Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for solar car
In an era where sustainability is paramount, the solar car presents a groundbreaking solution to the pressing challenges of urban mobility and environmental impact. As international B2B buyers seek innovative transportation solutions, understanding the intricacies of sourcing solar vehicles becomes essential. This guide delves into the diverse types of solar cars available, their applications across various markets, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
By providing insights into cost structures, technological advancements, and regulatory considerations, this resource empowers businesses from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Brazil and Nigeria—to make informed purchasing decisions. Solar cars not only promise reduced operational costs through solar charging capabilities but also align with global sustainability goals, offering a competitive edge in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
As you navigate this comprehensive landscape, you will gain valuable knowledge that enhances your understanding of the solar car market, ultimately leading to strategic investments in sustainable transportation solutions. Whether you are looking to integrate solar vehicles into your fleet or exploring potential partnerships with manufacturers, this guide serves as your essential roadmap in the evolving world of solar mobility.
Understanding solar car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Electric Vehicle | Equipped with integrated solar panels, capable of off-grid driving. | Fleet management, car-sharing services. | Pros: Reduces fuel costs, environmentally friendly. Cons: Higher initial investment, limited range in low sunlight. |
| Solar City Car | Compact design optimized for urban use, self-charging capabilities. | Urban mobility solutions, shared transport. | Pros: Space-efficient, low operational costs. Cons: Limited speed and range compared to traditional vehicles. |
| Solar-Powered Microcar | Small, lightweight vehicles designed for short trips and daily commutes. | Last-mile delivery, personal commuting. | Pros: Affordable, easy to maneuver in urban areas. Cons: Limited storage space, not suitable for long distances. |
| Solar Buses | Larger vehicles utilizing solar energy for public transport. | Public transportation systems, tourism. | Pros: Reduces operational costs, eco-friendly. Cons: High upfront cost, requires infrastructure support. |
| Solar-Powered RV | Recreational vehicles equipped with solar panels for off-grid living. | Tourism, outdoor adventures, rental services. | Pros: Self-sufficient, enhances travel experiences. Cons: Higher maintenance costs, limited space for amenities. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Solar Electric Vehicles for B2B Buyers?
Solar Electric Vehicles (SEVs) integrate solar technology with electric propulsion, allowing for reduced reliance on traditional fuel sources. These vehicles are particularly beneficial for fleet management and car-sharing services, where operational costs can significantly decrease due to lower fuel expenses. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment versus long-term savings, as SEVs may have a higher upfront cost but can yield substantial savings over time, especially in regions with abundant sunlight.
How Do Solar City Cars Cater to Urban Mobility Needs?
Solar City Cars are designed specifically for urban environments, featuring compact dimensions and self-charging solar panels. They are ideal for shared transportation platforms, providing a sustainable solution to urban congestion and emissions. For B2B buyers, the affordability and low operational costs make them an attractive option, although the limited speed and range should be evaluated based on specific use cases.
What Advantages Do Solar-Powered Microcars Offer for Last-Mile Delivery?
Solar-Powered Microcars are small, lightweight vehicles that excel in short-distance travel, making them suitable for last-mile delivery and personal commuting. Their affordability and ease of maneuverability in crowded urban areas are significant advantages for businesses looking to optimize logistics. However, buyers should be aware of the limited storage capacity, which may restrict their use for larger deliveries or longer trips.
How Can Solar Buses Transform Public Transportation Systems?
Solar Buses represent a larger category of solar vehicles that can significantly impact public transportation systems. By utilizing solar energy, they reduce operational costs and contribute to a greener public transport network. B2B buyers in the public sector should consider the high initial investment against the potential long-term savings and environmental benefits. Additionally, the successful implementation of solar buses often requires supportive infrastructure, which may vary by region.
What Benefits Do Solar-Powered RVs Provide for Tourism and Outdoor Rentals?
Solar-Powered RVs are designed for recreational use, equipped with solar panels to enable off-grid living. They cater to the tourism sector by providing travelers with a self-sufficient means of exploring remote areas without relying on traditional power sources. For B2B buyers in the rental market, these RVs can enhance customer experience, although considerations around maintenance costs and space for amenities should be factored into purchasing decisions.
Key Industrial Applications of solar car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of solar car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Mobility | Solar-powered city cars for shared mobility | Reduces urban congestion and emissions, lowers operational costs | Compliance with local regulations, battery technology, service support |
| Logistics & Delivery | Solar-assisted delivery vans | Extends range and reduces fuel costs, enhances sustainability | Vehicle durability, solar efficiency, and maintenance options |
| Tourism & Leisure | Solar-powered vehicles for eco-tours | Attracts eco-conscious customers, reduces operational costs | Customization options, partnership with local tourism agencies |
| Agriculture | Solar vehicles for farm operations | Lowers fuel expenses, supports sustainable farming practices | Terrain adaptability, battery life, and maintenance requirements |
| Emergency Services | Solar-powered emergency response vehicles | Ensures continuous operation in remote areas, reduces fuel dependency | Reliability in adverse conditions, rapid deployment capability |
How Can Solar Cars Enhance Urban Mobility Solutions?
