Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric car eec coc certificate
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing, understanding the intricacies of the EEC COC certificate is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking to navigate the complexities of compliance and market entry. The challenge often lies in sourcing electric vehicles that not only meet local regulations but also align with international standards, ensuring a smooth path to market. This guide delves deep into the world of EEC certification, providing a comprehensive overview of its types, applications, and the critical steps involved in securing this essential certification.
Our exploration includes vital insights into the certification process, the significance of the World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI), and the importance of E-MARK certificates for vehicle components. Furthermore, we will discuss supplier vetting strategies to ensure that you partner with reliable manufacturers who can consistently deliver compliant products. Understanding the cost implications and timelines associated with obtaining the EEC COC certificate will also be a key focus, enabling informed decision-making.
This guide is designed specifically for B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Vietnam and Nigeria. By providing actionable insights and expert knowledge, we empower you to make strategic purchasing decisions that comply with international standards while enhancing your competitive edge in the global electric vehicle market.
Understanding electric car eec coc certificate Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard EEC COC Certificate | Required for most electric vehicles; ensures compliance with EU regulations. | General sales to EU markets | Pros: Widely recognized; essential for market entry. Cons: Lengthy certification process. |
| Low-Speed Vehicle EEC COC | Specifically for low-speed electric vehicles; limited to lower power and speed thresholds. | Urban commuting, short-distance transport | Pros: Quicker approval; cost-effective for small vehicles. Cons: Limited market scope due to speed restrictions. |
| E-MARK Component Certification | Focuses on individual vehicle components; necessary for parts like lights and tires. | Component suppliers, manufacturers | Pros: Ensures quality and safety of parts. Cons: Requires consistent sourcing from certified suppliers. |
| Type Approval for Bicycles | Certification for electric pedal-assisted bicycles; includes safety and performance standards. | Bicycle manufacturers, urban mobility solutions | Pros: Expands market reach; meets specific niche demand. Cons: Complex compliance with multiple directives. |
| CE Marking for Electric Vehicles | Indicates conformity with EU health, safety, and environmental protection standards. | Broad market access within EU | Pros: Increases product credibility; enhances visibility. Cons: Requires ongoing compliance checks. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of the Standard EEC COC Certificate?
The Standard EEC COC Certificate is essential for electric vehicles intending to enter the European market. It ensures that the vehicle meets all EU regulations, including safety and environmental standards. This certification is crucial for manufacturers aiming to market their vehicles across EU member states. B2B buyers should consider the time and resources needed to obtain this certification, as it can be a lengthy process but ultimately provides a competitive advantage in the market.
How Does the Low-Speed Vehicle EEC COC Differ from Standard Certification?
The Low-Speed Vehicle EEC COC is tailored for electric vehicles designed for low-speed urban use, typically with a maximum speed of 45 km/h. This certification is less stringent than the standard EEC COC, making it faster and cheaper to obtain. B2B buyers targeting urban commuting solutions will find this certification beneficial, as it opens up opportunities in markets where low-speed vehicles are in demand. However, the limitations on speed may restrict the vehicle’s applications in broader markets.
What Role Does E-MARK Component Certification Play in Electric Vehicle Production?
E-MARK Component Certification is critical for individual parts of electric vehicles, such as lighting, tires, and safety systems. This certification ensures that components comply with EU standards, which is essential for manufacturers sourcing parts from various suppliers. Buyers must ensure they maintain consistent supplier relationships to uphold certification, as switching suppliers can complicate the overall EEC certification for the vehicle. This certification is particularly relevant for component manufacturers and assemblers aiming to sell within the EU.
What Are the Implications of Type Approval for Bicycles?
Type Approval for bicycles, particularly electric pedal-assisted models, is governed by specific EU standards that encompass safety, performance, and electromagnetic compatibility. This certification is crucial for manufacturers looking to sell electric bicycles in the EU, as it assures compliance with local regulations. B2B buyers should be aware that while this certification can enhance marketability, it requires adherence to multiple directives, which can complicate the approval process.
How Does CE Marking Enhance Market Access for Electric Vehicles?
CE Marking is a declaration that a product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection requirements. For electric vehicles, obtaining CE Marking is vital for accessing the EU market. This certification not only boosts product credibility but also improves visibility among consumers and partners. Buyers should consider the ongoing compliance requirements associated with CE Marking, as maintaining this certification involves regular audits and updates to ensure adherence to evolving standards.
Key Industrial Applications of electric car eec coc certificate
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric car eec coc certificate | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Transportation | Certification for electric taxis and ride-sharing services | Access to EU markets, compliance with safety regulations | Ensure all vehicle components have E-MARK certifications; partner with EU representatives for compliance. |
| Logistics and Delivery | EEC certification for electric delivery vehicles | Enhanced brand reputation and regulatory compliance | Source E-MARK certified components; maintain a consistent supply chain for parts. |
| Tourism and Leisure | Electric vehicles for city tours and rentals | Attract eco-conscious tourists; meet local regulations | Verify compliance with local and EU standards; consider vehicle design for tourism appeal. |
| Public Sector | Electric vehicles for municipal services | Cost savings on fuel and maintenance; improved public image | Engage with local authorities for compliance; ensure vehicles meet specific municipal needs. |
| Agriculture and Farming | Electric utility vehicles for farm operations | Reduction in operational costs; sustainability credentials | Assess battery life and charging infrastructure; ensure compliance with agricultural regulations. |
How is the Electric Car EEC COC Certificate Applied in Urban Transportation?
