Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric car low velociti
Navigating the complexities of sourcing electric car low velocity solutions can be a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. As the demand for eco-friendly transportation continues to rise, understanding the myriad options available—from compact city vehicles to specialized utility models—becomes essential. This comprehensive guide delves into various types of electric low-velocity vehicles, their applications across different sectors, and crucial insights on supplier vetting processes. Additionally, we will discuss cost considerations and market dynamics, empowering you to make informed purchasing decisions.
This resource is specifically tailored for B2B buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—countries like Saudi Arabia and Germany are leading in the transition to sustainable transport. By providing actionable insights and in-depth analysis, this guide equips you with the knowledge needed to navigate the global market effectively. Whether you’re looking to enhance your fleet, meet sustainability goals, or explore new business opportunities, our guide will serve as your roadmap in this evolving landscape, ensuring you stay ahead in the electric vehicle sector.
Understanding electric car low velociti Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Compact EVs | Small size, limited range (100-200 miles), optimized for city driving. | Ridesharing, delivery services, small fleet operations. | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to park. Cons: Limited range may not suit long-distance needs. |
| Luxury Electric SUVs | High performance, advanced tech, spacious interiors, premium features. | Corporate fleets, executive transportation, luxury rentals. | Pros: Enhanced comfort, strong brand image. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Electric Delivery Vans | Larger cargo capacity, often equipped with advanced logistics tech. | E-commerce, logistics companies, urban deliveries. | Pros: Reduces operational costs, eco-friendly. Cons: Higher upfront costs, longer charging times. |
| Electric Micro-Mobility | Lightweight, small vehicles (e-scooters, e-bikes) with short ranges. | Last-mile delivery, urban commuting, tourism. | Pros: Affordable, promotes sustainable transport. Cons: Limited range and speed. |
| Commercial Electric Trucks | Heavy-duty capabilities, long-range options, designed for hauling. | Freight transport, construction, utility services. | Pros: Lower fuel costs, reduced emissions. Cons: Higher purchase price, potential charging infrastructure needs. |
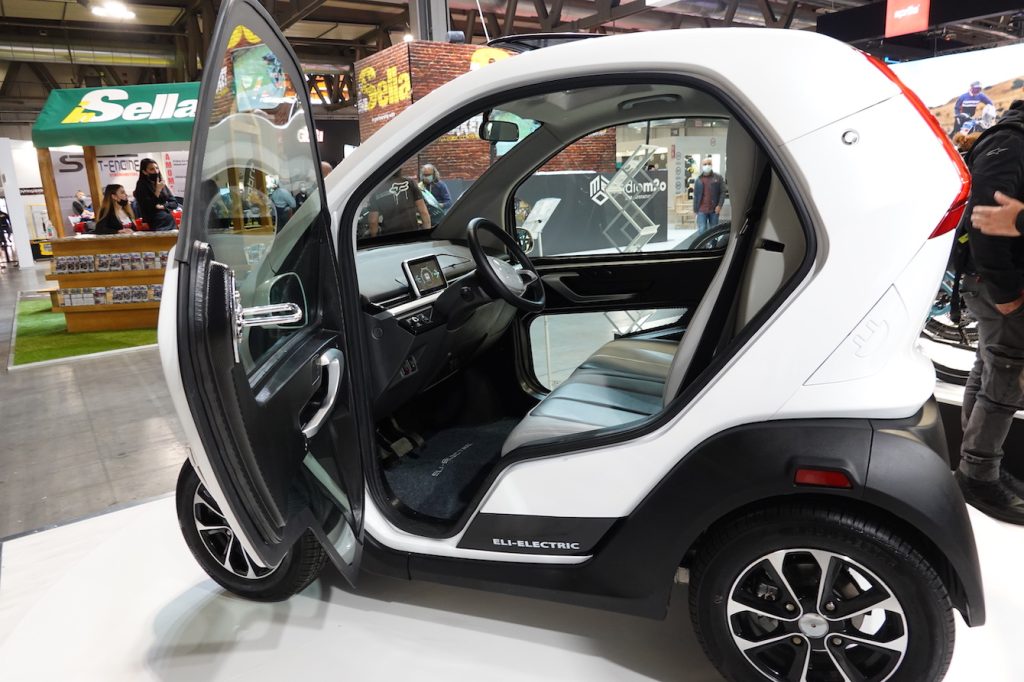
What Are Urban Compact EVs and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Urban compact electric vehicles (EVs) are designed primarily for city environments, featuring a small footprint and a range typically between 100 to 200 miles. These vehicles are ideal for businesses engaged in ridesharing, delivery services, or operating small fleets where space and maneuverability are critical. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the vehicle’s range against their operational needs, as the limited distance may necessitate multiple vehicle deployments for longer routes.
