Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for camion de transport daliments
In today’s interconnected global economy, sourcing the right camion de transport d’aliments (food transport trucks) is a critical challenge for businesses involved in the agricultural and food supply chains. With diverse applications ranging from transporting animal feed to fresh produce, selecting the appropriate vehicle can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This comprehensive guide is designed to equip international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, with the insights necessary to navigate this complex market.
Throughout this guide, we will explore various types of transport trucks, their specific applications, and the importance of compliance with hygiene standards. We will also delve into best practices for vetting suppliers, ensuring that your procurement process aligns with industry standards while optimizing costs. With actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide empowers you to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance your logistics operations and meet the demands of your business.
Whether you are a buyer in Nigeria seeking reliable transport solutions for livestock feed or a distributor in Germany looking to expand your fleet for fresh produce delivery, understanding the nuances of the camion de transport d’aliments market will enable you to achieve a competitive edge. Let’s embark on this journey to streamline your sourcing process and enhance your supply chain’s efficiency.
Understanding camion de transport daliments Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bulk Feed Truck | High-capacity, often equipped with pneumatic unloading | Transporting bulk animal feed from factories to farms | Pros: Efficient for large volumes; Cons: May require specialized loading/unloading facilities. |
| Tautliner Truck | Flexible tarpaulin cover for easy loading/unloading | Transporting packaged food products | Pros: Versatile; protects loads; Cons: Less secure than enclosed options. |
| Refrigerated Van | Temperature-controlled for perishable goods | Distribution of dairy, meat, and fresh produce | Pros: Maintains product quality; Cons: Higher operational costs. |
| Specialized Tanker | Designed for liquid food products, often compartmentalized | Transporting liquids like oils or liquid feed | Pros: Reduces contamination risk; Cons: Limited to liquid products. |
| Palletized Cargo Truck | Equipped for transporting goods on pallets | General food distribution, including retail and wholesale | Pros: Standardized loading; Cons: Less efficient for bulk transport. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Bulk Feed Trucks?
Bulk feed trucks are designed for the high-capacity transportation of animal feed, typically featuring pneumatic unloading systems. These trucks are ideal for agricultural businesses that require large quantities of feed delivered from production facilities to farms. When considering a bulk feed truck, B2B buyers should evaluate the truck’s capacity, compatibility with loading docks, and the efficiency of its unloading system to maximize operational productivity.
How Do Tautliner Trucks Serve the Food Transport Industry?
Tautliner trucks are characterized by their flexible tarpaulin covering, allowing for easy access and loading from the sides and top. This type of truck is particularly suitable for transporting packaged food products, as it provides protection against environmental factors while allowing for quick loading and unloading. Buyers should consider the truck’s structural integrity, load capacity, and the nature of the products being transported when selecting a tautliner.
Why are Refrigerated Vans Essential for Perishable Goods?
Refrigerated vans are equipped with temperature control systems that are crucial for transporting perishable goods such as dairy, meat, and fresh produce. These vehicles ensure that products remain at safe temperatures throughout the supply chain, reducing spoilage and maintaining quality. Buyers must assess the refrigeration unit’s efficiency, the vehicle’s size, and compliance with food safety regulations to ensure optimal performance.
What are the Benefits of Using Specialized Tankers for Liquid Food Products?
Specialized tankers are designed to transport liquid food products, often featuring compartmentalized sections to prevent cross-contamination. These tankers are essential for businesses that deal with oils or liquid feeds, as they ensure safe and compliant transportation. When purchasing a specialized tanker, B2B buyers should consider the tanker’s material, capacity, and cleaning protocols to ensure they meet industry standards.
How Do Palletized Cargo Trucks Facilitate General Food Distribution?
Palletized cargo trucks are designed for transporting goods on pallets, making them versatile for various food distribution needs. These trucks are particularly effective for retail and wholesale operations, as they allow for standardized loading and unloading processes. Buyers should focus on the truck’s payload capacity, pallet configuration compatibility, and overall durability to ensure efficient logistics management.
Key Industrial Applications of camion de transport daliments
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of camion de transport daliments | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Livestock | Transport of bulk animal feed from production facilities to farms | Ensures timely delivery of essential feed, reducing downtime and improving livestock productivity | Compliance with local food safety regulations, vehicle capacity, and type of feed being transported |
| Food Processing | Delivery of raw ingredients like grains and oils to processing plants | Streamlines supply chain, enhances production efficiency, and ensures quality control of ingredients | Need for temperature control, cleanliness standards, and reliable scheduling |
| Retail & Distribution | Distribution of packaged food products to retail outlets | Increases market reach and ensures product availability, enhancing customer satisfaction | Vehicle adaptability for various load types, route optimization for cost efficiency |
| Pharmaceuticals & Nutraceuticals | Transport of specialized nutritional products to healthcare facilities | Maintains product integrity and efficacy, crucial for patient care and compliance with health regulations | Specialized handling requirements and adherence to strict hygiene standards |
| Export & Import | International transport of food products across borders | Expands market opportunities and facilitates trade, crucial for growing businesses in emerging markets | Understanding of customs regulations, documentation, and temperature control during transit |
How Is ‘Camion de transport daliments’ Used in Agriculture & Livestock?
