Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric transport
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric transport, sourcing reliable and innovative solutions presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. As businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to transition to sustainable mobility options, understanding the diverse types of electric vehicles—ranging from electric bikes and scooters to more specialized options like electric unicycles and skateboards—becomes crucial. This comprehensive guide addresses the pressing need for informed decision-making in a market characterized by technological advancements and varied applications.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into the various types of electric transport, their applications in urban and rural settings, and key considerations for supplier vetting. We will also explore cost implications, performance metrics, and the regulatory landscape that influences purchasing decisions. By providing a thorough analysis of the electric transport market, this resource empowers B2B buyers to make strategic choices that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
As businesses navigate the complexities of integrating electric transport solutions, this guide serves as an essential tool for enhancing procurement strategies, fostering partnerships with credible suppliers, and ultimately, contributing to a greener future. Whether you are a buyer from Saudi Arabia, Vietnam, or beyond, understanding these dynamics is vital for leveraging the benefits of electric transport in your business operations.
Understanding electric transport Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Bikes | Two-wheeled, pedal-assist or throttle control, versatile | Last-mile delivery, employee commuting | Pros: Eco-friendly, physical activity; Cons: Bulky, limited range compared to cars |
| Electric Scooters | Stand-up design, lightweight, easy to maneuver | Urban transport, short-distance rentals | Pros: Compact, cost-effective; Cons: Limited cargo capacity, less stable than bikes |
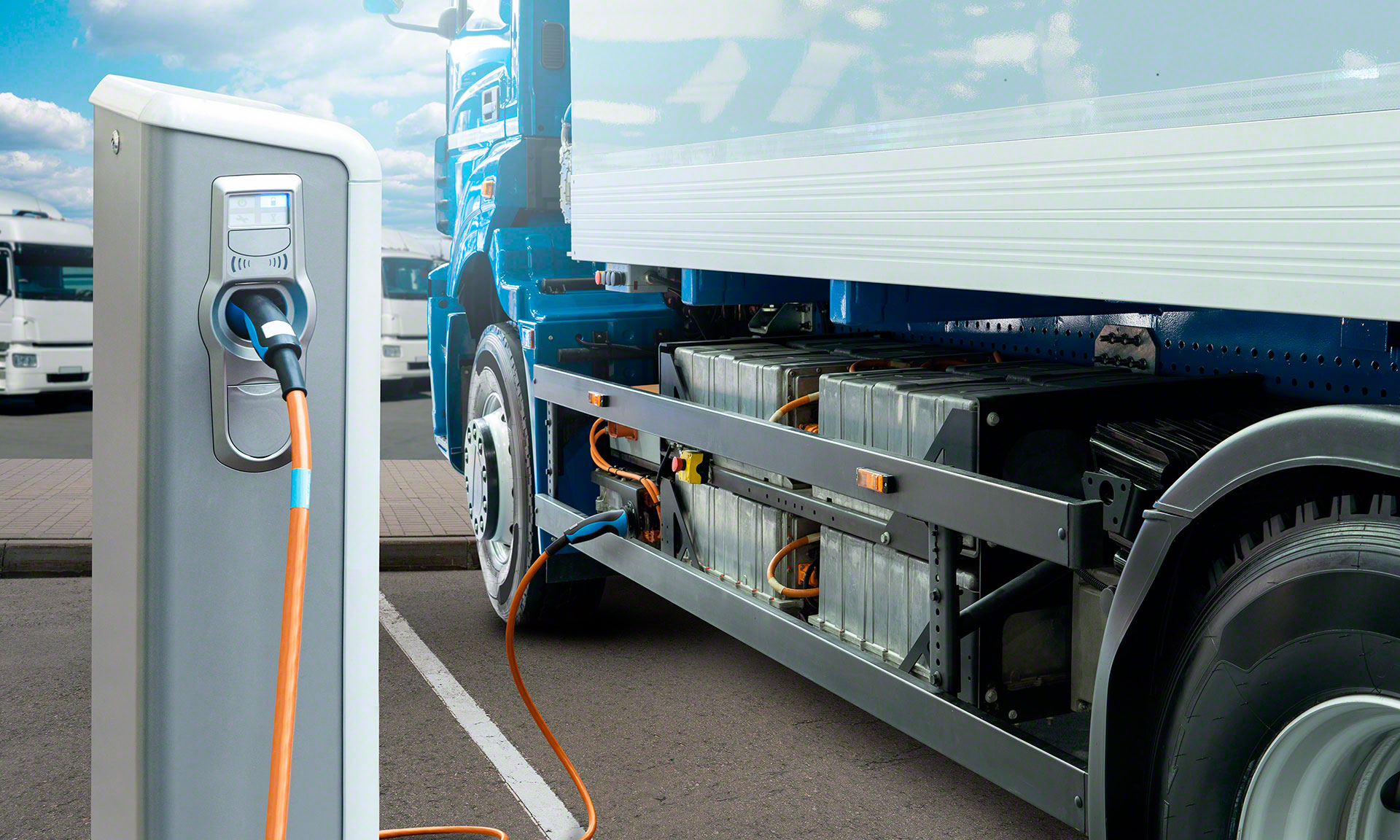
| Electric Cars | Four-wheeled, full electric power, longer range | Fleet operations, corporate transport | Pros: Zero emissions, high range; Cons: Higher upfront costs, charging infrastructure needed |
| Electric Skateboards | Board on four wheels, requires balance for steering | Recreational use, urban commuting | Pros: Fun, portable; Cons: Requires skill, limited cargo capacity |
| Hoverboards | Self-balancing, foot-controlled, compact | Leisure activities, short-distance travel | Pros: Easy to carry, intuitive; Cons: Learning curve, not suitable for rough terrain |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Electric Bikes for B2B Buyers?