How Do Luxury Electric SUVs Serve Corporate Needs?
Luxury electric SUVs combine high performance with advanced technology and spacious interiors, making them suitable for corporate fleets and executive transportation. These vehicles often come equipped with premium features that enhance the travel experience, appealing to high-end clients. B2B buyers should consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and depreciation, while also factoring in the vehicle’s potential to enhance brand image and client satisfaction.
What Benefits Do Electric Delivery Vans Offer to Logistics Companies?
Electric delivery vans are tailored for logistics operations, boasting larger cargo capacities and often integrated with advanced logistics technology. These vehicles are particularly advantageous for e-commerce businesses looking to reduce operational costs and carbon footprints. B2B buyers must assess charging infrastructure availability and the upfront costs against the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance to ensure a sound investment.
Why Are Electric Micro-Mobility Solutions Important for Last-Mile Delivery?
Electric micro-mobility solutions, such as e-scooters and e-bikes, provide an innovative approach to last-mile delivery and urban commuting. These lightweight vehicles are affordable and promote sustainable transport options, making them attractive to businesses focused on reducing their environmental impact. When considering these options, B2B buyers should weigh the limited range and speed against their specific operational requirements, especially in urban settings.
How Do Commercial Electric Trucks Impact Freight Transport?
Commercial electric trucks are designed for heavy-duty use, featuring long-range capabilities suited for freight transport and construction applications. These trucks help companies reduce fuel costs and emissions, aligning with growing environmental regulations. B2B buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including the initial purchase price and the need for charging infrastructure, to make an informed decision about integrating these vehicles into their operations.
Key Industrial Applications of electric car low velociti
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric car low velociti | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public Transportation | Electric shuttle services | Reduced operational costs and lower emissions | Availability of charging infrastructure, vehicle range |
| Logistics and Delivery Services | Last-mile delivery vehicles | Enhanced efficiency and sustainability | Load capacity, battery life, and maintenance requirements |
| Tourism and Hospitality | Electric tour vehicles | Improved guest experience and eco-friendly branding | Customization options, safety features, and comfort levels |
| Urban Mobility | Shared electric vehicle fleets | Cost savings and reduced urban congestion | Fleet management software, vehicle tracking, and servicing |
| Construction and Mining | Electric utility vehicles for site operations | Lower fuel costs and compliance with environmental regulations | Durability, off-road capability, and charging solutions |
How Are Electric Car Low Velociti Used in Public Transportation?
In the public transportation sector, electric vehicles are increasingly utilized for shuttle services. These low-velocity electric cars help reduce operational costs through lower fuel consumption and maintenance expenses while significantly decreasing greenhouse gas emissions. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing vehicles with robust battery life and reliable charging infrastructure is essential to ensure efficiency and service continuity.
What Role Do Electric Cars Play in Logistics and Delivery Services?
Electric low-velocity vehicles are transforming last-mile delivery services by offering a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional fuel-powered options. These vehicles are designed to navigate urban environments with ease, improving delivery times and reducing operational costs. Buyers in the logistics sector should consider factors such as load capacity and battery life to meet their specific delivery needs, especially in regions with varying infrastructure capabilities.
How Can Electric Tour Vehicles Enhance the Tourism Experience?
Electric tour vehicles are gaining traction in the tourism and hospitality industry, providing a unique and eco-friendly way for visitors to explore destinations. These vehicles not only enhance the guest experience through comfort and quiet operation but also align with the growing demand for sustainable tourism practices. B2B buyers should prioritize customization options and safety features to cater to diverse tourist preferences and regulatory requirements.