In the agriculture and livestock sector, the camion de transport daliments is pivotal for transporting bulk animal feed from production facilities directly to farms. This ensures that livestock receive timely and adequate nutrition, which is essential for maintaining health and productivity. Buyers in this sector must consider the vehicle’s compliance with local food safety regulations and its capacity to handle various types of feed. Efficient transport minimizes downtime on farms, allowing farmers to focus on productivity.
What Role Does It Play in Food Processing?
For food processing industries, these trucks are crucial in delivering raw ingredients such as grains, oils, and other materials to processing plants. The reliability and efficiency of these vehicles streamline the supply chain, significantly enhancing production capabilities. Buyers must ensure that their chosen trucks meet cleanliness standards and can accommodate temperature control if necessary. A consistent supply of quality ingredients is vital for maintaining product standards and meeting consumer demands.
How Does It Benefit Retail & Distribution?
In the retail and distribution sector, camion de transport daliments are used to distribute packaged food products to various retail outlets. This application increases market reach and ensures that products are readily available to consumers, enhancing overall customer satisfaction. Businesses need to consider the adaptability of the vehicles for different load types and the optimization of delivery routes to reduce costs and improve service efficiency.
What Is Its Importance for Pharmaceuticals & Nutraceuticals?
The transport of specialized nutritional products, including pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals, relies heavily on camion de transport daliments to maintain product integrity during transit. Ensuring that these products reach healthcare facilities without compromising quality is crucial for compliance with health regulations. Buyers in this sector must be aware of specialized handling requirements and the need for strict hygiene standards to safeguard product efficacy and safety.
How Does It Facilitate Export & Import?
In the context of export and import, camion de transport daliments enable the international transport of food products across borders, expanding market opportunities for businesses. This application is particularly important for companies in emerging markets looking to grow their presence globally. Buyers must navigate customs regulations, ensure proper documentation, and maintain temperature control during transit to protect product quality and comply with international standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘camion de transport daliments’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Supply Chain Management for Animal Feed Transportation
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face significant challenges in managing their supply chains, particularly when it comes to transporting animal feed. Delays in delivery can lead to stock shortages, impacting livestock health and productivity. This issue is exacerbated when suppliers do not communicate effectively about shipment schedules or changes, leaving buyers scrambling to adjust their operations. For businesses in regions like Africa and South America, where logistics can be particularly complex, these interruptions can have severe financial repercussions.
The Solution: To overcome these supply chain disruptions, buyers should prioritize working with logistics partners that offer integrated supply chain solutions. This includes real-time tracking systems and transparent communication channels. When sourcing a ‘camion de transport d’aliments’, buyers should ensure that the vehicles are equipped with GPS tracking technology, allowing for accurate monitoring of delivery times. Establishing a dedicated point of contact within the logistics provider can also enhance communication, ensuring that any potential delays are addressed proactively. Furthermore, collaborating with suppliers to create a more predictable delivery schedule can help mitigate the risk of stock shortages.
Scenario 2: Compliance with Hygiene and Safety Regulations in Food Transport
The Problem: Ensuring compliance with hygiene and safety regulations is a critical concern for B2B buyers in the food transport sector. Failure to adhere to standards can lead to contamination, resulting in product recalls and damage to brand reputation. This is particularly relevant for buyers transporting animal feed, which must meet stringent health regulations to protect livestock and ultimately, the food chain. Buyers often struggle to verify that their transportation partners are adhering to these regulations consistently.
The Solution: Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence when selecting a transportation partner. This involves requesting documentation that demonstrates compliance with relevant hygiene standards, such as Qualimat-Transport® certifications. Additionally, buyers should consider investing in transportation vehicles that are specifically designed for food safety, such as those with built-in cleaning systems and temperature control features. Regular audits of the logistics provider’s operations can help ensure ongoing compliance. Establishing a checklist of hygiene protocols to be followed during loading, transport, and unloading will also reinforce safety measures.
Scenario 3: Cost Management and Efficiency in Transport Operations
The Problem: Cost management is a significant pain point for B2B buyers involved in food transportation. Rising fuel prices, maintenance costs, and unforeseen logistics expenses can quickly erode profit margins. Buyers often find themselves in a reactive position, struggling to manage these costs without compromising service quality. This is particularly challenging in markets with fluctuating prices and demand, such as those in the Middle East and Europe.
