicles for logistics or transport, this can mean fewer recharges and increased operational efficiency. -
Range (Miles)
– Definition: Range refers to the distance a minielectric car can travel on a full charge.
– B2B Importance: Understanding the range is vital for fleet managers to optimize routes and schedules. A longer range reduces the frequency of charging stops, thus enhancing productivity. -
Charging Time (Hours)
– Definition: This indicates the time required to fully charge the vehicle’s battery, often differentiated by charging methods (Level 1, Level 2, DC Fast Charging).
– B2B Importance: Quick charging options allow businesses to minimize downtime. Knowing the charging time can help in planning operational strategies, especially for companies with high vehicle utilization rates. -
Horsepower (hp) and Torque (lb-ft)
– Definition: Horsepower measures the engine’s power output, while torque measures rotational force.
– B2B Importance: For businesses requiring performance vehicles, understanding these metrics helps assess whether the minielectric car meets specific operational needs, such as acceleration and load-bearing capacity. -
Warranty Terms
– Definition: Warranty terms often cover the battery and vehicle components, typically expressed in years or miles.
– B2B Importance: A comprehensive warranty can reduce long-term maintenance costs and provide peace of mind, making it an essential consideration for fleet purchases.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Minielectric Cars?
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance negotiations and streamline procurement processes. Here are some common terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can aid in sourcing quality components, ensuring that parts meet the required specifications and standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ can help businesses manage inventory levels and cash flow, particularly when considering bulk purchases. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services.
– Importance: Issuing an RFQ can facilitate competitive pricing and help buyers compare different suppliers effectively. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: These are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law.
– Importance: Understanding Incoterms is essential for determining responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs in international transactions, which is particularly relevant for buyers in diverse markets. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
– Definition: TCO refers to the comprehensive assessment of all costs associated with owning and operating a vehicle over its entire lifecycle.
– Importance: Evaluating TCO helps businesses understand the long-term financial implications of their electric vehicle investments, including purchase price, maintenance, charging costs, and potential savings.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more strategic decisions when investing in minielectric cars, ensuring that they meet their operational needs and maximize their return on investment.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the minielectric car Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers in the Mini Electric Car Sector?
The mini electric car sector is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. Rising fuel prices, increased urbanization, and a shift towards sustainable transportation have all contributed to the demand for electric vehicles (EVs). Governments worldwide are implementing stricter emissions regulations, incentivizing the adoption of EVs through tax credits and subsidies. In regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, this trend is further amplified by the need for energy-efficient transportation solutions that can navigate congested urban landscapes.
Emerging technologies play a pivotal role in shaping the market dynamics. Innovations in battery technology are enhancing the range and performance of mini electric cars, making them more appealing to B2B buyers. Additionally, advancements in charging infrastructure are addressing one of the primary concerns for potential EV users—charging convenience. Companies are increasingly looking for partnerships with local charging networks to ensure their fleets are adequately supported.
International B2B buyers must also consider regional trends. For instance, in Europe, the emphasis is on integration with smart city initiatives, while in Africa, the focus may be on affordability and access to charging stations. Understanding these regional nuances will be crucial for buyers looking to make informed sourcing decisions in the mini electric car sector.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing in the Mini Electric Car Market?
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it’s a key driver in the sourcing and production of mini electric cars. As environmental concerns escalate, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing practices. This includes transparency in the supply chain, particularly concerning the sourcing of raw materials such as lithium and cobalt, which are critical for battery production.
Moreover, the importance of “green” certifications is rising. Buyers are looking for manufacturers that comply with international environmental standards and possess certifications like ISO 14001. These certifications not only enhance brand reputation but also ensure that the production processes minimize environmental impact.
The shift towards sustainable materials is also noteworthy. Companies are exploring the use of recycled and bio-based materials in vehicle production to reduce the carbon footprint. By prioritizing suppliers with sustainable practices, B2B buyers can align their procurement strategies with their corporate social responsibility goals, thereby enhancing their market appeal and securing a competitive advantage.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the Mini Electric Car Market?
