Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for new electric cargo vehicle
As businesses increasingly pivot towards sustainability, sourcing new electric cargo vehicles has emerged as a critical challenge for international B2B buyers. With the global push for greener logistics, understanding the diverse options available can significantly impact operational efficiency and compliance with environmental regulations. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of the electric cargo vehicle landscape, detailing various types, applications, and key considerations for procurement, including supplier vetting and cost analysis.
In the dynamic markets of Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including regions like Nigeria and Vietnam, the need for reliable and efficient transportation solutions is paramount. This guide aims to empower B2B buyers by providing actionable insights that facilitate informed purchasing decisions. By navigating the complexities of electric cargo vehicle specifications, performance metrics, and available incentives, buyers can better align their fleet strategies with sustainability goals while ensuring cost-effectiveness.
Furthermore, we delve into the latest technological advancements and market trends that are shaping the electric cargo vehicle sector. By understanding these factors, businesses can enhance their operational capabilities, reduce their carbon footprint, and ultimately contribute to a more sustainable future. This guide is not just a resource; it is a strategic tool for businesses seeking to thrive in an increasingly eco-conscious marketplace.
Understanding new electric cargo vehicle Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| All-Electric Vans | High cargo capacity, zero emissions, advanced safety tech | Last-mile delivery, logistics | Pros: Eco-friendly, cost-effective, tech-savvy; Cons: Initial investment may be high. |
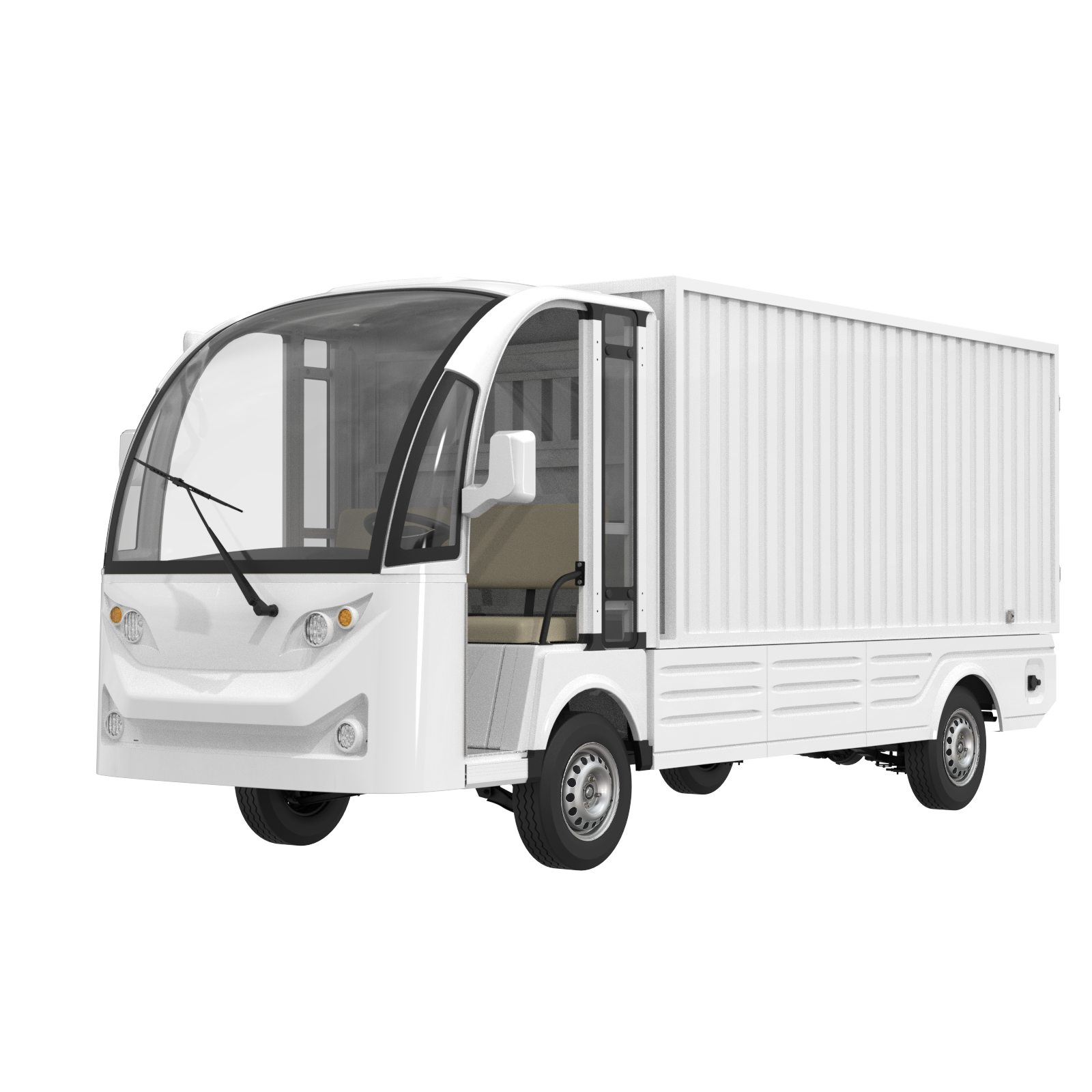
| Electric Box Trucks | Larger payloads, robust build, suitable for heavy goods | Freight transport, distribution centers | Pros: High payload capacity; Cons: Limited range compared to smaller models. |
| Electric Cargo Bikes | Compact size, maneuverable, efficient for urban areas | Urban deliveries, food and retail | Pros: Low operating costs, agile; Cons: Limited cargo space and range. |
| Electric Refrigerated Vans | Temperature-controlled, specialized insulation | Food transport, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Maintains product integrity; Cons: Higher maintenance costs. |
| Electric Utility Trucks | Built for multi-purpose utility work, rugged design | Construction, municipal services | Pros: Versatile; Cons: Heavier and may require specialized charging infrastructure. |
What are All-Electric Vans and Their B2B Suitability?
