Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric car cargo for goods delivery
In today’s rapidly evolving logistics landscape, sourcing electric car cargo for goods delivery presents a unique challenge for businesses aiming to enhance efficiency while reducing their carbon footprint. As global markets increasingly prioritize sustainability, the demand for electric delivery vehicles is on the rise. This comprehensive guide addresses the critical aspects of integrating electric cargo solutions into your supply chain, covering various vehicle types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries such as Vietnam and Saudi Arabia—will find actionable insights tailored to their specific market dynamics. This guide empowers decision-makers by offering a deep dive into the advantages of electric cargo vehicles, from their impressive payload capacities to their operational efficiencies in urban environments.
Moreover, we explore the latest innovations in electric vehicle technology, ensuring your business stays competitive in the global market. By navigating through supplier options and understanding the financial implications of adopting electric delivery solutions, you can make informed purchasing decisions that align with your sustainability goals and operational needs. Whether you’re looking to transition your fleet or expand your delivery capabilities, this guide serves as an essential resource for driving your business forward in the electrified logistics era.
Understanding electric car cargo for goods delivery Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| All-Electric Cargo Vans | Purpose-built, high payload capacity, AC/DC charging | Last-mile delivery, logistics | Pros: Large cargo space, zero emissions. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Walk-In Electric Delivery Vans | Spacious interior, designed for easy loading/unloading | Urban deliveries, courier services | Pros: Enhanced accessibility, reduced driver fatigue. Cons: Limited range compared to smaller vans. |
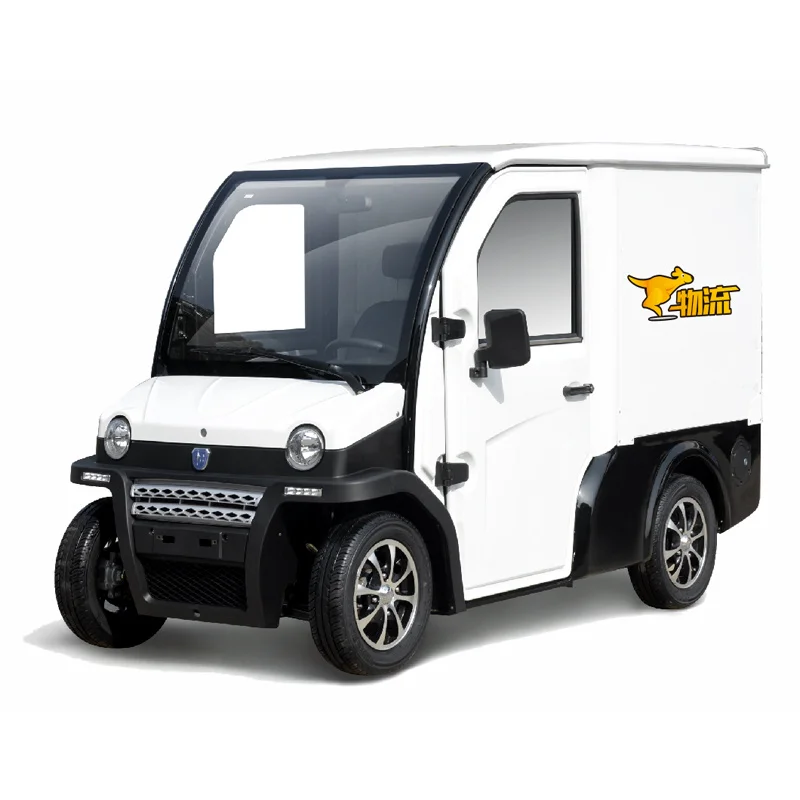
| Compact Electric Delivery Vehicles | Small size, high maneuverability, short turning radius | City deliveries, restricted access areas | Pros: Ideal for dense urban areas, lower operating costs. Cons: Limited payload capacity. |
| Electric Box Trucks | Larger cargo space, suitable for heavy loads | Freight transport, regional distribution | Pros: High payload, versatile applications. Cons: Requires more charging infrastructure. |
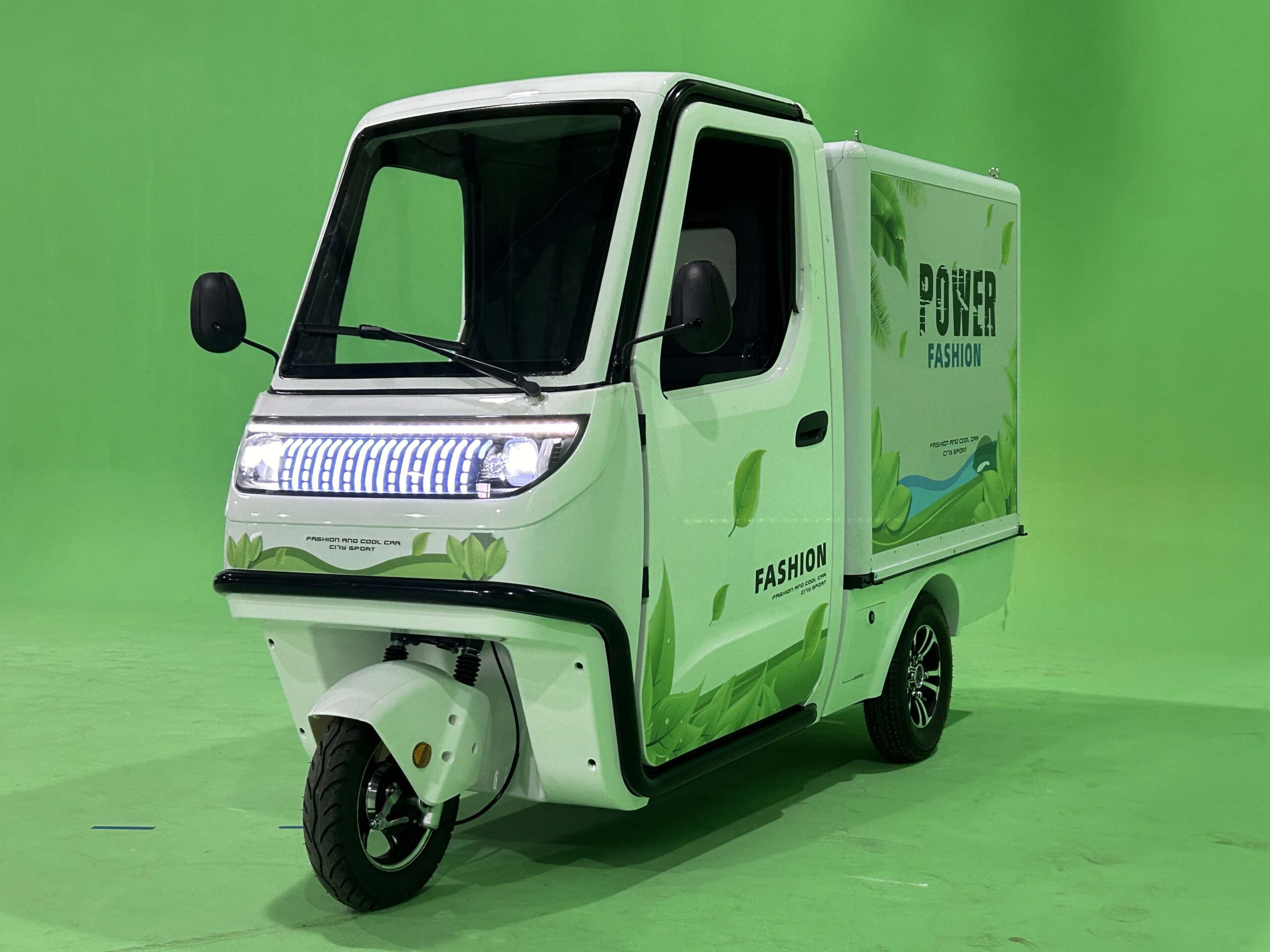
| Specialty Electric Vehicles | Customizable designs for specific delivery needs | Niche markets, specialized deliveries | Pros: Tailored solutions, can access hard-to-reach areas. Cons: Potentially higher costs and longer lead times. |
What Are the Characteristics of All-Electric Cargo Vans?
All-electric cargo vans are designed for high payload capacities, often exceeding 6,000 lbs, making them ideal for last-mile delivery and logistics. They typically feature dual charging options (AC/DC) for flexibility and can cover ranges up to 150 miles on a single charge. B2B buyers should consider the upfront investment versus long-term savings on fuel and maintenance, as these vehicles significantly reduce operational costs over time.
