Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for eec electric car
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicles, sourcing EEC electric cars presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. Companies in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly seeking sustainable transportation solutions that align with their operational needs while minimizing environmental impact. This guide is designed to provide a comprehensive overview of the EEC electric car market, covering various types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
As businesses strive to enhance their fleet efficiency and reduce their carbon footprint, understanding the nuances of EEC electric vehicles becomes paramount. This guide empowers decision-makers by offering insights into the latest technologies, charging infrastructure developments, and the benefits of integrating EEC electric cars into diverse operational contexts—from urban commuting to fleet management.
Moreover, we will delve into critical factors that influence purchasing decisions, including quality assurance, regulatory compliance, and after-sales support. By equipping international B2B buyers with the knowledge they need, this guide aims to facilitate informed purchasing decisions that not only meet current market demands but also pave the way for a sustainable future in transportation. Embrace the opportunity to drive innovation and growth in your business with EEC electric cars, setting a benchmark for eco-friendly practices in your region.
Understanding eec electric car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| City EEC Electric Car | Compact design, optimized for urban environments | Delivery services, ride-sharing | Pros: Maneuverable, low operating costs. Cons: Limited range for long-distance travel. |
| Utility EEC Electric Car | Versatile functionality, often includes cargo space | Logistics, maintenance, and service fleets | Pros: High payload capacity, multi-purpose. Cons: May lack speed and agility in urban settings. |
| Luxury EEC Electric Car | High-end features, superior comfort, advanced technology | Corporate fleets, executive transport | Pros: Impressive performance, brand prestige. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| EEC Electric Bus | Large capacity, designed for public transport | Public transportation, employee shuttles | Pros: Eco-friendly, cost-effective for mass transit. Cons: Requires significant infrastructure for charging. |
| EEC Golf Cart | Smaller size, designed for short-distance travel | Golf courses, resorts, and campuses | Pros: Affordable, easy to operate. Cons: Limited use outside designated areas. |
What Are the Characteristics of City EEC Electric Cars?
City EEC Electric Cars are designed for urban environments, boasting a compact design that allows for easy maneuverability in congested areas. These vehicles are ideal for businesses involved in delivery services or ride-sharing applications due to their low operating costs and eco-friendliness. However, potential buyers should consider the limited range of these cars, which may not suit long-distance travel needs.
How Do Utility EEC Electric Cars Meet Diverse Business Needs?
Utility EEC Electric Cars are characterized by their versatile functionality, often featuring cargo space for transporting goods. These vehicles are particularly beneficial for logistics and service fleets, as they can handle high payloads while remaining environmentally friendly. While they provide excellent utility, buyers should be aware that these vehicles may sacrifice speed and agility compared to smaller models.
What Makes Luxury EEC Electric Cars a Smart Choice for Corporate Fleets?
Luxury EEC Electric Cars offer high-end features and superior comfort, making them an attractive option for corporate fleets and executive transport. They come equipped with advanced technology, providing a premium driving experience. However, the higher initial investment may deter some buyers, despite the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance.
Why Are EEC Electric Buses Essential for Public Transportation?
EEC Electric Buses are designed for large capacity and public transport, making them a sustainable solution for mass transit systems. They significantly reduce emissions and operational costs, making them a wise investment for municipalities and businesses looking to enhance employee transportation. However, the requirement for substantial charging infrastructure can be a drawback for some buyers.
How Do EEC Golf Carts Serve Niche Markets?
EEC Golf Carts are smaller, designed primarily for short-distance travel, which makes them ideal for use in golf courses, resorts, and educational campuses. They are affordable and easy to operate, catering to businesses that need reliable, low-speed transport. However, their limited use outside designated areas may restrict their appeal for broader applications.
Key Industrial Applications of eec electric car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of eec electric car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Transportation | Electric buses for urban transit | Reduced operational costs and emissions | Availability of charging infrastructure and fleet size |
| Logistics and Delivery | Electric delivery vehicles | Lower fuel costs and enhanced sustainability | Vehicle range and cargo capacity |
| Tourism and Leisure | Electric shuttle services | Eco-friendly transport option for tourists | Comfort features and vehicle design |
| Agriculture | Electric utility vehicles | Cost-effective transportation for farm operations | Terrain adaptability and battery life |
| Corporate Fleets | Employee commuting solutions | Improved employee satisfaction and reduced costs | Charging solutions at workplaces |
How Can EEC Electric Cars Transform Public Transportation?