In the urban transportation sector, electric vehicles (EVs) such as taxis and ride-sharing services require EEC COC certification to operate legally within the EU. This certification assures compliance with stringent safety and environmental standards, which can significantly enhance a company’s marketability and trust among consumers. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, understanding the certification process is crucial. They must ensure that all vehicle components are sourced from E-MARK certified suppliers to avoid complications during certification renewal.
What Role Does EEC Certification Play in Logistics and Delivery?
Logistics companies are increasingly integrating electric delivery vehicles into their fleets to reduce carbon footprints and operational costs. The EEC COC certificate is essential for these vehicles to ensure they meet EU regulations, which can open doors to new markets and customers. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, securing E-MARK certified components and maintaining a reliable supply chain are critical. This not only guarantees compliance but also enhances the company’s reputation for sustainability.
Why is EEC Certification Important for Tourism and Leisure?
Tourism operators utilizing electric vehicles for city tours or rentals can significantly benefit from the EEC COC certification. This certification ensures that their vehicles comply with EU safety and environmental standards, appealing to eco-conscious travelers. Buyers must verify that their vehicles meet local regulations and consider design elements that enhance the tourist experience. Compliance with EEC certification can also improve operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
How Do Public Sector Entities Utilize EEC Certification?
Municipal services, including waste management and public transport, are increasingly adopting electric vehicles to promote sustainability. The EEC COC certification is vital for these vehicles, as it ensures they meet the required safety and environmental standards. For international buyers in Europe and beyond, collaborating with local authorities to ensure compliance with specific municipal needs is essential. Additionally, electric vehicles can lead to significant cost savings on fuel and maintenance, further incentivizing public sector investment.
What are the Benefits of EEC Certification in Agriculture and Farming?
In the agricultural sector, electric utility vehicles are being embraced for their cost-effectiveness and sustainability. EEC COC certification is crucial for these vehicles to meet regulatory requirements, ensuring they can operate legally within their regions. For buyers in Africa and South America, it is important to evaluate the charging infrastructure and battery life of these vehicles to maximize efficiency. Compliance with agricultural regulations is also necessary to ensure that the vehicles can be effectively integrated into farming operations, ultimately leading to reduced operational costs and enhanced sustainability credentials.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric car eec coc certificate’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Certification Requirements
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those new to the electric vehicle (EV) market, struggle with the complex and often ambiguous requirements for obtaining an EEC COC certificate. This process is crucial for ensuring compliance with EU regulations, but it can be overwhelming. Buyers may find themselves uncertain about the necessary documentation, such as the World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI), ISO certifications, and E-MARK certificates for individual vehicle components. This confusion can lead to delays in product launches, increased costs, and potential legal issues if vehicles are sold without proper certification.
The Solution: To navigate these complexities effectively, B2B buyers should develop a detailed checklist that outlines all requirements for EEC certification. This checklist should include the specific documents required, deadlines for submission, and responsible parties for each task. For instance, engaging a compliance consultant with expertise in EU regulations can provide valuable insights and assistance in gathering the necessary paperwork. Additionally, establishing a timeline that allows for ample review and potential revisions can mitigate delays. Buyers should also consider forming strategic partnerships with component suppliers who possess E-MARK certification, ensuring that all parts are compliant from the outset. This proactive approach will streamline the certification process and reduce the risk of non-compliance.
Scenario 2: Identifying Reliable Suppliers for Certified Components
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is the challenge of sourcing reliable suppliers for components that meet E-MARK certification requirements. Inconsistent quality and certification status of parts can jeopardize the overall EEC certification of the vehicle, leading to costly recalls or re-certifications. Buyers often face difficulties in verifying the compliance status of suppliers, especially when dealing with international vendors from regions like Africa or South America, where certification standards may vary.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, buyers should implement a robust supplier vetting process that includes not only reviewing certifications but also conducting on-site audits or requiring third-party verification of compliance. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers who consistently provide certified components can also enhance reliability. Buyers can utilize online platforms or industry networks to identify reputable suppliers and gather feedback from peers about their experiences. Additionally, keeping a database of suppliers’ certification statuses can help streamline future procurement processes and ensure that all components remain compliant throughout the production lifecycle.