The mini electric car segment has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially perceived as niche products, these vehicles are now at the forefront of the automotive industry’s transition to electrification. The introduction of the first mass-produced electric vehicles in the late 20th century laid the groundwork for today’s mini electric cars, showcasing the potential of compact, efficient designs.
In the early 2000s, the mini electric car market began gaining traction as consumers became more environmentally conscious. The technological advancements in battery capacity and charging infrastructure further accelerated this growth, allowing manufacturers to produce models that combine performance with efficiency. Today, mini electric cars are recognized for their agility in urban environments and their ability to meet the demands of eco-conscious consumers and businesses alike.
As the market continues to evolve, B2B buyers should stay attuned to historical trends, technological advancements, and consumer preferences to make informed decisions that align with the future of transportation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of minielectric car
-
How do I evaluate the best suppliers for minielectric cars?
When sourcing minielectric cars, it’s crucial to assess suppliers based on their experience, production capacity, and compliance with international standards. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in electric vehicle manufacturing and positive reviews from previous clients. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Additionally, evaluate their supply chain logistics, after-sales support, and ability to meet your specific requirements, including customization options. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for minielectric cars?
Minimum order quantities for minielectric cars can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the specific model. Generally, MOQs range from 10 to 50 units for initial orders, especially for customized vehicles. It’s advisable to negotiate MOQs based on your purchasing capabilities and market demands. Smaller MOQs may be available, but they could result in higher per-unit costs. Understanding the supplier’s production capabilities will help you make informed decisions. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing minielectric cars?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include a 30% upfront deposit and the remaining balance before delivery. Some suppliers may offer flexible payment options, such as letters of credit or installment payments, depending on the relationship and order size. Always ensure to clarify payment methods and timelines in your contract to avoid any misunderstandings. It’s also wise to verify the supplier’s financial stability before committing to large orders. -
What customization options are available for minielectric cars?
Many manufacturers offer a range of customization options for minielectric cars, including color, interior features, battery capacity, and technology packages. When sourcing, inquire about the extent of customization available and any associated costs. Understanding the lead times for customized orders is essential, as this may impact your project timeline. Ensure that the supplier can meet your specific requirements and provide samples or prototypes if needed. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for minielectric cars?
To guarantee quality assurance, request a detailed QA plan from your supplier, outlining their testing processes and standards. It’s advisable to conduct factory audits and product inspections during production phases. Look for suppliers that adhere to international quality standards and can provide documentation for their testing procedures. Establishing a clear communication channel for addressing quality issues is also crucial for maintaining product integrity. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing minielectric cars?
Logistics for importing minielectric cars involve understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Collaborate with logistics partners experienced in automotive imports to ensure compliance with local regulations in your country. Calculate all associated costs, including shipping, tariffs, and insurance, to get a clear picture of your total investment. Additionally, consider the supplier’s ability to provide necessary documentation for smooth customs clearance. -
What are the potential tax incentives for purchasing minielectric cars in my region?
Tax incentives for minielectric car purchases can significantly impact your overall costs. Many countries offer rebates, tax credits, or exemptions on import duties for electric vehicles. Research local regulations in your target markets, as these incentives can vary widely across regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Engaging with local authorities or tax consultants can provide clarity on available incentives and how to apply for them. -
How do I find reliable after-sales support for minielectric cars?