Urban mobility is increasingly challenged by traffic congestion and environmental concerns. Solar-powered city cars, designed for shared mobility, offer a sustainable alternative for urban transportation. These vehicles can autonomously charge using solar energy, significantly reducing operational costs associated with traditional fuel. Businesses considering this application must ensure compliance with local regulations regarding vehicle size and emissions, as well as evaluate the solar technology’s efficiency in their specific geographic areas.
What Benefits Do Solar-Assisted Delivery Vans Provide to Logistics Companies?
In the logistics and delivery sector, solar-assisted delivery vans can extend the range of operations while reducing dependence on fossil fuels. By integrating solar technology, these vehicles can charge during the day, which is particularly beneficial in sunny regions. This approach not only cuts fuel costs but also enhances the company’s sustainability profile, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers. Key considerations for sourcing include the durability of the vehicle for various terrains, the efficiency of the solar panels, and the availability of maintenance services.
How Can Solar-Powered Vehicles Transform Tourism Experiences?
Solar-powered vehicles present an opportunity for the tourism and leisure industry to offer eco-friendly travel options. These vehicles can be used for guided tours in natural settings, attracting eco-conscious travelers. By reducing operational costs through solar charging, tourism businesses can enhance their profitability while promoting sustainability. When sourcing these vehicles, companies should consider customization options to align with their brand, as well as potential partnerships with local tourism agencies to maximize exposure and customer engagement.
In What Ways Can Agriculture Benefit from Solar Vehicles?
In the agricultural sector, solar vehicles can significantly reduce fuel costs associated with farm operations. These vehicles can be used for transporting goods, equipment, and personnel across large farms, allowing for more efficient operations. The integration of solar technology promotes sustainable farming practices by minimizing the carbon footprint. Buyers in this sector should focus on the vehicle’s adaptability to various terrains, battery life for extended use, and the availability of support services to ensure seamless operations.
How Do Solar-Powered Emergency Response Vehicles Improve Service Delivery?
Emergency services can greatly benefit from solar-powered response vehicles, especially in remote areas where fuel supply may be inconsistent. These vehicles can operate continuously without reliance on traditional fuel sources, ensuring that emergency responders are always ready to act. When considering this application, businesses must prioritize the vehicle’s reliability under adverse conditions and its capability for rapid deployment to ensure effective service delivery in critical situations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘solar car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Initial Investment Costs for Solar Cars
The Problem: For B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, the initial investment in solar car technology can be a significant hurdle. Many organizations face budget constraints and may not fully understand the long-term cost benefits of integrating solar vehicles into their fleets. This financial barrier can deter potential buyers from exploring solar technology, despite its long-term savings on fuel and maintenance costs.
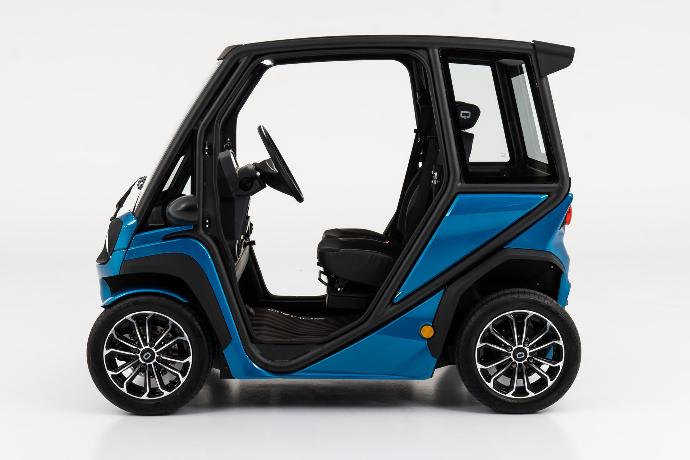
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, potential buyers should conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis that factors in not just the upfront costs but also the lifetime savings associated with solar vehicles. Engaging with manufacturers who offer leasing options or financing plans can also alleviate the immediate financial burden. For example, companies like Squad Mobility provide affordable pricing models and subscription services that lower the entry barrier. Additionally, buyers should explore government incentives or subsidies available for renewable energy vehicles, which can further offset initial costs. Collaborating with financial advisors who specialize in green technologies can provide tailored insights that facilitate informed decision-making.
Scenario 2: Addressing Range Anxiety and Charging Infrastructure
The Problem: A common concern for B2B buyers considering solar cars is the issue of range anxiety and the adequacy of charging infrastructure. In regions with inconsistent sunlight, such as parts of Europe and the Middle East, businesses may worry that solar vehicles won’t meet their operational range needs, especially for logistics and transportation services.
