Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 1 seat electric car
In an era where urbanization and environmental consciousness converge, the demand for compact and efficient transportation solutions is surging. The one-seat electric car represents a pivotal innovation for B2B buyers seeking to navigate the complexities of the global market. However, sourcing these vehicles can be challenging due to varying regulations, technological advancements, and market dynamics across regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Nigeria.
This comprehensive guide aims to empower international B2B buyers by exploring the diverse types of one-seat electric cars available, their applications in various sectors, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers. We will delve into the cost structures, highlighting affordability without compromising quality, and providing insights into the latest technological advancements that drive efficiency and sustainability.
By equipping buyers with actionable intelligence and market insights, this guide facilitates informed purchasing decisions, enabling businesses to leverage the growing trend of micro-mobility. Whether addressing urban congestion or enhancing last-mile delivery, understanding the landscape of one-seat electric cars will position B2B buyers to make strategic investments that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
Understanding 1 seat electric car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultra-Compact EV | Single-seat, lightweight, minimalistic design, affordable price | Last-mile delivery, personal mobility | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to park; Cons: Limited range and speed. |
| Micro-Mobility Vehicle | Small footprint, agile handling, can accommodate one passenger | Urban transport, shared mobility services | Pros: High maneuverability, quick charging; Cons: May lack cargo space. |
| Personal Mobility Pod | Enclosed design, safety features, eco-friendly materials | Individual transport in urban areas | Pros: Enhanced safety, weather protection; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Modular Electric Vehicle | Customizable configurations, adaptable for various uses | Fleet services, rental companies | Pros: Versatile applications, scalable design; Cons: Potentially complex maintenance. |
| Smart Electric Scooter | Integrated technology, connectivity features, one-person design | Urban commuting, short-distance travel | Pros: Lightweight, tech-savvy; Cons: Limited range and comfort for longer trips. |
What Characterizes Ultra-Compact EVs and Their B2B Relevance?
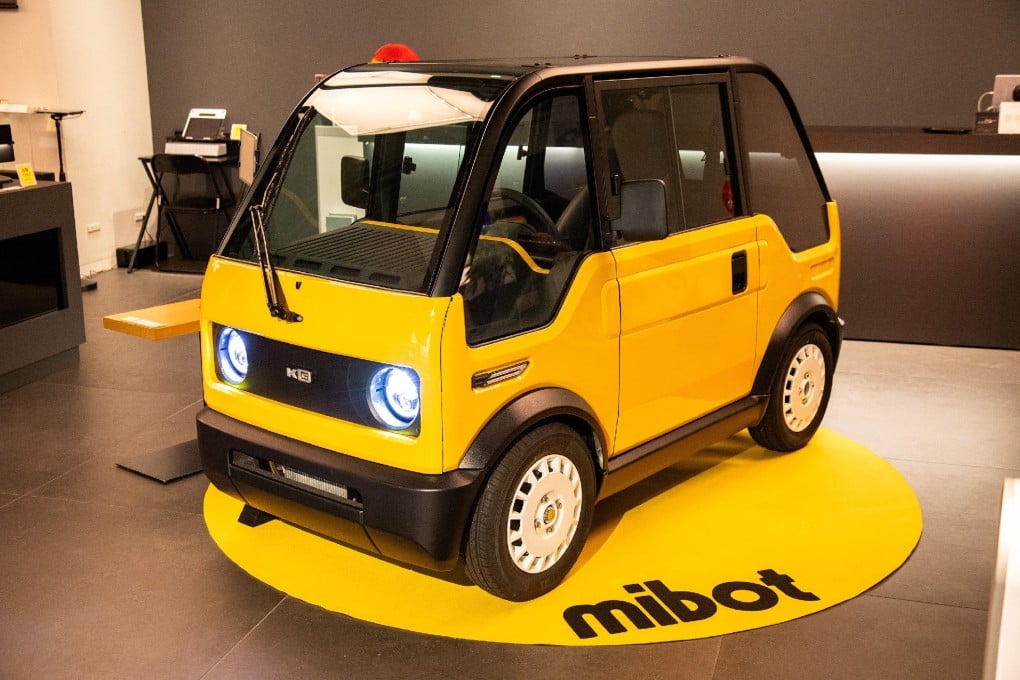
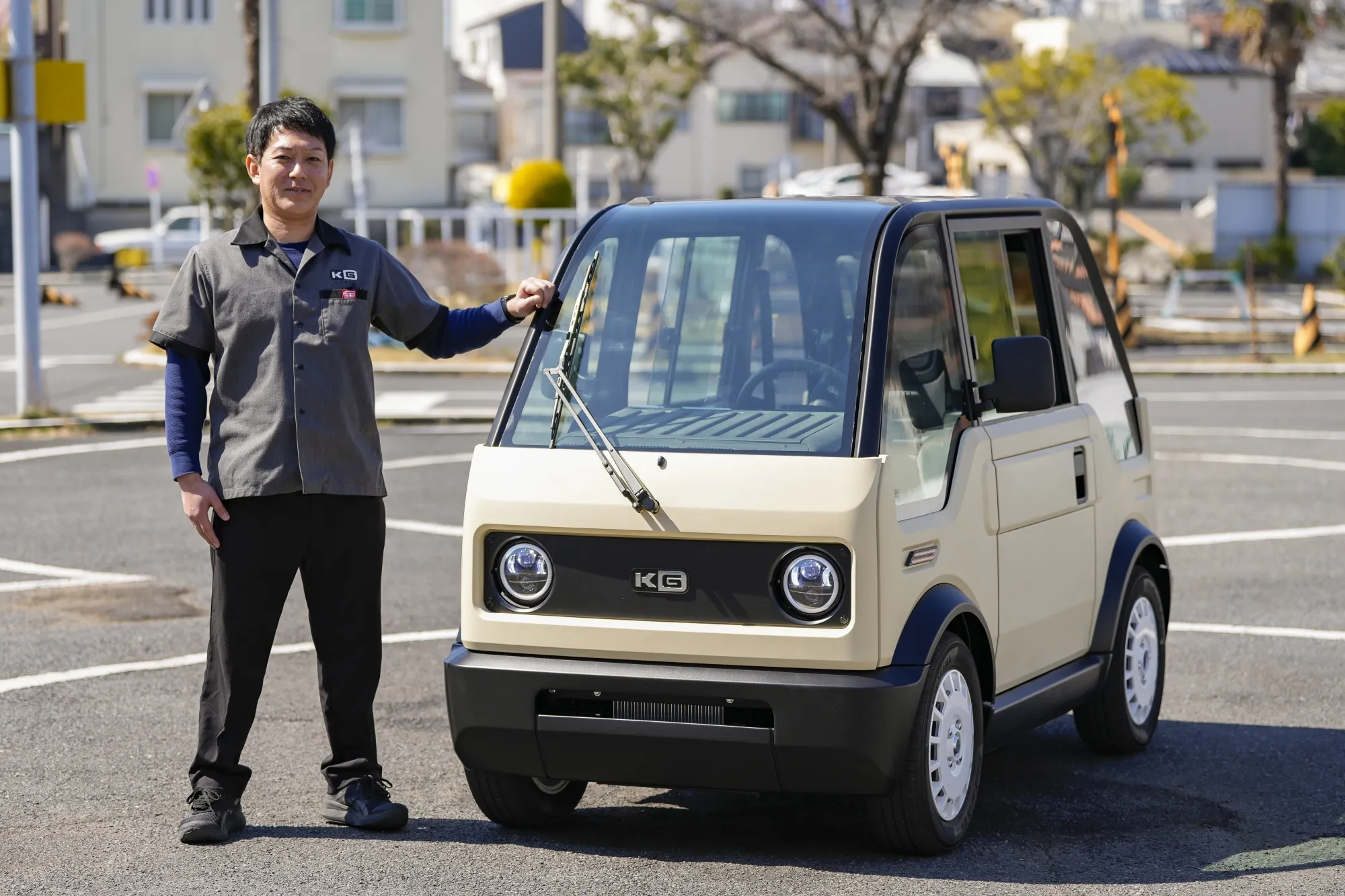
Ultra-compact electric vehicles, like Japan’s KG Motors mibot, are designed for efficiency and affordability. With a price point around $7,000 and a compact size, these vehicles are ideal for last-mile delivery services, particularly in regions with constrained urban spaces. B2B buyers should consider the practicality of these vehicles in navigating narrow streets and their suitability for rural areas with limited public transport. However, the limited range of around 62 miles may restrict their use in longer-distance applications.