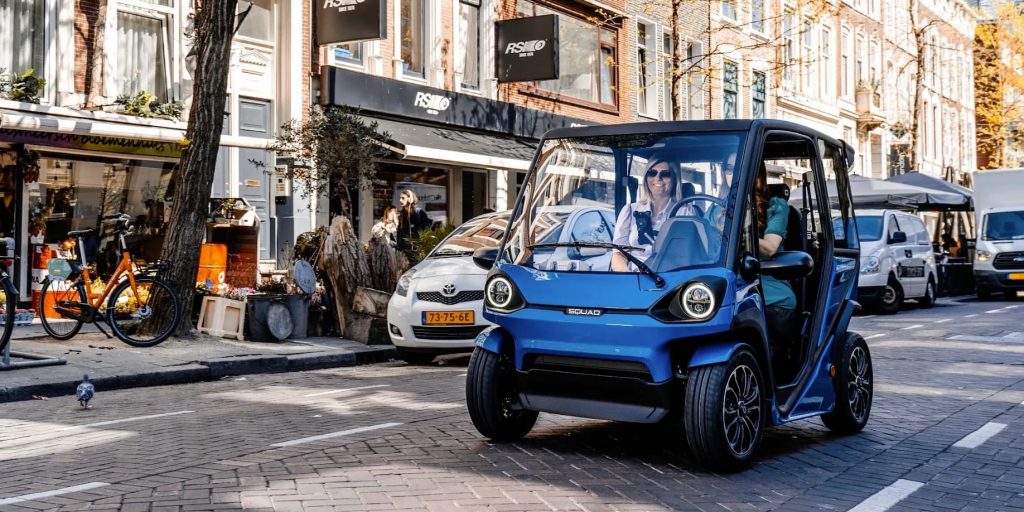
What Are the Benefits of Shared Electric Vehicle Fleets for Urban Mobility?
In urban mobility, shared electric vehicle fleets are becoming a popular solution to combat congestion and reduce transportation costs. These low-velocity electric cars are ideal for short-distance travel, making them a cost-effective choice for city dwellers. International buyers should focus on fleet management software capabilities and vehicle tracking systems to optimize operations and ensure a seamless user experience.
How Are Electric Utility Vehicles Used in Construction and Mining?
In the construction and mining industries, electric utility vehicles are employed for site operations, providing a cleaner alternative to traditional vehicles. These low-velocity electric cars help companies lower fuel costs and comply with stringent environmental regulations. Buyers should assess the durability and off-road capabilities of these vehicles, as well as the availability of efficient charging solutions to maximize productivity on-site.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric car low velociti’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Limited Charging Infrastructure
The Problem: In many regions, especially in emerging markets across Africa and South America, the lack of robust charging infrastructure poses a significant challenge for businesses looking to adopt electric vehicles (EVs), particularly those operating low-velocity electric cars for urban deliveries or shuttle services. B2B buyers often face uncertainties about the availability of charging stations, leading to concerns over vehicle range, downtime, and operational efficiency. The risk of running out of charge in areas with few charging options can deter companies from fully committing to electric fleets.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should conduct thorough research on local charging infrastructure before investing in electric car low velocity models. Partnering with local governments or private firms to advocate for the installation of charging stations can also be beneficial. Additionally, companies should consider investing in mobile charging solutions or collaborating with charging network providers to ensure access to reliable charging options. For instance, deploying a fleet management system that includes real-time tracking of charging station availability can help streamline operations and reduce anxiety around range issues.
Scenario 2: Understanding Regulatory Compliance and Incentives
The Problem: Different regions have varying regulations and incentives regarding electric vehicles, which can create confusion for B2B buyers. Companies in the Middle East and Europe may encounter stringent emission regulations, while those in South America might face bureaucratic hurdles or lack of clarity around available incentives for electric vehicle adoption. This uncertainty can lead to hesitation in making purchasing decisions, affecting overall fleet modernization strategies.
The Solution: B2B buyers should proactively engage with local industry associations and governmental bodies to gain insights into the specific regulations and incentives applicable to electric vehicles in their region. Establishing a compliance checklist tailored to their operations can help streamline the purchasing process and ensure adherence to local laws. Moreover, leveraging legal and financial advisors who specialize in EV regulations can provide clarity on tax credits, grants, and other financial incentives that can significantly reduce the total cost of ownership. This knowledge not only facilitates informed decision-making but also enhances the overall sustainability strategy of the business.
Scenario 3: Managing Maintenance and Operational Training Needs
The Problem: Transitioning to low-velocity electric cars often involves a steep learning curve for drivers and maintenance teams. B2B buyers may find that their workforce lacks the necessary training to operate and maintain electric vehicles effectively, which can lead to operational inefficiencies and increased costs due to improper handling or delayed maintenance. This challenge can be particularly pronounced in regions where traditional vehicles have dominated the market.
