Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for mini electric car 45 kmh
As urbanization accelerates globally, the demand for efficient and eco-friendly transportation solutions has never been more pressing. Sourcing mini electric cars that can navigate city streets at a speed of 45 km/h presents a viable answer to challenges such as traffic congestion and environmental concerns. This guide offers a thorough exploration of the mini electric car market, covering various types, applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting. It also delves into cost considerations, ensuring that B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Brazil and Saudi Arabia—are equipped with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
The burgeoning market for mini electric vehicles is not merely a trend; it represents a shift towards sustainable urban mobility. With features tailored for city driving, such as compact design and easy parking, these vehicles are ideal for businesses seeking to enhance their fleets or enter the mobility-as-a-service sector. This guide empowers international buyers by providing actionable insights, from understanding regulatory requirements to evaluating the best suppliers and models suited for their specific market needs. By leveraging this resource, businesses can navigate the complexities of sourcing mini electric cars, ultimately leading to smarter, more sustainable transportation solutions.
Understanding mini electric car 45 kmh Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar City Car | Integrated solar panels, lightweight design, compact size | Urban mobility solutions, car-sharing | Pros: Low emissions, cost-effective. Cons: Limited range in low sunlight. |
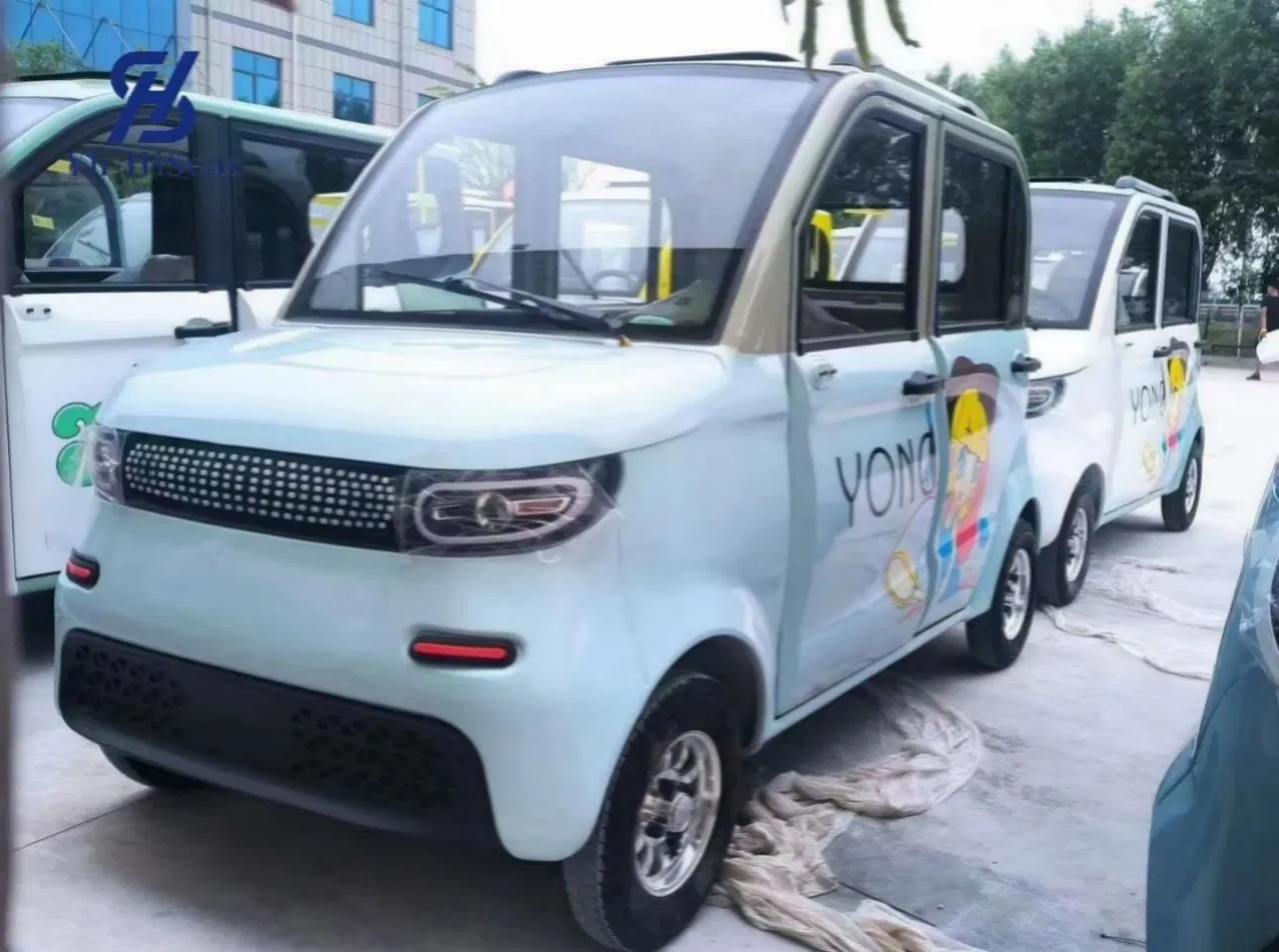
| Electric Quadricycle | Compact, two-seater design, easy to park, 75 km range | Last-mile delivery, urban commuting | Pros: Affordable, no driver’s license needed. Cons: Limited passenger capacity. |
| Swappable Battery Microcar | Portable batteries, designed for quick charging, lightweight | Rental services, shared mobility platforms | Pros: Flexible charging options, reduced downtime. Cons: Battery availability can be a concern. |
| Cargo-Friendly Mini Vehicle | Enhanced storage capacity, foldable design, suitable for transport | Goods delivery, logistics in urban areas | Pros: Versatile cargo space, efficient for deliveries. Cons: May lack passenger comfort. |
| High-Safety Urban Vehicle | Advanced safety features, stable structure, crash-tested design | Corporate fleets, employee transport | Pros: High safety standards, reliable. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Solar City Cars?
