Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for handicap electric car
The global market for handicap electric cars is evolving rapidly, presenting unique opportunities and challenges for B2B buyers. As the demand for accessible transportation solutions grows, international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face the pressing challenge of sourcing electric vehicles that cater specifically to individuals with mobility impairments. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the handicap electric car market, addressing critical aspects such as types of vehicles available, their applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
By delving into the latest innovations, including models like EcoCentre’s Eco M and Kia’s PV5 WAV, this guide empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their organizational goals and the needs of their communities. With detailed insights on the features that enhance accessibility, such as adjustable ramps and easy entry systems, this resource aims to facilitate a smoother procurement process. It also highlights the importance of understanding regional compliance and market trends, ensuring that buyers can navigate the complexities of the global landscape effectively.
Arming B2B buyers with the knowledge to identify reliable suppliers and assess the true value of handicap electric cars, this guide is an essential tool for those committed to improving mobility solutions for people with disabilities. The journey towards inclusive transportation starts here, making it possible for everyone to experience the freedom and independence that comes with accessible electric vehicles.
Understanding handicap electric car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compact Electric WAV | Compact design, adjustable ramps, suitable for urban environments | Urban mobility solutions, rental services | Pros: Easy to park, affordable. Cons: Limited space for larger wheelchairs. |
| Full-Size Electric WAV | Spacious interior, advanced accessibility features, higher capacity | Transport services, family use, care facilities | Pros: Ample space, versatile. Cons: Higher cost, less maneuverable in tight spaces. |
| Modular Electric Vehicle | Customizable layouts, interchangeable components for various needs | Fleet operators, specialized transport services | Pros: Adaptability for different users. Cons: Complexity in maintenance and repairs. |
| Hybrid Electric WAV | Combines electric and traditional fuel systems, extended range | Long-distance travel services, emergency transport | Pros: Greater range flexibility. Cons: More complex technology, potentially higher maintenance costs. |
| Luxury Electric WAV | Premium features, enhanced comfort, and advanced technology | Executive transport, high-end rental services | Pros: High comfort, brand prestige. Cons: Significant investment, higher operational costs. |
What are the Characteristics of Compact Electric WAVs?
Compact Electric Wheelchair Accessible Vehicles (WAVs) are designed with a smaller footprint, making them ideal for urban environments where parking space is limited. These vehicles often feature adjustable ramps that allow wheelchair users to enter without assistance. B2B buyers, particularly those in urban transport services or rental markets, will find these models appealing due to their affordability and ease of use. However, the limited interior space may restrict their suitability for larger wheelchairs or multiple passengers.
How Do Full-Size Electric WAVs Differ from Other Types?
Full-Size Electric WAVs provide a spacious interior that accommodates larger wheelchairs and multiple passengers. Equipped with advanced accessibility features, these vehicles are perfect for transport services catering to families or healthcare facilities. The ample space allows for comfortable travel, making them a preferred choice for B2B buyers focused on versatility and user comfort. However, their larger size can make them less maneuverable in congested areas, and they typically come at a higher price point.
What Makes Modular Electric Vehicles a Unique Option?
Modular Electric Vehicles stand out due to their customizable layouts and interchangeable components, allowing businesses to tailor them to specific user needs. This flexibility makes them suitable for fleet operators and specialized transport services that require varied accessibility solutions. While their adaptability is a significant advantage, B2B buyers should consider the complexity involved in maintenance and repairs, which may increase operational costs.
Why Choose Hybrid Electric WAVs for Long-Distance Travel?
Hybrid Electric WAVs combine electric power with traditional fuel systems, offering extended range capabilities that are beneficial for long-distance travel. These vehicles are ideal for emergency transport services or providers focused on long-haul travel. B2B buyers will appreciate the flexibility these models offer; however, the complexity of their technology can lead to higher maintenance costs, which should be factored into purchasing decisions.
What Are the Benefits of Luxury Electric WAVs?
Luxury Electric WAVs are designed for high-end markets, featuring premium materials and advanced technology that enhance user comfort. They are particularly suited for executive transport and high-end rental services, appealing to B2B buyers looking to provide a premium experience. While they offer significant advantages in comfort and brand prestige, the substantial investment and higher operational costs may limit their appeal to budget-conscious buyers.
Key Industrial Applications of handicap electric car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of handicap electric car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Transportation | Integration into accessible taxi services | Expands customer base by providing mobility solutions | Compliance with local regulations and safety standards |
| Healthcare | Patient transport for medical facilities | Enhances patient access to healthcare services | Reliability, ease of entry/exit, and maintenance support |
| Tourism and Hospitality | Wheelchair-accessible rental vehicles for tourists | Attracts a wider demographic, improving customer experience | Vehicle customization and local service availability |
| Education | Transport for students with disabilities | Ensures inclusivity and compliance with educational mandates | Adaptability for various mobility needs and safety features |
| Corporate Fleet Management | Accessible vehicles for employee transportation | Promotes diversity and inclusion in the workplace | Cost-effectiveness and fleet maintenance solutions |
How Can Handicap Electric Cars Enhance Public Transportation Services?