How Do Walk-In Electric Delivery Vans Enhance Urban Logistics?
Walk-in electric delivery vans, such as the BrightDrop Zevo series, offer spacious interiors that facilitate easy loading and unloading, making them particularly effective for urban deliveries. With a range of up to 272 miles, they are suitable for both city and highway operations. Buyers should evaluate the trade-off between range and interior space to optimize their delivery efficiency while ensuring compliance with sustainability goals.
Why Choose Compact Electric Delivery Vehicles for City Deliveries?
Compact electric delivery vehicles are specifically designed for tight urban environments, featuring a small footprint and exceptional maneuverability. They excel in navigating narrow streets and restricted access areas, making them perfect for city deliveries. While they have a lower payload capacity, their operational costs are significantly reduced, making them an attractive option for businesses focused on last-mile solutions.
What Advantages Do Electric Box Trucks Offer for Freight Transport?
Electric box trucks are ideal for freight transport and regional distribution, providing ample cargo space and the ability to handle heavier loads. Their versatility makes them suitable for various B2B applications, although they may require more robust charging infrastructure. Buyers should assess their distribution needs and charging capabilities to maximize the efficiency of these larger vehicles.
How Can Specialty Electric Vehicles Meet Unique Delivery Needs?
Specialty electric vehicles can be customized for specific delivery requirements, making them perfect for niche markets and specialized deliveries. Their tailored designs allow access to hard-to-reach areas, which can be a significant advantage for businesses operating in unique environments. However, potential buyers should be aware of the longer lead times and higher costs associated with these customized solutions.
Key Industrial Applications of electric car cargo for goods delivery
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric car cargo for goods delivery | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-commerce | Last-mile delivery in urban areas | Reduces delivery times and costs while enhancing customer satisfaction | Vehicle range, cargo capacity, and charging infrastructure |
| Food and Beverage | Grocery and meal delivery services | Ensures fresh product delivery and compliance with health regulations | Temperature control options, payload capacity, and reliability |
| Healthcare | Medical supply and equipment transportation | Facilitates timely delivery of critical supplies, improving patient care | Regulatory compliance, specialized cargo space, and safety features |
| Retail | Inventory restocking and merchandise distribution | Increases operational efficiency and reduces carbon footprint | Vehicle size, maneuverability in urban settings, and fleet management capabilities |
| Tourism and Hospitality | Deliveries to hotels, resorts, and tourist attractions | Enhances guest experience and supports local businesses | Vehicle accessibility, loading capacity, and local regulations |
How Can Electric Car Cargo Improve Last-Mile Delivery for E-commerce?