The Solution: To address this concern, businesses should prioritize comprehensive training programs for both drivers and maintenance personnel. Collaborating with electric vehicle manufacturers to develop tailored training modules that cover essential operational procedures, safety protocols, and basic troubleshooting techniques is crucial. Additionally, establishing a mentorship program where experienced EV users guide new drivers can foster a smoother transition. Regular workshops and refresher courses can also ensure that staff remain up-to-date with the latest technologies and best practices, ultimately leading to enhanced performance and reduced downtime for the electric fleet.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric car low velociti
What Are the Key Materials for Electric Car Low Velocity Applications?
In the evolving landscape of electric vehicles (EVs), particularly in low-velocity applications, the selection of materials plays a critical role in performance, safety, and sustainability. Here, we analyze several common materials used in electric cars, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Electric Car Design?
Aluminum is widely used in the automotive industry due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating up to 600°C and can withstand moderate pressures, making it suitable for various components including frames and body panels.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, which enhances energy efficiency and range in electric vehicles. Its corrosion resistance contributes to longevity, reducing maintenance costs over time.
Cons: However, aluminum can be more expensive than steel and may require specialized manufacturing techniques, such as welding or extrusion, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including battery fluids and coolants, making it ideal for structural components that interact with these elements.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as DIN and ASTM for aluminum alloys. The availability of aluminum recycling programs can also be a selling point in sustainability discussions.
What Role Does Steel Play in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Steel remains a staple in automotive manufacturing due to its strength and versatility. With a temperature rating that can exceed 800°C and high resistance to deformation under pressure, it is often used in critical structural components.
Pros: Steel is durable and cost-effective, making it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to balance quality with affordability. Its availability and established manufacturing processes simplify sourcing.
Cons: On the downside, steel is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact the efficiency of electric vehicles. Additionally, it is prone to corrosion unless treated, which can lead to higher long-term maintenance costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is well-suited for applications requiring high tensile strength, such as chassis and safety structures, but may require protective coatings to ensure compatibility with battery electrolytes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding steel grades and treatments, especially in regions with stringent environmental standards.
How Does Carbon Fiber Enhance Electric Vehicle Performance?
Carbon fiber composites are increasingly popular in high-performance electric vehicles due to their exceptional strength and lightweight properties. They can handle temperatures up to 300°C and are resistant to various chemicals.
Pros: The primary advantage of carbon fiber is its weight reduction, which significantly enhances vehicle performance and efficiency. It also offers excellent fatigue resistance, making it suitable for dynamic applications.
Cons: However, carbon fiber is considerably more expensive than both aluminum and steel, and its manufacturing processes can be complex and time-consuming.
Impact on Application: Carbon fiber is particularly effective in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in body panels and interior components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of carbon fiber suppliers and the potential for higher costs in regions where this material is less commonly produced.
What About Plastics and Composites in Electric Vehicles?
Plastics and composites are increasingly utilized in electric vehicles due to their lightweight nature and design flexibility. They typically have a temperature resistance of around 80-120°C, depending on the type.
Pros: These materials are cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs. They also provide good insulation properties, which is beneficial for electrical components.
Cons: The main drawback is their lower strength compared to metals, which may limit their use in structural applications. Additionally, some plastics can degrade under UV exposure or high temperatures.
Impact on Application: Plastics are ideal for non-structural components, such as interior fittings and housings for electronic devices, but care must be taken to select UV-resistant options.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards for plastics, including fire resistance and recyclability, particularly in markets with strict environmental regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Car Low Velocity Applications
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric car low velociti | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, frames | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Steel | Chassis, safety structures | Durable and cost-effective | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Low |
| Carbon Fiber | Body panels, high-performance components | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Plastics/Composites | Interior fittings, electronic housings | Cost-effective and design flexibility | Lower strength and potential UV degradation | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection process for electric car low velocity applications, ensuring that international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric car low velociti
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electric Car Low Velocity?
The manufacturing of electric cars, particularly those designed for low-velocity applications, involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is essential to ensure the quality and performance of the final product.
How Is Material Prepared for Electric Car Manufacturing?
Material preparation is the foundational step that dictates the quality of the components. This stage involves sourcing high-quality materials such as lightweight metals (aluminum, magnesium), composites, and high-strength steel. Manufacturers often utilize advanced techniques like laser cutting and CNC machining to ensure precision in shaping the materials.
Additionally, the preparation phase includes quality checks of the raw materials against international standards such as ISO 9001. This ensures that only materials meeting strict guidelines are used in production, thereby enhancing the durability and efficiency of the vehicles.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Electric Car Production?
Forming is the next critical stage, where materials undergo various processes to achieve desired shapes. Common techniques include stamping, extrusion, and injection molding, tailored to create components like chassis, body panels, and battery housings.