EEC electric cars, particularly buses, are increasingly being adopted in urban transit systems. These vehicles offer a sustainable alternative to traditional diesel-powered buses, significantly reducing operational costs through lower fuel expenses and maintenance needs. For international buyers in regions like Africa and South America, the availability of charging infrastructure is crucial. They must consider fleet size and the ability to integrate electric buses into existing transit systems effectively.
What Role Do EEC Electric Cars Play in Logistics and Delivery?
In the logistics sector, EEC electric delivery vehicles provide a cost-effective solution for last-mile delivery services. With zero emissions and reduced fuel costs, businesses can enhance their sustainability profile while meeting the growing demand for eco-friendly practices. Buyers should focus on vehicle range and cargo capacity to ensure they meet their delivery requirements efficiently, especially in densely populated urban areas.
How Are EEC Electric Cars Enhancing Tourism and Leisure Services?
Electric shuttle services powered by EEC electric cars are becoming popular in the tourism sector. These vehicles offer an eco-friendly transportation option, appealing to environmentally conscious travelers. Tour operators and hotels in regions such as the Middle East and Europe should prioritize comfort features and vehicle design to enhance the guest experience. Additionally, ensuring a seamless charging solution is vital for operational efficiency.
In What Ways Can EEC Electric Cars Benefit Agriculture?
In the agricultural sector, EEC electric utility vehicles can revolutionize farm operations by providing a quiet, efficient mode of transport for workers and equipment. These vehicles are particularly beneficial for large farms, where reducing carbon footprints is essential. Buyers should consider terrain adaptability and battery life, as these factors directly influence the vehicle’s performance in various agricultural settings.
How Can Corporate Fleets Leverage EEC Electric Cars for Employee Commuting?
Corporate fleets are increasingly integrating EEC electric cars to provide sustainable commuting solutions for employees. This approach not only reduces transportation costs but also boosts employee satisfaction and company image. Companies in regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia should ensure that charging solutions are readily available at workplaces, as this is a key consideration for the successful adoption of electric vehicles in their fleets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘eec electric car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Charging Infrastructure Limitations in Urban Areas
The Problem: B2B buyers in urban settings often encounter challenges related to the availability and reliability of charging infrastructure for EEC electric cars. For businesses that rely on electric vehicle (EV) fleets, such as delivery services or transportation companies, the lack of accessible charging stations can lead to operational inefficiencies. This can cause delays, increased downtime, and ultimately impact customer satisfaction. Furthermore, buyers who manage fleets may struggle with charging solutions if their vehicles are used in areas with inadequate public charging options, leading to concerns over the range and usability of EEC electric cars.
The Solution: To mitigate these issues, businesses should prioritize partnerships with local governments and private entities to advocate for the installation of more charging stations in key areas, such as warehouses, logistics hubs, and popular urban locales. Additionally, companies can explore investing in their own charging infrastructure at their depots or offices. By integrating smart charging solutions, such as fast chargers that reduce charging time, businesses can ensure that their fleets are always ready to operate efficiently. This proactive approach not only enhances the operational reliability of EEC electric cars but also positions companies as leaders in sustainable transportation, appealing to environmentally conscious customers.
Scenario 2: High Initial Investment Costs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the hurdle of high upfront costs associated with purchasing EEC electric cars. This financial barrier can deter companies, especially small to medium-sized enterprises, from transitioning their fleets to electric vehicles. Buyers may also be concerned about the return on investment (ROI) when considering the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, insurance, and charging costs.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis that includes potential savings from reduced fuel and maintenance costs over time. Additionally, they should investigate available government incentives, subsidies, or tax breaks that can significantly offset the initial costs of EEC electric cars. Partnering with financial institutions that specialize in green financing can also provide flexible payment options, making it easier to manage cash flow while transitioning to an electric fleet. By focusing on long-term savings rather than just initial expenditure, businesses can make a more informed decision that aligns with their sustainability goals.
Scenario 3: Limited Awareness and Knowledge about EEC Electric Cars
The Problem: B2B buyers often lack sufficient knowledge about EEC electric cars, including their benefits, features, and how they compare to traditional vehicles. This information gap can lead to hesitancy in making a purchase decision, as buyers may not fully understand the capabilities and advantages of EEC electric cars, particularly in terms of operational efficiency and environmental impact.
The Solution: To bridge this knowledge gap, businesses should invest in training and educational resources for their procurement teams and decision-makers. This could include workshops, webinars, or partnerships with manufacturers and industry experts to gain insights into the technology, benefits, and practical applications of EEC electric cars. Additionally, companies should leverage case studies and testimonials from other businesses that have successfully integrated EEC electric cars into their operations. By cultivating a well-informed team, businesses can confidently navigate the purchasing process and advocate for the adoption of electric vehicles, ensuring that their organizations remain competitive and aligned with global sustainability trends.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for eec electric car
What Are the Key Materials Used in EEC Electric Cars?
