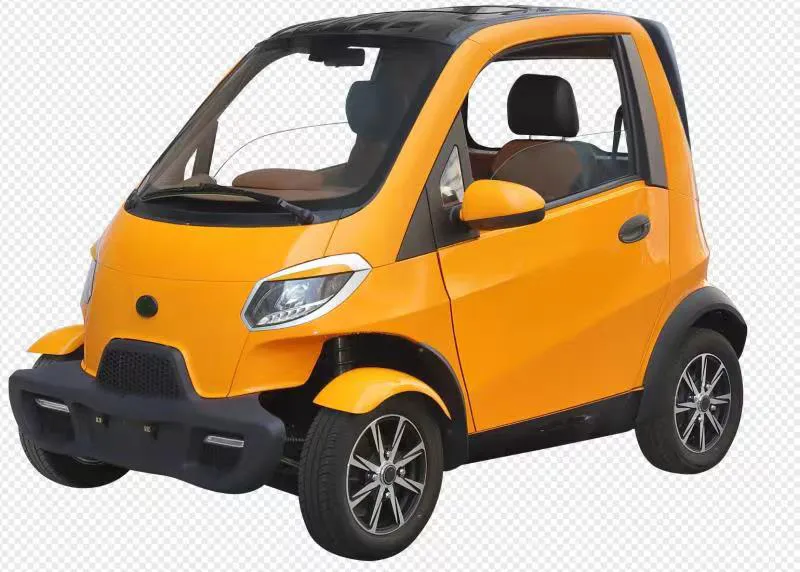
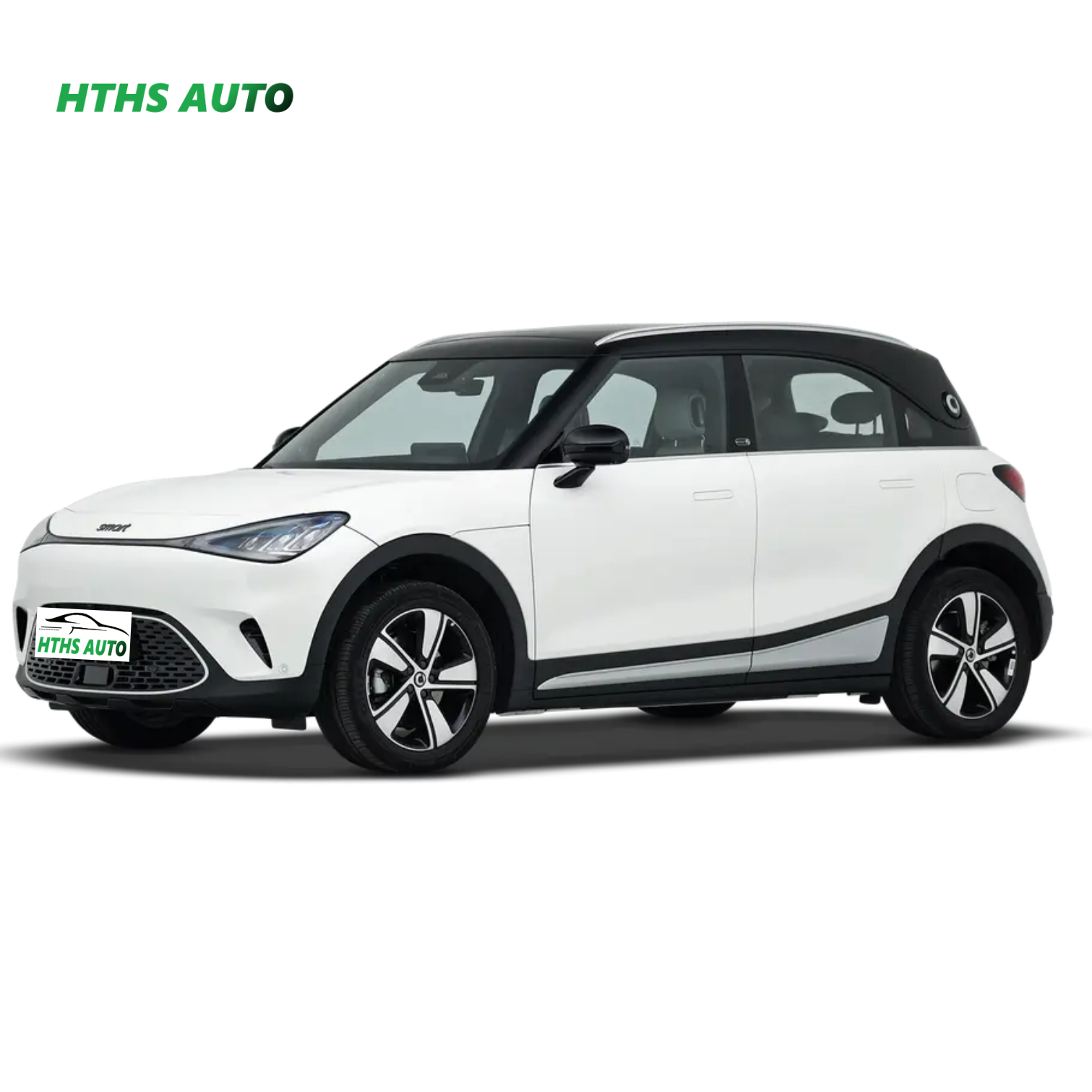
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric car for teenagers
As the demand for sustainable transportation solutions grows, navigating the global market for electric cars tailored for teenagers presents a unique challenge for B2B buyers. Sourcing electric vehicles (EVs) that meet the needs of young drivers involves understanding not only the features that appeal to this demographic—such as affordability, safety, and technological advancements—but also the distinct market dynamics across regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This comprehensive guide addresses these challenges by exploring various types of electric cars suitable for teenagers, their applications, and essential factors for supplier vetting.
