Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 100 km electric car
In an era where sustainability and cost-efficiency are paramount, international B2B buyers face the critical challenge of sourcing 100 km electric cars that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) not only promises substantial savings on fuel and maintenance but also meets the growing demand for environmentally friendly transportation solutions across diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted landscape of 100 km electric cars, offering insights into various vehicle types, their applications in different sectors, and effective strategies for supplier vetting.
By exploring the nuances of charging options, total cost of ownership, and the benefits of home versus public charging, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their unique requirements. Furthermore, it highlights the importance of understanding regional pricing variations and the influence of local infrastructure on operational efficiency. Whether you are looking to invest in a fleet of electric vehicles or seeking individual units for specific applications, this guide serves as an essential resource to navigate the complexities of the global market, ultimately enhancing your purchasing strategy and driving sustainable growth in your business.
Understanding 100 km electric car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compact Electric Vehicles | Smaller size, urban-friendly, typically lower range | Urban deliveries, fleet vehicles | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to park. Cons: Limited range may necessitate frequent charging. |
| Long-Range Electric Cars | Extended battery life, capable of 400 km or more per charge | Long-distance travel, executive transport | Pros: Reduced charging stops, suitable for long trips. Cons: Higher upfront costs. |
| Commercial Electric Vans | Larger cargo space, designed for utility and transport | Logistics, delivery services | Pros: High payload capacity, eco-friendly. Cons: Bulkier, may require dedicated parking. |
| Electric SUVs | Versatile, family-friendly, higher seating capacity | Employee transport, corporate use | Pros: Spacious, suitable for diverse needs. Cons: Generally more expensive than sedans. |
| Performance Electric Cars | High acceleration, advanced technology, sporty design | Corporate events, high-end rentals | Pros: Impressive performance, brand image. Cons: Higher maintenance costs, less practicality. |
What Are the Characteristics of Compact Electric Vehicles?
Compact electric vehicles (CEVs) are designed for urban environments, offering maneuverability and efficiency. Typically featuring a range of 100-200 km, they are ideal for short-distance travel, making them suitable for delivery services or small business fleets. When considering CEVs, B2B buyers should evaluate total cost of ownership, including charging infrastructure and potential savings on fuel compared to traditional vehicles. Their compact nature allows for easy parking in congested areas, enhancing operational efficiency.
How Do Long-Range Electric Cars Meet Business Needs?
Long-range electric cars (LRECs) are engineered for extended travel, boasting ranges often exceeding 400 km per charge. This makes them suitable for businesses requiring frequent long-distance travel, such as sales teams or executive transportation. When purchasing LRECs, companies should consider battery technology, charging options, and potential incentives for electric vehicle adoption. The higher upfront investment can be offset by lower operational costs and reduced downtime associated with charging.
What Advantages Do Commercial Electric Vans Offer?
Commercial electric vans are tailored for businesses needing to transport goods or services. With substantial cargo capacity and robust design, they are perfect for logistics and delivery operations. B2B buyers should focus on payload capacity, range, and charging infrastructure when evaluating these vehicles. While they may be bulkier and require dedicated parking, the environmental benefits and potential savings on fuel make them a strategic investment for companies looking to enhance their sustainability profile.
Why Are Electric SUVs Becoming Popular Among Businesses?
Electric SUVs combine the versatility of larger vehicles with the benefits of electric power. They are ideal for employee transport or corporate events, offering ample space and comfort. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of spacious interiors against the higher costs compared to sedans. The ability to accommodate families or groups makes them attractive for businesses focused on employee satisfaction and retention, while their eco-friendly nature aligns with corporate sustainability goals.
What Should Businesses Consider When Looking at Performance Electric Cars?
Performance electric cars deliver high acceleration and advanced technology, making them appealing for corporate events or high-end rentals. While they enhance a company’s image, B2B buyers must consider the higher maintenance costs and practicality of such vehicles. These cars often come with advanced features that can impress clients, but businesses should ensure that the investment aligns with their operational needs and budget constraints. Balancing performance with cost-effectiveness is crucial for maximizing ROI.