How Do Micro-Mobility Vehicles Fit into Urban Transport?
Micro-mobility vehicles are characterized by their small size and agility, making them perfect for urban transport solutions. These vehicles can easily maneuver through congested streets, serving as an excellent option for shared mobility services. B2B buyers in urban settings should evaluate their potential for reducing traffic congestion and providing efficient transportation alternatives. However, the trade-off may be a lack of cargo space, which could limit their use for businesses needing to transport goods.
What Advantages Do Personal Mobility Pods Offer?
Personal mobility pods provide a safe and enclosed environment for individual transport. They are particularly suited for urban areas where safety and eco-friendliness are paramount. B2B applications include employee transport services and individual commuting solutions. Buyers should consider the enhanced safety features and protection from weather elements. However, the higher initial investment may be a barrier for some businesses.
Why Consider Modular Electric Vehicles for Fleet Services?
Modular electric vehicles offer customizable configurations, making them adaptable for various business needs. They are particularly beneficial for fleet services and rental companies that require versatility in their vehicle offerings. B2B buyers should assess their potential for scalability and how they can be tailored to specific operational requirements. The complexity of maintenance may be a downside, requiring a more robust service strategy.
How Do Smart Electric Scooters Enhance Urban Commuting?
Smart electric scooters are designed with integrated technology for connectivity, making them an attractive option for urban commuting. They cater to the tech-savvy demographic and can be utilized in short-distance travel scenarios. B2B applications include corporate mobility programs and urban commuting solutions for employees. While their lightweight design enhances portability, buyers should be aware of their limited range and comfort for longer journeys.
Key Industrial Applications of 1 seat electric car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 1 seat electric car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Mobility | Last-mile delivery solutions | Reduces congestion and carbon footprint, enhancing delivery efficiency | Battery life, charging infrastructure, vehicle compactness |
| Public Transportation | Complementary transport in underserved areas | Provides affordable mobility options where public transport is lacking | Maintenance services, local regulations, affordability |
| Tourism and Leisure | Eco-friendly transport for tourists | Enhances visitor experience while promoting sustainable tourism | Vehicle design, rental agreements, local partnerships |
| Agriculture | Transport for farm workers and goods | Increases operational efficiency in rural areas with limited access | Durability, off-road capabilities, battery range |
| Corporate Fleets | Employee commuting solutions | Reduces fleet costs while promoting sustainability and corporate image | Fleet management software, charging solutions, vehicle reliability |
How Can 1 Seat Electric Cars Enhance Urban Mobility Solutions?