Handicap electric cars can be integrated into public transportation systems as accessible taxi services, facilitating mobility for individuals with disabilities. This innovation addresses the challenge of limited transportation options for wheelchair users, enabling them to travel independently. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, understanding local regulations and ensuring vehicles meet safety standards is crucial for successful implementation.
What Role Do Handicap Electric Cars Play in Healthcare Transport?
In the healthcare sector, handicap electric cars serve as vital patient transport vehicles for medical facilities. They provide a reliable means for patients with mobility challenges to access necessary medical care, thereby improving overall health outcomes. Buyers in this sector should prioritize features such as reliability, ease of entry and exit, and ongoing maintenance support to ensure seamless operations.
How Can the Tourism Industry Benefit from Handicap Electric Cars?
The tourism and hospitality sectors can leverage handicap electric cars as wheelchair-accessible rental vehicles, catering to a broader demographic of travelers. This approach not only enhances the customer experience but also fosters a more inclusive environment. For businesses in this space, vehicle customization and the availability of local service options are essential considerations to meet diverse customer needs effectively.
Why Are Handicap Electric Cars Important for Educational Institutions?
Educational institutions can utilize handicap electric cars to transport students with disabilities, ensuring compliance with inclusivity mandates. This application promotes equal access to education and enhances the overall learning experience for all students. Buyers should focus on the adaptability of vehicles to accommodate various mobility needs, along with essential safety features to protect young passengers.
How Do Handicap Electric Cars Improve Corporate Fleet Management?
Incorporating handicap electric cars into corporate fleet management promotes diversity and inclusion within the workplace. These vehicles can be utilized for employee transportation, ensuring that all staff members, regardless of mobility challenges, have equal access to work-related travel. Businesses should consider cost-effectiveness and available fleet maintenance solutions when sourcing these vehicles to optimize operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘handicap electric car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Accessibility Regulations for Electric Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers, such as fleet managers or vehicle procurement officers, often face the challenge of ensuring that handicap electric cars comply with various accessibility regulations and standards. Different countries and regions have unique legal requirements concerning vehicle modifications, safety features, and access technologies. This complexity can lead to confusion, potential non-compliance, and delays in procurement processes, ultimately affecting the ability to serve clients effectively.
The Solution: To navigate these regulatory landscapes, buyers should engage with local disability advocacy organizations and consult with legal experts who specialize in automotive compliance. A proactive approach includes conducting thorough research on the specific accessibility regulations applicable in target markets like Nigeria, Brazil, or European nations. Buyers should prioritize sourcing vehicles from manufacturers that provide detailed compliance documentation and can demonstrate a history of meeting or exceeding these standards. Additionally, establishing partnerships with local dealerships that understand regional regulations can help streamline the procurement process and ensure that all vehicles are compliant from the outset.
Scenario 2: Ensuring User Comfort and Safety Features in Electric Cars
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are concerned about the comfort and safety features of handicap electric cars for their end-users. Electric vehicles (EVs) can sometimes lack the robust safety features and user-friendly designs that wheelchair users require. For instance, inadequate securing mechanisms for wheelchairs or poorly designed ramps can pose significant risks during travel, resulting in user dissatisfaction and potential liability issues for businesses.
The Solution: Buyers should conduct hands-on evaluations of potential vehicles, focusing on safety features such as wheelchair securing systems, ramp stability, and overall vehicle ergonomics. Collaborating with end-users during the selection process can provide valuable insights into practical needs and preferences. It is advisable to source vehicles from manufacturers known for their commitment to user-centered design, ensuring that every aspect of the vehicle—from entry ramps to interior space—caters to the needs of individuals with disabilities. Furthermore, consider arranging for test drives and user trials to gather feedback before finalizing any purchases, which can help identify any necessary adjustments or additional features that may enhance user safety and comfort.
Scenario 3: Addressing Charging Infrastructure Challenges
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter difficulties related to the charging infrastructure available for electric vehicles, particularly in regions with limited electric vehicle (EV) support. In areas such as parts of Africa and South America, inadequate charging stations can lead to range anxiety and significantly impact the usability of handicap electric cars for users who rely on them for daily mobility.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should engage in strategic partnerships with local governments, utility companies, and charging network providers to advocate for the development of charging infrastructure that supports handicap electric cars. This collaboration can involve identifying key locations for charging stations that cater to the needs of users with disabilities, ensuring they are accessible and conveniently placed. Additionally, buyers should consider investing in vehicles that come equipped with fast-charging capabilities, enabling quicker turnaround times at charging stations. Educating clients about charging solutions, such as home charging setups or mobile charging units, can also enhance the overall accessibility and practicality of these vehicles, ultimately promoting wider adoption.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for handicap electric car
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Handicap Electric Cars?