In the fast-paced world of e-commerce, electric car cargo vehicles are becoming essential for last-mile delivery in urban areas. With their zero emissions, these vehicles align with sustainability goals while enabling rapid deliveries. They solve the problem of traffic congestion and parking limitations in city centers, allowing businesses to enhance customer satisfaction through timely service. For international buyers, considerations include ensuring the vehicle has adequate range and cargo capacity to meet varying delivery demands, along with access to charging infrastructure.
What Role Do Electric Delivery Vehicles Play in Food and Beverage Distribution?
Electric cargo vans are increasingly utilized for grocery and meal delivery services, especially in regions where fresh produce must be delivered quickly. These vehicles help maintain compliance with health regulations by ensuring timely deliveries of temperature-sensitive items. Buyers should consider options for temperature control, sufficient payload capacity, and the reliability of the vehicle in various weather conditions, particularly in regions with extreme climates like the Middle East or South America.
How Are Electric Vehicles Enhancing Healthcare Supply Chains?
In healthcare, electric cargo vehicles are vital for transporting medical supplies and equipment. Timely delivery can be critical for patient care, making the reliability of these vehicles paramount. Electric options can reduce operational costs associated with fuel and maintenance. When sourcing, international buyers must focus on regulatory compliance, specialized cargo space for sensitive items, and advanced safety features to protect drivers and cargo.
Why Are Retailers Turning to Electric Cargo Vans for Inventory Management?
Retail businesses are increasingly adopting electric cargo vans for efficient inventory restocking and merchandise distribution. These vehicles not only reduce operational costs but also contribute to lower carbon footprints, enhancing brand reputation. Retailers should consider vehicle size and maneuverability, especially in densely populated urban areas where traditional delivery vehicles may struggle. Fleet management capabilities are also essential for tracking deliveries and optimizing routes.
How Do Electric Delivery Vehicles Support the Tourism and Hospitality Sector?
In the tourism and hospitality industry, electric cargo vehicles are used to deliver supplies to hotels, resorts, and attractions. By improving delivery efficiency, these vehicles enhance the overall guest experience and support local businesses. Buyers in this sector should focus on vehicle accessibility, loading capacity for bulk supplies, and compliance with local regulations regarding emissions and transport. This ensures smooth operations and a positive impact on the environment.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric car cargo for goods delivery’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Range and Charging Infrastructure Challenges
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are concerned about the limited range of electric cargo vehicles, which can vary significantly between models. For businesses engaged in goods delivery, especially in regions like Africa and South America, the availability of reliable charging infrastructure can be sparse. This can result in delivery delays and operational inefficiencies, particularly when vehicles run out of battery during transit or have to return to base for charging.
The Solution: To mitigate range anxiety, B2B buyers should prioritize electric cargo vehicles with higher battery capacities and extended range capabilities. For instance, models such as the BrightDrop Zevo offer up to 272 miles of range, making them suitable for longer delivery routes. Additionally, companies should invest in establishing their own charging stations at strategic locations, particularly in depots or distribution centers. This can be complemented by utilizing mobile charging solutions for on-the-go charging. Collaborating with local governments or businesses to expand charging networks in underserved areas can further enhance operational efficiency and reliability.
Scenario 2: Payload Capacity and Vehicle Suitability Concerns
The Problem: Another common challenge faced by B2B buyers is ensuring that electric cargo vehicles can handle the necessary payload for their specific delivery needs. Many electric vans on the market may not have the same payload capacities as traditional combustion engine vehicles, which can lead to logistical issues, particularly for businesses that require transporting heavy or bulky items.
The Solution: Buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their delivery requirements and compare these needs against the specifications of available electric cargo models. For example, the EV Star Cargo has a payload capacity of up to 6,300 lbs, making it a viable option for heavy-duty deliveries. Engaging with manufacturers to understand customization options can also help tailor vehicles to specific needs, such as adding shelving or specialized storage solutions. By investing in vehicles designed for their operational demands, businesses can optimize their delivery processes without sacrificing performance.
Scenario 3: High Initial Costs and Financing Options
The Problem: The transition to electric cargo vehicles often involves significant upfront costs, which can be a barrier for many businesses, especially small and medium enterprises. This financial hurdle is compounded by the uncertainty surrounding potential savings from reduced fuel and maintenance costs, leading to hesitation in adopting electric vehicles.
The Solution: B2B buyers should explore various financing options, such as leasing arrangements, government incentives, and grants specifically designed for electric vehicle purchases. For instance, manufacturers like GM’s BrightDrop offer leasing programs that can reduce initial capital expenditures. Additionally, conducting a total cost of ownership analysis can provide insights into long-term savings, emphasizing the reduction in fuel and maintenance costs. Engaging with financial consultants who specialize in green technology can also help businesses navigate available financial solutions, ensuring a smoother transition to an electric fleet while optimizing cash flow.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric car cargo for goods delivery
What Are the Key Materials Used in Electric Car Cargo for Goods Delivery?
When selecting materials for electric car cargo solutions aimed at goods delivery, international B2B buyers must consider various factors including durability, cost, and specific regional requirements. Here, we analyze four common materials used in this context: aluminum, steel, composite materials, and plastics.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Electric Car Cargo Applications?
Aluminum is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal that offers excellent strength-to-weight ratios, making it a popular choice for electric vehicle (EV) cargo applications. Its key properties include a temperature rating up to 600°F and high resistance to corrosion, which is critical for vehicles operating in diverse environments.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight nature enhances vehicle efficiency and range. It is also relatively easy to manufacture and can be extruded into various shapes, making it versatile for cargo designs.
