Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric car without driving licence trade
As the demand for sustainable transportation rises globally, the electric car without a driving licence trade presents unique opportunities and challenges for B2B buyers. These innovative vehicles, often referred to as light quadricycles, provide a practical solution for diverse markets, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries such as Vietnam and Brazil. However, sourcing the right electric microcars that meet local regulations, safety standards, and consumer preferences can be daunting.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower international B2B buyers with the essential knowledge needed to navigate the electric car without a driving licence market. We will explore various types of vehicles available, their applications, and the latest regulatory requirements, ensuring you are well-informed about the unique specifications that define these electric cars. Additionally, we will cover critical aspects of supplier vetting, pricing structures, and cost considerations, enabling you to make strategic purchasing decisions.
By providing actionable insights and in-depth analysis, this guide equips you with the tools necessary to successfully engage with suppliers and adapt to the evolving landscape of electric mobility. Whether you’re looking to enhance your product offerings or enter new markets, understanding the nuances of the electric car without a driving licence trade will be key to your success.
Understanding electric car without driving licence trade Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Quadricycles | Weight under 425 kg, speed limit of 45 km/h, electric motor | Urban transport services, rental companies | Pros: Affordable, eco-friendly; Cons: Limited range and speed |
| Microcars | Compact design, suitable for urban commuting, low emissions | Delivery services, elderly transport | Pros: Easy to park, low operational costs; Cons: Smaller size may limit cargo capacity |
| Electric Utility Vehicles | Designed for light commercial use, higher weight capacity | Last-mile delivery, small business fleets | Pros: Versatile for goods transport; Cons: Higher initial investment |
| Personal Mobility Devices | Small, agile vehicles for individual use | Personal transport, short-distance travel | Pros: Increased independence for users; Cons: Limited passenger capacity |
| Shared Mobility Solutions | Fleet of vehicles for shared use, often managed by apps | Ride-sharing services, urban mobility initiatives | Pros: Cost-effective for users; Cons: Maintenance and management challenges |
What Are Light Quadricycles and Their B2B Applications?
Light quadricycles are specialized electric vehicles that weigh less than 425 kg and are limited to a maximum speed of 45 km/h. These vehicles are particularly suitable for urban environments where maneuverability and parking can be challenging. B2B applications include urban transport services and rental companies that cater to younger drivers or those seeking an alternative to scooters. Buyers benefit from their affordability and eco-friendliness, though they must consider the limited range and speed that may not meet all transport needs.
How Do Microcars Fit into the Electric Vehicle Market?
Microcars are compact electric vehicles designed for efficient urban commuting. With a focus on low emissions and practicality, they serve as an excellent option for delivery services and elderly transport. Their small size allows for easy parking and navigation through congested city streets, making them appealing for businesses focused on last-mile logistics. However, potential buyers should weigh the advantages of low operational costs against the limitations of cargo capacity due to their size.
What Are the Benefits of Electric Utility Vehicles?
Electric utility vehicles are tailored for light commercial applications, offering a higher weight capacity compared to microcars and quadricycles. These vehicles are ideal for businesses requiring efficient transport of goods over short distances, such as last-mile delivery services. The versatility of electric utility vehicles makes them attractive to small business fleets aiming to reduce their carbon footprint. However, prospective buyers should consider the higher initial investment, which may be offset by long-term savings on fuel and maintenance.
How Do Personal Mobility Devices Enhance Urban Transport?
Personal mobility devices, often small and agile, cater to individual transport needs in urban settings. They provide users with increased independence, particularly for those who may not have access to traditional vehicles. These devices are ideal for short-distance travel and can be particularly beneficial for businesses looking to offer flexible transport solutions. However, buyers should be aware of the limited passenger capacity, which may not suit all use cases.
What Are the Challenges and Opportunities in Shared Mobility Solutions?
Shared mobility solutions involve fleets of electric vehicles managed through digital platforms, allowing users to rent or share vehicles as needed. This model is gaining traction in urban mobility initiatives and ride-sharing services, providing cost-effective transport options for users. While the opportunity for reduced costs and increased accessibility is significant, businesses must also address challenges related to vehicle maintenance and fleet management to ensure reliability and customer satisfaction.
Key Industrial Applications of electric car without driving licence trade
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric car without driving licence trade | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Mobility Solutions | Last-mile delivery services using electric microcars | Enhanced efficiency in urban logistics, reduced emissions | Compliance with local regulations, vehicle range, and charging infrastructure availability |
| Tourism and Leisure | Eco-friendly transport options for tourists in urban areas | Attracts environmentally conscious tourists, increases mobility options | Vehicle design and comfort, local regulations, and availability of charging stations |
| Education and Youth Services | Transportation for students and young adults | Safe, affordable mobility for students, reduces traffic congestion | Safety features, affordability, and suitability for urban environments |
| Elderly Care Services | Personal transport for elderly individuals | Promotes independence and mobility for the elderly, reduces reliance on traditional vehicles | Comfort, ease of use, and safety features |
| Retail and Commercial Services | Employee commuting solutions for urban businesses | Cost-effective transport for employees, supports sustainable practices | Fleet management options, maintenance services, and total cost of ownership |
How Are Electric Cars Without Driving Licenses Transforming Urban Mobility Solutions?