All-electric vans are designed for businesses focused on sustainable logistics. With features like high cargo capacity and advanced safety technologies, they are ideal for last-mile delivery operations. The zero-emission aspect not only helps companies meet sustainability goals but also reduces long-term fuel costs. B2B buyers should consider the upfront investment against the potential savings on fuel and maintenance over time.
How Do Electric Box Trucks Differ in Functionality?
Electric box trucks offer substantial payload capabilities and are built to handle larger freight. They are particularly suitable for distribution centers and freight transport, allowing businesses to move goods efficiently over moderate distances. While they provide excellent capacity, buyers should weigh their higher purchase costs against the operational savings, especially in urban settings where emissions regulations are tightening.
Why Choose Electric Cargo Bikes for Urban Deliveries?
Electric cargo bikes are an innovative solution for businesses operating in congested urban environments. Their compact size and agility make them perfect for navigating traffic and delivering goods quickly. They are particularly effective for urban deliveries in the food and retail sectors. However, B2B buyers should be mindful of their limited cargo space and range, which may not meet the needs of larger deliveries.
What Are the Benefits of Electric Refrigerated Vans?
Electric refrigerated vans are essential for transporting temperature-sensitive goods, such as food and pharmaceuticals. They maintain product integrity through specialized insulation and temperature control systems. This type of vehicle is crucial for businesses in the food supply chain or health sectors. However, potential buyers should be aware of the higher maintenance costs associated with these specialized vehicles.
How Do Electric Utility Trucks Serve Diverse Industries?
Electric utility trucks are versatile vehicles designed for various applications, including construction and municipal services. Their rugged design and multi-purpose functionality make them suitable for demanding work environments. While they offer significant operational flexibility, B2B buyers must consider the heavier weight and the need for specialized charging infrastructure, which could impact operational efficiency.
Key Industrial Applications of new electric cargo vehicle
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of new electric cargo vehicle | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-commerce & Retail | Last-mile delivery solutions for online orders | Enhanced delivery efficiency and reduced operational costs | Vehicle range, payload capacity, and charging infrastructure availability |
| Food & Beverage Distribution | Temperature-controlled transportation of perishables | Improved product quality and reduced spoilage rates | Compliance with local food safety regulations and refrigeration capabilities |
| Construction & Infrastructure | Transport of tools and materials to job sites | Increased productivity and reduced carbon footprint | Vehicle durability, cargo volume, and ease of access for loading/unloading |
| Logistics & Supply Chain | Freight transportation for regional distribution | Cost-effective operations and reduced emissions | Fleet management integration and vehicle maintenance support |
| Healthcare | Medical supplies and equipment delivery | Timely access to critical supplies and improved patient care | Temperature control for sensitive items and reliability in transit |
How Are New Electric Cargo Vehicles Used in E-commerce & Retail?
In the e-commerce and retail sector, new electric cargo vehicles serve as pivotal assets for last-mile delivery solutions. As online shopping continues to surge, these vehicles facilitate timely deliveries, enhancing customer satisfaction while minimizing operational costs. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, considerations such as vehicle range and charging infrastructure are crucial to ensure efficient service in urban and rural areas alike.
What Role Do Electric Cargo Vehicles Play in Food & Beverage Distribution?
Electric cargo vehicles are increasingly used for transporting temperature-sensitive food and beverage products. Their ability to maintain controlled environments ensures the integrity of perishables, leading to reduced spoilage and waste. For businesses in the Middle East and Europe, compliance with local food safety regulations and the availability of refrigeration capabilities are essential factors when sourcing these vehicles.
How Do Electric Cargo Vehicles Improve Construction & Infrastructure Operations?
In the construction and infrastructure industry, electric cargo vehicles are ideal for transporting tools and materials to various job sites. Their lower carbon footprint aligns with sustainability goals while also boosting productivity through efficient logistics management. Buyers should consider vehicle durability and cargo volume to meet the demands of rigorous job site conditions, particularly in developing regions.
Why Are Electric Cargo Vehicles Important for Logistics & Supply Chain Management?
In logistics and supply chain management, electric cargo vehicles are transforming regional distribution by offering cost-effective transportation solutions with zero tailpipe emissions. This shift not only reduces operational costs but also aligns with global sustainability initiatives. Buyers need to focus on fleet management integration and the availability of maintenance support when considering these vehicles to ensure long-term operational efficiency.
How Are Electric Cargo Vehicles Enhancing Healthcare Delivery?
Electric cargo vehicles are crucial for the healthcare sector, particularly for the timely delivery of medical supplies and equipment. Their reliability ensures that critical supplies reach healthcare providers promptly, improving patient care outcomes. International buyers must prioritize temperature control features for sensitive items and the overall reliability of the vehicles to meet the urgent needs of healthcare services.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘new electric cargo vehicle’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Range for Long-Distance Deliveries
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in logistics and delivery services express concerns over the range limitations of new electric cargo vehicles. For businesses operating in regions with extensive delivery networks, such as those in Africa and South America, the fear of running out of charge mid-route can be a significant deterrent. This anxiety is compounded by the lack of widespread charging infrastructure in some areas, leading to operational inefficiencies and increased downtime.