The Solution: To mitigate these concerns, buyers should prioritize solar car models that offer hybrid capabilities or supplementary charging options. For instance, vehicles equipped with swappable batteries or those that can charge via standard electrical outlets can provide flexibility for businesses operating in areas with variable solar availability. Engaging with manufacturers that are developing robust charging networks can also enhance operational reliability. Furthermore, businesses can consider integrating solar panels into their facilities, creating an ecosystem that supports the solar cars while reducing reliance on external charging stations. This proactive approach not only addresses range anxiety but also aligns with sustainability goals, thereby enhancing the company’s green credentials.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Safety and Compliance with Regulations
The Problem: As solar cars gain traction, B2B buyers in sectors such as transportation and logistics must navigate a complex landscape of safety regulations and compliance standards. This can be particularly daunting in regions with strict automotive regulations, where failing to meet compliance can lead to fines or operational disruptions.
The Solution: To effectively manage safety and compliance challenges, organizations should partner with reputable solar car manufacturers that have a proven track record of meeting regulatory standards. Buyers should conduct thorough research into the safety features of the vehicles, such as crash structures, seat belts, and stability controls, which are crucial for urban use. Engaging with legal experts who specialize in automotive regulations in the target market can provide additional insights into compliance requirements. Furthermore, staying updated with local legislation regarding solar vehicles can help businesses adapt quickly to changes and ensure ongoing compliance. By prioritizing safety and regulatory adherence, companies can protect their investments and foster trust with stakeholders and customers alike.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for solar car
What Are the Key Materials Used in Solar Cars?
When considering the construction of solar cars, selecting the right materials is crucial for performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in solar car manufacturing: aluminum, composite materials, tempered glass, and photovoltaic (PV) panels. Each material has distinct properties, advantages, and disadvantages that can significantly impact the overall efficiency and appeal of solar vehicles.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Solar Car Design?
Aluminum is a lightweight yet strong material, making it an ideal choice for the chassis and body of solar cars. Its high strength-to-weight ratio allows for better energy efficiency, which is critical in solar-powered applications. Aluminum also exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, particularly when treated, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros: Aluminum is durable and can withstand harsh weather conditions. It is also relatively easy to manufacture and recycle, which aligns well with sustainability goals.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which can be higher than that of steel. Additionally, while aluminum is strong, it may not offer the same impact resistance as some composite materials.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s lightweight nature enhances vehicle performance, contributing to better range and efficiency. However, international buyers must consider compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN for structural integrity.
What Role Do Composite Materials Play in Solar Cars?
Composite materials, particularly carbon fiber and fiberglass, are increasingly being used in solar car construction. These materials provide exceptional strength while being significantly lighter than metals, which can lead to improved fuel efficiency and performance.
Pros: Composites offer high durability and resistance to fatigue, making them suitable for high-stress applications. They can also be molded into complex shapes, providing design flexibility.
Cons: The main limitations include higher manufacturing costs and complexity in the production process. Additionally, composites may not be as recyclable as metals, raising sustainability concerns.
Impact on Application: Composites can enhance aerodynamics and reduce weight, which is crucial for solar efficiency. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local recycling capabilities and the need for compliance with international standards.
Why Is Tempered Glass Essential for Solar Cars?
Tempered glass is often used in solar cars for windows and protective coverings over solar panels. Its strength and thermal resistance make it an ideal choice for environments where temperature fluctuations are common.
Pros: Tempered glass is highly durable and shatter-resistant, providing safety for passengers. It also offers excellent optical clarity, which is essential for visibility.
Cons: While it is strong, tempered glass can be heavier than plastic alternatives, potentially impacting the vehicle’s overall weight. Furthermore, it can be more expensive to produce.
Impact on Application: The use of tempered glass ensures safety and durability, but international buyers should consider regional regulations regarding vehicle glazing. Compliance with standards like JIS for safety glass is crucial.
How Do Photovoltaic Panels Influence Solar Car Performance?
Photovoltaic panels are the heart of solar cars, converting sunlight into electricity. The efficiency of these panels directly affects the vehicle’s range and energy independence.
Pros: Modern PV panels are becoming increasingly efficient and cost-effective, allowing for greater energy capture. They are also relatively easy to integrate into vehicle designs.
Cons: The primary limitation is their performance in low-light conditions, which can affect energy generation. Additionally, the initial cost of high-quality panels can be significant.
Impact on Application: The choice of PV technology can influence the overall performance of solar cars. Buyers should look for panels that meet international efficiency standards and consider local solar conditions when making purchasing decisions.
Summary Table of Strategic Material Selection for Solar Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for solar car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Chassis and body construction | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost than steel | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Body panels and structural components | High strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
| Tempered Glass | Windows and solar panel coverings | Durable and shatter-resistant | Heavier than alternatives | Medium |
| Photovoltaic Panels | Energy generation | Increasing efficiency and cost-effectiveness | Performance drops in low light | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers looking to invest in solar car technology. Understanding the properties and implications of each material can lead to more informed purchasing decisions that align with market demands and sustainability goals.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for solar car
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Solar Cars?