Key Industrial Applications of 100 km electric car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 100 km electric car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics & Delivery | Last-mile delivery services | Reduced operational costs and lower emissions | Battery capacity, charging infrastructure, fleet management systems |
| Public Transportation | Urban shuttle services | Enhanced public transport efficiency and sustainability | Vehicle range, passenger capacity, maintenance support |
| Tourism & Hospitality | Eco-friendly transportation for tourists | Improved brand image and customer satisfaction | Vehicle aesthetics, charging options, partnerships with local businesses |
| Agriculture | Farm-to-market transport | Cost-effective logistics and reduced carbon footprint | Durability, off-road capability, maintenance accessibility |
| Corporate Fleets | Employee transportation | Lower fuel costs and improved employee satisfaction | Fleet management solutions, vehicle customization, service agreements |
How Are 100 km Electric Cars Used in Logistics and Delivery?
In the logistics and delivery sector, 100 km electric cars serve as efficient last-mile delivery vehicles. They help businesses reduce operational costs by minimizing fuel expenses and lowering maintenance needs. As urban areas increasingly prioritize sustainability, electric vehicles align with regulatory requirements and customer expectations for eco-friendly practices. Buyers need to consider battery capacity to ensure vehicles can complete daily routes, as well as charging infrastructure to facilitate seamless operations.
What Role Do 100 km Electric Cars Play in Public Transportation?
Public transportation systems are integrating 100 km electric cars for urban shuttle services, enhancing efficiency while promoting sustainability. These vehicles can replace traditional diesel shuttles, resulting in reduced emissions and operating costs. For international buyers, especially in developing regions, the focus should be on vehicle range, passenger capacity, and the availability of maintenance support, as these factors will influence service reliability and overall operational success.
How Can 100 km Electric Cars Enhance Tourism and Hospitality?
In the tourism and hospitality industry, 100 km electric cars are used to offer eco-friendly transportation options for tourists. This not only improves the brand image of hotels and travel companies but also enhances customer satisfaction through sustainable practices. Buyers in this sector should focus on vehicle aesthetics and charging options to ensure that the fleet aligns with the luxury and convenience expected by travelers, as well as exploring partnerships with local businesses for charging solutions.
Why Are 100 km Electric Cars Valuable for Agriculture?
Agricultural businesses utilize 100 km electric cars for farm-to-market transport, providing a cost-effective logistics solution that reduces carbon footprints. These vehicles can navigate rural environments while ensuring timely delivery of goods. Buyers should consider the durability of electric cars and their off-road capabilities, as well as maintenance accessibility, to ensure that they can withstand the demands of agricultural operations and contribute to sustainable practices.
How Do Corporate Fleets Benefit from 100 km Electric Cars?
Corporate fleets are increasingly adopting 100 km electric cars for employee transportation. This shift leads to significant savings on fuel costs and enhances employee satisfaction through reduced commuting expenses. Companies looking to implement this solution must consider fleet management solutions, potential vehicle customization for branding, and service agreements to ensure ongoing support. By investing in electric cars, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to sustainability while optimizing operational efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘100 km electric car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Cost Dynamics of Electric Vehicle Charging
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially fleet managers or corporate procurement officers, face the challenge of understanding the true cost of operating a 100 km electric car. With various charging options—home, public slow chargers, and highway fast chargers—prices can vary significantly. This unpredictability complicates budgeting for electric vehicle (EV) fleets, especially in regions where energy prices fluctuate or where charging infrastructure is less developed.
The Solution: To effectively navigate the cost landscape, buyers should conduct a comprehensive analysis of their charging options. Start by assessing the availability of home charging solutions, as off-peak home charging can offer substantial savings—often around €3 to €3.50 for 100 km. Invest in smart home charging stations that allow for scheduled charging during off-peak hours, further optimizing costs. When public charging is necessary, leverage apps that provide real-time pricing and availability information, allowing fleet managers to plan routes and charging stops strategically. Buyers should also negotiate contracts with energy providers for EV-specific tariffs to maximize savings, especially in regions where electricity prices vary widely throughout the day.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Range Anxiety in Business Operations
The Problem: Range anxiety remains a significant concern for businesses considering the integration of 100 km electric cars into their fleets. For companies in industries such as logistics or delivery, the fear of running out of battery power mid-route can hinder the transition to electric vehicles. This anxiety can lead to hesitance in adopting EVs, particularly in regions with less developed charging infrastructure.
The Solution: To mitigate range anxiety, businesses should invest in advanced route planning tools that take into account the real-time status of charging stations along the planned routes. Implementing telematics systems can also provide insights into battery health and energy consumption patterns, enabling proactive management of vehicle range. Additionally, consider incorporating hybrid models into the fleet as a transitional strategy, allowing for flexibility in operations while building confidence in fully electric vehicles. Educating staff about eco-driving techniques can also enhance efficiency, further alleviating concerns about battery depletion.