One-seat electric cars can significantly improve last-mile delivery solutions in urban settings. With their compact size, these vehicles can navigate congested city streets and deliver goods directly to consumers. This not only reduces traffic congestion but also lowers emissions, addressing environmental concerns. For businesses, sourcing these vehicles requires consideration of battery life and charging infrastructure to ensure operational efficiency.
In What Ways Do 1 Seat Electric Cars Support Public Transportation?
In regions with inadequate public transportation, one-seat electric cars serve as a practical alternative, providing affordable mobility solutions. These vehicles can be deployed in underserved areas, where traditional public transport options are limited or non-existent. For B2B buyers in this sector, key considerations include vehicle maintenance services and compliance with local regulations to ensure smooth operations.
How Do 1 Seat Electric Cars Benefit the Tourism and Leisure Industry?
Tourism operators can utilize one-seat electric cars to offer eco-friendly transport options for visitors, enhancing the overall experience while promoting sustainability. These vehicles can be rented out to tourists, allowing them to explore destinations at their own pace. B2B buyers should focus on vehicle design and rental agreements that align with local tourism strategies, as well as establishing partnerships with local businesses for greater reach.
What Role Do 1 Seat Electric Cars Play in Agricultural Operations?
In agriculture, one-seat electric cars can be effectively used for transporting farm workers and goods across expansive rural areas. Their compact design allows them to maneuver through narrow paths and fields, increasing operational efficiency. Buyers in this sector must consider the durability of the vehicles, off-road capabilities, and battery range to meet the demands of agricultural environments.
How Can Corporations Leverage 1 Seat Electric Cars for Employee Commuting?
Corporations can integrate one-seat electric cars into their fleets to provide sustainable commuting options for employees. This not only reduces transportation costs but also enhances the company’s sustainability profile. When sourcing these vehicles, businesses should prioritize fleet management software, charging solutions, and vehicle reliability to ensure an effective commuting strategy.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘1 seat electric car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Urban Mobility for Small Businesses
The Problem: Many small businesses in densely populated urban areas face significant challenges with transportation logistics. As cities become increasingly congested, larger vehicles often struggle to navigate narrow streets and find parking. This limitation can hinder timely deliveries and customer service, ultimately affecting business operations and customer satisfaction. For businesses that require efficient, flexible transport solutions, the lack of appropriate vehicles can lead to lost revenue opportunities.
The Solution: B2B buyers can address this issue by investing in one-seat electric cars designed specifically for urban environments. These compact vehicles excel in maneuverability, allowing businesses to easily navigate tight spaces and congested streets. When sourcing these vehicles, buyers should prioritize models with a small footprint and advanced parking capabilities, such as the ability to cross-park directly onto sidewalks. Additionally, consider integrating fleet management software that tracks vehicle usage and optimizes routes, ensuring efficient use of the vehicle for deliveries or client visits. This strategic investment not only enhances operational efficiency but also positions the business as environmentally conscious, appealing to a growing base of eco-aware consumers.
Scenario 2: Affordability and Budget Constraints
The Problem: For many businesses, particularly startups or SMEs in emerging markets, budget constraints are a significant barrier to adopting electric vehicle (EV) technology. The initial cost of acquiring new vehicles can be daunting, especially when considering additional expenses such as maintenance, insurance, and charging infrastructure. This financial burden can deter businesses from transitioning to electric mobility, limiting their operational capabilities and growth potential.
The Solution: B2B buyers should explore affordable one-seat electric cars that offer competitive pricing without sacrificing quality. Engaging with manufacturers that provide financing options or leasing arrangements can help mitigate upfront costs. Additionally, potential buyers should investigate government incentives or subsidies available in their region that promote electric vehicle adoption. By leveraging these financial supports, businesses can significantly reduce their investment risk. It’s also advisable to conduct a total cost of ownership analysis, factoring in long-term savings on fuel and maintenance, to present a clearer picture of the financial benefits associated with switching to electric vehicles.
Scenario 3: Infrastructure Challenges in Emerging Markets
The Problem: In regions like Africa and South America, inadequate charging infrastructure poses a major challenge for businesses considering the adoption of one-seat electric cars. The fear of running out of battery power, commonly known as range anxiety, can prevent companies from fully committing to electric vehicles. Additionally, the lack of reliable power sources can complicate the logistics of maintaining a fleet of EVs, resulting in operational downtime and inefficiencies.
The Solution: To overcome these infrastructure challenges, B2B buyers should prioritize one-seat electric cars that offer flexible charging options, such as compatibility with standard household outlets. This feature allows businesses to charge vehicles at their facilities, mitigating reliance on public charging stations. Furthermore, forming partnerships with local energy providers can help establish a network of charging solutions tailored to the business’s operational needs. Buyers should also consider investing in portable charging units that can be deployed in various locations, ensuring that vehicles remain operational even in areas with limited access to electricity. By taking these proactive steps, businesses can create a sustainable and reliable transportation solution that supports their growth and operational goals.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 1 seat electric car
What Are the Key Materials for a One-Seat Electric Car?
When selecting materials for a one-seat electric car, it is crucial to consider properties that enhance performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. This guide analyzes several common materials that are suitable for this application, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Which Materials Offer Optimal Performance for Electric Vehicle Components?
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent thermal conductivity. It typically withstands temperatures up to 600°C (1112°F) and can handle moderate pressures.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which contributes to improved energy efficiency and range in electric vehicles. However, its cost can be higher compared to steel, and it may require specialized manufacturing techniques, such as welding or extrusion, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for the body and chassis of the vehicle, as it enhances performance without adding significant weight. It is compatible with various coatings for corrosion resistance, which is crucial in regions with high humidity or saline environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East may prefer aluminum due to its compliance with stringent environmental regulations. In Africa and South America, where cost sensitivity is higher, the initial investment may be a consideration, but the long-term benefits in energy savings could justify the expense.