When selecting materials for handicap electric cars, several factors must be considered, including performance properties, cost, manufacturing complexity, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the production of these vehicles.
Aluminum: A Lightweight Solution for Enhanced Mobility
Key Properties: Aluminum is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 600°F and can withstand moderate pressure.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum significantly improves vehicle efficiency and maneuverability, making it ideal for electric vehicles. However, it can be more expensive than steel and may require specialized welding techniques, which can complicate manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance is particularly advantageous in regions with high humidity or saline environments, making it suitable for markets in Africa and coastal areas in South America.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B209 for aluminum sheet and plate is crucial. Buyers in regions like Nigeria and Brazil should ensure that local suppliers can meet these specifications.
High-Strength Steel: Durability Meets Cost-Effectiveness
Key Properties: High-strength steel offers excellent tensile strength and impact resistance, with a temperature rating similar to aluminum but with greater resistance to deformation under pressure.
Pros & Cons: This material is generally less expensive than aluminum and provides robust safety features, making it a popular choice for structural components. However, its heavier weight can reduce overall vehicle efficiency and range.
Impact on Application: High-strength steel is particularly effective in areas requiring enhanced safety features, such as crash protection for wheelchair users.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards like ASTM A992 for structural steel and ensure that their suppliers can provide materials that meet local regulations in their respective regions.
Composite Materials: Innovation in Accessibility and Design
Key Properties: Composites, such as fiberglass or carbon fiber, are lightweight and can be engineered for specific strength and flexibility requirements. They often have excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand a wide range of temperatures.
Pros & Cons: Composites allow for innovative design possibilities and can significantly reduce vehicle weight, enhancing efficiency. However, they can be more expensive and complex to manufacture, requiring specialized skills and equipment.
Impact on Application: The use of composites can improve the aesthetics and comfort of handicap electric cars, making them more appealing to consumers and caregivers alike.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM D3039 for composite materials is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of skilled labor for composite manufacturing in their regions.
Thermoplastics: Versatility for Interior and Exterior Components
Key Properties: Thermoplastics are highly versatile, offering good impact resistance and the ability to withstand various temperatures. They can be molded into complex shapes, making them ideal for various applications.
Pros & Cons: These materials are lightweight and cost-effective, allowing for mass production. However, they may not offer the same level of durability as metals and can be susceptible to UV degradation over time.
Impact on Application: Thermoplastics are often used in interior components, such as seating and dashboard elements, where comfort and aesthetics are prioritized.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties of plastics. Additionally, understanding local recycling regulations for thermoplastics can be beneficial.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Handicap Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for handicap electric car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Vehicle chassis and body | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| High-Strength Steel | Structural components | Durable, cost-effective | Heavier, may reduce efficiency | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Body panels, seating | Innovative design, lightweight | Expensive, complex to manufacture | High |
| Thermoplastics | Interior components | Versatile, cost-effective | Less durable, UV degradation potential | Low |
In conclusion, selecting the right materials for handicap electric cars requires a balance of performance, cost, and compliance with international standards. By understanding the properties and implications of each material, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market demands.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for handicap electric car
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Handicap Electric Cars?
The manufacturing process of handicap electric cars, specifically designed for users with mobility challenges, involves multiple critical stages. Each stage is meticulously planned to ensure that the final product meets the highest standards of accessibility, safety, and performance.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and Why?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. Key materials typically include high-strength steel, aluminum, and advanced composites, which are chosen for their lightweight yet durable properties. These materials are essential to ensure that the vehicle can withstand the additional stresses associated with wheelchair access and to maintain efficiency in electric vehicle performance.
During this stage, materials undergo rigorous testing for quality and compliance with international standards. Suppliers must provide certifications that validate the materials’ properties, ensuring they meet or exceed regulatory requirements. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with robust material sourcing practices and certifications.
How Is the Forming Process Conducted for Accessibility Features?
The forming process involves shaping the prepared materials into the vehicle’s structural components. Advanced techniques such as hydroforming and stamping are commonly used to create complex shapes required for wheelchair ramps and secure seating areas.
For handicap electric cars, forming processes are designed to incorporate features like side-entry ramps and reinforced frames that facilitate easy access. Manufacturers often use CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to simulate and optimize these features before moving to production, ensuring that accessibility is seamlessly integrated into the vehicle’s design.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail for Electric Vehicles?
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form the complete vehicle. This includes the integration of electric drivetrains, batteries, and accessibility features like ramps and secure seating for wheelchair users.
