Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric vehicle cargo
As the global market for electric vehicle cargo continues to expand, B2B buyers face the critical challenge of sourcing the right electric cargo solutions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals. Whether you are looking to transition your fleet to electric vehicles in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, understanding the diverse offerings—from cargo vans to step vans—is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide delves into the various types of electric cargo vehicles available, their applications across different industries, and the key factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
Our comprehensive resource not only addresses the specifications and capabilities of leading electric cargo models but also highlights cost considerations, potential tax incentives, and the latest advancements in charging technology. By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights, this guide empowers you to navigate the complexities of sourcing electric vehicle cargo effectively. From evaluating performance metrics to understanding warranty options and after-sales support, you will gain the knowledge necessary to enhance your fleet’s efficiency while contributing to a greener future.
With this guide, you can confidently assess the best electric cargo solutions to meet your business needs, ensuring that you stay ahead in the competitive landscape of sustainable transportation.
Understanding electric vehicle cargo Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
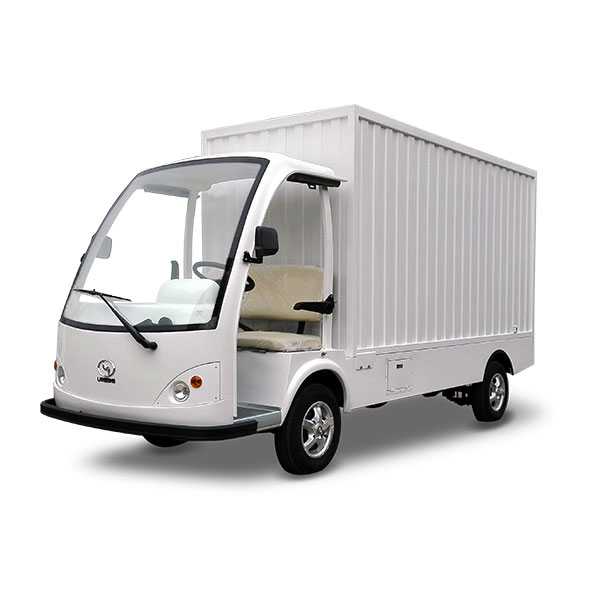
| Cargo Van | Versatile design, high cargo capacity, customizable | Delivery services, logistics | Pros: High payload capacity; Cons: Limited range compared to larger models. |
| Step Van | Open design for easy loading/unloading | Urban deliveries, mobile services | Pros: Easy access; Cons: May have lower cargo volume than enclosed vans. |
| Delivery Van | Focused on last-mile delivery, efficient range | E-commerce, food delivery | Pros: Optimized for short trips; Cons: Less suited for long hauls. |
| Utility Van | Built for specialized tasks, rugged construction | Construction, maintenance services | Pros: Durable and versatile; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Passenger Van | Configurable for transporting people and cargo | Shuttle services, group transport | Pros: Multi-functional; Cons: Lower cargo capacity when configured for passengers. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Cargo Vans in Electric Vehicles?
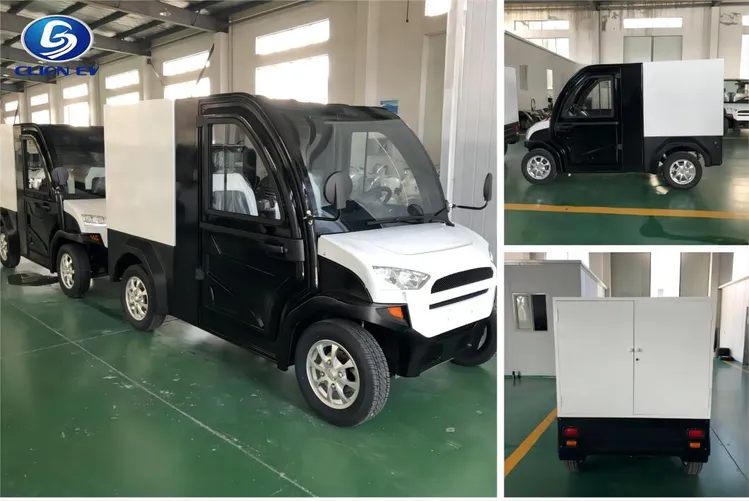
Cargo vans are designed for versatility, offering substantial cargo capacity and customizable configurations. They are ideal for businesses involved in delivery services and logistics, thanks to their ability to transport a wide variety of goods. When considering a cargo van, B2B buyers should evaluate payload capacities, battery range, and compatibility with charging infrastructure. While they provide high utility, buyers should also be aware that their range may be limited compared to other vehicle types.
How Do Step Vans Enhance Urban Delivery Efficiency?
Step vans feature an open design that allows for quick loading and unloading, making them particularly suitable for urban environments. They are often used in mobile services and urban deliveries, where fast access to cargo is essential. Buyers should consider the ease of access and maneuverability in tight spaces when selecting step vans. However, while they excel in accessibility, step vans may have a lower cargo volume compared to fully enclosed cargo vans, which could impact larger deliveries.
