Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric car ce certificate
In an increasingly competitive landscape, navigating the complexities of obtaining an electric car CE certificate poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. As electric vehicles (EVs) become a cornerstone of sustainable transportation, understanding the certification process is critical for manufacturers aiming to enter or expand within global markets, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide demystifies the essential components of the CE certification, providing valuable insights into the various types of certifications required, their applications, and the implications for market access.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, B2B buyers will find actionable strategies for vetting suppliers, understanding compliance costs, and ensuring adherence to safety and environmental standards. The CE marking serves not only as a passport to the European market but also as a benchmark for quality and reliability, which can significantly influence purchasing decisions. By arming themselves with knowledge on the intricacies of certification requirements and processes, buyers can make informed choices that enhance their competitive edge and foster sustainable partnerships.
This guide empowers B2B buyers to navigate the regulatory landscape with confidence, ensuring they are well-equipped to meet both local and international compliance standards while capitalizing on the growing demand for electric vehicles.
Understanding electric car ce certificate Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CE Marking | Mandatory for electric vehicles in the EU; ensures compliance with EU safety and health standards. | Entry into the European market; vehicle sales. | Pros: Widely recognized; essential for market access. Cons: Requires rigorous compliance process. |
| RoHS Compliance | Restricts hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, including EVs. | Component sourcing and manufacturing processes. | Pros: Promotes sustainability; protects human health. Cons: Increased complexity in sourcing compliant materials. |
| UKCA Marking | Required for products sold in Great Britain post-Brexit; mirrors CE marking requirements. | Selling in the UK market. | Pros: Necessary for compliance; similar to CE marking. Cons: Additional regulatory burden for manufacturers. |
| EMC Certification | Ensures electric vehicles do not interfere with other electronic devices and vice versa. | Product testing and validation. | Pros: Enhances product reliability; critical for consumer safety. Cons: Testing can be time-consuming and costly. |
| Vehicle Type Approval | Establishes a harmonized framework for the approval of motor vehicles across the EU. | Market entry and compliance verification. | Pros: Streamlines approval process; ensures safety standards. Cons: Can involve extensive documentation and testing. |
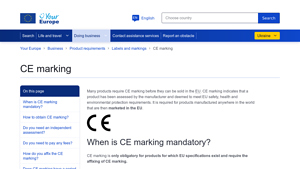
What is CE Marking and Why is it Essential for B2B Buyers?
CE marking is a crucial certification for electric vehicles entering the European market. It signifies compliance with EU health, safety, and environmental requirements, which are fundamental for ensuring product safety. B2B buyers must ensure their products meet these standards to access the vast EU market. The process involves appointing a notified body, preparing technical documentation, and undergoing a conformity assessment, making it a rigorous but necessary undertaking for manufacturers.
How Does RoHS Compliance Impact Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
RoHS compliance is vital for electric car manufacturers as it restricts the use of hazardous substances in components. This not only helps in reducing environmental pollution but also protects human health. B2B buyers need to consider the sourcing of compliant materials and the establishment of robust quality control systems. While it promotes sustainable practices, the complexity of ensuring compliance can increase the manufacturing process’s overall cost and time.
Why is UKCA Marking Important Post-Brexit?
UKCA marking has replaced CE marking for products sold in Great Britain after Brexit. It ensures that electric vehicles meet UK-specific safety and environmental standards. For B2B buyers, understanding the differences between CE and UKCA marking is essential for compliance when marketing products in the UK. The additional regulatory requirements may present challenges, but they are necessary for accessing this significant market.
What Role Does EMC Certification Play in Electric Vehicle Safety?
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) certification is crucial for electric vehicles to ensure they operate without interfering with other electronic devices. This certification is essential for B2B buyers focused on product reliability and consumer safety. While it enhances the credibility of the product, the testing process can be time-consuming and costly, requiring manufacturers to invest in thorough assessments to meet compliance.
How Does Vehicle Type Approval Facilitate Market Access?
Vehicle Type Approval establishes a standardized framework for motor vehicle approval across the EU. For B2B buyers, obtaining this certification is essential for demonstrating compliance with safety standards, thus facilitating smoother market entry. However, the process can involve extensive documentation and testing, which may be a barrier for some manufacturers. Understanding the requirements is key to successfully navigating the approval landscape.
