Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for delivery vehicle
In today’s rapidly evolving logistics landscape, sourcing the right delivery vehicles has become a critical challenge for businesses operating on a global scale. With the increasing demand for efficient and reliable delivery solutions, international B2B buyers must navigate a complex market filled with diverse vehicle options that cater to various operational needs. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, exploring the different types of delivery vehicles, their applications, and essential considerations for supplier vetting and cost analysis.
From electric vans designed for sustainable urban logistics to versatile trucks suited for long-haul deliveries, understanding the myriad of options available is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. In addition to vehicle specifications, this guide delves into the latest innovations in delivery vehicle technology, highlighting features that enhance driver safety and operational efficiency.
Furthermore, it addresses the unique needs of buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Saudi Arabia and Germany. By equipping decision-makers with actionable insights and best practices, this guide empowers businesses to optimize their delivery fleets, reduce operational costs, and ultimately improve customer satisfaction. Whether you’re looking to expand your fleet or replace aging vehicles, the information contained herein will facilitate strategic choices that align with your organizational goals.
Understanding delivery vehicle Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Walk-In Vans | High cargo capacity, low step-in height, customizable interiors | Parcel delivery, furniture transport | Pros: Spacious, easy access; Cons: Higher initial cost, may require specific driver training. |
| Box Trucks | Enclosed cargo area, various sizes, suitable for heavy loads | Moving services, construction materials | Pros: Versatile size options; Cons: Limited maneuverability in urban settings. |
| Electric Delivery Vans | Zero emissions, lower operating costs, advanced safety features | Eco-friendly logistics, urban deliveries | Pros: Sustainable, cost-effective; Cons: Higher upfront investment, limited range compared to fuel vehicles. |
| Cargo Bikes | Lightweight, pedal-assisted, compact design | Urban deliveries, small parcels | Pros: Eco-friendly, agile in traffic; Cons: Limited cargo capacity, not suitable for long distances. |
| Refrigerated Trucks | Temperature-controlled cargo area, specialized insulation | Food and pharmaceutical transport | Pros: Essential for perishable goods; Cons: Higher maintenance costs, requires power source for refrigeration. |
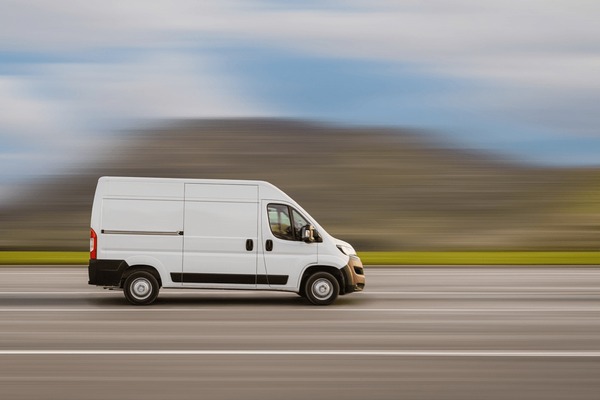
What Are the Characteristics of Walk-In Vans for Delivery Operations?
Walk-in vans are characterized by their spacious interiors, allowing easy access for drivers during frequent stops. They typically feature low step-in heights for convenience and can be customized with shelving and other organizational tools to enhance efficiency. Ideal for businesses involved in parcel delivery or transporting larger items like furniture, these vehicles offer a balance between cargo capacity and driver comfort. When considering a walk-in van, buyers should assess their operational needs, budget, and potential training requirements for drivers.
How Do Box Trucks Serve Various Industries?
Box trucks, also known as cube trucks, are designed with an enclosed cargo area that provides protection from the elements. They come in various sizes, making them suitable for transporting a wide range of goods, from furniture to construction materials. Their versatility makes them a popular choice for moving services and logistics companies. When purchasing a box truck, buyers should evaluate factors such as load capacity, fuel efficiency, and maneuverability, especially in urban environments.
What Are the Benefits of Electric Delivery Vans for Sustainable Logistics?
Electric delivery vans are becoming increasingly popular due to their zero-emission profiles and lower operating costs compared to traditional fuel vehicles. Equipped with advanced safety features and designed for urban logistics, these vans are ideal for businesses aiming to reduce their carbon footprint. However, potential buyers should consider the initial investment costs and the vehicle range, as these can vary significantly. Understanding local infrastructure for charging stations is also crucial for ensuring operational efficiency.
How Can Cargo Bikes Enhance Urban Delivery Efficiency?
Cargo bikes are a lightweight and eco-friendly option for urban deliveries, particularly for small parcels. Their compact design allows for easy navigation through congested streets, and many models come with pedal assistance to support longer distances. While they are highly efficient in urban settings, buyers should be aware of their limited cargo capacity and suitability for specific types of deliveries. Companies looking to adopt cargo bikes should assess their delivery volume and urban infrastructure to maximize this option’s benefits.