The Solution: To enhance cost efficiency, buyers should engage in strategic planning and route optimization. This involves utilizing advanced logistics software that analyzes delivery routes, identifies potential bottlenecks, and suggests more efficient paths. When procuring ‘camion de transport d’aliments’, buyers should opt for vehicles that are fuel-efficient and have lower maintenance costs. Additionally, forming long-term partnerships with transportation companies can lead to negotiated rates and bulk discounts. Buyers should also analyze their delivery schedules to align with demand cycles, ensuring that transportation resources are utilized effectively without incurring unnecessary expenses. Regular performance reviews of transport operations can also highlight areas for improvement and cost savings.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for camion de transport daliments
What Are the Key Materials for Camion de Transport D’aliments?
When selecting materials for a camion de transport d’aliments, it is crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of food transport trucks, focusing on their performance characteristics, costs, and compliance with international standards.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°F (427°C) and can handle pressures of up to 300 psi, making it suitable for various food transport applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it can withstand the rigors of transport without degrading. However, its high cost and manufacturing complexity can be a drawback, especially for budget-conscious buyers. Additionally, it may require specialized welding techniques for repairs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of food products, including liquids and solids, without altering their quality. Its non-reactive nature ensures that food safety is maintained throughout the transport process.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East must ensure compliance with food safety standards such as EU regulations and ISO certifications. Stainless steel grades like 304 and 316 are commonly preferred in these markets.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has a good strength-to-weight ratio, making it an ideal choice for transport vehicles. It is resistant to corrosion and can operate effectively within a temperature range of -40°F to 300°F (-40°C to 149°C).
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can lead to better fuel efficiency. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and may not withstand heavy impacts as well. Additionally, aluminum can be more expensive than other materials when considering long-term maintenance.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for transporting dry food products and certain liquids, but care must be taken with acidic foods, which can corrode the material over time.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding aluminum use in food transport, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where standards may vary. Compliance with ASTM standards is often necessary.
3. Polypropylene (PP)
Key Properties: Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer known for its chemical resistance and lightweight nature. It can withstand temperatures up to 220°F (104°C) and is highly resistant to moisture and various chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The cost-effectiveness of polypropylene makes it an attractive option for many buyers. However, its lower strength compared to metals can be a limitation, particularly in heavy-duty applications. It may also degrade over time when exposed to UV light.
Impact on Application: Polypropylene is ideal for transporting dry food products and can be used for interior linings in food transport vehicles. However, it is not suitable for high-temperature applications or for transporting liquids that require strict temperature control.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the polypropylene used complies with food safety regulations, such as those set by the FDA or local equivalents. In Europe, compliance with REACH regulations is essential.
4. Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP)
Key Properties: FRP combines fiberglass with resin, offering high strength and excellent insulation properties. It can handle temperatures up to 250°F (121°C) and is resistant to corrosion and chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of FRP contributes to improved fuel efficiency, while its durability makes it suitable for various food products. However, the initial manufacturing cost can be high, and repairs may be complex.
Impact on Application: FRP is particularly effective for transporting temperature-sensitive products, as its insulation properties help maintain stable temperatures. It is also non-reactive, ensuring food safety.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and local food safety regulations is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of repair services in their region, as FRP may require specialized skills for maintenance.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for camion de transport daliments | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Transporting a variety of food products | High durability and corrosion resistance | High cost and complex repairs | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight transport of dry food products | Low weight leading to fuel efficiency | Less durable than steel | Medium |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Interior linings for dry food transport | Cost-effective and lightweight | Lower strength and UV degradation | Low |
| Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) | Insulated transport of temperature-sensitive products | Excellent insulation properties | High initial cost and complex repairs | Medium |
This guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers in selecting the right materials for their food transport trucks, ensuring compliance with international standards and optimizing performance for their specific needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for camion de transport daliments
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Camion de Transport Daliments?
The manufacturing process for a camion de transport daliments involves several critical stages, each contributing to the vehicle’s overall performance and compliance with food safety standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The first step is the selection and preparation of materials. High-grade steel and aluminum are commonly used due to their strength and lightweight properties, which are crucial for fuel efficiency and load capacity. Manufacturers often source materials from certified suppliers to ensure they meet international quality standards. The materials undergo pre-treatment processes such as cleaning and coating to prevent corrosion, especially since these vehicles are frequently exposed to moisture and various weather conditions.
Forming
In the forming stage, raw materials are shaped into components using techniques such as stamping, bending, and cutting. Advanced machinery, including CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines, is typically employed to ensure precision in component dimensions. For instance, the tank or cargo area of the camion is formed to accommodate bulk food products, with specific designs to facilitate easy loading and unloading. The forming process is critical, as any discrepancies can lead to inefficiencies in transporting food products.
Assembly
The assembly stage involves the integration of various components, including the chassis, cargo area, and specialized equipment like pneumatic systems for bulk unloading. This stage requires skilled labor to ensure that all parts fit together seamlessly and function as intended. Quality assurance is integrated into this stage, with regular inspections to verify that assembly aligns with technical specifications.
