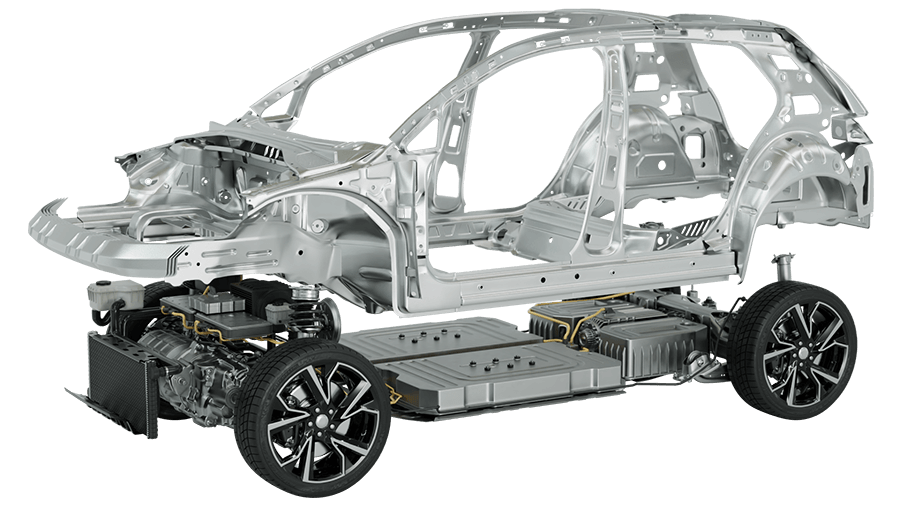
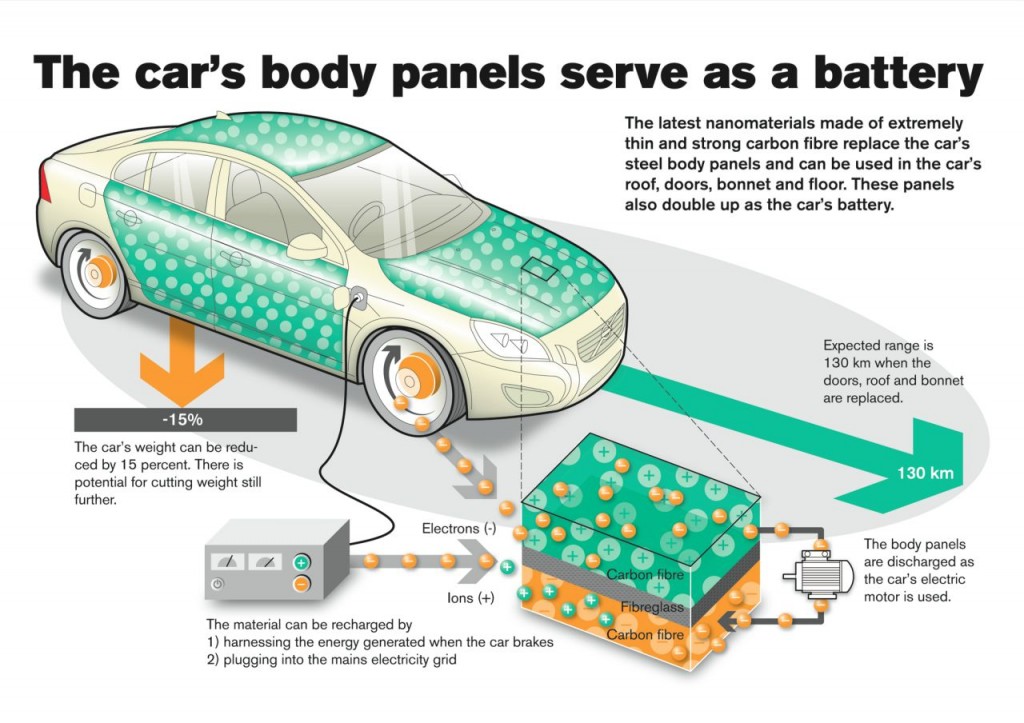
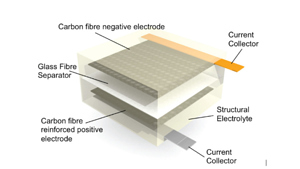
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for body panel electric vehicle
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicles (EVs), the demand for specialized body panel electric vehicles is surging. International B2B buyers face the challenge of sourcing high-quality components that not only meet performance standards but also align with sustainability goals. This comprehensive guide is designed to navigate the complexities of the global market for body panel electric vehicles, addressing critical factors such as types of materials, applications across various sectors, and supplier vetting processes.
Understanding the nuances of body panels—from aluminum to advanced composites—is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide delves into the characteristics of different materials, their applications in electric vehicle construction, and the implications for cost and performance. By equipping buyers with knowledge on industry standards and trends, we empower them to confidently select suppliers that can deliver innovative and reliable solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Targeting international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this guide emphasizes the importance of aligning procurement strategies with regional market dynamics. With insights into sourcing practices and the latest advancements in EV technology, stakeholders can enhance their competitive edge while contributing to the global shift towards sustainable transportation solutions.