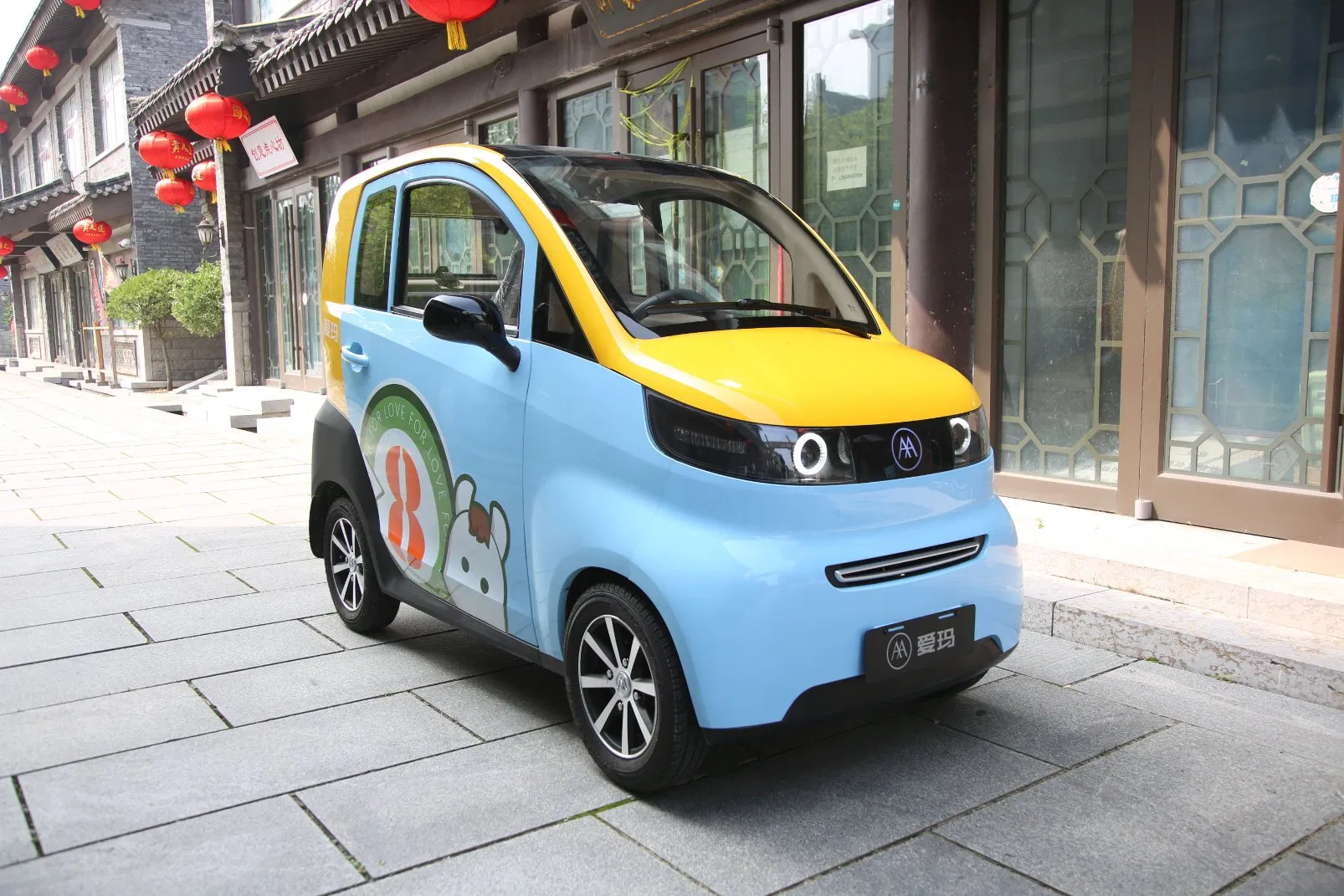
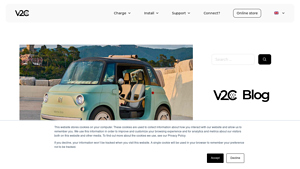
Solar city cars, such as the Squad, are designed with integrated solar panels that allow them to charge while parked, providing a sustainable urban mobility solution. Their compact size enables efficient parking and maneuvering in congested city environments, making them ideal for daily errands and short commutes. B2B buyers should consider the vehicle’s suitability for urban car-sharing initiatives, where sustainability and cost-effectiveness are paramount. However, the effectiveness of solar charging may vary based on geographic location and weather conditions.
How Do Electric Quadricycles Serve B2B Needs?
Electric quadricycles, like the Citroën Ami, offer a compact design that is easy to park and maneuver. With a range of around 75 km and a top speed of 45 km/h, they are well-suited for urban commuting and last-mile delivery applications. B2B buyers can leverage these vehicles for employee transport or as part of a rental fleet. The affordability and lack of licensing requirements make them accessible options, although their limited passenger capacity may restrict their use in larger groups.
What Advantages Do Swappable Battery Microcars Provide?
Swappable battery microcars focus on convenience and efficiency, allowing users to replace drained batteries quickly. This feature is particularly beneficial for rental services and shared mobility platforms, minimizing downtime and enhancing user experience. B2B buyers should evaluate the logistics of battery availability and charging infrastructure in their areas. While these vehicles offer flexibility, the reliance on a consistent supply of batteries can pose challenges.