In urban mobility solutions, electric microcars are becoming vital for last-mile delivery services. Businesses can utilize these compact vehicles to navigate congested city streets and deliver products efficiently, minimizing environmental impact. The demand for sustainable logistics is growing, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where urbanization is rapid. Buyers should consider vehicle range, compliance with local regulations, and the availability of charging infrastructure when sourcing these vehicles.
What Role Do Electric Microcars Play in the Tourism and Leisure Industry?
Electric microcars serve as eco-friendly transport options for tourists, enhancing the travel experience in urban settings. By offering a sustainable mode of transport, businesses can attract environmentally conscious travelers while providing convenient access to local attractions. This is particularly relevant in Europe, where tourism is a significant economic driver. Key considerations for sourcing include vehicle design, comfort, and the ability to meet local regulations regarding tourist transport.
How Can Electric Cars Without Licenses Benefit Education and Youth Services?
In education and youth services, electric microcars offer safe and affordable transportation options for students and young adults. These vehicles provide a viable alternative to traditional scooters and can help reduce traffic congestion around schools. For international buyers, especially in developing regions, understanding safety features and affordability will be crucial in selecting the right vehicles for their needs.
What Advantages Do Electric Microcars Offer for Elderly Care Services?
Electric cars without licenses can significantly enhance mobility for elderly individuals, allowing them to maintain independence. These vehicles are designed with safety and ease of use in mind, making them ideal for seniors who may struggle with traditional cars. Buyers in the elderly care sector should prioritize comfort and safety features when sourcing these vehicles, ensuring they meet the specific needs of their clientele.
How Are Electric Microcars Revolutionizing Retail and Commercial Services?
In retail and commercial services, electric microcars can serve as effective employee commuting solutions, promoting sustainable practices within organizations. They offer a cost-effective alternative for businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint while providing staff with convenient transportation. Key considerations for sourcing include fleet management options and the total cost of ownership, ensuring businesses can maximize their investment in these vehicles.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric car without driving licence trade’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance for License-Free Electric Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers in the electric car without a driving license trade often grapple with understanding and complying with the diverse regulations governing license-free vehicles. In regions like Europe and South America, these regulations can vary significantly, leading to confusion about vehicle specifications, licensing requirements, and operational restrictions. This lack of clarity can result in costly delays, misaligned product offerings, or even legal repercussions if vehicles do not meet local standards.
The Solution: To effectively navigate these regulatory waters, B2B buyers should invest time in comprehensive market research and establish relationships with local regulatory bodies. Engaging legal experts familiar with automotive regulations in target markets can provide valuable insights. Additionally, buyers should utilize platforms that aggregate regulatory information, ensuring they remain up-to-date with changes. When sourcing vehicles, insist on documentation that clearly outlines compliance with local laws, including vehicle classification, weight limits, and speed restrictions. This proactive approach not only mitigates risk but also enhances credibility in the marketplace.
Scenario 2: Addressing Consumer Education and Market Perception
The Problem: Many potential customers, especially in emerging markets, are unfamiliar with the concept of electric cars that can be driven without a license. This lack of understanding can lead to skepticism regarding safety, functionality, and overall value. B2B buyers may find it challenging to generate interest and drive sales when their target audience perceives these vehicles as inferior or overly niche.
The Solution: To combat this, B2B buyers should implement targeted educational campaigns that highlight the benefits of license-free electric vehicles. This includes organizing community workshops or webinars to explain the vehicles’ features, safety standards, and environmental impact. Leveraging social media platforms to share testimonials and success stories from satisfied users can also enhance credibility. Collaborating with local influencers who advocate for sustainable transportation can further amplify the message. Additionally, providing potential buyers with test drives can create a firsthand experience that dispels myths and fosters trust in the product.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Accessibility and Service Infrastructure
The Problem: A significant barrier to the adoption of electric cars without a license is the limited accessibility to charging infrastructure and service centers, particularly in less developed regions. B2B buyers may struggle to assure their customers that they can maintain and operate these vehicles efficiently. This concern can hinder sales, as potential customers fear being stranded due to insufficient charging options or facing difficulties in vehicle maintenance.
The Solution: B2B buyers should focus on developing partnerships with local businesses to establish a robust charging and service network. This can involve collaborating with electric utility companies to install charging stations in strategic locations, such as schools and shopping centers. Additionally, creating service agreements with local garages or automotive specialists to handle maintenance and repairs for electric vehicles can alleviate consumer concerns. Offering incentives, such as discounted charging rates or maintenance packages, can also attract more customers. Educating consumers about home charging options and providing resources for installation can further promote confidence in vehicle ownership, ensuring a more sustainable market growth.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric car without driving licence trade
What Are the Key Materials Used in Electric Cars Without a License?