Understanding body panel electric vehicle Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Body Panels | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, excellent thermal properties | Automotive manufacturing, fleet vehicles | Pros: Reduces overall vehicle weight, improves efficiency. Cons: Higher cost compared to traditional materials. |
| Composite Body Panels | Made from a mix of materials (e.g., carbon fiber, plastics) | High-performance vehicles, luxury EVs | Pros: Superior strength-to-weight ratio, customizable. Cons: Potentially more complex manufacturing processes. |
| Steel Body Panels | Traditional material, strong and durable | Mass production vehicles, budget EVs | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available. Cons: Heavier, may affect range and efficiency. |
| Solar-integrated Panels | Panels that incorporate solar technology into body design | Urban mobility solutions, eco-friendly fleets | Pros: Generates additional energy, sustainable. Cons: Initial investment may be high, efficiency varies with weather. |
| Modular Body Panels | Easily replaceable sections for repairs and upgrades | Fleet management, rental services | Pros: Reduces downtime for repairs, customizable. Cons: May require specialized skills for assembly. |
What Are the Characteristics and Suitability of Aluminum Body Panels in Electric Vehicles?
Aluminum body panels are favored for their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, making them ideal for electric vehicles (EVs) that prioritize efficiency and range. Their excellent thermal conductivity also aids in battery management systems. B2B buyers should consider aluminum for automotive manufacturing and fleet vehicles, particularly where performance and fuel efficiency are critical. However, the higher material cost may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
How Do Composite Body Panels Enhance Electric Vehicle Performance?
Composite body panels, made from materials like carbon fiber and advanced plastics, offer a remarkable strength-to-weight ratio. This makes them particularly suitable for high-performance and luxury electric vehicles, where both aesthetics and functionality are paramount. B2B buyers should assess the potential for customization and the advanced manufacturing techniques required. While the initial costs may be higher, the long-term benefits of reduced weight and enhanced performance can justify the investment.
What Role Do Steel Body Panels Play in Electric Vehicle Production?
Steel remains a staple in the automotive industry due to its durability and cost-effectiveness. It is commonly used in mass production vehicles and budget-friendly EVs. While steel body panels can provide a robust structure, their heavier weight can negatively impact the vehicle’s range and efficiency. B2B buyers looking for affordable options might find steel an attractive choice, but they should weigh the implications on overall vehicle performance.
What Are the Benefits of Solar-integrated Body Panels in Urban Electric Vehicles?
Solar-integrated panels represent an innovative approach to enhancing EV sustainability by embedding solar cells into the vehicle’s body. This technology is particularly appealing for urban mobility solutions, where vehicles can generate additional energy while parked or in motion. B2B buyers interested in eco-friendly fleets should consider the potential for reduced energy costs. However, the high initial investment and variable energy generation based on weather conditions may pose challenges.
How Do Modular Body Panels Improve Maintenance and Customization Options?
Modular body panels allow for easy replacement and upgrades, making them an excellent choice for fleet management and rental services. This design facilitates quick repairs, minimizing vehicle downtime. B2B buyers should evaluate the benefits of customization and ease of maintenance when considering modular options. While they may require specialized skills for assembly, the long-term operational efficiencies can lead to significant cost savings.
Key Industrial Applications of body panel electric vehicle
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of body panel electric vehicle | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Production of electric vehicles with lightweight body panels | Enhanced vehicle efficiency and performance | Material durability, weight specifications, and cost-effectiveness |
| Renewable Energy | Solar-integrated body panels for electric vehicles | Reduced energy costs and enhanced sustainability | Compatibility with solar technology and local climate considerations |
| Transportation & Logistics | Electric delivery vans with optimized body panels | Lower operational costs and improved fleet efficiency | Supply chain logistics, battery integration, and vehicle range |
| Urban Mobility | Development of shared electric vehicles with modular body panels | Flexibility in design and reduced maintenance | Customization options, sourcing of lightweight materials, and scalability |
| Automotive Aftermarket | Replacement body panels for electric vehicle repairs | Improved repair turnaround time and cost savings | Availability of OEM vs aftermarket parts and regional regulations |
How Are Body Panels Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, body panels for electric vehicles are crucial for creating lightweight structures that enhance overall efficiency. By utilizing materials such as aluminum and composite materials, manufacturers can significantly reduce vehicle weight, which in turn improves range and performance. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing durable yet lightweight materials is essential to meet local market demands and regulations. Additionally, understanding local manufacturing capabilities can facilitate smoother production processes.
What Role Do Solar-Integrated Body Panels Play in Renewable Energy?
Solar-integrated body panels represent a groundbreaking approach in the renewable energy sector, enabling electric vehicles to harness solar energy. By embedding solar cells into body panels, manufacturers can create vehicles that not only operate on electric power but also generate energy. This innovation can lead to reduced energy costs, particularly in sunny regions such as the Middle East. Buyers must consider the efficiency of solar technology, potential energy yield based on local climate, and the integration of these panels into existing vehicle designs.
How Do Body Panels Enhance Transportation and Logistics?
In the transportation and logistics sector, electric delivery vans equipped with optimized body panels can dramatically lower operational costs. These vehicles benefit from reduced weight, leading to improved battery efficiency and range. For B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Europe and the Middle East, it is crucial to assess the supply chain logistics related to sourcing body panels, as well as the integration of battery technology. Understanding local regulations regarding electric vehicles can further aid in compliance and operational efficiency.
What Advantages Do Modular Body Panels Offer for Urban Mobility?