For electric vehicles, manufacturers may also employ advanced forming methods such as hydroforming, which allows for more complex shapes while maintaining material integrity. This technique is particularly beneficial for producing lightweight structures that enhance vehicle efficiency and performance.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form the complete vehicle. This process typically involves robotic automation to ensure precision and efficiency. Automated assembly lines allow for consistent quality and faster production rates, which is essential in meeting global demand.
Key components such as the electric motor, battery packs, and electronic control units are integrated during this stage. Manufacturers must ensure that each assembly line adheres to strict quality standards, which can include real-time monitoring systems to track assembly accuracy.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Electric Cars?
Finishing processes are crucial for both aesthetic and functional aspects of electric vehicles. This stage includes painting, surface treatment, and applying protective coatings. Electric vehicles often require specialized coatings that enhance aerodynamics and reduce drag, contributing to overall performance.
Additionally, finishing processes also encompass thorough inspections to ensure that all components are assembled correctly and function as intended. This step is vital in preventing issues that could arise post-production, such as electrical faults or mechanical failures.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) in electric vehicle manufacturing is critical to ensuring that the final product meets both safety and performance standards. For international B2B buyers, understanding the quality assurance measures in place is essential for verifying supplier reliability.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Electric Car Manufacturing?
Manufacturers must adhere to various international quality standards. ISO 9001 is the most recognized quality management system standard, focusing on ensuring consistent quality in products and services. For electric vehicles, additional standards may apply, such as:
- ISO 26262: Addresses functional safety for automotive systems.
- CE Marking: Certifies that products meet EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for components such as lubricants and fluids.
Compliance with these standards not only boosts buyer confidence but also ensures that the vehicles can be marketed globally without regulatory hurdles.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to detect any discrepancies early on. The primary checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing process, this step ensures that assembly and forming stages are executed correctly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection checks the complete vehicle against performance and safety benchmarks before it leaves the factory.
Implementing these QC checkpoints helps manufacturers identify and rectify issues before they escalate, thus maintaining high-quality standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying supplier quality control processes is vital. Here are several effective methods:
What Audits and Reports Should B2B Buyers Request?
Buyers should request detailed quality assurance reports from suppliers, including data on production processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards. Regular audits of the manufacturing facilities can also provide insight into the supplier’s adherence to quality practices.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can occur at various stages of the manufacturing process, providing an additional layer of assurance for buyers. Third-party inspectors typically assess compliance with international standards and can highlight areas for improvement.
What Are the QC/CERT Nuances for International B2B Buyers in Different Regions?
Understanding the quality certification nuances in different regions is essential for B2B buyers. For instance, European buyers might prioritize CE marking, while buyers from the Middle East may look for certifications that align with local regulations. Buyers in Africa and South America should also be aware of regional standards that might affect the importation and use of electric vehicles.
Furthermore, cultural differences in business practices may influence how quality assurance is perceived and implemented. Therefore, establishing clear communication with suppliers regarding expectations and standards is crucial for successful international transactions.
By focusing on these comprehensive manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electric car low-velocity vehicles, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers that prioritize quality and compliance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric car low velociti’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement process for low-velocity electric vehicles (EVs) can be complex, particularly for international B2B buyers. This step-by-step checklist is designed to guide you through critical actions to ensure a successful sourcing experience. By following these steps, you can identify reliable suppliers, assess product specifications, and make informed purchasing decisions that align with your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is essential for sourcing low-velocity electric vehicles. This includes understanding the specific use cases, such as urban commuting or light-duty transport, and identifying necessary features like battery capacity, range, and performance metrics. Establishing these specifications will help you communicate effectively with potential suppliers and ensure that their offerings align with your needs.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Regulations
Stay informed about the latest trends in the electric vehicle market, particularly regulations that may impact your procurement. Different regions, especially in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, have varying standards for emissions, safety, and performance. Understanding these regulations will not only help you comply but also allow you to leverage incentives or subsidies that may be available for low-velocity electric vehicles.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before finalizing any agreements, it’s crucial to conduct a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, including their experience in manufacturing low-velocity electric vehicles, product catalogs, and client testimonials. Additionally, ask for case studies that demonstrate their capability to fulfill large orders or specific requirements similar to yours.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering possess the necessary certifications and comply with international standards. This may include ISO certifications, safety standards, and environmental compliance documents. Verifying these credentials is vital to mitigate risks and ensure that the products you procure are of high quality and legally compliant in your target markets.