How Do Cargo-Friendly Mini Vehicles Enhance Urban Logistics?
Cargo-friendly mini vehicles are designed with enhanced storage capacity, making them ideal for urban logistics and goods delivery. Their foldable designs maximize cargo space while maintaining a compact footprint, enabling efficient navigation through crowded areas. For B2B buyers in logistics, these vehicles represent a cost-effective solution to urban delivery challenges. However, potential buyers should assess the trade-off between cargo capacity and passenger comfort, as these vehicles may prioritize utility over comfort.
What Makes High-Safety Urban Vehicles a Smart Investment?
High-safety urban vehicles are built with advanced safety features and crash-tested designs, ensuring passenger protection in urban environments. These vehicles are suitable for corporate fleets and employee transport, where safety is a top priority. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment against long-term operational safety benefits. While these vehicles may come with a higher price tag, the peace of mind and reliability they offer can justify the expense, especially in high-traffic urban areas.
Key Industrial Applications of mini electric car 45 kmh
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of mini electric car 45 kmh | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Mobility | Ride-sharing platforms for short-distance travel | Reduced operational costs and increased utilization of fleet | Compliance with local regulations and licensing requirements |
| Retail and Delivery | Last-mile delivery services | Enhanced delivery speed and reduced carbon footprint | Battery range and charging infrastructure availability |
| Tourism | Eco-friendly transport for tourist attractions | Improved customer experience and attraction appeal | Customization options for branding and passenger comfort |
| Public Sector | Municipal services for public transport | Cost-effective and sustainable urban transport solutions | Accessibility features and maintenance support |
| Education | Campus transportation for students and staff | Safe and efficient transport options within educational institutions | Durability and safety standards to meet institutional requirements |
How Are Mini Electric Cars Used in Urban Mobility Services?
In urban mobility, mini electric cars operating at 45 km/h are ideal for ride-sharing platforms. They provide a cost-effective solution for short-distance travel, significantly reducing operational costs due to lower energy consumption compared to traditional vehicles. For B2B buyers, understanding local regulations and licensing requirements is crucial, particularly in regions like Africa and South America where urban transport laws may vary widely.
What Role Do Mini Electric Cars Play in Retail and Delivery Services?
For retail and delivery sectors, mini electric cars are increasingly utilized for last-mile delivery services. Their compact size and eco-friendly nature allow for rapid deliveries in congested urban areas while minimizing the carbon footprint. B2B buyers should consider the vehicle’s battery range and the availability of charging infrastructure to ensure efficient operations, especially in developing regions where access to power can be inconsistent.
How Can Tourism Benefit from Mini Electric Cars?
In the tourism industry, mini electric cars serve as an eco-friendly transport solution for tourist attractions. They enhance the visitor experience by providing a unique and sustainable mode of transport while also appealing to environmentally conscious travelers. When sourcing these vehicles, businesses should look for customization options that allow for branding and passenger comfort, which can be particularly appealing in competitive tourist markets across Europe and the Middle East.
Why Are Mini Electric Cars Important for Public Sector Initiatives?
Municipal services can leverage mini electric cars to improve public transport systems. These vehicles offer cost-effective solutions that align with sustainability goals, helping cities reduce their carbon emissions. B2B buyers in the public sector should prioritize accessibility features and maintenance support to ensure compliance with local regulations and to meet the needs of diverse populations.
How Do Mini Electric Cars Enhance Campus Transportation in Educational Institutions?
In educational settings, mini electric cars provide safe and efficient transportation for students and staff. Their compact design allows for easy navigation on campus, while their electric nature supports sustainability initiatives. Buyers from educational institutions should focus on durability and safety standards to meet institutional requirements, ensuring that the vehicles can withstand daily use while providing a secure environment for passengers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘mini electric car 45 kmh’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Urban Congestion with Limited Space
The Problem: Urban areas worldwide are grappling with severe traffic congestion and limited parking spaces. B2B buyers, particularly those involved in fleet management or urban mobility solutions, often struggle to find vehicles that can efficiently navigate tight spaces while providing the necessary functionality for daily tasks. The challenge lies in balancing the need for mobility with the realities of urban infrastructure, where traditional vehicles may be impractical due to size and maneuverability constraints.
The Solution: Mini electric cars with a maximum speed of 45 km/h offer an innovative solution to this problem. These vehicles are designed to fit seamlessly into congested urban environments, boasting compact dimensions that allow for easy parking and maneuvering. B2B buyers should consider sourcing models that emphasize space efficiency, such as the Squad Solar City Car, which can be parked crosswise, utilizing significantly less space than traditional cars. When specifying fleet needs, prioritize vehicles that are lightweight, energy-efficient, and equipped with features like swappable batteries to minimize downtime and enhance operational flexibility. Investing in a fleet of mini electric cars can reduce congestion, lower operational costs, and improve overall mobility efficiency within urban settings.
Scenario 2: Addressing Range Anxiety and Charging Concerns
The Problem: Despite the advantages of electric vehicles, range anxiety remains a significant concern for B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions where charging infrastructure is underdeveloped. Companies may hesitate to adopt mini electric cars for fear that insufficient charging options will limit their operational efficiency, particularly in remote or underserved areas.