Why Are Refrigerated Trucks Critical for Perishable Goods Transport?
Refrigerated trucks are specifically designed to transport temperature-sensitive goods, such as food and pharmaceuticals, ensuring they remain fresh during transit. These vehicles feature specialized insulation and temperature control systems, which are critical for compliance with health regulations. While they are essential for businesses dealing in perishables, potential buyers should consider the higher maintenance costs associated with refrigeration systems and the need for a reliable power source during transport. Understanding the specific requirements for temperature control can guide B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
Key Industrial Applications of delivery vehicle
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Delivery Vehicle | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-commerce & Retail | Last-mile delivery of goods directly to consumers | Enhances customer satisfaction through timely delivery | Vehicle size, fuel efficiency, and route optimization capabilities |
| Food & Beverage | Distribution of perishable goods to restaurants and stores | Ensures freshness and quality, reducing waste | Temperature control features, cargo space, and reliability |
| Healthcare | Transport of medical supplies and equipment | Critical for timely patient care and operational efficiency | Compliance with health regulations, vehicle customization for medical needs |
| Construction & Heavy Industry | Delivery of construction materials and equipment | Reduces downtime and increases project efficiency | Load capacity, durability, and off-road capability |
| Logistics & Freight | Inter-city freight transportation | Streamlines supply chain operations and reduces costs | Vehicle range, maintenance support, and fleet management solutions |
In the E-commerce & Retail sector, delivery vehicles are essential for last-mile logistics, ensuring that products reach consumers quickly and efficiently. This application has become increasingly vital as customer expectations for rapid delivery rise. Buyers in this sector should prioritize vehicles that are compact yet spacious enough to handle diverse product types, ensuring fuel efficiency and optimized routing to minimize costs.
In the Food & Beverage industry, delivery vehicles play a crucial role in transporting perishable items. These vehicles must be equipped with temperature control systems to maintain product quality and freshness during transit. For international buyers, understanding local regulations regarding food transport and ensuring vehicles meet these standards is vital to avoid penalties and ensure customer trust.
The Healthcare sector relies heavily on specialized delivery vehicles to transport medical supplies and equipment. Timely delivery can be a matter of life and death, necessitating vehicles that are reliable and compliant with health regulations. Buyers should consider vehicles that offer customization for specific medical needs, along with features that enhance safety and efficiency during transport.
In Construction & Heavy Industry, delivery vehicles are tasked with transporting materials and equipment to job sites. The ability to handle heavy loads and navigate rough terrains is critical. Buyers should focus on vehicles with high durability, sufficient load capacity, and the capability to operate in diverse environments, which can significantly reduce project delays and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Finally, in the Logistics & Freight industry, delivery vehicles are integral for inter-city transportation. These vehicles facilitate the smooth flow of goods across regions, helping businesses manage their supply chains effectively. Buyers should prioritize vehicles with a long operational range, robust maintenance support, and advanced fleet management solutions to optimize their logistics operations and reduce overall costs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘delivery vehicle’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Rising Fuel Costs for Delivery Fleets
The Problem: In today’s fluctuating economic climate, many B2B buyers are grappling with the challenge of rising fuel costs that significantly impact their delivery operations. Companies that rely heavily on traditional fuel-powered delivery vehicles find their operational expenses ballooning, which can erode profit margins and hinder competitive pricing strategies. This is particularly acute in regions where fuel prices are volatile, such as parts of Africa and South America. As delivery demands increase, maintaining a cost-effective fleet becomes a daunting task.
The Solution: Transitioning to an electric or hybrid delivery vehicle fleet can alleviate the burden of fuel costs. B2B buyers should thoroughly research and invest in electric vehicles (EVs) that offer long-range capabilities and efficient energy consumption, such as the BrightDrop Zevo or Rivian Commercial Van. When sourcing these vehicles, consider partnering with manufacturers that provide comprehensive fleet management solutions. These solutions often include route optimization tools that can maximize delivery efficiency and reduce energy consumption. Additionally, take advantage of government incentives for electric vehicle adoption, which can offset initial investment costs. By making this transition, companies not only reduce fuel expenses but also position themselves as environmentally responsible, appealing to sustainability-conscious clients.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Driver Safety and Comfort on the Road
The Problem: Driver safety and comfort are critical concerns for B2B buyers operating delivery fleets. Long hours on the road can lead to fatigue, which increases the risk of accidents and reduces overall productivity. For instance, delivery drivers in the Middle East face extreme weather conditions that can exacerbate these issues. A lack of ergonomic vehicle design can result in physical strain, further impacting driver well-being and operational efficiency.