The manufacturing process of solar cars involves several critical stages that ensure both efficiency and quality. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation
In this initial phase, manufacturers select and prepare materials suitable for solar vehicles. Lightweight materials such as aluminum and composite materials are often prioritized to enhance energy efficiency. The preparation involves cutting, treating, and testing materials to meet specific mechanical and thermal properties required for solar applications. -
Forming
This stage involves shaping the prepared materials into components. Advanced techniques such as extrusion, molding, and stamping are commonly used to create parts like the chassis, body panels, and solar arrays. The forming process must ensure that components are not only lightweight but also durable enough to withstand environmental stressors. -
Assembly
During assembly, individual components are brought together to create the final product. This process may include the installation of solar panels, electrical systems, and battery packs. Automated assembly lines often enhance precision and speed, while skilled labor is essential for tasks requiring intricate assembly, such as wiring and system integration. -
Finishing
The finishing stage encompasses surface treatments, painting, and final inspections. Aesthetic and protective coatings are applied to enhance durability and visual appeal. This stage also includes rigorous testing of the assembled vehicle to ensure it meets performance standards and safety regulations.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Solar Car Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of solar car manufacturing, ensuring that each vehicle meets international safety and performance standards.
-
What International Standards Are Relevant for Solar Car Quality Control?
Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 is crucial for solar car manufacturers. This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system and emphasizes continuous improvement. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may be necessary depending on the components and markets involved. -
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Solar Car Production?
Quality control checkpoints include Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
– IQC focuses on the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the production line.
– IPQC monitors the manufacturing process to detect and address issues in real-time.
– FQC involves comprehensive testing of the final product to ensure it meets all specifications and regulations before delivery. -
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Solar Car Manufacturing?
Testing methods include performance testing, safety testing, and environmental testing. Performance testing evaluates the efficiency of solar panels and battery systems, while safety testing examines crashworthiness and electrical safety. Environmental testing ensures that the vehicle can operate effectively in varying conditions, such as extreme temperatures and humidity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control in Solar Car Manufacturing?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential to ensure they are sourcing reliable products. Here are several strategies to consider:
-
Conducting Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control systems. These audits should assess compliance with international standards and industry-specific regulations. Buyers may also consider third-party audits for an impartial review. -
Requesting Quality Reports
Suppliers should be able to provide comprehensive quality reports detailing their QA processes, inspection results, and compliance with relevant standards. These documents can help buyers gauge the reliability of the products they intend to purchase. -
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors
Utilizing third-party inspection services can further validate a supplier’s quality control practices. Independent inspectors can assess product quality at various stages of the manufacturing process, ensuring adherence to specifications before shipment.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in quality assurance for solar cars. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective sourcing.
-
Regulatory Differences
Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements for solar vehicles. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local standards and ensure that suppliers comply with both international and regional regulations. This may include certifications specific to the markets they operate in. -
Cultural and Communication Factors
Effective communication is key when dealing with international suppliers. Language barriers and cultural differences can impact understanding quality expectations. Establishing clear communication channels and using standardized documentation can help mitigate these challenges. -
Supply Chain Considerations
Buyers should assess the entire supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final assembly. Understanding the origin of materials and the production processes can help identify potential quality issues. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers and maintaining open lines of communication can lead to improved quality assurance practices.
Conclusion
The manufacturing and quality assurance processes for solar cars are intricate and vital for ensuring product reliability and performance. By understanding the key stages of manufacturing, the importance of quality control, and the specific considerations for international buyers, B2B stakeholders can make informed decisions when sourcing solar vehicles. Emphasizing quality assurance not only enhances product value but also contributes to the broader mission of advancing sustainable mobility solutions worldwide.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘solar car’
To support B2B buyers in procuring solar cars, this guide provides a step-by-step checklist designed to streamline the sourcing process. By following these actionable steps, buyers can ensure they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly articulate the technical requirements for your solar car. Consider factors such as battery capacity, range per charge, integrated solar power capabilities, and vehicle size. Establishing these specifications upfront ensures that you focus on suppliers whose products meet your operational needs, particularly in varying climates and terrains.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay informed about the latest trends and advancements in solar vehicle technology. This includes understanding new solar panel efficiencies, battery technologies, and design innovations that enhance vehicle performance. Being aware of these trends helps you identify suppliers that are at the forefront of solar mobility, allowing you to leverage the most efficient and sustainable options available.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, including their experience in the solar car market, case studies, and references from similar clients. It’s essential to assess their production capabilities, customer service, and after-sales support to ensure they can meet your long-term needs.
- Look for:
- Certifications and awards in solar technology.
- Partnerships with renewable energy organizations.
Step 4: Assess Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Ensure that the solar cars you consider comply with local and international regulations. This includes safety standards, emissions regulations, and any specific requirements for solar-powered vehicles in your region. Compliance is crucial to avoid legal issues and ensure the vehicles can operate in your target markets.
Step 5: Request and Analyze Prototypes or Demonstrations
Whenever possible, arrange for prototypes or demonstrations of the solar cars you are considering. Testing the vehicles in real-world conditions can provide valuable insights into their performance, comfort, and usability. This hands-on experience is critical to validating that the vehicles meet your expectations and operational requirements.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in discussions with your selected suppliers to negotiate terms that align with your budget and operational needs. This includes pricing, payment terms, warranties, and after-sales service agreements. Clear agreements can prevent misunderstandings and ensure both parties have aligned expectations.
