Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for small electric vehicle
In an increasingly eco-conscious world, sourcing small electric vehicles (SEVs) presents both a unique opportunity and a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With the demand for sustainable transport solutions rising across diverse markets, from Africa to Europe, navigating the complexities of SEV procurement can be daunting. This guide serves as a vital resource for businesses looking to understand the multifaceted landscape of small electric vehicles, covering essential aspects such as types, applications, supplier vetting, and cost considerations.
By examining the latest innovations in SEV technology and performance, buyers can gain insights into how these vehicles can enhance operational efficiency and reduce carbon footprints. Whether your interest lies in utility vehicles for urban logistics or compact passenger cars for employee transport, our guide equips you with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions.
With a focus on specific regions—including the emerging markets of South America and the Middle East, as well as established markets like Germany and Saudi Arabia—this comprehensive resource empowers B2B buyers to identify reliable suppliers, understand local regulations, and evaluate total cost of ownership. As the landscape of electric mobility evolves, leveraging this guide will enable your business to thrive in the global marketplace, ensuring you remain at the forefront of sustainable transport solutions.
Understanding small electric vehicle Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) | Compact design, top speeds of 25 mph, street-legal in many areas | Local deliveries, campus transport | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to maneuver; Cons: Limited speed and range. |
| Micro Electric Vans | Small cargo space, flexible configurations, higher payload capacity | Urban deliveries, service vehicles | Pros: Versatile for cargo; Cons: Limited passenger capacity. |
| Compact Electric Cars | Designed for personal transport, typically 2-4 seats | Employee transport, car-sharing services | Pros: Good range, comfortable; Cons: Higher initial cost compared to LSVs. |
| Electric Scooters | Two-wheeled, lightweight, often foldable | Last-mile delivery, urban commuting | Pros: Highly portable, low operational costs; Cons: Less stable, limited cargo. |
| Electric Utility Vehicles | Larger size, designed for varied terrains, often rugged | Maintenance, landscaping, municipal use | Pros: Durable, high payload; Cons: Higher maintenance costs. |
What Are Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) and Their B2B Relevance?
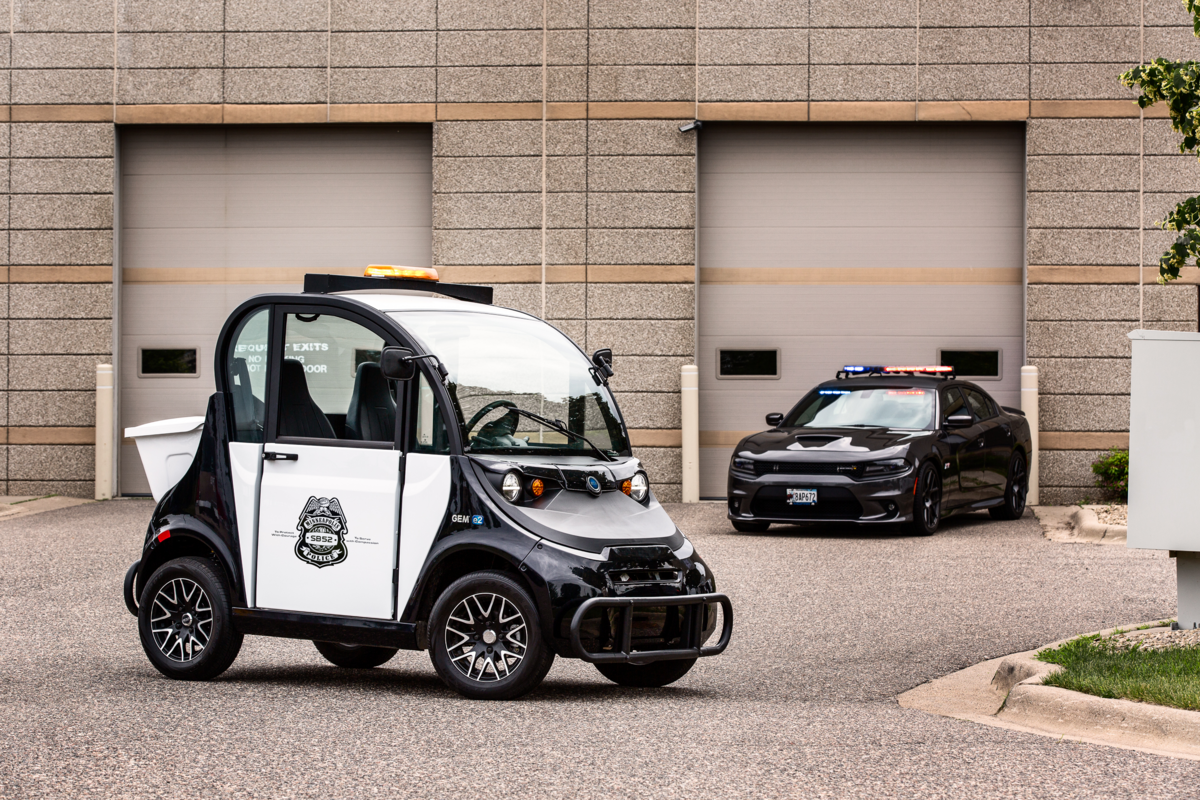
Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) are compact electric cars designed for urban environments, with maximum speeds typically capped at 25 mph. They are particularly advantageous for local deliveries or campus transport due to their maneuverability and low operational costs. B2B buyers should consider the regulatory environment in their region, as LSVs are street-legal in many areas and can significantly reduce transportation costs while promoting sustainability.