Reliable after-sales support is critical for maintaining operational efficiency with minielectric cars. When evaluating suppliers, inquire about their warranty policies, parts availability, and service options. Ensure that the supplier has a dedicated support team capable of addressing maintenance and repair needs. Additionally, consider the supplier’s network of service centers and their responsiveness to support requests, which can be crucial for minimizing downtime.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Minielectric Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
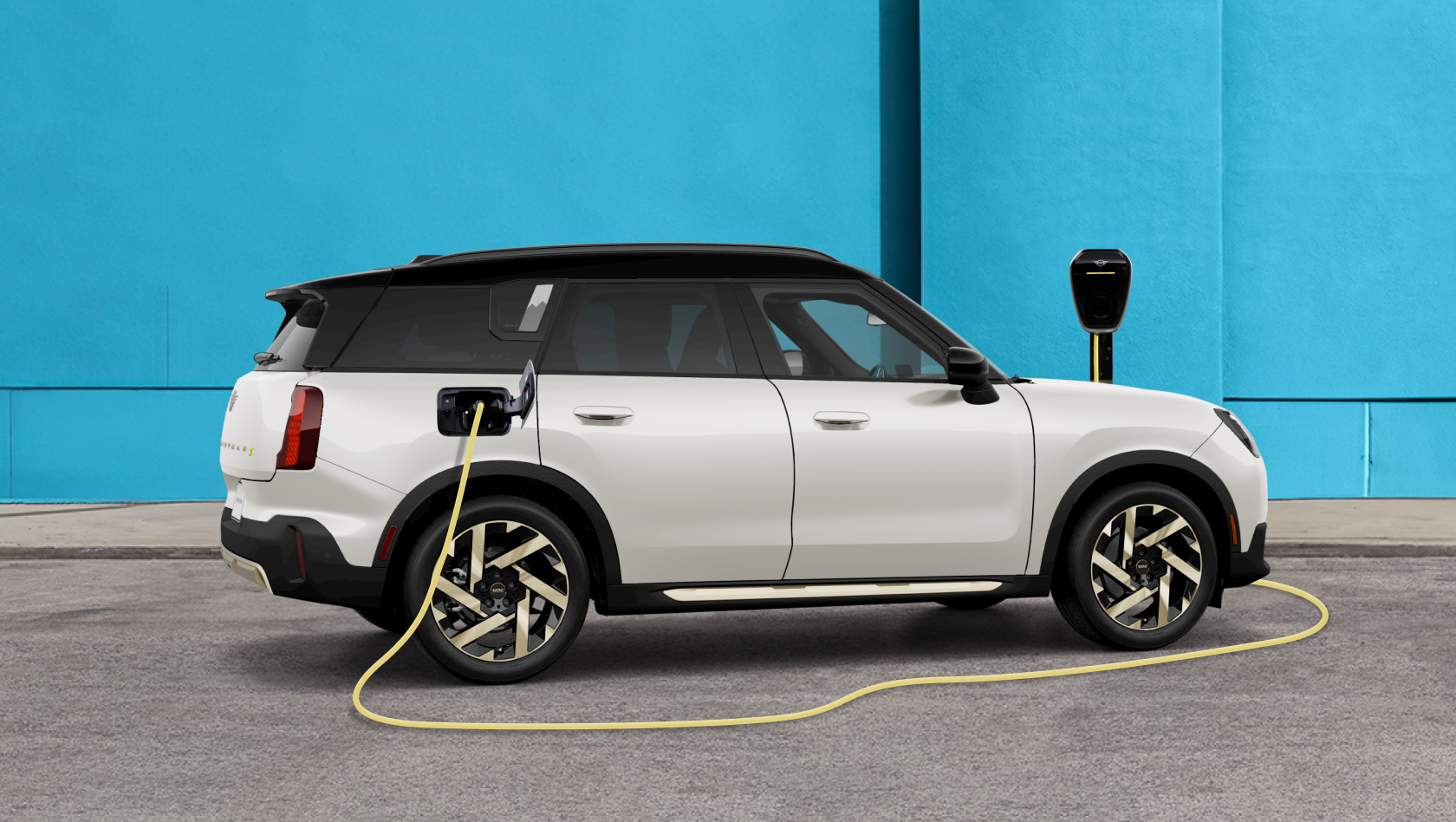
1. MINI – Countryman SE ALL4
Domain: seattlemini.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: {“model”:”MINI Countryman SE ALL4″,”horsepower”:”308 hp”,”torque”:”364 lb-ft”,”0-60 mph”:”5.4 sec”,”drivetrain”:”ALL4 Intelligent All-Wheel Drive”,”maximum_range”:”212 mi”,”battery_capacity”:”64.7 kWh”,”charging_time”:”29 min for 10-80% with DC Fast Charging”,”features”:[“Head-Up Display”,”Panoramic Moonroof”,”Sport Seats in leather-free Vescin”,”9.4-inch OLED Display”,”eight MINI Experience Modes…
2. Mini Cooper – Electric SE 2022/2023
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Electric Mini Cooper, model SE, 2022 and 2023 versions mentioned. Range of approximately 100 miles. Owners report it is fun to drive, solid performance, and efficient charging. Maintenance primarily involves tires and air filters, with brake fluid flush included in the first three years of free maintenance. Some models have a setting to emit noise while driving, which can be turned off. Owners hav…
3. Mini Cooper Electric – Key Review 2025
Domain: topgear.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Mini Cooper Electric Review 2025
– Prices: £26,840 – £38,640
– Versions: 181bhp Cooper E, 215bhp SE, 255bhp John Cooper Works
– Battery: 36.6kWh for Cooper E (up to 185 miles range), 49.2kWh for SE (up to 247 miles range), John Cooper Works rated up to 250 miles
– Performance: 0-62mph in 7.3s (Cooper E), 6.7s (SE), 5.9s (John Cooper Works)
– Weight: 1,600kg
– Dimensions: 3.8m long
– Features: 9.4i…
4. MINI – 2024 Cooper SE Electric Hardtop
Domain: lauderdalemini.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: MINI EV Lineup includes:
1. **2024 MINI Cooper SE Electric Hardtop**
– Starting Price: $30,900 MSRP
– Range: 114 miles per full charge
– Features:
– Lane departure warning
– Active driving assistant with pedestrian and front collision warning