Key Industrial Applications of electric car ce certificate
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric car ce certificate | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Compliance for electric vehicle production | Ensures market access to the EU and enhances consumer trust | Need for certified components and materials that meet CE standards |
| Charging Infrastructure | Certification of EV charging stations | Validates safety and interoperability, boosting user confidence | Sourcing from CE-compliant manufacturers to ensure adherence |
| Fleet Management | Certification for electric fleet vehicles | Facilitates compliance with local regulations, enhancing operational efficiency | Understanding local certification requirements and standards |
| Renewable Energy | Integration of electric vehicles with solar charging systems | Promotes sustainable practices and reduces carbon footprint | Ensuring all components are CE certified for compatibility |
| Export and Trade | CE marking for electric vehicles intended for European markets | Expands market opportunities and ensures compliance with EU regulations | Identifying notified bodies for conformity assessment and certification |
How is the electric car CE certificate utilized in automotive manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, the CE certificate is crucial for electric vehicle production. It ensures that vehicles meet EU safety, health, and environmental standards, which is a prerequisite for market entry. For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, understanding these compliance requirements is vital to avoid costly rejections or recalls. Manufacturers must source certified components and materials that align with CE standards, ensuring their production processes meet regulatory expectations.
What role does the CE certificate play in charging infrastructure?
The CE certificate is essential for the certification of electric vehicle charging stations, ensuring they comply with safety and interoperability standards. This compliance builds user confidence in the charging infrastructure, which is crucial for the adoption of electric vehicles. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, sourcing charging equipment from CE-compliant manufacturers is imperative to ensure long-term functionality and safety, while also facilitating seamless integration with various electric vehicle models.
How does the CE certificate impact fleet management operations?
In fleet management, the CE certificate is necessary for electric fleet vehicles to comply with local regulations. This compliance not only enhances operational efficiency but also mitigates risks associated with regulatory fines. Buyers from regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia must navigate local certification requirements while ensuring their fleet vehicles are CE-marked to facilitate smoother operations and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Why is CE marking important for renewable energy integration?
The CE marking is vital when integrating electric vehicles with renewable energy sources, such as solar charging systems. This certification promotes sustainable practices and helps businesses reduce their carbon footprint. For B2B buyers, ensuring all components of the charging system are CE certified is crucial for compatibility and compliance, particularly in regions focused on enhancing their green energy initiatives.
How does CE marking influence export and trade opportunities?
CE marking significantly impacts the export of electric vehicles to European markets, as it is a legal requirement for entry. This certification opens up new market opportunities for manufacturers and ensures compliance with stringent EU regulations. For B2B buyers, identifying notified bodies for conformity assessment is essential to navigate the certification process effectively, ensuring that products meet all necessary requirements before entering the European marketplace.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric car ce certificate’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Regulatory Requirements
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the multifaceted regulatory landscape surrounding electric car CE certification. The requirements can differ significantly based on the type of vehicle, its components, and the specific markets they intend to enter. For instance, a manufacturer may find that while their electric vehicle meets CE marking requirements, it might also need to comply with additional directives like RoHS or EMC. This complexity can lead to confusion and potential delays in product launch, affecting their competitiveness in the market.
The Solution: To overcome these regulatory challenges, B2B buyers should invest in comprehensive compliance training and resources. Engaging with a regulatory consultant who specializes in electric vehicle certifications can provide tailored guidance. Additionally, creating a detailed compliance checklist that outlines each directive applicable to their product will help streamline the certification process. Buyers can also consider using software tools designed for regulatory compliance management, which can assist in tracking requirements and maintaining documentation. Furthermore, collaborating with industry peers to share best practices can enhance their understanding of market-specific requirements, ensuring they remain compliant and competitive.
Scenario 2: The Cost of Non-Compliance
The Problem: A significant concern for B2B buyers is the financial implications of non-compliance with CE certification requirements. Failing to obtain the necessary certifications can lead to costly recalls, fines, and a damaged reputation. Buyers may underestimate the importance of investing in CE marking from the outset, leading to rushed compliance efforts that ultimately fall short. This scenario is particularly pressing for companies operating in regions with stringent regulatory frameworks, such as the EU, where the penalties for non-compliance can be severe.
The Solution: To mitigate the financial risks associated with non-compliance, B2B buyers should prioritize compliance as a core component of their product development strategy. Establishing a budget specifically for certification processes can prevent unexpected costs later on. It’s advisable to conduct a risk assessment early in the product lifecycle to identify potential compliance issues. Investing in early-stage testing and validation can also save costs down the line. Furthermore, forming partnerships with accredited testing laboratories can streamline the certification process, ensuring that products meet all necessary requirements before market entry. This proactive approach not only protects against penalties but can also enhance brand credibility.
Scenario 3: Supplier and Component Compliance Challenges
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges ensuring that their suppliers’ components comply with CE certification requirements. As electric vehicles consist of numerous parts sourced from various suppliers, a lack of transparency regarding the compliance status of these components can lead to significant risks. If a supplier fails to provide compliant materials, it can jeopardize the entire certification process for the vehicle, leading to delays and increased costs. Buyers may find it difficult to verify the compliance status of components, particularly when dealing with international suppliers from regions with varying regulatory standards.