High-Strength Steel
Key Properties: High-strength steel offers excellent tensile strength and impact resistance, with a yield strength typically ranging from 300 to 600 MPa. It can withstand high temperatures and is less prone to deformation under stress.
Pros & Cons: This material is relatively inexpensive and widely available, making it a popular choice for structural components. However, it is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact the vehicle’s range and efficiency.
Impact on Application: High-strength steel is suitable for areas requiring enhanced structural integrity, such as the frame and safety components. Its compatibility with various manufacturing processes, including stamping and welding, makes it versatile for production.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN is essential, especially in Europe. In regions like Nigeria, where local manufacturing capabilities may vary, sourcing high-strength steel that meets local regulations can be a challenge.
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP)
Key Properties: CFRP is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, with tensile strengths exceeding 600 MPa. It is also resistant to corrosion and can withstand a wide range of temperatures.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of CFRP is its lightweight nature, significantly improving energy efficiency. However, it is considerably more expensive than metals and requires specialized manufacturing techniques, which can increase production complexity.
Impact on Application: CFRP is ideal for components where weight savings are critical, such as body panels and interior structures. Its compatibility with various finishes and coatings allows for aesthetic customization.
Considerations for International Buyers: The high cost of CFRP may deter buyers in cost-sensitive markets like Africa and South America. However, for premium markets in Europe, such as Germany, the investment may be justified by performance benefits. Compliance with international standards is crucial for ensuring quality and safety.
What Is the Summary of Material Selection for One-Seat Electric Cars?
The following table summarizes the key materials discussed, providing an overview of their applications, advantages, disadvantages, and cost considerations for B2B buyers.
| Material | Typical Use Case for 1 seat electric car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body and chassis components | Lightweight, improving energy efficiency | Higher cost, requires specialized manufacturing | High |
| High-Strength Steel | Structural frame and safety components | Cost-effective and widely available | Heavier, potentially reducing range | Low |
| Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) | Body panels and interior structures | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost, complex manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to equip international B2B buyers with actionable insights to make informed decisions regarding the materials used in one-seat electric cars, considering factors such as performance, cost, and regional compliance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 1 seat electric car
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of a One-Seat Electric Car?
The manufacturing process for a one-seat electric car involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure efficiency and quality. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for the Manufacturing of One-Seat Electric Cars?
Material preparation is the first step, where raw materials such as aluminum, steel, and composite materials are sourced and inspected. These materials are chosen for their lightweight properties, which are essential for electric vehicle efficiency. Suppliers must adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, ensuring that the materials meet specific criteria for strength and durability.
During this stage, B2B buyers should verify supplier certifications and request material safety data sheets (MSDS) to assess the quality of materials being used. This initial scrutiny can prevent future complications during production and ensure compliance with international standards.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of One-Seat Electric Cars?
Forming is the next stage, where the prepared materials are shaped into components. This process typically includes techniques like stamping, extrusion, and molding. For example, the body panels of the vehicle may be stamped from sheets of aluminum, while the battery housing might be molded from high-strength plastics.
Advanced manufacturing techniques such as Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining are also utilized to achieve precision in component dimensions, which is critical for the assembly process. B2B buyers should consider asking about the technology used in forming processes, as this can directly impact the product’s overall quality and performance.
How Is the Assembly Process Conducted for One-Seat Electric Cars?
Assembly involves the integration of various components, including the electric motor, battery pack, chassis, and electronic systems. This stage typically employs a combination of manual labor and automation to ensure efficiency and accuracy. Key quality control checkpoints are established during assembly, including In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) measures to monitor assembly accuracy and functionality.
B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly line’s layout and workflow, as an optimized assembly process can significantly reduce production time and improve product reliability. Additionally, understanding the labor force’s training and expertise is vital for assessing quality outcomes.
What Finishing Techniques Are Commonly Used in Electric Car Manufacturing?
The finishing stage involves painting, coating, and final inspections. This not only enhances the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal but also provides protection against environmental factors. Advanced techniques such as robotic painting systems are often employed to ensure consistent quality and minimize human error.
During this stage, B2B buyers can request samples of the final finish and inquire about the durability tests conducted on coatings. Understanding the finishing process can offer insights into the long-term maintenance and resilience of the vehicle.
How Is Quality Assurance Managed in One-Seat Electric Car Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that each vehicle meets predefined quality standards. Various international standards, such as ISO 9001, along with industry-specific certifications like CE and API, guide the QA processes.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Electric Car Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints include Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint ensures that all materials and components received meet the specified quality standards before they enter production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the assembly process, this step monitors the quality of work in real-time, allowing for immediate corrective actions if issues arise.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection phase verifies that the completed vehicle adheres to all quality and safety standards before delivery.
B2B buyers should be aware of the frequency and rigor of these quality checks to ensure that their orders meet their expectations.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality in Electric Cars?
Testing methods include functional testing, stress testing, and safety evaluations. Functional testing examines the performance of the electric motor, battery efficiency, and overall vehicle functionality. Stress testing assesses the vehicle’s structural integrity under various conditions, while safety evaluations ensure compliance with crash test standards.
B2B buyers should request detailed reports on testing outcomes and protocols used by manufacturers. This transparency is crucial for establishing trust and ensuring that products meet market expectations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers must actively verify the quality control measures employed by their suppliers. This can be achieved through several strategies:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of the manufacturing facilities can help assess adherence to quality standards and operational efficiency.