Modular body panels in shared electric vehicles provide unparalleled flexibility in design and maintenance. This adaptability allows companies to customize vehicles based on urban demands and passenger needs, making them ideal for ride-sharing and public transport solutions. For international buyers, especially in rapidly urbanizing regions like Brazil, sourcing modular components that comply with local standards while ensuring ease of assembly and repair is vital for operational success.
How Does the Aftermarket for Body Panels Impact Electric Vehicle Repairs?
The automotive aftermarket plays a significant role in the maintenance of electric vehicles, particularly concerning body panel replacements. Sourcing high-quality replacement panels can lead to improved repair turnaround times and cost savings for businesses. Buyers in regions with developing automotive markets must weigh the benefits of OEM parts against aftermarket options, considering factors like availability, local regulations, and repair costs to ensure efficient service delivery and customer satisfaction.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘body panel electric vehicle’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Sourcing Durable Body Panels for Electric Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing body panels that are both lightweight and durable enough to withstand the rigors of electric vehicle performance. The challenge is compounded by the need for materials that can offer superior structural integrity while also being cost-effective. In regions like Africa and South America, where supply chains may be less stable, finding reliable suppliers for high-quality materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber can be particularly daunting. Buyers may face delays in production timelines, increased costs due to material wastage, and the risk of compromising vehicle safety and performance.
The Solution: To effectively address this issue, buyers should establish relationships with multiple suppliers specializing in advanced materials for electric vehicles. Conducting thorough market research to identify suppliers with a proven track record in producing high-strength, lightweight panels is crucial. Buyers should also consider investing in prototyping to test the durability and performance of body panels before committing to large orders. Collaborating with local universities or research institutions can provide insights into innovative materials and techniques, ensuring that the chosen panels meet both safety standards and performance expectations. Additionally, leveraging technology to streamline the supply chain can help mitigate delays and ensure a steady flow of materials.
Scenario 2: Challenges with Integration of Solar Technology into Body Panels
The Problem: As electric vehicles evolve, many manufacturers are looking to integrate solar technology into body panels, creating a dual-functionality that enhances energy efficiency. However, B2B buyers face significant challenges in ensuring that the solar cells seamlessly integrate with the body panels without compromising structural integrity or aesthetics. This integration process often involves complex engineering challenges, including the need for specialized adhesives and materials that can withstand environmental factors, which may not be readily available in all markets.
The Solution: To overcome these integration challenges, buyers should partner with engineering firms that specialize in solar technology and automotive design. Early collaboration can facilitate the development of tailored solutions that ensure both solar efficiency and structural soundness. Investing in R&D to explore the latest advancements in flexible solar cell technology can also provide a competitive edge. Additionally, engaging in pilot projects can help identify potential issues before full-scale production, allowing manufacturers to refine their processes and materials. This proactive approach can lead to more reliable solar integration in body panels, enhancing the overall value proposition of electric vehicles.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with International Standards and Regulations
The Problem: B2B buyers in the electric vehicle sector must navigate a complex landscape of international standards and regulations related to vehicle safety, environmental impact, and material sourcing. This is particularly challenging for companies looking to export vehicles to regions like Europe and the Middle East, where compliance requirements can be stringent and vary widely from one market to another. Failing to meet these standards can result in costly delays, legal issues, and damage to a company’s reputation.
The Solution: To effectively manage compliance challenges, buyers should invest in regulatory consulting services that specialize in the automotive industry. These experts can provide guidance on the specific requirements for different markets, ensuring that all body panel materials and designs meet necessary regulations. Developing a comprehensive compliance checklist that addresses both material sourcing and manufacturing processes can help streamline operations and reduce the risk of non-compliance. Additionally, staying informed about changes in regulations through industry associations and trade groups can provide valuable insights that help companies adapt quickly. By prioritizing compliance from the outset, businesses can not only avoid pitfalls but also position themselves as leaders in quality and safety in the electric vehicle market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for body panel electric vehicle
What Are the Key Materials for Body Panels in Electric Vehicles?
When selecting materials for body panels in electric vehicles (EVs), several factors must be considered, including performance, cost, and suitability for specific markets. Here, we analyze four common materials used in EV body panels: aluminum, steel, carbon fiber, and composite materials. Each material has unique properties and implications for international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Electric Vehicle Body Panels?
Aluminum is increasingly favored in the automotive industry due to its lightweight nature and excellent strength-to-weight ratio. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 600°C and offers good corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros: Aluminum panels enhance vehicle efficiency by reducing overall weight, which can lead to improved range and performance. They are also recyclable, aligning with sustainability goals.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost compared to steel, which can affect overall production budgets. Additionally, aluminum requires specialized manufacturing processes, which can complicate production.
For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial. In regions like Europe, where sustainability is prioritized, aluminum’s recyclability can be a significant selling point.
Why Is Steel Still a Popular Choice for EV Body Panels?
Steel remains a staple in automotive manufacturing, known for its durability and strength. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for structural applications.
Pros: Steel is generally more affordable than aluminum and offers excellent crashworthiness, making it a safe option for body panels. Its widespread availability also simplifies sourcing.
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact the vehicle’s range and performance. It is also prone to corrosion unless properly treated.
For buyers in regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, understanding local standards for steel quality and corrosion resistance is essential, especially in humid or coastal environments.
What Advantages Does Carbon Fiber Offer for Electric Vehicle Body Panels?
Carbon fiber is renowned for its exceptional strength and lightweight properties, often used in high-performance vehicles. It can withstand significant stress and has a temperature tolerance of around 200°C.