How Do Micro Electric Vans Fit into Urban Logistics?
Micro Electric Vans are characterized by their small cargo space and flexible configurations, making them ideal for urban deliveries and service vehicles. They can carry higher payloads than typical passenger vehicles, which is a significant advantage for businesses requiring efficient transport solutions. When purchasing, businesses should evaluate their specific cargo needs and the vehicle’s range to ensure it meets operational demands.
What Are the Benefits of Compact Electric Cars for Employee Transport?
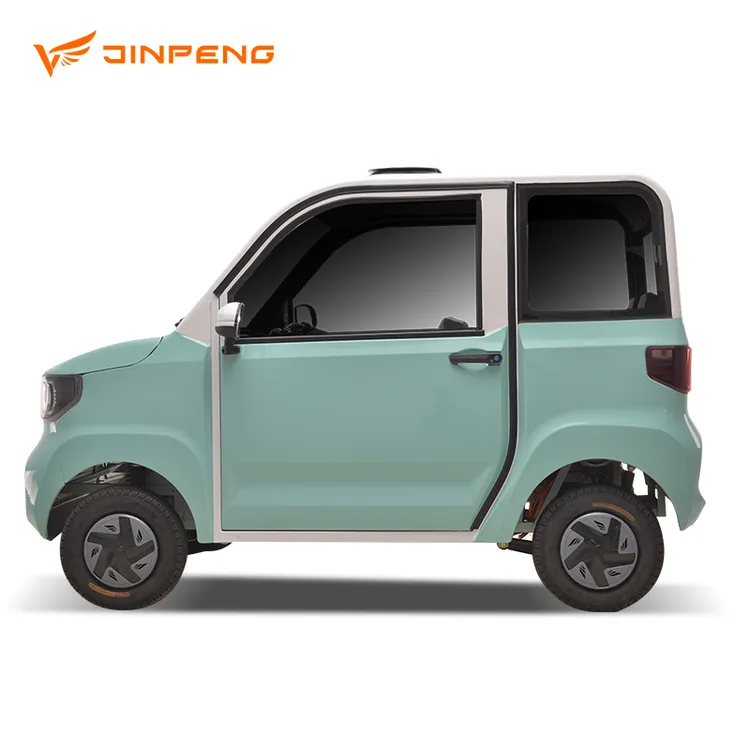
Compact Electric Cars are designed primarily for personal transport, accommodating 2-4 passengers. They provide a comfortable ride and a decent range, making them suitable for employee transport or car-sharing services. Buyers should consider the total cost of ownership, including potential tax incentives and maintenance savings, as these vehicles can be more expensive upfront but often lead to long-term savings.
Why Choose Electric Scooters for Last-Mile Delivery?
Electric Scooters are lightweight and portable, making them excellent for last-mile delivery and urban commuting. Their foldable design allows for easy storage and transport, which is a significant benefit for businesses in densely populated areas. However, buyers should be aware of their stability limitations and cargo capacity when integrating them into their fleet.
How Do Electric Utility Vehicles Serve Various Industries?
Electric Utility Vehicles are larger and designed for a variety of terrains, making them suitable for maintenance, landscaping, and municipal use. Their rugged design allows them to handle demanding tasks while providing a high payload capacity. Businesses should assess their operational environment and maintenance costs, as these vehicles may require more upkeep compared to smaller electric options.
Key Industrial Applications of small electric vehicle
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Small Electric Vehicle | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Logistics | Last-Mile Delivery Solutions | Enhanced efficiency in urban environments, reducing congestion and emissions. | Range capabilities, charging infrastructure, and payload capacity. |
| Hospitality and Tourism | Guest Transportation Services | Eco-friendly transport options that enhance guest experience and brand image. | Customization options, comfort features, and safety certifications. |
| Municipal Services | Maintenance and Utility Operations | Cost-effective and sustainable solutions for city maintenance and utility work. | Durability, operational range, and ease of maintenance. |
| Retail | In-Store and On-Site Customer Transport | Improved customer service through convenient transport options, increasing sales. | Vehicle size, maneuverability, and branding opportunities. |
| Agriculture | Farm Operations and Transport | Efficient transport of goods and personnel across agricultural sites, reducing labor costs. | Terrain adaptability, battery life, and load capacity. |
How Can Small Electric Vehicles Transform Urban Logistics?
In urban logistics, small electric vehicles (SEVs) are revolutionizing last-mile delivery solutions. Their compact size allows them to navigate congested city streets and park easily, which is crucial for timely deliveries. Additionally, SEVs contribute to reducing carbon emissions, aligning with the sustainability goals of many businesses. International buyers should consider range capabilities and charging infrastructure, especially in regions where power availability may vary, such as parts of Africa and South America.
What Role Do Small Electric Vehicles Play in Hospitality and Tourism?
In the hospitality and tourism sector, small electric vehicles enhance guest transportation services by offering eco-friendly options that improve the overall guest experience. Hotels and resorts can utilize these vehicles to transport guests around their properties or to nearby attractions, promoting a green brand image. Buyers in this sector should prioritize customization options, comfort features, and safety certifications, particularly in markets like Europe where regulatory standards are stringent.
How Are Small Electric Vehicles Beneficial for Municipal Services?
Municipal services are increasingly adopting small electric vehicles for maintenance and utility operations. These vehicles provide a cost-effective solution for city maintenance tasks, reducing fuel costs and emissions. They can navigate narrow streets and work in various urban environments, making them ideal for city use. Key considerations for sourcing include vehicle durability, operational range, and ease of maintenance, especially in regions with challenging terrain or limited service infrastructure.
