Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for passenger electric car
In today’s rapidly evolving transportation landscape, sourcing passenger electric cars presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. With increasing demand for sustainable and efficient mobility solutions, companies from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Brazil and Nigeria, must navigate a complex marketplace filled with diverse vehicle options. This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of passenger electric cars available, their applications, and the vital considerations for supplier vetting.
From compact urban shuttles to larger multi-passenger vehicles, our guide covers essential information on the specifications, performance, and cost-effectiveness of each type. We also address critical factors such as regulatory compliance, maintenance requirements, and charging infrastructure, enabling buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights and strategies, this guide empowers companies to successfully integrate passenger electric cars into their fleets. The ultimate goal is to facilitate sustainable growth while meeting the demands of an increasingly eco-conscious consumer base. Whether you are looking to enhance your transportation offerings or reduce your carbon footprint, this guide serves as your roadmap in the dynamic global market for passenger electric vehicles.
Understanding passenger electric car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neighborhood Electric Vehicle (NEV) | Top speed of 25 mph, street-legal, compact design | Urban transport, tourism, small fleets | Pros: Low operational costs, eco-friendly. Cons: Limited speed and range. |
| Electric Shuttle | Seats 6, low-speed vehicle with high comfort features | Employee transport, public transit | Pros: Spacious, customizable, zero emissions. Cons: Limited to low-speed environments. |
| Compact Electric Car | Standard car design, higher speeds, longer ranges | Personal use, car-sharing services | Pros: Versatile, suitable for urban and suburban areas. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Luxury Electric Vehicle | High-end features, advanced technology, superior performance | Executive transport, premium rentals | Pros: Enhanced comfort and status. Cons: Higher maintenance and purchase costs. |
| Utility Electric Vehicle | Cargo capacity, practical design for goods transport | Delivery services, municipal use | Pros: Functional, cost-effective for businesses. Cons: Limited passenger capacity. |
What are Neighborhood Electric Vehicles (NEVs) and Their B2B Benefits?
Neighborhood Electric Vehicles (NEVs) are battery-powered vehicles designed for low-speed travel, typically with a maximum speed of 25 mph. They are ideal for urban settings, where short trips are common, making them suitable for businesses in tourism and local transport sectors. B2B buyers should consider the low operational costs and environmental benefits of NEVs, but they must also be aware of their limited speed and range, which may affect their use in more extensive transportation networks.
How Do Electric Shuttles Serve Businesses?
Electric shuttles, such as the GEM e6, are designed to accommodate multiple passengers, making them perfect for employee transport and public transit applications. Their customizable features and comfortable seating enhance passenger experience, while zero emissions align with sustainability goals. Businesses looking to invest in shuttles should consider the operational efficiency and lower energy costs, but they should also be mindful of the limitations posed by low-speed design, which may not suit all routes.
Why Choose Compact Electric Cars for B2B Applications?
Compact electric cars offer a familiar vehicle design with the capability for higher speeds and longer ranges compared to NEVs. They are well-suited for personal use and car-sharing services, providing flexibility for businesses. When considering a compact electric car, B2B buyers should weigh the initial investment against the potential for versatility in urban and suburban environments, as well as the overall operating costs that can be significantly lower than traditional vehicles.
What Makes Luxury Electric Vehicles Attractive for Business Use?
Luxury electric vehicles combine high-end features with advanced technology, catering to businesses focused on executive transport or premium rentals. These vehicles offer enhanced comfort and status, making them appealing for corporate events or high-profile clients. However, B2B buyers need to consider the higher maintenance and purchase costs associated with luxury models, ensuring that the investment aligns with their brand image and customer expectations.
How Do Utility Electric Vehicles Meet Business Needs?
Utility electric vehicles are designed with practicality in mind, offering ample cargo capacity for goods transport. They are particularly beneficial for delivery services and municipal applications, providing a cost-effective solution for businesses that require functionality over passenger capacity. When purchasing utility electric vehicles, companies should focus on their operational efficiency and overall cost-effectiveness while considering the specific needs of their logistics and service operations.
Key Industrial Applications of passenger electric car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of passenger electric car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitality and Tourism | Electric shuttles for hotel and resort transportation | Enhanced guest experience, reduced carbon footprint | Vehicle range, charging infrastructure, maintenance costs |
| Urban Mobility and Transport | Neighborhood electric vehicles for city commuting | Cost-effective and sustainable urban transport solutions | Local regulations, vehicle safety standards, service support |
| Corporate Fleet Management | Employee transport solutions using electric cars | Lower operational costs, improved corporate sustainability | Fleet size, vehicle customization, battery options |
| Educational Institutions | Campus shuttle services with passenger electric cars | Eco-friendly student transport, reduced noise pollution | Vehicle capacity, charging facilities, safety features |
| Event Management | Electric vehicles for event transportation logistics | Efficient guest movement, alignment with green initiatives | Vehicle availability, logistical planning, service reliability |
How Are Passenger Electric Cars Used in Hospitality and Tourism?