Pros: The primary advantage of carbon fiber is its weight reduction, which can lead to enhanced performance and efficiency. It also offers superior aesthetics and can be molded into complex shapes.
Cons: The high cost of carbon fiber is a significant barrier, making it less accessible for mass-market vehicles. Additionally, its manufacturing process is complex and time-consuming.
International buyers should consider the local demand for high-performance vehicles when evaluating carbon fiber. Compliance with specific standards for manufacturing and safety is also critical.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Electric Vehicle Body Panels?
Composite materials, often a combination of plastics and fibers, are gaining traction in the EV market. They offer good temperature resistance and can be engineered for specific performance requirements.
Pros: Composites are lightweight and can be produced in various forms, allowing for design flexibility. They also exhibit excellent corrosion resistance.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex, and the initial costs may be higher than traditional materials. Additionally, composites may not have the same impact resistance as metals.
For B2B buyers in emerging markets, understanding the local capabilities for composite manufacturing and the associated standards is vital. The growing trend toward lightweight materials aligns with global sustainability goals, making composites a viable option.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Body Panels in Electric Vehicles
| Material | Typical Use Case for body panel electric vehicle | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight body panels for improved efficiency | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Steel | Structural components and body panels | Durable and cost-effective | Heavier, prone to corrosion | Low |
| Carbon Fiber | High-performance body panels | Lightweight and strong | Expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
| Composite | Custom-designed body panels | Design flexibility and corrosion resistance | Higher initial costs, lower impact resistance | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the advantages and limitations of various materials for electric vehicle body panels, enabling informed decision-making tailored to specific market needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for body panel electric vehicle
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Body Panels for Electric Vehicles?
The manufacturing of body panels for electric vehicles (EVs) involves several critical stages that ensure both quality and performance. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Body Panel Production?
Material preparation is the foundational step in the manufacturing process. The most common materials used for body panels in electric vehicles are aluminum, steel, and composite materials. Aluminum is favored for its lightweight properties and corrosion resistance, while steel provides durability and strength. Composite materials, such as carbon fiber, are increasingly used for high-performance applications due to their lightweight and high-strength characteristics.
Before the actual forming process begins, raw materials undergo stringent quality checks. This includes verifying material specifications through chemical and mechanical testing to ensure they meet industry standards. B2B buyers should inquire about suppliers’ sourcing practices to ensure that materials are obtained from reputable sources, as this directly impacts the quality of the final product.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the desired body panel configurations. Several techniques are employed, including stamping, hydroforming, and extrusion.
-
Stamping: This is the most common method used for producing metal body panels. It involves pressing a sheet of metal into a mold to create specific shapes. Advanced stamping techniques can also reduce material waste and improve efficiency.
-
Hydroforming: This method utilizes high-pressure hydraulic fluid to form complex shapes that would be difficult to achieve with traditional stamping. It is especially beneficial for creating lightweight structures with enhanced strength.
-
Extrusion: Often used for aluminum, extrusion involves forcing material through a die to create long shapes with a consistent cross-section. This technique is particularly useful for frames and support structures within the vehicle.
B2B buyers should evaluate the forming capabilities of their suppliers, as advanced techniques can lead to better material properties and reduced production costs.
How Are Body Panels Assembled?
After forming, the next step is assembly, where individual body panels are joined together to create the vehicle’s structure. This can be accomplished through various methods, including welding, adhesive bonding, and mechanical fastening.
-
Welding: Commonly used for steel and aluminum panels, welding provides a strong and durable joint. Techniques such as laser welding and spot welding are prevalent in modern manufacturing, offering precision and speed.
-
Adhesive Bonding: This technique is gaining traction, especially in the assembly of composite materials. Adhesives can offer flexibility and weight savings, and they are often used in conjunction with mechanical fasteners to ensure a robust assembly.
-
Mechanical Fastening: This includes the use of bolts, screws, and rivets. Mechanical fastening is often employed when disassembly is required, or when joining dissimilar materials.
In this stage, it is essential for B2B buyers to understand the assembly methods used by suppliers, as these can influence the vehicle’s overall performance and serviceability.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Body Panels?
Finishing processes are crucial for enhancing the aesthetic appeal and protecting body panels from environmental factors. Common finishing techniques include painting, coating, and surface treatments.
-
Painting: This involves applying a protective and decorative layer to the body panels. Advanced painting techniques, such as electrocoating, ensure uniform coverage and durability.
-
Coating: Various coatings, including anti-corrosion and UV-resistant formulations, are applied to enhance durability. These coatings can significantly extend the lifespan of body panels in harsh environments.
-
Surface Treatments: Techniques like anodizing for aluminum or galvanizing for steel improve corrosion resistance and surface hardness. B2B buyers should ensure that suppliers employ appropriate finishing processes to meet the specific environmental conditions of their target markets.
What Are the Quality Assurance Standards for Body Panels?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component in the manufacturing of body panels for electric vehicles. Adherence to international standards, such as ISO 9001, ensures that manufacturers maintain consistent quality throughout the production process.
Which International Standards Are Relevant to Body Panel Manufacturing?
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system. It focuses on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction, ensuring that suppliers have robust quality control measures in place.
-
CE Marking: Particularly relevant for the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. This is crucial for B2B buyers operating within Europe to ensure regulatory compliance.