With a focus on cost considerations, long-term savings, and the importance of environmental consciousness among today’s youth, this guide equips international buyers with actionable insights. From evaluating the latest models that offer impressive ranges and advanced safety features to understanding leasing options and the growing market for used EVs, you will find a wealth of information designed to empower informed purchasing decisions.
By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of sourcing electric cars for teenagers, ensuring that they meet both market demands and the expectations of young drivers. Embrace the opportunity to contribute to a more sustainable future while catering to the needs of the next generation of drivers.
Understanding electric car for teenagers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compact Electric Vehicles | Smaller size, lower price point, suitable for city driving | Ideal for urban car-sharing services | Pros: Affordable, easy to park. Cons: Limited space and range. |
| Mid-range Electric Sedans | Balanced range, comfort, and technology features | Family-focused leasing and rental services | Pros: Good range, family-friendly. Cons: Higher upfront cost. |
| Electric SUVs | Spacious interiors, advanced safety features, versatile | Corporate fleets, family-oriented businesses | Pros: Versatile, safe for families. Cons: More expensive, heavier. |
| Used Electric Vehicles | Lower price point, varied models, good for budget-conscious buyers | Resale markets, budget leasing options | Pros: Cost-effective, eco-friendly. Cons: Potential battery degradation. |
| High-Performance Electric Cars | Advanced technology, superior performance, luxury features | Premium rental services, corporate gifting | Pros: Impressive range and speed. Cons: High initial investment. |
What Are the Characteristics of Compact Electric Vehicles?
Compact Electric Vehicles (CEVs) are designed for efficiency and affordability, making them ideal for teenagers who primarily drive in urban settings. With their smaller size, they excel in maneuverability and parking, addressing the challenges faced by new drivers. For B2B buyers, CEVs are particularly relevant for car-sharing services targeting younger demographics or urban commuters. The lower price point and operational costs make them attractive for fleet management, although their limited range may restrict longer trips.
How Do Mid-range Electric Sedans Cater to Family Needs?
Mid-range Electric Sedans offer a balance of comfort, technology, and driving range, making them suitable for families with teenage drivers. These vehicles often come equipped with advanced safety features, enhancing the driving experience for new drivers. B2B applications include family-focused leasing programs and rental services aimed at parents seeking reliable vehicles for their children. While they provide a good range for daily commutes, the higher upfront costs can be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
Why Are Electric SUVs Popular Among Families?
Electric SUVs are increasingly favored for their spacious interiors and advanced safety features, making them a practical choice for families with teenagers. They provide ample room for passengers and cargo, which is beneficial for school activities and family outings. B2B buyers in the corporate sector may find these vehicles suitable for family-oriented businesses or corporate fleets, where safety and versatility are paramount. However, the higher price point and weight of these vehicles can be drawbacks for some buyers.
What Advantages Do Used Electric Vehicles Offer?
Used Electric Vehicles (UEVs) present a cost-effective option for budget-conscious families looking to purchase their teenager’s first car. With prices trending downward, UEVs provide excellent value, especially when considering federal incentives. B2B applications for UEVs include resale markets and budget leasing options for businesses aiming to offer affordable transportation solutions. While they are eco-friendly and economical, potential buyers should consider battery life and maintenance history to avoid issues related to battery degradation.
How Do High-Performance Electric Cars Enhance the Driving Experience?
High-Performance Electric Cars are designed for those seeking superior technology, speed, and luxury features. They appeal to teenagers interested in advanced driving experiences and cutting-edge technology. B2B applications include premium rental services targeting affluent customers or corporate gifting for executives. Despite their impressive range and performance, the high initial investment can be a significant barrier for many buyers, particularly families looking for practical starter vehicles for their teens.
Key Industrial Applications of electric car for teenagers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric car for teenagers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Education | School transportation services for teens | Reduces fuel costs and maintenance, promotes eco-friendly practices | Availability of charging infrastructure, fleet management solutions |
| Retail | Incentives for teen customers purchasing EVs | Attracts environmentally conscious consumers, boosts sales | Partnerships with EV manufacturers, financing options for buyers |
| Insurance | Tailored insurance products for electric vehicles | Lower risk profiles lead to competitive premiums | Data on safety features, battery life, and maintenance costs |
| Automotive Dealerships | Leasing programs for first-time teen drivers | Expands customer base, increases turnover of EV inventory | Flexible leasing terms, maintenance packages, and after-sales support |
| Government & NGOs | Subsidized programs for promoting EVs among young drivers | Supports environmental initiatives, enhances public image | Compliance with local regulations, partnerships for charging infrastructure |
How Can Educational Institutions Benefit from Electric Cars for Teenagers?
Educational institutions can utilize electric cars for school transportation services aimed at teenagers. By implementing electric vehicle (EV) fleets, schools can significantly reduce fuel costs and maintenance expenses while promoting sustainability. This initiative can also enhance the school’s reputation as a forward-thinking entity committed to environmental stewardship. Buyers in this sector must consider the availability of charging infrastructure and effective fleet management solutions to optimize operations.
What Advantages Do Retailers Gain from Promoting Electric Vehicles to Teenagers?