What Advantages Do Small Electric Vehicles Offer to Retail Businesses?
For retail businesses, small electric vehicles can serve as effective in-store and on-site customer transport solutions. They provide a convenient means for transporting customers between different areas of large retail complexes or nearby parking facilities, enhancing customer service and satisfaction. Retailers should consider vehicle size, maneuverability, and potential branding opportunities when sourcing these vehicles, particularly in urban areas of the Middle East and Europe, where foot traffic is high.
How Can Small Electric Vehicles Improve Agricultural Operations?
In agriculture, small electric vehicles are proving invaluable for operations and transport across farms. They facilitate the efficient movement of goods and personnel, significantly reducing labor costs and enhancing productivity. Buyers in the agricultural sector should focus on the vehicles’ terrain adaptability, battery life, and load capacity, especially in regions with diverse agricultural practices, such as South America and parts of Africa. This ensures that the vehicles can handle the specific demands of various farming environments.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘small electric vehicle’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Limited Charging Infrastructure for Small Electric Vehicles
The Problem: One of the most significant challenges faced by B2B buyers of small electric vehicles (EVs) is the limited availability of charging infrastructure. In many regions, particularly in emerging markets across Africa and South America, the existing charging stations are sparse, making it difficult for businesses to effectively deploy fleets of small EVs. This scenario can lead to operational inefficiencies, increased downtime, and ultimately impact the bottom line due to range anxiety among drivers and staff.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, businesses should conduct a thorough analysis of the local charging infrastructure before investing in small electric vehicles. This involves identifying existing charging stations, understanding the charging capabilities (e.g., Level 2 or DC Fast Charging), and assessing the projected growth of EV infrastructure in the area. Additionally, companies can engage with local government initiatives aimed at expanding charging networks or consider partnerships with charging station providers. Investing in vehicles with flexible charging options, such as those that can charge on standard home outlets, can provide greater operational flexibility. Furthermore, businesses should consider installing on-site charging stations at their facilities to ensure their fleet is always ready for operation.
Scenario 2: Understanding the Total Cost of Ownership for Small Electric Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to understand the total cost of ownership (TCO) associated with small electric vehicles. While the initial purchase price of electric vehicles may be higher than traditional gasoline vehicles, businesses need to consider long-term costs such as maintenance, fuel savings, and potential government incentives. This lack of clarity can lead to misinformed purchasing decisions and budget overruns.
The Solution: To address this pain point, businesses should conduct a comprehensive TCO analysis that factors in all relevant expenses over the vehicle’s lifecycle. This analysis should include initial costs, financing options, insurance, maintenance, and operational costs, including electricity rates and charging logistics. Buyers can leverage TCO calculators available online or consult with manufacturers to obtain detailed data on the expected savings from maintenance (e.g., fewer oil changes and brake replacements) and operational efficiency (e.g., lower energy costs per mile). Additionally, businesses should stay informed about local and federal incentives for electric vehicle purchases, which can significantly reduce upfront costs. By comparing these figures with traditional vehicles, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with Local Regulations for Small Electric Vehicles
The Problem: The regulatory environment surrounding electric vehicles can be complex, especially for international B2B buyers. Different countries and regions have varying laws regarding emissions, safety standards, and vehicle classifications. Navigating these regulations can be overwhelming, leading to potential non-compliance and financial penalties.
The Solution: To effectively manage compliance, businesses should proactively engage with local regulatory bodies to understand the specific requirements for small electric vehicles in their operating regions. This includes familiarizing themselves with vehicle classifications (e.g., low-speed vehicles), safety standards, and any necessary permits or inspections required for operation. Companies can also benefit from consulting legal or regulatory experts in the automotive field to ensure adherence to all laws. Additionally, manufacturers of small electric vehicles often provide documentation and guidance on compliance, which can simplify the process. By establishing a compliance checklist and regularly reviewing regulations, businesses can stay ahead of changes in the legal landscape and ensure their fleet operations remain uninterrupted.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for small electric vehicle
When selecting materials for small electric vehicles (EVs), it is essential to consider properties that directly influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the manufacturing of small electric vehicles, along with their implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in Small Electric Vehicles?
Aluminum is widely used in the automotive industry due to its favorable properties. It has a low density, high strength-to-weight ratio, and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for vehicle frames and body panels. Aluminum can withstand temperatures up to 600°C, which is beneficial for components near heat sources such as electric motors.
Pros: Aluminum offers significant weight savings, which can enhance the vehicle’s range and efficiency. Its corrosion resistance reduces maintenance costs over time.
Cons: The primary drawback of aluminum is its higher material cost compared to steel. Additionally, manufacturing processes for aluminum can be more complex, requiring specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including electric and thermal management systems. However, care must be taken to avoid galvanic corrosion when paired with dissimilar metals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. Buyers from regions like Europe may prioritize aluminum for its lightweight properties, while those in Africa and South America may weigh cost versus performance.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material for Small Electric Vehicles?
Steel remains a staple in vehicle manufacturing due to its strength and durability. It can withstand high pressures and is less expensive than aluminum, making it a cost-effective choice for structural components.
Pros: Steel’s robustness provides excellent crash protection and longevity. It is also readily available and can be easily formed into complex shapes.
Cons: The major downside is steel’s weight, which can negatively impact the vehicle’s efficiency and range. Additionally, steel is prone to corrosion unless treated with coatings.