Step 7: Plan for Integration and Support
Once a supplier is selected, develop a plan for integrating the solar cars into your fleet. This should include training for your staff on vehicle operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Additionally, establish a clear line of communication for ongoing support from the supplier to address any future needs or issues that may arise.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing solar cars effectively, ensuring they make choices that align with their sustainability goals and operational requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for solar car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Solar Cars?
When sourcing solar cars, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is vital for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences costs. Solar cars utilize advanced materials such as lightweight composites and high-efficiency solar panels. Buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers who can provide high-quality materials at competitive prices, as this can enhance the vehicle’s overall performance and sustainability.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the assembly and quality assurance of solar vehicles. Labor costs can vary by region, influenced by local wage standards and the availability of skilled workers. For example, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs might reduce overall expenses but could affect quality and production timelines.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running production facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Understanding a manufacturer’s overhead can provide insights into their pricing structure and help buyers evaluate the total cost of ownership.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be significant, especially for customized solar vehicle designs. Buyers should inquire about the tooling costs and whether they are included in the quoted price or if they will be an additional expense.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the solar cars meet safety and performance standards requires investment in QC processes. Buyers should assess the quality certifications of suppliers, as this can affect long-term maintenance costs and reliability.
-
Logistics: The cost of transporting solar cars from manufacturing sites to the end-user can vary widely depending on distance, mode of transport, and import/export regulations. Effective logistics planning can mitigate unforeseen expenses.
-
Margin: Profit margins can differ based on the supplier’s business model and market positioning. Understanding these margins can provide leverage during negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Solar Car Procurement?
Several factors can influence the pricing of solar cars, including volume, specifications, materials, quality certifications, supplier factors, and Incoterms.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often come with lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQs) to secure better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features can significantly impact the price. Buyers must clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected costs related to modifications.
-
Materials and Quality: The choice of high-quality materials may increase initial costs but can lead to lower maintenance and operational expenses over the vehicle’s lifecycle.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can greatly affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products, but this can be justified by their track record in quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for cost management. Incoterms dictate who bears responsibility for shipping costs and risks, which can impact the final price delivered to the buyer.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating Prices on Solar Cars?
For B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and cost-efficiency strategies are essential.
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Consider leveraging competitive offers from multiple suppliers to negotiate better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Look beyond the sticker price. Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes maintenance, fuel savings from solar power, and potential tax incentives for renewable energy vehicles.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of potential tariffs, taxes, and import duties that can affect the overall cost. Familiarize yourself with local regulations and incentives for solar energy adoption, which may offset some expenses.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Pricing for solar cars is highly variable and contingent on numerous factors, including market conditions, technological advancements, and regional economic conditions. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotations to ensure they are making informed decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing solar car With Other Solutions
When considering sustainable transportation solutions, it’s crucial to evaluate not only solar cars but also viable alternatives that can meet similar mobility needs. This analysis aims to provide B2B buyers with insights into how solar cars compare against other technologies such as electric vehicles (EVs) and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). Each option presents unique advantages and challenges that can influence decision-making.
| Comparison Aspect | Solar Car | Electric Vehicle (EV) | Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle (FCV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Up to 40 miles/day on solar; 400 miles full charge | Range varies; generally 200-400 miles per charge | 300-400 miles per tank |
| Cost | Starting at €6,250 | Average €30,000+ | Average €50,000+ |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires sunlight; limited in cloudy regions | Widely available charging infrastructure | Limited infrastructure; fewer refueling stations |
| Maintenance | Low; fewer moving parts | Moderate; battery maintenance required | Moderate; fuel cell maintenance needed |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting; short distances | Versatile; urban and rural use | Long-distance travel; freight transport |
How Do Solar Cars Stack Up Against Electric Vehicles (EVs)?
Solar cars, such as those developed by companies like Aptera and Squad, offer unique advantages for urban commuting, particularly in sunny regions. They are lightweight, have lower upfront costs, and require less maintenance due to fewer moving parts. However, their reliance on sunlight can be a limitation in areas with frequent cloud cover or during winter months. On the other hand, electric vehicles provide a broader range of performance and charging infrastructure, making them more suitable for diverse geographic areas. They do, however, come with higher costs and ongoing battery maintenance needs.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs)?
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are another alternative to solar cars, offering extended ranges and quick refueling times. They are particularly advantageous for long-distance travel and heavy-duty applications. However, the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is still underdeveloped, which can pose a significant challenge for users. Moreover, FCVs are generally more expensive than both solar cars and EVs, which may deter some B2B buyers. While they produce zero emissions during operation, the environmental impact of hydrogen production can vary depending on the source.
Conclusion: Which Sustainable Mobility Solution Should You Choose?
Selecting the right sustainable mobility solution hinges on specific business needs, geographic considerations, and budget constraints. For companies operating in sunny urban environments with short-distance travel requirements, solar cars could be the most cost-effective and eco-friendly option. Conversely, businesses needing versatile, long-range solutions may find electric vehicles or hydrogen fuel cell vehicles to be more suitable. Assessing these alternatives carefully will enable B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and sustainability initiatives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for solar car
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Solar Cars That B2B Buyers Should Know?