Electric bikes (e-bikes) combine traditional cycling with electric power, offering a versatile commuting solution. They are particularly suitable for last-mile delivery services and employee commuting, especially in urban areas. B2B buyers should consider factors such as battery range, weight capacity, and maintenance needs. E-bikes promote sustainability while providing employees with a healthier transportation option, making them an attractive investment for businesses looking to enhance their green credentials.
How Can Electric Scooters Benefit Your Business Operations?
Electric scooters are lightweight, stand-up vehicles ideal for navigating urban environments. They are especially beneficial for short-distance rentals and urban transport solutions. B2B buyers must assess the scooter’s speed, battery life, and durability, as these factors impact operational efficiency. Their compact design allows for easy parking and storage, making them a practical choice for businesses aiming to reduce their carbon footprint while providing employees or customers with quick, accessible transport options.
Why Should Businesses Consider Electric Cars for Their Fleets?
Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular in corporate fleets due to their zero-emission capabilities and longer ranges. They are suitable for companies focused on sustainability and reducing operational costs associated with fuel. B2B buyers should evaluate the initial investment, available incentives, and the necessary charging infrastructure. While electric cars may have a higher upfront cost, they can lead to significant savings in fuel and maintenance over time, making them a sound long-term investment.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Skateboards?
Electric skateboards offer a unique mode of transport that is both fun and practical for urban commuting. They are particularly appealing for recreational use and short-distance travel. However, B2B buyers must consider the skill level required to operate them effectively, as well as their limited cargo capacity. Their portability makes them easy to store and transport, making them a viable option for businesses looking to cater to younger demographics or provide alternative commuting solutions.
How Do Hoverboards Compare to Other Electric Transport Options?
Hoverboards are compact, self-balancing devices that are easy to carry and operate. They are primarily used for leisure activities and short-distance travel. While they offer an intuitive riding experience, B2B buyers should be mindful of their learning curve and limitations on rough terrain. Hoverboards can serve as a fun, engaging way to promote mobility within urban environments, appealing to businesses targeting younger consumers or those looking to enhance their product offerings with innovative transport solutions.
Key Industrial Applications of electric transport
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric transport | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics and Delivery | Electric Delivery Vans | Reduced operational costs and lower emissions | Vehicle range, charging infrastructure, maintenance support |
| Urban Mobility | Electric Buses | Enhanced public transport efficiency and sustainability | Compliance with local regulations, vehicle capacity, and technology integration |
| Tourism and Recreation | Electric Scooters and Bikes | Increased customer satisfaction and eco-friendly options | Rental management systems, safety features, and local service availability |
| Manufacturing and Warehousing | Electric Forklifts and Pallet Trucks | Improved safety and reduced operational noise | Load capacity, battery life, and compatibility with existing infrastructure |
| Agricultural Transport | Electric Tractors | Lower fuel costs and reduced environmental impact | Terrain adaptability, battery performance, and service networks |
How is Electric Transport Revolutionizing Logistics and Delivery Operations?
In the logistics and delivery sector, electric delivery vans are becoming increasingly popular. These vehicles provide a sustainable alternative to traditional fuel-powered vans, significantly reducing operational costs through lower fuel expenditures and maintenance needs. Additionally, they help businesses comply with stringent emission regulations, particularly in urban areas. Buyers should focus on the vehicle’s range, availability of charging infrastructure, and after-sales maintenance support to ensure seamless operations.
What Role Do Electric Buses Play in Urban Mobility Solutions?
Electric buses are transforming urban mobility by offering efficient, eco-friendly public transport solutions. They help cities reduce air pollution and noise levels while improving the overall passenger experience. This application is particularly relevant in regions like Europe, where public transport is critical for urban planning. When sourcing electric buses, businesses must consider compliance with local regulations, vehicle capacity, and the integration of advanced technologies such as real-time tracking systems.
How Can Electric Scooters Enhance the Tourism Experience?