The Solution: To address these supplier-related compliance issues, B2B buyers should implement a robust supplier evaluation and monitoring system. This system should include a rigorous vetting process for new suppliers, focusing on their history of compliance with CE certification and related directives. Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers about compliance expectations is crucial. Additionally, buyers can require suppliers to provide documentation of compliance for all components, such as declarations of conformity and test reports. Regular audits and compliance checks can further ensure that suppliers maintain the necessary standards. By fostering strong relationships with reliable suppliers and maintaining oversight, buyers can enhance the overall compliance of their products, facilitating a smoother certification process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric car ce certificate
What Are the Key Materials for Electric Car CE Certification?
When selecting materials for electric vehicles (EVs) that comply with CE certification, manufacturers must consider various factors, including performance properties, cost, and regulatory compliance. Here, we analyze four common materials used in electric cars: aluminum, high-strength steel, thermoplastics, and lithium-ion battery components.
How Does Aluminum Contribute to Electric Vehicle Performance?
Aluminum is widely used in electric vehicle construction due to its lightweight and high strength-to-weight ratio. This property enhances vehicle efficiency by reducing overall weight, which is crucial for maximizing battery range. Aluminum also exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros: The durability of aluminum contributes to longer vehicle lifespans, while its recyclability aligns with sustainability goals. However, the manufacturing complexity can increase costs, particularly in forming and welding processes.
Cons: Although aluminum is lightweight, it can be more expensive than traditional steel, impacting the overall vehicle cost. Additionally, its thermal conductivity may require careful design considerations to manage heat dissipation in battery systems.
What Role Does High-Strength Steel Play in Electric Cars?
High-strength steel is another popular choice for electric vehicle construction, especially in structural components. Its high tensile strength allows for thinner materials without compromising safety, which can be beneficial for weight reduction.
Pros: High-strength steel is generally more cost-effective than aluminum, providing a balance between performance and affordability. Its excellent crashworthiness enhances passenger safety, a critical factor in CE certification.
Cons: While it offers good corrosion resistance, high-strength steel may require additional coatings to maintain performance in harsh environments. The heavier weight compared to aluminum can also affect vehicle efficiency.
How Do Thermoplastics Enhance Electric Vehicle Design?
Thermoplastics are increasingly used in electric vehicles for interior components and some exterior parts. They are lightweight, versatile, and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Pros: Thermoplastics are generally less expensive than metals and can be produced with lower energy consumption. They also offer good impact resistance and can be easily recycled, aligning with sustainability efforts.
Cons: However, thermoplastics may not provide the same level of structural integrity as metals, which can be a concern for safety-critical components. Their temperature sensitivity can also limit their use in high-heat applications, such as near batteries.
What Are the Considerations for Lithium-Ion Battery Components?
Lithium-ion batteries are the heart of electric vehicles, and their components must meet stringent safety and performance standards to achieve CE certification. Key materials include lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are critical for energy density and performance.
Pros: Lithium-ion batteries offer high energy density, allowing for longer driving ranges. They are also rechargeable, making them a sustainable choice for electric vehicles.
Cons: The extraction of lithium and cobalt raises environmental and ethical concerns, which can impact compliance with sustainability regulations. Additionally, the cost of battery materials can fluctuate based on market demand, affecting overall vehicle pricing.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Car CE Certification
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric car ce certificate | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, structural components | Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance | Higher manufacturing costs, thermal conductivity | High |
| High-Strength Steel | Chassis, safety structures | Cost-effective, excellent crashworthiness | Heavier than aluminum, may require additional coatings | Medium |
| Thermoplastics | Interior components, some exterior parts | Lightweight, versatile, lower energy production | Limited structural integrity, temperature sensitivity | Low |
| Lithium-Ion Battery | Energy storage systems | High energy density, rechargeable | Environmental concerns, fluctuating material costs | High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with essential insights into material choices for electric vehicles. Understanding the properties and implications of these materials will facilitate informed decisions that align with CE certification requirements and market demands.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric car ce certificate
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electric Cars for CE Certification?
The manufacturing of electric cars involves several critical stages that ensure compliance with CE certification requirements. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a vital role in maintaining quality and safety standards essential for the CE marking.
How Does Material Preparation Contribute to CE Compliance?
Material preparation is the foundation of the manufacturing process. It involves sourcing raw materials that meet the stringent requirements set by CE directives, such as RoHS, which limits hazardous substances. Manufacturers must conduct thorough evaluations of material suppliers to ensure compliance. This step often includes verifying certificates of compliance and conducting audits to assess the supplier’s quality management systems.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Electric Car Components?
Forming processes in electric car manufacturing typically include stamping, molding, and machining. Advanced techniques such as injection molding for plastic components and precision machining for metal parts are common. Each technique must adhere to CE standards, ensuring that components are durable, safe, and environmentally friendly. For instance, battery casings must be designed to prevent leaks and ensure safety during operation.