When evaluating solar cars for commercial procurement, understanding essential technical properties is crucial. Here are some key specifications that buyers should consider:
-
Solar Panel Efficiency
Solar panel efficiency refers to the percentage of sunlight converted into usable electricity. High-efficiency panels maximize energy capture, allowing vehicles to generate more power from limited sunlight. For B2B buyers, selecting vehicles with efficient solar panels can lead to lower operational costs and increased sustainability, particularly in regions with abundant sunlight. -
Battery Capacity and Type
Battery capacity, typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), indicates how much energy a vehicle can store. The type of battery, whether lithium-ion or lead-acid, affects performance, lifespan, and charging speed. For businesses, understanding battery specifications is vital for ensuring the vehicle meets daily range requirements, especially in urban settings where charging infrastructure may be limited. -
Weight and Material Composition
The weight of a solar car significantly impacts its energy efficiency and performance. Lightweight materials, such as aluminum and carbon fiber, reduce energy consumption and enhance maneuverability. For B2B buyers, opting for vehicles constructed with advanced materials can improve overall operational efficiency and longevity, translating to lower maintenance costs. -
Range and Performance Metrics
The range of a solar car indicates how far it can travel on a full charge, including solar energy contributions. Performance metrics such as acceleration (0-60 mph time) and top speed are also essential. Buyers must consider these specifications to ensure the vehicle can meet the specific demands of their operational environment, especially in logistics and transportation sectors. -
Durability and Safety Ratings
Durability encompasses the vehicle’s ability to withstand various environmental conditions, while safety ratings reflect crashworthiness and occupant protection. For B2B buyers, investing in durable and safe vehicles is critical to minimizing liabilities and ensuring employee safety, particularly in commercial applications where vehicles are used frequently. -
Charging Time and Options
Charging time refers to how long it takes to fully recharge the battery from a depleted state, which can vary based on charging methods (e.g., solar, AC mains). Understanding charging options is essential for businesses to effectively plan vehicle usage and minimize downtime.
What Are Common Trade Terminology and Jargon Relevant to Solar Cars?
Familiarity with industry terminology can enhance communication and negotiation in the procurement process. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to the company that manufactures the original components or systems that are used in a vehicle. For buyers, working directly with OEMs can ensure they receive high-quality products tailored to their specifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for businesses to gauge the feasibility of a purchase based on their operational needs and budget constraints. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. B2B buyers should use RFQs to compare offers and negotiate favorable terms for solar vehicle procurement. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for buyers engaged in cross-border procurement of solar vehicles, ensuring clarity in logistics and cost responsibilities. -
MaaS (Mobility as a Service)
MaaS refers to a shift from personal vehicle ownership to shared, on-demand transportation services. Understanding this concept can help buyers align their procurement strategies with emerging trends in urban mobility and sustainability. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with purchasing, operating, and maintaining a vehicle over its lifetime. B2B buyers should evaluate TCO to make informed decisions that align with their budget and sustainability goals.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and sustainability objectives in the evolving solar car market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the solar car Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Solar Car Sector?
The solar car market is gaining momentum, driven by a convergence of environmental awareness, advancements in solar technology, and the urgent need for sustainable transportation solutions. Internationally, key drivers include increasing fuel prices, government incentives for electric vehicles (EVs), and consumer demand for eco-friendly options. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, B2B buyers are particularly focused on innovative solutions that can address local challenges, such as energy access and urban congestion.
Emerging technologies in the solar car sector are reshaping sourcing trends, with a notable shift towards integrated solar charging systems. Companies like Aptera Motors and Lightyear are leading the charge with vehicles that harness solar energy to extend range and reduce dependency on traditional charging infrastructures. In addition, lightweight materials and modular designs are becoming critical, allowing for more efficient manufacturing and better energy performance.
For international B2B buyers, understanding regional regulations and market entry strategies is essential. In Europe, for example, there is a strong push towards low-emission vehicles, while in Africa, the focus may be on affordable, off-grid solutions. Adapting to these dynamics will be key for successful sourcing and investment in solar car technologies.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Solar Car Industry?
Sustainability is at the core of the solar car industry, influencing both product development and sourcing strategies. As the market grows, B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to environmental stewardship. This includes assessing the lifecycle impact of materials used in solar cars, from production to end-of-life recycling.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. With the rise of eco-conscious consumers and regulatory pressures, companies are increasingly expected to provide transparency regarding their sourcing practices. This means ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly and that suppliers adhere to fair labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Fair Trade can serve as benchmarks for assessing supplier sustainability.
Moreover, as solar technology continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on using ‘green’ materials. Buyers should seek out suppliers that utilize recycled materials or innovative alternatives that minimize environmental impact. By prioritizing sustainability in sourcing, B2B buyers can not only enhance their brand reputation but also align with global efforts to combat climate change.
What is the Brief Evolution of the Solar Car Sector?