In the tourism and recreation sectors, electric scooters and bikes are increasingly being adopted as convenient mobility solutions for tourists. They provide an eco-friendly way for visitors to explore cities while enhancing customer satisfaction through ease of use and fun experiences. B2B buyers in this space should focus on sourcing scooters with robust rental management systems, safety features, and reliable local service availability to ensure a smooth operational flow.
What Benefits Do Electric Forklifts Offer in Manufacturing and Warehousing?
Electric forklifts and pallet trucks are becoming essential in manufacturing and warehousing environments. They enhance safety by reducing noise levels and minimizing the risk of accidents associated with gas-powered equipment. Additionally, they contribute to a cleaner workplace by eliminating harmful emissions. When sourcing electric forklifts, businesses must consider load capacity, battery life, and compatibility with existing warehouse systems to optimize operational efficiency.
How Are Electric Tractors Impacting Agricultural Transport?
Electric tractors are revolutionizing agricultural transport by providing a sustainable alternative to diesel-powered machinery. They significantly lower fuel costs and reduce the carbon footprint of farming operations, which is vital in regions facing environmental challenges. Buyers should assess the tractor’s adaptability to different terrains, battery performance under various agricultural conditions, and the availability of service networks to support ongoing operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric transport’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance for Electric Transport
The Problem:
B2B buyers in the electric transport sector often face significant challenges in navigating the regulatory landscape. Each region, especially across diverse markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, has its own set of laws regarding electric vehicles (EVs). Buyers may struggle with compliance issues related to safety standards, licensing, and insurance requirements. For instance, a company planning to introduce electric scooters in a new market may find it difficult to identify the specific regulations that govern the use of these vehicles, potentially leading to costly fines or the inability to operate.
The Solution:
To effectively address this pain point, B2B buyers should engage with local industry associations or consult legal experts specializing in transportation regulations. A comprehensive approach includes conducting thorough market research to understand the local laws and regulations governing electric transport. Buyers can also leverage technology, such as regulatory compliance software, that keeps them updated on changing laws. Additionally, developing relationships with local governments can provide insights into upcoming regulatory changes and help facilitate smoother entry into new markets. By prioritizing regulatory compliance from the outset, companies can avoid disruptions and foster a more favorable business environment.
Scenario 2: Limited Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles
The Problem:
One of the most significant challenges for businesses investing in electric transport is the lack of adequate charging infrastructure. In regions where electric vehicles are still gaining traction, such as parts of Africa and South America, buyers may find that the existing charging stations are few and far between. This limitation can hinder fleet operations and lead to concerns over the range of electric vehicles, ultimately affecting productivity and service delivery.
The Solution:
B2B buyers can address this issue by conducting a feasibility study to identify potential locations for installing charging stations. Partnering with local energy companies or municipalities can facilitate the development of a reliable charging network. Companies can also consider investing in mobile charging solutions or solar-powered charging stations, which are particularly beneficial in areas with limited access to the grid. By proactively developing charging infrastructure, businesses can enhance the operational efficiency of their electric fleets and provide a better service to their customers.
Scenario 3: High Initial Costs and Financing Options for Electric Transport
The Problem:
The upfront costs associated with acquiring electric transport vehicles can be a significant barrier for B2B buyers. This is particularly true for companies in developing markets where budgets are tighter, and the return on investment (ROI) period for electric vehicles may seem daunting. Buyers may hesitate to transition from traditional vehicles due to fears about financial viability and long-term sustainability.
The Solution:
To mitigate this financial challenge, B2B buyers should explore various financing options available for electric transport. This includes leasing agreements, government incentives, or grants aimed at promoting green technologies. Collaborating with financial institutions that specialize in green financing can also open up more favorable loan terms. Additionally, companies can conduct a cost-benefit analysis to demonstrate the long-term savings associated with reduced fuel costs and maintenance expenses compared to conventional vehicles. By clearly outlining the financial advantages and leveraging available funding, businesses can make informed decisions and confidently invest in electric transport solutions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric transport
What Are the Key Materials Used in Electric Transport Applications?
In the realm of electric transport, the selection of materials is crucial for optimizing performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in electric transport applications, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Electric Transport Applications?
Aluminum is a lightweight metal known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it a popular choice in electric vehicles (EVs) and electric bikes. Key properties include a high corrosion resistance and good thermal conductivity, which are essential for heat dissipation in battery systems.
Pros: Aluminum offers durability and is relatively easy to manufacture, allowing for complex shapes that can enhance aerodynamics. It is also recyclable, which aligns with sustainability goals.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which can be higher than other materials like steel. Additionally, while it is strong, aluminum can be less resilient under extreme impacts compared to some alloys.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly suitable for structural components and casings, but its performance can be affected by extreme temperatures, necessitating careful design considerations.
International Considerations: Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should be aware of compliance with standards such as EN and ASTM, particularly regarding safety and environmental regulations.
What Role Does Composite Materials Play in Electric Transport?
Composite materials, often a combination of fibers and resin, are increasingly used in electric transport for their high strength and low weight. They typically exhibit excellent fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance.
