Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric car no license
In an era where sustainable mobility is gaining momentum, the demand for electric cars that require no driver’s license is on the rise. This emerging market segment addresses a crucial challenge: how to provide accessible, eco-friendly transportation options for populations that may lack the necessary driving credentials. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the types and applications of electric cars without licenses, enabling B2B buyers to navigate their sourcing needs effectively.
From lightweight quadricycles designed for urban commuting to innovative models like the Microlino and Squad Solar Car, this guide delves into various vehicle options tailored to different markets. It covers essential aspects such as supplier vetting, pricing structures, and legal requirements across regions, ensuring that buyers can make informed decisions that align with local regulations and consumer preferences.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Nigeria and Vietnam—this guide serves as an invaluable resource. It empowers businesses to capitalize on the growing trend of license-free electric vehicles, fostering sustainable urban mobility solutions while addressing the unique needs of diverse markets. By equipping buyers with actionable insights, this guide facilitates strategic sourcing decisions that not only enhance mobility but also contribute to a greener future.
Understanding electric car no license Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Quadricycles | Weigh up to 425 kg, limited speed (up to 45 km/h), designed for urban use | Short-distance urban commuting | Pros: Cost-effective, accessible for younger drivers; Cons: Limited range and speed. |
| Compact Electric Cars | Higher speeds (up to 90 km/h), designed for everyday use | Small business transportation, ride-sharing | Pros: Versatile, suitable for various applications; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Solar City Cars | Powered by solar energy, compact design, minimal licensing requirements | Eco-friendly transport solutions | Pros: Sustainable, low operational costs; Cons: Dependence on sunlight availability. |
| Microcars | Extremely compact, designed for dense urban environments | Urban delivery services, personal mobility | Pros: Easy parking, low cost; Cons: Limited passenger capacity and cargo space. |
| E-scooter-like Vehicles | Two or three wheels, can be classified as light quadricycles | Last-mile delivery, rental services | Pros: Highly maneuverable, low cost; Cons: Less stable than four-wheeled options. |
What Are Light Quadricycles and Their B2B Relevance?
Light quadricycles are small electric vehicles that weigh up to 425 kg and are limited to a maximum speed of 45 km/h. They serve as an ideal solution for urban commuting, especially for businesses focusing on short-distance travel. B2B buyers can leverage these vehicles for fleet operations aimed at younger drivers or those without a traditional driver’s license. The affordability and accessibility make them appealing for companies looking to expand their transportation options while addressing urban congestion and emissions.
How Do Compact Electric Cars Fit into B2B Operations?
Compact electric cars are designed for everyday use, capable of reaching speeds of up to 90 km/h. They are suitable for small businesses requiring reliable transportation solutions, such as delivery services or employee commuting. While they represent a higher initial investment compared to lighter quadricycles, their versatility and ability to cover longer distances make them a valuable asset for companies looking to enhance their mobility offerings. Buyers should consider the balance between upfront costs and potential operational efficiency.
What Are the Advantages of Solar City Cars for Businesses?
Solar city cars represent a cutting-edge solution in sustainable urban mobility. These compact vehicles utilize solar energy for operation, minimizing reliance on conventional charging infrastructure. They are well-suited for businesses aiming to reduce their carbon footprint and operational costs. The ability to charge using solar energy can lead to significant savings over time. However, businesses must assess the feasibility of solar charging in their operational areas, particularly in regions with variable sunlight.
Why Choose Microcars for Urban Delivery Services?
Microcars are designed for dense urban environments, featuring a compact form factor that makes them ideal for navigating narrow streets and tight parking spaces. They serve various B2B applications, particularly in urban delivery services where space and efficiency are paramount. While their limited passenger and cargo capacity may pose challenges for larger shipments, their low operational costs and ease of use make them a practical choice for businesses focused on last-mile delivery solutions.
How Do E-scooter-like Vehicles Enhance Last-Mile Delivery?
E-scooter-like vehicles, which can be classified as light quadricycles, offer a unique solution for last-mile delivery. Their two or three-wheel design allows for high maneuverability in congested urban areas, making them ideal for quick deliveries. B2B buyers interested in rental services or delivery operations can benefit from their low acquisition costs and ease of use. However, potential buyers should weigh the stability and load-carrying limitations against the operational needs of their business.
Key Industrial Applications of electric car no license
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric car no license | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Mobility Services | Ride-sharing and micro-mobility solutions | Reduced operational costs and increased accessibility | Compliance with local regulations and safety standards |
| Logistics and Delivery | Last-mile delivery vehicles | Enhanced efficiency in urban environments | Vehicle range, charging infrastructure, and payload capacity |
| Tourism and Leisure | Sightseeing and rental services | Unique experience offerings that attract tourists | Customization options and fleet management capabilities |
| Educational Institutions | Campus transport for students and staff | Cost-effective and eco-friendly transportation | Durability, maintenance support, and charging solutions |
| Retail and Shopping | Shopping center shuttles | Increased customer footfall and satisfaction | Integration with existing transport systems and safety features |
How Are Electric Cars Without a License Used in Urban Mobility Services?