Manufacturers typically employ lean manufacturing principles to streamline this process, minimizing waste and ensuring that each vehicle is assembled efficiently. Key assembly techniques include robotic automation for precision tasks and manual assembly for complex integrations, ensuring that every detail is attended to.
How Are Finishing Touches Applied in the Manufacturing Process?
Finishing processes involve painting, interior installation, and final inspections. The finishing stage is crucial as it affects both the aesthetic appeal and the functional integrity of the vehicle.
High-quality paints and coatings are applied to protect against environmental factors while enhancing the vehicle’s appearance. During this stage, accessibility features are tested to ensure they function correctly and meet safety standards.
What International Quality Standards Are Relevant for Handicap Electric Cars?
Quality assurance is critical in the manufacturing of handicap electric cars, ensuring that products are safe, reliable, and meet customer expectations. Various international standards guide this process, including:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that organizations consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant for components used in the electric vehicle industry, these standards ensure that materials and processes meet industry specifications.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
To maintain high standards, manufacturers implement several quality control checkpoints throughout the production process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves the inspection of materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the assembly process helps identify and rectify issues in real time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the completed vehicle ensures that it meets all quality and safety standards before delivery.
Which Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Testing methods employed in the quality assurance of handicap electric cars include:
- Functional Testing: Verifies that all systems (e.g., electrical, mechanical) operate as intended.
- Safety Testing: Ensures compliance with safety standards, particularly for accessibility features.
- Durability Testing: Assesses the vehicle’s performance under various conditions to guarantee longevity and reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers can implement several strategies to ensure that their suppliers adhere to rigorous quality control practices:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing facilities can provide insights into their processes and adherence to quality standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand the testing and inspection protocols followed by suppliers.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality practices and product compliance.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several nuances in quality control must be considered:
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should ensure that suppliers understand and comply with local regulations, which can vary significantly across regions.
- Cultural and Market Differences: Understanding local market needs and expectations is vital for ensuring that products are suitable for the target demographic.
- Logistical Challenges: Consideration of shipping, customs, and delivery times is essential, as these can impact the overall quality of service and product availability.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance of handicap electric cars are complex and multifaceted. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers who prioritize quality and accessibility.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘handicap electric car’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring handicap electric cars, ensuring that the purchasing process is streamlined and effective. As the demand for accessible vehicles continues to grow, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is crucial to understand the specific requirements and considerations involved in sourcing these specialized vehicles.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical specifications is the first critical step in the sourcing process. Identify the essential features that the handicap electric car must have, such as ramp accessibility, seating capacity, and battery range.
– Consider the specific needs of your target users, including wheelchair dimensions and mobility aids that may be used.
– Ensure that the vehicle adheres to local regulations regarding accessibility and safety standards.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Performing thorough market research helps you understand the available options and competitive landscape. Investigate existing models and their specifications to identify which vehicles meet your criteria.
– Explore various manufacturers and their reputations within the accessibility vehicle market.
– Look for industry reports and reviews that highlight emerging trends and innovations, such as electric powertrains and sustainable materials.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to conduct a comprehensive evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from clients in similar industries or regions.
– Assess their production capabilities and experience in manufacturing handicap electric vehicles.
– Verify the supplier’s commitment to quality assurance and after-sales support, which are critical for long-term partnerships.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the vehicles and the suppliers comply with relevant certifications and regulations. This step is vital for guaranteeing safety, quality, and performance.
– Check for certifications related to electric vehicles, such as ISO standards and local automotive regulations.
– Confirm that the vehicles meet accessibility standards established by organizations like the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) or equivalent bodies in your region.
Step 5: Assess Financing and Budget Options
Review your financing options to ensure that the procurement process aligns with your budget. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs, is crucial.
– Investigate potential partnerships with financial institutions that specialize in funding accessible vehicles.
– Explore government grants or incentives for purchasing electric and accessible vehicles, which can significantly reduce upfront costs.
Step 6: Plan for Maintenance and Support
A robust maintenance plan is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of handicap electric cars. Evaluate the support services offered by suppliers.
– Determine if the supplier provides training for staff on vehicle operation and maintenance.
– Assess the availability of spare parts and service centers in your region to minimize downtime.
Step 7: Test Drive and User Feedback
Before finalizing your purchase, arrange for test drives and gather feedback from potential users. This step allows you to evaluate the vehicle’s performance in real-world conditions.
– Engage with wheelchair users and caregivers to assess ease of access and comfort.
– Use their insights to make informed decisions about which models best meet the needs of your clientele.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing handicap electric cars effectively, ensuring they provide mobility solutions that enhance independence for users with disabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for handicap electric car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Handicap Electric Cars?