The Solution: To effectively address range anxiety, B2B buyers should opt for mini electric cars that incorporate innovative charging solutions. For instance, models like the Squad Solar City Car feature integrated solar panels that allow for autonomous charging throughout the day, significantly extending the vehicle’s usability without relying solely on traditional charging stations. Additionally, buyers should consider establishing partnerships with local charging infrastructure providers to facilitate the installation of charging points at strategic locations. Training drivers on optimal usage and charging practices can further enhance the practicality of electric mini cars, ensuring that they meet operational needs without the fear of running out of charge.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Safety and Regulatory Compliance
The Problem: With varying regulations across different regions, B2B buyers face challenges in ensuring that their fleet of mini electric cars complies with local safety standards and legal requirements. In many cases, the complexity of regulations can deter companies from investing in these vehicles, particularly if they are unsure of the safety features necessary to protect passengers and meet compliance benchmarks.
The Solution: To navigate these regulatory hurdles, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on local vehicle regulations, specifically focusing on safety standards related to mini electric cars. Partnering with manufacturers that prioritize safety features—such as roll cages, seat belts, and crash structures—can streamline the compliance process. For example, the Citroën Ami is designed as a quadricycle, meeting specific safety standards for urban mobility, making it an attractive option for fleet buyers. Additionally, buyers should engage with local authorities to understand any additional requirements for operating mini electric cars within their regions. By prioritizing safety and compliance in their procurement strategy, companies can confidently integrate mini electric cars into their fleets, knowing they are operating within legal frameworks while providing safe transportation options.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for mini electric car 45 kmh
What Are the Key Materials for Mini Electric Cars Designed for Urban Mobility?
When selecting materials for mini electric cars, particularly those designed for urban mobility at speeds of 45 km/h, several factors must be considered. These include weight, cost, durability, and compliance with international standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the construction of mini electric cars, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Benefits of Using Aluminum in Mini Electric Cars?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent corrosion resistance, and can withstand a range of temperatures. Its strength-to-weight ratio is favorable for vehicle applications, making it ideal for enhancing efficiency and performance.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which contributes to better energy efficiency and handling. However, it can be more expensive than steel, and the manufacturing process may involve complex techniques such as extrusion and welding, which can increase production costs.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it suitable for various climates, particularly in humid or coastal regions. However, it may require protective coatings in harsh environments to maintain its integrity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN is crucial. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local availability and the cost implications of sourcing aluminum versus other materials.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material Choice for Mini Electric Cars?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability. It can withstand significant stress and is often used in structural components of vehicles.
Pros & Cons: Steel offers excellent durability and is generally lower in cost compared to aluminum. However, it is heavier, which can negatively impact energy efficiency. Additionally, steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, requiring regular maintenance.
Impact on Application: Steel’s robustness makes it suitable for safety-critical components like frames and chassis. However, its weight may limit the overall efficiency of electric vehicles designed for urban environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the steel used meets local and international standards for safety and performance. In regions with high humidity, such as parts of Brazil and the Middle East, corrosion-resistant coatings may be necessary.
What Role Does Composite Materials Play in Mini Electric Car Design?
Key Properties: Composites, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent fatigue resistance. They are also resistant to corrosion and can be molded into complex shapes.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their lightweight nature, which significantly enhances energy efficiency. However, they can be more expensive and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for body panels and interior components, where weight savings are critical. Their resistance to environmental factors makes them suitable for diverse climates.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of composite materials and the expertise required for their processing. Compliance with international standards is essential, especially in regions with strict automotive regulations.
How Is Plastic Utilized in Mini Electric Cars?
Key Properties: Plastics are lightweight, versatile, and can be molded into various shapes. They are also resistant to corrosion and can be produced at a low cost.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastics is their cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. However, they may not provide the same level of durability as metals and can be less environmentally friendly if not sourced responsibly.
Impact on Application: Plastics are commonly used for interior components, dashboards, and non-structural elements. Their lightweight nature contributes to overall vehicle efficiency.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the plastics used comply with safety standards and regulations in their respective markets. Sustainable sourcing practices are increasingly important, especially in European markets.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Mini Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for mini electric car 45 kmh | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, structural components | Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Steel | Chassis, safety structures | Durable, cost-effective | Heavier, prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Composites | Body panels, interior components | High strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive, complex processing | High |
| Plastics | Interior components, non-structural elements | Cost-effective, versatile | Less durable, potential environmental concerns | Low |
This analysis provides valuable insights for B2B buyers in various regions, helping them make informed decisions about material selection for mini electric cars that meet their specific market needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for mini electric car 45 kmh
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Mini Electric Cars?
The manufacturing process of mini electric cars, particularly those designed for urban mobility at speeds of 45 km/h, involves several critical stages. These include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing mini electric cars is the selection and preparation of materials. Lightweight materials such as aluminum and high-strength steel are commonly used to ensure energy efficiency and safety. The raw materials undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet industry standards. Suppliers must provide certifications that verify the quality and origin of materials, which is crucial for international buyers.
Forming Techniques
Once the materials are prepared, they are subjected to forming techniques such as stamping, bending, and welding. Advanced manufacturing technologies like CNC machining and robotic welding are employed to achieve precision and consistency. These techniques are essential in shaping the vehicle’s chassis and body components, ensuring they are lightweight yet durable. The use of automated systems can significantly enhance production efficiency and reduce human error, which is particularly important for meeting large-scale orders.
Assembly Process
The assembly stage involves the integration of various components, including the electric drivetrain, battery systems, and interior fittings. Each mini electric car may have unique features, such as swappable batteries or solar panels, which require specialized assembly techniques. Quality control checks are embedded in the assembly line, where workers conduct inspections at key stages to ensure components fit correctly and function as intended.