Impact on Application: Steel is suitable for high-stress applications, such as chassis and support structures. However, its heavier weight may necessitate more powerful battery systems to maintain performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that steel meets local standards for safety and performance. For instance, regions with high humidity, such as parts of the Middle East, may require additional corrosion-resistant treatments.
What Role Does Composite Material Play in Small Electric Vehicles?
Composite materials, particularly carbon fiber and fiberglass, are increasingly used in small electric vehicles due to their lightweight and high-strength properties. They can withstand a wide range of temperatures and are resistant to corrosion.
Pros: Composites significantly reduce vehicle weight, improving efficiency and range. They also offer design flexibility, allowing for unique shapes and aesthetics.
Cons: The primary limitation is the high cost of materials and manufacturing processes, which can be prohibitive for mass production. Additionally, repair and recycling of composites can be challenging.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for body panels and interior components where weight reduction is critical. However, they may not be suitable for high-load-bearing applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying standards for composite materials across regions. For example, European buyers may have stricter regulations regarding the use of composites in automotive applications.
How Do Battery Materials Affect Small Electric Vehicle Performance?
Battery materials, particularly lithium-ion, are crucial in determining the performance and efficiency of small electric vehicles. Lithium-ion batteries offer high energy density and efficiency, with a temperature tolerance of -20°C to 60°C.
Pros: They provide long-range capabilities and quick charging times, essential for urban environments. Their lightweight nature contributes to overall vehicle efficiency.
Cons: The main drawbacks include high costs and environmental concerns regarding lithium extraction and disposal. Additionally, battery performance can degrade over time, affecting vehicle range.
Impact on Application: Battery materials directly influence the vehicle’s range, charging speed, and overall performance. Compatibility with charging infrastructure is also a key consideration.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international battery safety standards is vital. Buyers in regions like Europe may also focus on sustainability and recycling practices when selecting battery materials.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Small Electric Vehicles
| Material | Typical Use Case for small electric vehicle | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Vehicle frames and body panels | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Steel | Chassis and structural components | Strong, cost-effective | Heavier, prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Composite | Body panels and interior components | Lightweight, design flexibility | High cost, difficult to repair | High |
| Battery Materials | Power source for electric drivetrain | High energy density, quick charging | High cost, environmental concerns | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, facilitating informed decisions that align with regional requirements and market trends.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for small electric vehicle
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Small Electric Vehicles?
The manufacturing process for small electric vehicles (EVs) involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure efficiency and quality. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to source reliable vehicles for commercial use.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, which involves sourcing high-quality materials that meet specific standards. Common materials include lightweight metals such as aluminum for the chassis, high-strength plastics for the body, and various composites for interior components. Suppliers often provide certification for these materials to ensure compliance with safety and environmental regulations. It is crucial for B2B buyers to verify the origin and quality of materials used, as they can significantly impact the vehicle’s performance and longevity.
Forming Techniques in Small Electric Vehicle Production
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into vehicle components. Techniques such as stamping, extrusion, and injection molding are widely used. For instance, chassis components may be stamped from sheets of metal, while interior parts could be produced using injection molding techniques. Advanced forming technologies, including 3D printing, are increasingly being utilized to create custom parts with complex geometries, enhancing design flexibility. Buyers should inquire about the forming techniques employed by manufacturers, as these can affect the customization options available.
Assembly Process: How Are Small Electric Vehicles Assembled?
The assembly process is where individual components come together to create the finished vehicle. This stage typically involves automated assembly lines, where robots and skilled workers collaborate to install parts like the electric motor, battery packs, and electronic systems. Quality control measures, such as real-time monitoring and feedback systems, are implemented during assembly to minimize defects. For B2B buyers, understanding the assembly process is vital, as it influences delivery timelines and the overall reliability of the vehicles produced.
Finishing Touches: What Is Involved in the Finishing Stage?
Finishing is the final manufacturing stage, where the vehicle undergoes painting, surface treatment, and installation of aesthetic components. This stage not only enhances the vehicle’s appearance but also protects it from environmental factors. For example, electrostatic painting provides a durable finish, while treatments can improve corrosion resistance. Buyers should consider the finishing options available, as they can affect the vehicle’s marketability and longevity.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Small Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in ensuring that small electric vehicles meet international standards and customer expectations. A robust QA process encompasses various checkpoints and testing methods throughout the manufacturing cycle.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers of small electric vehicles typically adhere to several international standards, including ISO 9001 for quality management systems. Additionally, compliance with industry-specific standards such as CE marking (European Conformity) and API (American Petroleum Institute) ensures that vehicles meet safety and performance criteria. Understanding these standards allows B2B buyers to gauge the quality and reliability of potential suppliers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are crucial for maintaining high standards throughout the manufacturing process. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage checks the quality of raw materials and components received from suppliers. Ensuring that these materials meet specified standards is essential for maintaining overall product quality.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, IPQC involves continuous monitoring and inspection of assembly procedures to catch defects early. This stage is critical in preventing costly rework and ensuring that the assembly process adheres to quality standards.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection occurs before vehicles are shipped to customers. This stage includes comprehensive testing of vehicle performance, safety features, and compliance with regulatory standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the performance and safety of small electric vehicles. Common testing techniques include:
-
Functional Testing: This involves testing all vehicle systems, including electrical, mechanical, and safety features, to ensure they operate as intended.
-
Durability Testing: Vehicles undergo rigorous testing under various conditions to assess their long-term performance and resilience. This may include simulations of extreme temperatures, humidity, and road conditions.