What Makes Delivery Vans Ideal for Last-Mile Services?
Delivery vans are specifically optimized for last-mile delivery scenarios, focusing on efficiency and range for short trips. These vehicles are increasingly popular in sectors like e-commerce and food delivery, where quick turnaround times are crucial. B2B purchasers should assess the range, charging options, and storage features to ensure they meet operational demands. However, their design may limit their effectiveness for long-haul journeys, making them less versatile than other types.
Why Choose Utility Vans for Specialized Tasks?
Utility vans are built for specialized applications, offering rugged construction and the ability to handle demanding tasks. They are commonly used in construction and maintenance services, where durability and functionality are paramount. Buyers should consider the specific needs of their operations, including the types of equipment to be transported. The initial investment may be higher, but the long-term benefits in terms of versatility and durability can justify the cost.
How Do Passenger Vans Serve Multi-Functional Needs?
Passenger vans can be configured to transport both people and cargo, making them a flexible choice for businesses that require multi-functional vehicles. They are often used in shuttle services or group transport, where comfort and space are priorities. B2B buyers should evaluate seating arrangements and cargo space to find the right balance for their needs. While passenger vans offer versatility, they may sacrifice some cargo capacity when configured for maximum seating, which could limit their utility in strictly cargo-focused applications.
Key Industrial Applications of electric vehicle cargo
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric vehicle cargo | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-commerce & Logistics | Last-Mile Delivery Vans | Reduced operational costs and improved delivery times | Range, charging infrastructure, and cargo capacity |
| Construction & Trades | Tool and Equipment Transport | Enhanced mobility for on-site operations | Vehicle durability, payload capacity, and charging speed |
| Food & Beverage | Mobile Catering and Delivery Services | Lower emissions and compliance with sustainability goals | Temperature control features and cargo space |
| Healthcare | Medical Supply Transport | Timely delivery of critical supplies | Reliability, temperature management, and vehicle range |
| Retail | In-Store Inventory Management and Restocking | Streamlined operations and reduced inventory loss | Customization options and fleet management capabilities |
How Are Electric Vehicle Cargo Solutions Transforming E-commerce and Logistics?
Electric vehicle (EV) cargo solutions are revolutionizing the last-mile delivery sector within e-commerce and logistics. Companies can deploy electric vans to navigate urban areas efficiently, significantly reducing fuel costs and carbon emissions. The ability to operate quietly and without tailpipe emissions meets growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly practices. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing vehicles with adequate range and access to charging infrastructure is critical to ensure operational efficiency.
What Role Do Electric Vehicles Play in Construction and Trades?
In the construction and trades industry, electric cargo vans are increasingly used for transporting tools and equipment to job sites. These vehicles provide enhanced mobility, allowing workers to arrive at locations with everything needed for the task at hand. The durability of these vehicles is paramount, as they must withstand rugged conditions. Buyers must consider the payload capacity and charging options, particularly in remote areas where conventional charging stations may be scarce, making partnerships with local charging providers essential.
How Are Electric Cargo Vehicles Benefiting the Food and Beverage Sector?
The food and beverage industry is leveraging electric cargo vehicles for mobile catering and delivery services. These vehicles not only minimize the carbon footprint but also comply with stringent sustainability regulations. The need for temperature control during transit is crucial for maintaining food safety standards. B2B buyers in this sector should prioritize vehicles with specialized features that allow for effective temperature management while ensuring adequate cargo space for various food items.
What Are the Advantages of Electric Cargo for Healthcare Supply Transport?
Electric cargo vehicles are vital in the healthcare sector for transporting medical supplies and equipment. Timely and reliable delivery of critical supplies can significantly impact patient care outcomes. Buyers must ensure that the vehicles they select are reliable, capable of maintaining necessary temperature controls for sensitive items, and possess sufficient range to cover extensive delivery routes. This is particularly important for international buyers who may face varied geographical challenges.
How Can Retailers Utilize Electric Vehicles for Inventory Management?
In the retail sector, electric cargo vehicles are used for in-store inventory management and restocking. These vehicles help streamline operations by reducing the time taken to restock shelves, ultimately minimizing inventory loss. Retailers looking to invest in electric cargo solutions should focus on customization options that suit their specific operational needs, as well as fleet management capabilities that can optimize route planning and vehicle maintenance. This is especially relevant for businesses in Europe, where sustainability practices are becoming increasingly important.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric vehicle cargo’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Range and Charging Infrastructure Challenges
The Problem: For B2B buyers in sectors such as logistics and delivery, one of the most significant challenges with electric vehicle cargo solutions is the limited driving range of electric vans compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. This is particularly concerning in regions where charging infrastructure is sparse, such as in parts of Africa and South America. A fleet manager may worry about the ability to complete routes without the vehicle running out of charge, leading to delays and increased operational costs.