-
API Standards: While primarily associated with the oil and gas industry, certain API standards can be relevant for specific manufacturing processes, especially when dealing with materials that must withstand high-pressure conditions.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Established?
Quality control checkpoints are essential in maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt. Ensuring that materials meet predefined specifications can prevent defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify and rectify issues in real-time. Techniques such as statistical process control (SPC) are often employed to track production metrics.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection stage ensures that the finished body panels meet all specifications and standards before shipment. This may include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and performance testing.
B2B buyers should require suppliers to provide documentation of these QC checkpoints to verify adherence to quality standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers adhere to quality standards, B2B buyers can take several proactive steps:
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards.
-
Reports: Requesting regular quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s performance metrics and any identified issues.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures and product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to consider the following nuances:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Each region has specific regulatory requirements that suppliers must meet. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are familiar with and comply with local regulations.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural nuances in business practices can facilitate smoother negotiations and collaborations. Establishing clear communication channels is vital.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: International shipping can introduce risks to product quality. Buyers should work with suppliers who have robust logistics strategies to mitigate these risks.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for body panels in electric vehicles are comprehensive and require careful consideration from B2B buyers. By understanding these processes and implementing due diligence in supplier selection, buyers can ensure they source high-quality components that meet their specific needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘body panel electric vehicle’
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving electric vehicle (EV) market, sourcing body panels effectively is crucial for manufacturers and suppliers aiming to enhance vehicle performance, aesthetics, and sustainability. This checklist provides a structured approach for B2B buyers looking to procure body panels for electric vehicles, ensuring that every aspect of the sourcing process is meticulously addressed.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for the body panels, including dimensions, weight, materials, and performance criteria. This step is essential as it sets the foundation for all subsequent sourcing activities. Consider:
– Material Requirements: Determine whether you need aluminum for its lightweight properties or composite materials for enhanced strength.
– Durability Standards: Specify resistance to environmental factors like corrosion and UV exposure.
Step 2: Research and Identify Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to compile a list of potential suppliers who specialize in electric vehicle body panels. This is vital to ensure you have access to the best quality and innovative products in the market. Focus on:
– Supplier Experience: Look for companies with a proven track record in the EV sector.
– Product Range: Ensure the supplier offers a variety of materials and customization options to meet your needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Don’t just rely on their website. Consider:
– Certifications and Compliance: Verify that suppliers meet international standards such as ISO or IATF certifications.
– Production Capabilities: Assess whether the supplier has the capacity to meet your order volume and delivery timelines.
Step 4: Request Samples and Conduct Quality Testing
Obtaining samples of body panels allows you to evaluate the quality firsthand. This step is important to ensure that the materials meet your specified requirements. Pay attention to:
– Material Properties: Test for strength, weight, and resistance to environmental factors.
– Fit and Finish: Assess the aesthetic quality and how well the panels fit with other vehicle components.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you’ve identified suitable suppliers and tested their products, it’s time to negotiate pricing and contract terms. Effective negotiation can lead to significant cost savings and better terms. Focus on:
– Volume Discounts: Discuss pricing based on order quantities.
– Payment Terms: Establish clear payment schedules that align with your cash flow needs.
Step 6: Plan Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Consider the logistics involved in transporting body panels from suppliers to your manufacturing facilities. This step is critical to avoid delays in production. Look into:
– Shipping Options: Evaluate various shipping methods for cost-effectiveness and speed.
– Inventory Management: Establish systems to track inventory levels and reorder points to prevent shortages.
Step 7: Establish a Feedback Loop
After procurement, create a feedback mechanism to assess supplier performance and product quality continuously. This is important for maintaining long-term relationships and improving future sourcing decisions. Consider:
– Regular Reviews: Schedule periodic assessments of supplier performance based on quality, delivery, and responsiveness.
– Open Communication: Foster a transparent dialogue with suppliers to address any issues promptly and collaboratively.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement process for electric vehicle body panels, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their technical and business needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for body panel electric vehicle Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Body Panel Electric Vehicle Sourcing?
When sourcing body panels for electric vehicles (EVs), understanding the comprehensive cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The key cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. Common materials for body panels include aluminum, steel, and composite materials. Aluminum is favored for its lightweight properties, enhancing vehicle efficiency, while steel offers strength and durability. The price of raw materials fluctuates based on global supply and demand dynamics, which can affect sourcing costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and are influenced by the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is essential for tasks such as welding and finishing, particularly when dealing with advanced materials like carbon fiber or composites. Understanding local labor market conditions in target sourcing regions can help in estimating overall costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facility maintenance, utilities, and indirect labor. Overhead can vary significantly depending on the location of the manufacturer and the scale of operations. Larger facilities may benefit from economies of scale, reducing the per-unit overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for custom body panels. Tooling costs are amortized over production volume, meaning that higher volumes can lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should consider potential tooling costs when negotiating contracts.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of body panels is paramount, especially in the automotive sector. QC processes can add to costs but are essential for maintaining standards. Certifications such as ISO/TS 16949 can influence sourcing decisions, as they demonstrate a commitment to quality.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are critical, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping mode, and tariffs can impact overall logistics expenses. Buyers should also consider Incoterms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process, which can influence the total cost.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a profit margin to cover risks and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary based on competition, demand, and the unique value proposition of the supplier.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Body Panel Sourcing Decisions?