Cons: The primary drawback is its higher cost compared to steel, which may be a concern for budget-sensitive buyers. Additionally, while aluminum is durable, it can be less impact-resistant than steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly suitable for applications requiring weight savings, such as last-mile delivery vehicles operating in urban environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B209 for aluminum sheet and plate is essential. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should also consider local availability and cost fluctuations.
What Role Does Steel Play in Electric Car Cargo Solutions?
Steel, particularly high-strength steel, is another common material used in cargo applications. It boasts high tensile strength and is capable of withstanding significant loads, making it ideal for heavy-duty cargo vehicles.
Pros: Steel is generally more affordable than aluminum and offers excellent durability and impact resistance. Its availability worldwide makes it a reliable choice for manufacturers.
Cons: The weight of steel can negatively impact the vehicle’s overall efficiency and range. Additionally, steel is prone to corrosion, necessitating protective coatings, which can increase manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Steel is particularly effective in applications requiring high strength and durability, such as transporting heavy goods over long distances.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards like ASTM A36 for structural steel. In regions with high humidity, additional corrosion resistance measures may be necessary.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Electric Car Cargo Performance?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, are increasingly being used in electric vehicle cargo applications due to their high strength-to-weight ratios and resistance to environmental factors.
Pros: Composites are lightweight, which can significantly enhance vehicle range and efficiency. They also offer excellent corrosion resistance and can be molded into complex shapes.
Cons: The primary limitations are the higher manufacturing costs and complexity associated with producing composite materials. Additionally, they may not be as widely available as metals.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly beneficial in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in urban delivery vehicles that require frequent stops and starts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM D3039 for tensile properties is crucial. Buyers should also assess local capabilities for composite manufacturing.
What Advantages Do Plastics Offer in Electric Car Cargo Design?
Plastics, particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene, are often used in electric vehicle cargo applications due to their lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties.
Pros: Plastics are cost-effective and can be easily molded into various shapes, allowing for flexibility in cargo design. They are also resistant to chemicals and moisture, making them suitable for various cargo types.
Cons: While durable, plastics can be less impact-resistant than metals and may degrade over time when exposed to UV light unless treated.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for lightweight cargo solutions, especially for goods that do not require heavy-duty protection.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM D638 for plastic tensile properties is essential. Buyers should also consider the environmental impact of plastic materials and their recyclability.
Summary Table of Strategic Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for Electric Car Cargo for Goods Delivery | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight cargo solutions for urban deliveries | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost than steel | High |
| Steel | Heavy-duty cargo applications for long-distance transport | Excellent durability and impact resistance | Heavier, prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Composites | Lightweight, complex-shaped cargo designs | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| Plastics | Cost-effective, flexible cargo solutions | Easy to mold and lightweight | Less impact-resistant, UV degradation | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with valuable insights into the various materials available for electric car cargo applications, helping them make informed decisions tailored to their specific operational needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric car cargo for goods delivery
What Are the Main Stages in Manufacturing Electric Car Cargo for Goods Delivery?
The manufacturing process for electric car cargo vehicles is multifaceted and involves several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality, reliable vehicles suitable for goods delivery.
Material Preparation
The first stage in manufacturing involves sourcing and preparing materials. Key materials include high-strength steel for the chassis, lightweight aluminum for body components, and advanced composite materials for energy efficiency. Suppliers must adhere to strict quality standards to ensure the integrity of these materials. For instance, steel must meet specifications for tensile strength, while battery components should be sourced from manufacturers that comply with international safety standards.
Forming
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This includes processes like stamping, bending, and welding to create the vehicle’s structure. Advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often employed for precision shaping of components. Techniques like hydroforming may also be utilized to create complex shapes that enhance aerodynamics and structural integrity. Each forming technique must be monitored to ensure it meets design specifications and tolerances.
Assembly
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form the finished vehicle. This process typically follows a modular assembly line approach, allowing for efficiency and flexibility. Key components, including the battery pack, electric motors, and control systems, are integrated during this phase. Skilled technicians oversee the assembly to ensure that components fit correctly and function as intended. Automated systems are also increasingly used to improve precision and reduce human error.
Finishing
The final manufacturing stage is finishing, which involves surface treatments, painting, and installing the vehicle’s interior. This stage not only enhances aesthetics but also provides protective coatings to prevent corrosion and wear. Quality checks at this stage ensure that the vehicle meets both visual and functional standards. Technologies such as robotic painting systems are utilized to ensure a consistent finish, while rigorous inspections are conducted to identify any defects.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Electric Car Cargo Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of electric car cargo vehicles, ensuring that each vehicle meets international and industry-specific standards.
What International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Assurance?
For electric vehicle manufacturers, adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential. This standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures that organizations consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, compliance with CE marking is crucial for products sold in the European market, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is typically broken down into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint ensures that all incoming materials meet specified standards before being used in production. Testing may include material property verification and dimensional checks.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the assembly phase, IPQC is used to monitor the manufacturing process. Random inspections and measurements are taken to ensure that components are being assembled correctly and that machines are functioning within specified tolerances.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, FQC involves comprehensive testing of the entire vehicle. This includes road tests, battery performance evaluations, and safety feature checks. Vehicles must pass these tests to be deemed ready for delivery.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Electric Vehicles?
Various testing methods are employed to evaluate the performance and safety of electric car cargo vehicles:
-
Battery Testing: This includes cycle testing to determine battery life, capacity testing to ensure it meets specifications, and safety testing for thermal and electrical stability.
-
Crash Testing: Compliance with safety regulations is verified through crash tests, which assess the vehicle’s structural integrity and occupant safety during impact.
-
Environmental Testing: These tests evaluate how vehicles perform under extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or humidity, ensuring reliability across diverse climates.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is vital for ensuring product reliability and compliance.