Finishing
Finishing processes include painting, coating, and applying decals. These not only enhance the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal but also provide an additional layer of protection against environmental factors. The finishing stage is also an opportunity to apply industry-standard hygiene coatings, crucial for vehicles transporting food products.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) in the manufacturing of camion de transport daliments is paramount to ensure food safety and compliance with international standards. The QA process typically adheres to various international and industry-specific standards.
What International Standards Govern the Manufacturing of Food Transport Trucks?
ISO 9001 is a key international standard for quality management systems that ensures organizations consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. For the food transport sector, compliance with regulations such as CE marking in Europe and API standards is also critical. These standards ensure that the vehicles are safe for transporting food products and are built to withstand specific operational conditions.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure compliance with standards. These include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality criteria before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, periodic checks are conducted to ensure that all components are being produced to the correct specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, a comprehensive inspection is conducted to verify that the finished product meets all quality and safety standards before delivery to clients.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
Common testing methods include:
- Visual Inspections: Checking for any visible defects in materials or assembly.
- Functional Testing: Ensuring that all systems, such as hydraulic lifts or pneumatic unloaders, function correctly.
- Stress Testing: Subjecting the vehicle to operational stresses to ensure durability under load conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is crucial. Here are several strategies to ensure reliable supplier QC:
What Steps Should Be Taken to Conduct Supplier Audits?
- On-Site Audits: Buyers can arrange for on-site inspections to evaluate the manufacturing facility’s capabilities and compliance with quality standards.
- Request for Documentation: Suppliers should provide documentation that details their quality management systems, including certifications and inspection reports.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party organizations for independent audits can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices.
How Can Buyers Use Reports and Certifications to Assess Quality?
Buyers should look for detailed reports from the supplier’s QC processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC. Certifications from recognized bodies can also provide assurance of compliance with international standards. Understanding the nuances of these certifications can help buyers assess the credibility of their suppliers effectively.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
When engaging with international suppliers, buyers must be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries may have varying regulatory requirements regarding food safety and transport, which must be adhered to.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding the local manufacturing culture and practices can help buyers communicate more effectively with suppliers.
- Logistical Considerations: Transporting food products across borders may introduce additional quality assurance challenges, such as maintaining temperature control during transit.
By taking these considerations into account, B2B buyers can ensure they choose suppliers who not only meet their quality expectations but also align with international standards for food safety and transport. This thorough approach to understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with camion de transport daliments is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘camion de transport daliments’
This guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in the procurement of food transportation trucks, specifically ‘camion de transport d’aliments.’ It provides a structured checklist that outlines the essential steps to ensure a successful purchase, focusing on quality, compliance, and supplier reliability.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider the type of food products to be transported (e.g., bulk, refrigerated, or palletized), the required capacity, and specific vehicle features such as insulation or compartmentalization. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and avoid costly misalignments later.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers. Look for companies that specialize in food transport vehicles and have a proven track record in your region. Utilize online directories, industry associations, and trade shows to compile a list of potential vendors. This foundational work will set the stage for informed decision-making.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Certifications ensure that the suppliers comply with industry standards and regulations. Verify if the suppliers possess relevant certifications, such as ISO standards, and specific food safety certifications (e.g., HACCP). This step is crucial for mitigating risks associated with food safety and ensuring that the transport vehicles meet hygiene requirements.
Step 4: Request and Review Proposals
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, request detailed proposals. Each proposal should include pricing, delivery timelines, vehicle specifications, and warranty details. Analyze these proposals carefully, comparing not only costs but also the value offered in terms of service, support, and additional features.
Step 5: Conduct Site Visits or Virtual Tours
If feasible, arrange site visits to the suppliers’ facilities. This allows you to assess their operational capabilities, quality control measures, and overall professionalism. If in-person visits are not possible, request virtual tours or video calls to gain insight into their processes. Observing their operations can provide valuable information that goes beyond written proposals.
Step 6: Verify References and Previous Work
Before making a final decision, contact references provided by the suppliers. Speak to other businesses that have procured similar vehicles and inquire about their experiences. Ask about the reliability of the trucks, the responsiveness of the supplier, and any issues that arose during the procurement process. This step helps ensure you choose a trustworthy supplier.
Step 7: Finalize the Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, ensure that all terms are clearly outlined in a purchase agreement. This should include payment terms, delivery schedules, warranty information, and any service agreements. Having a well-defined contract protects your interests and establishes clear expectations for both parties.
Following this checklist will streamline the process of sourcing ‘camion de transport d’aliments,’ ensuring that you secure a vehicle that meets your operational needs while aligning with industry standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for camion de transport daliments Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Sourcing ‘Camion de Transport Daliments’?
When sourcing ‘camion de transport daliments’, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary components influencing costs include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts the overall cost of the truck. High-quality steel and specialized components for food transport (like insulated containers) can increase initial expenses but may enhance durability and compliance with hygiene standards.