In urban mobility services, electric cars without a license serve as practical solutions for ride-sharing and micro-mobility. Their compact size and lower speed limits make them ideal for congested city environments, allowing operators to reduce operational costs while increasing accessibility for users who may not have a traditional driver’s license. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, it is crucial to ensure compliance with local regulations governing electric vehicles and to assess the safety standards that these vehicles must meet.
What Are the Benefits of Electric Cars Without a License in Logistics and Delivery?
Electric cars without a license are increasingly utilized in last-mile delivery scenarios, where they can navigate urban areas efficiently while minimizing environmental impact. These vehicles offer an enhanced solution for businesses looking to streamline their logistics operations. Buyers must consider the vehicle’s range, charging infrastructure, and payload capacity to ensure they meet the demands of their delivery routes, especially in regions with limited charging stations.
How Can Electric Cars Without a License Enhance Tourism and Leisure Services?
In the tourism sector, electric cars without a license can be used for sightseeing tours and rental services, providing a unique and eco-friendly experience for tourists. These vehicles appeal to younger audiences and environmentally-conscious travelers, offering an engaging way to explore cities. B2B buyers should focus on customization options that align with their branding and the specific needs of their clientele, alongside fleet management capabilities to maintain operational efficiency.
Why Are Electric Cars Without a License Ideal for Educational Institutions?
Educational institutions can leverage electric cars without a license for campus transport, facilitating easy movement for students and staff. These vehicles are cost-effective and environmentally friendly, aligning with sustainability goals. Buyers should prioritize the durability of the vehicles, as well as maintenance support and charging solutions, to ensure they can withstand daily use in diverse weather conditions, especially in regions with varying climates.
How Do Electric Cars Without a License Benefit Retail and Shopping?
In retail environments, electric cars without a license can be employed as shuttle services between shopping centers and nearby transport hubs, enhancing customer footfall and satisfaction. These services provide convenience for shoppers and can help reduce congestion in busy areas. When sourcing these vehicles, businesses should consider their integration capabilities with existing transport systems and the safety features necessary to ensure a secure shopping experience for customers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric car no license’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Challenges for License-Free Electric Cars
The Problem: As a B2B buyer, one of the primary concerns when sourcing electric cars that don’t require a license is the regulatory landscape. Different countries have varying laws regarding quadricycles and electric vehicles, particularly concerning speed limits, weight restrictions, and operational zones. Buyers often face confusion about which vehicles meet legal requirements in their target markets, leading to potential legal issues and financial losses from non-compliance. This complexity can stall procurement processes, as businesses may hesitate to invest in models that could be deemed illegal or unsuitable for their intended use.
The Solution: To effectively navigate these regulatory challenges, B2B buyers should engage with local automotive regulatory bodies and legal advisors who specialize in transportation laws. Establishing partnerships with manufacturers that have a strong understanding of regional laws can also be beneficial. When sourcing electric cars, prioritize those that are designed to comply with the specific regulations of your target market. For instance, vehicles like the Micro Microlino Lite are tailored to meet L6e quadricycle regulations, allowing for operation by individuals as young as 14. By ensuring that the selected models are compliant, buyers can streamline their procurement processes and minimize legal risks.
Scenario 2: Addressing Safety Concerns for Users of Electric Cars Without a License
The Problem: Safety is a paramount concern for businesses looking to adopt electric cars that do not require a license, especially when these vehicles are intended for use by younger drivers or inexperienced users. Many stakeholders, including fleet managers and organizational decision-makers, worry about the potential for accidents and the liability that comes with operating vehicles with reduced training requirements. This fear can hinder the adoption of innovative electric mobility solutions, leaving businesses reliant on outdated transportation methods.
The Solution: To address safety concerns, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing electric cars that come equipped with advanced safety features and robust construction. Vehicles like the Squad Solar City Car, designed with a full crash structure and roll cage, can provide a higher level of safety for users. Additionally, offering training sessions for users can greatly enhance safety and operational knowledge. Buyers should also consider integrating telematics solutions that monitor driving behavior and vehicle performance, allowing for real-time data analysis to identify risky driving habits. By focusing on safety, businesses can confidently implement electric cars without a license, ensuring user protection and reducing liability.
Scenario 3: Overcoming the Limited Range of License-Free Electric Vehicles
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is the limited range of electric cars that do not require a license. Many models are designed for urban commuting, which can lead to concerns about their ability to handle longer trips or extended use. This limitation can deter companies from investing in these vehicles, especially those in sectors like logistics or delivery services where longer distances are commonplace.
The Solution: To mitigate range anxiety, B2B buyers should conduct thorough market research to identify electric cars with superior range capabilities. For instance, models that offer battery-swapping options, like the Squad Solar City Car, provide a practical solution for extending operational range without the need for prolonged charging periods. Businesses can also consider implementing charging infrastructure in strategic locations to ensure that vehicles can be quickly recharged during the workday. Furthermore, fostering partnerships with local charging networks can enhance accessibility for users. By strategically selecting vehicles with longer ranges and establishing supportive infrastructure, companies can effectively integrate electric cars without licenses into their operations, maximizing their utility and efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric car no license
What Are the Key Materials for Electric Cars Without a License?