Step 5: Request Sample Vehicles for Testing
Once you have narrowed down potential suppliers, request sample vehicles to evaluate their performance firsthand. Conduct thorough tests focusing on aspects such as battery life, comfort, and handling under various conditions. This practical assessment will provide valuable insights into the vehicle’s suitability for your intended applications.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
After selecting a preferred supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. Consider discussing bulk order discounts or flexible payment options to optimize your procurement budget. Clear negotiations will help establish a strong partnership and ensure both parties have aligned expectations.
Step 7: Establish a Long-Term Relationship
Building a lasting relationship with your chosen supplier can yield benefits beyond a single transaction. Regular communication, feedback loops, and collaboration on future projects can enhance supply chain efficiency and foster innovation. Prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to customer service and continuous improvement.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing low-velocity electric vehicles and make informed decisions that contribute to their operational success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric car low velociti Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and pricing for electric car low velocity sourcing requires a detailed understanding of various components that contribute to the overall expenditure. This analysis is particularly critical for international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where market dynamics and buyer expectations can vary significantly.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Electric Car Low Velocity Sourcing?
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a primary factor in the pricing of electric vehicles (EVs). For low-velocity electric cars, materials such as lithium for batteries, aluminum for lightweight frames, and high-strength steel for structural integrity are crucial. Fluctuations in global supply chains can affect these costs, making it vital to establish relationships with reliable suppliers.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly across regions. In countries with higher labor costs, such as Germany, manufacturers may need to optimize automation to maintain competitive pricing. Conversely, in regions like Africa or South America, lower labor costs can be leveraged, but there may be trade-offs in terms of skill levels and manufacturing practices.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can help minimize these costs. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturer’s efficiency ratings and production capabilities.
-
Tooling: Investment in specialized tools and dies for manufacturing electric vehicles is significant. The tooling cost can be amortized over higher production volumes, making it imperative for buyers to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs) that can justify these upfront investments.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the safety and performance of electric vehicles is paramount. Implementing rigorous QC processes incurs additional costs, but these are essential for compliance with international standards. Buyers should look for manufacturers that provide certifications and quality assurance documentation.
-
Logistics: Transporting electric vehicles from the manufacturing site to the buyer’s location involves logistics costs, which can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and the chosen Incoterms. Understanding these costs is crucial for calculating the total landed cost of the vehicle.
-
Margin: The manufacturer’s profit margin is influenced by the overall cost structure and market demand. Buyers should be aware that lower prices may reflect compromises in quality or service.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Electric Car Low Velocity Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing, including:
- Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to discounts, so buyers should consider their purchasing capabilities and negotiate favorable terms.
- Specifications/Customization: Custom features can significantly increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
- Materials and Quality/Certifications: The choice of materials impacts durability and performance, and certifications may be required for compliance with local regulations.
- Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and quality assurances.
- Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms is essential for calculating the total cost of ownership. Buyers should negotiate terms that minimize their risk and exposure to additional costs.
What Tips Can Buyers Follow to Ensure Cost-Efficiency in Sourcing Electric Cars?
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage in open discussions with suppliers to explore price flexibility based on order size and long-term partnership potential.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Beyond the purchase price, consider maintenance, charging infrastructure, and resale value when assessing the overall investment.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Each region may have different tariffs, taxes, and incentives for electric vehicles. Buyers should research these factors to optimize their procurement strategy.
-
Request Indicative Prices: Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions. Always request updated quotes that reflect current market trends to make informed decisions.