The Solution: To address these challenges, B2B buyers should prioritize the selection of delivery vehicles that are designed with driver ergonomics and safety in mind. Models like the Rivian Commercial Van come equipped with features such as 360-degree cameras, advanced safety systems, and climate-controlled seating that promote comfort and reduce fatigue. When specifying vehicles for your fleet, consider conducting a driver survey to gather feedback on preferred features that enhance comfort and safety. Additionally, implementing regular training sessions on safe driving practices and fatigue management can further bolster driver safety. By investing in vehicles that support driver well-being, companies can enhance productivity and reduce turnover, ultimately leading to a more reliable delivery operation.
Scenario 3: Managing Fleet Maintenance and Downtime Effectively
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of unexpected vehicle breakdowns and maintenance issues that lead to costly downtime. For businesses in Europe and the Middle East, where delivery timelines are critical, even minor delays can result in lost contracts and dissatisfied customers. Managing maintenance schedules can be cumbersome, especially for larger fleets, where keeping track of each vehicle’s condition is a significant administrative burden.
The Solution: Implementing a proactive fleet management system can mitigate these issues. Buyers should consider investing in telematics solutions that provide real-time data on vehicle performance and maintenance needs. This technology allows for predictive maintenance, meaning that issues can be identified and addressed before they lead to breakdowns. Additionally, working with manufacturers that offer comprehensive service packages can streamline maintenance processes. For example, companies like Utilimaster provide insights from years of industry experience, helping businesses develop tailored maintenance plans that align with their operational needs. By adopting these proactive strategies, B2B buyers can minimize downtime, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure that their delivery commitments are met consistently.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for delivery vehicle
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum for Delivery Vehicles?
Aluminum is a popular choice in the manufacturing of delivery vehicles due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. With a high strength-to-weight ratio, aluminum can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various delivery applications. Its natural resistance to corrosion is particularly beneficial in environments with high humidity or exposure to road salt, which is common in many regions, including Europe and North America.
Pros and Cons of Using Aluminum in Delivery Vehicles
The primary advantage of aluminum is its durability combined with lightweight characteristics, which can lead to improved fuel efficiency. However, the manufacturing complexity can be higher compared to other metals, leading to increased production costs. Additionally, while aluminum is generally robust, it can be prone to dents and scratches, which may affect the vehicle’s aesthetics over time.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa and the Middle East, the choice of aluminum must consider local climatic conditions and road infrastructure. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM can also be a factor, as buyers may need to ensure that the aluminum used meets specific quality benchmarks.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material for Delivery Vehicles?
Steel is another common material used in the construction of delivery vehicles, particularly for structural components. Known for its high tensile strength, steel can handle heavy loads and is often used in the chassis and frame of delivery vehicles. Steel’s resistance to deformation under stress makes it a reliable choice for demanding applications.
Pros and Cons of Using Steel in Delivery Vehicles
The main advantage of steel is its strength and durability, which can lead to longer service life and lower maintenance costs. However, steel is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact fuel efficiency. Additionally, it is susceptible to rust and corrosion if not properly treated, requiring additional protective coatings, which can increase manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
For buyers in regions with high humidity or coastal environments, such as parts of South America, the risk of corrosion must be mitigated through appropriate treatments. Compliance with local and international standards is critical, especially for heavy-duty applications where safety is paramount.
What Are the Benefits of Composite Materials in Delivery Vehicles?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, are increasingly being used in delivery vehicles due to their lightweight and high strength properties. These materials can be tailored for specific applications, providing excellent performance in terms of thermal and chemical resistance.
Pros and Cons of Using Composites in Delivery Vehicles
The primary benefit of composites is their lightweight nature, which can significantly enhance fuel efficiency. They also offer superior corrosion resistance compared to metals. However, the cost of composite materials can be significantly higher, and their manufacturing processes can be more complex, leading to longer lead times.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
For international buyers, particularly in Europe, the adoption of composite materials may align with sustainability goals due to their potential for recycling. However, buyers must consider the availability of skilled labor and manufacturing capabilities in their region to handle these advanced materials.
How Do Electric Vehicles Influence Material Selection for Delivery Vehicles?
The rise of electric delivery vehicles has introduced new material considerations, particularly regarding battery weight and efficiency. Lightweight materials are essential to maximize range and performance, making aluminum and composites increasingly relevant.
Pros and Cons of Using Materials in Electric Delivery Vehicles
Using lightweight materials in electric delivery vehicles can enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. However, the initial investment can be high, and the technology is still evolving, which may lead to uncertainties in long-term performance.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
International buyers must stay informed about the evolving standards and regulations surrounding electric vehicles, particularly in Europe, where stringent emission regulations are in place. Understanding the local market’s readiness for electric delivery solutions is also crucial.
| Material | Typical Use Case for Delivery Vehicle | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, structural components | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Prone to dents, higher manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Steel | Chassis, frame | High strength, durable | Heavier, susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Composites | Specialized parts, body panels | Lightweight, customizable | High cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Electric Materials | Battery enclosures, lightweight frames | Enhanced efficiency, reduced operational costs | High initial investment, evolving technology | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for delivery vehicle
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for Delivery Vehicles?