When evaluating the cost structure for sourcing handicap electric cars, several key components must be considered. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts the overall cost. For electric vehicles, high-quality battery systems and lightweight materials are essential for performance and accessibility. Sourcing sustainable and durable materials may also appeal to environmentally conscious buyers, though they can elevate costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries with a lower cost of living, labor expenses may be reduced, but this can sometimes come with trade-offs in terms of skill levels and craftsmanship. Understanding local labor markets is crucial for accurate cost estimation.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all costs that are not directly tied to production but are necessary for the manufacturing process, such as utilities and facility maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead costs, which is vital for competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized tools for producing handicap-accessible features can be substantial. The cost can be amortized over larger production runs, making it essential to consider the minimum order quantities (MOQ) when negotiating with suppliers.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that vehicles meet safety and accessibility standards is non-negotiable. Implementing rigorous QC processes can raise costs but is essential for maintaining brand integrity and customer trust.
-
Logistics: Transportation of materials and finished vehicles adds to the overall cost. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and customs duties play significant roles, particularly for international buyers.
-
Margin: Finally, manufacturers and suppliers will factor in their desired profit margins. This can vary based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Handicap Electric Car Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of handicap electric cars in the B2B market:
-
Volume/MOQ: Discounts are often available for bulk purchases. Establishing a long-term partnership with suppliers can also lead to better pricing structures.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features tailored to specific user needs can significantly affect pricing. Buyers should clarify their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected costs later.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality and certified materials tend to increase costs but can enhance the vehicle’s durability and resale value. Buyers should weigh the long-term benefits against initial costs.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability and reputation can influence pricing. A well-established supplier may charge more but provide better service and product quality, reducing risks for buyers.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for international transactions. The chosen Incoterms can affect the total landed cost and should be clearly defined in contracts.
What Are Some Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Handicap Electric Cars?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can optimize sourcing decisions:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about price, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Leverage volume purchases to negotiate better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and potential resale value. This holistic view can guide smarter purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations that can affect overall costs. Researching and understanding the local market conditions is critical.
-
Local Partnerships: Establishing relationships with local distributors or dealers can facilitate smoother logistics and support, ultimately reducing costs and risks.
-
Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, including reviews and references, to ensure they meet your quality and service expectations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for handicap electric cars can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is advisable to obtain multiple quotes and conduct detailed analyses before finalizing any contracts to ensure the best value for your investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing handicap electric car With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Handicap Electric Cars
In the rapidly evolving landscape of mobility solutions for individuals with disabilities, various alternatives to handicap electric cars have emerged. These alternatives not only provide diverse functionalities but also cater to different needs, preferences, and budgets. This analysis compares handicap electric cars against two viable alternatives: traditional wheelchair-accessible vehicles (WAVs) and rideshare services designed specifically for individuals with mobility challenges.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Handicap Electric Car | Traditional Wheelchair-Accessible Vehicle | Rideshare Services for Disabled Users |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Local driving, up to 25 mph | Variable speeds, typically highway-capable | Varies by provider, generally flexible |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, lower operating costs | Higher upfront costs, ongoing maintenance | Generally pay-per-ride, can accumulate costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific infrastructure, dealer partnerships | Widely available, established market | Simple app-based access, no vehicle ownership needed |
| Maintenance | Lower due to electric components | Higher due to mechanical parts | Minimal, only dependent on service quality |
| Best Use Case | Daily personal use, independence | Long-distance travel, versatile needs | Occasional transport, flexibility in destinations |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Traditional Wheelchair-Accessible Vehicles (WAVs)
Traditional WAVs have been a staple in accessible transportation for years. These vehicles are typically modified versions of standard cars or vans, equipped with ramps or lifts to accommodate wheelchair users. The primary advantage of WAVs is their versatility; they can handle long-distance travel and various terrains, making them suitable for a range of uses, from personal to commercial.
However, WAVs often come with higher upfront costs and ongoing maintenance expenses due to their mechanical components. They also require specific modifications, which can lead to longer lead times for delivery. For businesses looking to invest in a fleet, WAVs may represent a significant capital investment, though they are often eligible for grants or subsidies aimed at improving accessibility.
Rideshare Services for Disabled Users
Rideshare services tailored for individuals with disabilities provide a flexible and convenient alternative to ownership of a handicap electric car or WAV. These services, available via mobile apps, allow users to request rides from drivers who are trained to assist passengers with mobility challenges.
The primary benefit of rideshare services is their convenience and lack of commitment to vehicle ownership. Users can travel without worrying about the costs associated with maintenance or insurance. However, the cost can accumulate with frequent use, and availability may vary based on location and demand. Furthermore, riders may have less control over the type of vehicle they are offered, which can affect comfort and accessibility.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the most appropriate mobility solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and the target demographic. Handicap electric cars offer a unique combination of independence and sustainability, while traditional WAVs provide versatility for a variety of travel scenarios. On the other hand, rideshare services present an innovative, cost-effective option for those who prioritize flexibility and convenience. By assessing these alternatives against organizational goals and user requirements, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance accessibility for individuals with disabilities.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for handicap electric car
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Handicap Electric Cars?