-
Safety Testing: Compliance with safety regulations is paramount. Vehicles are subjected to crash tests and assessments of safety features like airbags, seat belts, and electronic stability controls.
B2B buyers should inquire about the specific testing methods used by manufacturers, as this can provide insights into the vehicle’s reliability and safety.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure they are partnering with a reliable manufacturer. Here are some effective strategies:
What Audits and Reports Should Buyers Request?
Buyers should conduct regular audits of potential suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This can include:
-
On-site Audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to observe the processes firsthand and evaluate adherence to quality standards.
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control processes, test results, and compliance with relevant standards.
Are Third-Party Inspections Beneficial?
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. These independent entities can conduct thorough inspections and testing, providing unbiased evaluations of the manufacturer’s quality control practices. B2B buyers should consider incorporating third-party inspections into their sourcing strategy, especially when dealing with international suppliers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and standards is essential. Buyers should be aware of the following nuances:
-
Regional Standards Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements that manufacturers must meet. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with both international and local standards.
-
Logistical Considerations: Quality control processes may vary based on logistical capabilities. Buyers should evaluate how manufacturers handle quality assurance in the context of shipping and delivery, especially for cross-border transactions.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for small electric vehicles is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on the details of material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, as well as the importance of quality control standards and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business needs and ensure the procurement of high-quality vehicles.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘small electric vehicle’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers interested in sourcing small electric vehicles (EVs). Given the growing demand for sustainable transport solutions, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this checklist will help you navigate the procurement process efficiently.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical to ensure the vehicle meets your operational needs. Consider factors such as passenger capacity, range per charge, speed, and cargo capacity. For instance, if your operations require local deliveries, prioritize models with a compact design and adequate payload capabilities.
Step 2: Assess Local Regulations and Compliance
Understanding local regulations surrounding small electric vehicles is essential. Different regions may have specific requirements regarding emissions, safety standards, and vehicle classifications (e.g., low-speed vehicles). Research these regulations to ensure that the vehicles you consider are compliant and can be legally operated in your intended areas.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, including their history in the EV market, production capabilities, and references from similar industries. Look for suppliers with a proven track record and strong customer service support to assist with any post-purchase inquiries.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Quality Standards
Ensure that the vehicles meet industry certifications and quality standards. Look for compliance with international safety and environmental standards, such as ISO certifications or local equivalent certifications. This verification process helps mitigate risks associated with product quality and safety, especially in regions with diverse regulatory frameworks.
Step 5: Consider Customization Options
Customization can enhance the utility and appeal of small electric vehicles. Inquire about available options, such as different battery types, seating arrangements, and additional features like cargo space or enhanced audio systems. Customization ensures that the vehicle aligns with your branding and operational requirements.
Step 6: Analyze Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Evaluating the total cost of ownership is vital for budgeting and financial planning. This includes not only the initial purchase price but also maintenance costs, energy consumption, and potential tax incentives. Take into account the expected lifespan of the vehicle and any savings associated with reduced fuel and maintenance costs compared to traditional vehicles.
Step 7: Plan for Charging Infrastructure
Assess your charging infrastructure needs to ensure operational efficiency. Determine whether to invest in private charging stations or utilize public charging networks. Consider the charging speed and convenience, as well as the availability of charging stations in your operational areas to minimize downtime.
By following this checklist, you will be well-equipped to make informed decisions when sourcing small electric vehicles that meet your business needs while supporting sustainable transportation goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for small electric vehicle Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Small Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Understanding the cost structure of small electric vehicles (EVs) is crucial for B2B buyers looking to source effectively. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts cost. High-quality batteries, often lithium-ion, are the most expensive component, followed by the vehicle’s chassis and body materials. Sustainable materials can also add to costs but may appeal to environmentally conscious markets.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and depend on the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is essential for assembly and quality control, especially for intricate components like electric motors and battery systems.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production methods can help minimize these expenses, allowing for more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for manufacturing tools and molds can be significant, especially for custom designs. These costs are usually amortized over the production run, making high-volume orders more cost-effective.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that vehicles meet safety and performance standards incurs costs. This is particularly critical in international markets where compliance with local regulations is mandatory.
-
Logistics: Distribution costs, including shipping and handling, can vary based on the destination. Understanding local infrastructure and customs processes can help mitigate these expenses.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a profit margin to cover risks and ensure sustainability. This margin can fluctuate based on demand and competition in the market.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Small Electric Vehicle Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of small electric vehicles, which can vary significantly across regions:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate for better rates by committing to higher volumes.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as enhanced battery capacity or unique design elements, can increase costs. Buyers should carefully evaluate which features are essential for their market.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., safety or environmental) can elevate costs but may be necessary for compliance in certain markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge a premium, but this can translate to better quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for international buyers. Incoterms dictate who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties, all of which can affect total landed costs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Cost-Efficiency?
B2B buyers should consider several strategies to optimize their sourcing of small electric vehicles:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and terms. Leveraging potential long-term relationships can lead to favorable deals.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider the lifetime costs of the vehicle, including maintenance, energy consumption, and depreciation. This holistic view can lead to better financial decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and regional market conditions that can impact pricing. Understanding local regulations and incentives for EVs can also provide financial advantages.
-
Supplier Diversification: Relying on multiple suppliers can reduce risk and enhance bargaining power. This strategy can also help mitigate disruptions in the supply chain.