Scenario 3: Navigating Infrastructure Challenges for EV Charging
The Problem: In many regions, particularly in developing markets across Africa and South America, the lack of adequate charging infrastructure poses a significant barrier to the adoption of 100 km electric cars. B2B buyers may find it challenging to procure electric vehicles when the charging options are sparse, leading to operational inefficiencies and increased downtime.
The Solution: To address infrastructure challenges, B2B buyers should engage in partnerships with local governments and energy providers to advocate for the expansion of charging networks. Propose pilot projects that demonstrate the viability of electric vehicles in your business model, showcasing potential savings and environmental benefits. Additionally, consider investing in portable charging solutions that can be used at multiple locations, thus providing a flexible approach to charging needs. Explore opportunities for collaboration with other businesses to share charging resources, creating a community-based charging network that can enhance the viability of electric vehicle adoption across the region. By actively participating in infrastructure development, businesses can not only secure their own charging needs but also support the broader transition to electric mobility.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 100 km electric car
What Are the Key Materials for a 100 km Electric Car?
In the development of a 100 km electric car, material selection is crucial for optimizing performance, cost, and sustainability. Below, we analyze four common materials used in electric vehicles, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum: A Lightweight Champion
Key Properties: Aluminum boasts a low density, high strength-to-weight ratio, and excellent corrosion resistance. It can withstand a temperature range of -200°C to 600°C, making it suitable for various components in electric vehicles.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which enhances energy efficiency and range. However, it can be more expensive than steel and requires specialized manufacturing techniques, which may complicate production processes.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in the chassis and body panels of electric cars, contributing to overall weight reduction and improved performance. It is compatible with various media, including battery fluids and cooling systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider local recycling capabilities, as aluminum is highly recyclable. Compliance with standards such as ASTM and EN for material quality is essential.
Steel: The Traditional Workhorse
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for structural components.
Pros & Cons: Steel is relatively inexpensive and widely available, making it a go-to material for many manufacturers. However, its heavier weight can negatively impact the vehicle’s range and efficiency compared to lighter materials like aluminum.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used in the frame and safety structures of electric vehicles, providing robust crash protection. Its compatibility with various environmental conditions makes it a reliable choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local steel quality standards and be aware of the carbon footprint associated with steel production, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
Carbon Fiber: The Premium Option
Key Properties: Carbon fiber is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and rigidity. It can withstand temperatures up to 300°C, making it suitable for high-performance applications.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of carbon fiber significantly enhances vehicle performance and efficiency. However, it is one of the most expensive materials and requires complex manufacturing processes, which can increase production costs.
Impact on Application: Carbon fiber is often used in high-end electric vehicles for body panels and structural components, providing both aesthetic appeal and performance benefits.
Considerations for International Buyers: B2B buyers should consider the availability of local suppliers and the need for specialized manufacturing capabilities. Compliance with international standards for composite materials is also crucial.
Thermoplastics: The Versatile Alternative
Key Properties: Thermoplastics are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be molded into complex shapes. They can typically withstand temperatures up to 120°C.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of thermoplastics is their versatility and lower manufacturing costs compared to metals. However, they may not offer the same level of durability and heat resistance as metals or composites.
Impact on Application: Thermoplastics are often used in interior components, battery housings, and lightweight exterior parts, contributing to overall vehicle efficiency and design flexibility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the availability of thermoplastic materials in their region and ensure compliance with relevant safety and environmental standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for 100 km electric car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Chassis and body panels | Lightweight, enhances efficiency | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Steel | Frame and safety structures | Cost-effective, durable | Heavier, impacts range | Low |
| Carbon Fiber | Body panels and structural components | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Very expensive, complex manufacturing | High |
| Thermoplastics | Interior components and battery housings | Versatile, lower manufacturing costs | Less durable, lower heat resistance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers looking to optimize their electric vehicle offerings while considering factors such as cost, performance, and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 100 km electric car
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for a 100 km Electric Car?
The manufacturing of a 100 km electric car involves a series of intricate processes, each designed to ensure the vehicle meets stringent performance and safety standards. The main stages of manufacturing include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the first critical step in the manufacturing process. This involves sourcing high-quality materials that meet industry specifications. For electric vehicles (EVs), this typically includes advanced metals, composites, and battery components.
Suppliers must ensure that the materials used are lightweight yet durable, contributing to overall efficiency and performance. Additionally, manufacturers often engage in pre-production testing of materials to guarantee they can withstand various environmental conditions, which is especially important for markets in Africa and South America where climates can vary significantly.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Electric Car Production?