When considering the procurement of handicap electric vehicles (HEVs), understanding their technical properties is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are some essential specifications that play a pivotal role in the performance and usability of these vehicles:
1. Ramp Weight Capacity
The ramp weight capacity is a critical specification that determines the maximum weight that the ramp can safely support for wheelchair access. Typically, this capacity ranges from 300 kg to 400 kg. It is vital for buyers to assess this property to ensure it accommodates the diverse needs of users, including those who may have heavier wheelchairs or additional equipment.
2. Battery Range
Battery range refers to the distance an electric vehicle can travel on a single charge. For handicap electric cars, a range of 120 to 200 miles is often considered optimal. A longer battery range minimizes the need for frequent recharging, enhancing the vehicle’s usability for users who may not have immediate access to charging stations.
3. Turning Radius
The turning radius is the minimum circular turn that a vehicle can make. A smaller turning radius (ideally less than 35 feet) is advantageous for urban environments, allowing easier navigation through tight spaces and parking situations. This specification is particularly important for users who may have limited mobility and require more maneuverability.
4. Safety Features
Safety features such as anti-lock braking systems (ABS), traction control, and advanced airbag systems are critical for ensuring user protection. The inclusion of these features not only enhances the safety of passengers but also serves as a selling point for B2B buyers who prioritize compliance with safety regulations and standards.
5. Materials Used in Construction
The choice of materials, such as high-strength steel or lightweight aluminum, affects the vehicle’s durability and weight. Lightweight materials can improve battery efficiency, while high-strength materials enhance safety. Understanding material specifications can help buyers assess the vehicle’s long-term viability and maintenance needs.
6. Charging Time
Charging time is the duration required to recharge the vehicle’s battery fully. A fast-charging capability (ideally within 4-6 hours) is beneficial for users who may need to use the vehicle frequently. For B2B buyers, this property can influence operational efficiency, particularly for fleet operators.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Handicap Electric Vehicle Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms that buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of handicap electric cars, understanding OEM partnerships can help buyers identify reputable suppliers and ensure product quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, particularly for fleet purchases or larger orders.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by buyers to request pricing and other details from suppliers for specific products or services. Issuing an RFQ can streamline the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare options effectively.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps buyers navigate logistics, shipping responsibilities, and cost allocations.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period from placing an order to receiving the product. For handicap electric vehicles, a shorter lead time can be crucial for meeting urgent mobility needs, making it an important consideration for B2B buyers.
6. Warranty Period
The warranty period refers to the duration a manufacturer guarantees the vehicle against defects. A longer warranty can provide peace of mind for buyers, indicating the manufacturer’s confidence in their product’s durability and performance.
Understanding these technical specifications and trade terms will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions when procuring handicap electric vehicles, ensuring they meet the needs of their clients while navigating the complexities of the market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the handicap electric car Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Handicap Electric Car Sector?
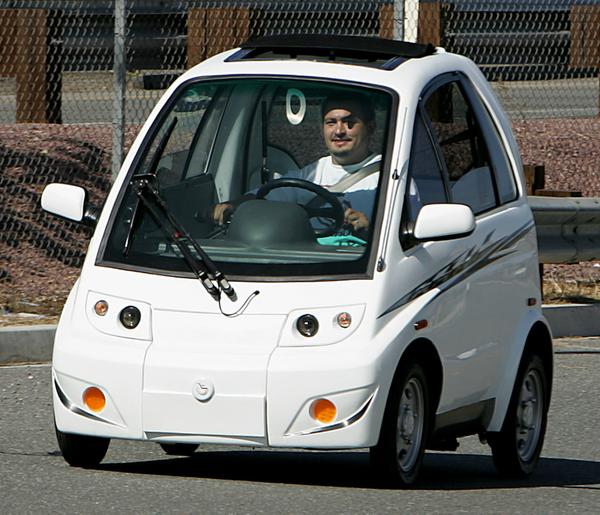
The handicap electric car sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by a combination of technological advancements, changing demographics, and increasing awareness of accessibility needs. Global drivers include an aging population, greater emphasis on sustainable transportation, and legislative pressures for improved accessibility. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for electric vehicles (EVs) is rising, particularly among B2B buyers looking to expand their fleets with accessible options. Companies like EcoCentre and Kia are leading the charge with innovative models designed for wheelchair users, offering features that enhance usability and independence.