-
Leverage Government Incentives: Many countries offer incentives for electric vehicle purchases, which can significantly reduce costs. Staying informed about these opportunities can enhance the overall value of your investment.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for small electric vehicles can vary widely based on specifications, regional market conditions, and supplier negotiations. This analysis provides indicative insights, and buyers should conduct thorough research and engage directly with suppliers to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing small electric vehicle With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Small Electric Vehicles
As businesses seek sustainable and cost-effective transportation solutions, it’s essential to explore various alternatives to small electric vehicles (SEVs). Each option has distinct features that cater to different operational needs, budgets, and environmental considerations. This analysis will compare small electric vehicles against two prominent alternatives: traditional gasoline vehicles and bicycles.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Small Electric Vehicle | Traditional Gasoline Vehicle | Bicycle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Up to 25 mph, ideal for urban settings | 30-150 mph, versatile for all terrains | 10-20 mph, limited by rider capability |
| Cost | $0.03/mile, lower energy costs | $0.12-$0.15/mile, higher fuel and maintenance costs | Minimal operational costs, no fuel needed |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure | Widely available fuel stations | No infrastructure needed, easy to park |
| Maintenance | Low, mainly battery care | Moderate to high, regular servicing needed | Minimal, mainly tire maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Urban short trips, light cargo | Long-distance travel, varied terrains | Short-distance commutes, eco-conscious transport |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Traditional Gasoline Vehicles
Traditional gasoline vehicles offer a high-speed range and versatility, making them suitable for long-distance travel and varied terrains. They are readily available and familiar to most users, with a vast support network for maintenance and fuel. However, they come with higher fuel costs, environmental concerns, and require regular maintenance, which can add to the total cost of ownership. For B2B buyers in regions with limited electric infrastructure, gasoline vehicles may remain a more practical choice despite the growing push for sustainability.
Bicycles
Bicycles represent an environmentally friendly alternative, especially for short-distance commuting. With minimal operational costs, bicycles require no fuel and have very low maintenance needs. They offer flexibility in terms of parking and can navigate congested urban areas effectively. However, their speed and capacity for cargo are limited compared to electric vehicles. B2B buyers focusing on sustainability and health benefits may find bicycles an appealing option, particularly in urban settings where bike lanes are available.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When selecting the appropriate transportation solution, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including operational requirements, budget constraints, and sustainability goals. Small electric vehicles excel in urban settings where short trips and reduced emissions are prioritized. In contrast, traditional gasoline vehicles may be necessary for longer distances and varied terrains, while bicycles can serve as an economical and eco-friendly choice for short commutes. By evaluating these aspects in relation to their specific needs, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational objectives and corporate responsibility initiatives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for small electric vehicle
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Small Electric Vehicles?
When considering small electric vehicles (EVs), several technical specifications are crucial for B2B buyers. Understanding these properties can significantly influence purchasing decisions and operational efficiency.
1. Battery Capacity and Type
Battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), indicates the energy storage capability of an electric vehicle. Common battery types include Lead-Acid, AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat), and Lithium-Ion. For instance, Lithium-Ion batteries are preferred for their higher energy density and longer life cycle, which can reduce operational costs over time. In a B2B context, a higher capacity allows for extended range and reduced downtime, critical for logistics and transportation businesses.
2. Range
The range of an electric vehicle refers to the distance it can travel on a single charge, typically measured in miles. For example, models like the GEM e2 boast a range of up to 113 miles. This is particularly important for businesses operating in urban environments where frequent short trips are common. A longer range minimizes the need for frequent charging, enhancing productivity.
3. Payload Capacity
Payload capacity indicates the maximum weight the vehicle can safely carry, including passengers and cargo. For instance, a small electric vehicle may have a payload capacity of around 800 lbs. This metric is vital for businesses that require transport of goods or personnel, as it directly affects operational efficiency and compliance with local regulations.
4. Top Speed and Classification
Top speed is crucial for determining the vehicle’s suitability for various applications. Many small electric vehicles are classified as Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs), with a maximum speed of 25 mph. This classification impacts where the vehicle can legally operate, making it essential for buyers to understand regional regulations to avoid legal complications.
5. Charging Options
Charging options include the types of charging stations compatible with the vehicle, such as Level 1 (standard outlets), Level 2 (home or public charging stations), and DC Fast Charging. Understanding these options helps businesses plan for infrastructure needs and operational logistics, especially in regions where charging availability may vary.
6. Safety Features
Safety specifications, such as the presence of three-point seat belts, back-up cameras, and advanced braking systems, are critical in ensuring the safety of passengers and cargo. These features not only comply with legal standards but also enhance the vehicle’s reliability and reputation, which can be crucial for businesses focused on safety.
What Common Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know?
Navigating the small electric vehicle market involves familiarizing oneself with industry terminology that can impact purchasing and operational strategies.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can provide insight into product quality and warranty options, crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for budget planning and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses avoid overstock or stockouts, optimizing supply chain efficiency.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specified products. For B2B buyers, issuing RFQs can facilitate competitive pricing and better negotiation terms, ensuring that procurement processes are cost-effective.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps businesses understand shipping costs, risk allocation, and delivery obligations, which is essential for smooth cross-border transactions.
5. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with owning a vehicle over its entire lifecycle, including purchase price, maintenance, and operating costs. Understanding TCO is crucial for businesses to evaluate the long-term financial implications of their electric vehicle investments.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals in the evolving small electric vehicle market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the small electric vehicle Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Small Electric Vehicle Market for International B2B Buyers?