The Solution: To mitigate these concerns, businesses should conduct a thorough analysis of their delivery routes and operational needs before purchasing electric vehicles. Using telematics and route optimization software can help identify the most efficient routes that stay within the vehicle’s range. Additionally, B2B buyers should prioritize manufacturers that offer models with extended ranges—such as the BrightDrop EV600, which boasts a range of up to 272 miles—and consider investing in a mix of Level 2 and Level 3 charging stations to ensure faster turnaround times. Partnering with local charging network providers can also enhance infrastructure access, allowing for strategic charging locations along critical delivery routes.
Scenario 2: High Initial Costs and Budget Constraints
The Problem: Many businesses are deterred from investing in electric vehicle cargo solutions due to the higher upfront costs associated with purchasing electric vans compared to their diesel or gasoline counterparts. This financial barrier can be particularly pronounced in emerging markets where budget constraints are critical for operational viability. A logistics company may find itself unable to justify the investment when traditional vehicles appear more economical in the short term.
The Solution: To address this pain point, B2B buyers should explore the financial incentives available for electric vehicle purchases, such as federal tax credits and grants specifically aimed at promoting green transportation. For instance, in the U.S., buyers may qualify for up to $7,500 in tax credits for electric vehicle purchases. Additionally, companies should consider total cost of ownership (TCO) analyses that take into account fuel savings, reduced maintenance costs, and potential carbon credits over the vehicle’s lifespan. Engaging with financial advisors who specialize in fleet management can provide further insights into financing options, such as leasing programs that allow companies to spread out the costs over time.
Scenario 3: Maintenance and Service Concerns
The Problem: Another common concern for B2B buyers is the perception that electric vehicles may require specialized maintenance, leading to potential downtime and loss of productivity. Fleet managers may worry about the availability of service centers equipped to handle electric vehicles, particularly in regions with less developed automotive service infrastructure. This can create hesitation in making the switch to electric cargo vans.
The Solution: To alleviate these concerns, businesses should prioritize purchasing electric vehicles from manufacturers that have established robust service networks. Companies like Rivian and Ram provide comprehensive warranty programs and have dedicated service teams to support fleet operations. B2B buyers should also invest in training for in-house maintenance teams to familiarize them with electric vehicle systems and upkeep. Additionally, establishing relationships with third-party service providers that specialize in electric vehicle maintenance can provide peace of mind. By ensuring that maintenance and service needs are effectively addressed, businesses can enjoy the benefits of electric vehicles without the risk of operational interruptions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric vehicle cargo
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in Electric Vehicle Cargo Applications?
Aluminum is a widely used material in electric vehicle (EV) cargo applications due to its favorable properties. It boasts a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for maintaining vehicle performance while minimizing overall weight. Aluminum also exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, which is crucial in varying climates, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East where humidity and temperature fluctuations are common. Additionally, aluminum can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for components exposed to heat during operation.
Pros and Cons of Aluminum:
The primary advantages of aluminum include its durability, lightweight nature, and resistance to corrosion, which enhances the longevity of cargo components. However, the manufacturing complexity can be higher compared to traditional steel, potentially leading to increased production costs. Furthermore, while aluminum is recyclable, the initial cost can be higher, which may deter some buyers, particularly in cost-sensitive markets.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material for Electric Vehicle Cargo?
Steel, particularly high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel, is another common choice for electric vehicle cargo applications. It offers excellent tensile strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel is also widely available and generally more affordable than aluminum, which can be a significant consideration for international buyers.
Pros and Cons of Steel:
The main advantage of steel is its strength and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for structural components. However, its susceptibility to corrosion can be a drawback, particularly in humid or coastal environments. To mitigate this, additional treatments or coatings may be necessary, increasing manufacturing complexity and costs.
What Role Does Composite Materials Play in Electric Vehicle Cargo?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP), are increasingly being utilized in electric vehicle cargo applications due to their lightweight and high-strength characteristics. Composites can be engineered to meet specific performance requirements, including temperature and pressure ratings, making them versatile for various cargo applications.
Pros and Cons of Composites:
The key advantages of composites include their lightweight nature and high resistance to corrosion and fatigue. However, they can be significantly more expensive than metals and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which could complicate supply chains. Additionally, the recycling of composite materials is not as straightforward as metals, posing potential environmental concerns.
What Are the Benefits of Using Thermoplastics in Electric Vehicle Cargo?
Thermoplastics, such as polypropylene and polycarbonate, are gaining traction in electric vehicle cargo applications due to their flexibility and impact resistance. These materials can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs that can enhance cargo functionality.
Pros and Cons of Thermoplastics:
The primary advantage of thermoplastics is their lightweight and cost-effective nature, making them suitable for various applications. They also offer good chemical resistance, which is essential for compatibility with different cargo types. However, thermoplastics may not provide the same level of structural integrity as metals or composites, which could limit their use in high-stress applications.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Vehicle Cargo
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric vehicle cargo | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Structural components, cargo boxes | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| Steel | Frame and structural support | High strength and cost-effective | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Composite | Custom cargo solutions, lightweight panels | High strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
| Thermoplastic | Interior components, lightweight fixtures | Flexible and impact-resistant | Lower structural integrity compared to metals | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers considering various materials for electric vehicle cargo applications. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material can help businesses make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs and regional conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric vehicle cargo
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Electric Vehicle Cargo?