Scenario 3: Understanding the Role of Authorized EU Representatives
The Problem: Many international B2B buyers, especially those from emerging markets, are unaware of the importance of having an authorized EU representative for EEC certification. Without this representative, it can be challenging to navigate the regulatory landscape, leading to misunderstandings and potential penalties. Buyers may also find it difficult to establish a line of communication with EU regulatory bodies, which can hinder their ability to address compliance issues promptly.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize the appointment of a knowledgeable authorized representative within the EU as part of their certification strategy. This representative can serve as a liaison between the manufacturer and EU regulatory authorities, facilitating communication and ensuring that all necessary documentation is submitted correctly. It is advisable to choose a representative with a proven track record in the EV sector and familiarity with the EEC certification process. Moreover, maintaining regular communication with this representative can help buyers stay informed about any changes in regulations or compliance requirements, allowing for swift adjustments to their certification strategies. By leveraging the expertise of an authorized EU representative, buyers can enhance their compliance efforts and focus on scaling their operations without the constant worry of regulatory setbacks.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric car eec coc certificate
What Are the Key Materials for Electric Car EEC COC Certification?
When selecting materials for electric vehicles (EVs) that require EEC COC certification, it is crucial to consider properties that impact performance, safety, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in electric cars, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
1. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for vehicle bodies and components. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°C and has a density of about 2.7 g/cm³.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum’s lightweight nature enhances energy efficiency and range, while its corrosion resistance prolongs the lifespan of components. However, it can be more expensive than steel, and the manufacturing process may require specialized techniques, increasing complexity.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with a variety of media, including battery fluids and cooling agents, which is critical for electric vehicle performance.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local regulations concerning aluminum sourcing and recycling. Standards such as ASTM B209 for aluminum sheets and plates are essential for quality assurance.
2. Steel
Key Properties:
Steel is known for its high strength and durability, with a melting point around 1370°C. It offers good resistance to deformation under pressure and is readily available.
Pros & Cons:
Steel is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, making it a popular choice for structural components. However, its weight can negatively impact vehicle efficiency and range compared to lighter materials like aluminum.
Impact on Application:
Steel components are generally compatible with most automotive fluids, but they may require coatings to prevent rust and corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers must consider compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ensure that the steel used meets local environmental regulations, especially in regions with stringent emissions guidelines.
3. Composite Materials
Key Properties:
Composites, particularly carbon fiber and fiberglass, are lightweight and offer high tensile strength. They can withstand temperatures up to 200°C and are resistant to corrosion.
Pros & Cons:
Composites can significantly reduce vehicle weight, improving efficiency. However, they are often more expensive and can complicate manufacturing processes due to the need for specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
These materials are particularly beneficial in battery enclosures and body panels, where weight reduction is critical for performance.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific composite standards in their regions, such as ASTM D3039 for tensile properties of composites, and consider the recyclability of these materials, which may be a concern in some markets.
4. Thermoplastics
Key Properties:
Thermoplastics are flexible, lightweight, and can be molded into complex shapes. They typically have a temperature resistance up to 120°C and are resistant to many chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
These materials are cost-effective and versatile, allowing for easy integration into various vehicle components. However, they may not provide the same structural integrity as metals and can be less durable under extreme conditions.
Impact on Application:
Thermoplastics are ideal for interior components and non-structural parts, where weight and cost savings are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers:
It is crucial for buyers to ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ISO 11469 for material identification and recycling, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric car eec coc certificate | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Vehicle body and structural components | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Steel | Chassis and structural components | Cost-effective, strong | Heavier, requires corrosion protection | Medium |
| Composite | Battery enclosures, body panels | Lightweight, high strength | Expensive, complex manufacturing | High |
| Thermoplastics | Interior components, non-structural parts | Cost-effective, versatile | Less durable under extreme conditions | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the key materials used in electric vehicles requiring EEC COC certification. Understanding the properties and implications of these materials is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that align with compliance and performance standards in various international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric car eec coc certificate
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Electric Cars with EEC COC Certification?
Manufacturing electric vehicles (EVs) that comply with the European Economic Community (EEC) Certificate of Conformity (CoC) involves several critical stages. Each stage is designed to ensure that the final product meets stringent safety and performance standards, which are essential for market acceptance in various regions, especially for international B2B buyers.
Material Preparation: What Raw Materials Are Used?
The manufacturing process begins with material preparation, where high-quality raw materials are sourced. Common materials for electric cars include:
- Metals: Steel and aluminum are primarily used for the chassis and body due to their strength-to-weight ratio.
- Plastics: For components like bumpers and interior fittings, lightweight plastics are preferred.
- Batteries: Lithium-ion batteries are the standard for EVs, chosen for their energy density and rechargeability.
Suppliers must ensure that materials comply with the relevant EEC standards, including certifications like CE marking for safety and environmental compliance. B2B buyers should verify the sourcing and certification of materials through supplier audits and documentation.
Forming: How Are Components Shaped?
The next stage, forming, involves shaping the raw materials into components. This can include various techniques such as:
- Stamping: Used for metal parts, where sheets of metal are stamped into the desired shapes.
- Injection Molding: This process shapes plastics into specific parts, allowing for complex designs.
- Machining: Precision machining is used for critical components, ensuring exact dimensions and specifications.
It is crucial for manufacturers to employ skilled technicians and advanced machinery to maintain quality throughout this stage. B2B buyers should inquire about the technology and machinery used in the manufacturing process, as this can greatly affect the quality of the final product.