What Audit Processes Should Buyers Consider?
Buyers should conduct regular audits of potential suppliers, focusing on their manufacturing processes and QC systems. This can include site visits to observe production practices, review documentation, and meet with QA personnel. Third-party inspections can also provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality assurance measures.
How Can Buyers Utilize Reports and Certifications?
Requesting detailed quality assurance reports from suppliers is essential. These reports should outline the methodologies used in QC processes, results from testing, and compliance with relevant standards. Certifications from recognized bodies, such as ISO, can also provide assurance of a supplier’s commitment to quality.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers need to navigate various QC nuances that can affect procurement. Understanding local regulations and standards is crucial, as these can vary significantly between regions. Additionally, language barriers and differences in business practices may pose challenges in ensuring quality compliance.
What Should Buyers Look for in Terms of Supplier Communication?
Effective communication is key in managing quality assurance across borders. Buyers should establish clear lines of communication with suppliers, ensuring that expectations regarding quality standards and delivery timelines are understood. Regular updates and feedback loops can help mitigate issues before they escalate.
How Can Buyers Leverage Technology for Quality Assurance?
Utilizing technology, such as cloud-based monitoring systems, can enhance visibility into supplier processes. These systems allow buyers to track production progress in real-time, receive alerts for any deviations from quality standards, and maintain an ongoing assessment of supplier performance.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for electric car cargo vehicles, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers capable of delivering high-quality, sustainable products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric car cargo for goods delivery’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure electric cars specifically designed for cargo delivery. As the demand for sustainable logistics solutions grows, understanding the nuances of electric vehicle (EV) procurement is essential for making informed decisions that align with operational needs, budget constraints, and sustainability goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline the technical requirements of the electric cargo vehicles. Consider factors such as payload capacity, range, and battery specifications.
- Payload Capacity: Ensure the vehicle can handle the weight of the goods you plan to transport. For instance, some models offer payload capacities up to 6,300 lbs, which may be necessary for larger deliveries.
- Range: Evaluate the distance the vehicle can cover on a single charge, aiming for models with a minimum range that meets your operational needs, ideally up to 272 miles for flexibility in logistics.
Step 2: Assess Charging Infrastructure Needs
Understanding your charging infrastructure is vital for seamless operations. Determine whether you require a Level 2 AC charger or a DC fast charger based on your fleet size and delivery schedules.
- Charging Time: Investigate the charging times associated with different models. For example, some vehicles can charge in as little as two hours with DC fast charging.
- Location of Charging Stations: Consider the availability of charging stations in your operational areas, especially for urban deliveries where access may be limited.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they align with your business goals and values. Request company profiles, references, and information about their after-sales support.
- Supplier Reputation: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in delivering electric cargo vehicles. Consider their experience in your specific region, as local regulations and support may vary.
- Customer Testimonials: Reach out to existing customers for insights into their experiences with the supplier and the vehicles’ performance in real-world conditions.
Step 4: Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Beyond the initial purchase price, assess the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, insurance, and operational costs.
- Maintenance Costs: Electric vehicles typically have lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts. Evaluate warranties and service agreements to mitigate unexpected expenses.
- Fuel Savings: Calculate potential savings from reduced fuel costs, especially in markets where fuel prices are high. Electric vehicles can significantly decrease your overall operating expenses.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the electric cargo vehicles comply with local emissions and safety regulations. This step is crucial for avoiding potential fines and operational disruptions.
- Certification and Standards: Check for certifications such as ISO or local government approvals that validate the vehicle’s compliance with environmental standards.
- Incentives: Research available government incentives for electric vehicle adoption in your region, which can reduce upfront costs and enhance ROI.
Step 6: Plan for Training and Integration
Implementing a new fleet of electric cargo vehicles requires training for drivers and logistics personnel.
- Driver Training: Ensure that drivers receive proper training on operating electric vehicles, including charging procedures and understanding vehicle-specific technology.
- Integration with Logistics Systems: Consider how the new vehicles will integrate with your existing logistics and tracking systems to maintain operational efficiency.
Step 7: Establish a Sustainability Framework
Align your electric vehicle procurement with your company’s sustainability goals to maximize the benefits of going electric.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Evaluate the potential reduction in carbon footprint and how this aligns with your brand’s commitment to sustainability.
- Reporting and Accountability: Develop metrics for tracking the performance of electric vehicles in terms of efficiency and emissions reduction to report on your sustainability initiatives.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electric cargo vehicles, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and a positive environmental impact.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric car cargo for goods delivery Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Electric Car Cargo Used in Goods Delivery?
When evaluating the costs associated with electric car cargo for goods delivery, various components play a critical role in determining the overall expense structure. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The primary material costs stem from the vehicle’s electric powertrain, battery systems, and lightweight composite materials used in the body. High-quality batteries, such as the 118 kWh options in the EV Star Cargo, can significantly influence costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce needed for vehicle assembly, programming, and maintenance. Skilled technicians may demand higher wages, particularly in regions with labor shortages.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facilities, utilities, and equipment used in the production process. Efficient manufacturing practices can help reduce these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized tools and machinery can be substantial but is essential for producing custom configurations. The tooling costs can be amortized over production runs, influencing unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that vehicles meet safety and performance standards incurs costs associated with testing and compliance. A robust QC process can prevent future warranty claims and enhance brand reputation.