When selecting materials for EEC electric cars, several factors such as performance, cost, and manufacturing complexity must be considered. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the production of EEC electric vehicles, focusing on their properties, advantages and disadvantages, application impacts, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Benefit EEC Electric Cars?
Aluminum is widely used in the automotive industry due to its lightweight properties and resistance to corrosion. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 600°C and can withstand significant pressure, making it ideal for various vehicle components.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, which enhances vehicle efficiency and range. It is also recyclable, contributing to sustainability efforts.
Cons: However, aluminum can be more expensive than steel and may require specialized manufacturing processes, increasing production costs.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in chassis and body panels, where weight reduction is crucial for performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN, particularly regarding safety and environmental regulations.
What Role Does Steel Play in EEC Electric Cars?
Steel remains a fundamental material in the automotive sector, known for its high tensile strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and is resistant to various environmental factors.
Pros: The advantages of steel include its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. It is widely available and can be formed into complex shapes, making it suitable for various applications.
Cons: On the downside, steel is heavier than aluminum, which may negatively impact the vehicle’s efficiency and range.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used in structural components, such as frames and reinforcements, where strength is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of high-strength steel options and ensure compliance with local standards, particularly in regions with specific regulations like Saudi Arabia.
How Does Composite Material Enhance EEC Electric Cars?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers, are increasingly being used in electric vehicles due to their lightweight and high-strength characteristics.
Pros: Composites offer significant weight savings and can be molded into complex shapes, enhancing design flexibility. They also provide excellent corrosion resistance.
Cons: The main drawback is the high cost of materials and manufacturing processes, which can be a barrier for mass production.
Impact on Application: Composites are often used in body panels and interior components, where weight reduction and aesthetics are important.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for specialized manufacturing processes and ensure that suppliers meet international quality standards.
What Is the Importance of Lithium-Ion Batteries in EEC Electric Cars?
Lithium-ion batteries are critical components in electric vehicles, providing the necessary energy storage for electric motors. They typically operate efficiently within a temperature range of -20°C to 60°C.
Pros: These batteries have a high energy density, allowing for longer driving ranges and faster charging times. They are also lightweight compared to other battery types.
Cons: However, lithium-ion batteries can be costly, and their performance may degrade over time, leading to concerns about longevity and sustainability.
Impact on Application: Lithium-ion batteries are essential for the propulsion of electric vehicles, directly affecting performance and user experience.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure compliance with international shipping and safety standards, particularly in regions with stringent regulations regarding battery disposal and recycling.
Summary Table of Material Selection for EEC Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for eec electric car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Chassis and body panels | Lightweight, enhances efficiency | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Steel | Structural components | Cost-effective, widely available | Heavier, impacts efficiency | Medium |
| Composite | Body panels and interior components | Lightweight, design flexibility | High cost, specialized manufacturing | High |
| Lithium-Ion Battery | Energy storage for propulsion | High energy density, lightweight | Costly, potential longevity issues | High |
By understanding these materials and their implications, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements in their respective markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for eec electric car
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of EEC Electric Cars?
The manufacturing process of EEC electric cars is a complex sequence of stages designed to ensure high-quality output. Understanding these stages can significantly benefit B2B buyers looking for reliable suppliers.
-
Material Preparation:
The process begins with the selection and preparation of raw materials, including high-strength steel, aluminum, and advanced composites. Suppliers must ensure that materials meet specific industry standards for durability and weight. Quality checks are performed at this stage to verify the integrity of materials before they proceed to the next phase. -
Forming:
This stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the required components of the electric car. Techniques such as stamping, extrusion, and injection molding are commonly used. Advanced technologies like computer numerical control (CNC) machining are also employed to achieve precise dimensions. Consistency in forming is crucial, as any deviations can lead to assembly challenges later in the process. -
Assembly:
The assembly phase is where individual components come together to form the vehicle. Automated assembly lines are often utilized to enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs. Key components such as the electric motor, battery packs, and electronic control units are integrated into the vehicle during this phase. Quality control measures, such as torque checks and alignment verifications, are implemented at various checkpoints to ensure proper assembly. -
Finishing:
The finishing stage involves painting, polishing, and applying protective coatings to enhance the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal and durability. This phase may also include final inspections and testing of all systems, such as electrical and safety features. A thorough quality check is performed to ensure that the car meets both visual and functional standards before it is deemed ready for delivery.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in EEC Electric Car Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is an essential component of the manufacturing process for EEC electric cars. It ensures that the vehicles meet international standards and customer expectations. Here are some key aspects of the quality assurance process:
-
Adherence to International Standards:
EEC electric car manufacturers typically adhere to international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Compliance with these standards helps ensure consistent product quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) are often sought to validate the safety and efficacy of electric vehicles. -
Quality Control Checkpoints:
Quality control is integrated at multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step verifies the quality of raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process help identify and rectify issues in real time.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive assessment at the end of the assembly process ensures that the finished product meets all quality and safety standards. -
Common Testing Methods:
Various testing methods are employed to evaluate the performance and safety of EEC electric cars. These include:
– Functional Testing: Assessing the operation of electrical systems, motors, and other components.