The manufacturing process for delivery vehicles consists of several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring the final product meets performance and safety standards while adhering to international regulations.
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves selecting high-quality materials that can withstand the rigors of delivery operations. Common materials include high-strength steel, aluminum, and advanced composites. Suppliers often conduct extensive testing to ensure material integrity and compliance with international standards.
Forming: In this stage, raw materials are shaped into components using techniques such as stamping, bending, and extrusion. Advanced technologies, such as CNC machining and 3D printing, are increasingly being employed to enhance precision and reduce waste. For instance, using CNC machines can lead to more accurate parts, which can be critical for the assembly process.
Assembly: The assembly process combines all individual components into the final delivery vehicle. This stage may involve robotic automation to improve efficiency and consistency. Quality assurance checkpoints are integrated here to ensure that each vehicle is assembled according to specifications. This is particularly important for delivery vehicles that require specific configurations, such as shelving for packages or ergonomic features for driver comfort.
Finishing: The final stage includes painting, coating, and installing any additional features. Finishing not only enhances the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal but also protects it from environmental factors. Surface treatments, such as galvanization, are often used to increase durability. This stage is crucial for complying with regulations regarding vehicle emissions and safety standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the manufacturing process for delivery vehicles, ensuring that every aspect of production meets or exceeds international standards. Adhering to guidelines such as ISO 9001 is essential for maintaining a consistent level of quality across all manufacturing stages.
Relevant International Standards: ISO 9001 is the most recognized quality management system standard, focusing on meeting customer requirements and enhancing satisfaction. Other industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for safety and API standards for performance, may also apply depending on the vehicle’s intended use and regional regulations.
Quality Checkpoints: Throughout the manufacturing process, several quality checkpoints are established:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. This initial verification is crucial for preventing defective parts from entering the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During assembly, IPQC checks are performed to monitor the production process and ensure compliance with quality standards. This may involve real-time inspections and adjustments to maintain quality.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, FQC involves a comprehensive inspection of the finished vehicle. This includes functional tests, safety checks, and compliance with specifications. Any discrepancies identified at this stage can lead to rework or rejection of the vehicle.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed for Delivery Vehicles?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure that delivery vehicles meet stringent performance and safety standards. Common tests include:
-
Durability Testing: Vehicles undergo stress tests to simulate real-world conditions, ensuring they can withstand the demands of daily use. This includes load tests for weight capacity and durability under varying environmental conditions.
-
Safety Testing: Crash tests and safety feature evaluations are conducted to ensure compliance with international safety regulations. This includes testing airbags, braking systems, and structural integrity.
-
Emissions Testing: For vehicles with combustion engines, emissions testing ensures compliance with environmental regulations. For electric delivery vehicles, battery performance and range testing are critical to ensure they meet operational requirements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive measures to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers, especially when dealing with international partners. Here are several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help assess their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. This should include a review of their certifications, such as ISO 9001, and an evaluation of their adherence to industry standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can provide insight into their quality control measures, testing results, and any corrective actions taken in response to identified issues.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes and product quality. This is particularly important when sourcing from regions with varying regulatory standards.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges regarding quality control and certification. Understanding these nuances is essential for successful procurement.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have specific regulations regarding vehicle safety and emissions. Buyers must ensure that suppliers are compliant with both local and international standards to avoid legal issues and ensure market access.
-
Cultural Differences: Quality expectations and standards can vary significantly across regions. B2B buyers should engage with suppliers to understand these differences and establish clear quality expectations from the outset.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Establishing transparent supply chains is vital for maintaining quality. Buyers should seek suppliers who provide visibility into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices to ensure alignment with their standards.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing delivery vehicles, ensuring they select reliable suppliers that meet their operational needs and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘delivery vehicle’
Introduction
In today’s competitive market, choosing the right delivery vehicle is crucial for optimizing logistics, reducing operational costs, and enhancing customer satisfaction. This practical sourcing guide provides B2B buyers with a step-by-step checklist to ensure they make informed decisions when procuring delivery vehicles that meet their specific business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Delivery Needs
Understanding your delivery requirements is the first step in selecting the right vehicle. Consider factors such as delivery volume, distance, and types of goods transported. This clarity helps in determining vehicle size, payload capacity, and fuel efficiency, which are essential for maximizing operational effectiveness.
- Volume and Weight: Assess the average size and weight of packages.
- Delivery Radius: Identify whether deliveries are local or regional to gauge fuel efficiency needs.
Step 2: Research Vehicle Types
Explore various vehicle types suitable for your delivery operations. Options may include vans, trucks, or electric vehicles, each with unique advantages. Understanding these types helps in aligning vehicle features with your operational demands.