-
Logistics: Transportation of finished vehicles to distribution points can add to the cost, especially if shipping internationally. Factors such as fuel prices and shipping routes can affect these logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Finally, the supplier’s desired profit margin will impact the final price. Suppliers often adjust margins based on market demand and competition.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Electric Cargo Vehicle Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of electric cargo vehicles, which are crucial for B2B buyers to consider.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often qualify for volume discounts, reducing the per-unit price. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can also affect negotiations.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can raise costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and any necessary certifications can drive up costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of using premium materials against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and production capabilities of suppliers can significantly influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer more reliable products but at a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding international shipping terms is essential. The choice of Incoterms can dictate who bears the cost and risk during transportation, affecting the total cost of ownership.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Ensure Cost-Efficiency in Electric Cargo Vehicle Purchases?
B2B buyers must adopt a strategic approach to sourcing electric cargo vehicles to maximize cost-efficiency.
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage in discussions with suppliers to explore flexible payment terms, discounts, and other options. Building a strong relationship can lead to better deals.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assess not just the purchase price but also operational costs such as maintenance, charging, and potential tax incentives. TCO gives a more comprehensive view of the investment.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances in International Markets: Different regions may have varying regulations, taxes, and import duties that affect pricing. Familiarize yourself with these factors to avoid surprises.
-
Leverage Local Partnerships: Establishing connections with local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and improve service responsiveness, particularly in regions with complex delivery environments.
In summary, the cost structure for electric car cargo vehicles encompasses multiple components, each influenced by specific pricing factors. By understanding these elements and applying strategic sourcing techniques, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational and financial goals.
Disclaimer: The prices discussed are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and regional factors. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric car cargo for goods delivery With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives for Goods Delivery
In the rapidly evolving landscape of logistics and delivery, the advent of electric car cargo solutions presents a compelling option for businesses seeking sustainable and efficient delivery methods. However, it is essential to evaluate alternatives that may also address the diverse needs of international B2B buyers. This section compares electric car cargo for goods delivery with two viable alternatives: traditional diesel vans and electric bicycles, highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Car Cargo For Goods Delivery | Traditional Diesel Vans | Electric Bicycles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Up to 150 miles range; 6,300 lbs payload | 400+ miles range; variable payload | 20-50 miles range; 300-500 lbs payload |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost; lower operational costs | Lower upfront cost; higher fuel and maintenance costs | Low upfront cost; minimal operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure; longer setup | Established infrastructure; quick adoption | Easy to integrate; minimal infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; fewer moving parts | Moderate maintenance; frequent servicing | Very low maintenance; easy repairs |
| Best Use Case | Mid to last-mile delivery in urban areas | Long-distance transport; larger cargo | Short-distance deliveries in congested areas |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Traditional Diesel Vans
Traditional diesel vans have long been the backbone of logistics and delivery services. With a range exceeding 400 miles, they are ideal for long-distance routes and can handle significant payloads. However, their operational costs can be high due to fuel expenses and regular maintenance. Additionally, increasing regulations on emissions may limit their viability in urban areas. For businesses operating in regions with stringent environmental standards, transitioning away from diesel may soon become necessary.
Electric Bicycles
Electric bicycles represent a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative for short-distance deliveries, particularly in congested urban areas. With minimal operational costs and low maintenance requirements, they offer an agile solution for navigating narrow streets and avoiding traffic. However, their limited range and payload capacity may not meet the needs of businesses requiring larger deliveries. Electric bicycles excel in last-mile logistics, making them suitable for courier services and small businesses focused on sustainability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Delivery Solution
When selecting the best delivery solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational needs, including range, payload requirements, and cost-effectiveness. Electric car cargo options provide a sustainable and efficient choice for mid to last-mile deliveries, particularly in urban settings. However, businesses with longer delivery routes or those needing to navigate tight spaces may find traditional diesel vans or electric bicycles more suitable. Ultimately, the decision should align with the company’s logistics strategy, sustainability goals, and the unique challenges of their target markets in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric car cargo for goods delivery
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Car Cargo for Goods Delivery?
When considering electric vehicles for cargo and goods delivery, several technical specifications are crucial for B2B buyers. Understanding these properties will help businesses make informed decisions that align with operational needs and sustainability goals.
1. Payload Capacity
Payload capacity refers to the maximum weight an electric delivery vehicle can carry, typically measured in pounds or kilograms. For instance, vehicles like the EV Star Cargo boast payload capacities of up to 6,300 lbs, while the BrightDrop Zevo can handle 3,180 lbs. This specification is vital for businesses as it determines how much product can be transported in a single trip, directly impacting efficiency and cost-effectiveness in logistics operations.
2. Range
Range indicates how far an electric vehicle can travel on a single charge, which is particularly important for last-mile delivery services. For example, the BrightDrop Zevo offers a range of up to 272 miles, while other models may provide between 150 to 200 miles. A longer range reduces downtime for charging and increases the number of deliveries that can be made within a specific time frame, making it a critical factor for B2B logistics planning.
3. Charging Options
Charging options encompass the types of charging systems available for the vehicle, including Level 2 AC and DC fast charging (DCFC). For instance, dual charging capabilities allow for flexibility in charging infrastructure. Understanding these options is essential for businesses to ensure that their electric vehicle fleet can be efficiently integrated into existing operations and that charging times align with delivery schedules.
4. Battery Capacity
Battery capacity, typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), indicates how much energy the vehicle’s battery can store. For example, the EV Star Cargo features an 118 kWh battery. A higher battery capacity generally translates to a longer range and the ability to support heavier payloads, which is crucial for operational efficiency. It also impacts the vehicle’s overall performance and lifespan, making it a key consideration for B2B buyers.