The Solution: To address range anxiety, buyers should prioritize electric cargo vehicles with a higher estimated range, such as models that offer up to 303 miles on a single charge. It is essential to conduct a thorough analysis of your delivery routes and assess the vehicle’s range against the distances involved. Collaborating with local governments or private companies to establish charging stations along common routes can also mitigate range concerns. Additionally, implementing a fleet management system that monitors battery levels and routes can optimize operations, ensuring vehicles are charged adequately before long-haul trips. Lastly, consider vehicles with fast-charging capabilities to minimize downtime during deliveries.
Scenario 2: High Initial Purchase Costs
The Problem: The upfront cost of acquiring new electric cargo vehicles can be a significant barrier for many businesses, particularly small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in emerging markets. Buyers often find it challenging to justify the initial investment when compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, especially if they are uncertain about the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance.
The Solution: To navigate the high initial costs, buyers should explore financing options such as leasing agreements or government incentives for electric vehicle purchases. Many manufacturers offer attractive leasing terms, allowing businesses to pay a lower monthly fee while benefiting from the advantages of electric vehicles. Additionally, it’s crucial to conduct a total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis that compares not only the purchase price but also the operational costs over time, including fuel savings, maintenance costs, and potential tax incentives. Engaging with suppliers who provide comprehensive support packages—including maintenance plans and warranties—can also help to ease financial concerns and enhance the value proposition of electric cargo vehicles.
Scenario 3: Concerns About Vehicle Performance and Reliability
The Problem: B2B buyers often worry about the performance and reliability of electric cargo vehicles, particularly in varying climates and road conditions. This is especially pertinent in regions with extreme weather, such as the Middle East and parts of Europe, where temperature fluctuations can impact battery performance and vehicle efficiency. Additionally, buyers may fear that new electric models may not be as rugged or durable as traditional vehicles.
The Solution: To ensure reliability, buyers should conduct thorough research on the specific electric cargo models suited for their operational needs, emphasizing those designed with robust battery management systems and proven performance in adverse conditions. Engaging with manufacturers that provide detailed specifications and case studies about performance in diverse environments can build confidence in the product. It’s also advisable to request trial periods or demo vehicles to assess performance firsthand. Lastly, consider vehicles equipped with advanced safety and driver assistance features that enhance operational reliability and driver confidence, ultimately leading to a smoother transition to electric cargo solutions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for new electric cargo vehicle
What Are the Key Materials for New Electric Cargo Vehicles?
In the development of new electric cargo vehicles, material selection plays a critical role in ensuring performance, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in electric cargo vehicle construction, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum: A Lightweight Powerhouse
Key Properties: Aluminum is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. It can withstand a wide range of temperatures and is non-magnetic, making it suitable for various applications in electric vehicles.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which enhances vehicle efficiency and range. However, it can be more expensive than steel and requires specialized manufacturing techniques, which may increase costs. Additionally, aluminum can be less durable under extreme stress compared to some other materials.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in the chassis and body panels of electric cargo vehicles, contributing to improved aerodynamics and fuel efficiency. Its corrosion resistance is particularly beneficial in regions with high humidity or saline environments, such as coastal areas in Africa and South America.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B209 for aluminum alloys is crucial. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should also consider local regulations regarding vehicle weight limits and emissions.
Steel: The Traditional Choice
Key Properties: Steel is renowned for its strength, durability, and versatility. It has high tensile strength and can withstand significant impacts, making it a popular choice for structural components.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of steel is its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing. It is widely available and can be easily welded and formed into various shapes. However, steel is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact the vehicle’s range and efficiency. Additionally, it is prone to corrosion unless properly treated.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used for the frame and structural components of electric cargo vehicles, providing robustness and safety. Its ability to absorb impact energy is particularly important for commercial vehicles that may encounter rough handling.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel. In regions like Africa and South America, where road conditions may be challenging, the durability of steel can be a significant advantage.
Composite Materials: The Future of Lightweighting
Key Properties: Composite materials, such as carbon fiber and fiberglass, offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. They can be engineered to meet specific performance requirements, including thermal and electrical insulation.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their lightweight nature, which can significantly improve vehicle efficiency. However, they tend to be more expensive and complex to manufacture, which can increase overall costs. Additionally, repair and recycling of composites can be more challenging compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Composites are increasingly used in body panels and interior components of electric cargo vehicles, where weight savings can lead to enhanced performance. Their resistance to environmental degradation makes them suitable for various climates.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM D3039 for composite materials is essential. Buyers should also consider local manufacturing capabilities, as composite production may require specialized facilities that are not widely available in some regions.