In the hospitality and tourism sector, passenger electric cars, such as electric shuttles, are increasingly utilized for transporting guests within hotels and resorts. These vehicles enhance the guest experience by providing a comfortable, eco-friendly alternative to traditional transportation. Moreover, they support the industry’s sustainability goals by reducing carbon emissions. For international buyers, sourcing considerations include evaluating the vehicle’s range to cover the property effectively and ensuring access to charging infrastructure to minimize downtime.
What Role Do Neighborhood Electric Vehicles Play in Urban Mobility?
Neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs) serve as a practical solution for urban commuting, especially in densely populated areas. With a top speed of 25 mph, these vehicles are ideal for short trips, offering a cost-effective and sustainable transport option. This application is particularly beneficial for businesses aiming to reduce transportation costs while promoting an eco-friendly image. Buyers must consider local regulations regarding NEV usage and the availability of charging stations to ensure compliance and operational efficiency.
How Can Corporate Fleet Management Benefit from Passenger Electric Cars?
Corporate fleet management can leverage passenger electric cars for employee transportation, enhancing sustainability initiatives while reducing operational costs. By integrating electric vehicles into their fleets, companies can lower fuel expenses and maintenance costs over time. For businesses in regions like Africa or South America, key considerations include vehicle customization to meet specific corporate branding needs and ensuring reliable service support for maintenance and repairs.
Why Are Electric Cars Ideal for Educational Institutions?
Educational institutions can benefit significantly from using passenger electric cars for campus shuttle services. These vehicles not only provide eco-friendly transportation for students and staff but also contribute to a quieter campus environment, reducing noise pollution. When sourcing these vehicles, institutions should focus on capacity to accommodate large groups, the availability of charging facilities on campus, and the safety features of the vehicles to ensure student well-being.
How Do Electric Vehicles Enhance Event Management Logistics?
In the event management sector, passenger electric cars can streamline transportation logistics by efficiently moving guests and staff between venues. This application aligns with the growing trend of sustainability in event planning, appealing to environmentally conscious attendees. Event organizers should consider the availability of electric vehicles during peak times, the logistical planning required for efficient transport routes, and the reliability of the service provider to ensure a seamless experience for all participants.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘passenger electric car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Limited Charging Infrastructure in Emerging Markets
The Problem: In many regions, particularly in Africa and South America, charging infrastructure for electric vehicles (EVs) is still in its infancy. B2B buyers looking to invest in passenger electric cars often face the challenge of inadequate charging stations, which can lead to operational disruptions and range anxiety among users. This lack of infrastructure can deter potential customers from adopting electric vehicles, fearing that they will be unable to charge them conveniently during daily operations.
The Solution: To address this challenge, B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with local governments and private enterprises to develop charging infrastructure. Engaging in community discussions to advocate for the installation of charging stations in strategic locations—such as shopping centers, hotels, and transportation hubs—can create a robust network that supports passenger electric car usage. Additionally, consider sourcing electric vehicles that offer flexible charging options, such as compatibility with standard home outlets or the inclusion of fast-charging capabilities. Investing in vehicles with solar panel options can also provide sustainable charging alternatives, particularly in sunny regions. This proactive approach not only eases range anxiety but also positions your business as a leader in promoting sustainable transportation solutions.
Scenario 2: Managing Total Cost of Ownership Amidst Initial Investment Concerns
The Problem: Many businesses are hesitant to invest in passenger electric cars due to the perceived high upfront costs compared to traditional vehicles. In regions with limited budget flexibility, such as parts of the Middle East and Africa, this initial investment can deter organizations from transitioning to electric options, despite the long-term savings associated with reduced fuel and maintenance costs.
The Solution: To overcome this financial barrier, B2B buyers should conduct a comprehensive Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis that includes not only the purchase price but also potential savings on fuel, maintenance, and tax incentives available for electric vehicles. Presenting these findings to stakeholders can provide a clearer picture of the financial benefits over time. Additionally, exploring financing options, such as leasing or government grants for electric vehicle purchases, can alleviate the burden of upfront costs. Collaborating with vehicle manufacturers to secure bulk purchase discounts or extended warranties can further enhance the financial feasibility of integrating passenger electric cars into your fleet.