In the burgeoning market for electric cars without a license, material selection plays a crucial role in ensuring product performance, safety, and compliance with regional regulations. Below, we analyze several common materials used in these vehicles, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties and Applications of Aluminum in Electric Cars?
Aluminum is widely used in the construction of electric vehicles due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating that allows it to withstand a range of operating conditions, making it suitable for various components, including body frames and battery housings.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight properties contribute to improved energy efficiency and vehicle range. It is also relatively easy to manufacture, allowing for complex shapes and designs.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it can be more expensive than steel, and its manufacturing processes can be complex. Additionally, it may require special welding techniques, which could increase production costs.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various media makes it ideal for components exposed to moisture and corrosive environments, which are common in urban settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local recycling capabilities and the availability of aluminum alloys that comply with international standards like ASTM or DIN.
How Does Steel Contribute to the Durability of Electric Cars?
Steel remains a popular choice for structural components in electric cars, including chassis and safety cages. It offers high tensile strength and impact resistance, essential for vehicle safety.
Pros: Steel is relatively low-cost and widely available, making it an economical choice for manufacturers. Its durability ensures long-lasting performance under various conditions.
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact energy efficiency and range. It is also susceptible to corrosion unless adequately treated.
Impact on Application: Steel’s strength makes it suitable for safety-critical applications, but its weight may limit the vehicle’s performance in terms of speed and range.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local safety regulations and standards, such as JIS in Japan or EN in Europe, which may dictate specific steel grades for automotive applications.
What Role Does Plastic Play in the Design of Electric Cars?
Plastics are increasingly used in electric vehicles for interior components, body panels, and battery housings. They can be engineered to provide a range of properties, including impact resistance and thermal stability.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs. They are also resistant to corrosion and can be produced at a lower cost compared to metals.
Cons: While plastics can be durable, they may not provide the same level of strength as metals. Additionally, some plastics can degrade over time when exposed to UV light unless treated.
Impact on Application: The versatility of plastics allows for customization in design, but manufacturers must consider their long-term durability and environmental impact.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the recycling capabilities for plastics in their region and ensure that materials meet local environmental regulations.
How Does Composite Material Enhance Electric Vehicle Performance?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers, are increasingly used in high-performance electric vehicles. They offer high strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for performance-oriented applications.
Pros: Composites are incredibly lightweight and can significantly enhance vehicle performance and efficiency. They also offer excellent corrosion resistance.
Cons: The high cost of composite materials can be a barrier for many manufacturers. Additionally, the complexity of the manufacturing process may require specialized equipment and expertise.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly suitable for applications where weight savings are critical, such as in the construction of body panels and structural components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of composite manufacturing capabilities in their region and ensure compliance with international standards for automotive materials.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Cars Without a License
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric car without driving licence trade | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body frames, battery housings | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Steel | Chassis, safety cages | High strength and low cost | Heavier, susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Plastic | Interior components, body panels | Lightweight and moldable | Less strength, potential UV degradation | Low |
| Composite | High-performance body panels, structural components | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive overview of the materials that can significantly impact the performance and compliance of electric cars without a license. Understanding these materials will enable informed decision-making in the procurement process, ensuring that products meet both market demands and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric car without driving licence trade
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electric Cars Without a Driving License?
The manufacturing process for electric cars that can be driven without a license, commonly referred to as light quadricycles or microcars, involves several key stages. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers looking to source vehicles that meet both regulatory standards and market demands.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The first stage in manufacturing involves the preparation of materials. Lightweight materials such as aluminum and high-strength steel are often preferred due to their strength-to-weight ratios, which are critical for maintaining compliance with weight restrictions (usually under 425 kg) for license-free vehicles. Additionally, manufacturers may use composite materials for body panels to enhance durability while keeping weight low.
Sourcing materials from reputable suppliers is essential. B2B buyers should ensure that materials are certified to meet international quality standards, which can affect the overall performance and safety of the vehicles.
How Is the Forming Process Conducted?
The forming process involves shaping the prepared materials into the desired components of the vehicle. Key techniques include:
- Stamping: Used for producing body panels and structural components. This process requires precision machinery to ensure uniformity and adherence to safety standards.
- Extrusion: Often utilized for creating complex shapes from aluminum, which can be used in frame construction.
- Injection Molding: Employed for producing plastic components like interior fittings and dashboard elements.
The goal during this stage is to create components that not only fit well but also comply with safety regulations and performance criteria.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
The assembly stage is where the manufactured components come together to form a complete vehicle. This stage typically includes:
- Chassis Assembly: The frame is constructed first, providing a foundation for other components.