How Is Assembly Performed to Meet CE Certification Standards?
The assembly stage combines various components into a finished product. This process is highly regulated, especially for critical systems such as the electrical and battery systems. Adhering to CE guidelines involves:
- Integration of Components: Ensuring that all parts fit together correctly and function as intended.
- Testing During Assembly: Conducting inspections at various checkpoints to verify that components meet technical specifications.
- Documentation: Keeping detailed records of the assembly process, which is crucial for CE compliance and future audits.
What Are the Key Finishing Processes for Electric Cars?
Finishing processes include painting, coating, and applying seals to protect against environmental factors. These processes are not just cosmetic; they also play a role in safety and durability. For CE certification, manufacturers must ensure that finishes are applied in compliance with environmental regulations, such as the REACH directive, which governs the use of chemicals in products.
How Is Quality Control Implemented in Electric Car Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is a pivotal aspect of electric car manufacturing, particularly for meeting CE certification requirements. Manufacturers typically adopt an integrated QC system aligned with international standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Electric Car Manufacturing?
Quality control is conducted at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival. Suppliers must provide documentation proving compliance with CE and other relevant standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC involves monitoring processes to ensure that they adhere to predefined quality standards. This may include real-time inspections and testing of components.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the car is assembled, FQC verifies the overall quality of the final product. This stage includes comprehensive testing, such as safety checks and functionality assessments, to ensure compliance with CE directives.
What International and Industry-Specific Standards Are Relevant for Electric Car QC?
In addition to ISO 9001, several industry-specific standards are crucial for electric car manufacturers seeking CE certification:
-
ISO/IEC 17025: This standard pertains to the competence of testing and calibration laboratories, ensuring that testing methods used for compliance are reliable and accurate.
-
Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) Standards: These standards focus on quality assurance within the automotive sector, providing guidelines for effective quality control practices.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier QC is essential. Here are several effective methods:
-
Conducting Audits: Regular audits of suppliers help ensure that their quality management systems are robust and compliant with CE standards. Buyers should request access to audit reports and corrective action plans.
-
Requesting Documentation: Buyers should ask for certifications, test reports, and compliance documentation for components and materials used in the manufacturing process.
-
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing processes and QC measures.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate specific nuances when dealing with suppliers in different regions:
-
Understanding Regional Regulations: Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations that may affect CE compliance, as these can vary significantly between countries.
-
Language and Communication Barriers: Effective communication is critical. Buyers should ensure that suppliers understand CE requirements and can provide documentation in a language that is clear and understandable.
-
Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality control and compliance. Buyers should be sensitive to these differences and work collaboratively with suppliers to meet CE standards.
Conclusion
Manufacturing electric cars that meet CE certification requirements is a complex process that necessitates meticulous attention to detail at every stage, from material preparation to finishing. For B2B buyers, understanding these manufacturing processes and the associated quality control measures is essential to ensure compliance and product safety. By leveraging rigorous QC practices and verifying supplier capabilities, buyers can confidently navigate the electric vehicle market and expand their reach in a rapidly evolving industry.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric car ce certificate’
The following guide provides a structured approach for international B2B buyers looking to procure the CE certificate for electric cars. This certification is crucial for ensuring compliance with European regulations, which can facilitate market access and enhance product credibility.
Step 1: Understand CE Marking Requirements
Before initiating the certification process, familiarize yourself with the CE marking requirements specific to electric vehicles. This includes directives such as the Low-Voltage Directive, EMC Directive, and Vehicle Type Approval Directive. Understanding these requirements will help you identify the necessary steps to achieve compliance and avoid potential pitfalls.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications of your electric car, including its design, components, and intended use. This step is vital as it forms the basis of your technical documentation, which will be reviewed during the certification process. Ensure that all specifications align with the relevant EU directives to streamline your path to certification.
Step 3: Appoint a Notified Body
Engaging a Notified Body is often a mandatory step in obtaining CE certification, especially for complex products like electric cars. A Notified Body is an independent organization authorized to assess your product’s compliance with EU directives. Choose a Notified Body that specializes in automotive or electric vehicle assessments to ensure they have the necessary expertise.
Step 4: Prepare Technical Documentation
Compile comprehensive technical documentation that demonstrates compliance with CE requirements. This should include design calculations, risk assessments, and test reports. Maintain thorough records, as these documents will be essential for both the Notified Body assessment and for future audits by regulatory authorities.
Step 5: Conduct a Conformity Assessment
Undergo the conformity assessment procedure, which may involve testing and inspection of your electric vehicle. This assessment is critical for validating that your vehicle meets all applicable EU standards. Depending on your product, this may include laboratory testing for safety and performance metrics, so be prepared for potential costs and timelines.