The solar car sector has evolved significantly since its inception. The early concepts primarily focused on experimental vehicles that demonstrated the feasibility of solar technology in transportation. Over the past two decades, advancements in solar panel efficiency and battery technology have paved the way for commercially viable solar cars.
Notably, the introduction of hybrid models and fully solar-powered vehicles has broadened the market. Early pioneers like the Solar Car Challenge have contributed to public interest and innovation in this space. Today, companies like Aptera and Squad Mobility are not only enhancing vehicle performance but also addressing practical needs such as urban mobility and energy independence. This evolution reflects a growing recognition of the role solar cars can play in achieving sustainable transportation goals worldwide.
By understanding these dynamics, B2B buyers can better navigate the complexities of sourcing solar car technologies and align their investments with market trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of solar car
-
1. How do I solve the challenge of sourcing reliable suppliers for solar cars?
To source reliable suppliers for solar cars, begin by conducting thorough market research to identify established manufacturers with a proven track record. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or industry-specific trade shows to connect with potential suppliers. Verify their credentials, certifications, and customer reviews. Engaging in direct communication can help gauge their responsiveness and willingness to meet your needs. It’s also beneficial to request samples or conduct factory visits to assess production capabilities and quality control processes. -
2. What is the best payment method for purchasing solar cars internationally?
The best payment method for international solar car purchases often depends on the transaction size and the relationship with the supplier. Options include letters of credit, which provide security for both parties, or escrow services that ensure funds are released only upon meeting specified conditions. For smaller transactions, bank transfers or credit cards may suffice, though they carry higher risks. Always negotiate favorable terms and consider using trade finance services to mitigate risks associated with currency fluctuations and international trade. -
3. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for solar cars?
Minimum order quantities for solar cars can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the type of vehicle. Generally, established manufacturers may have MOQs ranging from 5 to 50 units, while smaller or newer companies might accept lower quantities. It’s crucial to discuss MOQs upfront during negotiations and assess whether bulk purchasing can yield cost benefits. Consider your market demand and storage capabilities when determining the optimal order size. -
4. How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing solar cars?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing solar cars, implement a robust QA process that includes pre-shipment inspections and compliance with international standards. Request detailed specifications and certifications from suppliers to verify their adherence to safety and quality standards. Consider hiring third-party inspection services to conduct on-site evaluations during manufacturing and before shipment. Establishing clear communication regarding quality expectations and having a return policy in place can also safeguard your interests. -
5. What customization options are available for solar cars?
Customization options for solar cars can range from design modifications, such as color and branding, to technical specifications like battery capacity and solar panel integration. Many manufacturers offer tailor-made solutions to meet specific market needs, especially in regions with unique climate conditions. Discuss your requirements with suppliers to explore available options. Understanding the implications of customization on lead times and costs is essential for effective planning. -
6. How do I evaluate the sustainability impact of solar cars?
Evaluating the sustainability impact of solar cars involves assessing their lifecycle emissions, energy efficiency, and material sourcing. Look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with environmental standards, such as ISO 14001. Additionally, inquire about the vehicle’s energy consumption and the efficiency of its solar charging systems. Understanding the supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices, including the use of recycled materials and waste management strategies, is crucial for making environmentally responsible purchasing decisions. -
7. What logistical considerations should I be aware of when importing solar cars?
When importing solar cars, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Choose between sea or air freight based on your budget and urgency. Familiarize yourself with import duties, taxes, and documentation required for compliance with local regulations. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can help streamline the process and ensure timely delivery. It’s also wise to account for potential delays caused by regulatory inspections or shipping disruptions. -