- Powertrain Installation: Electric motors and battery systems are installed. Given the unique requirements for electric vehicles, this involves ensuring that all electrical connections are secure and compliant with industry standards.
- Interior Fitting: This includes the installation of seats, controls, and safety features. Ergonomics is particularly important, especially since these vehicles are often targeted at younger drivers or those seeking an alternative to traditional cars.
Quality checks are integrated throughout the assembly process to ensure that each vehicle adheres to specified standards.
How Is the Finishing Process Executed?
The finishing stage involves painting, surface treatment, and final inspections. Manufacturers often employ:
- Powder Coating: This technique is used for applying a durable finish to the vehicle’s exterior, enhancing aesthetics while providing corrosion resistance.
- Quality Inspections: Each vehicle undergoes a thorough inspection to ensure that it meets all specifications. This includes checking for paint imperfections, alignment of components, and functionality of safety features.
This stage is crucial, as it not only affects the vehicle’s appearance but also its longevity and reliability.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for the Electric Car Without Driving License Trade?
Quality assurance is an integral part of the manufacturing process for electric cars without a driving license. Adhering to recognized standards ensures safety, reliability, and market competitiveness.
Which International Standards Should Be Considered?
ISO 9001 is a key quality management standard that many manufacturers strive to comply with. It outlines the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 can help manufacturers streamline their processes, enhance customer satisfaction, and ensure product quality.
Additionally, other industry-specific certifications may apply, including:
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: Relevant for specific components, particularly those related to safety and performance.
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate compliance with these standards, as they reflect a commitment to quality.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is typically segmented into several key checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing process, this stage includes regular checks to identify defects early and make necessary adjustments.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection that occurs before the vehicle is shipped. This includes functional testing of electrical systems, safety features, and overall performance.
These checkpoints help ensure that any defects are caught and rectified before the product reaches the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
Verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential for B2B buyers, especially in international markets. Here are several methods:
What Audits and Reports Should Be Requested?
B2B buyers should request detailed reports from suppliers that outline their QC processes, including:
- Quality Management System Documentation: This should include procedures for each QC checkpoint.
- Audit Reports: Regular audits by third-party organizations can provide an unbiased assessment of a manufacturer’s adherence to quality standards.
Conducting supplier audits can also be beneficial. This allows buyers to assess the manufacturing environment, review QC processes firsthand, and ensure compliance with international standards.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Confidence?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide additional assurance regarding the quality of the products. These services typically include:
- Factory Inspections: Assessing the manufacturing process and equipment.
- Product Inspections: Evaluating finished products against specified standards.
Third-party inspectors can provide objective reports that can help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances regarding QC and certification.
How Do Regional Regulations Impact Quality Standards?
Different regions may have varying regulations and standards that affect manufacturing practices. For instance, while the CE marking is essential for European markets, other regions may have their own certification requirements. Understanding these nuances is vital for compliance and market entry.
What Should Buyers Consider Regarding Supply Chain Transparency?
Transparency within the supply chain is becoming increasingly important. B2B buyers should seek suppliers who provide clear documentation of their sourcing, manufacturing, and QC processes. This not only enhances trust but also ensures that all aspects of production are compliant with relevant standards.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards for electric cars without a driving license is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and robust QC practices, buyers can ensure they select reliable suppliers who meet international standards and market needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric car without driving licence trade’
In the evolving landscape of urban mobility, sourcing electric cars that can be driven without a traditional driving license presents unique opportunities for B2B buyers. This guide provides a structured approach to help you navigate the procurement process effectively.
Step 1: Identify Market Demand
Understanding the local market demand is crucial. Evaluate demographics and target customer segments that would benefit from electric cars without a license, such as young drivers, urban dwellers, and those needing mobility solutions without extensive licensing requirements. Conduct surveys or research to gauge interest levels and preferences in specific regions.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical specifications for the electric vehicles you wish to source. Consider factors such as:
– Weight and Size: Ensure vehicles comply with legal definitions for light quadricycles, typically under 425 kg.
– Performance Metrics: Focus on speed (max 45 km/h) and range (ideally over 75 km for urban use).
Defining these criteria will streamline your search for suitable models that meet regulatory standards.
Step 3: Research Potential Suppliers
Thorough research into potential suppliers is essential. Look for manufacturers specializing in electric vehicles that meet your specifications. Key aspects to investigate include:
– Reputation and Experience: Consider suppliers with a proven track record in the electric vehicle market.
– Certifications: Verify that they comply with relevant safety and environmental regulations.
This step ensures you partner with reliable sources that can deliver quality products.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Offerings
Once you have a list of potential suppliers, evaluate their offerings. Request detailed product catalogs and specifications to compare features such as:
– Battery Life and Charging Options: Look for options that offer fast charging capabilities.
– Warranty and Support Services: Assess the warranty terms and after-sales support.
Evaluating these offerings helps you choose a supplier that aligns with your business needs and customer expectations.