Step 6: Draft an EU Declaration of Conformity
Once your product passes the conformity assessment, draft an EU Declaration of Conformity. This document must declare that your electric car meets all relevant EU directives and standards. It serves as an official statement of compliance and should accompany your product when marketed within the EU.
Step 7: Affix the CE Marking
After successfully completing the previous steps, affix the CE marking to your electric car and its technical documentation. Ensure that the CE mark is displayed prominently and is accompanied by the identification number of the Notified Body, if applicable. This marking is essential for legal marketing within the EU and enhances consumer trust in your product.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of obtaining a CE certificate for electric cars, ensuring compliance and facilitating access to European markets.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric car ce certificate Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Electric Car CE Certificates?
When sourcing electric car CE certificates, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The cost components generally include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: This refers to the documentation and testing materials needed to demonstrate compliance with CE regulations. While the CE marking itself doesn’t require physical materials, the technical documentation and test reports do.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the personnel involved in preparing technical documentation, conducting tests, and managing the certification process. This might include engineers, compliance officers, and administrative staff.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to the production of electric vehicles, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. These costs are typically spread across all units produced, impacting the overall price of certification.
-
Tooling: Depending on the specific requirements of the CE marking process, investment in specialized tools or equipment may be necessary. This is particularly relevant if modifications to existing vehicles are required to meet compliance standards.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures is essential to ensure that all components and processes comply with CE requirements. This may involve third-party inspections and audits, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: The costs associated with transporting products for testing and certification can vary significantly, especially for international shipments. Understanding Incoterms is vital to manage these logistics costs effectively.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This can vary widely based on market conditions and the supplier’s pricing strategy.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of CE Certification?
Several factors can influence the pricing of CE certification for electric cars:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Manufacturers that commit to larger quantities may negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Unique specifications or modifications can increase costs. Customization often requires additional testing and documentation, leading to higher certification fees.
-
Materials: The choice of materials used in the electric car’s components can impact compliance costs. Using RoHS-compliant materials, for example, may be more expensive upfront but can reduce long-term liabilities.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers with higher quality standards or additional certifications may charge premium prices. However, these certifications can add value by ensuring compliance and reducing risks.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the certification body or supplier also affect pricing. Well-established organizations may charge more for their services due to their expertise and trustworthiness.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms and conditions is essential. Buyers should clarify who is responsible for costs during transport, which can significantly affect the total cost of ownership.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing CE Certificates?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate the terms and prices with suppliers. Leverage your purchasing volume and long-term relationship potential to secure better rates.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just initial pricing. Factor in long-term compliance costs, potential fines for non-compliance, and warranty implications.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of the specific regulations that apply in your target markets. Different regions may have varying compliance costs and certification requirements, which can influence pricing.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on potential certification bodies. Compare their services, pricing structures, and customer reviews to ensure you choose the most cost-effective option.
-
Understand Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local regulatory frameworks. This knowledge can help you anticipate potential additional costs related to certification and compliance.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on numerous factors, including the specific requirements of the electric vehicle, changes in regulatory frameworks, and market conditions. Always consult with certification experts for the most accurate and current pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric car ce certificate With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Electric Car CE Certification
As the electric vehicle (EV) market expands globally, regulatory compliance through certifications like the CE marking becomes increasingly crucial. However, there are alternative solutions that companies can consider for market entry and product compliance. This analysis compares the CE certification with two viable alternatives: the UKCA marking and voluntary certification programs. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific operational and market needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Car CE Certificate | UKCA Marking | Voluntary Certification Programs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High compliance with EU standards | Ensures compliance with UK regulations | Varies; often lacks rigorous testing |
| Cost | Potentially high; involves fees for notified bodies | Similar to CE; costs depend on assessment complexity | Generally lower; may not require independent testing |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires detailed technical documentation and assessments | Similar requirements to CE, but with UK-specific regulations | Easier; less documentation required |
| Maintenance | Ongoing documentation and compliance checks needed | Regular updates to meet changing regulations | Minimal maintenance; less stringent |
| Best Use Case | Essential for accessing EU markets | Necessary for products sold in Great Britain | Useful for companies seeking faster market entry without strict regulations |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
UKCA Marking: Navigating the Post-Brexit Landscape
The UKCA marking emerged after the UK’s exit from the EU, replacing the CE marking for products sold in Great Britain. It serves a similar purpose, ensuring products meet local safety, health, and environmental standards. The UKCA marking is essential for companies targeting the British market, as it facilitates compliance with UK-specific regulations. However, the process can mirror that of CE marking, which may involve fees for assessments by UK-based conformity assessment bodies. While it provides access to the UK market, companies must remain vigilant about the evolving regulatory landscape.