Once materials are prepared, the forming stage begins. This includes processes such as stamping, extrusion, and molding. For example, the body of the electric car is often produced through stamping techniques that shape metal sheets into predefined forms.
Advanced forming techniques, such as hydroforming, are also utilized to create complex shapes that enhance aerodynamics and structural integrity. The use of robotics in these processes not only increases precision but also improves production efficiency, a crucial factor for B2B buyers looking to scale their operations.
How Is the Assembly Process Structured for Electric Cars?
The assembly stage is where all components come together to form the complete vehicle. This process typically follows a production line model, where each station is responsible for specific assembly tasks. Key components such as the electric drive system, battery packs, and electronic systems must be integrated seamlessly.
Quality checks are integrated into the assembly process, often referred to as In-Process Quality Control (IPQC). This ensures that any defects are caught early, reducing waste and rework costs. For international buyers, understanding the assembly protocols can help in evaluating potential suppliers and their ability to meet quality standards.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Finishing processes are essential for both aesthetics and protection. These may include painting, coating, and detailing. A well-applied finish not only enhances the vehicle’s appearance but also protects against corrosion and wear, which is vital for longevity, especially in regions with harsh weather conditions.
The finishing stage also includes extensive testing of electronic systems and battery performance, ensuring that the vehicle meets specific operational standards before leaving the factory.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Electric Cars?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for electric vehicles. Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 is fundamental for establishing a quality management system that ensures consistency and reliability in production.
What International and Industry-Specific Standards Should B2B Buyers Know?
For B2B buyers, understanding the relevant international and industry-specific standards is crucial. In addition to ISO 9001, standards such as CE marking in Europe and API specifications for certain components are vital for compliance. These certifications indicate that the products meet specific safety, health, and environmental protection requirements.
Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should also consider local regulations that might affect the import and use of electric vehicles. Familiarizing themselves with these standards will help them make informed purchasing decisions.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Implemented in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure quality standards are met. These checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials and components as they arrive at the manufacturing facility. Suppliers must provide certification that their products meet required specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the assembly process, this checkpoint verifies that each stage of manufacturing adheres to quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This comprehensive evaluation occurs after the assembly is complete. It includes functional testing of the vehicle’s systems, safety checks, and performance assessments.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and safety of electric vehicles. Common methods include:
-
Functional Testing: Verifies that all vehicle systems operate as intended.
-
Durability Testing: Assesses how well the vehicle can withstand environmental stressors over time.
-
Battery Performance Testing: Ensures that the battery meets its specified range and charging capabilities.
-
Crash Testing: Essential for safety compliance, this testing evaluates how well the vehicle protects occupants in the event of a collision.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, verifying the quality control practices of potential suppliers is crucial to ensure product reliability. Buyers should consider the following approaches:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems and practices. This includes reviewing production processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to share their quality control reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices, ensuring adherence to industry standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various quality control nuances when sourcing electric vehicles. This includes understanding the specific requirements of different markets and ensuring compliance with local regulations.
Buyers should also be aware of potential language barriers and cultural differences that may affect communication with suppliers. Establishing clear expectations and fostering open lines of communication can mitigate misunderstandings and enhance collaboration.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for a 100 km electric car are complex yet essential for delivering a reliable product. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers that adhere to the highest quality standards. This not only enhances the buyer’s reputation but also contributes to the overall sustainability and efficiency of the electric vehicle market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘100 km electric car’
Introduction
This guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure 100 km electric cars. Given the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions across various regions, understanding the procurement process can lead to significant cost savings and operational efficiencies. This step-by-step approach will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing electric vehicles effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before diving into the procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider factors such as vehicle range, battery capacity, charging options, and maintenance needs. These specifications will serve as a benchmark for evaluating potential suppliers and ensuring that the vehicles meet your operational demands.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Regulations
Stay informed about the latest market trends and regulatory requirements specific to electric vehicles in your region. This knowledge is crucial for understanding the competitive landscape and ensuring compliance with local laws. For instance, some countries offer incentives for electric vehicle purchases, which can significantly impact your total cost of ownership.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your needs and standards. Request detailed company profiles, product specifications, and case studies from similar clients. Look for suppliers with a strong reputation for quality and reliability, as well as those who can provide robust after-sales support and service.
- Key Considerations:
- Supplier certifications and industry standards.
- Customer reviews and testimonials.
- Presence in your target markets (Africa, South America, Middle East, Europe).