When considering the manufacturing of electric cars that do not require a driver’s license, material selection plays a crucial role in product performance, safety, and market acceptance. Here we analyze four common materials used in these vehicles: aluminum, high-strength steel, composite materials, and plastics. Each material has unique properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Electric Cars Without a License?
Aluminum is a popular choice for electric vehicles due to its lightweight properties, which contribute to improved energy efficiency and range. Key properties include excellent corrosion resistance and a good strength-to-weight ratio. The use of aluminum can enhance vehicle performance, particularly in terms of acceleration and braking.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, lightweight, and offers good thermal conductivity, making it suitable for battery enclosures and structural components. It is also relatively easy to manufacture and can be recycled efficiently.
Cons: The primary disadvantage of aluminum is its higher cost compared to steel, which can impact the overall vehicle price. Additionally, aluminum requires specialized welding techniques, which may complicate manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Aluminum components can withstand various environmental conditions, making them suitable for urban mobility applications. However, buyers must ensure compliance with international standards like ASTM and DIN for safety and performance.
What Role Does High-Strength Steel Play in Electric Vehicle Design?
High-strength steel (HSS) is often used in the chassis and structural components of electric cars without a license. Its key properties include excellent tensile strength and impact resistance, which are critical for passenger safety.
Pros: HSS is cost-effective and provides superior strength, allowing for thinner components that reduce overall vehicle weight while maintaining safety standards. This material is widely available and adheres to various international standards.
Cons: While HSS is strong, it is heavier than aluminum, which can affect energy efficiency. Additionally, it may be more susceptible to corrosion unless properly treated.
Impact on Application: HSS is particularly suited for regions with varying climates, as it can endure harsh conditions when adequately protected. Buyers should consider the local availability of HSS and compliance with standards like JIS or EN.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Electric Vehicle Performance?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, are increasingly used in electric vehicles for their lightweight and high-strength properties. These materials are particularly beneficial in reducing overall vehicle weight without compromising structural integrity.
Pros: Composites offer excellent fatigue resistance and thermal stability, making them ideal for high-performance applications. They can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Cons: The primary limitation of composites is their high manufacturing cost and complexity. They often require specialized equipment and expertise, which can be a barrier for manufacturers in emerging markets.
Impact on Application: Composites can be particularly advantageous for electric cars targeting urban environments, where weight reduction can lead to better efficiency. However, B2B buyers must ensure that the composite materials meet relevant international standards for safety and performance.
What Are the Advantages of Using Plastics in Electric Cars?
Plastics are widely used in electric vehicles for components such as dashboards, interior fittings, and body panels. Key properties include lightweight, corrosion resistance, and ease of molding.
Pros: Plastics are cost-effective and can be produced in large quantities with relatively low energy consumption. They also allow for greater design flexibility and can be recycled.
Cons: The main disadvantage is that plastics may not provide the same level of structural integrity as metals, which can be a concern for safety-critical components. Additionally, some plastics can degrade under UV exposure unless treated.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for various applications in electric cars, especially in regions with milder climates. Buyers should consider the environmental impact of plastic use and ensure compliance with local recycling regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Cars Without a License
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric car no license | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, battery enclosures | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost than steel | High |
| High-Strength Steel | Chassis and structural components | Cost-effective and strong | Heavier than aluminum | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Body panels, interior components | Lightweight and design flexibility | High manufacturing cost | High |
| Plastics | Interior fittings, non-structural components | Cost-effective and versatile | Lower structural integrity | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the various materials used in electric cars without licenses, enabling informed decisions that align with performance, safety, and market requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric car no license
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of License-Free Electric Cars?
The manufacturing of electric cars without a license, also known as quadricycles or voiturettes, involves several key stages that ensure the vehicles are safe, efficient, and compliant with international standards.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Commonly Used?
The first stage of the manufacturing process involves sourcing high-quality materials. Manufacturers typically use lightweight materials such as aluminum and high-strength steel to optimize performance while adhering to weight restrictions. The battery technology employed is crucial; lithium-ion batteries are prevalent due to their energy density and efficiency. Additionally, manufacturers may utilize composite materials for body panels to enhance durability and reduce overall vehicle weight.
How Are License-Free Electric Cars Formed?
In the forming stage, raw materials are processed into usable components. Techniques such as stamping, bending, and extrusion are common for shaping metal parts. For electric car bodies, manufacturers might use injection molding for plastic components or advanced techniques like hydroforming for more complex shapes. This stage is critical for ensuring that each part meets the specifications required for safety and performance.
What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
During the assembly phase, various components, such as the chassis, electric motor, battery pack, and interior features, are brought together. This is often done on an assembly line, where each worker or robotic system is responsible for a specific task. Attention to detail is paramount, as the integration of electrical systems with mechanical components must be flawless to prevent future malfunctions.