The small electric vehicle (SEV) market is experiencing a significant transformation driven by a convergence of technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifting consumer preferences. Globally, the push for sustainable transportation solutions is accelerating as countries implement stricter emissions regulations and governments provide incentives for electric vehicle (EV) adoption. In regions like Europe, especially Germany, the demand for small electric vehicles is bolstered by aggressive climate goals aimed at reducing carbon footprints. Similarly, in the Middle East and Africa, the increasing urbanization and the need for efficient transportation systems are creating opportunities for SEV deployment.
Emerging B2B tech trends include the integration of smart technologies such as IoT and AI, which enhance vehicle connectivity and operational efficiency. For instance, fleet management systems utilizing data analytics can optimize route planning and reduce operational costs. Furthermore, the rise of battery technology, particularly in energy density and charging speed, is enabling longer ranges and shorter charging times, making SEVs more appealing for commercial use. International buyers must also be aware of the growing trend of customization, allowing businesses to tailor vehicles to specific operational needs, from passenger transport to last-mile delivery.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing the Small Electric Vehicle Market?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the small electric vehicle sector, with a strong emphasis on minimizing environmental impact throughout the supply chain. For international B2B buyers, sourcing vehicles with a focus on ethical practices is essential. This includes selecting manufacturers that prioritize sustainable materials, such as recycled plastics and low-impact manufacturing processes. Additionally, the use of green certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, is becoming increasingly important for verifying the sustainability claims of suppliers.
Ethical sourcing is not only about environmental impact but also encompasses social responsibility. Buyers should consider the labor practices of their suppliers, ensuring fair wages and safe working conditions for workers involved in the production of components and vehicles. By choosing partners who adhere to ethical standards, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and align with the growing consumer demand for responsible products. This trend is particularly relevant in regions like South America and Africa, where ethical sourcing can significantly impact local communities.
What Is the Historical Context of the Small Electric Vehicle Market?
The evolution of the small electric vehicle market can be traced back to the late 19th century when electric vehicles were among the first types of automobiles. However, the market faced significant challenges with the advent of gasoline-powered vehicles, which offered greater range and convenience. It wasn’t until the late 20th century, with rising fuel prices and growing environmental concerns, that the electric vehicle market began to regain traction.
In recent years, technological advancements, particularly in battery technology and charging infrastructure, have catalyzed a resurgence in interest towards small electric vehicles. Today, SEVs are seen as viable solutions for urban mobility, catering to the needs of businesses looking for efficient, eco-friendly transportation options. This historical context is essential for B2B buyers to understand the market’s maturation and the ongoing innovations that continue to shape its future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of small electric vehicle
-
How do I evaluate the reliability of a supplier for small electric vehicles?
When sourcing small electric vehicles, it’s crucial to vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in the industry, positive customer reviews, and certifications that demonstrate compliance with international safety and environmental standards. Request samples or visit production facilities if possible. Additionally, check for their ability to provide after-sales support and warranty options. Engaging in discussions with existing clients can also provide insights into their reliability and service quality. -
What are the key features to consider when selecting a small electric vehicle for business use?
When choosing a small electric vehicle for commercial applications, consider factors like range, charging options, payload capacity, and safety features. Evaluate the vehicle’s intended use—be it local deliveries, passenger transport, or utility services. Look for models with customizable features to meet specific operational needs, such as storage solutions or enhanced safety systems. Additionally, assess the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and energy costs, to ensure it aligns with your budget and operational goals. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for small electric vehicles?
Minimum order quantities for small electric vehicles can vary significantly by manufacturer and model. Generally, MOQs range from 5 to 50 units for bulk orders, depending on the supplier’s production capabilities and the specific vehicle configurations. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements directly with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you anticipate ongoing needs or wish to establish a long-term partnership. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of small electric vehicles?
Payment terms for small electric vehicles often include options like full upfront payment, a deposit with the balance upon delivery, or installment payments over a specified period. Suppliers may also offer financing options or leasing agreements, particularly for larger orders. Always clarify terms in writing and ensure they align with your cash flow requirements and financial capabilities before finalizing the agreement. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for small electric vehicles purchased internationally?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing small electric vehicles from international suppliers, request detailed quality control processes and certifications that meet your regional standards. Conduct inspections during production and before shipping. Collaborating with third-party inspection services can further mitigate risks by providing unbiased assessments of the vehicles. Establish clear quality benchmarks in your contract to hold suppliers accountable for any discrepancies. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing small electric vehicles?
When importing small electric vehicles, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and tariffs. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger shipments. Ensure your supplier provides necessary documentation, including bills of lading and customs declarations. Familiarize yourself with local import laws and engage a customs broker to navigate the process smoothly, minimizing delays and additional costs. -
Are there tax incentives or subsidies available for purchasing electric vehicles in my region?
Many countries offer tax incentives or subsidies to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles. These may include reduced registration fees, tax credits, or grants for businesses investing in electric mobility. Research local and regional programs specific to your area, as they can significantly reduce the overall cost of procurement. Engaging with local government agencies or industry associations can provide valuable insights into available incentives. -
What customization options are available for small electric vehicles?