Finishing Touches
The finishing stage includes painting, application of decals, and installation of safety features like seat belts and roll cages. This stage not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the vehicle but also adds to its safety and durability. Manufacturers often use environmentally friendly paints and coatings to align with sustainability goals, appealing to eco-conscious B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Standards Relevant to Mini Electric Cars?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, particularly for international B2B transactions. Adhering to recognized standards ensures that the vehicles meet safety, reliability, and performance benchmarks.
International Standards
ISO 9001 is one of the most widely recognized international quality management standards. It emphasizes a systematic approach to managing processes, ensuring that products consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. For mini electric cars, compliance with ISO 9001 signifies that the manufacturer has established a quality management system that is regularly audited and improved.
Industry-Specific Standards
In addition to ISO 9001, mini electric cars must also comply with specific industry standards such as CE marking in Europe and various automotive safety regulations. These certifications indicate that the vehicle meets essential safety and environmental requirements. B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers hold these certifications to mitigate risks associated with non-compliance.
What Are the Common Quality Control Checkpoints in Mini Electric Car Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure the final product meets established standards.
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
IQC is the first line of defense in quality assurance. It involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. This step is crucial, as the quality of materials directly impacts the vehicle’s performance and safety.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During the manufacturing process, IPQC checkpoints monitor various stages of production. This includes checking for proper assembly, alignment of parts, and functionality of electrical systems. The goal of IPQC is to identify and rectify issues before they escalate, thus reducing waste and rework.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
FQC occurs at the end of the production line, where the completed mini electric car undergoes comprehensive testing. This includes road testing, safety assessments, and performance evaluations. Only vehicles that pass these tests are deemed ready for delivery to customers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures.
Conducting Supplier Audits
One effective way to verify quality control practices is through supplier audits. These audits can be scheduled regularly and should focus on assessing compliance with international standards and internal quality procedures. Buyers should inquire about the frequency of these audits and the qualifications of the personnel conducting them.
Requesting Quality Control Reports
Buyers should request detailed quality control reports from suppliers, which should include data on defect rates, inspection results, and corrective actions taken for any issues identified. This documentation is invaluable for assessing the supplier’s commitment to quality.
Engaging Third-Party Inspections
In addition to internal audits, engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These agencies can conduct thorough evaluations and provide certification that may be required for international trade.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges when it comes to quality control.
Understanding Regional Standards
Different regions may have varying standards and regulations for electric vehicles. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local requirements to ensure compliance. For example, while CE marking is essential for European markets, other regions may have distinct certifications.
Language and Cultural Barriers
Language and cultural differences can complicate communication regarding quality expectations. Buyers should establish clear guidelines and expectations upfront, possibly including bilingual contracts or documents to mitigate misunderstandings.
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations
Finally, international buyers must consider logistics and supply chain factors that can impact quality. Delays in shipping can lead to compromised quality if products are not stored or handled properly during transit. Establishing clear agreements with suppliers on how products will be packaged and shipped can help maintain quality standards.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for mini electric cars, ensuring they receive high-quality, reliable products tailored to their market needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘mini electric car 45 kmh’
Introduction
Sourcing a mini electric car with a top speed of 45 km/h involves a thorough understanding of technical specifications, supplier capabilities, and market dynamics. This guide provides a structured checklist to help B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigate the procurement process effectively. By following these steps, you can ensure a successful purchase that meets your operational needs and sustainability goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is essential for ensuring the mini electric car meets your operational requirements. Consider factors such as range, charging time, capacity, and safety features. For instance, a vehicle with a range of at least 75 km and a charging time of around 4 hours is optimal for urban mobility.
Step 2: Research Regulatory Compliance
Ensure that the mini electric car complies with local regulations in your target markets. Different regions may have specific requirements regarding emissions, safety standards, and vehicle classifications. Familiarize yourself with regulations such as EU L6 and L7 classifications or local low-speed vehicle (LSV) laws to avoid potential legal issues.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a comprehensive evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, product specifications, and references from other buyers in similar industries. Look for suppliers with experience in the mini electric vehicle market and a proven track record of meeting delivery timelines and quality standards.
- Check for certifications: Verify that the supplier holds relevant industry certifications, which can indicate adherence to quality and safety standards.
Step 4: Assess Sustainability Practices
Sustainability is a key consideration in modern procurement. Investigate the supplier’s approach to sustainability, including the materials used in manufacturing and their energy sources. For example, some vehicles come with integrated solar panels that enhance energy efficiency, making them more appealing for eco-conscious buyers.
Step 5: Request Prototypes or Demonstrations
Before finalizing your order, request prototypes or arrange for product demonstrations. This allows you to evaluate the vehicle’s performance, comfort, and usability in real-world conditions. Pay attention to features such as maneuverability in urban environments and ease of parking, which are crucial for daily operations.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve identified a suitable supplier and product, negotiate the terms of the contract. Discuss pricing, payment options, warranty, and after-sales service. Ensure that you have clear agreements on support for maintenance, parts availability, and potential training for your team on the vehicle’s operation.
Step 7: Plan for Logistics and Distribution
Consider the logistics involved in transporting the mini electric cars to your location. Assess shipping options, import duties, and delivery timelines. Additionally, plan for local distribution, especially if you intend to deploy the vehicles across multiple locations within your market.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement process for mini electric cars, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their business objectives and market demands.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for mini electric car 45 kmh Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Mini Electric Cars?
When analyzing the cost structure for sourcing mini electric cars designed to operate at 45 km/h, several key components must be considered. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the desired profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Lightweight materials like aluminum and high-strength plastics can enhance energy efficiency but may come at a higher price. Sourcing sustainable materials can also align with the growing consumer preference for eco-friendly products.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Asia, may offer cost advantages, while countries in Europe or North America may incur higher labor expenses due to stricter labor laws and higher wages.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes and technologies can reduce overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for customized designs. Buyers should consider the tooling costs relative to the expected production volume to determine if it is economically viable.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is essential, especially in the automotive sector. Implementing rigorous QC processes can incur additional costs but ultimately reduce warranty claims and enhance brand reputation.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs must be factored into the total cost. These can vary significantly based on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer and the chosen Incoterms, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping.