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Before finalizing any contracts, request samples of the vehicles. Conduct hands-on testing to assess performance, comfort, and usability. Consider:
– User Experience: Gather feedback from potential end-users to evaluate their satisfaction.
– Durability and Maintenance Needs: Analyze the build quality and ease of maintenance.
Testing ensures that the vehicles not only meet specifications but also appeal to your target market.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in negotiations to finalize pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. Important points to discuss include:
– Volume Discounts: Ask for pricing adjustments based on larger orders.
– Delivery Logistics: Clarify shipping costs and timelines to avoid unexpected delays.
Negotiating favorable terms can significantly impact your overall cost and operational efficiency.
Step 7: Establish a Compliance Framework
Ensure compliance with local regulations regarding electric vehicles without licenses. This includes:
– Licensing Requirements: Understand the AM license framework in your target markets.
– Insurance and Safety Standards: Ensure that the vehicles meet local safety and insurance requirements.
Establishing a compliance framework protects your business from legal liabilities and enhances customer trust.
By following this structured approach, B2B buyers can effectively source electric cars that cater to the growing demand for accessible, eco-friendly transportation solutions without the need for a traditional driving license.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric car without driving licence trade Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Electric Cars Without a License?
When sourcing electric cars without a license, also known as light quadricycles, understanding the cost structure is critical for B2B buyers. The main cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The primary materials for electric cars include metals, plastics, and batteries. Lithium-ion batteries, essential for electric vehicles, can significantly influence overall costs. Prices for raw materials fluctuate based on global demand and availability, impacting the final pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Europe, the manufacturing expenses may be more substantial compared to regions like Southeast Asia or South America. The complexity of manufacturing electric vehicles also requires skilled labor, which can further influence pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can mitigate overhead costs, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial investments in tooling for production can be substantial. Customization or special features may require unique tooling, which can increase upfront costs but might be justified by higher selling prices or market differentiation.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that vehicles meet safety and performance standards is vital. Costs associated with QC processes, including testing and certification, can add to the overall expense. Buyers should seek suppliers with robust QC practices to ensure product reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation of vehicles from manufacturing sites to distribution centers or end customers involves significant costs. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) play a crucial role in determining logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of the vehicles.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Electric Cars Without a License?
Understanding the factors that influence pricing is essential for international B2B buyers. Key influencers include:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger volumes can significantly reduce per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQ) with suppliers can yield better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features or specifications may lead to higher costs. Buyers should evaluate whether the additional features justify the increased price or if standard models meet their needs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., safety standards, environmental compliance) can raise costs but also enhance the vehicle’s marketability and resale value.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a strong reputation may charge premium prices, but they often offer better quality assurance and customer support. Assessing the supplier’s reliability and track record can inform purchasing decisions.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms is crucial for managing logistics costs and risks. Buyers should negotiate terms that align with their shipping capabilities and cost structures.
What Are the Best Practices for Negotiating Pricing for Electric Cars Without a License?
For B2B buyers, negotiation strategies can significantly impact cost-efficiency:
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding the market landscape, including competitor pricing and product offerings, can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Emphasize the long-term savings associated with electric vehicles, such as lower fuel and maintenance costs, to justify higher initial prices.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to new products.
-
Be Prepared to Walk Away: If negotiations do not yield favorable terms, being willing to explore other suppliers can create leverage in discussions.
Conclusion: What Should International Buyers Consider When Sourcing Electric Cars Without a License?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, sourcing electric cars without a license requires careful consideration of cost components and price influencers. The landscape is evolving, with increasing demand for sustainable transportation solutions. Buyers should remain informed and proactive in negotiations to ensure they achieve competitive pricing while securing high-quality vehicles.
Disclaimer:
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier agreements, and other factors.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric car without driving licence trade With Other Solutions
Understanding the Alternatives to Electric Cars Without a Driving Licence
As the demand for sustainable and accessible transportation solutions increases, various alternatives to electric cars that can be driven without a traditional driving licence are emerging in the market. These alternatives cater to different needs, preferences, and regulatory environments, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis explores how electric cars without a driving licence stack up against other viable options.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Car Without Driving Licence Trade | E-Scooters | Public Transportation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Max speed: 45 km/h | Max speed: 25-30 km/h | Varies by service |
| Cost | €7,990 – €12,000 | €300 – €1,500 | €1 – €5 per ride |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple legal requirements (AM licence) | Minimal setup; no licence needed | Dependent on local infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Moderate (battery and motor upkeep) | Low (tire and battery checks) | Minimal (service provider’s responsibility) |
| Best Use Case | Urban and suburban travel, short distances | Last-mile connectivity | Commuting, longer distances |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
E-Scooters
E-scooters have gained immense popularity due to their affordability and ease of use. With prices ranging from €300 to €1,500, they provide a cost-effective solution for short-distance travel. They are lightweight, easily portable, and require minimal maintenance. However, their maximum speed typically caps at 25-30 km/h, which may not suit all users’ needs. Additionally, they may be subject to local regulations that restrict where they can be used, making them less versatile than electric cars without a licence.