Scenario 3: Addressing Workforce Concerns About Electric Vehicle Familiarity and Safety
The Problem: Employees may express apprehension regarding the transition to passenger electric cars, particularly in terms of operating new technology and safety. This is especially prevalent in regions where traditional vehicles dominate, leading to resistance that can hinder the effective implementation of electric vehicles in a company’s transportation fleet.
The Solution: To mitigate these concerns, B2B buyers should invest in comprehensive training programs that educate employees about the operation, benefits, and safety features of electric vehicles. This training can include hands-on demonstrations and workshops that familiarize staff with one-pedal driving, regenerative braking, and the vehicle’s safety systems. Additionally, providing ongoing support and resources, such as instructional videos and FAQs, can help alleviate fears and build confidence in using electric vehicles. Highlighting the environmental benefits and potential cost savings can further motivate employees to embrace this transition. By fostering a culture of innovation and support, organizations can ensure a smoother integration of passenger electric cars into their operations, enhancing overall employee satisfaction and productivity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for passenger electric car
What Are the Key Materials for Passenger Electric Cars?
When selecting materials for passenger electric cars, manufacturers must consider properties that enhance performance, safety, and sustainability. Here, we analyze four common materials: aluminum, high-strength steel, composite materials, and lithium-ion batteries, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Electric Car Manufacturing?
Aluminum is widely used in electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. With a temperature rating that can withstand extreme conditions, aluminum is suitable for various components, including body panels and structural elements.
Pros: Aluminum’s low density contributes to improved energy efficiency and range, which is critical for electric vehicles. It also allows for easier manufacturing processes, such as extrusion and stamping.
Cons: While aluminum provides significant weight savings, it can be more expensive than traditional steel. Additionally, its lower tensile strength compared to steel may require design considerations to ensure structural integrity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for diverse environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should be aware of the availability and cost fluctuations of aluminum. Compliance with international standards, such as ASTM and EN, is crucial to ensure safety and performance.
What Role Does High-Strength Steel Play in Electric Vehicles?
High-strength steel (HSS) is another critical material in passenger electric cars, particularly for structural components. Its high tensile strength and durability make it suitable for safety-critical applications, such as frames and chassis.
Pros: HSS provides excellent impact resistance, which enhances passenger safety during collisions. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to aluminum and other advanced materials.
Cons: The weight of high-strength steel can negatively impact the overall energy efficiency of electric vehicles. Additionally, manufacturing processes may be more complex due to the need for specialized techniques to form and weld HSS.
Impact on Application: HSS is compatible with various environmental conditions, though it may require protective coatings to prevent corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that HSS components meet local safety standards and regulations, particularly in regions with stringent vehicle safety requirements.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Electric Vehicle Design?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, are increasingly used in electric vehicles for their lightweight and high-strength properties. These materials are particularly advantageous for non-structural components, such as interior panels and body parts.
Pros: Composites can significantly reduce vehicle weight, improving range and efficiency. They also offer excellent corrosion resistance and design flexibility.
Cons: The primary drawback of composites is their high cost and complex manufacturing processes, which may limit their widespread adoption in budget-sensitive markets.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for various applications, including aesthetic components, but may not be ideal for high-load structural elements.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of composite manufacturing facilities and skilled labor in their regions, as well as compliance with relevant standards.
What Are the Key Considerations for Lithium-Ion Batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries are the heart of electric vehicles, providing the necessary energy storage for propulsion. Their performance characteristics, including energy density and cycle life, are critical for EV applications.
Pros: Lithium-ion batteries offer high energy density, allowing for longer driving ranges. They also have a relatively low self-discharge rate, making them efficient for daily use.
Cons: The cost of lithium-ion batteries remains high, and there are concerns about resource availability and environmental impact associated with lithium extraction.
Impact on Application: These batteries are compatible with various charging infrastructures, including fast chargers, which is crucial for user convenience.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must be aware of local regulations regarding battery recycling and disposal, as well as the availability of charging infrastructure in their regions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Passenger Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for passenger electric car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, structural components | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, lower tensile strength | Medium |
| High-Strength Steel | Chassis, safety-critical components | Excellent impact resistance | Heavier, complex manufacturing | Low |
| Composite Materials | Interior panels, non-structural components | Lightweight, design flexibility | High cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Lithium-Ion Battery | Energy storage for propulsion | High energy density, low self-discharge | High cost, environmental concerns | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in passenger electric cars, helping them make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for passenger electric car
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Passenger Electric Cars?