Pros: Composites can be tailored for specific applications, offering design flexibility and reduced weight, which enhances energy efficiency in electric vehicles.
Cons: The manufacturing process for composites can be complex and costly, requiring specialized equipment and expertise. Additionally, they may not be as easily recyclable as metals.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for body panels and interior components, but their performance can vary based on the specific resin and fiber used.
International Considerations: B2B buyers should consider compliance with international standards like ISO for material testing and performance, particularly in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
Why Is Steel Still Relevant in Electric Transport Manufacturing?
Steel remains a staple material in electric transport, particularly for structural components. It offers high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for safety-critical applications.
Pros: Steel is relatively inexpensive and widely available, with established manufacturing processes. It also provides excellent impact resistance, which is crucial for vehicle safety.
Cons: The main disadvantages include its weight, which can hinder energy efficiency, and susceptibility to corrosion if not properly treated or coated.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used in frames and chassis, where strength is paramount. However, additional weight can affect range and performance in electric vehicles.
International Considerations: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and EN is essential, especially for buyers in Africa and South America, where local regulations may differ.
How Do Lithium-Ion Batteries Impact Electric Transport?
Lithium-ion batteries are critical for electric transport, providing the energy storage necessary for operation. They have a high energy density and are rechargeable, making them ideal for electric vehicles.
Pros: Lithium-ion batteries offer long cycle life and fast charging capabilities, which are essential for user convenience and operational efficiency.
Cons: They can be expensive and require careful handling to avoid safety risks such as overheating or fire. Additionally, sourcing materials like lithium can raise ethical and environmental concerns.
Impact on Application: These batteries are central to the functionality of electric vehicles, influencing range and performance. Their efficiency can be affected by temperature variations, necessitating thermal management systems.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure compliance with international safety standards such as IEC and UL, particularly in regions where battery recycling and disposal regulations are evolving.
Summary of Material Selection for Electric Transport
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric transport | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Structural components, casings | Lightweight, corrosion resistant | Higher cost compared to steel | Medium |
| Composite | Body panels, interior components | Tailored design, low weight | Complex manufacturing process | High |
| Steel | Frames, chassis | High strength, impact resistance | Heavier, corrosion risk | Low |
| Lithium-Ion Battery | Energy storage in electric vehicles | Long cycle life, fast charging | High cost, safety handling required | High |
This guide serves as a valuable resource for international B2B buyers, helping them navigate material selection in the electric transport sector while considering performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric transport
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Processes for Electric Transport?
The manufacturing of electric transportation vehicles, such as electric bikes, scooters, and other personal mobility devices, involves a series of intricate processes that ensure quality, performance, and safety. The main stages of manufacturing typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The first stage begins with the selection of materials, which often includes lightweight metals such as aluminum or high-strength steel, along with advanced plastics and composites for body panels. These materials are chosen not only for their durability but also for their weight-to-strength ratio, which is crucial for electric vehicles. Quality control starts here, as materials must meet specific standards to ensure they are suitable for the intended use.
Forming
In the forming stage, raw materials undergo processes like stamping, bending, and machining to create the individual components of the vehicle. This may involve high-precision CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining for parts like frames and axles. Techniques like hydroforming may also be employed to create complex shapes with minimal weight. Ensuring dimensional accuracy at this stage is vital for the subsequent assembly process.
Assembly
The assembly stage involves fitting together the various components, including the electric drivetrain, battery systems, and control electronics. This is often done in a cleanroom environment to prevent contamination, especially for sensitive electronic components. Automated assembly lines may be utilized to increase efficiency, but manual assembly remains crucial for quality checks and the integration of complex systems.
Finishing
Finally, the finishing stage includes painting, coating, and surface treatments that enhance durability and aesthetics. This stage also involves final quality checks to ensure that all components meet the required specifications before the product is packaged and shipped.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Electric Transport Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of electric transport vehicles to guarantee safety, reliability, and compliance with international standards.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Many manufacturers adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which provides a framework for quality management systems. In addition to this, industry-specific certifications like CE marking in Europe or API standards for components may be required. These certifications indicate that products meet essential safety and environmental requirements.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, with critical checkpoints at various stages:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials and components are inspected for compliance with specifications before they are accepted for production. This ensures that only high-quality materials enter the manufacturing process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, ongoing inspections are conducted to verify that the assembly and manufacturing processes are operating within defined parameters. This may involve monitoring machine performance, checking dimensions, and ensuring proper assembly techniques are used.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products leave the factory, a thorough inspection and testing regimen is performed. This includes functional testing of electric systems, battery performance evaluations, and safety checks to ensure that the vehicle is ready for the market.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Electric Transport Manufacturing?
Testing methods for electric transport vehicles are diverse and designed to evaluate various aspects of performance, safety, and reliability. Common testing methods include:
-
Electrical Testing: This verifies the performance of the electric drivetrain and battery systems, ensuring they meet the specified power and range requirements.