Several price influencers can significantly affect the cost of sourcing body panels:
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) can vary by supplier and affects pricing. Larger orders generally qualify for volume discounts, which can reduce the per-unit cost.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized body panels tailored to specific designs or functionalities may incur additional costs. Buyers should be clear about their specifications upfront to receive accurate quotes.
-
Materials: As mentioned, the choice of materials influences cost. Buyers should assess the long-term benefits of investing in higher-quality materials against their initial costs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Suppliers with recognized certifications may command higher prices but provide assurance of quality. Assessing the trade-off between price and quality is essential for long-term partnerships.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge a premium but offer lower risks.
What Are Some Tips for B2B Buyers in Negotiating Costs?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some actionable negotiation tips:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the complete cost associated with sourcing body panels, including purchase price, maintenance, and potential resale value. A lower upfront cost may not always equate to better value.
-
Negotiate Based on Volume: Leverage higher order volumes to negotiate better prices. Suppliers are often more willing to offer discounts for larger commitments.
-
Assess Local Market Conditions: Being aware of local economic conditions in the supplier’s region can provide leverage in negotiations. For example, understanding labor costs and material availability can inform discussions about pricing.
-
Explore Alternative Suppliers: Diversifying the supplier base can mitigate risks and provide leverage during negotiations. It also allows buyers to compare prices and quality across different providers.
-
Consider Long-Term Partnerships: Building relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Long-term contracts may provide stability for both parties, leading to mutual benefits.
Disclaimer
Prices and cost structures outlined in this analysis are indicative and can vary significantly based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and regional factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and engage in direct discussions with suppliers to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing body panel electric vehicle With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives for Body Panel Electric Vehicles
In the evolving landscape of electric vehicle (EV) technology, body panel electric vehicles (BPEVs) represent a unique solution, integrating advanced materials and sustainable design. However, it is essential for B2B buyers to consider viable alternatives that may better align with their operational needs, budget constraints, and market conditions. Below is a comparative analysis of BPEVs against two notable alternatives: Solar-Assisted Electric Vehicles (SAEVs) and Traditional Electric Vehicles (TEVs).
| Comparison Aspect | Body Panel Electric Vehicle | Solar-Assisted Electric Vehicle | Traditional Electric Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High power output (400 kW) and moderate range (200 miles) | Moderate range (160 miles) with solar augmentation | Varies widely, typically higher range (200-400 miles) |
| Cost | Premium pricing due to bespoke features and advanced materials | Moderate initial cost, potential for lower long-term energy costs | Varies, generally lower upfront cost than BPEVs |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex manufacturing process, requires specialized components | Integrates solar technology; simpler assembly but requires sun exposure | Well-established manufacturing and supply chains |
| Maintenance | Higher due to specialized materials and bespoke design | Moderate; solar components may require occasional checks | Generally lower maintenance; proven technology |
| Best Use Case | Luxury markets seeking unique, high-performance vehicles | Urban environments with ample sunlight, eco-conscious consumers | Mass-market adoption, varied consumer needs |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Solar-Assisted Electric Vehicles?
Solar-Assisted Electric Vehicles (SAEVs) utilize solar panels integrated into their body design to generate supplemental energy. This innovation can significantly enhance the vehicle’s efficiency, especially in sunny regions. Pros include reduced reliance on charging infrastructure and potential cost savings on electricity. However, their performance is limited by weather conditions, and they typically have a shorter range compared to BPEVs and TEVs. Thus, while they are ideal for urban settings with high sunlight exposure, their practicality may diminish in less favorable climates.
How Do Traditional Electric Vehicles Compare?
Traditional Electric Vehicles (TEVs) are well-established in the market, utilizing conventional battery technology without the added complexity of integrated solar panels. They offer a range of options suited for various consumer segments, from economy to luxury. TEVs often benefit from lower initial costs and a wide availability of service and parts, making them attractive to buyers. However, they may not utilize the latest lightweight materials and advanced designs found in BPEVs, which could affect performance in terms of speed and energy efficiency.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
For B2B buyers, the choice between body panel electric vehicles and their alternatives hinges on several factors: the target market, operational budget, and long-term sustainability goals. Buyers focused on luxury and bespoke offerings may lean towards BPEVs, while those operating in regions with abundant sunlight might find SAEVs advantageous. Conversely, organizations requiring reliable, cost-effective solutions for mass-market deployment may prefer TEVs. Ultimately, assessing the specific needs of the business and the driving conditions of the target market will guide the decision-making process effectively.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for body panel electric vehicle
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Body Panels in Electric Vehicles?
When it comes to body panels in electric vehicles (EVs), several technical properties play a pivotal role in their performance, durability, and overall effectiveness. Understanding these specifications is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Grade
The material grade of body panels is essential for ensuring structural integrity and weight efficiency. Common materials include aluminum, steel, and composite materials. Aluminum, for instance, offers a high strength-to-weight ratio, which is vital for enhancing vehicle range by reducing overall weight. Steel, while heavier, provides superior durability and crash protection. B2B buyers must evaluate the material grades based on their specific applications and performance criteria.
2. Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. In body panel manufacturing, maintaining strict tolerances is critical for proper fit and finish, which directly impacts aerodynamics and aesthetic appeal. Tolerance levels can affect assembly processes and the overall quality of the vehicle. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturer’s capabilities to ensure that they meet industry standards.
3. Surface Finish
The surface finish of body panels influences not only aesthetics but also functionality. A smooth finish can enhance aerodynamics, while specialized coatings can improve corrosion resistance and UV protection. B2B buyers should consider how different surface finishes align with their branding and performance goals, as well as maintenance requirements.