The manufacturing of passenger electric cars involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets high standards of quality and performance. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Processed?
The first step in manufacturing electric vehicles (EVs) is sourcing high-quality materials. This includes metals for the chassis, battery components, and various plastics for interior parts. Advanced materials such as lightweight aluminum and high-strength steel are often preferred to enhance performance and energy efficiency.
Once sourced, materials undergo rigorous preparation, including cutting, machining, and heat treatment. The goal is to ensure that every component meets the required specifications before moving to the next stage. This phase may also involve the use of automated systems for precision and efficiency.
How Are Components Formed in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Forming processes involve transforming raw materials into usable components. This stage often employs techniques such as stamping, molding, and extrusion. For instance, the body panels of the electric car are typically stamped from sheet metal, while battery cases may be molded from high-strength polymers.
Innovative forming techniques, such as hydroforming and 3D printing, are increasingly utilized to create complex shapes that traditional methods cannot achieve. These techniques not only reduce material waste but also speed up production times, a crucial factor for B2B buyers looking to meet growing market demand.
What Does the Assembly Process Involve for Electric Cars?
The assembly stage is where all individual components come together to form a complete vehicle. This process typically involves multiple assembly lines and is often characterized by a combination of manual labor and automated systems.
Electric vehicles require specialized assembly techniques, particularly for the battery and electric motor integration. Workers must adhere to stringent safety and quality protocols to ensure that high-voltage components are correctly installed and insulated. Additionally, the assembly process may involve real-time monitoring systems to track progress and quality.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the electric vehicle manufacturing process. It ensures that each vehicle meets international safety and performance standards before reaching the market.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Manufacturers typically adhere to several international standards, including ISO 9001 for quality management systems. Compliance with these standards is essential for B2B buyers, as it assures them that the manufacturer follows established protocols for quality control.
In addition to ISO standards, electric vehicle manufacturers may also need to comply with industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for products sold in Europe and SAE J2358 for occupant protection in low-speed vehicles. Understanding these certifications can help B2B buyers assess the credibility of potential suppliers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated at various stages of production to catch defects early. Key checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Quality checks during the manufacturing process help identify issues before they escalate. This may include monitoring assembly processes and conducting inline tests.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished vehicle, ensuring that it meets all safety and performance standards before delivery.
These checkpoints are critical for maintaining high-quality standards, and B2B buyers should inquire about a manufacturer’s specific QC processes.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality in Electric Vehicles?
Testing methods vary depending on the component being evaluated. Common testing techniques include:
- Functional Testing: Ensures that all systems, including the battery, electric motor, and safety features, operate correctly.
- Durability Testing: Simulates real-world conditions to assess how the vehicle performs over time, including stress testing on the chassis and suspension.
- Safety Testing: Involves crash tests and other safety evaluations to ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
B2B buyers should ask manufacturers for detailed reports on testing outcomes to verify compliance with safety and performance standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to observe the manufacturing process and QC practices firsthand. This can provide invaluable insights into the supplier’s operational capabilities.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and certifications can help assess a supplier’s commitment to quality assurance. This includes documentation on compliance with ISO standards and any relevant industry certifications.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. This is particularly important for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct in-house inspections.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East, understanding the nuances of quality control is crucial. Factors such as local regulations, import standards, and logistical challenges can impact the quality assurance process.
Buyers should be aware of regional certifications that may differ from international standards. Additionally, they should consider the supplier’s ability to provide documentation in multiple languages and ensure that the quality control processes align with local expectations.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for passenger electric cars, ensuring that they receive high-quality, compliant vehicles that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘passenger electric car’
Introduction
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure passenger electric cars. With the growing demand for eco-friendly transportation solutions, it is crucial to follow a structured approach when sourcing these vehicles. This checklist will help ensure that you make informed decisions that align with your organizational needs and sustainability goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is fundamental to ensure that the electric vehicles meet your operational requirements. Consider factors such as seating capacity, range, speed, and safety features. A well-defined specification will streamline your search and help you communicate effectively with suppliers.
- Seating Capacity: Determine how many passengers you need to accommodate.
- Range Requirements: Assess the distance your vehicles will need to cover on a single charge.
- Safety Standards: Ensure compliance with local and international safety regulations.
Step 2: Research Available Models
Invest time in researching various passenger electric car models available in the market. Different models may offer unique features suited for specific applications, such as urban transport or tourist services. Understanding the options will empower you to choose the vehicle that best fits your needs.