-
Safety Testing: Various safety tests, including crash tests and stress testing, are performed to assess how the vehicle withstands real-world conditions.
-
Environmental Testing: Vehicles are subjected to tests that simulate extreme weather conditions to ensure they can operate reliably across different environments.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Here are some effective strategies:
-
Audits: Conducting supplier audits can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality control systems. These audits should review compliance with international standards and assess the effectiveness of their quality management systems.
-
Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports from suppliers that outline their quality assurance processes, testing results, and certifications. This documentation can help buyers evaluate the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing practices. These services can offer additional assurance that the products meet the required standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating the complexities of quality control and certification can be particularly challenging for international B2B buyers. Different regions have varying requirements, and understanding these nuances is essential:
-
Regional Compliance: Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and standards that may affect product compliance. For example, electric vehicles sold in Europe must comply with CE marking, while those in the U.S. may need to meet specific DOT (Department of Transportation) standards.
-
Documentation: Ensuring that all required documentation is available and up to date is crucial. This includes compliance certificates, safety testing results, and warranties.
-
Cultural Considerations: Building relationships with suppliers in different regions may also require understanding cultural norms and practices. Effective communication can facilitate smoother transactions and foster trust.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for electric transport vehicles are intricate yet crucial for ensuring product reliability and safety. B2B buyers must be diligent in evaluating suppliers and understanding international standards to make informed purchasing decisions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric transport’
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric transport, sourcing the right vehicles and infrastructure is critical for businesses looking to capitalize on this trend. This checklist aims to provide B2B buyers with a structured approach to effectively procure electric transport solutions, ensuring that decisions are well-informed and aligned with organizational goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by clearly outlining the technical specifications that meet your operational needs. Consider factors such as vehicle type (e.g., electric bikes, scooters, or cars), range, battery capacity, and payload capabilities. This step is vital as it sets the foundation for your sourcing strategy and ensures that the products you select will perform effectively in your intended applications.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Engage in thorough market research to understand the current landscape of electric transport options. Identify leading manufacturers, emerging brands, and market trends specific to your region, such as Africa or South America. This information will help you gauge the competitive landscape and identify potential suppliers that align with your business needs.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making any commitments, conduct a comprehensive evaluation of potential suppliers. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies that highlight previous projects, particularly those in similar industries or geographical areas. This step is crucial to ensure that your chosen supplier has a proven track record and can deliver quality products consistently.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the products and suppliers you are considering meet all necessary industry certifications and regulatory compliance requirements. This may include safety standards, environmental regulations, and quality assurance certifications specific to electric vehicles. Compliance not only mitigates risks but also enhances your company’s credibility in the market.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty Options
Evaluate the after-sales support and warranty policies provided by potential suppliers. Look for suppliers that offer comprehensive maintenance packages, training programs, and responsive customer service. A robust support system is essential for minimizing downtime and ensuring the longevity of your electric transport fleet.
Step 6: Request Samples or Demonstrations
Whenever possible, request samples or arrange for product demonstrations. This hands-on experience can provide invaluable insights into the usability, performance, and quality of the electric transport options you are considering. It also allows for real-time assessment of features that may be critical for your specific operational environment.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Contracts
Once you have selected a supplier, enter into negotiations regarding pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. Be clear about your expectations and ensure that all agreements are documented in a formal contract. This final step is essential to safeguard your investment and establish a strong working relationship with your supplier.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electric transport solutions, ensuring that they not only meet their current needs but are also positioned for future growth in this dynamic market.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric transport Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Electric Transport Sourcing?
When assessing the costs associated with sourcing electric transport vehicles, several key components must be considered. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The primary materials for electric transport vehicles typically include metals (such as aluminum for frames), batteries (lithium-ion being the most common), and various electronic components. The quality and sourcing of these materials significantly influence costs, especially given the fluctuating prices of raw materials.
-
Labor: Labor costs are another substantial component, encompassing both direct labor involved in assembly and indirect labor for management and support roles. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but it’s essential to assess the skill level and productivity of the workforce.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce these costs, making it crucial for suppliers to adopt lean manufacturing principles.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be necessary for specialized vehicle designs. The initial investment in tooling can be high, but it is amortized over larger production runs, making it vital to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs).
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in quality control systems ensures product reliability and compliance with safety standards. This can add to upfront costs but will reduce warranty claims and enhance brand reputation in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the distance from the manufacturing site to the buyer’s location, as well as the chosen Incoterms. Efficient logistics strategies can help mitigate these costs, particularly for international buyers.
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary based on market conditions, brand reputation, and competitive positioning. A thorough understanding of market dynamics can help buyers negotiate better prices.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Electric Transport Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of electric transport vehicles.
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to achieve better pricing while ensuring that their demand justifies the purchase.