- Electric vs. Gasoline: Consider sustainability and long-term cost savings.
- Specialized Vehicles: Investigate vehicles designed for specific industries, like refrigerated vans for food delivery.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Options
Before making a purchase, it’s essential to vet potential suppliers thoroughly. This involves reviewing their reputation, product offerings, and after-sales service. A reliable supplier can significantly impact your operational success.
- Company Profiles: Request detailed company information and check their industry experience.
- References: Ask for case studies or testimonials from businesses similar to yours.
Step 4: Assess Vehicle Specifications
Dive into the technical specifications of the vehicles you are considering. Look for important features such as cargo space, fuel efficiency, and safety ratings. This evaluation ensures that the vehicle can handle your delivery operations effectively.
- Cargo Volume: Ensure the vehicle has sufficient space for your typical load.
- Safety Features: Prioritize vehicles equipped with advanced safety technologies to protect drivers and cargo.
Step 5: Consider Financing Options
Understanding financing options can significantly affect your procurement decision. Evaluate leasing versus purchasing, and investigate any available financing incentives or tax credits, especially for electric vehicles.
- Leasing vs. Buying: Analyze the benefits of each option based on cash flow and long-term costs.
- Incentives: Research local government incentives for purchasing electric vehicles, which can lower overall costs.
Step 6: Test Drive and Evaluate Performance
Before finalizing your decision, arrange for test drives of potential vehicles. This hands-on experience allows you to assess comfort, handling, and overall performance, ensuring the vehicle meets your operational standards.
- Driver Comfort: Ensure that the vehicle is comfortable for long hours on the road.
- Performance Metrics: Evaluate acceleration, braking, and maneuverability in real-world scenarios.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you’ve selected a vehicle and supplier, carefully review the purchase agreement. Ensure it includes all agreed-upon terms, warranties, and service options. A clear contract protects your investment and outlines the supplier’s responsibilities.
- Warranties and Service Plans: Confirm that adequate support is available for maintenance and repairs.
- Delivery Timeline: Establish clear timelines for vehicle delivery and any additional services.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing delivery vehicles, ultimately enhancing their logistics operations and customer satisfaction.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for delivery vehicle Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Delivery Vehicle Sourcing?
When sourcing delivery vehicles, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall price. Vehicles constructed with lightweight, durable materials like aluminum or advanced composites can improve fuel efficiency but may come at a higher upfront cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be influenced by local wage standards. Skilled labor for assembly and vehicle customization might increase costs, especially if the vehicle is produced in countries with higher labor rates.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, affecting the final price.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized vehicles can be a significant expense, particularly for unique designs or modifications. Buyers should consider whether the tooling costs are amortized over a larger production run to achieve economies of scale.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures can increase costs but is essential for ensuring reliability and safety, especially for vehicles used in demanding delivery environments.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including transportation and handling, are critical in the overall pricing structure. International buyers must account for potential tariffs and customs duties, which can add to the final cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding market competition can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Delivery Vehicles?
Several factors can influence the pricing of delivery vehicles:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs. Negotiating for bulk purchasing can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features can substantially increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: High-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) can raise costs but may provide long-term value through durability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The choice of supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may offer reliability but at a premium, while newer entrants might provide more competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms is vital. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, affecting the total landed cost of the vehicle.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Delivery Vehicle Prices?
To maximize value and minimize costs in delivery vehicle sourcing, consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage your position as a bulk buyer to negotiate better terms. Be prepared to discuss pricing based on your total order volume and potential for future orders.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not only the purchase price but also operational costs like fuel efficiency, maintenance, and resale value. An initially higher investment in a more efficient vehicle can yield long-term savings.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: When sourcing vehicles from different regions, consider currency fluctuations, local taxes, and varying shipping costs. These factors can significantly impact the final price.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Understanding market dynamics and regional demand can provide leverage in negotiations. Keeping abreast of technological advancements, such as electric vehicles, can also inform your decisions and potentially lead to lower operational costs.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Pricing for delivery vehicles can fluctuate based on multiple factors, including market conditions, raw material costs, and global supply chain disruptions. The figures provided in this analysis are indicative and should be verified with suppliers for the most accurate and current pricing before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing delivery vehicle With Other Solutions
In the rapidly evolving logistics landscape, businesses must evaluate various delivery solutions to optimize their operations. While delivery vehicles are a cornerstone of transportation, alternative methods and technologies can also achieve similar objectives. This analysis compares delivery vehicles against two viable alternatives: drone delivery systems and autonomous delivery robots, each with distinct advantages and challenges.
| Comparison Aspect | Delivery Vehicle | Drone Delivery System | Autonomous Delivery Robot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High capacity, versatile routes | Quick delivery for small packages | Efficient for short distances, limited capacity |
| Cost | High initial and operational costs | Moderate initial costs, low operational costs | Low initial costs, moderate operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires infrastructure and permits | Regulatory hurdles and air traffic management | Minimal infrastructure, but limited by urban planning |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance required | Minimal, but battery replacement needed | Low maintenance; regular charging required |
| Best Use Case | Bulk goods, longer distances | Urgent small parcel deliveries | Last-mile delivery in urban areas |
How Do Delivery Vehicles Compare to Drone Delivery Systems?