How Is the Finishing Stage Conducted?
The final manufacturing stage is finishing, which includes painting, surface treatment, and quality checks. Paint processes must not only be aesthetically pleasing but also provide corrosion resistance. Manufacturers often employ automated systems for painting to ensure uniformity and quality. Additionally, this stage may involve applying decals or branding, which is vital for commercial vehicles targeting B2B buyers.
What Quality Assurance Practices Should B2B Buyers Expect?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for license-free electric cars. It encompasses various checks and balances to ensure that the final product meets safety and performance standards.
Which International Standards Apply to Electric Cars?
International standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, are essential for manufacturers. Compliance with CE marking indicates that the product meets European safety, health, and environmental protection standards. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as those from the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG), are crucial for ensuring that quality standards are maintained throughout the production process.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established at various stages of the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of materials received from suppliers. It ensures that all components meet the specified standards before entering the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the assembly process, IPQC checks are performed to monitor the quality of workmanship and adherence to specifications. This is particularly important in the assembly of complex electrical systems.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before a vehicle leaves the manufacturing facility, a thorough inspection is conducted to verify that it meets all performance and safety standards. This includes testing electrical systems, battery performance, and overall vehicle functionality.
What Common Testing Methods Are Utilized in Quality Assurance?
Manufacturers employ a range of testing methods to validate the quality of their vehicles:
-
Functional Testing: This involves evaluating the vehicle’s performance under various conditions to ensure it operates as intended. For electric cars, this includes testing acceleration, braking, and battery efficiency.
-
Safety Testing: Compliance with safety regulations is vital. Testing may include crash simulations, electrical safety tests, and emissions testing to ensure the vehicle meets environmental standards.
-
Durability Testing: Vehicles are subjected to stress tests to evaluate how they perform over time. This includes simulating extreme conditions to ensure reliability in diverse environments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers need to take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers.
What Audit Processes Should Buyers Implement?
Conducting audits of manufacturing facilities is one of the most effective ways to assess a supplier’s quality control practices. Buyers should request detailed reports of past audits and certifications. This includes:
-
Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide unbiased evaluations of the manufacturing processes and quality standards.
-
Supplier Quality Reports: Manufacturers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC checks.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control across different regions is essential. Variations in regulatory requirements and standards can impact product quality. Buyers should consider:
-
Local Regulations: Familiarize themselves with local automotive regulations in target markets, as these can differ significantly from international standards.
-
Cultural Factors: Acknowledge cultural differences in manufacturing practices and expectations. This understanding can help in establishing stronger partnerships with suppliers.
-
Logistical Considerations: Ensure that logistics and supply chain management practices are robust, as these can affect the timely delivery of quality products.
Conclusion
Manufacturing and quality assurance processes for license-free electric cars are intricate and demand meticulous attention to detail. For B2B buyers, understanding these processes is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. By focusing on supplier quality control, international standards, and robust testing methods, businesses can ensure they acquire vehicles that meet their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric car no license’
This guide aims to provide B2B buyers with a clear and actionable checklist for sourcing electric cars that do not require a driver’s license. As demand for sustainable and accessible transportation options grows, understanding the procurement process for these vehicles is essential for businesses looking to invest in this market.
Step 1: Identify Your Target Market
Understanding your target demographic is the first step in sourcing electric cars without a license. Analyze the needs and preferences of potential users in your region, such as urban commuters, teenagers, or businesses that require fleet vehicles. Knowing your audience will help tailor your procurement strategy and select models that meet their expectations.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before approaching suppliers, outline the technical specifications required for the electric cars. Consider factors such as range, speed limitations, battery capacity, and vehicle dimensions. These criteria will help narrow down your options and ensure that the selected vehicles comply with local regulations regarding license-free driving.
- Range: Look for vehicles with a range suitable for your target market’s daily usage.
- Speed: Ensure the models comply with the maximum speed limits set for no-license vehicles.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they meet your quality and service standards. Request detailed company profiles, including their manufacturing capabilities, experience in the industry, and customer testimonials. This step is critical to avoid potential issues with product quality or support.
- Case Studies: Ask for examples of successful partnerships with other businesses.
- Certifications: Verify that suppliers adhere to industry standards and regulations.
Step 4: Assess Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the electric cars comply with the specific regulations in your target markets. Different regions may have varying requirements for no-license vehicles, including weight limits, speed restrictions, and safety standards. Compliance is crucial to avoid legal issues and ensure smooth market entry.
- Documentation: Request official documentation proving compliance with local laws.
- Testing: Inquire about any testing or certifications the vehicles have undergone.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you’ve identified suitable suppliers, engage in negotiations regarding pricing and terms of sale. Consider factors such as volume discounts, leasing options, and payment terms that can affect the overall cost of procurement. Establishing favorable terms can significantly impact your budget and profitability.
- Leasing vs. Buying: Evaluate the benefits of leasing vehicles versus outright purchase.