– Safety Testing: Evaluating the vehicle’s crashworthiness and compliance with safety regulations.
– Environmental Testing: Ensuring the vehicle performs well under various environmental conditions, such as temperature extremes and humidity.
What Should B2B Buyers Look for in Supplier Quality Assurance Practices?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance practices is crucial. Here are actionable insights:
-
Supplier Audits and Inspections:
Conducting on-site audits can provide valuable insights into a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who are open to audits and provide clear documentation of their quality assurance practices. -
Requesting Quality Reports:
Suppliers should be able to furnish detailed quality reports, including data on testing outcomes and compliance with international standards. These reports can help buyers assess the reliability and credibility of the supplier. -
Third-Party Inspections:
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality assurance processes. This practice is particularly beneficial for buyers who may not have the resources to conduct thorough inspections themselves. -
Understanding Certification Nuances:
Different markets have unique regulatory requirements. For instance, vehicles sold in Europe must comply with EU regulations, while those in the Middle East may require specific local certifications. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with the relevant regulations in their target markets to avoid potential legal issues.
How Do Cultural and Regional Factors Influence Quality Assurance Expectations?
Cultural and regional nuances can significantly impact quality assurance expectations in the manufacturing of EEC electric cars. Buyers from different backgrounds may prioritize different aspects of quality:
-
Expectations for Transparency:
In regions where business relationships are built on trust, such as in parts of Africa and the Middle East, buyers may place a higher emphasis on transparency in quality assurance processes. Suppliers should be prepared to share detailed information about their manufacturing and testing procedures. -
Importance of After-Sales Support:
In markets like South America and parts of Europe, the expectation for after-sales support can shape quality assurance practices. Suppliers should offer robust after-sales services, including warranty support and maintenance, to meet these expectations. -
Adaptation to Local Standards:
Regional regulations can vary widely, necessitating that suppliers adapt their quality assurance practices accordingly. Buyers should assess whether suppliers have the capability to meet local regulatory requirements without compromising on quality.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in place for EEC electric cars, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select reliable suppliers that meet their quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘eec electric car’
To assist B2B buyers in the procurement of EEC electric cars, this guide provides a structured checklist designed to streamline the sourcing process. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they make informed decisions, leading to successful and sustainable purchases.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specific features and requirements of the EEC electric cars you intend to procure. Consider factors such as battery capacity, range, charging options, and safety features. Detailed specifications will help you communicate your needs effectively to potential suppliers and ensure that the vehicles meet your operational demands.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reputable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify manufacturers and exporters with a solid reputation in the electric vehicle industry. Look for companies that have extensive experience in producing EEC electric cars and positive reviews from previous clients. Utilize industry forums, trade shows, and online platforms to gather information about potential suppliers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering have the necessary certifications and comply with international standards. This includes quality control certifications, safety compliance, and environmental regulations. Such certifications not only indicate the reliability of the supplier but also assure you that the vehicles meet global safety and quality benchmarks.
- Key Certifications to Look For:
- ISO 9001 for quality management
- CE certification for safety standards in Europe
- Local regulatory approvals relevant to your region
Step 4: Request and Review Product Samples
Before finalizing your order, request product samples or demonstrations of the EEC electric cars. Evaluating the vehicles firsthand allows you to assess their quality, performance, and comfort. This step is crucial for ensuring that the cars align with your expectations and operational needs.
Step 5: Analyze Pricing and Payment Terms
Gather detailed quotations from shortlisted suppliers and analyze their pricing structures. Look beyond the initial cost; consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and charging infrastructure. Additionally, clarify payment terms, warranty conditions, and any potential discounts for bulk purchases.