High-Strength Steel: Enhanced Durability
Key Properties: High-strength steel combines the benefits of traditional steel with enhanced mechanical properties, allowing for thinner sections without compromising strength. It offers excellent impact resistance and is often used in safety-critical applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of high-strength steel is its ability to reduce vehicle weight while maintaining safety and structural integrity. However, it can be more expensive than standard steel and may require advanced manufacturing techniques, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application: High-strength steel is ideal for safety features such as crumple zones and reinforcement structures in electric cargo vehicles. Its performance in crash scenarios makes it a preferred choice for manufacturers focused on safety.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A992 is crucial for high-strength steel applications. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should also be aware of regulations regarding vehicle safety and emissions.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for new electric cargo vehicle | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Chassis and body panels | Lightweight, enhances efficiency | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Steel | Frame and structural components | Cost-effective, durable | Heavier, prone to corrosion | Low |
| Composite Materials | Body panels and interiors | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive, complex repair | High |
| High-Strength Steel | Safety features and reinforcement structures | Reduces weight while maintaining safety | More expensive, advanced manufacturing needed | Med |
By understanding the properties, advantages, and considerations of these materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for new electric cargo vehicle
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing New Electric Cargo Vehicles?
The manufacturing of new electric cargo vehicles involves several critical stages that ensure quality and performance. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing vehicles.
Material Preparation: How Are Components Sourced and Prepared?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves sourcing high-quality materials such as aluminum, steel, and advanced composites for the vehicle’s chassis, body, and battery systems. Suppliers must be vetted for their ability to meet international standards, particularly those that emphasize sustainability and safety.
Before manufacturing, materials undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet specifications. This includes testing for tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and weight considerations. Buyers should consider suppliers that utilize certified materials, as this can impact the vehicle’s overall performance and longevity.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Vehicle Components?
The forming stage employs various techniques to shape the materials into components. Common methods include stamping, extrusion, and molding. For electric cargo vehicles, advanced technologies like hydroforming and laser cutting are increasingly used to create complex shapes that optimize weight and strength.
Precision is critical in this stage; therefore, utilizing computer numerical control (CNC) machines can enhance accuracy and reduce waste. B2B buyers should inquire about the forming techniques used by their suppliers, as this can directly affect the vehicle’s durability and operational efficiency.
Assembly: How Are Electric Cargo Vehicles Assembled?
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form the complete vehicle. This process often follows a modular approach, allowing for easier integration of electrical systems, battery packs, and safety features. Automated assembly lines are increasingly common, ensuring consistency and reducing human error.
During assembly, vehicles undergo several quality checks, including torque tests on critical fasteners and alignment checks for drivetrains. For international buyers, understanding the assembly process and the technology used can be crucial for assessing the reliability of the vehicles they intend to purchase.
Finishing: What Final Touches Are Applied Before Delivery?
Finishing involves painting, interior fitting, and final quality checks. This stage not only enhances the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal but also applies protective coatings to improve durability. Advanced finishing techniques, such as powder coating and electrostatic painting, are often employed to ensure a high-quality finish.
Additionally, the final quality assurance checks (FQC) ensure that each vehicle meets both design specifications and performance standards. Buyers should request documentation of these processes, as it provides insight into the quality of the final product.
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance in Electric Cargo Vehicles?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of electric cargo vehicles. Various international and industry-specific standards guide manufacturers in maintaining quality throughout the production process.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international standards for quality management systems. It sets the criteria for a company’s ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has robust processes in place for quality control.
In addition to ISO standards, buyers should also look for compliance with environmental standards such as ISO 14001, which addresses a company’s environmental impact. Such certifications are essential for buyers focused on sustainability, particularly in regions where environmental regulations are becoming more stringent.
What Industry-Specific Certifications Are Important?
For electric cargo vehicles, certifications like CE marking (for compliance with European safety and health standards) and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may also be relevant, particularly if the vehicle is used in industrial applications. These certifications ensure that the vehicle meets specific safety, performance, and environmental criteria.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing Electric Cargo Vehicles?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are vital in ensuring that electric cargo vehicles are manufactured to the highest standards. Understanding these checkpoints can help B2B buyers assess the reliability of their suppliers.
How Are Incoming Quality Control (IQC) Checks Conducted?
Incoming Quality Control (IQC) is the first line of defense in quality assurance. This stage involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production line. A robust IQC process verifies that all materials meet specified standards and are free from defects, ensuring that only high-quality inputs are used in manufacturing.
What Happens During In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)?
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) involves monitoring the manufacturing process itself. This includes regular inspections and testing of components during the assembly phase. Common methods include visual inspections, functional testing, and statistical process control (SPC) techniques.
B2B buyers should inquire about the IPQC measures in place at their suppliers, as this can significantly influence the final product’s quality. Regular audits and process validations can help ensure that production remains within tolerances.
What Does Final Quality Control (FQC) Entail?
Final Quality Control (FQC) is the last checkpoint before vehicles are delivered to customers. This stage involves comprehensive inspections, including performance testing, safety assessments, and verification of compliance with all applicable standards.
Documentation of FQC procedures is essential for buyers, as it provides assurance that the vehicle has passed all necessary checks. Buyers should request detailed reports on FQC results to confirm the quality of the vehicles they are purchasing.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verification of a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly those in international markets where standards may vary.
What Audit Processes Should Be Implemented?
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems and compliance with international standards. Buyers should establish a schedule for these audits and consider third-party inspections to ensure unbiased evaluations.
In addition, requesting detailed quality assurance reports from suppliers can help buyers understand the effectiveness of their QC processes and identify potential areas for improvement.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play?
Third-party inspections can serve as an additional layer of assurance for buyers. These inspections can include factory audits, material checks, and final vehicle inspections. Engaging a recognized third-party service can add credibility to the verification process, particularly in international transactions.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for B2B Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
Understanding regional nuances in quality control can significantly impact purchasing decisions for B2B buyers.