- Features Comparison: Look at aspects like battery technology, charging time, and comfort features.
- Market Trends: Stay updated on the latest innovations in electric vehicle technology.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can deliver quality vehicles that meet your specifications. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from clients in similar industries or regions. A reliable supplier will have a solid reputation and proven track record.
- Certifications: Verify that the supplier holds necessary certifications and complies with industry standards.
- After-Sales Support: Assess their customer service and support offerings, as these are crucial for maintenance and operational continuity.
Step 4: Request Proposals and Quotes
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed proposals and quotes. This step will provide insight into pricing, delivery timelines, and warranty options. Comparing these proposals will help you identify the best value for your investment.
- Cost Breakdown: Look for transparency in pricing, including any additional costs for customization or maintenance.
- Warranty Terms: Understand the warranty coverage and service agreements offered by each supplier.
Step 5: Assess Financing Options
Explore various financing options available for purchasing passenger electric cars. Many suppliers offer flexible financing solutions that can ease the financial burden of procurement. Understanding your financing options will help you make a cost-effective decision.
- Leasing vs. Buying: Evaluate the pros and cons of leasing compared to outright purchasing.
- Incentives: Research any government incentives or subsidies available for electric vehicle purchases in your region.
Step 6: Conduct a Pilot Program
Before making a large-scale commitment, consider running a pilot program with your selected electric vehicles. This will allow you to assess performance, user satisfaction, and operational efficiency in real-world conditions.
- Feedback Collection: Gather feedback from drivers and passengers to identify any issues or areas for improvement.
- Performance Metrics: Analyze data on range, charging times, and overall user experience to inform your final decision.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once satisfied with the pilot results, finalize the purchase agreement with your chosen supplier. Ensure that all terms, including delivery schedules, payment plans, and service agreements, are clearly outlined. A well-structured agreement will safeguard your interests and facilitate a smooth transaction.
- Review Terms: Carefully read through the contract to avoid any hidden clauses or misunderstandings.
- Establish Communication Channels: Set up clear communication pathways with your supplier for ongoing support and collaboration.
By following this structured checklist, you can effectively navigate the procurement process for passenger electric cars, ensuring that your investment aligns with your organizational objectives and sustainability efforts.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for passenger electric car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Passenger Electric Cars?
When sourcing passenger electric cars, several cost components significantly influence the overall pricing structure. Understanding these components is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their investments.
-
Materials: The cost of materials is a primary driver in electric vehicle pricing. Key components such as batteries, electric motors, and lightweight materials (like aluminum and composites) impact the overall cost. The choice of battery technology—AGM, Li-ion, or advanced solid-state—can vary the price substantially. For instance, lithium-ion batteries generally offer better performance but come at a higher price point.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce required for assembly, quality control, and technical support. Regions with lower labor costs can help reduce the overall pricing of electric vehicles. However, skilled labor is essential for high-quality assembly, particularly for complex electric powertrains.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes all indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can mitigate these costs, impacting the final price offered to buyers.
-
Tooling: Initial investments in tooling and molds can be significant, especially for customized electric vehicle designs. These costs are amortized over production runs, meaning larger orders can reduce the per-unit tooling cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that vehicles meet safety and performance standards incurs additional costs. Compliance with international certifications can also affect pricing, particularly for markets in Europe and North America, where standards are stringent.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for delivering vehicles or components to international markets must be factored in. This includes warehousing, shipping, and potential tariffs, which can vary widely between regions.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a margin to cover business risks and ensure profitability. Understanding the margin expectations of potential suppliers can aid in negotiations.
What Influences Pricing for Passenger Electric Cars?
Several factors can influence the pricing of passenger electric cars, especially in international markets.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often lead to volume discounts, making it advantageous for businesses to consolidate their purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can increase costs. Buyers should be clear about their requirements to avoid unexpected pricing increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials or certifications (such as safety and environmental standards) can raise the price. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of these features against their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and reliability can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices due to their brand value and assurance of quality.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international transactions. These terms define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, impacting the total landed cost of the vehicles.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Passenger Electric Cars?
To navigate the complexities of sourcing passenger electric cars, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage volume commitments and long-term partnerships to negotiate better pricing and terms. Suppliers may be more willing to offer discounts for larger orders or consistent business.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial purchase price, maintenance costs, energy consumption, and resale value. This holistic view helps identify the most cost-effective options.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Different regions may have varying expectations and standards that can influence pricing. For example, electric vehicles in Europe may incur higher compliance costs due to stricter regulations.