Delivery vehicles are highly effective for transporting larger shipments over varied distances. They can handle multiple packages simultaneously, making them ideal for bulk deliveries. However, the costs associated with purchasing, maintaining, and operating these vehicles can be significant.
On the other hand, drone delivery systems excel in speed, especially for small packages. They can bypass traffic and reach remote areas quickly. However, they face challenges related to regulatory compliance, airspace management, and limited payload capacity. Businesses must weigh the advantages of rapid delivery against the complexities of integrating drone technology into their existing logistics frameworks.
What Are the Advantages of Autonomous Delivery Robots?
Autonomous delivery robots provide a unique solution for last-mile delivery, particularly in urban environments. They can navigate sidewalks and pedestrian areas, reducing the need for extensive road infrastructure. Their low operational costs and minimal maintenance requirements make them an attractive option for businesses looking to streamline last-mile logistics.
However, these robots are limited in their cargo capacity and operational range, making them unsuitable for larger deliveries or longer distances. Additionally, they may face challenges with navigation in crowded or complex environments, which can hinder their effectiveness.
Conclusion: Which Delivery Solution is Right for Your Business?
Choosing the right delivery solution depends on your specific operational needs and constraints. If your business requires bulk transport over longer distances, traditional delivery vehicles may remain the best option. Conversely, if your focus is on rapid, small-scale deliveries within urban areas, drone systems or autonomous robots could offer significant advantages. Assessing your delivery volume, budget, regulatory landscape, and customer expectations will guide you in selecting the most suitable method for your logistics strategy.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for delivery vehicle
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Delivery Vehicles?
Understanding the essential technical properties of delivery vehicles is critical for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some of the most important specifications to consider:
-
Payload Capacity
The payload capacity indicates the maximum weight a vehicle can carry, excluding its own weight. For delivery vehicles, this is crucial as it directly affects operational efficiency. A higher payload capacity allows businesses to transport more goods in a single trip, reducing fuel costs and improving delivery times. -
Cargo Volume
This measurement defines the internal space available for cargo, usually expressed in cubic feet or cubic meters. For delivery operations, especially in last-mile logistics, maximizing cargo volume can lead to significant efficiency gains. Businesses must ensure that the cargo volume meets their specific delivery requirements to avoid underutilization or the need for additional trips. -
Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency, typically measured in miles per gallon (MPG) or liters per 100 kilometers, is a critical metric for controlling operational costs. Delivery businesses face rising fuel prices, so investing in vehicles with higher fuel efficiency can lead to significant savings over time. Electric vehicles (EVs) also offer lower operational costs compared to traditional combustion engines. -
Safety Features
Modern delivery vehicles come equipped with a range of safety features, such as collision avoidance systems, blind-spot monitoring, and 360-degree cameras. These features are essential for protecting drivers and reducing liability for businesses. Investing in vehicles with advanced safety technologies can also improve driver morale and retention. -
Vehicle Dimensions
Dimensions such as length, width, and height are vital for ensuring that vehicles can navigate urban environments and fit into designated loading areas. Buyers must consider these dimensions in relation to their delivery routes to avoid logistical challenges. -
Durability and Build Quality
The materials used in the construction of delivery vehicles, such as high-strength steel or composite materials, affect durability and maintenance costs. A vehicle designed for heavy-duty use will withstand the rigors of daily deliveries better than standard models, thus reducing downtime and maintenance expenses.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Delivery Vehicle Industry?
Navigating the delivery vehicle market requires familiarity with specific trade terminology. Here are some essential terms to understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce the original components used in the manufacturing of delivery vehicles. Understanding OEM relationships is important for buyers who may need replacement parts or wish to maintain vehicle warranties. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ can help in budgeting and inventory management, particularly when procuring fleet vehicles or spare parts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from potential suppliers. It helps businesses compare costs and terms from different vendors, enabling more informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms can help buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery responsibilities. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with owning a delivery vehicle over its entire lifecycle, including purchase price, maintenance, fuel, insurance, and depreciation. Understanding TCO helps businesses assess the long-term financial impact of their vehicle choices. -
Telematics
Telematics refers to the integration of telecommunications and monitoring systems in vehicles. This technology allows businesses to track vehicle location, performance, and driver behavior in real time, leading to improved efficiency and reduced operational costs.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions when selecting delivery vehicles that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the delivery vehicle Sector
What are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Delivery Vehicle Sector?