4. Weight Distribution
Weight distribution is crucial for vehicle handling and safety. Body panels must be designed to ensure even weight distribution across the vehicle to optimize performance. In electric vehicles, achieving an ideal weight distribution can help in battery management and range efficiency. Buyers should evaluate how body panel designs contribute to the overall vehicle dynamics.
5. Environmental Resistance
Given the diverse climates in regions such as Africa and the Middle East, environmental resistance is a significant property. Body panels must be resistant to factors such as corrosion, heat, and UV exposure. This is particularly important for vehicles designed for outdoor and urban environments. B2B buyers should prioritize manufacturers who utilize advanced materials and coatings that enhance durability against environmental factors.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Body Panel Electric Vehicle Industry?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B space. Here are some key terms that buyers should be familiar with:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces components that are used in another company’s products. In the context of body panels for electric vehicles, OEMs may supply parts to automobile manufacturers. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers to ensure they are sourcing quality parts that meet industry standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly important for B2B buyers, as it can significantly impact inventory management and cost-effectiveness. Buyers must negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. For body panels, an RFQ can help buyers compare prices and terms from multiple manufacturers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. Including detailed specifications in an RFQ can lead to more accurate quotes.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers involved in global sourcing, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. This knowledge can help in negotiating contracts and managing logistics effectively.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. In the body panel industry, lead times can vary significantly based on material availability and manufacturing capabilities. B2B buyers should assess lead times to align production schedules and avoid delays in vehicle assembly.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions in the dynamic electric vehicle market, ensuring that they select the right body panel solutions for their needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the body panel electric vehicle Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Body Panel Electric Vehicle Sector?
The body panel electric vehicle (EV) sector is experiencing transformative changes driven by several global factors. Increased regulatory pressure for reduced emissions and the push for sustainability are leading to heightened demand for electric vehicles across various regions, particularly in Europe, Africa, South America, and the Middle East. The emergence of advanced materials such as aluminum, carbon fiber, and innovative composites is reshaping the design and manufacturing processes, making vehicles lighter and more efficient. Moreover, the integration of solar technology, as seen in models like the Sono Sion, showcases a shift towards multifunctional body panels that can harness energy while enhancing vehicle aesthetics.
B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that offer not only innovative materials but also the ability to integrate cutting-edge technologies into body panel production. The trend of customization is gaining traction, where manufacturers are offering tailored body panels to meet unique market demands, reflecting local tastes and preferences. Digital platforms and advanced manufacturing techniques, including 3D printing, are being leveraged to streamline production and reduce lead times, making it easier for businesses to adapt to market changes swiftly. International partnerships are crucial, especially for companies in Africa and South America, as they seek to tap into European technology and innovation to enhance local manufacturing capabilities.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Body Panel Electric Vehicle Supply Chain?
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it has become a fundamental principle in the body panel electric vehicle sector. The environmental impact of sourcing materials, such as aluminum and composites, necessitates a shift towards more sustainable practices. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that adhere to ethical sourcing standards, ensuring that materials are obtained responsibly and with minimal environmental degradation. This is particularly important for markets in Africa and South America, where local ecosystems are often at risk.
Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and the use of recycled materials can significantly enhance a supplier’s credibility in the marketplace. Companies that invest in green certifications not only demonstrate their commitment to sustainability but also appeal to a growing demographic of environmentally conscious consumers. Additionally, the focus on reducing carbon footprints throughout the supply chain, from sourcing to production and logistics, is becoming a key differentiator for businesses. By adopting sustainable practices and transparent supply chains, companies can establish a competitive edge in the increasingly eco-aware global market.
What Is the Brief Evolution of the Body Panel Electric Vehicle Sector and Its Importance for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of the body panel electric vehicle sector can be traced back to the early days of electric mobility, where traditional materials dominated the manufacturing landscape. As technological advancements emerged, particularly in battery efficiency and renewable energy integration, manufacturers began exploring alternative materials to improve vehicle performance and sustainability. The introduction of lightweight materials such as aluminum and composite panels marked a significant turning point, allowing manufacturers to enhance range and efficiency.
In recent years, the sector has witnessed a surge in innovation, with startups and established automakers alike investing heavily in R&D to create vehicles that are not only environmentally friendly but also aesthetically pleasing and customizable. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial, as it highlights the importance of staying ahead of market trends and sourcing the right materials to meet future demands. Companies that can navigate this landscape effectively will not only contribute to a more sustainable future but will also position themselves as leaders in the rapidly growing electric vehicle market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of body panel electric vehicle
-
How do I solve supply chain issues when sourcing body panels for electric vehicles?
To address supply chain challenges, establish a diversified network of suppliers across different regions. This minimizes risk by ensuring that if one supplier faces issues, others can step in. Additionally, engage in regular communication with suppliers to monitor their capabilities and potential disruptions. Consider implementing just-in-time inventory strategies to reduce overhead costs while maintaining a steady supply. Utilizing technology, such as supply chain management software, can also enhance visibility and streamline logistics, ensuring timely deliveries. -
What is the best material for body panels in electric vehicles?