-
Margin: Finally, the margin set by the manufacturer will influence the final pricing. This margin often reflects the market positioning of the vehicle, competitive landscape, and expected return on investment.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Total Cost of Mini Electric Cars?
Several factors influence the pricing of mini electric cars, making them variable for different buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger volumes often leads to lower per-unit costs. Establishing a Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) can provide leverage for negotiation, resulting in cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features and specifications can increase costs. Buyers should assess their needs carefully and consider standard options to keep costs manageable.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications can lead to increased costs but may also yield benefits in terms of durability and market acceptance. Ensuring compliance with local regulations can prevent costly penalties.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but the peace of mind can justify the premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. They define the cost responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the total landed cost.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs and Pricing?
To maximize value while sourcing mini electric cars, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Highlighting long-term relationships can lead to favorable terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes maintenance, energy consumption, and resale value, rather than just the initial purchase price. This holistic view can guide better investment decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to economic conditions, tariffs, and taxes. Familiarize yourself with these factors to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: When approaching suppliers, ask for detailed breakdowns of costs. This transparency allows for better comparisons and informed decision-making.
-
Stay Updated on Market Trends: The mini electric vehicle market is rapidly evolving. Keeping abreast of technological advancements and shifts in consumer preferences can provide a competitive edge in negotiations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for mini electric cars can vary based on numerous factors, including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and geographical considerations. The figures provided are indicative and should be verified with specific suppliers to obtain accurate quotes tailored to your sourcing needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing mini electric car 45 kmh With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Mini Electric Cars Limited to 45 km/h
In the evolving landscape of urban mobility, mini electric cars limited to 45 km/h are gaining traction as efficient solutions for short-distance travel. However, businesses seeking to optimize their transportation options should consider various alternatives that offer similar benefits. This analysis will compare mini electric cars with two viable alternatives: electric bicycles and scooters, and solar-powered vehicles, focusing on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Mini Electric Car 45 km/h | Electric Bicycles & Scooters | Solar-Powered Vehicles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Max speed: 45 km/h, range: 100 km (including swappable batteries) | Max speed: 25-30 km/h, range: 50-100 km | Max speed: 45 km/h, range: 75 km (depends on sunlight) |
| Cost | Starting at €6,250, low operating costs (no road tax) | Starting at €300-€1,500, low maintenance | Starting at €10,000, potential savings on fuel |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires limited infrastructure; can park in small spaces | Minimal infrastructure needed; can be parked anywhere | Requires designated charging stations, limited by sunlight |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to simplicity of design | Regular maintenance for tires and brakes | Maintenance dependent on battery and solar panel efficiency |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting, short trips, sharing platforms | Short commutes, recreational use, urban areas | Urban commuting, eco-friendly initiatives, sunny regions |
In-depth Analysis of Alternatives
Electric Bicycles and Scooters
Electric bicycles and scooters are increasingly popular for urban mobility due to their affordability and versatility. They are ideal for short distances, particularly in congested urban areas where parking is limited. The initial investment is significantly lower compared to mini electric cars, making them accessible for a broader range of consumers. However, their lower speed and range may limit their use for longer commutes. Additionally, they require regular maintenance, particularly for tires and brakes, which can be a consideration for businesses looking for low-maintenance solutions.
Solar-Powered Vehicles
Solar-powered vehicles, like the Squad Solar City Car, offer an innovative alternative that combines sustainability with urban mobility. With the ability to recharge using sunlight, these vehicles promise low operational costs and zero emissions, appealing to eco-conscious consumers. However, the initial investment can be higher, and their performance is contingent on sunlight availability, which may not be reliable in all regions. Furthermore, they may require designated charging infrastructure, which could complicate implementation in areas lacking such facilities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When evaluating transportation solutions, B2B buyers should assess their specific requirements, including budget, operational costs, and the nature of their mobility needs. Mini electric cars offer a compelling option for businesses focused on urban commuting and sharing platforms, while electric bicycles and scooters may serve well for companies emphasizing cost-efficiency and flexibility. Solar-powered vehicles are ideal for organizations committed to sustainability but may necessitate a higher upfront investment and depend on favorable environmental conditions. Ultimately, the choice should align with the organization’s operational goals and the unique demands of the markets they serve.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for mini electric car 45 kmh
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Mini Electric Car with a 45 km/h Speed?
Understanding the essential technical properties of mini electric cars, particularly those designed for urban mobility with a maximum speed of 45 km/h, is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are several critical specifications:
-
Battery Capacity and Type
– Definition: Battery capacity is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) and indicates how much energy the battery can store. Common types include lithium-ion and swappable batteries.
– B2B Importance: Battery capacity directly impacts the vehicle’s range and operational efficiency. For B2B buyers, understanding battery options helps in evaluating the suitability of the vehicle for specific urban applications and user needs. -
Vehicle Dimensions and Weight
– Definition: This includes the overall length, width, height, and curb weight of the vehicle. For example, a compact design may measure around 2 meters in length and weigh less than 600 kg.
– B2B Importance: Smaller dimensions facilitate easier parking and maneuverability in congested urban areas, making them attractive for shared mobility services. Weight influences energy efficiency and handling, critical for fleet operators. -
Safety Features and Ratings
– Definition: Safety features often include a roll cage, crash structure, seat belts, and advanced braking systems. Safety ratings are typically assessed by regulatory bodies.