Customization options for small electric vehicles can vary by manufacturer but often include choices in battery capacity, color, interior features, and additional technology integrations. Some suppliers offer bespoke solutions to cater to specific business needs, such as enhanced cargo space or specialized seating arrangements. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available configurations, ensuring the final product meets your operational and branding needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Small Electric Vehicle Manufacturers & Suppliers List
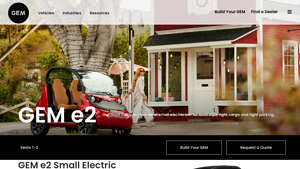
1. GEM – e2 Compact Electric Car
Domain: gemcar.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: GEM e2 is a compact two-seater small electric car designed for local trips and light cargo. Key specifications include:
– Seating Capacity: 1-2 passengers
– Range: Up to 113 miles between charges
– Dimensions: Length 103 in (262 cm), Width 55.5 in (141 cm), Height 73 in (186 cm)
– Turning Radius: 125 in (317.5 cm)
– Wheelbase: 69 in (175 cm)
– Front Suspension: MacPherson Strut with 5.6 in (…
2. Car Magazine – Best Small Electric Cars 2025
Domain: carmagazine.co.uk
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Best small electric cars 2025: 1. Renault 5 E-Tech – Best all-round small electric car. Pros: Style icon, great interior, low pricing. Cons: Limited real-world range, tight rear-seat space. Battery options: 40kWh (194 miles WLTP) and 52kWh (255 miles WLTP). Starting price: £22,995. 2. Fiat Grande Panda – Best for design and practicality. Pros: Stylish, practical, comfortable. Cons: Limited rear sp…
3. Fiat – 2024 500e Electric Vehicle
Domain: fiatusa.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: The 2024 Fiat 500e is an all-electric 2-door vehicle featuring:
– $1,500 Retail Bonus Cash Allowance towards purchase
– 100% electric with a range of up to 162 miles in city driving
– DC fast charging capability to charge up to 40 miles in 5 minutes
– Assisted Driving Level 2 Autonomy
– 1.1 billion miles of testing completed
– Available in four trims: Inspired By Music, Inspired By Beauty, I…
4. Volvo – EX30 Electric SUV
Domain: volvocars.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: {“model”:”Volvo EX30″,”type”:”Small fully electric SUV”,”powertrain”:”Twin Motor Performance”,”battery_capacity”:”69 kWh”,”electric_range”:”Up to 253 miles (EPA)”,”0_to_60″:”3.4 seconds”,”max_engine_power”:”422 hp”,”cargo_capacity”:”12.4 cu. ft. (up to 27.8 cu. ft. with rear seats folded)”,”maximum_towing_capacity”:”2000 lbs”,”charging_duration”:”10-80% in 26.5 minutes (DC 200kW)”,”features”:”One …
5. TELO – All-Electric Mini Truck
Domain: telotrucks.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: {“model”:”TELO MT1″,”type”:”All-Electric Mini Truck”,”dimensions”:{“length”:”152 in”,”width”:”73 in”,”height”:”67 in”},”bed_size”:{“length”:”60-96 in”,”width”:”56 in”,”depth”:”18 in”},”seating_capacity”:{“options”:[2,5,8]},”performance”:{“acceleration_0_60″:”6.0 s”,”power”:”300 hp”,”payload_capacity”:”2000 lbs”,”towing_capacity”:”6600 lbs”},”battery”:{“standard_range”:”260 mi”,”long_range”:”350 mi…
6. Hyundai – 2025 Ioniq 6
Domain: cars.usnews.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {“best_electric_cars”: [{“rank”: 1, “model”: “2025 Hyundai Ioniq 6”, “score”: 8.9, “msrp”: “$37,850 – $54,600”, “mpge”: “111-151 City / 94-120 Hwy”}, {“rank”: 2, “model”: “2025 Dodge Charger Daytona”, “score”: 8.8, “msrp”: “$57,995 – $64,995”, “mpge”: “N/A”}, {“rank”: 3, “model”: “2025 Nissan Leaf”, “score”: 8.0, “msrp”: “$28,140 – $36,190”, “mpge”: “121-123 City / 98-99 Hwy”}, {“rank”: 4, “model”…
7. Cars.com – Electric Vehicle Models
Domain: cars.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: [{“model”:”Nissan Leaf”,”starting_price”:”$29,280″,”epa_estimated_range”:”149-212 miles”},{“model”:”Fiat 500e”,”starting_price”:”$32,495″,”epa_estimated_range”:”141-149 miles”},{“model”:”Hyundai Kona Electric”,”starting_price”:”$34,470″,”epa_estimated_range”:”200-261 miles”},{“model”:”Chevrolet Equinox EV”,”starting_price”:”$34,995″,”epa_estimated_range”:”307-319 miles”},{“model”:”Toyota bZ4X”,”st…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for small electric vehicle
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Small Electric Vehicles?
As the market for small electric vehicles (EVs) expands globally, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing becomes essential for B2B buyers. Understanding the versatility and cost-effectiveness of vehicles like the GEM e2 and MINI electric models can significantly enhance operational efficiency. These compact EVs not only cater to local transportation needs but also offer sustainable solutions with low operational costs, making them ideal for businesses focused on reducing their carbon footprint.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business Operations?
Engaging in strategic sourcing allows businesses to leverage competitive pricing, innovative technology, and tailored solutions that align with their specific requirements. By focusing on reliable suppliers and understanding the diverse range of features and configurations available, companies can maximize their investment in small electric vehicles. This proactive approach ensures that buyers are well-equipped to meet both current demands and future challenges in an evolving market.
What’s Next for International B2B Buyers?
Looking ahead, the demand for small electric vehicles is poised to grow, driven by increasing environmental regulations and consumer preferences for sustainable options. B2B buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships with manufacturers and suppliers who can provide not only vehicles but also support in charging infrastructure and maintenance. Embrace the opportunity to innovate your fleet and invest in the future of transportation today.