By understanding these cost components and pricing influencers, B2B buyers can make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric car low velociti With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives for Electric Car Low Velociti
As businesses explore sustainable transportation solutions, understanding the alternatives to electric car low velociti (ECLV) is crucial. ECLV vehicles offer unique benefits, particularly in urban settings where low-speed operations are common. However, various other technologies and methods can achieve similar goals of reducing emissions and enhancing mobility. This analysis will compare ECLV with two viable alternatives: electric scooters and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Car Low Velociti | Electric Scooters | Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate speed (up to 45 mph) for urban use | Low speed (up to 30 mph) | High speed (up to 70 mph) |
| Cost | High initial investment, low operating costs | Low initial cost, moderate maintenance | High initial investment, higher fuel costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure | Easy to deploy, minimal infrastructure needed | Requires hydrogen refueling stations |
| Maintenance | Moderate; battery replacement needed | Low; simple maintenance | Moderate; complex technology |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting and short trips | Short-distance travel in urban areas | Longer distances with quick refueling needs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Scooters
Electric scooters are an increasingly popular mode of urban transport, particularly in congested city areas. They are cost-effective, with lower initial investments compared to ECLV vehicles. Moreover, they require minimal infrastructure, making them easy to implement. However, their performance is limited to lower speeds, which may not be suitable for all commuting needs. Maintenance is also relatively low, but durability and safety can be concerns in busy environments.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles represent a cutting-edge alternative that combines the benefits of electric propulsion with the refueling speed of traditional gasoline vehicles. They can achieve higher speeds and longer ranges, making them suitable for longer trips. However, the high initial investment and the need for specialized refueling infrastructure can be significant drawbacks. Additionally, the availability of hydrogen refueling stations is limited in many regions, which may restrict their practicality for some businesses.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right transportation solution, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including performance requirements, budget constraints, and operational needs. Electric car low velociti is ideal for businesses focused on urban commuting with moderate speed requirements, while electric scooters offer a budget-friendly and easy-to-implement option for short-distance travel. On the other hand, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles may be suitable for organizations needing to cover longer distances quickly but require investment in refueling infrastructure. Ultimately, the choice will depend on the specific operational context and strategic goals of the business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric car low velociti
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Car Low Velocity?
Understanding the technical specifications of electric cars, especially those designed for low-speed applications, is crucial for B2B buyers. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Battery Capacity (kWh)
This specification indicates the amount of energy a battery can store, influencing the vehicle’s range and performance. For low-velocity electric cars, battery capacity may range from 20 kWh to 60 kWh, allowing for efficient energy use in urban settings. A higher capacity translates to longer driving ranges, which is essential for fleet operators in regions with limited charging infrastructure. -
Motor Power (kW)
The power output of the electric motor directly affects the vehicle’s acceleration and top speed. Low-velocity electric cars typically have motors ranging from 5 kW to 15 kW. Understanding motor power helps buyers assess whether the vehicle meets their operational needs, such as city deliveries or personnel transport. -
Weight (kg)
The weight of the vehicle impacts its energy efficiency and handling characteristics. For low-velocity electric cars, maintaining a lightweight design (often under 1,200 kg) is crucial for optimizing battery performance and reducing wear on tires and brakes. Buyers should consider weight when evaluating the potential for operational cost savings. -
Range (km)
The range defines how far a vehicle can travel on a single charge. Low-velocity electric cars usually offer ranges from 50 km to 150 km, making them suitable for short trips and urban commuting. Understanding range is vital for fleet management, ensuring that vehicles can complete daily routes without frequent recharging. -
Charging Time (hours)
Charging time is a critical factor for operational efficiency. Low-velocity electric cars may require between 4 to 8 hours for a full charge using standard charging stations. Quick charging capabilities can reduce downtime, which is particularly important for businesses with tight schedules. -
Material Composition
The materials used in the construction of electric cars, such as aluminum or composite materials, can affect weight, durability, and cost. Understanding the material grades and their properties can assist B2B buyers in evaluating vehicle longevity and maintenance requirements.
Which Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know for Electric Cars?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the electric vehicle market. Here are key terms that buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to the company that manufactures the original parts and equipment that are used in the vehicle. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for ensuring quality and compatibility, especially when sourcing parts for maintenance or upgrades. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers who need to manage inventory and cash flow, as it can affect purchasing strategies and supplier negotiations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. For electric vehicles, issuing RFQs can help buyers compare costs and capabilities among different manufacturers, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B transactions, as they clarify shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with owning and operating a vehicle, including purchase price, maintenance, insurance, and fuel (or charging) costs. B2B buyers should assess TCO to evaluate the long-term financial implications of electric vehicle investments. -
Lifecycle Assessment (LCA)
LCA is a method for assessing the environmental impacts associated with all stages of a vehicle’s life, from production to disposal. B2B buyers focused on sustainability will find LCA insights valuable for making environmentally responsible purchasing decisions.
By understanding these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can navigate the electric car low velocity market more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and sustainability goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric car low velociti Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Electric Car Low Velocity Sector?
The electric car low velocity sector is witnessing a paradigm shift driven by several global factors. Firstly, an increasing emphasis on sustainable transportation solutions is propelling demand for electric vehicles (EVs) that are environmentally friendly and energy-efficient. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions like Europe, where governments are implementing stringent emissions regulations and offering incentives for electric vehicle adoption. In contrast, markets in Africa and South America are rapidly urbanizing, creating a growing need for affordable and efficient low-velocity electric cars to meet the transportation demands of burgeoning populations.