– Apple CarPlay
– 8.8-inch touchscreen
– Dynamic digital instrument cluster
2. **2023 MINI Countryman P…
5. MINI – Electric Cars Range
Domain: stratstone.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: MINI Electric Cars Range includes: 1. MINI Aceman – first sole MINI electric car with classic MINI looks. 2. MINI Cooper Electric – familiar looks with iconic go-kart handling, fully-electric. 3. MINI Countryman Electric – most practical MINI, now fully-electric. Benefits of buying an electric MINI: Low Running Costs, Zero Emissions, Performance with instantaneous torque. Pricing: MINI Cooper Elec…
6. TELO – TELO MT1 All-Electric Mini Truck
Domain: telotrucks.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “TELO MT1”, “type”: “All-Electric Mini Truck”, “dimensions”: {“length”: “152 in”, “width”: “73 in”, “height”: “67 in”}, “bed_size”: {“length”: “60-96 in”, “width”: “56 in”, “height”: “18 in”}, “seating_capacity”: [2, 5, 8], “performance”: {“0-60_mph”: “6.0 s”, “power_hp”: “300 hp”, “payload”: “2000 lbs”, “towing_capacity”: “6600 lbs”}, “battery”: {“standard_range”: “260 mi”, “long…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for minielectric car
As the global market shifts towards sustainability, the strategic sourcing of mini electric cars presents a unique opportunity for B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The advantages of electric vehicles, such as lower maintenance costs, significant fuel savings, and government incentives, are compelling reasons to consider integrating these vehicles into your fleet. The MINI electric models, with their distinctive design and impressive range, exemplify the blend of functionality and style that can appeal to diverse markets.
Investing in electric vehicles not only aligns with environmental goals but also enhances corporate image and operational efficiency. By prioritizing partnerships with reputable manufacturers and leveraging local charging infrastructure, businesses can facilitate seamless transitions to electric mobility.
Looking ahead, the demand for mini electric cars will continue to rise, driven by consumer preferences and regulatory frameworks aimed at reducing carbon footprints. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to engage in strategic sourcing initiatives that will position them at the forefront of this electric revolution. Embrace the future of mobility and capitalize on the benefits of mini electric cars to drive your business forward.