Emerging trends in B2B sourcing include a shift towards integrated mobility solutions that combine vehicle accessibility with advanced technology, such as smart driving systems and telematics. Buyers are increasingly interested in partnerships with manufacturers that prioritize user-centric designs and sustainable practices. The focus on electric mobility is also reshaping procurement strategies, as businesses seek to align with global sustainability goals while meeting the needs of their customers. Collaborative platforms and supply chain transparency are becoming essential as companies navigate the complexities of sourcing in this evolving market.
How Important Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Handicap Electric Car Market?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming cornerstones in the handicap electric car sector. Environmental impact considerations are at the forefront, with manufacturers striving to reduce their carbon footprints through energy-efficient production methods and the use of recyclable materials. For B2B buyers, aligning with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Ethical supply chains are equally critical. B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers who adhere to fair labor practices and prioritize community engagement. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade can provide assurance of a supplier’s commitment to ethical practices. Additionally, utilizing green materials—like biodegradable composites and sustainably sourced metals—can significantly reduce the environmental impact of electric vehicles. As consumers and businesses alike become more environmentally conscious, sourcing from suppliers who embody these values can create a competitive advantage in the market.
What is the Brief Evolution and History of the Handicap Electric Car Sector?
The evolution of the handicap electric car sector has been marked by significant milestones, reflecting broader trends in automotive design and accessibility. The concept of accessible vehicles gained traction in the late 20th century, initially focusing on modifications of traditional internal combustion engine cars. However, the introduction of electric vehicles in the early 21st century opened new avenues for innovation, allowing manufacturers to design vehicles from the ground up with accessibility in mind.
As awareness of disability rights grew, the demand for specialized vehicles surged, prompting manufacturers to invest in research and development. Companies like EcoCentre and Kia have emerged as key players, integrating advanced technology and thoughtful design into their offerings. The transition to electric mobility is not just about sustainability; it also represents a significant leap forward in providing independence and freedom to individuals with mobility challenges. This evolution continues to shape the landscape of the handicap electric car market, offering exciting opportunities for B2B buyers to engage with a sector that is both socially responsible and innovative.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of handicap electric car
-
How do I ensure the quality of handicap electric cars before purchasing?
To guarantee quality, B2B buyers should conduct thorough supplier vetting. This includes checking certifications, quality control processes, and customer reviews. Requesting samples or visiting the manufacturing facility can provide firsthand insight into production standards. Additionally, establish clear quality assurance (QA) protocols in your purchasing agreement, specifying the required standards and testing methods for the vehicles. -
What is the best electric vehicle model for wheelchair accessibility?
Models like the Eco M and Kia PV5 WAV are designed specifically for wheelchair accessibility, offering features such as adjustable ramps and curb-side entry systems. When selecting a model, consider factors such as ease of use, safety features, and the vehicle’s ability to accommodate various wheelchair types. Engaging with manufacturers for detailed specifications can help identify the best fit for your needs. -
What customization options are available for handicap electric cars?
Customization options vary by manufacturer but may include modifications for seating arrangements, ramp configurations, and specialized controls for wheelchair users. Discuss your specific requirements with the supplier to explore available upgrades, such as enhanced safety features or additional storage solutions. Ensure that any customizations comply with local regulations and safety standards. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for handicap electric cars?
MOQs can vary significantly between manufacturers, often depending on their production capabilities and existing inventory. Generally, larger orders may lead to more favorable pricing and terms. Contact potential suppliers to inquire about their MOQs and explore possibilities for smaller initial orders or pilot programs to assess the market before committing to larger purchases. -
How can I navigate international trade regulations when importing handicap electric cars?
Understanding international trade regulations is crucial for a smooth import process. Research the import duties, taxes, and any compliance standards specific to your country. Collaborating with a logistics provider familiar with automotive imports can streamline the process. Additionally, ensure that the vehicles meet both local and international safety standards to avoid potential legal issues. -
What payment terms are common when sourcing handicap electric cars?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation. Common terms include upfront deposits, installment payments, or letters of credit. It’s essential to clarify payment expectations in advance and consider utilizing escrow services to protect both parties during the transaction. Establishing a good relationship with the supplier can also facilitate more favorable terms. -
How do I evaluate the reliability of suppliers for handicap electric cars?
To assess supplier reliability, examine their track record, including years in business, client testimonials, and industry certifications. Request references from previous clients and investigate their production capabilities and after-sales support. Additionally, attending trade shows or industry expos can provide opportunities to meet suppliers in person and evaluate their offerings firsthand. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when sourcing handicap electric cars?