Public Transportation
Public transportation systems offer an established solution for urban commuting, with costs per ride often ranging from €1 to €5. This option is highly beneficial for those living in cities with robust transit networks. However, its effectiveness heavily relies on the availability and reliability of services, which can vary significantly across regions. While it is generally low maintenance for users, public transport may not provide the same level of convenience and flexibility that personal vehicles offer. Long wait times and overcrowding can also detract from the user experience.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When considering the best transportation solution for your business or community, it’s crucial to evaluate the specific needs and preferences of your target audience. Electric cars without a driving licence are ideal for those who prioritize independence and safety, particularly for younger drivers or those who may not have traditional driving licences. In contrast, e-scooters serve as a flexible, low-cost option for short trips, while public transportation remains a reliable choice for cost-effective commuting in urban settings.
Ultimately, B2B buyers should analyze factors such as local regulations, target demographics, and the infrastructure available in their region. By aligning the chosen transportation solution with these considerations, businesses can effectively address the mobility needs of their customers while promoting sustainable practices.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric car without driving licence trade
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Cars Without a License?
In the burgeoning market for electric cars that can be driven without a traditional driving license, understanding the essential technical specifications is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are some critical properties that influence purchasing decisions:
-
Curb Weight
– Definition: The curb weight of a vehicle is its total weight when it is not loaded with passengers or cargo but includes all fluids (oil, coolant, and a full tank of fuel).
– Importance: For electric quadricycles, the curb weight must be under 425 kg to qualify as a lightweight vehicle. This specification is vital for compliance with regulations, impacting marketability in regions that enforce strict vehicle classifications. -
Maximum Speed
– Definition: The top speed a vehicle can achieve, typically limited in license-free vehicles to 45 km/h.
– Importance: This specification affects usability, especially in urban environments where traffic conditions are a concern. It also defines the target market, catering primarily to younger drivers and those seeking an economical transportation solution. -
Motor Power Rating
– Definition: The power output of the electric motor, usually measured in kilowatts (kW). For these vehicles, the power cannot exceed 6 kW.
– Importance: The motor power rating influences performance metrics such as acceleration and efficiency. B2B buyers need to consider how motor specifications align with market demands for speed and range. -
Battery Capacity
– Definition: Measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), battery capacity indicates how much energy the battery can store, affecting the vehicle’s range.
– Importance: Higher battery capacity translates to longer distances between charges, making vehicles more appealing to consumers. Understanding battery technology and its lifecycle is essential for buyers looking to invest in sustainable options. -
Charging Time
– Definition: The duration required to fully charge the vehicle’s battery, typically expressed in hours or minutes.
– Importance: Quick charging capabilities enhance the vehicle’s practicality and convenience for users. B2B buyers must assess charging infrastructure availability in their target markets, which can influence purchasing decisions.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in the Electric Car Without a License Sector?
Navigating the jargon of the electric vehicle industry can be challenging for B2B buyers. Here are some common terms that are essential to understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: In the electric car market, understanding who the OEMs are can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and manufacturers for components and vehicles. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory planning. Buyers should ensure that their order quantities align with their operational needs to avoid excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A business process where a company solicits bids from suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Importance: RFQs are essential for comparing offers from multiple suppliers, allowing buyers to make informed decisions based on cost and value. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that are widely used in international commercial transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact the total cost of procurement. -
L6e Category
– Definition: A classification for light quadricycles in Europe, which encompasses vehicles that meet specific criteria for weight and speed.
– Importance: Knowledge of the L6e category is essential for compliance with local regulations. Buyers must ensure that the vehicles they source meet these classifications to operate legally in their markets.
By grasping these technical specifications and industry terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the electric car without a license trade more effectively, making informed decisions that align with their business strategies and customer needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric car without driving licence trade Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Electric Car Without Driving Licence Trade?
The electric car without a driving licence market, particularly in the form of lightweight quadricycles, is witnessing significant growth globally. Factors driving this trend include increasing urbanization, a shift towards sustainable transportation, and evolving regulations that support the use of such vehicles. In many regions, especially in Europe, these vehicles are seen as an ideal solution for short-distance travel, particularly for younger drivers and those seeking alternatives to traditional cars. The appeal is particularly strong in densely populated urban areas where parking and traffic congestion are major concerns.
Emerging B2B tech trends include advancements in battery technology and electric drivetrains, making these vehicles more efficient and appealing to buyers. Companies are increasingly investing in electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure, including charging stations tailored for lightweight vehicles. For international B2B buyers, understanding the regulatory landscape is crucial, as compliance can vary significantly by region. For instance, while European markets have well-defined categories and regulations, other regions such as Africa and South America are still developing their frameworks, presenting both challenges and opportunities for market entry.