How Do Regulatory Differences Affect Quality Assurance?
Regulatory environments differ across regions, influencing the standards and certifications required for electric cargo vehicles. Buyers in Africa and South America may encounter challenges related to local regulations and standards, which can vary widely by country.
In contrast, buyers in Europe may benefit from stringent regulations that promote higher safety and environmental standards. Understanding these regional differences is critical for ensuring compliance and avoiding costly delays or penalties.
What Should Buyers Know About Cultural and Market Differences?
Cultural perceptions of quality and reliability can also impact supplier relationships. Buyers should consider how these perceptions influence negotiations and expectations regarding quality assurance. Building strong partnerships with suppliers who understand local market dynamics can enhance the quality of the procurement process.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for new electric cargo vehicles, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘new electric cargo vehicle’
Introduction
In an era of increasing environmental consciousness and technological advancement, sourcing a new electric cargo vehicle (ECV) is a strategic decision for businesses aiming to enhance efficiency and sustainability. This practical checklist will guide international B2B buyers through the essential steps to successfully procure electric cargo vehicles, ensuring that you make informed choices that align with your operational needs and goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your procurement process. Consider factors such as cargo capacity, range, and payload capabilities that align with your business operations. For instance, if you require a vehicle for urban deliveries, prioritize models with a shorter range but higher maneuverability.
Step 2: Assess Your Budget and Financing Options
Understanding your financial parameters is crucial for selecting the right electric cargo vehicle. Identify your budget for both initial purchase and ongoing operational costs, including maintenance and charging infrastructure. Explore financing options such as leasing, which may offer lower upfront costs and tax benefits that can enhance cash flow.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in electric vehicle sales and support, as well as those offering robust warranty and service packages.
- Check for certifications: Ensure that suppliers comply with local and international standards for electric vehicles, such as safety and environmental regulations.
Step 4: Analyze Vehicle Features and Performance
Examine the specific features of the electric cargo vehicles you are considering. Look for advanced safety features, infotainment systems, and driver assistance technologies that can enhance operational efficiency and safety.
- Consider connectivity options: Vehicles with built-in telematics can provide valuable data for fleet management, optimizing routes, and monitoring performance.
Step 5: Investigate Charging Infrastructure Needs
Understanding the charging requirements for your electric cargo vehicle fleet is essential for seamless operations. Assess the availability of charging stations in your operational area and consider the installation of on-site charging solutions.
- Evaluate charging speed: Different vehicles have varying charging capabilities; ensure that your chosen model aligns with your expected downtime and operational schedule.
Step 6: Review Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Look beyond the initial purchase price and evaluate the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, energy consumption, and potential government incentives. Analyzing TCO will help you understand the long-term financial implications of your investment.
- Consider resale value: Investigate how electric cargo vehicles hold their value in the market, as this can significantly impact your overall cost effectiveness.
Step 7: Plan for Employee Training and Integration
Finally, prepare a strategy for integrating the new electric cargo vehicles into your existing fleet. This includes training your drivers on the unique operational aspects of electric vehicles and ensuring that maintenance staff are equipped to handle any specific requirements.
- Engage with suppliers for training: Many manufacturers offer training programs that can help ease the transition and ensure that your team is well-prepared to operate and maintain the new vehicles effectively.
By following these steps, you can navigate the complexities of procuring electric cargo vehicles, ensuring that your investment supports your business goals while contributing to a sustainable future.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for new electric cargo vehicle Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing New Electric Cargo Vehicles?
When evaluating the cost structure for new electric cargo vehicles, several core components come into play. These include:
-
Materials: The primary materials for electric vehicles (EVs) include high-strength steel, aluminum for lightweight construction, and lithium-ion batteries. The costs of these materials can fluctuate based on global market trends and availability.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct labor for assembly and indirect labor for support functions. Skilled labor is crucial, especially in the electric vehicle sector, where technical expertise is required for assembly and quality control.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, which is vital for maintaining competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs relate to the initial investment in molds and machinery necessary for production. This is particularly significant for customized vehicles, where specific tooling may be required.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that vehicles meet safety and performance standards is essential. QC processes add to the overall cost but are necessary to minimize defects and maintain brand reputation.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on distance and mode of transport. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is crucial to navigate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs clearance.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can be influenced by demand, competition, and the perceived value of the vehicle.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Electric Cargo Vehicles?
Several factors can influence the pricing of electric cargo vehicles, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities can lead to significant discounts. Buyers should consider their demand forecasts to negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features such as enhanced battery capacity, specialized shelving, or advanced safety technology can increase costs. Buyers should assess the necessity of these features against their operational needs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the certifications required (e.g., safety, environmental) can impact pricing. Higher quality and certified materials typically come at a premium.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also affect pricing. Well-established suppliers may command higher prices but often provide better warranties and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and customs duties, which can significantly affect the overall cost.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in Electric Cargo Vehicle Procurement?
B2B buyers looking to optimize costs when sourcing electric cargo vehicles should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers to negotiate better terms. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can also yield favorable pricing and terms.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): While the initial purchase price is important, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, fuel savings (electricity vs. diesel), and potential tax credits or incentives for electric vehicles. This holistic view can reveal long-term savings.