5. Vehicle Dimensions
Vehicle dimensions, including length, width, and height, affect maneuverability, especially in urban environments where space is limited. Smaller vehicles with compact designs can navigate narrow streets and fit into tight parking spaces, which is essential for urban deliveries. Understanding the dimensions helps businesses select vehicles that meet their specific delivery route requirements.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Electric Car Cargo for Goods Delivery?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for B2B buyers to navigate procurement and logistics effectively. Here are several common trade terms relevant to electric car cargo for goods delivery.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce components or vehicles that are sold under another company’s brand name. For instance, a vehicle manufacturer might produce electric delivery vans that are branded by a logistics company. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers evaluate product quality and warranty services.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant for B2B buyers looking to procure electric vehicles in bulk. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases effectively and negotiate better terms with suppliers.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This is common in B2B transactions, especially when sourcing electric vehicles. A well-structured RFQ helps ensure that buyers receive competitive pricing and terms.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms, such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is crucial for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs and liability during transport.
5. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO refers to the comprehensive assessment of all costs associated with owning and operating a vehicle over its entire lifecycle, including purchase price, maintenance, insurance, and fuel costs. Understanding TCO is essential for B2B buyers to evaluate the long-term financial impact of investing in electric delivery vehicles.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and contribute to sustainability goals in their logistics operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric car cargo for goods delivery Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in Electric Car Cargo for Goods Delivery?
The electric car cargo sector is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. The rising demand for sustainable logistics solutions is a primary driver, with businesses increasingly seeking to reduce their carbon footprints. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, government regulations promoting electric vehicles (EVs) and incentives for adopting green technologies are encouraging fleet operators to transition to electric cargo solutions. Furthermore, the surge in e-commerce and the need for efficient last-mile delivery services are propelling the demand for electric delivery vehicles.
Emerging technologies such as telematics and route optimization software are reshaping sourcing trends. These technologies enable businesses to track vehicle performance, manage maintenance schedules, and optimize delivery routes, ultimately improving operational efficiency. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources for vehicle charging is becoming increasingly important, especially in regions with abundant solar or wind resources, allowing companies to further lower their operational costs and enhance sustainability efforts.
International buyers should also be aware of the competitive landscape, which features a range of electric cargo vehicles catering to different needs—from compact vans ideal for urban deliveries to larger vehicles for extensive logistics operations. As manufacturers innovate and introduce new models with improved range and payload capacities, businesses must stay informed to select the most suitable solutions for their logistics requirements.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Your Business in the Electric Delivery Sector?
Sustainability is not just a buzzword; it is a critical component of operational strategy for companies in the electric car cargo sector. The environmental impact of traditional fossil fuel-powered delivery vehicles is significant, contributing to pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, electric vehicles offer a cleaner alternative, with zero tailpipe emissions and reduced overall energy consumption.
For B2B buyers, adopting electric cargo solutions is increasingly linked to brand reputation and customer expectations. Companies that prioritize sustainability are often viewed more favorably by consumers and partners alike, leading to increased loyalty and market competitiveness. Additionally, ethical sourcing practices are vital; this includes ensuring that materials used in electric vehicles are sourced responsibly and that supply chains adhere to fair labor practices.
As part of a commitment to sustainability, businesses should also look for certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications that validate their efforts in promoting sustainable practices. By aligning procurement strategies with sustainability goals, companies can drive positive environmental change while enhancing their market position.
How Has the Electric Cargo Delivery Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the electric car cargo sector can be traced back to the increasing awareness of environmental issues and the need for sustainable transport solutions. Initially, electric vehicles were limited in range and performance, hindering their adoption in commercial applications. However, advancements in battery technology and a growing network of charging infrastructure have significantly improved the viability of electric delivery vehicles.
Over the past decade, major automotive manufacturers have entered the electric cargo market, introducing a variety of models tailored to different logistical needs. This has created a more competitive landscape, driving innovation and reducing costs. As a result, electric delivery vehicles have gained traction, becoming a practical choice for businesses looking to enhance their delivery capabilities while minimizing their environmental impact.
In summary, the electric car cargo sector is not only a response to market demand but also a strategic move towards sustainable and efficient logistics. By staying abreast of market dynamics and sourcing trends, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and sustainability objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric car cargo for goods delivery
-
How do I choose the right electric cargo vehicle for my delivery needs?
Selecting the appropriate electric cargo vehicle involves assessing your specific delivery requirements, including payload capacity, range, and the type of goods transported. Evaluate the vehicle’s specifications against your operational needs, such as daily mileage and delivery frequency. Consider factors like charging infrastructure in your area, potential incentives for electric vehicle adoption, and the vehicle’s ability to navigate urban environments, particularly in regions with strict emissions regulations. -
What are the key benefits of using electric cargo vehicles for goods delivery?
Electric cargo vehicles offer numerous advantages, including reduced operational costs due to lower fuel expenses and maintenance requirements. They also contribute to sustainability efforts by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality, especially in urban areas. Additionally, many regions offer tax incentives or subsidies for electric vehicle purchases, which can further enhance cost-effectiveness and support a company’s green initiatives. -
What is the typical range of electric cargo vehicles?
The range of electric cargo vehicles varies by model, but many options on the market provide between 150 to 272 miles on a single charge. It’s essential to choose a vehicle that meets your daily delivery route requirements. Additionally, consider charging options and times, as some vehicles support fast charging, significantly reducing downtime during operations. -
How do I vet suppliers of electric cargo vehicles?
To effectively vet suppliers, conduct thorough research into their reputation, experience, and customer reviews. Request references and case studies that demonstrate successful deployments in similar markets. Evaluate their support services, including warranty, maintenance, and parts availability. It’s also beneficial to visit their facilities if possible, ensuring they adhere to quality standards and best practices in manufacturing. -
What customization options are available for electric cargo vehicles?