Voluntary Certification Programs: A Flexible Approach
Voluntary certification programs offer an alternative for companies looking to enter markets quickly without the stringent requirements of CE or UKCA marking. These programs typically involve less rigorous testing and documentation, making them easier to obtain. However, they may not carry the same weight in terms of consumer trust and market acceptance. Businesses opting for this route should be cautious, as voluntary certifications can lack the credibility needed in highly regulated markets, potentially impacting product acceptance and brand reputation.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Certification for Your Needs
In deciding between the electric car CE certificate and its alternatives, B2B buyers must evaluate their target markets, compliance requirements, and operational capacities. For businesses focused on the European market, the CE marking remains a critical component for ensuring product safety and regulatory compliance. Conversely, companies targeting the UK market should consider the UKCA marking, while those seeking a quicker, less formal entry might explore voluntary certification programs. Ultimately, the choice should align with the company’s strategic goals, customer expectations, and the regulatory landscape of the regions they intend to serve.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric car ce certificate
What Are the Key Technical Properties Required for Electric Car CE Certification?
When pursuing CE certification for electric vehicles, manufacturers must pay close attention to several critical technical properties. Understanding these specifications is essential for ensuring compliance and gaining market access, particularly in the European Union. Below are some of the key properties relevant to electric cars:
-
Material Composition
The materials used in electric vehicles, such as metals, plastics, and composites, must meet specific standards to ensure safety and performance. For example, battery housings must be made from materials that can withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion. Complying with these material requirements not only assures quality but also reduces liability and enhances the vehicle’s marketability. -
Electrical Safety Ratings
Electrical components in electric vehicles must adhere to established safety ratings, such as the Low-Voltage Directive (LVD). This ensures that systems like batteries, wiring, and charging units are designed to prevent short circuits and electrical fires. For B2B buyers, understanding these ratings is crucial for assessing supplier reliability and product safety. -
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
Electric vehicles must be designed to avoid interference with other electronic devices, as mandated by EMC regulations. This involves testing components to ensure they do not emit electromagnetic interference (EMI) and are resistant to external EMI. For international buyers, this property is particularly important in regions with dense electronic infrastructure, ensuring seamless integration into the market. -
Thermal Management Systems
Effective thermal management is vital for maintaining battery performance and longevity. Manufacturers must design systems that regulate temperature, preventing overheating and enhancing efficiency. This property is essential for B2B buyers looking to invest in electric vehicles that promise durability and reliability in varying climates. -
Safety and Crash Test Standards
Compliance with safety standards, including crash testing protocols, is mandatory for CE certification. These tests assess the vehicle’s ability to protect occupants during collisions. For B2B stakeholders, understanding these standards helps in evaluating the safety of potential purchases and the reputation of manufacturers.
What Are Common Trade Terms Relevant to Electric Car CE Certification?
Navigating the world of electric vehicle certification involves understanding specific trade jargon that can impact business operations. Here are some essential terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of electric vehicles, OEMs are crucial as they supply essential components like batteries and electric motors. Understanding the role of OEMs can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and assess the quality of components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for B2B buyers, as it influences purchasing decisions and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ can help companies plan their budgets and supply chains more effectively. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent by a buyer to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. For electric vehicle manufacturers, issuing an RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure competitive pricing from multiple suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms can help B2B buyers navigate shipping, insurance, and risk management when importing electric vehicles or components. -
Notified Body
A notified body is an organization designated by EU member states to assess the conformity of products before they can be marketed. In the context of CE certification, understanding the role of notified bodies is essential for manufacturers to ensure compliance and facilitate market entry. -
Declaration of Conformity
This is a document in which the manufacturer declares that their product meets all applicable EU regulations. It is a crucial component of the CE marking process. B2B buyers should be aware of this document as it ensures that the products they are purchasing have been properly certified for safety and compliance.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when engaging with electric vehicle manufacturers and suppliers, ultimately driving business success in a rapidly evolving market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric car ce certificate Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Influencing the Electric Car CE Certificate Market?
The electric vehicle (EV) sector is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing global demand for sustainable transportation solutions, stringent regulatory standards, and advancements in battery technology. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are keenly aware of the implications of compliance with certifications like the CE mark. This certification serves as a crucial gateway for accessing the European market, where consumer safety and environmental protection regulations are paramount.
Current trends indicate a shift towards digital platforms for sourcing and compliance management. B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging technology to streamline the certification process, utilizing software solutions that facilitate document management and compliance tracking. Moreover, the rise of electric vehicles has led to emerging partnerships between manufacturers and certification bodies, fostering a collaborative approach to meet evolving regulatory requirements. This trend is particularly evident in countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, where local manufacturers are seeking to align with international standards to enhance market competitiveness.
How Does Sustainability Impact Sourcing in the Electric Car CE Certificate Sector?