-
Research Local Incentives: Many countries offer incentives for electric vehicle purchases, which can significantly lower the effective price. Buyers should investigate available subsidies or tax credits in their region.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes that can affect the final cost. Engaging with local experts or consultants can provide valuable insights into navigating these complexities.
Conclusion
In summary, sourcing new electric cargo vehicles involves a multifaceted cost structure influenced by various factors. By understanding these components and leveraging strategies tailored to their specific market conditions, international B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals. Always remember that indicative prices may vary, and thorough due diligence is essential to ensure the best value for your investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing new electric cargo vehicle With Other Solutions
Exploring Viable Alternatives to New Electric Cargo Vehicles
As businesses seek to modernize their logistics and delivery operations, the introduction of new electric cargo vehicles presents an innovative solution. However, it’s crucial to evaluate these vehicles against other viable alternatives to determine the best fit for unique operational needs. Below, we compare new electric cargo vehicles with two alternative solutions: traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and hybrid vehicles.
| Comparison Aspect | New Electric Cargo Vehicle | Traditional ICE Vehicle | Hybrid Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Up to 272 miles range; zero emissions | High range; emissions dependent on fuel type | Moderate range; lower emissions than ICE |
| Cost | Starting at $46,425; potential tax credits | Generally lower upfront cost, but higher fuel costs | Higher upfront cost than ICE, lower fuel costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure; long-term savings | Established infrastructure; immediate availability | Requires both fuel and charging infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts | Higher maintenance due to engine complexity | Moderate maintenance; more complex than electric, simpler than ICE |
| Best Use Case | Urban last-mile delivery; sustainability-focused businesses | General logistics; areas with established fuel infrastructure | Mixed-use environments; businesses transitioning to electric |
Analyzing Traditional Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles
Traditional ICE vehicles have long been the backbone of logistics and cargo transport. Their advantages include a well-established infrastructure, immediate availability, and generally lower upfront costs. However, they come with significant drawbacks, such as higher fuel costs and emissions, which can impact sustainability goals. For businesses operating in regions with limited access to charging stations, ICE vehicles may remain the most practical option, particularly in rural or less developed areas.
Understanding Hybrid Vehicles
Hybrid vehicles represent a middle ground between traditional ICE vehicles and fully electric options. They utilize a combination of gasoline and electric power, offering improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions compared to their ICE counterparts. While hybrids can be advantageous for businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint without completely transitioning to electric, they still require both fuel and charging infrastructure. Their upfront costs are typically higher than ICE vehicles, but lower than fully electric options, making them a viable choice for companies exploring a gradual shift towards electrification.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the appropriate cargo vehicle for your business, consider your operational needs, budget, and sustainability goals. New electric cargo vehicles are ideal for companies prioritizing environmental responsibility and efficient urban delivery. In contrast, traditional ICE vehicles may suit businesses with immediate logistics needs in regions lacking charging infrastructure. Hybrid vehicles offer a transitional option for companies seeking to balance operational efficiency with a gradual move towards electrification. Assessing these factors will help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives and market conditions.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for new electric cargo vehicle
What Are the Key Technical Properties of New Electric Cargo Vehicles?
Understanding the essential technical properties of electric cargo vehicles is crucial for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some key specifications to consider:
1. Payload Capacity
Payload capacity refers to the maximum weight a vehicle can safely carry, including cargo and passengers. This specification is critical for businesses that rely on transporting goods, as exceeding this limit can lead to legal penalties and increased maintenance costs. For example, vehicles like the BrightDrop can handle up to 3,710 lbs, allowing businesses to optimize delivery efficiency without compromising safety.
2. Cargo Volume
Cargo volume denotes the total space available for goods within the vehicle. Measured in cubic feet, this metric is essential for logistics and supply chain operations. A higher cargo volume can reduce the number of trips required for deliveries, thereby enhancing productivity. The BrightDrop models offer cargo volumes up to 614.7 cu. ft., catering to diverse business needs.
3. Range
Range is the distance a vehicle can travel on a single charge. It is a pivotal factor for companies operating in areas with limited charging infrastructure. With an estimated range of up to 272 miles, electric cargo vehicles can facilitate longer delivery routes without frequent recharging, thus improving operational efficiency.
4. Charging Time
Charging time indicates how long it takes to fully recharge the vehicle’s battery. Quick charging capabilities can significantly reduce downtime, which is crucial for businesses with tight delivery schedules. Understanding the charging options available, such as fast-charging stations, can help businesses plan their logistics more effectively.
5. Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR)
GVWR represents the maximum operating weight of the vehicle, including its own weight and the weight of cargo. It is essential for compliance with local regulations and impacts insurance and licensing requirements. Vehicles with a GVWR of 11,000 lbs, like the BrightDrop models, provide flexibility for various load types while ensuring regulatory compliance.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to New Electric Cargo Vehicles?
Familiarity with industry terminology can enhance communication and negotiation processes for B2B buyers. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of electric cargo vehicles, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and assess the quality of components used in the vehicle.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for businesses planning to purchase electric cargo vehicles in bulk, as it can affect overall costs and inventory management.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price bids from suppliers. This process is crucial for securing competitive pricing and ensuring that the specifications of electric cargo vehicles meet the buyer’s needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms can help businesses navigate shipping and logistics effectively, ensuring clarity in cost allocation and risk management.
5. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with the purchase and operation of a vehicle over its entire lifespan. For electric cargo vehicles, this includes initial purchase price, maintenance, charging costs, and depreciation. Understanding TCO can aid businesses in making more informed financial decisions regarding their fleet.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their purchasing strategies and optimize their operations in the growing market for electric cargo vehicles.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the new electric cargo vehicle Sector
What Are the Global Drivers and Trends Influencing the New Electric Cargo Vehicle Market?
The new electric cargo vehicle market is driven by several global trends that are reshaping the logistics and transportation sectors. First, the increasing regulatory push for sustainability and the reduction of carbon emissions is prompting businesses to transition to electric vehicles (EVs). Countries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are implementing stricter environmental regulations, compelling companies to adopt cleaner technologies. Additionally, the rising cost of fossil fuels is incentivizing businesses to explore cost-effective alternatives, with electric cargo vehicles offering lower operating costs in the long run.
Emerging technologies such as advanced battery systems and telematics are also reshaping the market dynamics. Innovations in battery technology are leading to increased range and reduced charging times, making electric cargo vehicles more viable for long-distance logistics. Furthermore, the integration of IoT and AI in fleet management enables businesses to optimize routes, monitor vehicle performance, and improve overall efficiency. These technological advancements are particularly appealing to B2B buyers looking to enhance operational efficiencies in markets like Nigeria and Vietnam, where logistics challenges are significant.
Lastly, the rise of e-commerce and last-mile delivery services is creating a surge in demand for electric cargo vehicles. Companies are recognizing the need to adapt their fleets to meet the growing expectations of consumers for faster and more sustainable delivery options. As a result, international buyers are increasingly sourcing electric cargo vehicles that can efficiently handle the demands of modern logistics.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Your B2B Strategy?
Sustainability is no longer a mere buzzword; it has become a critical component of business strategy, especially in the B2B sector. The environmental impact of sourcing electric cargo vehicles extends beyond just emissions. Companies are now focused on the entire lifecycle of their vehicles, from production to disposal. Adopting electric cargo vehicles helps businesses reduce their carbon footprint and align with global sustainability goals, which is increasingly important for consumers and stakeholders alike.
Moreover, ethical sourcing practices are becoming essential as companies aim to ensure that their supply chains adhere to environmental and social standards. This includes using ‘green’ certifications and materials in the manufacturing process. Buyers should look for suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 or LEED. These certifications not only enhance the credibility of the supplier but also provide assurance to B2B buyers that they are investing in vehicles that minimize environmental harm.
Incorporating sustainability into sourcing strategies can also yield significant financial benefits. Many governments offer incentives, such as tax credits for electric vehicle purchases, which can offset initial costs. By prioritizing sustainable sourcing, businesses can improve their brand image and appeal to a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers, thereby enhancing their competitive edge in the market.
What Is the Evolution of Electric Cargo Vehicles in the B2B Context?
The evolution of electric cargo vehicles has been marked by technological advancements and shifting market demands. Initially, electric vehicles were considered niche products, primarily used in urban settings for short-distance deliveries. However, as battery technology improved, manufacturers began to develop electric cargo vehicles capable of longer ranges and heavier payloads, making them suitable for a broader range of applications.
In recent years, the surge in e-commerce has accelerated this evolution, with businesses increasingly recognizing the need for sustainable transportation solutions. Major automotive manufacturers have entered the market, bringing innovation and scale, which has led to a competitive landscape that benefits buyers with more options and better pricing. As the market matures, electric cargo vehicles are becoming integral to logistics strategies worldwide, particularly in regions facing stringent emissions regulations and urban congestion challenges. This trend is likely to continue, as businesses prioritize sustainability and efficiency in their operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of new electric cargo vehicle
-
How do I determine the right electric cargo vehicle for my business needs?
To select the appropriate electric cargo vehicle, assess your operational requirements, including cargo volume, payload capacity, and range. Consider factors such as the average distance of deliveries, types of goods transported, and urban versus rural driving conditions. Additionally, evaluate the vehicle’s charging infrastructure compatibility in your region. Engaging with suppliers for test drives and consultations can provide insights tailored to your business model. -
What are the main advantages of electric cargo vehicles over traditional fuel-powered vehicles?
Electric cargo vehicles offer numerous benefits, including lower operational costs due to reduced fuel expenses, maintenance, and tax incentives in many regions. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to sustainability goals and improving air quality. Furthermore, advancements in technology have enhanced their performance, with many models providing substantial range and cargo capacity, making them suitable for various logistics needs. -
What are the standard payment terms for purchasing electric cargo vehicles?
Payment terms can vary significantly among suppliers, but common options include upfront payments, leasing agreements, or financing plans. Many manufacturers offer flexible payment terms, such as monthly installments over a specified period. It’s crucial to discuss and negotiate these terms during the procurement process, considering factors like interest rates, down payments, and any available grants or incentives that may reduce overall costs. -
How can I ensure the quality of electric cargo vehicles before purchasing?
To ensure vehicle quality, conduct thorough research on manufacturers and their reputation. Request detailed specifications, performance data, and certifications related to safety and emissions. Arrange for a pre-purchase inspection or test drives to assess the vehicles firsthand. Additionally, inquire about warranty options and after-sales support, as these factors play a critical role in long-term satisfaction and reliability. -
What customization options are available for electric cargo vehicles?
Customization options for electric cargo vehicles often include modifications for cargo space, shelving systems, and specialized equipment for specific industries. Some manufacturers may offer bespoke solutions tailored to your operational needs, such as refrigeration units for perishable goods or enhanced safety features. It’s advisable to communicate your requirements early in the procurement process to ensure the chosen vehicle meets your business specifications. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for electric cargo vehicles?