Step 4: Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Understanding the total cost of ownership is vital for making an informed decision. Beyond the initial purchase price, consider factors such as charging costs, maintenance expenses, and potential savings from reduced fuel consumption. For example, charging at home during off-peak hours can drastically reduce operational costs.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve identified potential suppliers, enter into negotiations to secure favorable terms. Discuss pricing, warranties, and service agreements to ensure you are getting the best value. Be prepared to negotiate on delivery timelines, payment terms, and any additional features or services that could enhance the vehicle’s value.
Step 6: Conduct a Pilot Program
Before making a large-scale purchase, consider implementing a pilot program. This allows you to test the vehicles in real-world conditions and evaluate their performance against your expectations. Gather feedback from drivers and stakeholders to assess usability, comfort, and operational efficiency.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase and Plan for Integration
After successful evaluations and negotiations, finalize the purchase agreement. Develop an integration plan that includes training for your team on vehicle operation and maintenance, as well as strategies for incorporating the new electric vehicles into your existing fleet. This will ensure a smooth transition and maximize the benefits of your investment.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement of 100 km electric cars, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and sustainability initiatives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 100 km electric car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing a 100 km Electric Car?
When sourcing a 100 km electric vehicle (EV), understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials such as lithium for batteries, aluminum for the frame, and rare earth elements for electric motors significantly impacts the overall pricing. Prices for these materials can fluctuate based on market demand and geopolitical factors.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can influence manufacturing expenses. Countries with higher labor costs may see increased vehicle prices, while regions with lower labor costs might provide more competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory maintenance, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, thereby lowering the overall cost of the vehicle.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs can be a significant upfront investment. The tooling cost must be amortized over the production volume, affecting the per-unit price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the vehicles meet safety and performance standards incurs additional costs. Rigorous QC processes are necessary, especially when exporting to regions with strict regulations.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and customs duties, play a critical role in the total cost. The distance from the manufacturing site to the buyer’s location can greatly influence logistics expenses.
-
Margin: The profit margin set by manufacturers and suppliers can vary. Understanding the industry standard for margins in the EV market helps buyers gauge the fairness of pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of 100 km Electric Cars?
Several factors influence the pricing of electric vehicles, which B2B buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically secure better pricing per unit. Buyers should evaluate their needs to determine the optimal order size that balances cost efficiency and inventory management.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (like ISO standards) may increase upfront costs but can lead to savings in the long run through enhanced durability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and location can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their services, but they can also offer better reliability and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms (Incoterms) is crucial. The chosen terms dictate responsibilities between the buyer and seller, affecting the final cost. For example, “CIF” (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can lead to higher upfront costs but offer peace of mind regarding shipping.
What Tips Can B2B Buyers Use to Optimize Pricing for Electric Cars?
To ensure cost-efficiency when sourcing electric vehicles, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Pricing: Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate better terms, especially for large orders. Leverage competitive bids to drive down costs.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Evaluate long-term costs, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential government incentives for EVs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances in International Markets: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional variations in EV pricing. Currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local incentives can all affect the final price.
-
Consider Long-term Partnerships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing agreements and more favorable terms over time.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for sourcing a 100 km electric car can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and regional regulations. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and engage in direct discussions with manufacturers to obtain accurate and current pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 100 km electric car With Other Solutions
Exploring Viable Alternatives to the 100 Km Electric Car
As businesses and consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability and cost-effectiveness in transportation, various alternatives to the 100 km electric car emerge. Each solution presents unique advantages and challenges, making it crucial for B2B buyers to assess which option best aligns with their operational needs and budget constraints.