-
Labor: Skilled labor for manufacturing and assembly is a significant cost driver. Regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, may see increased pricing compared to manufacturers in regions with lower wage structures.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs related to production, including utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility maintenance. Efficient production processes can help minimize these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific designs or functionalities can add to initial costs. Buyers should consider whether the investment in specialized tooling is justified by the anticipated volume of orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure compliance with international standards, especially for food transportation. Implementing strict QC measures may increase costs, but they are essential for maintaining product integrity and safety.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs are vital considerations. These costs can vary significantly depending on the location of the supplier and the final destination. Efficient logistics planning can mitigate some of these expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a profit margin to cover risks and ensure sustainability. Understanding the supplier’s pricing strategy can help buyers negotiate better.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of ‘Camion de Transport Daliments’?
Several factors influence the pricing of ‘camion de transport daliments’, including:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes usually lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, so buyers should assess their needs carefully.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized trucks that meet specific operational requirements may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential price increase.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The use of certified materials can increase costs but is often necessary to meet regulatory standards. Buyers should verify the certifications relevant to their region.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may command higher prices but can also offer better service and support.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery can significantly affect pricing. Understanding the implications of different Incoterms (like FOB, CIF) is essential for calculating the total landed cost.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating ‘Camion de Transport Daliments’ Prices?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing structures. Understanding their cost components can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Focus on Cost Efficiency: Evaluate not just the purchase price but the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), including maintenance, fuel efficiency, and operational longevity. A higher upfront cost may lead to lower overall costs in the long run.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: Different regions may have varying standards and practices. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of local regulations and market conditions that could impact pricing.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive quotes that break down costs. This transparency can aid in identifying areas for negotiation.
-
Consider Long-term Relationships: Establishing a long-term partnership with a supplier can lead to better pricing and service over time. Regular communication and feedback can enhance collaboration and mutual benefit.
By comprehensively understanding the cost structure, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing ‘camion de transport daliments’, ensuring they achieve both quality and cost-effectiveness.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing camion de transport daliments With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions for Food Transport
In the competitive landscape of food logistics, businesses often seek alternatives to traditional food transport trucks (camion de transport d’aliments). Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of different solutions can guide B2B buyers in selecting the most effective method for their operations. Below, we compare camion de transport d’aliments with two viable alternatives: rail transportation and refrigerated shipping containers.
| Comparison Aspect | Camion De Transport Daliments | Rail Transportation | Refrigerated Shipping Containers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High flexibility for short-haul transport; suitable for various terrains. | Excellent for bulk transport over long distances; consistent delivery schedules. | Ideal for maintaining temperature-sensitive products; versatile for international shipping. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; operational costs can vary based on fuel and maintenance. | Generally lower cost per ton-mile, but requires infrastructure investment. | Higher upfront costs, but reduced spoilage can offset expenses. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires less infrastructure and can be deployed quickly. | Limited by rail network availability; requires loading/unloading facilities. | Requires specialized containers and logistics management. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance necessary; high wear and tear from road conditions. | Lower maintenance costs; more durable over long distances. | Maintenance primarily focused on refrigeration units; generally reliable. |
| Best Use Case | Local deliveries, short-distance transport, and flexible routing. | Bulk transport of feed or grains over long distances, intercity deliveries. | International shipping of perishable goods, particularly seafood, dairy, and meats. |
Understanding the Pros and Cons of Each Alternative
Rail Transportation
Rail transportation is an efficient alternative, particularly for bulk food products over long distances. Its primary advantage lies in its cost-effectiveness for large shipments, as it can transport substantial quantities at a lower cost per ton-mile. However, the dependency on rail infrastructure can be a drawback, especially in regions with limited rail access. Additionally, while rail transport is reliable, the need for loading and unloading facilities can introduce delays.
Refrigerated Shipping Containers
Refrigerated shipping containers offer a specialized solution for temperature-sensitive products, ensuring that perishables maintain optimal conditions during transport. This method is particularly advantageous for international shipping, as it supports long transit times without compromising product quality. However, the initial investment in refrigerated containers can be significant, and logistics management must be carefully coordinated to minimize spoilage. Additionally, this method may not be as flexible for local deliveries compared to trucks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
When selecting the appropriate solution for food transport, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the nature of the products, distance, cost constraints, and logistical capabilities. For businesses focused on local distribution and flexibility, camion de transport d’aliments remains a strong contender. In contrast, those requiring bulk transport over long distances may find rail transportation more advantageous, while companies engaged in international trade of perishables may benefit from investing in refrigerated shipping containers. Ultimately, a thorough evaluation of operational needs will lead to the best choice for efficient and effective food transport.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for camion de transport daliments
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Food Transport Truck?