- Reports: Requesting quality assurance reports and documentation can provide insights into the supplier’s QA processes.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality control measures.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For international buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding local regulations and compliance standards is essential. Each region may have specific requirements regarding vehicle emissions, safety, and technology standards that must be met.
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations and ensure that their suppliers can meet them. This may involve additional certifications or modifications to the vehicle designs to comply with local laws, which can affect timelines and costs.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for one-seat electric cars are pivotal in ensuring that these vehicles meet the demands of the market. By understanding the stages of manufacturing, the importance of quality control, and the nuances of international compliance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives. Investing time in verifying supplier capabilities and quality assurance practices will ultimately lead to successful partnerships and high-quality products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘1 seat electric car’
This guide provides a structured approach for B2B buyers interested in sourcing a one-seat electric car. As the demand for compact and efficient vehicles rises globally, especially in regions with urban congestion and limited public transport, understanding the procurement process is crucial for making informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital to ensure that the one-seat electric car meets your operational needs. Consider factors such as range, charging time, maximum speed, and safety features. For instance, a range of at least 100 kilometers may be necessary for urban commuting in regions with limited charging infrastructure.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Competitors
Stay informed about current market trends and competitor offerings to identify the best options available. Research the latest developments in electric vehicle technology, such as battery efficiency and vehicle design. Understanding the competitive landscape, including pricing and feature comparisons, will help you make a more strategic purchasing decision.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers to ensure reliability and product quality. Request detailed company profiles, including their production capabilities, previous client references, and case studies. This step is crucial as it minimizes risks associated with quality control and supply chain disruptions.
- Check for Certifications: Verify that suppliers meet international standards for electric vehicles, such as ISO certifications or local regulatory approvals.
- Assess Financial Stability: Review the financial health of the supplier to ensure they can fulfill your order without risk of bankruptcy or operational issues.
Step 4: Request Samples and Conduct Trials
Before finalizing your order, request samples or arrange for a trial period to assess the vehicle’s performance firsthand. Testing the vehicle in real-world conditions can reveal insights into usability, comfort, and efficiency that specifications alone cannot provide. This step is essential for verifying that the vehicle aligns with your operational requirements.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Engage in negotiations to ensure that you secure the best possible terms and pricing. Discuss bulk purchasing discounts, warranty options, and after-sales support. Understanding the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and charging infrastructure, is crucial to achieving long-term value from your investment.
Step 6: Plan for After-Sales Support and Maintenance
Ensure that the supplier offers comprehensive after-sales support, including maintenance services and parts availability. A robust support system can significantly impact the longevity and operational efficiency of your fleet. Look for suppliers who provide training for your staff on vehicle maintenance and usage.
Step 7: Finalize Logistics and Delivery Arrangements
Once you have selected a supplier and agreed on terms, finalize the logistics of delivery. Consider factors such as shipping methods, lead times, and potential customs regulations if sourcing from international suppliers. Efficient logistics planning can prevent delays and ensure that your vehicles are operational as soon as possible.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the sourcing process for one-seat electric cars effectively, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their business needs and market demands.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 1 seat electric car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing a One-Seat Electric Car?
When analyzing the cost structure for sourcing a one-seat electric car, several key components must be considered. The primary cost elements include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the profit margin.
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Lightweight materials such as aluminum and advanced composites can enhance performance but may raise the price. Conversely, opting for conventional materials could reduce costs but affect the vehicle’s efficiency and durability.
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. In countries with higher wage standards, such as Germany, labor costs can constitute a larger portion of the total expenses compared to countries in Africa or South America, where labor may be less expensive.
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and salaries of non-production staff. Effective management of manufacturing overhead can lead to significant cost savings.
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for custom designs. Buyers should evaluate the tooling costs relative to the expected volume of production, as higher volumes can justify the upfront expense.
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures is essential to ensure product reliability and customer satisfaction. However, these measures come with additional costs, which should be factored into the pricing strategy.
Logistics: Transportation and handling of components and finished vehicles can add to costs, especially for international buyers. Understanding Incoterms and their implications on shipping responsibilities can help manage these logistics costs effectively.
Margin: Finally, the profit margin that suppliers incorporate into their pricing can vary based on market demand, competition, and perceived value. It is essential for buyers to understand these dynamics to negotiate effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of One-Seat Electric Cars?
Several factors influence the pricing of one-seat electric cars, which can vary by region and market conditions.
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher volume orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their demand forecasts to optimize pricing.
Specifications and Customization: Custom features can significantly increase the base price. Buyers should assess whether the added functionality justifies the additional cost or if standard models meet their needs.
Materials: As previously mentioned, the choice of materials can greatly affect pricing. Buyers should weigh the benefits of high-quality materials against budget constraints.
Quality and Certifications: Products that meet specific certifications or quality standards often come at a premium. For international buyers, ensuring compliance with local regulations is crucial, which may influence sourcing decisions.
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of the supplier can impact pricing. Long-term partnerships may provide leverage for better pricing and terms, while new suppliers might necessitate a higher price point to mitigate risk.
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing shipping costs and responsibilities. Different terms can shift costs between buyer and seller, affecting the overall pricing structure.
What Are the Best Practices for International B2B Buyers in Sourcing One-Seat Electric Cars?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost efficiency.
Negotiation: Leverage volume and long-term relationships to negotiate better terms. Understanding the supplier’s cost structure can provide insights into areas where negotiations can be more effective.
Cost-Efficiency: Conduct a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis to evaluate the long-term expenses associated with the electric vehicle, including maintenance, charging infrastructure, and resale value.