Many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor electric cargo vehicles to specific business needs. These can include modifications to the cargo area, such as shelving or refrigeration units, and branding opportunities like decals or wraps. Discuss your requirements with the supplier, as they may also offer bespoke solutions to accommodate unique operational demands or regulatory compliance. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for electric cargo vehicles?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers. Some manufacturers may allow single-unit purchases, while others might require bulk orders to provide competitive pricing. It’s advisable to discuss your needs directly with suppliers to explore options that fit your business model, especially if you are looking to establish a long-term partnership. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing electric cargo vehicles?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier and the size of the order. Common arrangements include upfront payments, financing options, or leasing agreements. Be sure to clarify the payment structure, including any deposits required, installment plans, and the availability of financing through third-party institutions. Understanding these terms will help in budgeting for your vehicle acquisition. -
How do I ensure the quality of electric cargo vehicles before purchase?
To guarantee quality, request detailed product specifications and certifications from the supplier. Conduct pre-purchase inspections or arrange for third-party assessments of the vehicles. Additionally, inquire about the manufacturer’s quality assurance processes and warranties. It’s also beneficial to review feedback from existing customers to gauge performance and reliability in real-world conditions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Electric Car Cargo For Goods Delivery Manufacturers & Suppliers List
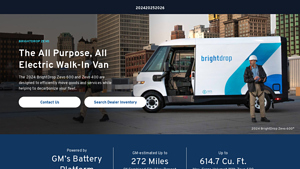
1. BrightDrop – Zevo 600 & Zevo 400 Electric Delivery Vehicles
Domain: gmenvolve.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: 2024 BrightDrop Zevo 600 and Zevo 400 electric delivery vehicles designed for efficient goods movement and fleet decarbonization. Key specifications include:
– Powered by GM’s Battery Platform
– Estimated range: Up to 272 miles (combined city/highway)
– Cargo volume: Zevo 600 – 614.7 cu. ft., Zevo 400 – 412.1 cu. ft.
– Lease offer: $599/month for 36 months, $2,999 due at signing
– Starting pr…
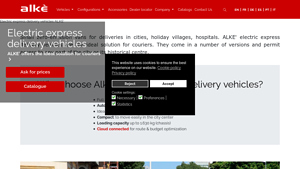
2. Alke – Electric Delivery Vehicles
Domain: alke.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Alke’ electric express delivery vehicles are designed for couriers and come in various versions suitable for urban environments. Key features include:
– Full electric with no circulation limits
– Autonomy of up to 200 km with a 20 kWh Lithium battery
– Maximum load capacity of 1,630 kg (chassis)
– Compact width of 138 cm for easy maneuverability in city centers
– Minimum turning radius of 260…
3. Westward Industries – MAX-EV Delivery Line
Domain: westwardindustries.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: MAX-EV Delivery Line includes two main models: MAX-EV 4 and MAX-EV 3. The MAX-EV 4 is a street-legal LSV (low-speed vehicle) designed for micro-distribution and last-mile delivery, capable of carrying nearly 66 cubic feet of cargo with an optional 1500lb payload. It features an industrial-grade build and a cargo van body, with a refrigerated option coming soon. The MAX-EV 3 is an electric mini car…
4. Matson – EV Transport Suspension
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Shipping Carrier Matson suspends EV transport effective immediately due to the risk of vehicle fires and lack of strategies to deal with EV fires.
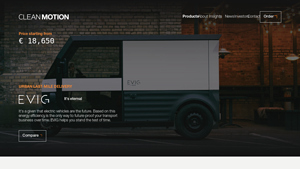
5. CleanMotion – EVIG
Domain: cleanmotion.se
Introduction: Product Name: EVIG
Price: Starting from € 18,650
Target Application Areas: Urban last-mile delivery, parcel and post, service management, pallet freight, temperature-sensitive goods transport.
Key Specifications:
– Max Speed: 60 km/h (available as motorcycle or moped)
– Cargo Space: 2.5 m³
– Cargo Weight: 350 kg
– Solar Power: 570 W
– Range: 100 / 200 km
Cost Efficiency:
– Purchasing Cost: 1/3 of…
6. IndigoTech – Smart EV Last-Mile Delivery Vehicles
Domain: indigotech.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Last-Mile Delivery vehicles are purpose-built Smart EVs designed for transporting and shipping packages, goods, and food. They feature a lightweight design that drives lower costs for Transportation as a Service, maximizing cargo space and operational efficiency. Key features include: Lower Total Cost of Ownership due to reduced maintenance costs and energy consumption; Maximized Efficiency and Ra…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric car cargo for goods delivery
The transition to electric car cargo for goods delivery represents a pivotal opportunity for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and sustainability. Key takeaways emphasize the significant advantages of electric vehicles, including reduced operational costs, lower emissions, and the ability to navigate urban environments with ease. Solutions such as the EV Star Cargo and BrightDrop Zevo offer robust payload capacities and impressive ranges, making them ideal for both last-mile delivery and larger logistics operations.
Strategic sourcing of electric delivery vehicles not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also positions companies to meet the rising demand for eco-friendly logistics solutions. As international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe consider their fleet options, the emphasis on total cost of ownership and the long-term benefits of electrification should guide their purchasing decisions.
Looking ahead, now is the time for businesses to invest in electric cargo solutions that will future-proof their operations and contribute positively to the environment. Engage with suppliers, explore available models, and take decisive action to integrate electric vehicles into your logistics strategy—it’s a step towards sustainable growth and competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving market.