Retailers can capitalize on the growing trend of eco-conscious consumers by offering incentives for teenagers purchasing electric vehicles. This strategy not only attracts a younger demographic but also aligns with broader sustainability goals. By integrating EV promotions into their marketing campaigns, businesses can boost sales and enhance brand loyalty. Retailers should focus on establishing partnerships with EV manufacturers and providing financing options that make purchasing more accessible for young buyers.
How Can the Insurance Sector Tailor Products for Electric Cars Targeting Teen Drivers?
The insurance industry can create specialized insurance products for electric vehicles targeting teen drivers. Given the advanced safety features and lower risk profiles associated with EVs, insurers can offer competitive premiums, making electric cars more appealing to young drivers. Key considerations for insurance providers include collecting data on safety features, battery life, and maintenance costs to accurately assess risk and pricing.
What Opportunities Exist for Automotive Dealerships with Electric Car Leasing for Teens?
Automotive dealerships can benefit from offering leasing programs specifically designed for first-time teen drivers. These programs can enhance customer engagement and increase the turnover rate of EV inventory. By providing flexible leasing terms and comprehensive maintenance packages, dealerships can attract young drivers and their families. It is essential for dealerships to ensure robust after-sales support to build trust and encourage repeat business.
How Can Governments and NGOs Promote Electric Cars Among Young Drivers?
Governments and NGOs can play a pivotal role in promoting electric cars among teenagers through subsidized programs. These initiatives can help lower the cost barrier for young drivers, encouraging them to adopt sustainable practices early in life. By supporting the development of charging infrastructure and aligning with environmental goals, such programs can enhance public image and community engagement. Buyers in this sector need to ensure compliance with local regulations and foster partnerships for effective implementation.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric car for teenagers’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Cost Constraints in Electric Vehicle Purchases for Teenagers
The Problem: B2B buyers, particularly educational institutions and fleet managers looking to provide electric vehicles (EVs) for teen drivers, often face significant budget constraints. The upfront costs of new electric vehicles can be prohibitive, especially in markets with fluctuating currency values and economic instability. This financial challenge is compounded by the need for buyers to ensure that the vehicles they choose are both safe and practical for young drivers, who may not have prior driving experience.
The Solution: To effectively navigate these financial constraints, buyers should explore the used electric vehicle market. Many used EVs are now available at significantly lower prices due to federal incentives aimed at promoting cleaner transportation. For instance, consider sourcing pre-owned models from certified dealers who can provide vehicle history reports and warranties. Additionally, leveraging partnerships with local governments or non-profits may unlock funding opportunities specifically designated for youth transportation initiatives. Buyers should also focus on models known for reliability and low maintenance costs, such as the Nissan Leaf or Chevrolet Bolt, which offer robust safety features and are well-regarded for their value retention in the second-hand market. By prioritizing these strategies, B2B buyers can maximize their budgets while ensuring access to safe and environmentally friendly vehicles for teenagers.
Scenario 2: Addressing Range Anxiety in Electric Cars for Young Drivers
The Problem: A common concern among B2B buyers, such as schools or youth organizations, is the issue of range anxiety associated with electric vehicles. Many teenagers are inexperienced drivers, and the fear of running out of battery power during a trip can deter organizations from adopting EVs. This is particularly relevant in regions where charging infrastructure may be limited or inconsistent, leading to hesitation in transitioning to electric options.
The Solution: To alleviate concerns about range anxiety, B2B buyers should opt for electric models with extended range capabilities and ensure robust charging solutions are in place. When selecting vehicles, focus on those that provide at least 200 miles of range per charge, such as the Kia EV6 or Volkswagen ID.4. Additionally, establishing partnerships with local charging station providers can enhance accessibility, allowing for installations at schools or community centers. Buyers should also consider implementing a charging management system that tracks vehicle usage and charging patterns, ensuring that vehicles are always ready for use. Educating both drivers and parents about the practicality of daily driving ranges can further mitigate anxiety, emphasizing that the average teen driver typically covers less than 40 miles per day.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Safety Features Meet Teenage Driver Needs
The Problem: Safety is a paramount concern for B2B buyers when selecting electric vehicles for teenagers. Many young drivers are still in the learning phase and may not be equipped to handle high-stakes driving situations. Buyers must ensure that the vehicles chosen come equipped with advanced safety technologies to protect these novice drivers, as well as to comply with insurance requirements.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize electric cars that come standard with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Features such as automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assist, and adaptive cruise control are crucial for enhancing safety for young drivers. When researching potential models, create a checklist based on safety ratings from reputable sources such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) or Euro NCAP. Additionally, establishing a comprehensive driver education program that includes training on how to utilize these safety features can further enhance the safety of young drivers. Collaborating with insurance companies to understand potential discounts for vehicles equipped with these advanced features can also provide financial incentives for B2B buyers. By focusing on safety and education, organizations can foster a safer driving environment for teenage drivers and mitigate risks associated with inexperience.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric car for teenagers
What Are the Key Materials for Electric Cars Designed for Teenagers?
When selecting materials for electric cars aimed at teenage drivers, it is essential to consider properties that enhance safety, durability, and overall performance. The following analysis focuses on four common materials used in electric vehicles (EVs): aluminum, high-strength steel, plastics, and lithium-ion batteries. Each material has unique characteristics that affect the vehicle’s performance, cost, and suitability for young drivers.
How Does Aluminum Contribute to Electric Car Performance?
Aluminum is widely used in electric car manufacturing due to its lightweight properties, which contribute to improved energy efficiency and range. Key properties include excellent corrosion resistance and a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for structural components and body panels.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight nature enhances vehicle performance and range, which is particularly beneficial for teenage drivers who may not have extensive driving experience. It also offers good recyclability, aligning with the environmental values of many young consumers.