Assembly: What Are the Key Steps in Assembling Electric Cars?
Once components are formed, they are brought together in the assembly stage. Key steps include:
- Chassis Assembly: The vehicle’s frame is built first, incorporating the suspension and drivetrain.
- Electrical Systems Integration: This involves installing the battery, wiring, and electronic control units, which are critical for the vehicle’s operation.
- Body Assembly: The outer body panels are attached to the chassis, followed by windows, doors, and interior fittings.
Quality control during assembly is crucial to ensure that all components fit correctly and function as intended. B2B buyers should look for manufacturers that use standardized assembly processes and maintain thorough documentation of each step.
Finishing: How Is the Final Product Prepared for Sale?
The finishing stage includes painting, detailing, and final inspections. Manufacturers typically use:
- Powder Coating: This technique is often employed for a durable finish on metal parts.
- Quality Checks: Final inspections assess the vehicle’s overall appearance and functionality, ensuring compliance with safety standards.
To verify the quality of finishing, B2B buyers should request detailed reports and samples of previous work from potential suppliers.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Important for EEC COC Certification?
Quality assurance is a critical component of the manufacturing process, particularly for electric vehicles that require EEC COC certification. Adhering to international standards is essential for market entry and consumer safety.
Which International Standards Should Be Considered?
Manufacturers should comply with several international quality standards, including:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system, ensuring consistent product quality.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- E-MARK Certification: Specific to vehicle components, ensuring they meet EU regulations.
B2B buyers should confirm that their suppliers possess the necessary certifications and maintain an up-to-date compliance status.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is conducted at various stages of production to identify and rectify defects early. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Evaluates raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing process to monitor and verify that production is proceeding according to specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The last check before the vehicle is shipped, ensuring that it meets all quality and safety standards.
B2B buyers can enhance their confidence in supplier quality by asking for detailed QC reports and documentation of inspections.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can implement several strategies to verify a supplier’s quality control measures:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers’ facilities to assess compliance with quality standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors to evaluate the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols.
- Documentation Review: Requesting access to quality management system documents, inspection reports, and test results to ensure transparency.
What Are the Unique QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification:
- Regulatory Differences: Each region may have different regulatory requirements for electric vehicles. Understanding these is essential for ensuring compliance.
- Supply Chain Stability: Consistency in sourcing certified components is critical. Buyers should confirm that suppliers have reliable supply chains to prevent disruptions.
- Cultural Considerations: Familiarity with local market conditions and customer expectations can enhance collaboration with suppliers and facilitate smoother transactions.
By paying attention to these nuances, B2B buyers can better navigate the complexities of sourcing electric vehicles that meet EEC COC certification standards, ensuring compliance and market readiness.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric car eec coc certificate’
To successfully procure an electric car EEC COC certificate, it is vital for B2B buyers to navigate the certification process carefully. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to streamline your sourcing efforts, ensuring compliance and efficiency in your operations.
Step 1: Understand EEC Certification Requirements
Before initiating the certification process, familiarize yourself with the essential requirements for EEC certification. This includes understanding the terminology like COC (Certificate of Conformity) and WVTA (Whole Vehicle Type Approval). Knowing these terms will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and certification bodies.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications of the electric vehicles you intend to certify. This includes aspects like motor power, battery type, and vehicle dimensions. Precise specifications are crucial as they directly influence the certification requirements and the components that need E-MARK certification.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
It’s essential to ensure that your suppliers hold the necessary certifications, including ISO certifications and E-MARK certifications for components. This verification protects you from potential compliance issues later on, as using non-certified parts can jeopardize the entire certification of the vehicle.
- Check for ISO Certification: Ensure it aligns with the scope of your vehicle production.
- E-MARK Certification for Components: Verify that critical components such as lights, tires, and brakes are sourced from certified suppliers.
Step 4: Engage an Authorized EU Representative
Having an authorized representative in the EU is a mandatory requirement for EEC certification. This representative can facilitate communication with EU regulatory bodies and assist in the certification process. Choose someone knowledgeable about EU regulations and with experience in the automotive sector.
Step 5: Compile Necessary Documentation
Gather all required documentation to support your EEC certification application. This includes technical data sheets, quality control reports, and compliance certificates for individual components. A well-organized documentation package can expedite the approval process.
- Technical Data Sheets: Should include detailed specifications and test results.
- Quality Control Reports: Provide evidence of the manufacturing process and quality assurance measures.
Step 6: Conduct Pre-Certification Testing
Before submitting your application, conduct thorough pre-certification testing on your vehicles. This testing should cover all safety, performance, and compliance aspects as per EU standards. Identifying and rectifying issues before the official certification can save time and costs.
Step 7: Submit Application and Follow Up
Once all documentation is prepared and testing is complete, submit your EEC certification application to the appropriate authority. After submission, maintain regular communication to track the progress of your application. Prompt follow-ups can help resolve any queries or additional requirements from the certification body.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of obtaining an EEC COC certificate for electric vehicles, ensuring compliance and enhancing their market readiness.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric car eec coc certificate Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing an Electric Car EEC COC Certificate?