| Comparison Aspect | 100 Km Electric Car | Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle | Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Up to 100 km range; fast acceleration | Longer range (500+ km); refueling in minutes | 50-70 km electric range; gasoline backup |
| Cost | €3 – €10.80 per 100 km | Higher upfront costs; €7 – €10 per kg hydrogen | €4 – €8 per 100 km (combined) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure | Limited refueling stations; growing network | Compatible with existing fuel stations |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance; fewer moving parts | Moderate; fuel cell systems can be complex | Moderate; dual systems increase complexity |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting, short trips | Long-distance travel, fleet operations | Versatile; urban and rural applications |
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles: Pros and Cons
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) operate using hydrogen gas to produce electricity, offering a longer range compared to electric cars. They can be refueled in a matter of minutes, making them suitable for long-distance travel or fleet operations where downtime must be minimized. However, the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is still limited, particularly in regions outside of major urban centers. Additionally, the production and storage of hydrogen can be costly, which may deter some businesses from investing in this technology.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles: Advantages and Disadvantages
Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) combine electric and gasoline engines, providing the flexibility of electric driving for short trips and a gasoline engine for longer journeys. This dual approach can reduce fuel costs significantly, especially in urban settings where electric range is utilized. However, the complexity of maintaining two powertrains may lead to higher maintenance costs and requires a careful balance in managing battery and fuel use. PHEVs may be a good option for businesses that operate in diverse environments, needing both urban and rural capabilities.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When evaluating alternatives to the 100 km electric car, B2B buyers should consider factors such as range requirements, infrastructure availability, and total cost of ownership. While electric cars offer significant savings and sustainability benefits for urban commuting, hydrogen FCVs may be better suited for extensive travel needs. Meanwhile, PHEVs provide a flexible option for businesses that require versatility in their operations. Analyzing these factors against the specific operational needs will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their sustainability goals and budgetary constraints.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 100 km electric car
What Are the Critical Technical Properties of a 100 km Electric Car?
Understanding the key technical specifications of a 100 km electric car is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those involved in procurement and fleet management. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Battery Capacity (kWh)
– The battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), indicates the amount of energy the battery can store. For a vehicle designed to travel 100 km, a battery capacity of around 18 kWh is typical, offering efficient energy consumption while maintaining performance. This specification is crucial for buyers as it directly influences range, charging time, and overall operational costs. -
Energy Consumption (kWh/100 km)
– This metric measures how much energy the vehicle uses to travel 100 km. Typical consumption rates range from 15 to 22 kWh/100 km. Understanding energy consumption helps businesses estimate operating costs and make informed decisions regarding charging infrastructure and energy procurement strategies. -
Charging Time (Hours)
– Charging time varies depending on the type of charger used—home chargers can take several hours, while fast chargers can recharge a battery to 80% in about 30 minutes. This specification is vital for fleet operators who must minimize downtime and ensure vehicles are ready for use. -
Vehicle Weight (kg)
– The weight of the vehicle affects its range, energy efficiency, and handling. A well-designed electric car balances weight with performance, typically ranging from 1,200 to 1,800 kg. Weight considerations are critical for B2B buyers focused on logistics and transport efficiency. -
Motor Power (kW)
– The motor power, measured in kilowatts (kW), influences the vehicle’s acceleration and overall performance. An electric car may have motor power ratings from 50 kW to over 200 kW. Buyers should evaluate motor power in the context of their operational needs, especially for applications requiring quick acceleration or heavy loads. -
Range (km)
– While the focus here is on the 100 km range, understanding the maximum range of the vehicle is essential for planning long-distance travel. A vehicle with a range exceeding 300 km is often preferred for its flexibility in various operational scenarios, thus enhancing its attractiveness for fleet purchases.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon Relevant to 100 km Electric Cars?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can facilitate smoother negotiations and partnerships. Here are some commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for B2B buyers, as it often dictates product quality and warranty support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for procurement teams as it impacts inventory management and cash flow considerations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a business process where a company solicits bids from suppliers for specific products or services. This term is critical for buyers looking to compare prices and negotiate terms effectively. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are a series of pre-defined international trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. They clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global transactions, making them essential for international procurement processes. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
– TCO represents the total cost of owning a vehicle over its lifespan, including purchase price, maintenance, insurance, and fuel costs. This metric helps businesses evaluate the long-term financial implications of purchasing electric vehicles. -
Lifecycle Assessment (LCA)
– LCA is a methodology for assessing the environmental impacts associated with all the stages of a product’s life, from raw material extraction to disposal. This term is increasingly relevant as companies aim to improve sustainability in their supply chains.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that their investments in 100 km electric cars align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 100 km electric car Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the 100 km Electric Car Market?
The 100 km electric car market is experiencing transformative growth due to several global drivers. First, rising fossil fuel prices and increasing environmental awareness have led consumers and businesses alike to seek more sustainable transportation options. Governments across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are incentivizing electric vehicle (EV) adoption through subsidies, tax breaks, and infrastructure investments. This regulatory push fosters a favorable environment for international B2B buyers looking to enter or expand in the EV sector.
Emerging technologies also play a crucial role. Innovations in battery technology, such as lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, have improved efficiency and reduced charging times, making electric vehicles more appealing. Additionally, advancements in smart charging solutions, including mobile apps for real-time charging station availability, are enhancing the user experience. For B2B buyers, sourcing partnerships with technology providers can yield competitive advantages in the rapidly evolving electric vehicle landscape.