-
Specifications and Customization: Tailored solutions may incur additional costs. Buyers must weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases and lead times.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. Additionally, vehicles that meet specific quality certifications (like ISO or safety standards) may command higher prices due to the assurance of quality and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capabilities can significantly affect pricing. Establishing a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better terms and conditions.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They determine the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk, which can influence total pricing.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency in Electric Transport Sourcing?
-
Negotiate Effectively: Leverage your buying power by negotiating terms, especially if purchasing in bulk. Be prepared with data on market prices and competitor offerings.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When evaluating pricing, consider the TCO, which includes initial costs, maintenance, energy consumption, and potential resale value. This perspective can lead to better long-term savings.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Different regions have varying cost structures influenced by local regulations, tariffs, and market demand. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should factor in these nuances while negotiating.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of trends in electric vehicle technology, battery advancements, and regulatory changes can provide a competitive edge and inform better purchasing decisions.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Always obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing and terms. This can reveal discrepancies and opportunities for negotiation.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for electric transport vehicles can fluctuate based on market conditions, supply chain issues, and economic factors. Therefore, the prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and should be verified through direct communication with suppliers for accuracy.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric transport With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Electric Transport
In the evolving landscape of transportation, electric transport solutions such as electric vehicles (EVs), scooters, and bikes are gaining traction for their environmental benefits and efficiency. However, various alternatives also exist, each with unique attributes that may suit different operational needs. This section explores how electric transport compares to other viable solutions, specifically focusing on traditional fossil fuel vehicles and public transportation systems.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Transport | Traditional Fossil Fuel Vehicles | Public Transportation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency; lower emissions; range varies by model | Good range; high emissions; performance varies widely | Reliable for fixed routes; can be slower due to stops |
| Cost | Higher upfront costs; lower long-term operating costs | Lower initial investment; higher fuel and maintenance costs | Generally low cost per trip; may require monthly passes |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure; growing but still limited in some areas | Infrastructure widely available; easier adoption in rural areas | Established networks in urban areas; minimal investment needed |
| Maintenance | Generally lower maintenance costs; fewer moving parts | Higher maintenance costs; more frequent repairs needed | Minimal maintenance for users; costs borne by operators |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting; last-mile transport; eco-conscious businesses | Long-distance travel; flexible routes; heavy loads | Cost-effective for mass transit; commuting in urban settings |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Traditional Fossil Fuel Vehicles
Pros: Traditional vehicles are often more familiar to users and come with a well-established infrastructure, making them easier to integrate into existing operations. They typically have a wide range of models that can handle various loads and distances, providing flexibility for businesses that require extensive transport capabilities.
Cons: However, fossil fuel vehicles come with higher long-term operating costs due to fuel expenses and maintenance needs. They also contribute significantly to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, which can be detrimental to corporate sustainability goals.
2. Public Transportation
Pros: Public transportation systems, such as buses and trains, offer a cost-effective means of moving large groups of people. They reduce the need for individual vehicles, decreasing overall traffic congestion and emissions in urban areas. For businesses, providing employees with public transit passes can enhance productivity and save costs associated with parking and fuel.
Cons: The effectiveness of public transportation can be limited by fixed routes and schedules, making it less flexible for companies with dynamic operational needs. Additionally, in regions where public transport infrastructure is lacking, this option may not be viable.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business
When selecting the most suitable transportation solution for your business, it is essential to assess your specific operational needs, budget constraints, and sustainability goals. Electric transport offers a forward-thinking approach that aligns with eco-conscious initiatives and provides long-term savings despite higher initial costs. Conversely, traditional vehicles may serve better for flexibility and established infrastructure, while public transportation is ideal for cost-effective mass transit solutions. By carefully weighing these alternatives, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and align with their strategic objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric transport
What are the Key Technical Properties in Electric Transport?
When engaging with electric transport, understanding critical technical specifications is essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key properties:
1. Battery Capacity (Ah or Wh)
Battery capacity is typically measured in ampere-hours (Ah) or watt-hours (Wh) and indicates how much energy the battery can store. A higher capacity means longer operational ranges, which is crucial for fleet managers and businesses that rely on electric vehicles for extensive travel. Selecting a vehicle with an appropriate battery capacity can significantly reduce downtime and operational costs.
2. Charging Time (Hours)
Charging time refers to the duration required to fully charge an electric vehicle’s battery. This metric affects fleet management and operational efficiency; shorter charging times can lead to increased vehicle availability. For businesses in logistics or transportation, understanding the charging infrastructure and times is vital for optimizing routes and schedules.
3. Max Speed (km/h)
The maximum speed of electric transport vehicles is a crucial specification, particularly for compliance with local regulations and for ensuring safety during operations. B2B buyers should consider their intended use—whether for urban commuting or longer journeys—to select models that meet speed requirements without compromising safety.
4. Weight Capacity (kg)
Weight capacity indicates how much weight a vehicle can safely carry. This specification is particularly important for businesses that plan to use electric transport for deliveries or transporting goods. Exceeding weight limits can lead to increased wear and tear, safety hazards, and potential legal repercussions.