When considering a camion de transport d’aliments, understanding the technical properties is crucial for ensuring compliance with industry standards and optimizing operational efficiency. Here are some key specifications:
-
Material Grade
The materials used in the construction of food transport trucks, such as stainless steel or food-grade aluminum, are vital for hygiene and durability. Stainless steel is resistant to corrosion and easy to clean, which is essential for maintaining food safety standards. Choosing trucks made from high-grade materials minimizes contamination risks and prolongs the vehicle’s lifespan, which is a significant consideration for B2B buyers. -
Payload Capacity
This refers to the maximum weight a truck can carry, often expressed in kilograms or tons. For food transport, understanding payload capacity is critical as it directly affects operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Selecting a truck with the appropriate payload capacity ensures compliance with legal limits while maximizing delivery volumes, which is especially important for businesses in regions with strict transportation regulations. -
Temperature Control Systems
Many food products require specific temperature conditions to remain safe and viable. Trucks equipped with advanced temperature control systems, including refrigeration units, are essential for transporting perishable goods. This capability helps businesses maintain the quality of their products and adhere to food safety regulations, thereby protecting their reputation and minimizing waste. -
Hygiene Compliance Standards
Compliance with hygiene standards, such as Qualimat-Transport® in Europe, is non-negotiable in the food transport sector. Trucks must be designed and maintained to meet these standards, ensuring that they are cleaned and disinfected regularly. B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers can demonstrate adherence to these standards, as it impacts the safety and quality of food products. -
Versatility of Loading Options
The ability to accommodate various loading and unloading methods—such as bulk loading or palletized goods—is essential. Trucks that support multiple loading configurations can adapt to different operational needs, making them more valuable for companies with diverse product lines. This flexibility can lead to reduced loading times and improved logistics efficiency. -
Safety Features
Safety features, including anti-lock braking systems (ABS) and stability control, are critical for protecting both the vehicle and its cargo. For B2B buyers, investing in trucks with enhanced safety features can reduce the risk of accidents, thereby lowering insurance costs and enhancing the overall safety of the supply chain.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Food Transport Industry?
Understanding industry-specific jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the food transport sector. Here are some common trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of food transport trucks, knowing the OEM can help buyers ensure they are sourcing high-quality components that meet industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, understanding the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, as it affects the overall cost and volume of food transport trucks they can procure. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request price quotations for specific products or services. This process allows businesses to compare offers and negotiate better terms, ensuring they get the best value for their investment in food transport solutions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in shipping goods. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to understand their obligations regarding shipping costs, insurance, and liability during the transport of food products. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving it. In the food transport sector, shorter lead times can be critical to maintaining supply chain efficiency and ensuring that perishable goods reach their destinations promptly. -
Tare Weight
This is the weight of the truck itself without any cargo. Knowing the tare weight is important for calculating payload capacity and ensuring that loads remain within legal limits, which is especially pertinent in regions with strict regulations.
In summary, understanding both the technical specifications and trade terminology associated with camion de transport d’aliments is essential for B2B buyers. This knowledge enables informed decision-making, ensuring compliance with industry standards and optimizing logistics operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the camion de transport daliments Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Camion de Transport Aliments Sector?
The camion de transport aliments sector is experiencing significant growth driven by various global factors. The increasing demand for efficient and reliable food transportation is being propelled by the rise in e-commerce and the need for fast-paced supply chains, particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America. Additionally, technological advancements are reshaping the logistics landscape; innovations such as real-time tracking systems, route optimization software, and automated loading and unloading processes are becoming standard. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for partners who can provide these technological solutions to enhance operational efficiency.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for international buyers. The adoption of eco-friendly practices, including the use of fuel-efficient vehicles and the implementation of waste reduction strategies, is gaining traction. In Europe and the Middle East, regulatory frameworks are pushing companies to adopt greener practices, which can influence sourcing decisions. B2B buyers must stay abreast of these trends to ensure compliance and align with market expectations.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Decisions in the Camion de Transport Aliments Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are not just buzzwords; they are critical components influencing the camion de transport aliments sector. The environmental impact of transportation logistics is substantial, with transportation accounting for a significant portion of global greenhouse gas emissions. As a result, many companies are now prioritizing sustainable practices, including the use of low-emission vehicles and alternative fuels, to reduce their carbon footprint.
Incorporating ethical supply chains is equally important, as consumers and businesses alike are demanding transparency in sourcing. B2B buyers should seek suppliers with certifications that demonstrate commitment to sustainability, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or Fair Trade certification. By prioritizing suppliers who adhere to these standards, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing demand for ethically sourced products.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Camion de Transport Aliments Sector?
The evolution of the camion de transport aliments sector can be traced back to the early 20th century, when advancements in transportation technology began to transform how food was delivered. Initially, local farmers sold their products directly to consumers through short supply chains. However, as industrialization progressed, the demand for larger-scale food production and distribution grew. Innovations in refrigeration, pasteurization, and transportation logistics paved the way for the development of specialized vehicles for food transport.