The manufacturing process for electric vehicle (EV) cargo solutions involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure efficiency, performance, and sustainability. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The first step involves sourcing high-quality materials that meet the specifications for electric vehicle construction. This typically includes lightweight alloys for the chassis, high-strength steel for structural components, and advanced composites for body panels. Suppliers often undergo rigorous vetting to ensure compliance with international standards and sustainability practices.
-
Forming: During the forming stage, raw materials are shaped into components through techniques such as stamping, extrusion, and molding. Advanced technologies like computer numerical control (CNC) machining are employed to achieve precise dimensions. Manufacturers often utilize simulation software to optimize the forming process, reducing waste and improving material yield.
-
Assembly: In the assembly phase, individual components are brought together to create the vehicle. This process may include integrating the electric powertrain, battery systems, and electronic controls. Automated assembly lines equipped with robotics enhance efficiency and precision. Furthermore, manufacturers implement modular designs, allowing for flexibility in production and easier upgrades for future models.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves surface treatments, painting, and quality checks. Eco-friendly paints and coatings are increasingly being used to enhance durability while minimizing environmental impact. This stage also includes the installation of safety features and infotainment systems, ensuring the vehicle meets both performance and driver comfort standards.
Which Quality Control Measures Are Essential in Electric Vehicle Cargo Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is paramount in the production of electric vehicle cargo, ensuring that each unit adheres to stringent safety and performance standards. B2B buyers should be familiar with the various QC measures and international standards that govern this sector.
-
International Standards Compliance: Manufacturers typically comply with ISO 9001, a quality management standard that ensures consistent quality in products and services. Additionally, certifications such as CE marking for European markets and API standards for components may be relevant, depending on the specific applications of the EV cargo.
-
QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify defects early. This includes regular inspections and tests on assembled components.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Before vehicles leave the manufacturing facility, they undergo a comprehensive evaluation, which includes functional tests, safety checks, and performance assessments. -
Common Testing Methods: Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality of EV cargo. These may include:
– Durability Testing: Evaluating how well components withstand stress and wear over time.
– Performance Testing: Assessing the vehicle’s range, charging time, and overall efficiency.
– Safety Testing: Ensuring compliance with crash safety standards and electrical system safety.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is crucial. Here are effective strategies to ensure compliance and quality:
-
Conducting Audits: Regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and QC measures. Buyers should request access to audit reports and findings from previous assessments to gauge the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Requesting Documentation: Suppliers should provide documentation that outlines their quality management systems, including certifications, quality policies, and inspection protocols. This documentation can serve as a basis for evaluating their compliance with international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s manufacturing practices and quality assurance. These inspections can be particularly valuable for verifying compliance with local and international regulations.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with international suppliers, B2B buyers should be aware of certain nuances that can affect quality control:
-
Understanding Regional Standards: Different regions may have specific standards and regulations that manufacturers must adhere to. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these requirements to ensure that products meet local compliance needs.
-
Cultural and Communication Barriers: Effective communication is key to understanding a supplier’s quality control processes. Buyers should consider language barriers and cultural differences that may affect how quality issues are addressed.
-
Sustainability Practices: Increasingly, buyers are looking for suppliers who prioritize sustainability in their manufacturing processes. This includes using recycled materials, minimizing waste, and adopting eco-friendly practices. Verifying a supplier’s commitment to sustainability can enhance a buyer’s brand image and align with global market trends.
-
Building Long-Term Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can foster better communication and collaboration on quality control issues. Buyers should engage in regular discussions about quality expectations and improvements, creating a partnership that benefits both parties.
Conclusion: The Importance of Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance in Electric Vehicle Cargo
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for electric vehicle cargo are critical for delivering reliable, high-performance vehicles that meet the demands of modern businesses. By understanding these processes and implementing robust QC strategies, B2B buyers can ensure they partner with manufacturers that prioritize quality, safety, and sustainability. As the electric vehicle market continues to grow, making informed decisions will be essential for businesses looking to invest in this transformative technology.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric vehicle cargo’
Introduction
As the demand for sustainable transportation solutions grows globally, sourcing electric vehicle (EV) cargo options has become essential for businesses looking to enhance operational efficiency and reduce environmental impact. This practical sourcing guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of sourcing the right electric vehicle cargo. Consider factors such as cargo capacity, range, powertrain options, and vehicle dimensions. This clarity ensures that the vehicles will meet your operational requirements, allowing for seamless integration into your existing logistics framework.
- Cargo Volume: Determine the amount of space needed for your typical loads.
- Range: Assess the maximum distance required between charging stations, especially in regions with limited infrastructure.