Market dynamics are shifting as well. Increasing competition among automakers, particularly from Asian manufacturers like NIO and Tesla, is driving down prices and improving vehicle quality. Buyers should stay informed about trends in production capabilities and supply chain management to ensure they are sourcing from reliable partners that can meet growing demand while maintaining quality.
How Can Businesses Embrace Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the 100 km Electric Car Sector?
As the electric vehicle sector grows, sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount for businesses in the 100 km electric car market. The environmental impact of battery production, particularly lithium extraction, poses significant challenges. Therefore, B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as sourcing raw materials responsibly and minimizing carbon footprints during production.
Furthermore, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Businesses are increasingly held accountable for the environmental and social impacts of their supply chains. Acquiring ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, can enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to eco-conscious consumers and partners. B2B buyers should seek manufacturers who utilize recycled materials and adopt circular economy principles, thereby reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
In addition, transparency in sourcing is critical. Establishing partnerships with suppliers that provide full visibility into their supply chains can help mitigate risks related to unethical practices. By choosing partners committed to sustainability, businesses can contribute to a greener future while also enhancing their market positioning.
What Is the Historical Context of the 100 km Electric Car Market?
The 100 km electric car market has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, electric vehicles were seen as niche products, often hindered by technological limitations such as limited battery range and high costs. However, the late 2000s marked a turning point with the introduction of models like the Nissan Leaf and the Tesla Roadster, which garnered mainstream attention and consumer interest.
In recent years, advancements in battery technology and growing environmental concerns have catalyzed a surge in electric vehicle adoption. Today, the 100 km electric car is not only a viable option for consumers but is also increasingly becoming the preferred choice for businesses aiming to reduce their carbon footprint. This evolution reflects a broader societal shift towards sustainability and innovation, making it imperative for B2B buyers to stay abreast of developments in the electric vehicle market to remain competitive.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 100 km electric car
-
How do I evaluate the total cost of ownership for a 100 km electric car?
To evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) for a 100 km electric car, consider not just the purchase price but also operational costs. This includes charging expenses, maintenance, insurance, and potential government incentives. Charging costs can vary widely depending on whether you use home or public charging, with home charging during off-peak hours being the most economical. Additionally, factor in depreciation and any local tax benefits or exemptions that may apply. A comprehensive TCO analysis will help you make informed budgeting decisions. -
What charging options are available for 100 km electric cars?
For 100 km electric cars, charging options typically include home charging stations, public slow chargers, and fast chargers. Home charging is often the most cost-effective, especially if done during off-peak hours. Public charging stations offer flexibility but can vary in pricing, with slow chargers being cheaper than fast chargers. It’s also important to consider the availability of charging infrastructure in your region, as this can influence your operational strategy and overall costs. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing 100 km electric cars internationally?
When sourcing 100 km electric cars internationally, consider factors such as supplier reliability, product certifications, and compliance with local regulations. Research potential suppliers thoroughly, looking for customer reviews and industry reputation. Also, evaluate the supplier’s ability to provide after-sales support, warranty services, and spare parts availability. Logistics and shipping costs should also be factored into your sourcing strategy to ensure a smooth supply chain. -
How can I customize a 100 km electric car for my business needs?
Customization options for 100 km electric cars can include modifications to battery capacity, interior features, and technological integrations. Many manufacturers offer tailored solutions for fleet buyers, such as branding opportunities and specific technology setups. Engage with suppliers early in the procurement process to discuss your specific requirements and assess their willingness and capability to accommodate customization requests. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for purchasing 100 km electric cars?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for 100 km electric cars vary by manufacturer and model. Some suppliers may offer competitive pricing for larger orders, while others might have lower MOQs to accommodate smaller businesses. It’s essential to discuss your purchasing plans with potential suppliers to understand their policies and negotiate terms that suit your business needs. Be mindful that larger orders may also provide advantages in terms of pricing and delivery timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electric cars?
Payment terms for sourcing electric cars can vary significantly among suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront payments, payment upon delivery, or installment plans. Some manufacturers may offer financing options or leasing agreements, which can be advantageous for businesses looking to manage cash flow. Always review the payment terms carefully and negotiate conditions that align with your financial strategy. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when purchasing electric cars?
To ensure quality assurance when purchasing electric cars, request detailed information about the manufacturer’s quality control processes and certifications. Look for compliance with international safety and performance standards. Conduct thorough inspections or audits of the vehicles, either remotely or in-person, before finalizing the purchase. Additionally, consider suppliers that offer warranties or guarantees to mitigate risks associated with product defects. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric cars?