- Warranty and Service: Negotiate warranty terms and after-sales service support.
Step 6: Plan for Logistics and Distribution
Develop a logistics plan to manage the transportation and distribution of the electric cars once procured. Consider factors such as shipping methods, storage facilities, and the timeline for delivery. A well-planned logistics strategy ensures that you can promptly meet market demand without delays.
- Shipping Options: Explore various shipping methods to find the most cost-effective solutions.
- Inventory Management: Prepare for storage and handling of the vehicles upon arrival.
Step 7: Implement Marketing Strategies
Finally, create a marketing strategy to promote the newly sourced electric cars in your target markets. Highlight the benefits of no-license vehicles, such as accessibility, cost savings, and environmental impact. Effective marketing will help establish your brand and attract potential customers.
- Targeted Campaigns: Utilize digital marketing and social media to reach your audience effectively.
- Partnerships: Consider collaborations with local businesses or influencers to enhance visibility.
By following this comprehensive checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for electric cars that do not require a driver’s license, ensuring a successful investment in this growing market.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric car no license Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Electric Cars Without a License?
When analyzing the cost structure of electric cars without a license, several key components come into play.
-
Materials: The primary materials include the battery, chassis, electric motor, and various electronic components. The battery, in particular, constitutes a significant portion of the overall cost, driven by lithium-ion technology and other raw materials such as cobalt and nickel. Fluctuations in these raw material prices can directly affect sourcing costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the manufacturing location. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, the overall cost of production may be reduced. However, skilled labor for assembly and quality control may still command higher wages, especially in Europe or regions with advanced manufacturing standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility maintenance, and indirect labor costs associated with production. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs, impacting the pricing structure positively.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for production can be substantial, especially for custom designs. These costs are typically amortized over the production volume, meaning that higher volume orders can significantly reduce the per-unit tooling cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with safety and performance standards is critical, particularly in international markets. QC processes can add to overall costs but are essential for maintaining brand reputation and meeting regulatory requirements.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, can vary widely based on the distance from the manufacturing site to the buyer’s location. Incoterms also play a crucial role, as they define responsibilities between buyers and sellers regarding transport and risk.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically factor in a profit margin that reflects the risk and investment involved in producing electric cars without a license. This margin can vary based on market conditions, competition, and demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Electric Cars Without a License?
Several factors influence the pricing of electric cars without a license:
-
Volume/MOQ: Ordering in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers often have minimum order quantities (MOQs) that can affect pricing, making it crucial for buyers to understand their needs and negotiate accordingly.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the additional expenses incurred.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., safety, environmental) can raise production costs. Buyers should ensure that the selected suppliers can meet necessary standards to avoid future liabilities.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while newer entrants might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms is vital. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the total landed cost of the product.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Electric Cars Without a License?
To maximize cost-efficiency and ensure a favorable deal, buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage bulk orders and long-term commitments to negotiate better pricing. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can also lead to more favorable terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider factors such as maintenance, charging infrastructure, and potential resale value. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher long-term expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Different regions may have varying regulations, taxes, and tariffs affecting pricing. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of these factors to make informed decisions.
-
Conduct Market Research: Stay updated on market trends and competitor pricing. This knowledge can empower buyers to negotiate better deals and select the most suitable suppliers.
-
Seek Local Partnerships: In regions with developing markets, partnering with local entities can enhance distribution efficiency and reduce logistics costs.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures mentioned are indicative and can vary significantly based on numerous factors including market conditions, regional economic factors, and individual supplier terms. Always perform due diligence and seek multiple quotes before finalizing sourcing agreements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric car no license With Other Solutions
In today’s evolving transportation landscape, businesses are increasingly seeking sustainable and efficient mobility solutions. The ‘electric car no license’ category—often referred to as quadricycles—offers a unique opportunity for individuals and companies alike. However, several alternatives exist that may also meet the needs of B2B buyers. This analysis compares electric cars that require no license with alternative solutions, focusing on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Car No License | Micro Electric Car | Solar City Car |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Limited to 45 km/h | Limited to 40 km/h | Limited to 45 km/h |
| Cost | €24,900 – €63,240 | Approx. €14,000 | Approx. €18,000 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure | Minimal setup needed | Solar charging reduces dependency on grids |
| Maintenance | Moderate | Low | Low |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting | Short-distance trips | Eco-friendly urban mobility |
What Are the Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Micro Electric Cars?
Micro electric cars, such as the Microlino Lite, are compact and designed to cater to a younger audience, as they can be driven by individuals as young as 14 in some regions. They are ideal for short-distance trips, such as commuting to school or running errands. The lower cost (approximately €14,000) makes them accessible, but their limited speed and range may not suit all users. Additionally, while they require minimal setup, they still depend on charging infrastructure, which can be a limitation in areas with underdeveloped electricity networks.
How Does the Solar City Car Stand Out?