Cons: The primary drawback of aluminum is its cost, which can be higher than traditional steel. Additionally, manufacturing processes for aluminum can be more complex, potentially impacting production timelines.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and air, making it suitable for exterior applications. However, care must be taken in joining aluminum with other materials to prevent galvanic corrosion.
International Considerations: B2B buyers should be aware of compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN for aluminum alloys. In regions like Europe and the Middle East, there are increasing regulations around lightweight materials for energy efficiency.
What Role Does High-Strength Steel Play in Electric Cars?
High-strength steel is another material commonly used in electric vehicles, particularly for safety-critical components like the chassis and structural reinforcements. It offers excellent tensile strength and impact resistance.
Pros: High-strength steel is relatively cost-effective compared to aluminum and provides robust safety features, which are crucial for inexperienced teenage drivers. Its durability ensures long-term performance and reliability.
Cons: The weight of high-strength steel can negatively impact the vehicle’s overall efficiency and range. This is a significant consideration for electric vehicles, where every kilogram matters.
Impact on Application: High-strength steel is compatible with various automotive applications, particularly in crash zones where energy absorption is vital.
International Considerations: Compliance with safety standards such as Euro NCAP in Europe is essential for high-strength steel components. B2B buyers should also consider the availability of high-strength steel grades in their respective markets.
How Are Plastics Utilized in Electric Vehicles?
Plastics are increasingly being used in electric vehicles for interior components, dashboards, and lightweight body panels. They offer versatility and can be engineered to meet specific performance criteria.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight, which can help improve overall vehicle efficiency. They can also be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative design solutions.
Cons: While plastics are generally resistant to corrosion, they can be less durable than metals and may degrade over time, especially when exposed to UV light.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for non-structural components and can be engineered for specific applications, such as sound dampening or thermal insulation.
International Considerations: B2B buyers should ensure that plastics used comply with environmental regulations, particularly in Europe, where there are stringent laws regarding plastic waste and recycling.
What Are the Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries in Electric Cars?
Lithium-ion batteries are the heart of electric vehicles, providing the necessary energy storage for propulsion. They are known for their high energy density and efficiency.
Pros: Lithium-ion batteries offer excellent energy capacity, allowing for longer driving ranges, which is crucial for teenage drivers who may be commuting to school or extracurricular activities.
Cons: The cost of lithium-ion batteries remains high, and they require careful management to ensure safety and longevity. Additionally, they can pose environmental challenges at the end of their life cycle.
Impact on Application: Lithium-ion batteries are compatible with electric vehicle applications and are designed to withstand a range of operating conditions, including temperature variations.
International Considerations: B2B buyers must consider compliance with international battery standards and recycling regulations, especially in Europe and North America, where there are strict guidelines for battery disposal and recycling.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Cars for Teenagers
| Material | Typical Use Case for Electric Car for Teenagers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels and structural components | Lightweight, improves range | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| High-Strength Steel | Chassis and safety reinforcements | Cost-effective, robust safety | Heavier, impacts efficiency | Medium |
| Plastics | Interior components and lightweight panels | Versatile, lightweight | Less durable, UV degradation | Low |
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | Energy storage for propulsion | High energy density, longer range | High cost, environmental challenges | High |
By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with the needs of teenage drivers while adhering to international standards and regulations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric car for teenagers
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electric Cars for Teenagers?
Manufacturing electric cars designed for teenagers involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets safety, affordability, and performance standards. The primary stages of manufacturing include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each of these stages employs specific techniques tailored to the unique requirements of electric vehicles (EVs).
How Is Material Prepared for Electric Car Production?
The manufacturing process begins with material preparation, which includes sourcing and processing raw materials such as metals, plastics, and battery components. Key materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel are essential for battery production. Suppliers must ensure that these materials are ethically sourced and comply with international standards to avoid issues related to sustainability and human rights.
In addition, manufacturers often adopt lightweight materials such as aluminum and advanced composites to enhance vehicle efficiency and range. This is particularly important for electric cars aimed at teenagers, as lighter vehicles generally have better energy efficiency and handling characteristics.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Electric Car Components?
Forming processes transform raw materials into usable parts. Techniques such as stamping, extrusion, and molding are common in the production of car body panels, battery housings, and interior components. For instance, stamping is used to create complex shapes for body panels, while injection molding is often employed for producing plastic parts like dashboards and trims.
Advanced manufacturing technologies, including 3D printing, are increasingly utilized to produce prototypes and custom parts. This flexibility allows manufacturers to innovate quickly and adapt to market trends, particularly in the youth segment where design preferences can change rapidly.
How Does the Assembly Process Work for Teen-Focused Electric Cars?
The assembly stage is where various components come together to form the complete vehicle. This involves integrating the powertrain, electrical systems, and safety features. Manufacturers focus on modular assembly techniques, which allow for easier repairs and upgrades.
For electric cars designed for teenagers, emphasis is placed on incorporating advanced safety technologies such as automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assistance, and comprehensive infotainment systems. These features not only enhance safety but also appeal to the tech-savvy nature of younger drivers.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied in Electric Car Manufacturing?
Finishing processes enhance the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal and protect it from environmental factors. Techniques such as painting, coating, and surface treatment are employed. For electric cars, manufacturers often use eco-friendly paints and coatings that reduce volatile organic compounds (VOCs), aligning with the values of environmentally conscious consumers.
In addition, battery packs undergo specialized finishing procedures to ensure they are sealed and insulated properly, which is crucial for safety and performance. Quality control checks during the finishing stage are vital to ensure that each vehicle meets stringent safety standards.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for Electric Cars?