Step 2: Research Available Models
Conduct thorough research on the latest electric cargo vehicle models available in the market. Evaluate different manufacturers’ offerings, focusing on specifications that meet your defined needs. Understanding the competitive landscape will enable you to identify vehicles that offer the best value and performance.
- Performance Metrics: Look for information on horsepower, torque, and load capacity.
- Charging Options: Assess the compatibility with various charger types, such as Level 2 and Level 3 chargers.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to conduct a comprehensive evaluation. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from businesses in similar sectors. A well-vetted supplier should demonstrate a track record of reliability and customer satisfaction.
- Certifications: Verify that suppliers have relevant industry certifications and compliance with international standards.
- After-Sales Support: Inquire about the availability of maintenance services and warranty coverage.
Step 4: Assess Total Cost of Ownership
Understanding the total cost of ownership (TCO) is vital for making an informed purchasing decision. This includes the initial purchase price, financing options, maintenance costs, and potential tax incentives. Evaluating TCO helps in predicting the long-term financial impact of your investment.
- Incentives: Research local and federal incentives for electric vehicle purchases, which can significantly offset costs.
- Maintenance: Factor in the costs associated with battery maintenance and potential charging infrastructure investments.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations and Test Drives
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request demonstrations and test drives of the vehicles. This hands-on experience allows you to assess the vehicle’s performance and suitability for your business needs.
- Driver Feedback: Involve your drivers in the process to gather insights on comfort and usability.
- Performance Evaluation: Pay attention to how the vehicle handles under load and its maneuverability in urban environments.
Step 6: Finalize Contractual Agreements
Once you have selected a supplier and model, ensure that all contractual agreements are clear and comprehensive. Review terms related to delivery timelines, payment conditions, and service agreements to avoid potential disputes.
- Delivery Schedule: Confirm the expected delivery timeframe to align with your operational plans.
- Service Agreements: Ensure that maintenance and support services are explicitly detailed in the contract.
Step 7: Plan for Charging Infrastructure
Implementing an effective charging infrastructure is crucial for maximizing the efficiency of your electric vehicle cargo fleet. Assess your current facilities and determine the necessary upgrades or installations for charging stations.
- Location of Chargers: Strategically position chargers to minimize downtime and optimize fleet operations.
- Charging Speed: Consider the types of chargers needed to meet your operational requirements effectively.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the complexities of sourcing electric vehicle cargo, ensuring their investments contribute to both operational success and sustainability goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric vehicle cargo Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Electric Vehicle Cargo Sourcing?
When sourcing electric vehicle (EV) cargo solutions, understanding the underlying cost structure is essential. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The raw materials used in manufacturing electric vans, such as lightweight metals for the chassis and high-capacity batteries, significantly influence costs. Prices for these materials can fluctuate based on global supply chain dynamics and demand.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for the assembly and integration of advanced technologies in EVs. Labor costs can vary by region, impacting the overall pricing. In regions with a robust automotive workforce, such as Germany, labor costs may be higher but can result in superior craftsmanship.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses associated with factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and machinery used in the production of EVs represent a significant investment. Tooling costs can be amortized over higher production volumes, making it critical for buyers to consider supplier capabilities and their production volume requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring high standards through rigorous QC processes is vital for EV reliability. Investing in quality assurance can add to the upfront costs but can save money in the long term by reducing warranty claims and enhancing brand reputation.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for delivering EVs from the manufacturer to the buyer can vary based on distance, shipping methods, and regional regulations. International buyers should consider potential tariffs and import duties in their total logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will incorporate a profit margin into the final price. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Electric Vehicle Cargo?
Several factors influence the pricing of electric vehicle cargo solutions:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their operational needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as enhanced battery capacity or specialized cargo configurations, can increase costs. Buyers should balance their specific needs against budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) can raise costs but may lead to better performance and longevity, ultimately enhancing the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and financial stability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but they often provide superior service and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial for assessing total landed costs. Incoterms dictate who bears the risk and responsibility for shipping costs, which can significantly impact pricing.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Sourcing Electric Vehicle Cargo?
To navigate the complexities of sourcing electric vehicle cargo, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate with Suppliers: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating terms, especially for larger orders. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to better pricing and service.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors such as maintenance, energy consumption, and potential tax incentives, which can significantly impact long-term costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and potential import tariffs that can affect pricing.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive quotes that break down costs. This transparency helps identify areas for negotiation and ensures no hidden fees.