The Solar City Car, like the Squad model, represents an innovative approach to urban mobility by incorporating solar technology. This vehicle is designed for sharing platforms and private use, making it a versatile solution for daily commutes or errands. Its ability to charge itself through solar energy significantly reduces dependence on traditional charging stations. While the initial cost is competitive at around €18,000, its performance is similar to that of the electric car no license. It has low maintenance needs, but the effectiveness of solar charging can vary depending on geographic and seasonal conditions.
Conclusion: Which Solution Should B2B Buyers Choose?
When selecting the right mobility solution, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including their specific use case, geographic location, and budget. If the primary need is for urban commuting without the requirement for a driver’s license, an electric car no license may be the best choice due to its higher performance and established market presence. However, for businesses focused on sustainability and innovative technology, exploring micro electric cars or solar city cars could provide unique advantages, especially in regions with robust solar potential. Ultimately, the decision should align with the operational goals and infrastructure capabilities of the business, ensuring a balance between cost, efficiency, and sustainability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric car no license
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of License-Free Electric Cars?
When considering the procurement of electric cars that do not require a driver’s license, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for B2B buyers. These specifications not only influence the vehicle’s performance but also its compliance with local regulations, which can vary widely between regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here are some critical properties to consider:
1. Weight Limitations
License-free electric cars, often classified as quadricycles, typically have weight restrictions that vary by region. For instance, light quadricycles must not exceed an unladen weight of 425 kg. This is vital for manufacturers to ensure compliance with local vehicle regulations, affecting market access and sales strategies.
2. Speed Capabilities
Most license-free electric vehicles are limited to a maximum speed of 45 km/h (28 mph) for light quadricycles. This speed cap is designed to enhance safety for inexperienced drivers. Understanding speed limitations is crucial for B2B buyers targeting markets with specific regulations, as it influences consumer acceptance and operational use cases.
3. Battery Specifications
The battery capacity, usually measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), is a significant factor affecting the vehicle’s range and performance. For example, many license-free electric cars offer ranges between 220 km to 500 km on a single charge. B2B buyers should prioritize battery longevity and charging times, as these affect user satisfaction and operational efficiency.
4. Material Composition
The materials used in the construction of these vehicles can impact durability, weight, and overall performance. Common materials include lightweight metals and composites that enhance efficiency. Buyers must consider material grades to ensure that vehicles meet specific safety and durability standards, which can be particularly important in diverse markets.
5. Charging Infrastructure Compatibility
Understanding the compatibility of vehicles with various charging systems is essential. Many license-free electric cars support fast charging capabilities, allowing them to recharge from 20% to 80% in approximately 20 to 30 minutes. This feature is critical for fleet operators who need to minimize downtime, thus affecting procurement decisions.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in the Electric Car Industry?
In addition to technical properties, familiarizing oneself with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the electric vehicle sector. Here are some commonly used terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that manufactures products or components that are purchased by another company and sold under that company’s brand name. In the electric car sector, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers assess the reliability and quality of the vehicles they are purchasing.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a buyer must purchase from a supplier. This term is significant for B2B buyers, as it affects pricing structures and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their procurement strategies effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. B2B buyers should be adept at crafting RFQs to ensure they receive competitive pricing and terms, especially when dealing with multiple suppliers in the electric vehicle market.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, covering aspects such as shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B buyers to mitigate risks and clarify the logistics of vehicle delivery.
5. L6e and L7e Classifications
These classifications refer to specific categories of light quadricycles under EU regulations. The L6e category typically covers vehicles with a maximum speed of 45 km/h, while L7e includes those with higher speed limits. Familiarity with these classifications is essential for compliance and market entry strategies.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can navigate the electric car no license market more effectively, ensuring informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory environments.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric car no license Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Trends Affecting the Electric Car No License Sector?
The electric car no license sector is witnessing transformative changes driven by shifting consumer preferences and regulatory developments. Globally, the demand for small, affordable, and eco-friendly vehicles is surging, particularly among younger demographics and urban dwellers seeking alternatives to traditional cars and scooters. Factors such as increasing urban congestion, rising fuel prices, and a growing emphasis on sustainable transportation options are propelling the popularity of electric quadricycles or “voiturettes.”
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is critical. Emerging technologies, such as battery-swapping systems and solar charging solutions, are reshaping sourcing strategies. Buyers should focus on suppliers that integrate these innovations to enhance vehicle efficiency and reduce downtime. Additionally, local regulations in markets like Nigeria and Vietnam are evolving to accommodate these vehicles, creating opportunities for businesses to tap into new customer segments.
Notable trends include the rise of compact city cars designed for ease of use and affordability, such as the Microlino Lite and Squad Solar City Car, which cater to regulations allowing operation without a driver’s license. This trend aligns with the global push towards sustainable urban mobility, making it essential for B2B buyers to align their procurement strategies with these technological advancements and market demands.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Decisions in the Electric Car No License Sector?
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it is a crucial factor influencing B2B procurement decisions in the electric car no license sector. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing environmentally friendly materials and production processes, recognizing that ethical sourcing can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty. Companies are urged to assess their supply chains for sustainability, ensuring that materials are sourced from suppliers who adhere to strict environmental standards and practices.