8. How do I assess the market demand for solar cars in my region?
Assessing market demand for solar cars involves conducting thorough market research that includes analyzing consumer trends, regulatory incentives, and competitor offerings. Utilize surveys, focus groups, and local industry reports to gather insights about potential customers’ preferences and willingness to adopt solar vehicles. Collaborating with local stakeholders, such as government agencies and environmental organizations, can provide valuable data. Understanding the unique challenges and opportunities in your region is vital for making informed investment decisions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Solar Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
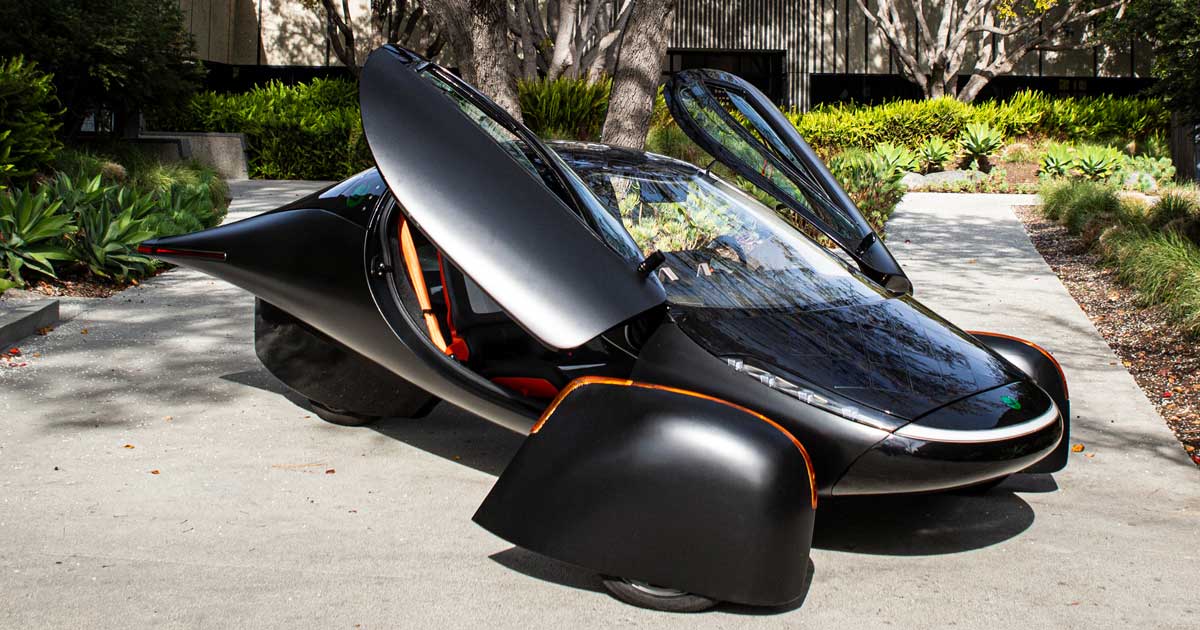
1. Aptera – Solar Electric Vehicle
Domain: aptera.us
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Aptera is a solar electric vehicle designed to be highly efficient, requiring no charging for most daily use. Key specifications include:
– Integrated solar cells generating approximately 700 watts
– Up to 40 miles of solar-powered driving per day
– 400 miles of range per full charge
– Acceleration from 0-60 mph in less than 6 seconds
The vehicle is currently in testing and validation, and sp…
2. Repsol – Solar Cars
Domain: repsol.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Solar cars are vehicles that utilize solar energy as their primary power source. They work by converting sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic cells, which are typically mounted on the car’s surface. This electricity powers the vehicle’s electric motor, allowing it to drive without relying on fossil fuels. Solar cars are part of the broader movement towards sustainable and renewable energy …
3. Aptera – Solar Range Innovation
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. Aptera: Claims to add about 40 miles of range per day from solar panels; unique design. 2. Sono Sion: Claims to add 21 miles of range per day from solar panels; faced market entry challenges and has gone bust. 3. Lightyear: Claims over 40 miles of range per day in summer with current panel technology. 4. Current solar panel efficiency is around 20%, with new designs claiming potential upper lim…
4. Stanford Solar Car Project – Sustainable Engineering Innovation
Domain: stanfordsolarcarproject.weebly.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Stanford Solar Car Project is a student-run, non-profit organization founded in 1989, focused on environmentally sustainable technology and hands-on engineering. It offers students valuable engineering and business experience while promoting clean energy awareness. The project emphasizes innovation, empowering students to utilize cutting-edge technologies for impactful change. It has a legacy of o…
5. The Conversation – Solar Cars Overview
Domain: theconversation.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Solar cars exist and are showcased in events like the World Solar Challenge, a race held every two years in Australia. These cars are designed to run solely on solar energy, but they resemble science fiction vehicles rather than conventional cars. Key challenges for solar-powered cars include: 1. Limited surface area for solar panels: A standard car has about 100 to 110 square feet of surface area…
6. Science Learn – Solar Cars
Domain: sciencelearn.org.nz
Introduction: Solar cars are powered by electricity generated from solar energy through photovoltaic (PV) cells. They are primarily built for racing and are becoming faster and more efficient each year. Benefits of solar cars include reduced reliance on fossil fuels, cost-free solar energy, no pollution, and an unlimited energy source. However, challenges include limited solar power availability during the day,…
7. CNET – Aptera Solar EV
Domain: cnet.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, CNET – Aptera Solar EV, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for solar car
As the global demand for sustainable transportation continues to rise, the strategic sourcing of solar cars presents a compelling opportunity for international B2B buyers. Key insights reveal that companies like Aptera, Lightyear, and Squad are pioneering innovative solar technologies that not only reduce dependence on traditional energy sources but also offer significant cost savings and environmental benefits. By investing in these advanced solar vehicles, businesses can enhance their sustainability initiatives, streamline operations, and meet the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly transportation solutions.
Strategic sourcing in the solar car sector is not just about acquiring vehicles; it involves aligning with manufacturers that prioritize cutting-edge technology, scalability, and adaptability to diverse markets, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East. These markets are poised for growth, making now an opportune time for stakeholders to establish partnerships that can lead to mutual benefit and market expansion.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers are encouraged to embrace this solar mobility movement. By integrating solar vehicles into their fleets or service offerings, companies can not only contribute to a greener future but also position themselves as leaders in the sustainable transport revolution. Explore these opportunities and be part of a transformative journey towards a more sustainable world.