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, electric vehicles may have varying tax incentives or import tariffs that can influence total costs. Buyers should also consider currency fluctuations when negotiating contracts.
Supplier Research: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, including their production capabilities, financial stability, and customer reviews. This due diligence can help mitigate risks associated with sourcing.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and other external factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct their own research and obtain specific quotes tailored to their requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing 1 seat electric car With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the 1 Seat Electric Car for Urban Mobility
As urban areas continue to grow, the demand for efficient, affordable, and compact transportation solutions is on the rise. The 1 seat electric car represents a novel approach to personal mobility, particularly in densely populated or rural regions. However, various alternatives exist that may also fulfill similar needs. This analysis compares the 1 seat electric car with two viable alternatives: the Microlino, a compact two-seater electric vehicle, and shared mobility services, such as electric scooters and bikes.
| Comparison Aspect | 1 Seat Electric Car | Microlino | Shared Mobility Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Range: 60 miles | Range: 228 km | Range: Variable (up to 30 km) |
| Top Speed: 37 mph | Top Speed: 56 mph | Top Speed: 15-25 mph | |
| Cost | Approx. $7,000 | Starting at CHF 159/month | Subscription/Pay-per-use |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires parking space | Fits in small parking spots | No parking needed |
| Maintenance | Low (fewer parts) | Moderate (battery upkeep) | Low (service dependent) |
| Best Use Case | Individual transport in low-density areas | Urban commuting, short trips | Urban settings, flexible use |
What Are the Pros and Cons of the Microlino Compared to a 1 Seat Electric Car?
The Microlino stands out as a compact two-seater electric vehicle that offers a broader range of applications than a single-seat model. With a maximum range of 228 kilometers and a top speed of 56 mph, it is suitable for both urban commuting and weekend outings. Its design allows for easy parking and maneuverability in tight spaces. However, it comes with a higher entry cost and slightly more complex maintenance due to its larger battery system. Additionally, it may not appeal to those specifically needing a solo transportation solution.
How Do Shared Mobility Services Compare to the 1 Seat Electric Car?
Shared mobility services, such as electric scooters and bikes, provide an entirely different approach to urban transportation. These services are typically subscription-based or pay-per-use, making them accessible without significant upfront costs. They are ideal for short trips in congested urban areas, where parking is often a challenge. However, their range is limited compared to a 1 seat electric car, and users may face availability issues during peak times. Furthermore, shared mobility lacks the personal ownership aspect, which may deter some users who prefer having their own vehicle.
Choosing the Right Solution: What Should B2B Buyers Consider?
For B2B buyers looking to invest in a transportation solution, the decision should be based on specific needs and use cases. If the primary requirement is for individual, affordable transportation in low-density areas, the 1 seat electric car is a compelling option. However, if the focus is on urban commuting with occasional passenger capacity, the Microlino may be more suitable. Alternatively, for companies seeking flexible transportation solutions without the burden of ownership, shared mobility services offer a cost-effective and convenient option. Ultimately, understanding the target market, operational requirements, and budget constraints will guide buyers to the most effective solution for their mobility needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 1 seat electric car
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of a One-Seat Electric Car?
When considering a one-seat electric car, it’s crucial to understand its technical specifications that impact performance, safety, and overall usability. Here are key properties that B2B buyers should evaluate:
1. Battery Capacity and Range
Battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), determines how far the vehicle can travel on a single charge. A typical one-seat electric car may offer battery options ranging from 5.5 kWh to 15 kWh, affecting its range from 60 to 228 kilometers. Understanding battery capacity is vital for buyers focused on operational efficiency and customer satisfaction, as it directly influences the vehicle’s usability in both urban and rural settings.
2. Charging Time
Charging time reflects how quickly the vehicle can be replenished using standard power sources. For instance, a one-seat electric car might take 2 to 5.5 hours to charge fully, depending on the battery size. This property is significant for fleet operators who require quick turnaround times and for consumers who value convenience. A shorter charging time enhances the vehicle’s practicality, particularly in markets with limited charging infrastructure.
3. Weight and Size Specifications
The kerb weight of the vehicle, typically around 496 kg for compact models, affects performance, efficiency, and handling. Smaller dimensions, such as a length of 2519 mm and a width of 1473 mm, enable easier navigation in congested urban areas. These specifications are crucial for B2B buyers targeting markets with dense traffic or limited parking, as they can influence consumer adoption and satisfaction.
4. Powertrain and Performance Metrics
Performance metrics, such as maximum speed (up to 90 km/h) and acceleration (0-50 km/h in 5 seconds), define the driving experience. A robust powertrain with a maximum power output of 12.4 kW ensures that the vehicle meets the demands of urban mobility. Buyers should prioritize performance specifications to attract customers looking for nimble and responsive vehicles.
5. Material Composition and Safety Features
The choice of materials, such as aluminum for the outer skin and high-strength steel for the chassis, influences durability, weight, and safety. It is important for B2B buyers to understand how these materials affect production costs and vehicle longevity. Additionally, safety features such as crumple zones and advanced braking systems should be highlighted to meet regional safety regulations and consumer expectations.
What Are Common Trade Terminologies in the One-Seat Electric Car Market?
Familiarity with industry-specific jargon can facilitate smoother negotiations and partnerships. Here are some essential terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of electric vehicles, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers source quality components effectively and maintain compatibility across different vehicle models.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ signifies the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ can aid in inventory management and budgeting, ensuring that they can meet demand without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer submits to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. Utilizing RFQs can streamline the procurement process, helping buyers obtain competitive pricing for one-seat electric cars and their components.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in global trade, as they delineate who bears the risk and cost at various stages of transportation.
5. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with the acquisition and operation of a vehicle over its lifespan, including purchase price, maintenance, insurance, and depreciation. B2B buyers should evaluate TCO to ensure they are making economically sound investments that provide value over time.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that their investments in one-seat electric cars align with market demands and operational goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the 1 seat electric car Sector
What Are the Key Drivers and Trends Shaping the 1 Seat Electric Car Market?
The global market for single-seat electric vehicles (EVs) is gaining traction, driven by urbanization, environmental concerns, and a shift towards sustainable transportation. As cities become more congested and the demand for efficient mobility solutions rises, single-seat EVs offer a compact and cost-effective alternative. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial.
In regions like Africa and South America, where public transport infrastructure is often inadequate, single-seat EVs can provide essential mobility solutions. Countries like Nigeria are witnessing a surge in demand for affordable and efficient transport options, aligning with the introduction of budget-friendly models such as KG Motors’ mibot, priced at around $7,000. In Europe, especially in urban centers like Germany, the trend is towards smaller, more maneuverable vehicles that can navigate narrow streets and tight parking spaces, similar to the Microlino concept.
Emerging technologies, such as enhanced battery efficiency and charging solutions, are also reshaping the sourcing landscape. For instance, advancements in lithium-ion battery technology are enabling manufacturers to produce vehicles with longer ranges and shorter charging times, appealing to both individual consumers and businesses looking for fleet solutions. Additionally, the rise of smart charging infrastructure will play a pivotal role in facilitating the adoption of single-seat EVs, making them more practical for everyday use.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the 1 Seat Electric Car Sector?
Sustainability is a cornerstone of the single-seat electric car sector, influencing both product development and sourcing practices. The environmental impact of traditional vehicles is prompting manufacturers to seek greener alternatives, which is particularly relevant for B2B buyers focused on corporate social responsibility. Companies investing in single-seat EVs can enhance their brand reputation by aligning with sustainable practices.
Ethical sourcing is paramount in this context. As demand for electric vehicles grows, the sourcing of materials—especially those used in batteries, like lithium and cobalt—has come under scrutiny. International B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to ethical mining practices and offer transparency in their supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) can help buyers identify companies committed to sustainability.
Moreover, the use of recycled materials in manufacturing processes can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with single-seat EV production. As the market continues to evolve, buyers who emphasize sustainability in their sourcing decisions will not only meet regulatory requirements but also cater to a growing consumer base that values environmentally friendly products.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the Rise of Single-Seat Electric Cars?
The evolution of single-seat electric vehicles can be traced back to the early 20th century, when electric cars were first introduced as a practical alternative to gasoline-powered vehicles. However, it wasn’t until the late 20th century, amidst growing environmental awareness and advancements in battery technology, that electric vehicles began to gain significant traction.
The modern resurgence of single-seat EVs is largely attributed to urbanization and the need for efficient transportation in densely populated areas. The introduction of compact models, such as the Japanese mibot and European Microlino, reflects a shift in consumer preferences toward smaller, more agile vehicles. This evolution highlights a broader trend in the automotive industry, where the focus is increasingly on sustainability, affordability, and practicality—essential factors for international B2B buyers looking to invest in the future of mobility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 1 seat electric car
-
How do I choose the right single-seat electric car for my business needs?
When selecting a single-seat electric car, consider factors like range, charging time, and suitability for your target market. Assess the vehicle’s performance in urban versus rural settings, especially if you plan to distribute in areas with limited public transport. Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including purchase price, maintenance, and energy costs. Conduct market research to understand local preferences and regulations, which will help you identify models that best meet your business objectives. -
What are the typical payment terms when sourcing single-seat electric cars internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier but often include options such as advance payment, letter of credit, or installment payments. Standard terms might require a deposit of 30% upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipment. It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs and to confirm the payment method accepted by the supplier. Always ensure that your payment terms are documented in a formal agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for single-seat electric cars?
MOQs can differ significantly based on the manufacturer and the model of the vehicle. Some suppliers may have an MOQ as low as 10 units, while others might require larger orders to justify production costs. Discuss your purchasing plans with potential suppliers to determine their flexibility on MOQs. If you are starting small, consider negotiating a trial order to assess the market response before committing to larger quantities. -
How can I ensure the quality of single-seat electric cars from suppliers?
To ensure quality, conduct thorough vetting of potential suppliers, including reviewing their production capabilities, certifications, and past performance. Request samples or pilot units to evaluate build quality and performance. Additionally, consider third-party inspections during production and before shipment to verify that the vehicles meet your specifications. Establish clear quality assurance standards in your contracts to hold suppliers accountable. -
What customization options are available for single-seat electric cars?
Customization options can vary by manufacturer and may include features like battery size, color, interior design, and tech integrations. Discuss your specific requirements with suppliers to determine their capabilities and flexibility in modifying existing models. Customization can enhance your brand’s identity and better meet the needs of your target market, making it an essential aspect of your sourcing strategy. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing single-seat electric cars?
Logistics is critical when importing vehicles. Consider the transportation method (air, sea, or land) based on cost and urgency. Evaluate import tariffs, customs regulations, and any environmental certifications required in your target market. Work with experienced logistics partners to streamline the process, ensuring timely delivery and compliance with local laws. Always factor in potential delays and plan for contingencies in your supply chain. -
How do I handle after-sales support and maintenance for single-seat electric cars?
After-sales support is vital for customer satisfaction and retention. Establish a clear service agreement with your suppliers regarding warranty terms, spare parts availability, and service training for your team. Consider setting up partnerships with local service centers to facilitate maintenance and repairs. Providing robust after-sales support can enhance your reputation and foster long-term relationships with your customers. -
What are the emerging trends in the single-seat electric car market?