When sourcing an electric car EEC COC certificate, understanding the cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margins.
-
Materials: This encompasses the costs associated with obtaining E-MARK certified components, which are mandatory for compliance. Materials can include batteries, motors, and various electrical components that must meet EU standards.
-
Labor: Labor costs involve the workforce engaged in production, certification processes, and compliance checks. Skilled labor is often necessary for ensuring that products meet the stringent requirements set forth by EU regulations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses that support the production process. For manufacturers aiming for EEC certification, these overheads can be significant, especially if they require advanced testing facilities.
-
Tooling: Investment in specialized tools and equipment to produce vehicles that meet EEC standards can be a considerable upfront expense. These tools are often tailored for specific vehicle types and compliance requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Maintaining high standards requires a robust QC process. This includes testing components and final products to ensure compliance with EEC regulations, which can add to overall costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs must be factored in, especially for international transactions. Compliance with Incoterms is crucial to understand responsibilities for shipping costs, risks, and insurance.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin on top of these costs, which can vary based on the supplier’s market position, reputation, and service quality.
What Influences Pricing for Electric Car EEC COC Certificates?
Several factors impact the pricing structure for electric car EEC COC certificates:
-
Volume/MOQ: Pricing often decreases with larger order volumes. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to achieve cost efficiencies.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can significantly influence costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications can lead to increased costs, but they often enhance the vehicle’s marketability and compliance with international standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and location can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their expertise and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial for determining who bears the shipping costs and risks, which can affect the total landed cost of the vehicle.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can lead to better pricing and terms. Here are some actionable tips:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Understand market rates for EEC COC certificates and benchmark against competitors to support your negotiation stance.
-
Build Long-Term Relationships: Establishing a rapport with suppliers can lead to better terms and potential discounts on future orders.
-
Seek Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Insights: Evaluate the TCO, including maintenance and operational costs, which can be more significant than the initial purchase price. This will help in making informed decisions.
-
Be Clear on Payment Terms: Discuss payment options upfront, as favorable terms can enhance cash flow and reduce financial risk.
-
Consider Alternative Suppliers: If negotiations stall, be prepared to explore other suppliers. A competitive landscape can provide leverage in negotiations.
What Should Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Indicative Prices?
It is important to note that prices for electric car EEC COC certificates can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. Buyers should always request quotes tailored to their specific needs and confirm that these quotes include all potential costs, including logistics and customs duties. This proactive approach ensures a clear understanding of the total financial commitment involved in sourcing electric vehicles compliant with EU standards.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric car eec coc certificate With Other Solutions
Exploring Viable Alternatives to the Electric Car EEC COC Certificate
In the realm of electric vehicle (EV) compliance, the Electric Car EEC COC (Certificate of Conformity) serves as a crucial certification for accessing markets like the European Union. However, businesses exploring entry into diverse global markets may consider alternative solutions that can provide similar benefits with varying implications on cost, performance, and implementation. Below, we compare the EEC COC certification with two alternative methods: ISO 9001 Certification and CE Marking.
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Car EEC COC Certificate | ISO 9001 Certification | CE Marking |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Ensures compliance for EU market entry, covering vehicle safety and environmental standards. | Focuses on quality management processes, leading to improved product quality and customer satisfaction. | Confirms that products meet EU safety, health, and environmental requirements. |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on testing and compliance processes. | Generally low to moderate, focused on internal process improvements. | Low to moderate, based on self-assessment and documentation costs. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires extensive documentation and adherence to EU regulations; can be complex. | Requires thorough internal audits and process documentation but is widely recognized and structured. | Easier to implement as it primarily requires self-declaration and supporting documentation. |
| Maintenance | Ongoing compliance checks needed for component certifications. | Requires regular audits and updates to processes. | Minimal, mainly documentation updates when product specifications change. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for manufacturers targeting the EU market with electric vehicles. | Suitable for companies aiming for quality improvement across all sectors. | Best for companies looking to enter the EU market with various products, not limited to vehicles. |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
ISO 9001 Certification
ISO 9001 certification is an internationally recognized standard for quality management systems (QMS). It helps organizations ensure they meet customer and regulatory requirements consistently. The primary advantage of this certification is its focus on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction, which can enhance a company’s reputation and operational efficiency. However, ISO 9001 does not specifically address vehicle compliance, making it less suitable for electric vehicle manufacturers looking to enter regulated markets like the EU.
CE Marking
CE marking is a certification that indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area. It is particularly advantageous for companies that wish to market products across multiple categories, as it facilitates easier access to the EU market. The ease of implementation and lower costs associated with CE marking make it attractive for many manufacturers. However, it does not provide the same level of assurance regarding vehicle-specific safety and performance standards as the EEC COC certificate.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Certification for Your Business
When selecting the appropriate certification for electric vehicles, B2B buyers must consider their target markets, regulatory requirements, and the nature of their products. The EEC COC certificate is essential for compliance within the EU, ensuring vehicles meet stringent safety and environmental standards. In contrast, ISO 9001 certification offers a broader approach to quality management, while CE marking provides a more accessible route to market entry for a range of products. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on specific business objectives, market strategies, and the regulatory landscape of the regions in which companies operate.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric car eec coc certificate
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Electric Car EEC COC Certification?