Step 6: Verify After-Sales Support and Service Options
Inquire about the after-sales support provided by the supplier. Reliable after-sales service is vital for the long-term performance of your EEC electric vehicles. Ensure that the supplier offers comprehensive support, including maintenance services, availability of spare parts, and training for your staff.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Agreement and Contract
Once you have selected a supplier, draft a detailed agreement outlining all terms and conditions of the purchase. Include specifications, delivery timelines, payment terms, and warranty details in the contract. A clear agreement protects both parties and helps prevent misunderstandings.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing EEC electric cars more effectively, ensuring a successful procurement process that aligns with their operational and sustainability goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for eec electric car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing EEC Electric Cars?
When considering the sourcing of EEC electric cars, understanding the cost structure is paramount. The main cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and supplier margin.
-
Materials: The cost of materials, including batteries, electric motors, and body components, significantly influences the overall price. High-quality materials often lead to better performance and longevity, but they can also raise costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this could impact quality. It’s crucial to evaluate the skill level of the workforce in the supplier’s region.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and administrative expenses associated with production. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, which is vital for competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Investment in specialized tools and equipment can be a significant upfront cost. However, such investments often lead to improved production efficiency and product quality in the long run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures that the vehicles meet safety and regulatory standards, which can incur additional costs. However, these measures are essential for minimizing defects and enhancing customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the destination. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and import/export regulations play a critical role in logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins will also affect the final price. It’s essential to understand the typical margins in the industry to negotiate effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Affect EEC Electric Car Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of EEC electric cars, particularly in international B2B transactions.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk purchases, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized vehicles may incur additional costs due to the need for specialized parts or processes. Clear communication of specifications can help mitigate unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials impacts both cost and performance. For instance, opting for premium battery technology can enhance range and efficiency but will increase upfront costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Vehicles that meet specific quality standards or certifications may come at a higher price. However, investing in certified vehicles can lead to lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) due to reduced maintenance and longer lifespan.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can significantly influence pricing. Established manufacturers with a track record of quality may charge a premium, but they often provide better after-sales support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping arrangements, impacting the overall cost and risk.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in EEC Electric Car Sourcing?
Navigating the complexities of sourcing EEC electric cars can be challenging. Here are actionable tips for buyers:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage bulk purchasing and long-term contracts to negotiate better prices. Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can also lead to more favorable terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, fuel savings, and resale value. Sometimes, a higher upfront cost can lead to significant long-term savings.
-
Research Pricing Nuances: Understand regional pricing differences and market demand. For instance, demand fluctuations in regions like Africa or South America may affect availability and pricing.
-
Consider Total Logistics Costs: Factor in all logistics costs when evaluating supplier pricing. Choose suppliers with efficient shipping options to minimize these costs.
-
Stay Informed on Regulatory Changes: Keep abreast of changes in import/export regulations and environmental standards in your region, as these can influence costs and pricing structures.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough research and supplier evaluations before making procurement decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing eec electric car With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to the EEC Electric Car
In the rapidly evolving automotive landscape, businesses are increasingly faced with the challenge of selecting the most suitable transportation solutions. The EEC electric car represents a sustainable and innovative option, but it is essential to compare it with other viable alternatives to make an informed decision. Below is a comparative analysis of the EEC electric car against two notable alternatives: hydrogen fuel cell vehicles and traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | EEC Electric Car | Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle | Traditional Internal Combustion Engine Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque, smooth acceleration | Quick refueling, good range | Established performance, but less efficient |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost, low operating costs | Higher initial cost, moderate operating costs | Lower initial cost, higher fuel and maintenance costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to implement with existing charging infrastructure | Limited refueling stations, requires infrastructure development | Widely available infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to fewer moving parts | Moderate maintenance, but parts can be expensive | Higher maintenance costs and complexity |
| Best Use Case | Urban and suburban applications | Long-distance travel and heavy-duty applications | General-purpose transportation |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) operate by converting hydrogen gas into electricity, which powers an electric motor. The primary advantages of FCVs include their quick refueling time, similar to traditional gasoline vehicles, and the potential for long driving ranges. However, the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is still limited, particularly in developing regions like Africa and South America. This can pose significant challenges for businesses relying on consistent access to refueling stations. Additionally, while the technology is advancing, the initial costs of hydrogen vehicles remain high compared to the EEC electric car.
Traditional Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles
ICE vehicles have been the cornerstone of transportation for over a century. They are generally less expensive upfront and have widespread refueling infrastructure, making them accessible in nearly all regions. However, ICE vehicles are less efficient and produce greenhouse gas emissions, which can be a significant drawback for businesses focused on sustainability. Operating costs can also be higher due to fluctuating fuel prices and maintenance needs. For companies prioritizing eco-friendliness and lower operating expenses, traditional vehicles may not align with their long-term goals.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution
When choosing the right transportation solution, B2B buyers must consider several factors, including performance requirements, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and the intended use case. The EEC electric car offers a compelling combination of eco-friendliness, low operating costs, and suitability for urban environments. In contrast, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles may be better suited for long-distance travel, while traditional ICE vehicles provide familiarity and extensive infrastructure. Ultimately, the decision will depend on the specific needs and priorities of the business, including sustainability goals, budget constraints, and operational requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for eec electric car
What Are the Key Technical Properties of EEC Electric Cars?