– B2B Importance: High safety standards are essential for liability and customer satisfaction. Buyers must ensure vehicles meet local safety regulations and can withstand urban driving conditions. -
Charging Time and Infrastructure Compatibility
– Definition: This refers to how long it takes to recharge the vehicle’s battery, often around 4-8 hours for standard charging, and compatibility with existing charging infrastructure.
– B2B Importance: Efficient charging options reduce downtime for businesses, particularly in fleet operations. Compatibility with local infrastructure can influence the decision to adopt specific vehicle models. -
Energy Efficiency
– Definition: Measured in kilometers per kWh, this indicates how far the vehicle can travel per unit of energy consumed.
– B2B Importance: Higher energy efficiency translates to lower operational costs, making vehicles more economical for businesses focused on sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Mini Electric Cars?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for navigating the procurement and operational landscape of mini electric cars. Here are several important terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or vehicles that are sold under another brand’s name.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality standards and sourcing strategies for vehicle components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ is critical for B2B buyers, especially those looking to purchase vehicles in bulk for fleet use, as it directly impacts inventory costs and supplier negotiations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A formal request sent to suppliers asking for pricing, terms, and conditions for specific goods or services.
– Relevance: An RFQ process helps buyers gather competitive pricing and service offers, enabling informed decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers regarding the delivery of goods under sales contracts.
– Relevance: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers to clarify shipping responsibilities, costs, and risk management in cross-border transactions. -
MaaS (Mobility as a Service)
– Definition: An emerging trend that integrates various forms of transportation services into a single accessible and customer-friendly platform.
– Relevance: B2B buyers, particularly those in urban mobility sectors, must consider how vehicles fit into MaaS frameworks to enhance service offerings and customer experience.
By grasping these technical specifications and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the mini electric car 45 kmh Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Mini Electric Car 45 km/h Sector?
The mini electric car sector, particularly vehicles limited to 45 km/h, is experiencing a transformative shift driven by urbanization, environmental concerns, and regulatory changes. Globally, cities are adopting stricter emissions regulations, which is catalyzing demand for electric mobility solutions. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, international B2B buyers are witnessing a surge in the adoption of these vehicles as a viable alternative for urban transport. Key trends include the integration of solar charging capabilities, as seen with the Squad Solar City Car, which enhances energy efficiency and reduces operational costs. Furthermore, the rise of Mobility as a Service (MaaS) platforms is reshaping how consumers access transportation, fostering an ecosystem where shared electric vehicles become commonplace.
Emerging technologies in battery management and lightweight materials are also pivotal. Companies are increasingly exploring swappable battery systems, which not only minimize downtime but also cater to the growing demand for flexible charging solutions. With the European Union’s push for sustainable urban mobility, international buyers must stay attuned to advancements in vehicle design that prioritize compactness and efficiency, ensuring that these vehicles can navigate congested urban environments with ease.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Mini Electric Car Market?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the mini electric car sector, influencing purchasing decisions and corporate practices alike. The environmental impact of vehicle manufacturing and operation is under scrutiny, leading to a rising demand for ethical sourcing practices. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and ensuring minimal waste during production. The integration of green certifications—such as ISO 14001 for environmental management—serves as a significant indicator of a manufacturer’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the growing emphasis on life-cycle assessments allows buyers to evaluate the environmental impact of mini electric cars from production to disposal. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers from regions where eco-friendly initiatives are gaining traction, such as Brazil and Saudi Arabia. As sustainability becomes a competitive advantage, companies that invest in transparent supply chains and environmentally friendly materials will stand out in the marketplace.
What Has Been the Evolution and History of Mini Electric Cars?
The evolution of mini electric cars dates back to the early 2000s, driven by advancements in battery technology and a growing awareness of environmental issues. Initially, these vehicles catered primarily to niche markets, but as urban populations surged and congestion became a pressing concern, the demand for compact, efficient transportation solutions soared. The introduction of regulatory frameworks, particularly in Europe, has further propelled the market forward, encouraging manufacturers to innovate.
Today, mini electric cars have evolved into sophisticated urban mobility solutions, featuring enhanced safety measures, improved battery ranges, and user-friendly designs. The historical context of these vehicles underscores a significant shift towards sustainable transport solutions that align with the needs of modern urban dwellers, offering a glimpse into the future of mobility. As the sector continues to develop, B2B buyers must remain informed about historical trends that shape current market dynamics and anticipate future innovations that will redefine urban transport.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of mini electric car 45 kmh
-
How can mini electric cars address urban mobility challenges?
Mini electric cars, particularly those with a top speed of 45 km/h, are designed to alleviate issues such as traffic congestion, parking scarcity, and urban emissions. Their compact size allows for efficient maneuvering in tight spaces, making them ideal for cities where larger vehicles struggle. Additionally, many models feature solar charging capabilities, reducing reliance on traditional power sources and contributing to sustainable urban transport solutions. -
What are the key benefits of sourcing mini electric cars for my business?
Sourcing mini electric cars can provide numerous benefits, including cost savings on fuel and maintenance, reduced parking fees, and exemptions from congestion charges in many urban areas. These vehicles are often designed for easy operation without the need for a full driver’s license, broadening the potential user base. Furthermore, their appeal in eco-conscious markets can enhance your brand’s image as a sustainable transport provider. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for mini electric cars?
When vetting suppliers, assess their manufacturing capabilities, compliance with local and international regulations, and reputation within the industry. Request references and case studies that demonstrate their experience in producing mini electric cars. It’s also important to evaluate their after-sales support, warranty terms, and the availability of spare parts to ensure long-term serviceability of the vehicles. -
What customization options are available for mini electric cars?