When considering the EEC Certificate of Conformity (COC) for electric vehicles, several critical technical properties must be understood by B2B buyers. These properties not only ensure compliance with international standards but also play a significant role in operational efficiency, safety, and market acceptance.
1. World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI)
The WMI is a unique code assigned to each vehicle manufacturer, crucial for vehicle identification. It ensures traceability and compliance with regulations in the EU. For international buyers, understanding the importance of WMI helps in verifying the legitimacy of manufacturers and their products, thereby reducing risks associated with counterfeit vehicles.
2. ISO Certification
ISO certification signifies that a manufacturer meets international quality management standards. Buyers should pay attention to the scope of production and the validity of this certification. An ISO-certified manufacturer is more likely to produce reliable and high-quality vehicles, which is essential for maintaining a good reputation in competitive markets.
3. E-MARK Certification for Components
E-MARK certification pertains to the compliance of individual vehicle components like lights and tires with EU safety standards. It is critical for buyers to ensure that all components used in their electric vehicles are E-MARK certified, as using uncertified parts can jeopardize the entire vehicle’s certification, leading to legal and financial ramifications.
4. Charging Time and Range
Understanding the specifications regarding charging time and operational range is vital for buyers. Electric vehicles typically have varying charging times (from 3 to 10 hours) and ranges (60 to 115 kilometers). These specifications influence the usability of the vehicle in different markets, particularly in regions with limited charging infrastructure.
5. Motor Power and Speed
The motor power, often measured in kilowatts (KW), and maximum speed are critical for determining the vehicle’s performance. For instance, a vehicle with a 2.2 KW motor may have a speed limit of 45 km/h. Buyers must assess these specifications in relation to their target market’s regulations and consumer expectations.
6. Curb Weight and Load Capacity
Curb weight is the total weight of the vehicle without passengers or cargo, which affects its performance and efficiency. Load capacity indicates how much weight the vehicle can safely carry. Both metrics are essential for understanding the practical applications of the vehicle, especially in commercial settings.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Electric Car EEC COC Certification?
Navigating the landscape of electric vehicle certification involves familiarizing oneself with specific industry jargon that can impact transactions and compliance processes.
1. Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or vehicles that are sold under another company’s brand. In the context of EEC certification, understanding OEM relationships is essential for ensuring that all components meet the necessary compliance standards.
2. Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ helps in planning inventory and budgeting, especially when considering new suppliers for electric vehicles or parts.
3. Request for Quotation (RFQ)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. In the context of electric vehicles, an RFQ can help buyers compare costs and ensure they are getting competitive pricing for certified vehicles.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers, as they dictate shipping responsibilities, risk transfer, and cost allocation.
5. Homologation
Homologation is the process of certifying that a vehicle meets regulatory standards for sale in a specific market. It is essential for buyers to understand homologation requirements to avoid costly delays in bringing vehicles to market.
6. Type Approval
Type approval is a confirmation that a vehicle meets all regulatory requirements before it can be sold in a market. This term is critical for buyers to grasp, as it impacts the legal compliance and marketability of electric vehicles within the EU and other regions.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing electric vehicles for compliance with EEC certification requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric car eec coc certificate Sector
What Are the Key Drivers Shaping the Electric Car EEC COC Certificate Market?
The electric vehicle (EV) market is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by an increasing global demand for sustainable transportation solutions. Key factors influencing this market include stringent environmental regulations, the rise of electric mobility, and advancements in battery technology. For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigating the complexities of EEC certification becomes crucial. The EEC (European Economic Community) Certificate of Conformity (COC) is mandatory for vehicles sold within the EU, ensuring they meet safety and environmental standards.
Emerging B2B tech trends are also reshaping the sourcing landscape. Digital platforms facilitate the sourcing process, allowing buyers to access a wider range of manufacturers and certifications more efficiently. Additionally, the adoption of blockchain technology is enhancing transparency in supply chains, which is vital for verifying the authenticity of EEC certifications and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. As the market evolves, businesses that leverage technology for efficient sourcing and compliance management will have a competitive edge.
How Can Sustainability Influence Sourcing in the Electric Vehicle Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a central focus for B2B buyers in the electric car sector. The environmental impact of sourcing practices is under scrutiny, compelling companies to adopt ethical supply chains. This shift not only aligns with consumer preferences for greener products but also helps in meeting regulatory requirements. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who utilize sustainable materials and processes, such as recyclable components and renewable energy in manufacturing.
Moreover, certifications related to sustainability, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, are becoming important in the sourcing process. These certifications provide assurance that suppliers adhere to environmental best practices, making them more attractive to international buyers. Incorporating ‘green’ materials in production not only reduces the carbon footprint but also enhances the overall appeal of electric vehicles, as consumers are more inclined to purchase products that are environmentally responsible.