Sustainability is not just a buzzword; it is a driving force in the sourcing strategies of electric vehicle manufacturers. As environmental concerns escalate, the importance of ethical supply chains has come to the forefront. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, which includes the use of ‘green’ materials and adherence to environmental regulations such as the RoHS directive.
The demand for sustainable sourcing practices is reflected in the growing interest in certifications that validate environmental claims, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems. Buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who can provide evidence of compliance with these standards, ensuring that the components used in electric vehicles are sourced responsibly and do not contain hazardous materials. This focus on sustainability not only enhances brand reputation but also meets the expectations of environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Historical Context of Electric Car CE Certification?
The evolution of electric car CE certification can be traced back to the increasing awareness of environmental issues and the subsequent development of regulatory frameworks aimed at promoting safety and sustainability in the automotive industry. Initially, the CE marking was primarily associated with consumer electronics and machinery, but as the electric vehicle market expanded, so did the scope of CE certification.
Over the past decade, regulatory bodies in Europe have established more rigorous standards for electric vehicles, encompassing directives that address safety, electromagnetic compatibility, and the restriction of hazardous substances. This evolution reflects a broader shift towards integrating sustainability into product development and market entry strategies. As a result, international B2B buyers must navigate a more complex landscape of compliance requirements, making it essential to stay informed about the latest regulations and certifications that govern the electric vehicle sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric car ce certificate
-
How do I ensure compliance with CE marking requirements for electric cars?
To ensure compliance with CE marking requirements, start by familiarizing yourself with the relevant EU directives, such as the Low-Voltage Directive and the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive. Collaborate with a notified body if your electric car requires independent assessment. Prepare comprehensive technical documentation that includes design specifications, test reports, and risk assessments. Finally, conduct a thorough conformity assessment to confirm that your vehicle meets all necessary EU safety, health, and environmental standards before affixing the CE mark. -
What are the potential costs involved in obtaining a CE certificate for electric vehicles?
The costs associated with obtaining a CE certificate can vary significantly based on the complexity of the electric vehicle and the specific directives applicable. If you opt to conduct the conformity assessment internally, there may be no fees. However, hiring a notified body for independent assessment will incur fees, which can range from hundreds to thousands of euros, depending on the scope of services needed. It’s advisable to budget for both testing and documentation preparation costs when planning your certification process. -
What documentation is required for CE marking an electric car?
To obtain CE marking for an electric car, you must compile a technical dossier that includes detailed design and manufacturing information, test results, and risk assessments. Essential documents include the EU Declaration of Conformity, which declares that your product complies with all relevant EU directives. Additionally, you should maintain records of the conformity assessment process, including any correspondence with notified bodies and test reports, to demonstrate compliance if requested by authorities. -
How can I verify the credibility of a notified body for CE marking?
To verify the credibility of a notified body, consult the NANDO database, which lists all notified bodies recognized by EU member states. Look for bodies that specialize in electric vehicles and related technologies. Ensure that the notified body is competent in the specific directives applicable to your product. Additionally, review their accreditation and past performance, including client testimonials and case studies, to gauge their reliability and expertise in handling CE marking assessments. -
What are the implications of Brexit on CE marking for electric vehicles sold in the UK?
After Brexit, products sold in Great Britain must now comply with UKCA (UK Conformity Assessed) marking instead of CE marking. While the requirements are similar, manufacturers need to ensure that their products meet UK-specific regulations. If you are exporting to the UK, you may need to engage UK-based conformity assessment bodies for compliance. It’s crucial to stay updated on any new regulations that may arise as the UK continues to develop its own standards. -
Can I customize my electric vehicle design while obtaining CE certification?
Yes, you can customize your electric vehicle design while obtaining CE certification; however, any modifications may necessitate re-evaluating compliance with EU directives. Depending on the extent of the changes, you may need to conduct additional testing or update your technical documentation. It’s advisable to consult with your notified body during the design phase to ensure that your customizations align with CE marking requirements and do not compromise safety or performance standards. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for suppliers of electric vehicles with CE certification?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for electric vehicles can vary by supplier and depend on several factors, including production capacity and the type of vehicle being manufactured. Typically, larger manufacturers may have higher MOQs due to economies of scale, while smaller or specialized manufacturers might offer more flexible terms. It’s essential to discuss MOQs with potential suppliers upfront to ensure that their offerings align with your business needs and market demand. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with suppliers for CE-certified electric vehicles?