Logistics is a critical aspect of sourcing electric cars. Consider shipping methods, transit times, and costs associated with importing vehicles. Engage a logistics partner with experience in automotive transport to ensure compliance with regulations and minimize delays. Additionally, factor in the need for specialized transport arrangements for handicap vehicles to prevent damage during transit.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Handicap Electric Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
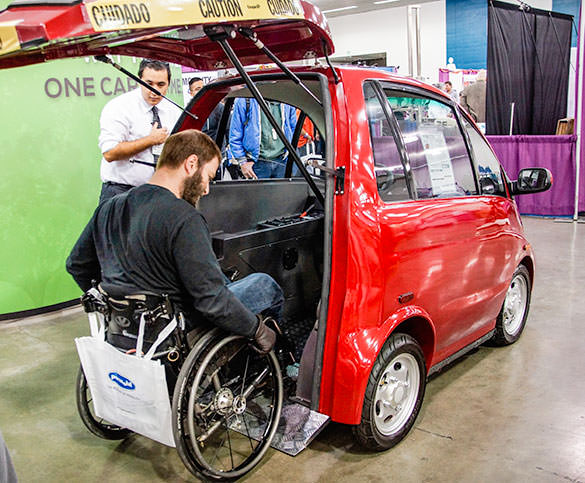
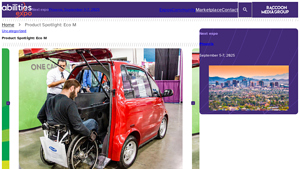
1. EcoCentre – Eco M
Domain: abilities.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Eco M
Manufacturer: EcoCentre
Type: Accessible Electric Vehicle
Launch Date: Expected in the second quarter of 2025
Key Features:
– Compact design with a small footprint
– Adjustable rear ramp for easy wheelchair access
– No transfers required; users can roll in, lock down, and drive off
– Maximum speed of 25 mph, suitable for local streets
– Aimed at providing independence for whee…
2. eVITA – Electric Wheelchair Accessible Vehicle
Domain: electricmotorengineering.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: eVITA is an electric state-of-the-art vehicle concept designed for wheelchair accessibility (eWAV). Developed by Callum in collaboration with Motability Operations, it incorporates inclusive design principles throughout its development. The vehicle features a ground clearance of 160 mm, similar to that of a sedan, allowing for easier access and increased interior height for wheelchair users. Motab…
3. Moto Electric Vehicles – ADA Electric Shuttles
Domain: motoelectricvehicles.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: ADA electric shuttles and handicap golf carts equipped with ramps and lifts, accommodating 4 to 27 passengers. Ideal for event transportation, church or campus buses, parking lot shuttles, and other handicap-accessible needs. Features include customizable styles, colors, trim, and seating designs. Accessories available such as ADA-compliant ramps, backup cameras, and beacon lights. Models include:…
4. Kempf – Hand Controls for Paraplegic Drivers
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Hand controls for paraplegic drivers, specifically the Kempf system and Sure Grip’s Feather Lite model. The Kempf system includes a second ring in the middle of the steering wheel that acts as an accelerator pedal and is compatible with regenerative one-pedal driving. The Sure Grip’s Feather Lite model features a push rock style. The discussion also mentions the Tesla Model X, Tesla Model 3, and H…
5. BraunAbility – Electric & Hybrid Vehicle Adaptations
Domain: braunability.eu
Introduction: BraunAbility offers adaptations for electric and hybrid vehicles, focusing on two main categories: hybrids/electric cars built on fossil fuel platforms (e.g., Peugeot e-208, Volkswagen Golf GTE, Ford Kuga) and fully electric cars (e.g., Tesla, Polestar). Pros for hybrids include straightforward adaptation due to shared design elements with standard cars, while cons involve potential complications …
6. Energy Saving Trust – Electric Vehicles for Disabled Drivers
Domain: energysavingtrust.org.uk
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Electric vehicles (EVs) for disabled drivers offer several benefits, including lower running costs (approximately £760 cheaper per year compared to petrol or diesel), reduced maintenance costs (around £200 cheaper annually), and a smoother driving experience due to automatic transmissions. EVs can be adapted for specific needs, including wheelchair accessibility. Financial support options include …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for handicap electric car
In navigating the evolving landscape of handicap electric vehicles, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal factor for international B2B buyers. The recent innovations, such as the Eco M and Kia’s PV5 WAV, highlight the industry’s commitment to enhancing mobility for individuals with disabilities. These vehicles not only facilitate independence but also address the pressing need for sustainable and accessible transportation solutions.
The growing demand for wheelchair-accessible electric vehicles (eWAVs) presents a unique opportunity for businesses to invest in products that meet both social responsibility and market needs. By forming strategic partnerships with manufacturers and leveraging emerging technologies, buyers can ensure they are at the forefront of this vital sector.
As we look to the future, it is essential for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to engage actively with manufacturers and industry leaders. This collaboration can drive innovation and create a more inclusive mobility ecosystem. We encourage you to explore these opportunities, align your sourcing strategies with market trends, and contribute to a future where accessible electric vehicles are a standard rather than a niche.