The environmental impact of electric vehicles extends beyond their operation; it encompasses the entire lifecycle from manufacturing to disposal. B2B buyers should seek suppliers who utilize green certifications and sustainable materials, such as recyclable batteries and eco-friendly manufacturing processes. This commitment not only addresses consumer demand for environmentally responsible products but also positions companies to benefit from potential government incentives and subsidies aimed at promoting sustainable practices.
Furthermore, fostering ethical supply chains can mitigate risks associated with supply disruptions and enhance resilience. In regions like Africa and South America, where sourcing materials can be challenging, establishing partnerships with local suppliers who prioritize sustainability can create a competitive edge.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Electric Car No License Sector Relevant for B2B Buyers?
The electric car no license sector has evolved significantly over the past two decades. Initially, these vehicles were perceived as niche products primarily catering to specific demographics, such as teenagers and urban commuters. However, as urbanization accelerates and environmental concerns heighten, the sector has gained traction across diverse consumer segments.
Regulatory changes in Europe, particularly the introduction of the L6e and L7e quadricycle classifications, have enabled manufacturers to develop compact, low-speed electric vehicles that do not require a driver’s license. This evolution has opened new markets for B2B buyers, allowing them to explore innovative models like the Citroën Ami and Fiat Topolino, which blend functionality with accessibility.
In recent years, technological advancements, including improved battery technologies and integrated smart features, have further propelled the sector’s growth. For B2B buyers, staying attuned to these historical shifts is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions and leveraging opportunities in this burgeoning market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric car no license
-
How do I determine the best electric car without a license for my market?
To select the ideal electric car without a license for your market, consider local regulations, market demand, and consumer preferences. Research the specifications of popular models, such as range, speed, and safety features. Engage with potential buyers through surveys or focus groups to understand their needs. Additionally, analyze competitors’ offerings in your region to identify gaps that your product can fill, ensuring a competitive advantage. -
What are the key specifications to look for in a license-free electric car?
When evaluating license-free electric cars, focus on specifications such as maximum speed (typically limited to 45 km/h for quadricycles), range on a single charge, battery capacity, and charging time. Other important factors include vehicle weight, safety features, and comfort. Additionally, consider local regulations that may affect vehicle classification and usage, ensuring compliance with the laws in your target market. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for electric cars without a license?
The MOQ for electric cars without a license can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the specific model. Typically, manufacturers may require an MOQ ranging from 10 to 100 units for bulk purchases. It’s crucial to communicate your needs directly with suppliers to negotiate the best terms. Additionally, consider the potential for future orders to establish a long-term partnership. -
How can I vet suppliers for electric cars without a license?
Vetting suppliers involves researching their background, production capacity, and market reputation. Request references from previous clients and assess their experience in exporting to your region. Evaluate their compliance with international safety and environmental standards, and consider visiting their facilities if feasible. Additionally, inquire about their after-sales support and warranty terms to ensure they can meet your ongoing needs. -
What are the payment terms typically offered for electric car purchases?
Payment terms for electric car purchases can vary widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include advance payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or installment plans for larger orders. It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow while ensuring the supplier has a solid commitment to fulfilling the order. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric cars?
When importing electric cars, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs in your destination country. Choose a logistics partner experienced in handling automotive imports to navigate these complexities effectively. Additionally, ensure that the vehicles are compliant with local safety standards and that you have all necessary documentation for customs clearance to avoid delays. -
How can I customize electric cars to meet local market demands?
Customization options for electric cars may include altering features such as battery size, color, interior design, and technology integrations. Engage with your target audience to identify specific preferences and requirements. Collaborate with the manufacturer early in the process to ensure that your customization requests can be accommodated without significant delays or cost increases. -
What quality assurance processes should I expect from suppliers?