By the 1920s, the introduction of motorized vehicles significantly enhanced the efficiency of food distribution, allowing for the transportation of perishable goods over longer distances. Today, the sector is characterized by a complex network of suppliers, logistics providers, and technology-driven solutions, making it vital for B2B buyers to understand its historical context to navigate current market dynamics effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of camion de transport daliments
-
1. How do I ensure the quality of food transport trucks before purchasing?
To ensure the quality of food transport trucks, request detailed specifications and certifications from potential suppliers, focusing on hygiene standards such as Qualimat-Transport®. Evaluate the supplier’s compliance with international food safety regulations and their maintenance practices for vehicles. Additionally, consider visiting the production facility to inspect the manufacturing process and materials used. Engaging in third-party inspections or audits can further provide assurance of the quality and reliability of the trucks. -
2. What features should I look for in a food transport truck?
The best food transport truck should have specialized features such as temperature control, proper insulation, and compliance with hygiene regulations. Look for trucks equipped with compartmentalized storage for transporting different types of food simultaneously. Consider the vehicle’s load capacity, ease of loading/unloading, and the presence of cleaning systems to maintain hygiene. Additionally, assess the durability of the materials used in construction, which should withstand the rigors of frequent use and exposure to various food products. -
3. What are the common payment terms for purchasing food transport trucks?
Payment terms for purchasing food transport trucks can vary widely among suppliers. Common arrangements include upfront payment, a deposit followed by final payment upon delivery, or installment payments over a specified period. Always negotiate terms that align with your cash flow capabilities. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods that offer buyer protection. Ensure that the terms are clearly defined in the contract to avoid any disputes later. -
4. How do I verify the credibility of a food transport truck supplier?
To verify the credibility of a supplier, check for industry certifications and customer testimonials. Research their business history, including how long they have been operating and their reputation in the market. Utilize platforms like LinkedIn or industry-specific forums to connect with other buyers for firsthand feedback. Request references from previous clients and follow up with them to discuss their experiences. A reliable supplier should be transparent about their operations and willing to provide documentation upon request. -
5. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) when sourcing food transport trucks?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for food transport trucks can vary by manufacturer and the type of customization required. Some suppliers may have a MOQ of one unit, especially for standard models, while others may require larger orders for customized vehicles. It’s crucial to discuss your needs directly with the supplier to understand their MOQ policy. If you are looking for a smaller order, consider negotiating or exploring suppliers who specialize in smaller-scale operations. -
6. How do international shipping logistics work for food transport trucks?
International shipping logistics for food transport trucks involve several steps, including selecting a reliable freight forwarder, arranging for transportation, and ensuring compliance with customs regulations. It’s essential to prepare all necessary documentation, such as bills of lading, commercial invoices, and customs declarations. Coordinate with your supplier to determine the most efficient shipping method—whether by sea, air, or land. Consider factors like transit time, cost, and the need for specialized handling to maintain vehicle integrity during transport. -
7. What are the common customization options for food transport trucks?
Customization options for food transport trucks can include temperature control systems, specialized storage compartments, and branding elements such as paint and decals. Depending on your specific requirements, you may also consider modifications to the truck’s suspension for better load handling or enhancements for easier loading/unloading. Engage with the supplier early in the process to discuss available options and ensure that the modifications comply with relevant regulations and standards in your region. -
8. How can I ensure compliance with international food safety standards during transport?
To ensure compliance with international food safety standards during transport, select trucks that meet or exceed hygiene regulations such as the FDA or EU standards. Implement strict cleaning protocols and ensure that the transportation process adheres to these guidelines. Regular training for drivers and staff on food safety practices can further enhance compliance. Additionally, maintain detailed records of each transport, including temperature logs and cleaning schedules, to provide documentation in case of audits or inspections.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
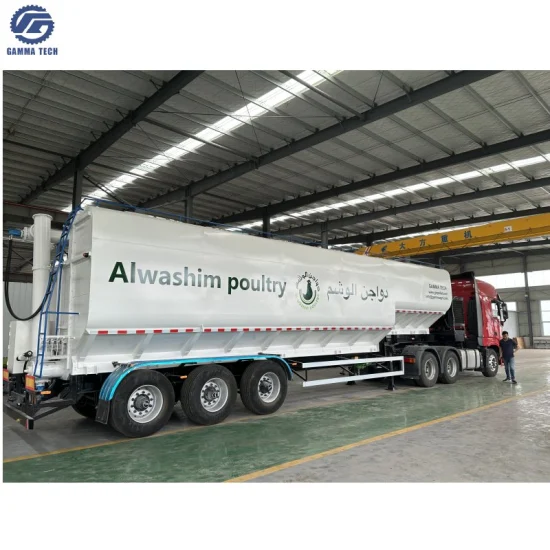
Top 8 Camion De Transport Daliments Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Jet Transporte – Transport d’Aliments et Logistique Efficace