Emerging trends include increased demand for compact and affordable electric vehicles, particularly in urban areas where space is limited. Sustainability and environmental concerns are driving innovations in battery technology and recycling. Additionally, advancements in connectivity and autonomous features are becoming more common, appealing to tech-savvy consumers. Staying informed about these trends can help you position your offerings effectively and anticipate market shifts.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 1 Seat Electric Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Microlino – Compact Electric Car
Domain: microlino-car.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Microlino Car details:
– Space for 2 adults and three beer crates.
– Fully charged in 4 hours on a standard household socket.
– Fits in any parking space, allowing cross-parking and easy exit onto the sidewalk.
– Trunk volume: 230 liters, accommodating shopping bags, 1 large suitcase, 2 pieces of hand luggage, or 3 beer crates.
– Maximum range: 228 km.
– Maximum speed: 90 km/h.
– Kerb weigh…
2. KG Motors – mibot
Domain: evxl.co
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Product Name: mibot
Manufacturer: KG Motors
Price: $7,000 (¥1 million)
Production Goal: 3,300 units
Pre-sales: Over half of production goal secured
Height: Under 4.9 feet (1.5 meters)
Range: 62 miles (100 kilometers)
Top Speed: 37 mph (60 km/h)
Charging Time: 5 hours
Production Start: October 2025
First Delivery: March 2026 (first 300 units to Hiroshima and Tokyo)
Target Market: Rural and urban se…
3. KG Motors – $7,000 Single-Seat Electric Car
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: $7,000 single-seat electric car, popular in Japan, developed by KG Motors, designed for narrow streets, prototype displayed in Roppongi.
4. Mibot – Mini EV
Domain: electrek.co
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Product Name: mibot mini EV
Price: ¥1 million ($7,000)
Size: 2,490 mm (98 inches) long
Seating: Single-seat
Range: Up to 100 km (62 miles)
Maximum Speed: 60 km/h (37 mph)
Production Start: October 2025
First Batch Delivery: March 2026 (300 units)
Total Planned Deliveries: 3,300 units by March 2027
Annual Production Goal: 10,000 mini EVs
Market Position: Competing against Nissan’s Sakura and other …
5. KG Motors – mibot
Domain: straitstimes.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Product Name: mibot
Manufacturer: KG Motors
Type: Single-seat electric car
Price: 1 million yen (approximately $8,930)
Height: Under 1.5 meters
Range: 100 km
Charging Time: 5 hours
Top Speed: 60 km/h
Production Start Date: October 2025
Initial Delivery: First 300 units to be delivered in Hiroshima and Tokyo by March 2026
Total Units Planned: 3,300 units by March 2027
Annual Production Goal: 10,000…
6. Facebook – World’s Narrowest Fiat Panda
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: world’s narrowest fiat panda, fully functional, single-seater, electric car
7. Zigy – Electric Quadricycle Concept
Domain: newatlas.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: The Zigy is a single-seater electric quadricycle concept designed by Andrea Mocellin and Dexet Technologies, aimed at addressing urban congestion. Key specifications include:
– Length: 1.95 m (6.4 ft)
– Wheelbase: 1.59 m
– Width: 1.1 m (3.6 ft)
– Height: 1.6 m (5.3 ft)
– Curb weight: 353 kg (778 lb)
– Motor: 12-kW (peaks at 21 kW)
– Maximum torque: 135 Nm (99.5 lb.ft)
– Top speed: 77 km/h …
8. KG Motors – Minimum Mobility EV
Domain: startupselfie.net
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: KG Motors Minimum Mobility EV is a compact, single-seat electric vehicle designed for urban environments. It has a range of 100 km (62 miles) and a charge time of five hours. The vehicle measures 2.5 meters in length and 1 meter in width, featuring a symmetrical, retro design inspired by 1980s Polaroid cameras. Priced at approximately 1 million yen (around $6,700), it offers an economical solution…
9. TELO – All-Electric Mini Truck
Domain: telotrucks.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “TELO MT1”, “type”: “All-Electric Mini Truck”, “dimensions”: {“length”: “152 in”, “width”: “73 in”, “height”: “67 in”}, “bed_size”: {“length”: “60-96 in”, “width”: “56 in”, “depth”: “18 in”}, “seating_capacity”: [2, 5, 8], “performance”: {“0-60_mph”: “6.0 s”, “power_hp”: “300 hp”, “payload”: “2000 lbs”, “towing_capacity”: “6600 lbs”}, “battery”: {“standard_range”: “260 mi”, “long_range”: …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 1 seat electric car
In the evolving landscape of electric vehicles, the emergence of one-seat electric cars represents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers. These compact vehicles, exemplified by models like KG Motors’ mibot and the Microlino, address the pressing needs of urban and rural mobility by offering affordability, efficiency, and innovative design. Their strategic sourcing not only enhances market competitiveness but also aligns with the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions across diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
For B2B stakeholders, the key takeaway lies in recognizing the potential of these compact EVs to serve as essential components of local transportation ecosystems. By investing in these vehicles, businesses can cater to a burgeoning market that prioritizes cost-effective and practical mobility options. Furthermore, as public transportation systems face challenges globally, one-seat electric cars can fill the gap, providing a viable alternative for personal transport.
Looking ahead, the demand for one-seat electric vehicles is poised to rise. B2B buyers should seize this opportunity to explore partnerships with manufacturers and distributors, thereby positioning themselves at the forefront of the electric mobility revolution. Embrace this shift in transportation dynamics to drive growth and innovation in your market.