The delivery vehicle sector is undergoing a significant transformation driven by several global factors. The rise of e-commerce, particularly accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, has led to an unprecedented demand for last-mile delivery solutions. International B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking vehicles that can efficiently handle urban delivery challenges. In this context, technologies such as route optimization software and telematics are becoming essential tools for enhancing operational efficiency. Furthermore, the shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is gaining momentum, driven by governmental policies and consumer demand for sustainability.
Emerging trends include the integration of automation and AI in fleet management, which allows businesses to make data-driven decisions that can optimize routes and reduce operational costs. Companies are also focusing on vehicle ergonomics and safety features to improve driver satisfaction and retention. As the delivery landscape becomes more competitive, international buyers must stay informed about these trends to ensure they are investing in the most effective and future-proof delivery solutions.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Delivery Vehicle Sector?
Sustainability is no longer an option but a necessity for businesses in the delivery vehicle sector. The environmental impact of traditional combustion engine vehicles has prompted both consumers and companies to prioritize greener alternatives. International B2B buyers are increasingly looking for vehicles that not only offer operational efficiencies but also align with their sustainability goals. This includes investing in electric or hybrid vehicles that can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses are expected to maintain transparent supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the use of sustainable materials can enhance a company’s reputation and meet the expectations of environmentally conscious consumers. Buyers should actively seek partnerships with manufacturers that prioritize ethical practices in their sourcing strategies, ensuring that their fleet contributes positively to both the environment and society.
What is the Evolution of Delivery Vehicles and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The delivery vehicle sector has evolved significantly from traditional vans and trucks to modern, tech-enabled solutions that incorporate advanced safety features, connectivity, and sustainability. Initially, delivery vehicles were primarily focused on capacity and fuel efficiency. However, the rise of e-commerce and changing consumer behaviors have necessitated a shift toward more versatile and flexible vehicles designed for urban environments.
Today, delivery vehicles are equipped with features such as real-time tracking, automated route optimization, and electric powertrains. This evolution reflects the broader trends in logistics and supply chain management, where efficiency, sustainability, and customer experience are paramount. For international B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with market demands and future-proof their operations. Investing in the latest technologies and sustainable practices will not only enhance operational efficiency but also build a brand that resonates with the values of today’s consumers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of delivery vehicle
-
How do I choose the right delivery vehicle for my business needs?
Choosing the right delivery vehicle depends on several factors, including the volume and type of goods you transport, your delivery range, and operational costs. Evaluate vehicles based on cargo capacity, fuel efficiency, maintenance requirements, and driver comfort. For international buyers, consider local regulations and the availability of parts and service support. It’s also wise to consult with suppliers who can provide insights tailored to your specific market conditions and operational needs. -
What are the best delivery vehicles for urban environments?
For urban delivery, compact vans or electric vehicles are often the best choices due to their maneuverability and eco-friendliness. Models like the BrightDrop Zevo and Rivian Commercial Van are designed for last-mile logistics, offering features like low step-in heights and advanced safety systems. These vehicles help navigate tight city streets while minimizing environmental impact, which is increasingly important in urban areas with stringent emissions regulations. -
What customization options are available for delivery vehicles?
Most manufacturers offer a range of customization options to meet specific operational needs. This can include shelving, cargo management systems, and vehicle branding. Inquire about additional features like climate control for sensitive goods, advanced navigation systems, and driver assistance technologies. Customizations can enhance efficiency and driver comfort, making it essential to discuss your requirements early in the procurement process. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for delivery vehicles?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between manufacturers and models. While some suppliers may accommodate single-unit purchases, others might require orders of five or more vehicles to secure favorable pricing. It’s advisable to negotiate MOQs based on your fleet requirements and potential for future orders. Establishing a good relationship with suppliers can also lead to more flexible terms. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing delivery vehicles?
Payment terms for delivery vehicles typically include options for upfront payment, financing, or leasing. Many suppliers offer financing solutions with flexible payment plans to accommodate cash flow needs. Be sure to clarify terms regarding deposits, installment payments, and any applicable taxes or fees. Understanding these terms upfront will help you manage your budget effectively and avoid unexpected costs. -
How do I vet suppliers when sourcing delivery vehicles internationally?
When sourcing vehicles internationally, thorough supplier vetting is crucial. Look for suppliers with a solid reputation, verified credentials, and positive reviews from previous clients. Request references and conduct background checks. It’s also beneficial to visit manufacturing facilities if possible, or utilize third-party inspection services to ensure quality control. Establishing clear communication and understanding cultural differences can also enhance the partnership. -
What quality assurance measures should I consider when buying delivery vehicles?