Minimum order quantities can vary by supplier and region. Some manufacturers may allow single-unit purchases, while others may have MOQs to optimize production and reduce costs. If you are considering a bulk purchase, inquire about potential discounts or financing options that can be beneficial for larger orders. Engaging with multiple suppliers can provide a clearer picture of available options and pricing structures. -
How do I vet suppliers when sourcing electric cargo vehicles internationally?
To vet suppliers, start by checking their industry reputation through reviews and references from previous clients. Evaluate their financial stability and compliance with international standards. Engage with the supplier to discuss their production capabilities, lead times, and after-sales support. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing facilities if possible, or request certifications that verify their adherence to quality and safety regulations. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric cargo vehicles?
When importing electric cargo vehicles, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties specific to your region. Work closely with logistics providers experienced in automotive imports to ensure compliance with local laws and timely delivery. Additionally, assess the availability of charging infrastructure upon arrival, as this will be critical for your operations. Engaging a customs broker can help navigate the complexities of international shipping and facilitate a smoother process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 New Electric Cargo Vehicle Manufacturers & Suppliers List
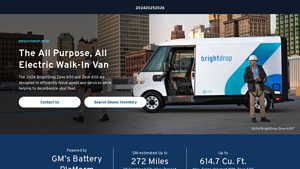
1. Chevrolet – 2025 BrightDrop 400 & 600
Domain: chevrolet.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: 2025 Chevrolet BrightDrop 400 starting at $46,425 after cash offers; 2025 Chevrolet BrightDrop 600 starting at $47,925 after cash offers. BrightDrop 400 max cargo volume: 412.1 cu. ft., max payload: 3,710 lbs., max GVWR: 11,000 lbs. BrightDrop 600 max cargo volume: 614.7 cu. ft., max payload: 3,350 lbs., max GVWR: 11,000 lbs. Up to 272 mi. estimated combined city/hwy range for BrightDrop 400; up t…
2. BrightDrop – Zevo 600 & 400 Electric Delivery Vehicles
Domain: gmenvolve.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Product Name: BrightDrop Zevo 600 and Zevo 400
Type: Electric Delivery Vehicles
Key Features:
– All Electric Walk-In Van
– Designed for efficient goods and services movement
– Helps decarbonize fleets
– Powered by GM’s Battery Platform
– Estimated range: Up to 272 miles (combined city/highway)
– Max cargo volume:
– Zevo 600: 614.7 cu. ft.
– Zevo 400: 412.1 cu. ft.
– Lease Offer: $599/month fo…
3. Tesla – Robovan
Domain: topelectricsuv.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: [{‘model’: ‘Tesla Robovan’, ‘features’: {‘travel_cost’: ‘5-10 cents per mile’, ‘design’: ‘fully autonomous, art deco inspired, no traditional windshield’, ‘capacity’: ‘up to 20 passengers’, ‘interior’: ‘lounge-style with flat floor, ambient lighting, large screens’, ‘commercial_version’: ‘planned for goods transport’, ‘launch_date’: ‘unconfirmed, may not arrive before 2028’}}, {‘model’: ‘Ford E-Tr…
4. Rivian – Commercial Electric Vans
Domain: rivian.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Rivian Fleet offers electric work and commercial vans starting at $79,900. The Rivian Commercial Van is designed for sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and equipped with advanced safety features. Key features include 360-degree cameras for safety, patented energy-saving microclimate seats for comfort, and a reduction of operational GHG emissions by 50% or more compared to internal combustion vehi…
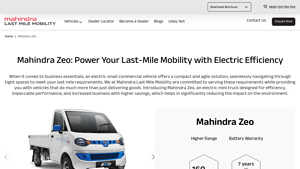
5. Mahindra – Mahindra Zeo Electric Mini Truck
Domain: mahindralastmilemobility.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Mahindra Zeo
Type: Electric Mini Truck
Power: 30 kW PMS motor
Peak Torque: 114 Nm
Top Speed: 60 km/h
Cargo Box Size: 7.4 feet
Payload Capacity: 765 kg
Battery: 21.3 kWh IP67-rated
Range: 160 km on a single charge
Charging Time: 100 km range in 60 minutes (fast charging)
Wheelbase: 2500 mm
Turning Radius: 4.3 meters
Gradeability: 32%
Seating Capacity: Driver + 1
Drive Modes: Power and…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for new electric cargo vehicle
The transition to electric cargo vehicles represents a pivotal moment for businesses across diverse international markets. As outlined in this guide, strategic sourcing of electric cargo vehicles like the Chevrolet BrightDrop series not only enhances operational efficiency but also aligns with sustainability goals. Companies can leverage incentives such as tax credits and lower operating costs, making the switch to electric both financially and environmentally beneficial.
B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize sourcing vehicles that offer robust performance, advanced safety features, and a strong range of cargo capacity. The BrightDrop models exemplify these qualities, designed to meet the demands of last-mile logistics while contributing to fleet decarbonization.
Looking ahead, the electric vehicle market is poised for significant growth. By embracing this shift now, international buyers can position themselves as leaders in sustainability and innovation within their industries. Take action today—evaluate your fleet needs, explore the available electric options, and make informed sourcing decisions that will benefit your business for years to come.