Quality assurance is a critical component of the manufacturing process, especially for electric vehicles aimed at teenagers. The complexity of EV technology necessitates rigorous quality control measures to guarantee safety and reliability.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems are pivotal in ensuring that manufacturers adhere to best practices. Compliance with these standards is essential for B2B buyers, as they provide a framework for consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
Additionally, regional certifications like CE marking in Europe and API standards for components ensure that products meet local regulatory requirements. Buyers should verify that their suppliers hold the necessary certifications to avoid legal and operational issues.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Electric Car Production?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process. Incoming Quality Control (IQC) checks raw materials upon arrival, ensuring that they meet specified standards. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) monitors production processes in real time, allowing for immediate corrective actions if deviations occur. Finally, Final Quality Control (FQC) ensures that the finished product undergoes comprehensive testing before it is dispatched.
Common testing methods include stress testing for battery packs, crash testing for safety features, and performance assessments for driving dynamics. These tests are crucial for ensuring the vehicle’s reliability and safety, especially for inexperienced teenage drivers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers. Regular audits are essential to assess compliance with international standards and internal quality protocols. Buyers should request audit reports that detail the findings and any corrective actions taken.
Engaging third-party inspection services can also provide an unbiased evaluation of manufacturing quality. These inspections can occur at various stages of production, offering insights into the supplier’s adherence to quality standards and manufacturing practices.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and quality standards is essential. Variations in quality expectations and certifications can complicate the procurement process.
Buyers should familiarize themselves with specific regional requirements, such as emission standards and safety regulations, which may differ significantly from one country to another. Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences may impact communication regarding quality expectations, necessitating clear and consistent dialogue between buyers and suppliers.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for electric cars targeted at teenagers are multifaceted and require careful consideration. By understanding the stages of manufacturing, the importance of quality control, and how to verify supplier practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they procure safe, reliable, and appealing electric vehicles for young drivers. As the market for electric cars continues to grow, being knowledgeable about these processes will provide a competitive edge in navigating this evolving landscape.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric car for teenagers’
Introduction
As the demand for electric vehicles (EVs) continues to rise globally, procuring electric cars specifically for teenagers presents unique challenges and opportunities for B2B buyers. This checklist aims to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that the selected vehicles not only meet safety and budgetary requirements but also align with the values of younger drivers.
Step 1: Identify Budget Constraints
Establishing a clear budget is essential when sourcing electric cars for teenagers. Consider both the upfront costs and the total cost of ownership, including insurance, charging infrastructure, and maintenance. Given the price variations across regions, it’s vital to account for local market conditions and potential incentives for electric vehicle purchases.
Step 2: Assess Safety Features
Safety is paramount when selecting vehicles for young drivers. Look for models equipped with advanced safety features such as automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assist, and collision warning systems. These technologies not only enhance the safety of teenage drivers but also provide peace of mind for parents and guardians.
Step 3: Evaluate Driving Range and Charging Options
Understanding the driving range of the vehicles is critical, especially for teenagers who may have varied driving patterns. Aim for models with a range that accommodates daily commutes and extracurricular activities without frequent recharging. Additionally, assess the availability of home and public charging stations, as this can significantly impact the practicality of an EV.
- Sub-bullet: Check local charging infrastructure and home charging options.
- Sub-bullet: Research EV models that offer fast-charging capabilities for convenience.
Step 4: Research Vehicle Reliability and Maintenance
Electric vehicles typically require less maintenance than their gas-powered counterparts, but reliability is still a key factor. Investigate the manufacturer’s reputation for reliability and customer satisfaction. Look for warranties that cover the battery and powertrain, as these components are critical for long-term usage.
Step 5: Consider Lease vs. Purchase Options
Evaluate whether leasing or purchasing is more suitable for your target demographic. Leasing often provides access to newer models with the latest technology at lower monthly payments, making it an attractive option for teenagers. However, purchasing may be more cost-effective in the long run, especially with the declining prices of used EVs.
- Sub-bullet: Analyze the total cost of leasing versus purchasing over the expected duration of use.
- Sub-bullet: Investigate potential tax credits or incentives for both leasing and purchasing.
Step 6: Check for Environmental Impact and Sustainability Initiatives
Many young drivers are environmentally conscious, making it important to consider the sustainability credentials of the vehicles. Look for manufacturers that prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials in production and offering carbon offset programs. This not only aligns with the values of the younger generation but also enhances brand reputation.
Step 7: Solicit Feedback from Current Users
Gather insights from current owners of the vehicles you are considering. This can be achieved through online reviews, forums, or direct interviews. Understanding real-world experiences regarding performance, comfort, and reliability will provide a clearer picture and help in making an informed decision.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make strategic and informed decisions when sourcing electric cars for teenagers, ensuring that they meet both practical and ethical considerations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric car for teenagers Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Electric Cars for Teenagers?
When evaluating the cost structure for electric cars targeted at teenagers, several critical components must be analyzed. Materials comprise the largest expense, particularly for batteries, which utilize expensive raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. The labor cost includes assembly line workers and skilled technicians necessary for high-tech components, which can be substantial due to the specialized skills required. Manufacturing overhead covers factory costs, utilities, and administrative expenses, while tooling costs relate to the machinery used to produce specific components, particularly the battery and drivetrain systems.