Understanding the technical specifications of EEC electric cars is essential for B2B buyers, as these properties directly impact performance, efficiency, and long-term operational costs. Here are several critical specifications:
-
Battery Capacity (kWh)
Battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), indicates the amount of energy the battery can store. A higher capacity generally translates to a longer driving range between charges, which is crucial for fleet operators who need to maximize uptime. For instance, a vehicle with a 60 kWh battery can typically travel between 200 to 300 kilometers on a single charge, making it suitable for urban and regional transport. -
Motor Power Output (kW)
The power output of the electric motor, expressed in kilowatts (kW), determines the vehicle’s acceleration and overall performance. A higher power output allows for faster acceleration, which is advantageous in congested urban settings. Fleet managers should consider the required power output based on their operational needs, such as whether the vehicle will be transporting heavy loads or navigating hilly terrains. -
Charging Time (hours)
Charging time refers to the duration needed to fully charge the vehicle’s battery. Fast-charging capabilities can significantly enhance operational efficiency, particularly for businesses with tight schedules. Understanding the charging infrastructure available in the target market is essential; for example, a vehicle that supports fast charging (e.g., 0-80% in 30 minutes) can be a game changer for logistics companies. -
Vehicle Weight (kg)
The weight of the electric vehicle affects its range, efficiency, and handling. Lighter vehicles generally consume less energy, thereby extending their range. Additionally, for fleet operators, knowing the vehicle’s weight is important for compliance with local regulations regarding load limits. -
Safety Standards Compliance
EEC electric cars must meet specific safety standards, such as ISO 26262 for functional safety in automotive systems. Compliance ensures that the vehicle is designed to minimize risks associated with electrical and mechanical failures. B2B buyers should inquire about the certifications obtained by the manufacturer to ensure product reliability and safety for end-users. -
Warranty and Service Offerings
Understanding the warranty period for critical components like batteries and electric motors is vital for B2B buyers. A comprehensive warranty can significantly reduce maintenance costs and downtime. Additionally, service offerings such as after-sales support and availability of spare parts should be considered to ensure operational continuity.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to EEC Electric Cars?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology can aid B2B buyers in negotiations and procurement processes. Here are some common trade terms related to EEC electric cars:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of EEC electric cars, OEMs provide essential components such as batteries, motors, and electronic systems. Buyers should evaluate OEM partnerships to ensure the availability of quality components. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cash flow. For instance, if a manufacturer has a MOQ of 50 units, a buyer must assess whether this aligns with their demand forecasts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and other terms for specific products or services. B2B buyers should use RFQs to gather competitive pricing and detailed product specifications, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms, such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), helps B2B buyers understand shipping costs and liabilities. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is crucial for B2B buyers to manage their supply chain effectively and avoid disruptions in operations. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO is a financial estimate intended to help buyers assess the direct and indirect costs of a product or system. For EEC electric cars, TCO includes purchase price, maintenance, insurance, and energy costs, providing a comprehensive view of long-term expenses.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when procuring EEC electric vehicles, ensuring alignment with their operational needs and market conditions.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the eec electric car Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the EEC Electric Car Sector?
The EEC electric car sector is undergoing significant transformation driven by a combination of global environmental policies, rising fuel costs, and technological advancements. The push towards sustainable transportation is fueled by governments aiming to meet emissions targets, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East. These regions are implementing stricter regulations on traditional combustion vehicles, creating a robust demand for electric alternatives. Additionally, the growing concern over air pollution and climate change has made electric vehicles (EVs) more appealing to consumers and businesses alike.
Emerging B2B tech trends are reshaping how electric vehicles are sourced and utilized. Innovations in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and vehicle connectivity are at the forefront. For instance, workplace charging solutions are becoming essential for businesses, as they support employees who may not have access to home charging. This is particularly relevant for B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where the infrastructure is still developing. Furthermore, the trend towards fleet electrification is gaining momentum, with companies recognizing the long-term cost savings associated with electric fleets.
International B2B buyers should also be aware of the shifting landscape in sourcing strategies. There is an increasing preference for manufacturers that demonstrate reliability and compliance with international safety standards. Buyers are encouraged to establish partnerships with reputable suppliers who prioritize quality control and are committed to sustainable practices. This shift not only enhances supply chain resilience but also aligns with the growing demand for ethical sourcing.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the EEC Electric Car Market?