What Is the Historical Context of EEC Certification in the Electric Vehicle Market?
EEC certification has its roots in the European Union’s push for standardization and safety in the automotive industry. Initially established to regulate traditional vehicles, the framework has evolved to encompass electric vehicles, reflecting the shift towards sustainable transport. The introduction of the new standard 168/2013 in January 2016 marked a significant change, providing clearer guidelines for certification and compliance.
As electric vehicles gain popularity, the importance of EEC COC certification has grown, making it essential for international B2B buyers to understand the certification process. This knowledge is crucial not only for compliance but also for ensuring that products meet the expectations of consumers in increasingly eco-conscious markets. Understanding the evolution of EEC certification helps buyers appreciate the regulatory landscape and anticipate future changes that may impact sourcing strategies in the electric vehicle sector.
Conclusion
In summary, the electric car EEC COC certification sector is characterized by dynamic market forces driven by sustainability, technological advancements, and evolving regulatory frameworks. International B2B buyers must remain vigilant and informed to navigate these changes effectively, ensuring their sourcing practices align with both compliance requirements and sustainability goals. Emphasizing ethical sourcing and staying updated on certification processes will be key to success in this rapidly changing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric car eec coc certificate
-
How do I obtain an EEC COC certificate for my electric vehicle?
To obtain an EEC COC (Certificate of Conformity) for your electric vehicle, you must ensure compliance with EU regulations. This involves acquiring a World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI), obtaining ISO certification for your manufacturing processes, and ensuring that all vehicle components meet E-MARK standards. Additionally, you will need to appoint an authorized representative in the EU who can facilitate the certification process. Once these steps are completed, you can submit your application to the relevant EU authorities for approval. -
What are the key requirements for EEC certification of electric vehicles?
The key requirements for EEC certification include having a unique WMI, ISO certification, E-MARK certifications for individual vehicle components, and appointing an authorized representative in the EU. Each component, such as lights and tires, must be sourced from certified suppliers to maintain compliance. Regular audits and documentation are necessary to ensure ongoing adherence to EU standards and to facilitate the renewal of the EEC certificate when required. -
What is the typical timeline for receiving an EEC COC certificate?
The timeline for receiving an EEC COC certificate can vary significantly depending on the complexity of your vehicle and the completeness of your documentation. Generally, the process can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months. Factors influencing the timeline include the efficiency of your manufacturing processes, the readiness of your compliance documentation, and the responsiveness of the EU authorities. Engaging with experienced consultants can help expedite the process. -
How can I verify the credibility of a supplier for electric vehicles?
To verify the credibility of a supplier, conduct thorough due diligence. Check for their certification status, particularly ISO and EEC certifications. Request references from previous clients and assess their production capacity and quality assurance processes. Visiting the supplier’s manufacturing facility and evaluating their compliance with international standards can provide deeper insights into their reliability. Additionally, leveraging platforms that specialize in supplier ratings can be beneficial. -
What customization options are available for electric vehicles?
Customization options for electric vehicles can vary by supplier but typically include modifications to battery capacity, motor specifications, color, and interior features. Some manufacturers also offer OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) options, allowing you to design unique vehicle models tailored to specific market needs. It’s advisable to discuss your customization requirements upfront with suppliers to ensure they can accommodate your needs while maintaining compliance with EEC standards. -
What are the common payment terms in B2B transactions for electric vehicles?
Common payment terms in B2B transactions for electric vehicles often include a deposit upfront (typically 30% to 50%) with the balance due upon delivery or before shipment. Some suppliers may also offer letters of credit or payment upon receipt of shipping documents. It’s essential to clarify payment terms before finalizing the contract to avoid misunderstandings. Ensure that the payment methods are secure and offer buyer protection. -
How do I ensure quality assurance during the manufacturing process?
To ensure quality assurance during manufacturing, establish clear communication with your supplier regarding quality standards and expectations. Request regular updates and inspections at various production stages. Implement a final inspection process before shipment to verify compliance with all specifications and standards. Additionally, consider third-party quality assurance services to provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric vehicles?