Quality Control (QC) is another essential cost component. Given the safety concerns associated with teenage drivers, robust QC processes are vital to ensure all vehicles meet stringent safety standards. Finally, logistics costs, which encompass transportation and warehousing, can fluctuate based on the location of suppliers and the final delivery points. Margins in the electric vehicle sector can vary, often influenced by competition and market demand.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Electric Cars for Teenagers?
Several factors can significantly influence pricing in the electric vehicle market. Volume or Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) is a major consideration; bulk orders often come with discounts, allowing B2B buyers to negotiate better prices. Specifications and customization also play a role; for instance, adding advanced safety features or unique designs can increase costs. The choice of materials directly affects pricing, especially if premium components are selected for enhanced performance or safety.
Quality certifications can lead to higher costs as manufacturers may need to invest more in compliance and testing to achieve these standards. Supplier factors, such as reliability and reputation, can also affect pricing; established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record. Lastly, the choice of Incoterms can impact the total landed cost, influencing logistics and risk management strategies.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Electric Car Prices?
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding negotiation tactics can lead to significant cost savings. Start by conducting thorough market research to grasp current pricing trends and competitor offerings. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations, allowing them to leverage competitive pricing against suppliers.
Focusing on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is essential. This includes not only the purchase price but also factors such as maintenance, fuel savings, and resale value. Electric cars typically offer lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts, which can be a selling point in negotiations.
Buyers should also be aware of pricing nuances based on geographical factors. For instance, import tariffs, local taxes, and incentives can vary widely between countries. Buyers in regions with incentives for electric vehicle purchases may negotiate more effectively by emphasizing the long-term cost benefits associated with EV ownership.
What Should International Buyers Consider When Sourcing Electric Cars?
International buyers must navigate a complex landscape when sourcing electric cars for teenagers. It’s crucial to account for currency fluctuations that can affect pricing, especially in volatile markets. Understanding local regulations regarding electric vehicles, including emissions standards and safety requirements, is vital to ensure compliance and avoid costly penalties.
Additionally, buyers should consider establishing long-term relationships with suppliers to secure better pricing and terms. Leveraging regional partnerships can also facilitate smoother logistics and potentially lower costs through shared resources.
Conclusion
While the initial costs associated with electric cars for teenagers can be significant, understanding the various cost components and price influencers allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions. By employing effective negotiation strategies and considering the total cost of ownership, international buyers can effectively manage expenses while contributing to a sustainable future. It is advisable to consult with local experts to navigate specific regional nuances, ensuring a successful sourcing strategy.
Disclaimer: Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and regional factors.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric car for teenagers With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Electric Cars for Teenagers
In the evolving landscape of transportation options for teenagers, electric vehicles (EVs) have gained considerable attention due to their numerous benefits, including lower operational costs and environmental consciousness. However, it is essential to consider viable alternatives that may also suit the needs of young drivers. This analysis compares electric cars for teenagers with two prominent alternatives: used gasoline-powered cars and ride-sharing services.
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Car For Teenagers | Used Gasoline-Powered Car | Ride-Sharing Service |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Smooth acceleration, quiet operation, advanced safety features | Varied performance based on model, potential for higher emissions | No personal vehicle performance; dependent on service quality |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost; potential savings in fuel and maintenance | Lower initial cost; higher long-term fuel and maintenance expenses | Pay-per-use model; costs can accumulate quickly with frequent use |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure; may involve higher insurance costs | Readily available, no special infrastructure needed | Simple to use via apps; no ownership responsibilities |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts | Higher maintenance needs, especially for older models | No maintenance responsibilities; costs are covered by service provider |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for environmentally conscious families and daily commuting | Suitable for budget-conscious buyers needing immediate transportation | Best for infrequent use or urban environments with high traffic |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Used Gasoline-Powered Cars?
Used gasoline-powered cars remain a popular choice for many first-time drivers due to their affordability and availability. While they generally have a lower initial purchase price compared to new electric vehicles, they come with higher long-term operational costs, including fuel, insurance, and maintenance. Older models may require frequent repairs, which can add to the overall expense. Additionally, they do not provide the same environmental benefits as EVs, making them less appealing to eco-conscious families.
How Do Ride-Sharing Services Compare to Electric Cars for Teenagers?
Ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft offer a flexible transportation solution without the need for car ownership. This model is particularly advantageous for teenagers who may not drive daily or who live in urban areas where public transport is more accessible. However, the costs can accumulate quickly, especially for regular use, and there is no control over the vehicle’s safety features or performance. Additionally, ride-sharing may not instill the same sense of responsibility and independence that comes with owning a car, which is an important factor for many teenagers and their parents.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Transportation Solution for Teenagers
When evaluating transportation options for teenagers, B2B buyers should consider various factors, including budget constraints, safety features, maintenance needs, and the environmental impact of their choices. Electric cars stand out for their long-term savings and eco-friendliness, making them an attractive option for families committed to sustainability. However, used gasoline-powered cars and ride-sharing services present viable alternatives depending on immediate needs and financial considerations. Ultimately, the best choice will align with the values and lifestyle of the family while addressing the practicalities of teenage driving.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric car for teenagers
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Electric Cars for Teenagers?
When considering electric vehicles (EVs) for teenagers, several technical properties are crucial for ensuring safety, performance, and cost-effectiveness. Understanding these specifications helps B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with the needs of younger drivers.
1. Battery Capacity (kWh)
Battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), indicates the amount of energy stored in the battery and directly influences the vehicle’s range. For teenagers, a battery capacity of around 30-60 kWh is often sufficient, offering a range that supports daily commuting without frequent charging. This specification is vital for B2B buyers as it affects both the initial purchase price and long-term operational costs.