When negotiating payment terms with suppliers for CE-certified electric vehicles, consider options such as upfront deposits, installment payments, or letters of credit to mitigate risk. Aim for terms that allow you to assess product quality before full payment is made. Standard terms might include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation, followed by a final payment before delivery. Ensure clarity on payment schedules and any penalties for late payments to foster a trustworthy supplier relationship.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Electric Car Ce Certificate Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. CE Marking – Essential Compliance Certification
Domain: europa.eu
Introduction: CE marking is a certification that indicates a product’s compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. It is mandatory for certain products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA). The CE marking process involves ensuring that the product meets all relevant EU requirements, which may include testing, documentation, and quality assurance. Obtaining the CE marking d…
2. Joint Charging – EV Charger Certification
Domain: jointcharging.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: The EV Charger Certificate is essential for operators and manufacturers of electric vehicle charging systems to ensure high standards of performance and safety. It verifies compliance with globally recognized standards, which is crucial in a competitive market. The CE certification, based on IEC61851, applies to both off-board and on-board equipment, allowing for charging with AC power supply (up …
3. Cyber Switching – Dual EV Charging Stations
Domain: cyberswitching.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Featured Products: Electric Vehicle Chargers Commercial Dual EV Charging station with Cable management, Dual CSE1 Level-2, 48A, RFID – $3,290.00 – $3,890.00; Electric Vehicle Chargers Commercial Dual 48A EV Charging station with Cable management, Dual CSE3 Level-2 with display, RFID, CTEP – $3,490.00 – $4,090.00; Electric Vehicle Chargers Commercial Dual EV Charging station, Dual CSE1 Level-2, 48A…
4. CNEV Charger – CE Certification Essentials
Domain: cnevcharger.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: CE certification is crucial for charging pile products to ensure safety and quality, allowing them to enter the European market. The certification covers electrical safety, electromagnetic compatibility, and radiation requirements. Key elements of CE certification include a visible CE mark, safety and electromagnetic compatibility statements, product information (name, model, manufacturer details)…
5. EXCAR – 48 Voltage Golf Electric Car
Domain: excar.com.cn
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “48 Voltage Golf Electric Car”,”Model Number”: “M1S4+2″,”Brand Name”: “EXCAR”,”Certification”: “CE”,”Place of Origin”: “China”,”Controller”: “USA Curtis Controller 350A”,”Motor”: “ADC Separately Excited 48V 3.7kw”,”Battery”: “USA Trojan Lead-acid Wet Batteries”,”Max Speed”: “25km/h or 45km/h”,”Charging Time”: “8-10 Hours”,”Dimensions (L x W x H)”: “3500 x 1200 x 1800 mm”,”Net Weig…
6. Enc-Lab – E-Mark Certification
Domain: enc-lab.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: EU Vehicle Certification Overview: E-mark certification is required for automotive electrical products to access the EU market, as per EU Directive 72/245/EEC and amendments to Directive 95/54/EC. E-mark certification is imperative for vehicle electrical and electronic products, which must undergo testing and certification for EU customs clearance. The E-mark is issued under regulations from the E…
7. Reddit – EV Certificate Course
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: EV CERTIFICATE: An online certificate course focused on electric vehicles, covering basics, operation, batteries, and charging systems. Recommended by users in the EV charging community, with a specific course suggested through SME: https://www.sme.org/training/electric-vehicle-fundamentals-evf-certification/.
8. Wiss Energy – Key Certifications for EV Chargers
Domain: wissenergy.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Key certifications for EV chargers include UL certification, CE certification, ETL certification, CTEP certification, and ENERGY STAR certification. UL certification ensures safety and interoperability, while CE certification guarantees compliance with EU safety and environmental standards. ETL certification is important for public installations, CTEP certification ensures accurate billing, and EN…
9. EU – Electric Vehicle Registrations 2023
Domain: eea.europa.eu
Introduction: In 2023, electric vehicles accounted for 22.7% of new car registrations and 7.7% of new van registrations in the EU. A total of 2.4 million new electric cars were registered, up from 2 million in 2022. Registrations of new battery electric cars (BEVs) grew by 37%, while plug-in hybrid cars (PHEVs) fell by almost 4%. The average mass of BEVs was 1,880kg, and PHEVs were around 1,958kg. The average e…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric car ce certificate
The complexities surrounding the CE certification for electric vehicles are not just regulatory hurdles; they represent vital pathways to market access and consumer trust. As manufacturers navigate the requirements set forth by the EU, understanding the critical aspects of CE marking, from safety standards to environmental compliance, is paramount. By investing in strategic sourcing, businesses can ensure they partner with suppliers who meet these stringent criteria, thereby enhancing product integrity and brand reputation.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, stand to gain significantly by prioritizing compliance with CE standards. This proactive approach not only opens doors to lucrative European markets but also aligns with global sustainability goals, an increasingly important factor for consumers and regulators alike.
Looking ahead, the electric vehicle industry is poised for exponential growth. Now is the time for international buyers to engage with compliance experts and certified suppliers to secure their place in this evolving market. By embracing strategic sourcing and prioritizing certifications like CE, businesses can lead the charge toward a sustainable and profitable future in the electric vehicle sector.