-
Stay Informed About Incentives: Investigate local and international tax credits or incentives for electric vehicle purchases, as these can substantially reduce overall costs.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for electric vehicle cargo solutions can vary widely based on specifications, supplier agreements, and market conditions. Buyers are encouraged to seek detailed quotes from multiple suppliers and consider all associated costs when making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric vehicle cargo With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Electric Vehicle Cargo Solutions
As businesses increasingly focus on sustainability and efficiency, electric vehicle (EV) cargo solutions are gaining traction. However, it’s essential to consider viable alternatives that could meet similar operational needs. This analysis compares electric vehicle cargo with traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vans and alternative fuel vehicles, such as compressed natural gas (CNG) vans. Each option presents unique benefits and drawbacks that B2B buyers should evaluate based on their specific operational requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Vehicle Cargo | Internal Combustion Engine Vans | Compressed Natural Gas Vans |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Up to 272 miles range; instant torque | Varies; generally lower torque response | Moderate range; slower acceleration |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost; potential tax credits | Lower initial cost; higher fuel costs | Moderate cost; lower fuel costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure | Widely available refueling stations | Limited infrastructure in some regions |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance costs; fewer moving parts | Higher maintenance; more moving parts | Moderate maintenance; specialized parts |
| Best Use Case | Urban deliveries; eco-conscious fleets | General cargo transport; diverse applications | Fleets focused on cost savings |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Internal Combustion Engine Vans?
Internal combustion engine vans are a well-established solution for cargo transport, offering a range of performance options and generally lower initial costs compared to electric vehicles. However, their reliance on fossil fuels results in higher long-term fuel expenses and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, maintenance costs tend to be higher due to the complexity of their engines and the need for regular servicing. For businesses operating in rural areas or regions with limited EV infrastructure, ICE vans may provide a more practical option in the short term.
How Do Compressed Natural Gas Vans Compare?
Compressed natural gas (CNG) vans present a middle-ground alternative, utilizing a cleaner-burning fuel source compared to traditional gasoline or diesel. CNG vehicles can lower operational greenhouse gas emissions, making them attractive to environmentally conscious businesses. However, their effectiveness is often limited by the availability of refueling stations, which can be a significant drawback in many regions. Additionally, while the initial purchase price is usually lower than electric vehicles, the savings on fuel can vary, depending on local natural gas prices.
Conclusion: Which Cargo Solution Is Right for Your Business?
When choosing between electric vehicle cargo and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider their operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term sustainability goals. Electric vehicles shine in urban delivery scenarios where emissions are a concern, while internal combustion engine vans may be more suited for varied and widespread applications. CNG vans offer a compromise, providing a cleaner alternative to gasoline but may require careful consideration of infrastructure availability. Ultimately, the best choice will depend on the specific requirements of the business, including route planning, fleet size, and environmental impact objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric vehicle cargo
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Vehicle Cargo?
Understanding the technical specifications of electric vehicle (EV) cargo is crucial for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their logistics and operational efficiency. Here are several critical specs to consider:
-
Payload Capacity
This refers to the maximum weight that an electric cargo vehicle can safely carry, including both cargo and passengers. For example, vehicles like the Ram ProMaster EV can support a significant payload while maintaining performance. Knowing the payload capacity is vital for businesses to ensure compliance with weight regulations and to optimize their transportation logistics. -
Driving Range
The driving range indicates how far an electric vehicle can travel on a single charge. Models like the BrightDrop 400 offer ranges up to 272 miles, making them suitable for long-haul deliveries. A longer driving range reduces the frequency of charging stops, which is essential for improving delivery efficiency and minimizing downtime. -
Charging Capabilities
Electric vehicles come with different charging options—Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 (DC fast charging). Understanding these options is crucial for fleet operators to plan charging infrastructure and manage operational costs effectively. For instance, Level 3 chargers can significantly reduce charging times, enhancing fleet productivity. -
Cargo Volume
This measurement represents the total space available for cargo within the vehicle. For example, the Rivian Commercial Van offers around 487 cubic feet of cargo volume. A higher cargo volume allows businesses to maximize load capacity, reducing the number of trips required and thereby lowering transportation costs. -
Battery Warranty
Electric vehicles typically come with warranties covering the battery and e-powertrain for a specified duration or mileage, such as 8 years or 100,000 miles. Understanding warranty terms is essential for businesses to assess the long-term reliability and total cost of ownership of their electric fleet.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Electric Vehicle Cargo Sector?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations in the B2B landscape. Here are several key terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce vehicles or vehicle components that are sold under another company’s brand name. Understanding who the OEM is can help buyers assess the quality and reliability of the electric vehicles they are considering for purchase. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For electric vehicles, understanding MOQ can help businesses plan their purchasing strategy and manage inventory levels effectively, particularly when investing in fleet vehicles. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process used to invite suppliers to bid on specific products or services. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ for electric vehicle cargo can ensure competitive pricing and help identify the best suppliers for their needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are a set of predefined international trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for understanding the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping, including risk management and cost allocation. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with the purchase and operation of a vehicle over its entire lifecycle, including purchase price, maintenance, insurance, and fuel costs. Evaluating TCO helps businesses make informed decisions about investing in electric vehicle cargo solutions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and financial strategies in the evolving landscape of electric vehicle logistics.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric vehicle cargo Sector
What Are the Key Drivers and Trends Shaping the Electric Vehicle Cargo Market?