2. Electric Range (miles)
The electric range refers to how far a vehicle can travel on a single charge. For teen drivers, a range of 100-250 miles is generally ideal, allowing for daily use without anxiety about running out of power. Understanding range is essential for B2B buyers to match vehicle capabilities with the driving habits of young users, ensuring practicality and convenience.
3. Charging Time (hours)
Charging time indicates how long it takes to recharge the vehicle’s battery. Generally, Level 1 chargers (standard home outlets) take longer (up to 20 hours), while Level 2 chargers (240V outlets) can recharge in 4-8 hours. Fast DC chargers can complete charging in under an hour. B2B buyers should consider the charging infrastructure available to teenage users to ensure accessibility and reduce downtime.
4. Safety Ratings
Safety ratings assess how well a vehicle protects its occupants in the event of a collision. Organizations like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) provide these ratings. For teen drivers, vehicles with high safety ratings (5-star ratings) are recommended, as they often come equipped with advanced safety features like automatic emergency braking and lane-keeping assist. B2B buyers must prioritize safety to meet the expectations of parents and guardians.
5. Weight and Size Class
The weight and size class of a vehicle affect its handling, maneuverability, and energy efficiency. Lighter vehicles generally offer better efficiency and handling, which is beneficial for inexperienced drivers. For B2B buyers, selecting compact or subcompact electric cars can be advantageous, as they are easier for teens to drive and park.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Electric Vehicle Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is crucial for B2B buyers to navigate the electric vehicle market effectively. Here are some essential trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the EV industry, OEMs are responsible for the design and production of electric vehicles, including their battery systems and electronic components. Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify quality and reliability in the vehicles they consider.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B transactions involving electric cars, knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases to meet demand without overcommitting financial resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. In the context of electric vehicles, an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms from various manufacturers, ensuring they receive competitive offers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B buyers, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk during transport, particularly when sourcing electric vehicles from different regions.
5. EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment)
EVSE refers to the equipment used to charge electric vehicles, which includes charging stations and related infrastructure. For B2B buyers, understanding EVSE options is critical for ensuring that the electric cars purchased can be charged conveniently and efficiently.
Conclusion
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with electric vehicles for teenagers is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on battery capacity, electric range, charging time, safety ratings, and vehicle size, buyers can ensure they are selecting the right vehicles for young drivers. Familiarity with industry terms such as OEM, MOQ, RFQ, Incoterms, and EVSE will further enhance decision-making and facilitate smoother transactions in the growing EV market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric car for teenagers Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Electric Car for Teenagers Sector?
The electric vehicle (EV) market for teenagers is witnessing transformative growth, driven by several global factors. First, the increasing awareness of environmental sustainability among younger generations is propelling demand for electric cars as first vehicles. This demographic is more environmentally conscious than previous generations, often prioritizing eco-friendly choices. Moreover, governments worldwide are incentivizing EV purchases through tax credits and rebates, making these vehicles more accessible.
In regions like Africa and South America, the potential for EV adoption is amplified by the growing infrastructure for charging stations, which is gradually overcoming range anxiety. Meanwhile, in Europe, particularly Germany, regulations are pushing automakers to produce more affordable models aimed at younger drivers. The emergence of technology-focused sourcing trends, including connected vehicle technology and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), is shaping the market landscape. B2B buyers should look for partnerships with manufacturers that offer not only cost-effective models but also the latest safety features to appeal to both teens and their parents.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Electric Car Market for Teenagers?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the electric car for teenagers sector, with a growing emphasis on ethical sourcing practices. The environmental impact of EVs is significantly lower than that of traditional vehicles, primarily due to reduced carbon emissions and lower maintenance requirements. However, B2B buyers must also consider the source of materials used in manufacturing these vehicles. Lithium, cobalt, and other essential minerals for EV batteries often come from regions with questionable labor practices and environmental concerns.
Thus, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should seek manufacturers committed to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and ensuring fair labor conditions. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to the Responsible Minerals Initiative can serve as indicators of a company’s commitment to sustainability. By prioritizing suppliers who maintain these standards, businesses can align with the values of environmentally conscious consumers and contribute positively to the global market.
What Has Been the Evolution of Electric Cars for Teenagers?
The evolution of electric cars targeted at teenagers has been significant over the past two decades. Initially viewed as niche products, EVs have evolved into practical, affordable, and stylish options for young drivers. Early models like the Nissan Leaf paved the way by demonstrating the viability of electric vehicles, but advancements in battery technology and design have led to a new wave of offerings that cater to the preferences of today’s youth.
As manufacturers have recognized the potential market for electric cars among younger drivers, they have increasingly focused on affordability, safety, and features appealing to tech-savvy teens. Innovations such as enhanced safety features and connectivity options have made these vehicles more attractive, while ongoing reductions in production costs have made EVs more accessible. This evolution reflects a broader trend in the automotive industry towards sustainability and innovation, setting the stage for a future where electric vehicles are the norm for new drivers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric car for teenagers
-
How do I choose the right electric car for teenagers?
Selecting the right electric car for teenagers involves considering factors such as safety features, cost, range, and ease of use. Look for models with advanced safety technologies like automatic emergency braking and lane-keeping assist, which are crucial for new drivers. Affordability is key; evaluate both purchase prices and the long-term savings from lower fuel and maintenance costs. Additionally, consider the range of the vehicle—most teenagers won’t need a long-range model, making shorter-range options more budget-friendly and practical for daily commutes. -
What is the best budget-friendly electric car for teenagers?