Quality assurance measures can include certifications from recognized industry standards, warranty offerings, and post-purchase support. Ensure that the vehicles you’re considering have undergone rigorous testing for safety and performance. Additionally, inquire about the manufacturer’s maintenance programs and availability of spare parts in your region. This will help ensure that your fleet remains operational with minimal downtime. -
How can I optimize my delivery routes to maximize efficiency?
To optimize delivery routes, consider using advanced route planning software that factors in real-time traffic, weather conditions, and delivery windows. Tools such as Route4Me or Circuit can help streamline your logistics, reducing fuel consumption and improving delivery times. Training drivers on efficient driving practices and regularly analyzing route performance data can further enhance operational efficiency, leading to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Delivery Vehicle Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Rivian – Electric Commercial Vans
Domain: rivian.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Rivian Fleet offers electric work and commercial vans starting at $79,900. The Rivian Commercial Van is designed to maximize uptime while ensuring driver safety and comfort, featuring 360-degree cameras and patented energy-saving microclimate seats. It aims to reduce operational GHG emissions by 50% or more compared to internal combustion alternatives. Key dimensions include a length of 248.5 inch…
2. Utilimaster – Parcel Delivery Fleet Vehicles
Domain: utilimaster.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Utilimaster offers a range of parcel delivery fleet vehicles designed for efficiency and productivity. Key products include: 1. **Velocity Utility Service** – Enhances fleet management and operational efficiency. 2. **Walk-in Vans** – Standard delivery vehicles. 3. **Truck Bodies** – Industry standard for heavy-duty commercial delivery. 4. **Velocity Series** – Designed for large product/package d…
3. GM – BrightDrop Zevo 600 & Zevo 400
Domain: gmenvolve.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
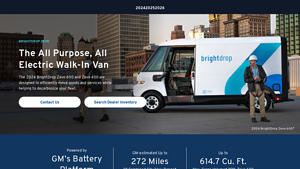
Introduction: 2024 BrightDrop Zevo 600 and Zevo 400 electric delivery vehicles designed for efficient goods movement and fleet decarbonization. Key specifications include:
– Powered by GM’s Battery Platform
– Estimated range: Up to 272 miles combined (city/highway)
– Cargo volume: Zevo 600 – 614.7 cu. ft., Zevo 400 – 412.1 cu. ft.
– Lease offer: $599/month for 36 months, $2,999 due at signing
– Starting pr…
4. Freepik – Delivery Vehicle Images
Domain: freepik.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Delivery vehicle images available for free download on Freepik. Categories include warehouse, supply chain, post office, food delivery, delivery truck, pizza delivery, cargo van, delivery motorcycle, transportation management, and distribution center. Various formats such as vectors, illustrations, photos, icons, videos, PSD templates, mockups, and 3D models are offered. The platform features AI t…
5. Chevrolet – 2025 BrightDrop 400 & 600
Domain: chevrolet.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: 2025 Chevrolet BrightDrop 400: Starting price $46,425 after cash offers, up to 272 mi combined city/hwy range, max cargo volume 412.1 cu. ft., max payload 3,710 lbs., max GVWR 11,000 lbs. 2025 Chevrolet BrightDrop 600: Starting price $47,925 after cash offers, up to 303/234 mi city/hwy range, max cargo volume 614.7 cu. ft., max payload 3,350 lbs., max GVWR 11,000 lbs. Features include low step-in …
6. Typsy – Types of Delivery Vehicles
Domain: typsy.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Course Title: Types of Delivery Vehicles
Duration: 2m 37s
Format: 100% online, learn at your own pace
Instructor: Scott Landers, co-founder and CEO of Figure 8 Logistics
Key Learnings:
– Understanding ownership of delivery vehicles
– Identifying suitable vehicles for different types of food delivery
– Analyzing delivery zones to choose the best vehicle
Included in the Course:
– Welcome – Food de…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for delivery vehicle
As global logistics continue to evolve, the strategic sourcing of delivery vehicles has become paramount for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and sustainability. B2B buyers must prioritize vehicles that not only meet their specific delivery needs but also align with broader goals such as reducing operational costs and minimizing environmental impact. The emergence of electric and hybrid vehicles offers compelling advantages, including lower emissions and significant fuel savings, making them a wise investment for forward-thinking companies.
Moreover, leveraging innovative fleet management practices can drive productivity and ensure optimal vehicle utilization. Buyers should engage with suppliers who understand the complexities of their operations and can provide tailored solutions, from vehicle selection to route optimization and maintenance support.
Looking ahead, the demand for efficient delivery solutions is expected to grow, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By embracing strategic sourcing now, international B2B buyers position themselves to capitalize on emerging trends and technologies in the delivery vehicle market. Seize this opportunity to enhance your logistics operations—evaluate your fleet needs, consider sustainable options, and partner with industry experts to navigate the future of delivery vehicles effectively.