The electric vehicle (EV) cargo sector is experiencing a significant transformation driven by multiple global factors. A primary driver is the urgent need for sustainable logistics solutions, which is prompting businesses to adopt electric cargo vehicles to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. As governments worldwide implement stricter emissions regulations and offer incentives for EV adoption, international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly considering electric cargo solutions to align with sustainability goals.
Current B2B tech trends are also influencing sourcing decisions. Advanced technologies, such as telematics and fleet management software, are becoming essential for optimizing the operational efficiency of electric fleets. Buyers are looking for vehicles equipped with state-of-the-art safety features, connectivity options, and varying charging capabilities to meet diverse operational needs. The emergence of flexible financing options and leasing models is making it easier for businesses to integrate electric vehicles into their fleets without significant upfront investments.
Moreover, the market is witnessing a shift towards customized solutions tailored to specific business needs. Manufacturers are offering a variety of configurations and upfit options, allowing buyers to select vehicles that meet their unique cargo requirements. This level of customization is particularly appealing to companies looking to enhance their service offerings while minimizing environmental impact.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Electric Vehicle Cargo Sector?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the electric vehicle cargo sector, significantly influencing purchasing decisions among B2B buyers. The environmental impact of logistics operations is prompting businesses to seek out electric cargo vehicles that contribute to reduced operational carbon footprints. Implementing electric fleets can lead to a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions by 50% or more compared to traditional internal combustion vehicles, making them an attractive option for companies committed to corporate social responsibility.
Ethical sourcing plays a crucial role in the decision-making process for international buyers. As the demand for sustainable materials grows, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on ethical supply chains that ensure responsible sourcing of materials used in electric vehicle production. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED for green building practices are becoming essential for companies looking to validate their sustainability claims.
In addition, utilizing ‘green’ materials in vehicle manufacturing, such as recycled plastics and sustainable metals, is gaining traction. Buyers are encouraged to consider manufacturers that prioritize sustainable practices, as this not only enhances their brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer preference for environmentally responsible products.
What Is the Evolution of the Electric Vehicle Cargo Market?
The evolution of the electric vehicle cargo market has been marked by significant milestones that have shaped its current landscape. Initially, electric vehicles were seen as niche products, primarily used in urban settings for short-range deliveries. However, technological advancements in battery efficiency and charging infrastructure have expanded the applicability of electric cargo vehicles across various sectors.
The introduction of robust government policies and incentives has also accelerated market growth. For instance, tax credits and grants for electric vehicle purchases have encouraged businesses to transition to electric fleets. As a result, manufacturers have responded by developing a wider range of electric cargo options, catering to diverse industry needs while maintaining a focus on sustainability.
Today, the electric vehicle cargo market is positioned for exponential growth, driven by the dual pressures of environmental responsibility and the need for cost-effective logistics solutions. As international B2B buyers continue to prioritize sustainability, the adoption of electric cargo vehicles is set to become a standard practice across various industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric vehicle cargo
-
1. How do I select the right electric vehicle cargo for my business needs?
To select the right electric vehicle (EV) cargo, consider your specific operational requirements, including payload capacity, driving range, and charging infrastructure. Evaluate the size and configuration of the vehicle, such as cargo vans versus step vans, to ensure it meets your logistical demands. Additionally, assess the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and energy costs. Engaging with manufacturers to discuss customization options can further tailor the vehicle to your unique business operations. -
2. What are the key features to look for in an electric cargo van?
When evaluating electric cargo vans, prioritize features like battery range, cargo space, and payload capacity. Advanced technology, such as driver-assist systems and an intuitive infotainment interface, enhances safety and operational efficiency. Furthermore, charging capabilities are crucial; look for compatibility with various charger levels (Level 1, Level 2, Level 3) to ensure flexibility in your charging options. Lastly, warranty and support services can significantly impact long-term reliability and maintenance costs. -
3. How can I ensure the quality and reliability of electric vehicle cargo suppliers?
To ensure supplier quality and reliability, conduct thorough research on potential manufacturers. Look for established companies with a proven track record in the EV market, and check customer reviews and case studies. Request references and inquire about their compliance with international standards and certifications. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities or attending industry expos to assess their production capabilities and technology firsthand. -
4. What customization options are available for electric cargo vans?
Customization options for electric cargo vans often include shelving, flooring, and specialized upfits tailored to specific industries (e.g., refrigeration for food transport). Suppliers may also offer modifications in terms of vehicle layout and technology integration, such as telematics systems for fleet management. Engaging directly with the manufacturer or an authorized dealer can provide insights into available custom solutions and help align the vehicle with your operational needs. -
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for electric cargo vehicles?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly between manufacturers. While some may allow single-unit purchases, others might have higher MOQs, especially for custom configurations. It’s essential to discuss your fleet needs with the supplier to understand their policies and explore potential flexibility. Bulk orders may also come with negotiated pricing advantages, which can be beneficial for larger businesses looking to expand their fleet. -