When importing electric cars, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Evaluate different transportation options to determine the most cost-effective and efficient method for your needs. Understand the import duties and taxes applicable in your region, as these can significantly impact total costs. Collaborate with a logistics partner experienced in automotive imports to navigate the complexities of international shipping and ensure compliance with local regulations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
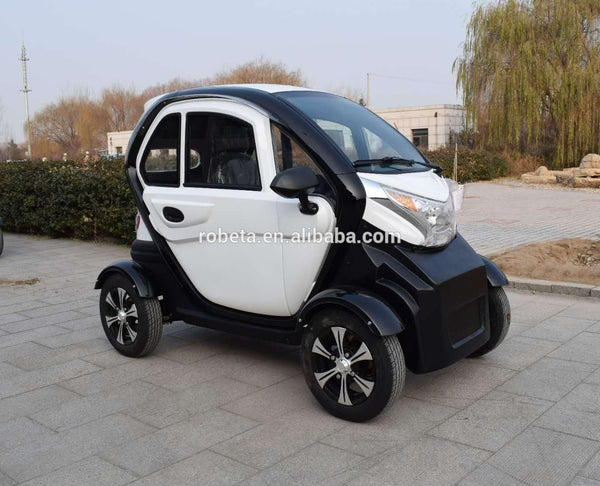
Top 4 100 Km Electric Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Short-Range EV Solution
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Normal sized EVs with a range of less than 100km are not being mass produced. The user expresses a desire for an EV designed specifically for short-range driving, as 99% of their driving is within 100km, and most of that is within 25km. They suggest that a smaller battery capacity (1/4 of current EVs) could significantly reduce costs, making EVs more affordable (potentially $9k-$10k). They mention…
2. NIO – ET7 Electric Sedan
Domain: nio.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: NIO ET7: Electric sedan with a range of up to 1000 km. Equipped with a 150kWh ultralong-range battery pack. Dimensions: Length 5,101 mm, Width 1,987 mm, Wheelbase 3,060 mm. Features include AI chassis system, NIO assisted and intelligent driving, frameless soft-close doors, and 7 exterior color options. Interior includes business-class seats with zoned heating, ventilation, hot stone massage, and …
3. EV Box – Longest Range Electric Vehicles
Domain: blog.evbox.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Shortest EV range: 95 km (59 miles) – Smart Fortwo EQ; Average EV range: 348 km (216 miles); Longest EV range: 685 km (426 miles) – Lucid Air Dream Range Edition. Top 5 longest range EVs: 1. Lucid Air Dream Edition: 645 – 685 km (401 – 425 miles); 2. Lucid Air Grand Touring: 665 km (413 miles); 3. Mercedes EQS: 565 – 640 km (351 – 397 miles); 4. Tesla Model S: 550 – 570 km (342 – 354 miles); 5. Lu…
4. EVDB – Most Efficient EVs
Domain: evdb.nz
Introduction: {“most_efficient_evs”: [{“model”: “Tesla Model 3”, “range_km”: 520, “consumption_kWh_per_100km”: 13.8, “running_cost_per_100km”: 3.45}, {“model”: “Mini Cooper E”, “range_km”: 305, “consumption_kWh_per_100km”: 13.8, “running_cost_per_100km”: 3.45}, {“model”: “Mini Aceman SE”, “range_km”: 406, “consumption_kWh_per_100km”: 13.8, “running_cost_per_100km”: 3.45}, {“model”: “Tesla Model 3 Long Range”, “…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 100 km electric car
In summary, the journey towards a sustainable future with 100 km electric vehicles (EVs) presents numerous opportunities for strategic sourcing. Understanding the diverse charging options—from cost-effective home charging during off-peak hours to flexible public charging networks—allows businesses to optimize their operational budgets significantly. The total cost of ownership further highlights the financial advantages of EVs, with potential savings of €1,500 to €3,000 annually compared to conventional vehicles.
For international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing of electric vehicles is not merely a matter of environmental responsibility; it is a vital component of a forward-thinking business strategy. By investing in EVs, companies can enhance their brand image, meet regulatory requirements, and appeal to an increasingly eco-conscious consumer base.
As the electric vehicle market evolves, staying informed and agile in sourcing strategies will be crucial. Embrace the transition to electric mobility and explore partnerships that can help leverage the financial and environmental benefits of 100 km electric cars. The future is electric—make your move today.