When importing electric vehicles, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs clearance procedures, and delivery timelines. Select a reliable logistics partner experienced in handling automotive imports. Ensure that all necessary documentation, including the EEC COC, is prepared for customs to avoid delays. Familiarize yourself with the import regulations of your destination country to ensure compliance and smooth operations upon arrival.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Electric Car Eec Coc Certificate Manufacturers & Suppliers List
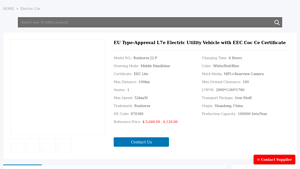
1. Run Horse – Low Speed Electric Utility Vehicle
Domain: runhorseev.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Low Speed Mini Passenger Car EEC COC Certification Electric Utility Vehicle
– Size: 2390x1200x1700 mm
– Curb Weight: 416 kg
– Loading Capacity: 150 kg
– Max Speed: 45 km/h
– Battery: 105Ah lithium battery
– Max Range: 115 km
– Charging Time: Full charge in 3 hours with fast charger
– Seating Capacity: 2 seats
– Wheelbase: 1580 mm
– Min Ground Clearance: 180 mm
– Power System: A/C Motor 60V 3000W
-…
2. Automatic Electric Car – FWD-QH4
Domain: automaticelectriccar.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: {“Model Number”:”FWD-QH4″,”Motor Power”:”2.2 KW (2200W)”,”Maximum Speed”:”45KM/H”,”Voltage”:”60V”,”Curb Weight”:”341kg (Without Batteries Weight)”,”Charging Time”:”6-8 hours”,”Dimensions”:”2605*1295*1610MM”,”Max Load”:”225kg”,”Driving Range”:”60km (with 58Ah battery), 80-100 km (with 80Ah battery)”,”Battery”:”60V 58AH Lead-acid battery”,”Passenger Capacity”:”2-3 (2 doors, 3 seats)”,”Body Type”:”Cl…
3. Fodauto – FWD-QH4 Electric Passenger Vehicle
Domain: fodauto.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Model: FWD-QH4
Driving Type: Electric
Use For: Passenger
Body Type: Closed
Certification: EEC
Dimension (L*W*H): 2605*1295*1610MM
Net Weight: 341kg (Without batteries weight)
Maximum Speed: 25-45km/h
Max Load: 225kg
Driving Range: 60km
Motor: Brushless 60V 2200W
Battery: 60V 58AH
Charging Time: 8-10 hours
Tyre: 125/65-12*4
Passenger Capacity: 2-3 (2 doors, 3 seats)
Customization: YES
4. Yunlong – Y2-C Electric Vehicle
Domain: bev-cars.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Brand: Yunlong
Model: Y2-C
Certification: EEC L6e
Supply Ability: 1000 units/month
Minimum Order Quantity: 1 unit
Port: Qindao
Delivery Terms: 20-40 days after receiving deposit
Load Capacity: 2 units for 1*20’ GP, 8 units for 1*40 HQ
Dimensions (L*W*H): 2890*1180*1780 mm
Wheelbase: 1840 mm
Ground Clearance: 160 mm
Curb Weight: 405 kg
Max Speed: 45 km/h
Max Range: 80-100 km
Seating Capacity: 1 per…
5. Weiyun – EEC COC Certificate 3000W Lithium Battery Mini Smart Electric Car
Domain: indiamart.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”:”EEC COC CERTIFICATE 3000W Motor LITHIUM BATTERY MINI SMART ELECTRIC CAR FOR ADULT FAMILY USE”,”Price”:”₹ 150000″,”Place of Origin”:”Jiangsu, China”,”Brand Name”:”weiyun”,”Max Speed”:”40km/h”,”Motor”:”3000w motor”,”Shipping Information”:{“Availability”:”In Stock”,”Ships From”:”Jaipur”,”Delivery Time”:”2 TO 3 WORKING DAYS”,”Packaging”:”COMES WITH FULL WARRANTY”},”Company Information…
6. Runhorse – J2-P Electric Scooter
Domain: diplomatie.gouv.ne
Introduction: {“Model”:”Runhorse J2-P”,”Charging Time”:”6 Hours”,”Steering Mode”:”Middle Handlebar”,”Color Options”:”White/Red/Blue”,”Certificate”:”EEC L6e”,”Multimedia”:”MP5 + Rearview Camera”,”Max Distance”:”100 km”,”Mini Ground Clearance”:”160 mm”,”Seater”:”1″,”Dimensions (L*W*H)”:”2890*1180*1780 mm”,”Max Speed”:”52 km/h”,”Transport Package”:”Iron Shelf”,”Trademark”:”Runhorse”,”Origin”:”Shandong, China”,”HS …
7. EV Remarketing – Certificate of Conformity
Domain: ev-remarketing.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: COC document (Certificate of Conformity) is an official certification issued by vehicle manufacturers, ensuring compliance with European safety and environmental standards. It includes comprehensive technical data about the vehicle such as brand, model, year of manufacture, and Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). The COC document is crucial for vehicle registration, especially for imported vehicl…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric car eec coc certificate
In navigating the complex landscape of electric vehicle (EV) certification, particularly the EEC COC, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to ensure compliance and market readiness. Understanding the mandatory components—such as the World Manufacturer Identifier, ISO certifications, E-MARK for parts, and the role of an authorized EU representative—is essential for seamless entry into the European market.
By establishing strong relationships with certified suppliers and maintaining consistent sourcing of E-MARK components, businesses can mitigate risks associated with certification complications and enhance their product offerings. This proactive approach not only ensures compliance but also builds credibility with stakeholders and customers alike.
Looking ahead, the demand for electric vehicles is set to grow, driven by global sustainability initiatives and consumer preferences. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, now is the time to leverage strategic sourcing practices to position your business favorably within this burgeoning market. Engage with trusted partners and invest in the necessary certifications to unlock new opportunities and drive growth in the electric vehicle sector.