5. Durability and Material Grade
The durability of electric transport vehicles often depends on the materials used in their construction. Understanding the material grade can help buyers assess the longevity and performance of the vehicle under various conditions. This aspect is vital for businesses operating in diverse environments, such as construction sites or rural areas.
6. Operational Range (km)
Operational range refers to the distance a vehicle can travel on a single charge. For B2B buyers, this metric is critical for planning routes and understanding how often vehicles will need recharging. A longer operational range can provide greater flexibility and efficiency, particularly in regions with limited charging infrastructure.
What are Common Trade Terms in Electric Transport?
Familiarity with trade terminology enhances communication and negotiation in the electric transport sector. Here are some essential terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the electric transport industry, knowing whether a supplier is an OEM can influence purchasing decisions, as OEMs often provide higher-quality components and support.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Understanding MOQs helps businesses plan their purchases and avoid excess inventory.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and availability of specific products. B2B buyers should use RFQs to gather competitive pricing and terms from multiple vendors, facilitating better negotiation and decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border transactions, as they dictate shipping responsibilities, risk transfer, and costs.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period from placing an order to the delivery of the product. For electric transport, understanding lead times is vital for inventory planning and ensuring that vehicles are available when needed, particularly in fast-paced markets.
6. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO is a financial estimate that helps buyers understand the total cost of acquiring and operating a vehicle over its lifetime. This term is especially important for B2B buyers in evaluating the long-term value of electric transport solutions compared to traditional vehicles.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the electric transport landscape with confidence, ensuring they make strategic decisions that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric transport Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in Electric Transport?
The electric transport sector is experiencing rapid transformation, driven by a confluence of technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and shifting consumer preferences. Globally, the push for carbon neutrality and sustainable transport solutions is reshaping markets. Key trends include the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the expansion of supporting infrastructure, such as charging stations. In regions like Africa and South America, where urbanization is accelerating, electric bikes and scooters are emerging as viable last-mile solutions, addressing both environmental concerns and urban congestion.
International B2B buyers are keenly interested in emerging technologies like battery management systems and smart charging solutions. These innovations not only enhance the performance of electric vehicles but also reduce operational costs. Additionally, as cities worldwide implement stricter emissions regulations, the demand for electric transport solutions is set to rise. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe are particularly focused on integrating sustainable practices into their sourcing strategies, often prioritizing suppliers who can provide detailed product lifecycle assessments.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence B2B Decisions in Electric Transport?
Sustainability is a core consideration for B2B buyers in the electric transport sector. The environmental impact of sourcing materials, particularly for batteries, is significant. Lithium, cobalt, and nickel mining can lead to substantial ecological degradation if not managed responsibly. Therefore, buyers are increasingly seeking partners who prioritize ethical sourcing and transparency in their supply chains.
Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Responsible Cobalt Initiative are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to establish trust and credibility in the marketplace. Additionally, the use of recycled materials and sustainable practices in manufacturing processes not only enhances the environmental profile of products but also appeals to eco-conscious buyers. This alignment with sustainability goals can significantly enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
How Has the Electric Transport Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of electric transport can be traced back to the late 19th century, with early electric vehicles emerging as a viable alternative to steam and gasoline-powered modes. However, the real turning point came in the 21st century, driven by technological advancements in battery technology and growing concerns over fossil fuel dependence. The advent of compact, efficient lithium-ion batteries has paved the way for the resurgence of electric vehicles, enabling longer ranges and faster charging times.
Today, electric transport encompasses a diverse array of options, from electric bikes and scooters to larger commercial vehicles. The sector’s growth is further fueled by supportive government policies and incentives aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable urban mobility. As a result, international B2B buyers are now positioned to capitalize on this dynamic market, leveraging innovative technologies and ethical sourcing practices to meet the demands of a rapidly changing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric transport
-
How do I choose the right electric transport solution for my business needs?
Selecting the appropriate electric transport solution involves assessing your specific operational requirements, such as the type of goods you transport, distance, and the terrain. Consider factors like load capacity, battery life, and charging infrastructure. Additionally, evaluate the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational costs. Engaging with suppliers for demonstrations can also provide insights into performance and suitability. -
What are the common payment terms for international suppliers of electric transport?
Payment terms can vary significantly between suppliers, but typical arrangements include advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30/60/90 days after shipment. It’s essential to discuss and negotiate these terms early in the procurement process. Ensure that the payment method aligns with your cash flow and risk management strategies, especially when dealing with international transactions. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for electric transport vehicles?
MOQs can differ based on the manufacturer and the type of electric transport vehicle. Some suppliers may offer flexible options, especially for new businesses, while others may have stringent MOQs to ensure production efficiency. It’s advisable to inquire about potential discounts for larger orders or the possibility of mixed orders to meet your needs while keeping costs manageable. -
How can I vet suppliers of electric transport to ensure quality and reliability?