6. What payment terms are typically offered for electric cargo vehicles?
Payment terms for electric cargo vehicles can range from upfront payments to financing options. Many manufacturers offer flexible financing solutions, including leasing arrangements that can help manage cash flow. It’s advisable to discuss payment terms during the negotiation phase, ensuring clarity on down payments, installment schedules, and any potential interest rates. Additionally, inquire about any available tax incentives that could offset initial costs. -
7. How do international buyers manage logistics and delivery for electric cargo vans?
International buyers should work closely with suppliers to understand logistics and delivery timelines. Factors such as customs regulations, shipping methods, and local infrastructure can impact delivery. It’s beneficial to partner with logistics companies experienced in handling international vehicle shipments to streamline the process. Additionally, ensure that your supplier provides clear documentation and support to navigate any regulatory requirements in your region. -
8. Are there tax incentives for purchasing electric cargo vehicles in my region?
Tax incentives for electric cargo vehicles vary by country and region. Many governments offer tax credits, deductions, or rebates to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles. It’s essential to consult with a local tax advisor to explore the specific incentives available in your area. Additionally, manufacturers may provide guidance on applicable incentives during the purchasing process, helping you maximize potential savings on your investment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Electric Vehicle Cargo Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Rivian – Electric Commercial Vans
Domain: rivian.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Rivian Fleet offers electric work and commercial vans starting at $79,900. The Rivian Commercial Van is designed for sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and safety, featuring 360-degree cameras and patented energy-saving microclimate seats. It aims to reduce operational GHG emissions by 50% or more compared to internal combustion vehicles. Key dimensions include a length of 248.5 inches, height of…
2. Chevrolet – 2025 BrightDrop 400 & 600
Domain: chevrolet.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: 2025 Chevrolet BrightDrop 400: Starting price $46,425 after cash offers, estimated range up to 272 miles, max cargo volume 412.1 cu. ft., max payload 3,710 lbs., GVWR 11,000 lbs. 2025 Chevrolet BrightDrop 600: Starting price $47,925 after cash offers, estimated range up to 303 miles (AWD), max cargo volume 614.7 cu. ft., max payload 3,350 lbs., GVWR 11,000 lbs. Features include low step-in height,…
3. EV Blazer – Cargo Space Consideration
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Looking for an electric SUV with good cargo space that isn’t outrageously expensive. Currently considering the EV Blazer and the Ioniq 5. The user works at farmers markets and needs space for a table, tent, and inventory. They currently own an EV Equinox and like it. The Ioniq 5 has a 15 amp plug which is seen as useful. The user is leaning towards the Blazer due to its size and current financing …
4. Tesla – Model S
Domain: topspeed.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: [{“model”:”Tesla Model S”,”total_cargo_space”:”61.4 cubic feet (64.6 with frunk)”,”cargo_space_with_seats”:”25 cubic feet”,”cargo_space_with_seats_folded”:”61.4 cubic feet”,”drivetrain”:”AWD, Dual or Triple Motor”,”power_output”:”670-1020 horsepower”,”range”:”396-405 miles”,”charging_time”:”30 minutes @ 250 kW”},{“model”:”Kia Niro EV”,”total_cargo_space”:”63.7 cubic feet”,”cargo_space_with_seats”:…
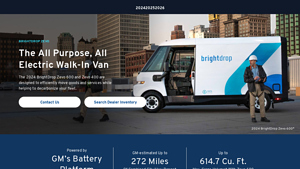
5. GM – BrightDrop Zevo 600 and Zevo 400
Domain: gmenvolve.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Product Name: BrightDrop Zevo 600 and Zevo 400
Type: Electric Delivery Vehicles
Key Features:
– All Electric Walk-In Van
– Designed for efficient goods and services movement
– Helps decarbonize fleets
– Powered by GM’s Battery Platform
– GM-estimated up to 272 miles of combined city/highway range
– Maximum cargo volume: Zevo 600 – 614.7 cu. ft., Zevo 400 – 412.1 cu. ft.
– Lease offer: $599 per mon…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric vehicle cargo
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Electric Vehicle Cargo Operations?
As the electric vehicle (EV) market continues to expand, B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to optimize their operations. By selecting the right EV cargo solutions, such as the Ram ProMaster EV, Rivian Commercial Van, and Chevrolet BrightDrop, businesses can significantly reduce operational costs while enhancing sustainability. These vehicles not only offer impressive range and cargo capacity but also come equipped with advanced technology and safety features, making them ideal for various commercial applications.
Investing in electric cargo solutions allows companies to capitalize on government incentives and tax credits, further improving their bottom line. Additionally, the availability of different charging options ensures that businesses can seamlessly integrate these vehicles into their logistics networks, minimizing downtime.
Looking ahead, international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should seize this opportunity to electrify their fleets. By embracing electric vehicle technology, organizations can position themselves as leaders in sustainability, meet increasing regulatory demands, and enhance their operational efficiency. Start your journey towards a greener future today—explore your electric cargo options and make strategic sourcing a priority for your business.