The optimal material for body panels in electric vehicles largely depends on the desired balance between weight, strength, and cost. Aluminum is favored for its lightweight properties and corrosion resistance, which improves energy efficiency. Steel, while heavier, offers excellent durability and strength, making it suitable for structural components. Advanced composites, like carbon fiber, provide superior performance at a higher cost, making them ideal for high-end models. Ultimately, the choice should align with the vehicle’s performance goals and market segment. -
How can I customize body panels to meet specific requirements?
Customization of body panels can be achieved through collaboration with manufacturers who offer bespoke design services. Define your specific requirements regarding dimensions, weight, aesthetics, and performance characteristics. Utilize CAD software to visualize and refine designs before production. Establish clear communication with your supplier regarding material choices and finishes to ensure compliance with your brand standards. It may also be beneficial to pilot small batches to test designs before committing to larger production runs. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for body panels in electric vehicle production?
Minimum order quantities for body panels can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the design. Typically, MOQs may range from a few hundred to several thousand units. When negotiating with suppliers, consider discussing flexible MOQs, especially if you are entering a new market or testing a new product line. Some manufacturers may offer lower MOQs for prototype runs or initial orders, allowing you to assess quality before scaling up. -
What payment terms are common in B2B transactions for electric vehicle components?
Payment terms in B2B transactions for electric vehicle components usually include options like net 30, net 60, or advance payment. It’s vital to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and procurement cycle. Consider utilizing letters of credit for larger transactions, which can provide security for both parties. Additionally, explore the possibility of milestone payments based on production stages, which can help manage financial risk and ensure timely delivery. -
How do I ensure quality assurance for body panels sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance for internationally sourced body panels, implement a comprehensive quality control program that includes pre-production samples, in-process inspections, and final product evaluations. Establish clear specifications and standards that suppliers must adhere to. Consider third-party quality audits or inspections to verify compliance with your standards. Additionally, building strong relationships with suppliers can foster open communication regarding quality issues, enabling quicker resolutions. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing body panels?
When importing body panels, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose between air freight for expedited delivery or sea freight for cost-effectiveness, depending on your urgency and budget. Familiarize yourself with import duties and compliance requirements in your region to avoid unexpected costs. Work with a logistics partner who has experience in handling automotive components to streamline the process and ensure timely delivery. -
How do I vet suppliers for body panels in the electric vehicle sector?
Vetting suppliers for body panels involves assessing their manufacturing capabilities, certifications, and track record in the electric vehicle industry. Request references and case studies to evaluate their experience with similar projects. Conduct site visits, if possible, to inspect their facilities and quality control processes. Additionally, check for industry certifications such as ISO 9001 or IATF 16949, which indicate adherence to quality management standards. Establishing clear criteria for evaluation will help ensure you partner with reliable and competent suppliers.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Body Panel Electric Vehicle Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. MotorTrend – Structural Battery Composite
Domain: motortrend.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Structural battery composite (SBC) is a multifunctional composite material that can replace traditional structural panels in vehicles while also storing energy. It utilizes raw carbon-fiber strands as a negative electrode and employs a lithium-iron-phosphate/graphene-oxide coating to serve as a structural cathode. The current energy storage capacity is about 24 watt-hours per kilogram, with expect…
2. Facebook – Innovative Electric Vehicle Design
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: an innovative concept in electric vehicle design where carbon fiber-based body panels double as energy storage devices
3. Solar Conversion – Gas-Powered Cars
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Conversion of popular gas-powered automobiles to incorporate solar panels into their body panels, similar to what Aptera does. The concept involves using the body/frame of existing gas-powered cars, like a ’65 Mustang, to create a solar-powered vehicle.
4. National Material – Aluminum Solutions for Electric Vehicles
Domain: nationalmaterial.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Aluminum is increasingly popular for electric vehicle construction due to its lightweight, durability, and corrosion resistance. It enhances fuel efficiency and extends driving range. Key applications include the body-in-white structure, battery housing, and components like stators and rotors. Aluminum is 100% recyclable and relatively low-cost, making it an environmentally sustainable choice. Nat…
5. Wiley – Energized Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics
Domain: onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, Wiley – Energized Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. LinkedIn – Energy-Storing Body Panels for EVs
Domain: linkedin.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Energy-storing body panels for electric vehicles (EVs) can power electric motors and the entire electrical framework of a car. These panels are made from nanomaterials, featuring a thin film of high-energy density created by sandwiching an electrolyte with all-carbon electrodes. They can be installed on various surfaces of the vehicle, including roof panels, doors, bonnets, and floors. Supercapaci…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for body panel electric vehicle
In today’s rapidly evolving electric vehicle (EV) market, strategic sourcing for body panels is critical for manufacturers aiming to enhance performance and sustainability. The shift towards lightweight materials such as aluminum, carbon fiber, and innovative composites not only improves vehicle efficiency but also aligns with environmental regulations and consumer preferences. Understanding regional material availability and production capabilities is essential for international buyers, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
Collaboration with specialized suppliers, like those developing integrated solar technologies, can further differentiate products and offer unique value propositions to customers. By leveraging local partnerships, companies can streamline their supply chains, reduce costs, and ensure timely delivery of high-quality components.
As the market continues to grow, international B2B buyers are encouraged to explore innovative sourcing strategies that prioritize quality, sustainability, and technological advancements. Embracing these trends will not only enhance competitiveness but also position businesses as leaders in the electric vehicle revolution. Engage with suppliers and industry experts today to stay ahead of the curve and capitalize on the opportunities within the body panel electric vehicle segment.