How is Sustainability Influencing B2B Sourcing in the Electric Car Without Driving Licence Sector?
Sustainability is a cornerstone of the electric car without a driving licence trade. As global concerns about climate change and environmental degradation rise, B2B buyers are prioritizing sustainable sourcing practices. The demand for ethical supply chains, which emphasize transparency and social responsibility, is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of business operations. Buyers are looking for suppliers that adhere to environmentally friendly practices, such as using recycled materials and renewable energy in manufacturing processes.
Green certifications are increasingly important in this sector. Suppliers that can demonstrate compliance with recognized standards, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, are more likely to gain trust from international buyers. The importance of sourcing ethically extends beyond just compliance; it also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty. As the market matures, B2B buyers should actively seek partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize sustainability and can provide verifiable credentials related to their environmental impact.
What is the Brief Evolution of the Electric Car Without Driving Licence Market?
The concept of electric cars without a driving licence has evolved significantly over the past two decades. Initially viewed as niche products, these lightweight quadricycles have gained traction due to increasing urbanization and the need for sustainable transport solutions. Early models were primarily basic vehicles with limited features, but advancements in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated options with enhanced safety features, longer ranges, and better performance.
Regulatory changes across various regions have also played a pivotal role in this evolution. For instance, in Europe, the introduction of the AM licence category has made it easier for younger drivers to access these vehicles. This evolution reflects a broader societal shift towards embracing electric mobility solutions that cater to diverse consumer needs, making the electric car without a driving licence an increasingly viable option for urban transportation. As the market continues to develop, B2B buyers must remain agile, adapting to trends and regulations that will shape the future of this sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric car without driving licence trade
-
How do I evaluate potential suppliers for electric cars without a driving license?
When evaluating suppliers, consider their experience in manufacturing electric vehicles, especially lightweight quadricycles. Request information on their certifications, production capacity, and compliance with international safety standards. Additionally, assess their track record through customer references and case studies. A reliable supplier should also provide clear communication and responsiveness to inquiries. It’s beneficial to conduct factory visits or audits if possible to verify their operations and quality assurance processes. -
What is the best electric car without a license for urban use?
The ideal electric car for urban environments is one that offers compact dimensions, a range sufficient for daily commuting, and ease of parking. Models like the Citroën Ami or Fiat Topolino are popular choices, featuring a maximum speed of 45 km/h and a range of approximately 75 km. Their lightweight design and maneuverability make them perfect for city driving, especially in areas with restricted access for larger vehicles. Evaluate your local market preferences and regulations to determine the best fit. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for electric cars without a license?
MOQs can vary significantly among suppliers, typically ranging from 10 to 50 units for electric cars without a license. Factors influencing MOQ include the manufacturer’s production capacity, model popularity, and customization options. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Smaller orders may be available but could come with higher per-unit costs, impacting your overall budget. -
What customization options are available for electric microcars?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for electric microcars, including color choices, interior materials, and additional features like enhanced safety systems or upgraded battery capacity. Some suppliers may also allow branding opportunities, such as adding your company logo. Discuss your requirements during the initial negotiations to ensure the supplier can meet your specifications and to understand any associated costs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electric cars without a license?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and your negotiation leverage. Common arrangements include a deposit upfront (usually 20-30%) with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans, especially for bulk orders. Ensure that all payment terms are clearly outlined in the purchase agreement to avoid any misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for electric cars without a license?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed documentation of the supplier’s quality control processes, including testing protocols for safety and performance. It’s beneficial to inquire about third-party certifications that validate their compliance with international standards. Consider implementing a quality inspection phase, where an independent inspector reviews the vehicles before shipment, ensuring they meet your specifications and regulatory requirements. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing electric cars without a license?
When importing electric cars, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Research the logistics providers who specialize in vehicle transportation and ensure they have experience with international shipments. Additionally, understand the documentation required for customs clearance, including import licenses and safety certifications. Plan for lead times in shipping and customs processing to align with your distribution strategy. -
What regulations should I be aware of when trading electric microcars internationally?