Domain: jetransporte.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Transport d’aliments pour animaux d’élevage, transport de vrac ou de palettes, optimisation de la planification et des coûts, solutions rapides et efficaces, statistiques personnalisées sur chaque livraison, interlocuteur dédié pour suivi personnalisé, conformité aux normes d’hygiène Qualimat-Transport®, protocoles stricts de nettoyage et désinfection, systèmes de désinfection embarqués, flotte de…
2. Recolte – Guide d’Aide à la Décision sur le Transport Alimentaire
Domain: recolte.ca
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Le Guide d’aide à la décision sur les véhicules de transport alimentaire est conçu pour aider les organismes en sécurité alimentaire et les entreprises d’économie sociale à naviguer les défis logistiques et financiers liés au transport d’aliments. Il se compose de deux chapitres : 1) Estimation des coûts de transport, qui aborde des questions clés comme le besoin d’un camion réfrigéré et la compar…
3. CLW – 3 Axle 63000 Liters Bulk Feed Truck
Domain: clw-camion.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “3 Axle 63000 Liters Bulk Feed Transportation Truck”, “capacity”: “63cbm/63000Litres”, “dimensions”: “13750x2550x4000mm”, “wheelbase”: “7080+1310+1310 mm”, “GVW”: “40000 kgs”, “payload_weight”: “27290 kgs”, “empty_weight”: “12710 kgs”, “tire_quantity”: “12 pieces”, “tire_specifications”: “11R22.5 14PR”, “axle”: “Fuwa 3 * 13 tons axle, 16 tons brake pad”, “suspension”: “Fuwa 16 ton…
4. STEF – Solutions de Transport Frigorifique
Domain: stef.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: STEF propose des solutions de transport frigorifique adaptées aux produits alimentaires, incluant des options pour des températures de -25°C à +18°C. Les services incluent la collecte et distribution en 24 à 48 heures, du colis au camion complet, avec des livraisons partout en France. Les offres spécifiques comprennent : 1. DAILYFOOD pour les détaillants avec trois créneaux horaires de livraison ;…
5. Cargo County – Transport de Produits Périssables
Domain: cargocounty.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Entreprise de transport d’aliments et légumes spécialisée dans la logistique d’expédition de produits périssables. Services offerts : transport de fruits, légumes, viande, poisson, plantes et autres denrées périssables avec des camions à température contrôlée. Transport environnemental de type serre pour plantes vivantes, garantissant une température constante et un emballage spécialisé. Transport…
6. Isuzu – Camion d’alimentation animale 6×4 Giga
Domain: isuzujp.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Camion d’alimentation animale 6×4 Isuzu Giga 15 tonnes, Châssis 6X4 ISUZU GIGA, boîte de vitesses manuelle FAST à 12 vitesses, moteur diesel 350HP, capacité de chargement de 30cbm, dimensions 10600x2500x4000mm, poids brut 26000kg, poids à vide 12800kg, moteur diesel 6 cylindres en ligne, norme d’émission Euro V, pneus 12.00R20, frein pneumatique, système de décharge électrique ou hydraulique, vite…
7. SafetyCulture – Transport Alimentaire Solutions
Domain: safetyculture.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Le transport alimentaire est le processus d’acheminement des aliments du producteur aux consommateurs, crucial pour la sécurité alimentaire. Les méthodes de transport incluent l’air, la route, le rail et l’eau, avec le transport routier étant le plus courant en France. Les entreprises doivent maintenir la fraîcheur, la sécurité et la qualité des aliments pour éviter des interruptions d’activité et…
8. CSC – Camion d’Alimentation en Vrac 22 CBM
Domain: fr.csc-trucks.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Camion d’alimentation en vrac à 6 roues de 22 CBM, Capacité du réservoir de 22 CBM, Matériau du réservoir en acier au carbone, Utilisé pour le transport d’aliments en vrac, Meilleur moteur et transmission Yuchai adoptés, Réservoir d’alimentation en vrac soudé automatiquement par machine, Peinture de haute qualité pour temps chaud et froid.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for camion de transport daliments
In the realm of food transport, the strategic sourcing of ‘camion de transport d’aliments’ is pivotal for optimizing supply chains and ensuring food safety. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of collaboration with logistics providers that offer tailored solutions, such as cost-effective routing and compliance with hygiene standards. By leveraging specialized vehicles and technology, businesses can enhance operational efficiency while minimizing costs.
As global markets evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for reliable food transportation continues to rise. Companies must prioritize partnerships with experienced transport providers that understand regional challenges and regulations. This approach not only safeguards product integrity but also strengthens the overall supply chain.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers are encouraged to invest in strategic sourcing practices that align with their business goals. Emphasizing quality and compliance will be essential in navigating the complexities of international food transport. Engaging with knowledgeable suppliers and adopting innovative logistics solutions will position businesses for sustained growth in an increasingly competitive landscape. Now is the time to take action—connect with reputable transport partners and streamline your sourcing strategy to meet the demands of tomorrow.