Suppliers of electric cars without a license should have robust quality assurance (QA) processes in place. This includes compliance with international safety standards, regular inspections during production, and testing of vehicles before delivery. Request documentation of their QA protocols and inquire about warranties or guarantees that protect against defects. A reliable supplier will prioritize quality to maintain their reputation and ensure customer satisfaction.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Electric Car No License Manufacturers & Suppliers List
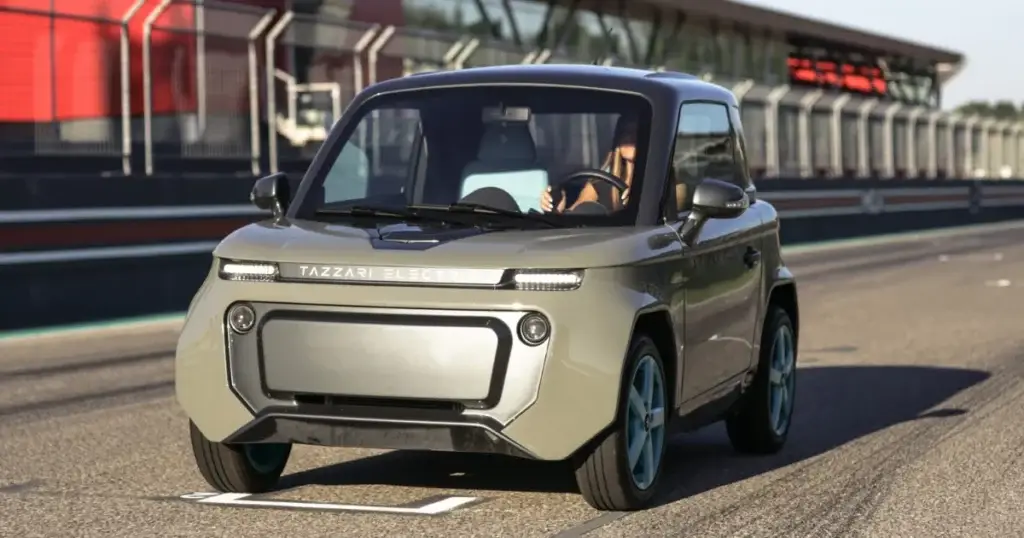
1. Movemnt – Microlino Lite Mini Electric Car
Domain: movemnt.net
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Micro Microlino Lite model, mini electric car, requires no driver’s license, designed for sustainable mobility, adapted for drivers as young as 14, top speed limited to 45 km/h, 12 hp (12 PS) electric motor, maximum speed of 28 mph (40 km/h), complies with L6e quadricycle regulations, goes on sale in Europe this spring.
2. Reddit – Low Speed Electric Vehicles (LSEVs)
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Electric cars that can be driven without a license in China are often classified as Low Speed Electric Vehicles (LSEVs) or referred to as 老头乐 (old geezers delight). They are small electric vehicles that resemble scooters with a larger, enclosed body. These vehicles are primarily used by elderly individuals in rural areas, as they do not require a driver’s license. However, they may pose safety ris…
3. Microlino – Electric Micro-Car
Domain: newatlas.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: The Microlino Lite is an electric micro-car that debuted at the Geneva Motor Show. Key features include a top speed of 45 km/h (28 mph), a standard city range of 100 km (62 miles) per charge, and an optional 11-kWh battery for up to 180 km per charge. It is classified as an L6e vehicle in Europe, allowing some drivers without a license to operate it. The car has a 6-kW motor that peaks at 9 kW, an…
4. Citroën – Ami 100% Electric
Domain: hotcars.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: 1. Citroën Ami: 100% electric, 46 miles range, 5.5 kWh battery, simple exterior and interior, Citroën Switch for navigation and media access.
2. Renault Twizy: 6.1 kWh battery, 56 miles range, 17 horsepower, optional doors, MSRP over $15,000.
3. Aixam Coupé GTI: Diesel engine, 310 miles range, sport-themed suspension, ABS braking system, 3.5-inch TFT screen, leather seats.
4. Mahindra e2o: Lithium…
5. Citroën – Ami 100% Electric Quadricycle
Domain: citroen.co.uk
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Citroën Ami 100% Electric Quadricycle
– Price: From £7,695 OTR for standard model, £8,095 OTR for colour versions.
– Electric: 100% electric vehicle.
– Range: 46-mile range (WMTC).
– Top Speed: 28 mph.
– Charging: Full charge in 4 hours.
– Dimensions: 2.41m long, 1.39m wide, 1.52m high.
– Turning Circle: 7.2m.
– Interior Storage: 63L to 200L (if passenger seat used for storage).
– Warranty: 2-year…
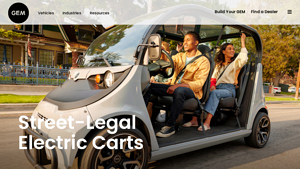
6. Gemcar – Street-Legal Electric Carts
Domain: gemcar.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Street-Legal Electric Carts are designed for on-road driving with a speed of up to 25 mph (40 km/h). They include features such as:
– Enclosed cabs with optional full doors
– High-back upholstered seats with bolster support
– Occupant protection system (OPS) certified to SAE J2358 standards
– Standard safety features: 3-point seat belts, headlights, tail lights, brake lights, parking brake, tu…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric car no license
As the demand for sustainable urban mobility rises, the market for electric cars that do not require a driver’s license is rapidly expanding. These vehicles, including compact quadricycles and innovative models like the Microlino Lite and Squad Solar City Car, offer a unique opportunity for businesses to cater to a growing demographic, particularly among younger drivers and those seeking economical transport solutions.
Strategic sourcing in this segment not only ensures access to the latest technologies and models but also aligns with global trends towards eco-friendly transportation. By leveraging partnerships with manufacturers and suppliers, businesses can enhance their offerings, reduce operational costs, and meet regulatory requirements across diverse markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Looking ahead, the potential for growth in the no-license electric car market is significant. International B2B buyers are encouraged to explore these opportunities, focusing on sourcing vehicles that meet local regulations while providing value to consumers. Embracing this trend will not only contribute to sustainable development but also position businesses as leaders in the evolving landscape of urban mobility.