Each country has specific regulations regarding the importation of vehicles, including safety standards, emissions requirements, and licensing for drivers. Familiarize yourself with the laws in your target markets, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where regulations may differ significantly from Europe. Compliance with these regulations is crucial to avoid fines or confiscation of vehicles. Consult with legal experts or trade consultants to navigate these complexities effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
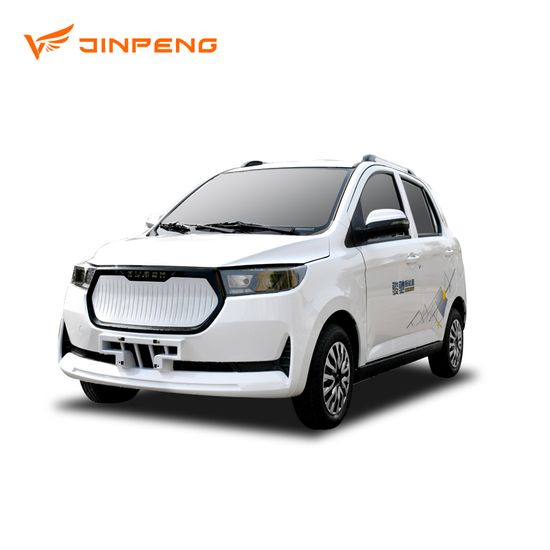
Top 8 Electric Car Without Driving Licence Trade Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – LSEVs for Elderly in China
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Electric vehicles that can be driven without a license in China are often referred to as LSEVs (Low Speed Electric Vehicles) or 老头乐 (old geezers delight). These vehicles are typically small, resembling scooters with an enclosed body, and are primarily used by elderly individuals in rural areas. They may not have safety and quality guarantees, and there are concerns about their lack of insurance an…
2. Desner – A05 Electric Car
Domain: en.clickpetroleoegas.com.br
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Italian electric car, Desner A05, costs R$64,5 thousand, can be driven by 14-year-olds without a driver’s license, classified as L6e quadricycle. Offers up to 120 km autonomy, maximum speed of 45 km/h, 3 kW engine, 7.2 kWh battery, recharges in 6 hours. Features include three doors, seating for two, trunk space, tablet-sized screen, digital cockpit, high-performance speakers, optional heating and …
3. Citroën – Ami Electric Car
Domain: dezeen.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Citroën Ami is an electric car available on a subscription service that does not require a driving license. It can be operated by individuals as young as 14 in France and 16 in other European countries, provided they have passed a road safety certificate. The car is classified as a fully electric quadricycle, capable of speeds up to 28 mph (45 km/h), with a range of up to 43 miles (70 km) on a sin…
4. Ami One – Key Features
Domain: m.economictimes.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Ami One is an urban mobility vehicle designed for intelligent economy. Key features include:
– Design: Symmetrical parts with identical doors, different opening directions for safety and access, identical bumpers, wings, rocker panels, and reversible Daytime Running Lights.
– Engine: 100% electric, charges in 2 hours, top speed of 30 mph (28 mph or 45 kmph), range of 60 miles, CO2 emissions of 0.
…
5. Movemnt – Microlino Lite Mini Electric Car
Domain: movemnt.net
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Micro Microlino Lite model, mini electric car, requires no driver’s license, designed for sustainable mobility, allows drivers as young as 14, top speed limited to 45 km/h, 12 hp (12 PS) electric motor, maximum speed of 28 mph (40 km/h), complies with L6e quadricycle regulations, goes on sale in Europe this spring.
6. Sinotruk – Solar Electric Car
Domain: cn-sinotruk.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”:”Low Price Chinese 4 Wheel Green Energy Cheap Solar Electric Car Without Driving Licence”,”SKU”:”11544″,”Category”:”Electric car”,”Description”:”Solar-powered electric vehicle that converts solar energy into electric energy, reducing costs and being environmentally friendly.”,”Features”:[“Energy-saving and environment-friendly”,”Charge anytime when there is sunlight”,”Lead-acid bat…
7. Facebook – Electric Vehicle Licensing
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Getting your driver’s license in an Electric Car is becoming a reality in SA. Motorists are concerned about EV range and the impact of load shedding on electric cars. Transitioning to an electric vehicle requires a change in mindset from liters to kilowatts per 100km.
8. ICICI Lombard – Insurance Solutions
Domain: icicilombard.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: ICICI Lombard offers various insurance products including Car Insurance, Two Wheeler Insurance, Travel Insurance, Health Insurance, Home Insurance, Third Party Car Insurance, and Third Party Two Wheeler Insurance. The blog discusses the necessity of a driving license for operating electric vehicles in India, stating that a valid driving license is mandatory for driving electric four-wheelers. It e…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric car without driving licence trade
As the market for electric cars without a driving license gains momentum, strategic sourcing becomes essential for B2B buyers aiming to capitalize on this growing trend. These lightweight quadricycles, designed for urban mobility and environmentally conscious consumers, offer a unique solution that caters to various demographics, from teenagers to the elderly. By understanding the specifications and pricing of leading models, businesses can make informed purchasing decisions that align with market demands and regulatory requirements.
International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize partnerships with reliable manufacturers and suppliers to ensure access to quality vehicles. The potential for profitability in this sector is significant, especially as urbanization continues to drive the need for compact, efficient transportation solutions.
Looking ahead, the electric car market without a license is poised for expansion, fueled by increasing consumer interest in sustainable mobility options. Now is the time for B2B buyers to engage with industry stakeholders, explore innovative financing options, and position themselves strategically to meet future demand. Embrace this opportunity to lead in the evolving landscape of electric mobility.