For budget-conscious buyers, the Chevrolet Bolt EUV and Nissan Leaf are excellent choices. Both models provide reliable performance, reasonable range, and advanced safety features without breaking the bank. The Bolt EUV offers flexibility with its hatchback design, while the Leaf is well-suited for short daily drives. Additionally, the growing market for used EVs can yield affordable options, often enhanced by governmental incentives that lower upfront costs. -
What should I consider when sourcing electric cars for teenagers internationally?
When sourcing electric cars for teenagers in international markets, consider local regulations, charging infrastructure, and import tariffs. Research the environmental policies of the target countries, as these may affect EV adoption and government incentives. Additionally, assess the availability of parts and service networks to ensure long-term support for the vehicles. It’s also wise to gauge consumer preferences and safety standards that may vary by region. -
How can I vet suppliers for electric cars for teenagers?
To vet suppliers, start by checking their credentials and reputation in the market. Look for reviews, testimonials, and case studies from other B2B clients. Evaluate their compliance with international safety and quality standards, and request certifications to confirm. It’s also beneficial to visit their facilities or request a virtual tour to inspect their production processes. Establishing clear communication regarding expectations, delivery timelines, and after-sales support is essential for building a trustworthy relationship. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for electric cars?
Minimum order quantities for electric cars can vary significantly by supplier and model. Many manufacturers may offer flexible MOQs for B2B buyers, especially when starting a new partnership. However, larger orders often lead to better pricing and terms. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and negotiate terms that align with your business strategy. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing electric cars?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but most will require a deposit upfront, typically ranging from 10% to 30% of the total order value. Balance payments are often due before shipment or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans, especially for larger orders. Ensure that you clarify all payment terms, including currency, payment methods, and any potential penalties for late payments, to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for electric cars sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, work with suppliers who adhere to internationally recognized quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Request detailed product specifications and quality control processes during the manufacturing phase. It’s also beneficial to conduct pre-shipment inspections or hire third-party QA agencies to assess the vehicles before they leave the supplier’s facility. Establish clear benchmarks for performance, safety, and durability to maintain high-quality standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for importing electric cars?
When importing electric cars, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and local regulations. Choose a reliable logistics partner experienced in handling automotive imports. Understand the documentation required for customs, including import permits and compliance with local vehicle standards. Additionally, factor in lead times for shipping and the potential need for local distribution networks to deliver vehicles to your end customers efficiently.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Electric Car For Teenagers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Hyundai – Ioniq 5
Domain: insideevs.com
Introduction: [{‘name’: ‘Hyundai Ioniq 5’, ‘starting_MSRP’: ‘$41,800’, ‘EPA_range’: ‘220-303 miles’, ‘safety_rating’: ‘IIHS Top Safety Pick Plus’, ‘features’: [‘forward collision avoidance’, ‘blindspot monitoring’, ‘parking collision avoidance’, ‘smooth and comfortable ride’, ‘350 kW fast charging’]}, {‘name’: ‘Chevrolet Equinox EV’, ‘starting_MSRP’: ‘$33,600’, ‘EPA_range’: ‘285-319 miles’, ‘features’: [‘gradua…
2. Cars – Pros and Cons of EVs for Teen Drivers
Domain: cars.usnews.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Pros of EVs for Teen Drivers: Lower energy costs, lower maintenance costs, great safety features, lower environmental impact, familiarity with new technology, more variety than expected. Cons: Range and range anxiety, responsibility of charging, unknown battery capacity in used models, need for a home charger, affordability issues, fewer model choices, potential higher costs than gas cars, unfamil…
3. Used Electric Vehicles – Affordable First Cars
Domain: autos.yahoo.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Used electric vehicles (EVs) such as the Nissan Leaf, Chevrolet Bolt, and Hyundai Kona Electric are becoming popular choices for teens’ first cars due to their affordability, reliability, and low maintenance costs. A used 2016 Nissan Leaf was purchased for $8,000 with 20,000 miles and sold for $6,500 after three years, resulting in only $2,000 in depreciation and upkeep. EVs generally have fewer m…
4. Forbes – Teen Electric Vehicle Guide
Domain: forbes.com
Registered: 1993 (32 years)
Introduction: This company, Forbes – Teen Electric Vehicle Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Kia – Soul EV 2018
Domain: topspeed.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: 1. 2018 Kia Soul EV +
– Average Used Price: $14,532
– Power: 109-horsepower single-motor FWD
– Range: 11 miles (around-town)
– Safety Features: Standard rearview camera, stability control
– Tech: Kia’s UVO interface, Android Auto, Apple CarPlay, LED interior lighting
2. 2020 Kia Niro EV EX
– Average Used Price: $14,494
– Power: 201-horsepower single-motor FWD …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric car for teenagers
In the evolving landscape of electric vehicles (EVs) for teenagers, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for B2B buyers. Key takeaways include the importance of affordability, advanced safety features, and maintenance efficiency that EVs provide, making them an ideal choice for young drivers. As international markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, continue to embrace sustainability, the demand for accessible and environmentally-friendly transportation options is set to grow.
Buyers should focus on sourcing models that not only meet budget constraints but also cater to the technological preferences of today’s youth. The trend towards leasing and the availability of used EVs offer great opportunities to enhance product portfolios while addressing the financial concerns of families.
Looking ahead, the potential for innovation in electric vehicles is vast, with advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure poised to further enhance the appeal of EVs for young drivers. International B2B buyers are encouraged to capitalize on these trends by integrating strategic sourcing practices that align with market demands, ensuring they stay ahead in this dynamic sector. Embrace the future of mobility—source responsibly, and drive change.