Many manufacturers offer customization options such as color schemes, seating configurations, and additional features like air conditioning or enhanced battery capacity. Depending on your business needs, inquire about branding opportunities that allow you to incorporate your company’s logo or specific design elements. Customization can also extend to functionality, such as adding storage solutions or tech upgrades like smartphone connectivity. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for mini electric cars?
Minimum order quantities for mini electric cars can vary significantly by supplier. Some manufacturers may offer flexible MOQs for small businesses or startups, while others may require bulk orders to optimize production costs. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs directly with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you’re looking to integrate these vehicles into a fleet or sharing platform. -
What payment terms can I expect when purchasing mini electric cars?
Payment terms often depend on the supplier’s policies and the volume of your order. Many suppliers may offer options such as upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, or financing arrangements. It’s crucial to clarify these terms before finalizing your purchase, as well as to ensure that they align with your budget and cash flow considerations. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for mini electric cars?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed information on the supplier’s QA processes, including testing standards and certifications for their vehicles. Many reputable manufacturers adhere to international safety and quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Additionally, consider conducting your own inspections or audits of the manufacturing facility to verify compliance with these standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing mini electric cars?
Logistics for importing mini electric cars involve evaluating shipping methods, customs regulations, and local transportation requirements. Choose a reliable logistics partner familiar with automotive imports to navigate the complexities of international shipping. It’s also essential to understand the tax implications and potential tariffs involved in the import process, as these can significantly affect your overall cost structure.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Mini Electric Car 45 Kmh Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Citroën – Ami 100% Electric Quadricycle
Domain: citroen.ie
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: {“model”:”Citroën Ami 100% Electric Quadricycle”,”starting_price”:”€9,990 RRSP”,”range”:”75 KM”,”charging_time”:”4 hours”,”top_speed”:”45 KM/H”,”type”:”100% Electric”,”dimensions”:{“length”:”2.41 m”,”width”:”1.39 m”,”height”:”1.52 m”},”features”:{“easy_parking”:”Yes”,”turning_circle”:”7.20 m”,”seating_capacity”:”2 seats”,”storage_capacity”:”63 Litres to 200 Litres (if using passenger seat as stora…
2. Citroën – AMI & Fiat – Topolino
Domain: v2charge.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: 1. Citroën AMI:
– Price: from €7,200
– Dimensions: 2.41m (L) x 1.39m (W)
– Weight: 485 kg
– Motor: 6 kW (8 hp)
– Battery capacity: 5.5 kWh
– Range: 75 km
– Acceleration: 0 to 45 km/h in 10 seconds
– Load capacity: 64 kg
2. Fiat Topolino:
– Price: under €10,000
– Dimensions: 2.53m (L) x 1.39m (W)
– Top speed: 45 km/h
– Quick charging: Full charge in…
3. Hezonev – 45km/h Electric Car for Elderly
Domain: hezonev.com
Introduction: Product Name: 45km/h Electric Car For Elderly
Speed: 45 km/h
EEC Certificate: Yes
Passenger Capacity: 2-4 persons
Dimensions (L*W*H): K-3: 2050×1250×1545 mm, K-7: 2500×1250×1545 mm, K-8S: 2500×1250×1545 mm
Wheel Base: K-3: 1450 mm, K-7: 1900 mm, K-8S: 1900 mm
Curb Weight: K-3: 560 kg, K-7: 540 kg, K-8S: 640 kg
Motor Type: K-3: AC Motor, K-7: DC Motor, K-8S: AC Motor
Motor Power: K-3: 3 kw, K-7: 2….
4. Boing Boing – $1700 Mini Electric Jeep Review
Domain: bbs.boingboing.net
Introduction: $1700 mini electric Jeep knockoff reviewed
5. ARI Motors – ARI 452 Electric Vehicle
Domain: ari-motors.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: ARI 452 for 2 Passengers:
– Ideal for narrow city centers
– Top speed: 45 km/h (28 mph)
– Can be driven with a class AM moped license in many countries
– Energy consumption: 6 kWh per 100 km
– Approximate cost: EUR 1.20 per 100 km
– Range: Up to 250 km with LiFePO4 battery (standard lead gel battery offers up to 120 km)
– Charging: Standard 230 V socket, no expensive installations needed
-…
6. Facebook – Electric Four-Wheeler
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Electric Vehicles | Factory direct sales long distance mini electric four-wheeler
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for mini electric car 45 kmh
As the demand for sustainable urban mobility solutions intensifies, the strategic sourcing of mini electric cars that operate at 45 km/h presents a compelling opportunity for international B2B buyers. These vehicles, such as the Squad Solar City Car and Citroën Ami, highlight a shift towards efficient, eco-friendly transport options tailored for urban environments. With their compact design, affordability, and minimal regulatory barriers, these cars are well-suited for diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Strategic sourcing not only reduces procurement costs but also enhances supply chain resilience and sustainability. The integration of solar charging capabilities and swappable batteries further positions these vehicles as innovative solutions to tackle urban congestion and emissions. Buyers should consider aligning their sourcing strategies with manufacturers that prioritize safety, comfort, and environmental impact.
Looking ahead, the potential for growth in the mini electric vehicle market is significant. By investing in these solutions now, businesses can not only meet the evolving needs of urban commuters but also contribute to a greener future. Engage with manufacturers and explore partnership opportunities to capitalize on this burgeoning market. Your strategic sourcing decisions today can pave the way for sustainable mobility solutions tomorrow.