To vet suppliers, conduct thorough research into their reputation, industry experience, and client testimonials. Request references and check their certifications and compliance with international standards. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities or arranging for a third-party audit to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. A strong track record in after-sales support is also a key indicator of reliability. -
What customization options are available for electric transport vehicles?
Customization options can vary widely among manufacturers. Common modifications include battery size, color, branding, and additional features such as storage solutions or enhanced safety measures. When discussing customization, ensure that the changes align with your operational requirements and that the supplier can accommodate your requests without significant delays in delivery. -
How do I manage logistics for importing electric transport vehicles?
Managing logistics involves coordinating shipping, customs clearance, and local distribution. Collaborate with logistics providers who have experience in handling electric vehicles, as they can navigate regulatory requirements effectively. Ensure you have all necessary import documentation, and consider the total landed cost, including tariffs, taxes, and shipping fees, to avoid unexpected expenses. -
What are the key quality assurance practices to look for when sourcing electric transport?
When sourcing electric transport, look for suppliers with robust quality assurance (QA) processes, including regular inspections, testing protocols, and adherence to international standards such as ISO certification. Inquire about their warranty policies and support services. A supplier that provides detailed documentation on quality checks and certifications will give you greater confidence in the reliability of the products. -
How can electric transport contribute to sustainability goals for my business?
Integrating electric transport into your operations can significantly reduce your carbon footprint, aligning with global sustainability initiatives. Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, and their energy efficiency often translates to lower operational costs. Additionally, promoting the use of electric transport can enhance your brand’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers, offering a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Electric Transport Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Best Buy – Electric Transportation
Domain: bestbuy.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Electric Transportation options available at Best Buy include Electric Bikes, Electric Scooters, Kids’ Scooters & Ride-ons, Kick Scooters, Electric Go Karts, Hoverboards, Safety Gear & Accessories, and Electric Car Chargers. Key brands featured are Tesla, Rexing, GEM, Segway, NIU, LIVALL, and Heybike. The LIVALL C21 smart helmet is certified up to 28 mph with advanced safety features. Electric veh…
2. Yunextraffic – Electric Transport Solutions
Domain: yunextraffic.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Electric transport includes all modes of transportation powered by electric engines, such as electric cars, e-bikes, e-scooters, buses, and trucks. These vehicles utilize electricity stored in batteries or generated through fuel cells. Key benefits include environmental friendliness (zero harmful emissions), driving innovation (advanced battery technologies and smart charging systems), energy effi…
3. Segway – Innovative Mobility Solutions
Domain: segway.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Segway – Innovative Mobility Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
4. Enel X – Electric Public Transportation Solutions
Domain: corporate.enelx.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Enel X offers electric public transportation solutions aimed at creating zero-emissions mobility for sustainable cities. Key features include: 1. End-to-End Offering: Comprehensive solutions from electric services management to urban mobility planning, including charging station construction and fleet operation. 2. Vehicle Selection and Financing: Assistance in choosing suitable vehicle fleets and…
5. Moto Electric Vehicles – Electric Shuttles
Domain: motoelectricvehicles.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Electric Shuttles – Passenger Trailers, Buses, Trams, and Carts: Moto Electric Vehicles offers a range of electric shuttles designed for transporting guests, visitors, and staff in low-speed environments such as resorts, convention centers, airports, and campuses. The electric trams and multi-passenger trailers are environmentally friendly, quieter, and cleaner alternatives to gasoline-powered veh…
6. EEA – Electric Vehicles Overview
Domain: eea.europa.eu
Introduction: Electric vehicles (EVs) including electric cars, vans, trucks, and buses are essential for reducing negative impacts of road transport on health, environment, and climate. Key facts include: 1) EVs produce 17-30% fewer greenhouse gases (GHG) compared to petrol and diesel vehicles over their life cycle. 2) Production emissions are higher initially but are offset by lower emissions during use. 3) Li…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric transport
As the electric transport sector continues to evolve, strategic sourcing remains crucial for businesses looking to capitalize on this growth. B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must focus on understanding the diverse range of electric mobility solutions available, from electric bikes to scooters and specialized vehicles. By prioritizing partnerships with reliable suppliers and manufacturers, companies can enhance their procurement processes, ensuring they acquire high-quality products that meet market demands.
The value of strategic sourcing extends beyond cost savings; it fosters innovation and sustainability, aligning with global trends toward greener transportation options. Buyers should leverage market insights to identify trends in electric vehicle technology and consumer preferences, enabling them to make informed purchasing decisions.
Looking ahead, the potential for electric transport solutions is vast, particularly in regions experiencing rapid urbanization and infrastructural development. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with emerging technologies and explore new avenues for collaboration. By doing so, they can position themselves at the forefront of the electric transport revolution, driving both profitability and positive environmental impact. Embrace this opportunity to lead in sustainable transport solutions—your next strategic partnership could redefine your business’s future.