-
Seek Local Partnerships: Collaborating with local distributors or suppliers can provide insights into market dynamics and help mitigate logistics costs.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is important to note that prices for passenger electric cars can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors and are subject to change. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and engage with multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing passenger electric car With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Passenger Electric Cars
As the demand for sustainable transportation solutions grows, businesses are increasingly exploring various alternatives to passenger electric cars. These alternatives not only provide eco-friendly options but also cater to diverse operational needs, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. In this analysis, we will compare passenger electric cars with two viable alternatives: electric shuttles and neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs).
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Passenger Electric Car | Electric Shuttle (GEM e6) | Neighborhood Electric Vehicle (Club Car CRU) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High speed (up to 120 mph) | Low speed (up to 25 mph) | Low speed (up to 25 mph) |
| Cost | Higher upfront investment | Moderate cost, ~$14,000+ | Moderate cost, ~$10,000+ |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure | Street-legal, minimal setup | Street-legal, minimal setup |
| Maintenance | Moderate; depends on usage | Low; maintenance-free options | Low; lithium-ion battery reduces upkeep |
| Best Use Case | Long-distance travel, family | Urban transport, short trips | Neighborhood travel, leisure activities |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Shuttle (GEM e6)
Electric shuttles, such as the GEM e6, are designed specifically for urban transport and can accommodate multiple passengers comfortably. With a top speed of 25 mph, they are ideal for short-distance travel in city environments. The upfront cost is moderate, and maintenance is low due to their electric nature. However, their limited speed may not be suitable for longer journeys, making them best for local transportation solutions like hotels, campuses, or theme parks.
Neighborhood Electric Vehicle (Club Car CRU)
The Club Car CRU offers a unique blend of style and functionality, designed for leisurely neighborhood travel. Like the GEM e6, it operates at a maximum speed of 25 mph, making it suitable for low-traffic areas. The CRU is relatively affordable and features lithium-ion batteries, which contribute to lower maintenance costs over time. However, it may lack the performance and range necessary for longer commutes or commercial applications, limiting its utility for businesses focused on extensive travel routes.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When evaluating transportation solutions, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational requirements, including the intended use case, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. Passenger electric cars are ideal for long-distance travel and family use, while electric shuttles and NEVs excel in urban settings and short-range applications. Assessing factors such as performance, cost, and ease of implementation will help businesses select the most appropriate vehicle type to enhance their sustainability efforts and operational efficiency. By aligning vehicle characteristics with business objectives, companies can make informed decisions that meet both their logistical needs and environmental goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for passenger electric car
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Passenger Electric Cars?
Understanding the technical specifications of passenger electric cars is crucial for B2B buyers. These properties not only influence vehicle performance but also impact operational costs and regulatory compliance. Here are some key specifications to consider:
1. Range
The range refers to the distance a vehicle can travel on a single charge. It is typically measured in miles or kilometers. For B2B buyers, range is vital because it determines the vehicle’s suitability for specific applications, such as urban commuting or long-distance travel. A higher range can reduce downtime for charging, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
2. Battery Capacity
Battery capacity is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) and indicates the amount of energy stored in the battery. This directly affects both the range and the vehicle’s performance. Understanding battery capacity helps buyers assess the vehicle’s suitability for their energy needs and operational patterns, as well as its long-term maintenance costs.
3. Payload Capacity
Payload capacity refers to the maximum weight that a vehicle can safely carry, including passengers and cargo. It is crucial for businesses that require transportation of goods alongside passengers. Knowing the payload capacity helps businesses ensure compliance with local regulations and optimize vehicle utilization.
4. Top Speed
Top speed is the maximum speed a vehicle can achieve, typically measured in miles per hour (mph) or kilometers per hour (km/h). This specification is important for understanding the vehicle’s performance in urban settings where speed limits are often lower. It also impacts safety and operational efficiency in various driving conditions.
5. Charging Time
Charging time is the duration required to fully charge the vehicle’s battery. It varies depending on the charger type (e.g., Level 1, Level 2, DC Fast Charging). For B2B buyers, knowing the charging time is essential for planning operational schedules and minimizing downtime.
6. Weight and Dimensions
The overall weight and dimensions of the vehicle influence its maneuverability and performance. A lighter vehicle may offer better efficiency, while dimensions can affect parking and storage capabilities. Buyers need to consider these factors based on their specific operational environments.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Passenger Electric Car Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations. Here are some essential trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the electric vehicle sector, understanding OEM relationships can help businesses identify reliable suppliers and assess product quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ helps in budget planning and inventory management, ensuring they meet supplier requirements while optimizing stock levels.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotations from suppliers. This term is crucial for B2B transactions, as it initiates the procurement process and helps businesses compare pricing and terms from different manufacturers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to navigate shipping logistics and cost responsibilities.
5. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with the acquisition and operation of a vehicle over its lifespan, including purchase price, maintenance, insurance, and energy costs. For B2B buyers, evaluating TCO is critical for making informed purchasing decisions that align with budget constraints and operational needs.
6. Lifecycle Assessment (LCA)
LCA is a technique to assess environmental impacts associated with all stages of a product’s life from cradle to grave. For buyers focused on sustainability, understanding LCA can help in selecting vehicles that align with corporate social responsibility goals.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in passenger electric cars, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and sustainability initiatives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the passenger electric car Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Passenger Electric Car Market?
The passenger electric car sector is experiencing rapid growth, driven by several global factors. First, increasing environmental awareness and governmental regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions are propelling demand for electric vehicles (EVs). Countries are implementing incentives for EV adoption, such as tax breaks and subsidies, which significantly impact purchasing decisions. Additionally, advancements in battery technology are enhancing the performance and affordability of electric cars, making them more attractive to consumers and businesses alike.
Emerging technologies, such as connected vehicle systems and autonomous driving capabilities, are reshaping the market dynamics. B2B buyers must stay abreast of these advancements to leverage competitive advantages in their operations. For instance, fleet operators in Africa and South America can optimize logistics and reduce operational costs through the integration of EVs equipped with telematics systems that track vehicle health and performance.
Moreover, the increasing availability of charging infrastructure across Europe, the Middle East, and emerging markets is easing range anxiety, thereby encouraging more businesses to invest in electric passenger vehicles. As international B2B buyers navigate these market dynamics, understanding local regulations and consumer preferences will be critical for successful sourcing and deployment of electric vehicles.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Decisions in the Passenger Electric Car Sector?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the passenger electric car industry, and B2B buyers must prioritize environmental impact in their sourcing strategies. Electric vehicles are touted for their zero-emission capabilities, but the sustainability narrative extends beyond the vehicles themselves to include the entire supply chain. Companies are increasingly held accountable for the sourcing of materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are essential for battery production. Ethical sourcing practices that ensure these materials are obtained without human rights violations and environmental degradation are becoming non-negotiable for many businesses.
Furthermore, the importance of ‘green’ certifications is rising. B2B buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers who possess certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and LEED for sustainable building practices. These certifications not only enhance a company’s brand reputation but also align with the growing consumer demand for transparency and sustainability. By integrating ethical sourcing into their procurement processes, businesses can significantly bolster their sustainability credentials, attract environmentally-conscious clients, and comply with increasingly stringent regulations.
What Is the Historical Context of the Passenger Electric Car Market?
The evolution of the passenger electric car market dates back to the late 19th century, when electric vehicles first emerged as a viable alternative to gasoline-powered cars. However, the advent of the internal combustion engine and subsequent mass production techniques led to the decline of electric vehicles for much of the 20th century. It wasn’t until the late 1990s and early 2000s, spurred by environmental concerns and technological advancements, that electric vehicles began to gain traction again.
In recent years, the market has been further transformed by significant investments from both established automotive manufacturers and new entrants focused solely on electric vehicles. This resurgence has been characterized by a shift in consumer attitudes, as more individuals and businesses recognize the long-term benefits of electric vehicles, not only for sustainability but also for operational efficiency and cost savings. For international B2B buyers, understanding this historical context can provide valuable insights into the market’s current trajectory and future opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of passenger electric car
-
How do I choose the right passenger electric car for my business needs?
Selecting the ideal passenger electric car involves assessing your specific operational requirements, such as passenger capacity, range, and terrain. Consider factors like the vehicle’s top speed and safety features, especially in urban areas. Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including energy costs, maintenance, and potential government incentives for electric vehicles in your region. It’s also beneficial to test drive various models to gauge comfort and usability for your intended application. -
What are the key specifications to look for in a passenger electric car?
When evaluating passenger electric cars, focus on specifications such as battery capacity, range, and charging time. Additionally, consider the vehicle’s seating capacity and comfort features, as well as safety ratings from recognized authorities. Ensure the car complies with local regulations for electric vehicles, including speed limits and safety standards. Lastly, assess the availability of customization options to better align the vehicle with your business needs. -
What are the payment terms typically offered by suppliers of passenger electric cars?