Sustainability is at the core of the EEC electric car market, influencing both production and sourcing practices. The environmental impact of electric vehicles is significantly lower than that of traditional vehicles, primarily due to their zero emissions during operation. However, it is crucial for B2B buyers to consider the entire lifecycle of the vehicle, including the sourcing of materials and manufacturing processes. The demand for ethical supply chains is rising, with companies seeking to minimize their carbon footprint and ensure responsible sourcing of components.
Certification for green materials and practices is becoming increasingly important. Buyers should look for suppliers who are certified by recognized organizations that verify the sustainability of their manufacturing processes. This includes adherence to international standards for environmental management, such as ISO 14001. Additionally, the sourcing of materials like lithium for batteries must be scrutinized, as ethical mining practices are essential for minimizing environmental degradation and promoting social responsibility.
Investing in EEC electric vehicles from manufacturers committed to sustainability not only enhances corporate social responsibility but also aligns with the values of environmentally conscious consumers. This can lead to improved brand reputation and customer loyalty, particularly in markets where sustainability is a key purchasing factor.
What is the Brief Evolution and History of EEC Electric Cars in the B2B Context?
The evolution of EEC electric cars is rooted in the broader transition toward sustainable transportation that began in the late 20th century. Initially, electric vehicles were seen as niche products, primarily used in urban settings. However, advancements in battery technology and growing concerns about climate change have propelled electric vehicles into the mainstream.
In the early 2000s, several manufacturers began producing electric vehicles with improved range and efficiency, making them more viable for various applications, including commercial fleets. The introduction of EEC regulations in Europe further standardized the classification and performance requirements for electric vehicles, fostering international trade and investment in electric mobility.
Today, EEC electric cars are recognized not only for their environmental benefits but also for their cost-effectiveness and technological advancements. This evolution has opened up significant opportunities for B2B buyers, as they seek to integrate electric vehicles into their operations, align with sustainability goals, and respond to consumer demand for greener alternatives. As the market continues to expand, the importance of strategic sourcing and partnerships will be critical for success in the evolving landscape of electric mobility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of eec electric car
-
How do I ensure the quality of EEC electric cars from suppliers?
To ensure quality when sourcing EEC electric cars, it’s crucial to conduct thorough supplier vetting. Start by verifying the manufacturer’s certifications, such as ISO and CE, which indicate adherence to international quality standards. Request samples or visit production facilities to assess manufacturing processes. Additionally, review customer testimonials and seek references from other businesses that have successfully sourced vehicles from the supplier. Establishing a clear quality assurance (QA) process, including pre-shipment inspections, can further mitigate risks. -
What are the essential features to look for in an EEC electric car?
When evaluating EEC electric cars, prioritize features such as battery capacity, charging options, and safety features. Look for vehicles with a robust battery that offers a longer range to minimize downtime. Charging versatility—whether at home, work, or public stations—is vital for operational flexibility. Additionally, advanced safety features like anti-lock braking systems, airbags, and stability control enhance passenger safety. Finally, consider smart connectivity options that facilitate fleet management and monitoring. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for EEC electric cars?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for EEC electric cars can vary significantly by supplier and model. Generally, MOQs range from 10 to 50 units for bulk orders, but some manufacturers may offer lower MOQs for new clients or specific models. It’s advisable to discuss your requirements directly with suppliers to negotiate favorable terms. Establishing a long-term partnership can also lead to better pricing and flexibility in future orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing EEC electric cars?
Payment terms for EEC electric cars typically include options such as a deposit followed by the balance upon delivery or shipment. Commonly, suppliers may request a 30% to 50% deposit upfront, with the remaining amount due before shipment or upon delivery. Always clarify payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers or letters of credit, to avoid complications. It’s wise to use secure payment methods and consider escrow services for large transactions to protect both parties. -
How can I customize EEC electric cars for my business needs?
Most manufacturers offer customization options for EEC electric cars to meet specific business requirements. Customization may include alterations to vehicle design, color, features, or additional technology integrations. Initiate discussions with suppliers to understand the extent of customization available and any associated costs. Providing detailed specifications and clear communication about your needs will help ensure the final product aligns with your expectations. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing EEC electric cars?
When importing EEC electric cars, logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Evaluate whether to use air or sea freight based on urgency and budget. Ensure you understand the import regulations in your country, including tariffs and taxes. Collaborating with a freight forwarder experienced in automotive imports can streamline the process. Plan for potential delays and maintain open communication with your supplier regarding shipping schedules. -
What are the advantages of EEC electric cars for businesses?
EEC electric cars offer numerous advantages for businesses, such as reduced fuel costs and lower maintenance expenses compared to traditional vehicles. They are environmentally friendly, aligning with corporate sustainability goals and potentially enhancing brand reputation. Additionally, electric cars can provide tax incentives or rebates in various regions, further lowering operational costs. Their quiet operation and ease of use make them ideal for urban environments, allowing businesses to operate more efficiently. -
How can I find reliable suppliers of EEC electric cars?
Finding reliable suppliers of EEC electric cars involves researching potential manufacturers through trade shows, online platforms, and industry directories. Look for suppliers with a solid track record and positive reviews from other B2B buyers. Engaging in direct communication with suppliers can help assess their responsiveness and willingness to meet your needs. Additionally, consider joining industry associations or networking groups to gain insights and recommendations on reputable suppliers in the electric vehicle market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 4 Eec Electric Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Yunrong – Eec Electric Car
Domain: yunronev.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Eec Electric Car by Taizhou Yunrong Technology Co., Ltd. is an innovative and eco-friendly vehicle designed for sustainable transportation. It features a modern and sleek design, advanced technology, and a powerful electric motor, ensuring a comfortable and luxurious driving experience. The car is emission-free, making it suitable for both urban and rural areas. The manufacturer adheres to stringe…
2. HDK – Electric Vehicle Components
Domain: hdkexpress.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: OEM Eec Electric Car Suppliers, HDK Electric Vehicle Home Products: CLASSIC 2 – 4KW AC MOTOR, 400A CONTROLLER, 48V 110AH LITHIUM BATTERY, 10X7″ ALUMINUM WHEEL; CLASSIC 4 – 4KW AC MOTOR, 400A CONTROLLER, 48V 110AH LITHIUM BATTERY, 10X7″ ALUMINUM WHEEL; CARRIER 4 – 6.3KW AC MOTOR, 400A CONTROLLER, 48V 110AH LITHIUM BATTERY, 10X7″ ALUMINUM WHEEL; CARRIER 6 – 6.3KW AC MOTOR, 400A CONTROLLER, 48V 110AH…
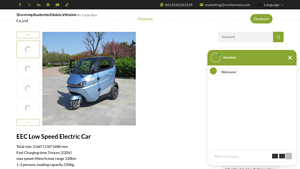
3. Run Horse – EEC Low Speed Electric Car
Domain: runhorseev.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Product Name: EEC Low Speed Electric Car
Total Size: 2160*1150*1680 mm
Battery: 105Ah LiFePo4 Battery with BMS System
Motor: 3000 AC Motor
Charging Time: 3 hours (220V)
Max Speed: 45 km/h
Max Range: 120 km
Seating Capacity: 1-3 persons
Loading Capacity: 150 kg
Wheels: 3 wheels
Seating: 2 seats with belts, 1 handlebar
Tires: Front 120/70-R12, Rear 135/70-R12
Features: Front and rear disc brakes, Al…
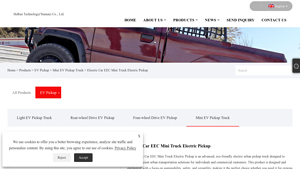
4. Mini Electric Pickup – Electric Car EEC Mini Truck
Domain: minielectricpickup.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “Electric Car EEC Mini Truck Electric Pickup”, “Key Features”: {“Environmentally Friendly”: “Utilizes pure electric power with zero tailpipe emissions.”, “Powerful Performance”: “Equipped with efficient battery technology and electric motor system for outstanding power performance and extended range.”, “Multi-Functional Design”: “Spacious cargo space for goods transport, express d…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for eec electric car
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business with EEC Electric Cars?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of EEC electric cars presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers seeking sustainable and cost-effective transportation solutions. With their ability to be charged at home, work, or central depots, EEC electric vehicles are particularly advantageous for fleet operators, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These vehicles not only help reduce fuel costs and carbon footprints but also align with the growing global emphasis on eco-friendly practices.
As businesses navigate the evolving landscape of electric vehicle technology, prioritizing quality and reliability in sourcing partners is essential. Manufacturers such as Taizhou Yunrong Technology Co., Ltd. and EDACAR EV Co., Ltd. exemplify the commitment to superior standards and innovative features that enhance the driving experience while adhering to international safety regulations.
Looking ahead, the demand for electric vehicles is set to rise significantly. Now is the time for B2B buyers to engage with reputable suppliers to secure advantageous terms and foster long-term partnerships. Embrace the future of transportation today—choose EEC electric cars to drive your business toward a more sustainable tomorrow.