Payment terms can vary significantly between suppliers, but common practices include a down payment followed by installment payments or financing options. Many manufacturers offer lease agreements that allow for lower upfront costs. It’s essential to review the terms carefully, including interest rates, payment schedules, and any additional fees. Engaging in direct negotiations with suppliers can often yield more favorable terms tailored to your business’s financial capabilities. -
How do I verify the credibility of a supplier for passenger electric cars?
To verify a supplier’s credibility, start by researching their business history, customer reviews, and industry reputation. Request references from previous clients and check if they have relevant certifications or comply with international quality standards. Engaging with trade associations or attending industry events can also provide insights into a supplier’s reliability. Additionally, consider conducting a site visit to their production facilities if feasible, as this can give you a clearer picture of their operations. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for passenger electric cars?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for passenger electric cars can vary widely based on the manufacturer and the model. Some suppliers may have a MOQ as low as one vehicle, while others might require bulk orders to qualify for discounts or special pricing. Always inquire about MOQs during negotiations and consider the potential for future orders to establish a long-term relationship with the supplier, which could lead to more flexible terms. -
What customization options are available for passenger electric cars?
Customization options for passenger electric cars can include modifications to seating arrangements, color choices, and additional features such as upgraded audio systems or enhanced safety features. Some manufacturers offer tailored packages that cater to specific business needs, such as fleet branding or specialized cargo solutions. Discuss your requirements with the supplier to explore all available options and ensure the vehicle aligns with your operational goals. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing passenger electric cars?
When importing passenger electric cars, consider the logistics of shipping, customs clearance, and local regulations. Research the import duties and taxes applicable in your country, as these can significantly affect the total cost. Establish a reliable logistics partner experienced in handling automotive imports to ensure smooth transportation and compliance with all regulations. Additionally, plan for potential delays in customs and factor in the time required for vehicle registration and inspection upon arrival. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for passenger electric cars?
To ensure quality assurance for passenger electric cars, request detailed documentation regarding the manufacturing processes and quality control measures employed by the supplier. Many manufacturers provide warranties that cover defects and performance issues, which can serve as a form of assurance. Conduct inspections upon delivery to verify that the vehicles meet your specifications. Additionally, consider implementing a regular maintenance schedule and training programs for staff to uphold vehicle performance and safety standards over time.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 3 Passenger Electric Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. MotoEV – Deluxe Street Legal Golf Cart
Domain: motoelectricvehicles.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: This company, MotoEV – Deluxe Street Legal Golf Cart, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
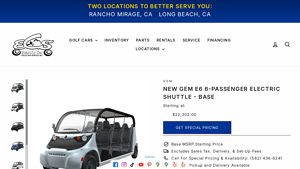
2. GEM – e6 6-Passenger Electric Shuttle
Domain: electriccarsalesandservice.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: {“name”:”New GEM e6 6-Passenger Electric Shuttle – Base”,”starting_price”:”$22,302.00″,”description”:”The GEM e6 is a street-legal, 6-passenger vehicle designed for eco-friendly transportation, featuring a robust 6.5 kW AC motor, long range maintenance-free AGM battery, and a 1 kW standard onboard charger. Optional upgrades include lithium-ion batteries and fast chargers, along with versatile rear…
3. Evgo – Electric Vehicle Charging Solutions
Domain: evgo.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Types of Electric Vehicles: 1. Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs): Powered solely by an electric battery, zero emissions, capable of fast charging and L2 charging. 2. Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): Larger battery and electric motor, has a gas tank and charging port, can charge using L2 chargers. 3. Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs): Low-emission vehicles using an electric motor to assist ga…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for passenger electric car
As the global shift toward sustainable transportation accelerates, the strategic sourcing of passenger electric vehicles (EVs) presents a unique opportunity for B2B buyers across diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of selecting vehicles that not only meet local regulatory requirements but also align with sustainability goals and operational efficiency. Models like the GEM e6 and Club Car CRU showcase the versatility and safety features that are critical for urban mobility solutions.
Investing in electric vehicles can significantly reduce operational costs, with energy expenses as low as $0.03 per mile. Moreover, the integration of advanced battery technologies ensures longer ranges and improved reliability, catering to the needs of businesses in rapidly urbanizing regions.
Looking ahead, international buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that offer customizable solutions, robust support, and innovative financing options. Embracing this transition not only enhances corporate responsibility but also positions businesses at the forefront of the evolving transportation landscape. Now is the time to act—explore your options for sustainable passenger electric vehicles and drive your business forward into the future of mobility.