B2B tech trends are also evolving, with advancements in battery technology, such as solid-state batteries, promising longer ranges and shorter charging times. Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies, including IoT connectivity and AI-driven driving assistance systems, is enhancing user experiences and safety. International B2B buyers should pay close attention to emerging partnerships between tech firms and automotive manufacturers, as these collaborations are likely to shape the future landscape of low-velocity electric vehicles.
Finally, market dynamics are influenced by shifting consumer preferences. As luxury brands like Cadillac introduce innovative concepts aimed at a more affluent clientele, buyers in emerging markets are seeking cost-effective solutions without compromising quality. This creates opportunities for manufacturers to cater to diverse segments within the electric car low velocity market.
How is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Electric Car Low Velocity Sector?
Sustainability plays a critical role in the electric car low velocity sector, influencing both consumer choices and business operations. The environmental impact of sourcing materials for electric vehicles, particularly lithium, cobalt, and nickel used in batteries, has prompted calls for more ethical supply chains. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including responsible mining and recycling initiatives.
The importance of ‘green’ certifications and materials cannot be overstated. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to the Responsible Cobalt Initiative are becoming essential for companies aiming to establish credibility in the market. Buyers should look for suppliers who can provide transparency in their sourcing processes, including the provenance of materials and the social impact of their supply chains. This not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for ethically produced goods.
In regions like Europe, where sustainability regulations are stringent, the pressure on manufacturers to adopt greener practices is even higher. B2B buyers must remain vigilant in assessing the sustainability credentials of their suppliers, ensuring that their sourcing strategies contribute positively to the environment while also meeting regulatory requirements.
What is the Brief Evolution and History of Electric Car Low Velocity Vehicles?
The evolution of electric car low velocity vehicles can be traced back to the early 20th century, when electric cars were a popular mode of transportation before the rise of gasoline-powered vehicles. However, the modern electric vehicle revolution gained momentum in the early 21st century, driven by technological advancements and growing environmental awareness.
The introduction of more efficient battery technologies and government incentives has reignited interest in electric vehicles, particularly in urban settings where low-velocity options are ideal for short commutes. Companies like Tesla have set the standard for electric mobility, leading to a surge in market entries from traditional automotive manufacturers and new startups alike. As electric vehicle technology continues to advance, the focus is increasingly shifting toward low-velocity applications that cater to the needs of urban consumers, making electric cars not just a sustainable alternative but also a viable everyday solution for transportation.
In summary, international B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape characterized by rapid technological advancements, sustainability considerations, and evolving consumer preferences to successfully source and invest in electric car low velocity vehicles.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric car low velociti
-
How do I evaluate potential suppliers for electric car low velocity models?
To effectively evaluate suppliers, start by checking their industry reputation and experience in manufacturing electric vehicles, particularly low velocity models. Request samples or visit their production facilities if possible. Assess their compliance with international quality standards, certifications, and their track record for timely delivery. Additionally, gather feedback from current clients regarding their experiences. This comprehensive approach will help ensure you partner with a reliable supplier that meets your specific needs. -
What are the customization options available for electric car low velocity models?
Customization options for electric car low velocity models can vary widely among manufacturers. Commonly offered customizations include battery capacity, range, color schemes, interior finishes, and technology integrations like advanced infotainment systems. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities. Some manufacturers may offer bespoke solutions, allowing for unique designs tailored to your business branding or operational needs, enhancing the vehicle’s appeal to your target market. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for electric car low velocity models?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can differ significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the vehicle. Typically, manufacturers may require a MOQ ranging from 10 to 100 units for electric car low velocity models. However, smaller quantities may be negotiable, especially for new partnerships or test orders. Always clarify the MOQ during discussions with suppliers to ensure alignment with your purchasing capabilities and business strategy. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electric car low velocity models?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region, but common practices include a deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due prior to delivery. Some suppliers may offer flexible payment options, including letters of credit or installment plans, especially for larger orders. It’s essential to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow and financial strategy while ensuring security for both parties. Always document agreed terms in a formal contract to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for electric car low velocity models?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed information on the supplier’s quality control processes, including certifications like ISO 9001. Engage in pre-production meetings to discuss quality expectations and conduct regular inspections during manufacturing. You may also consider hiring a third-party inspection service to assess the vehicles before shipment. Establishing clear quality standards and performance benchmarks in your contract can also help maintain accountability and product quality. -
What logistics considerations are important when importing electric car low velocity models?
When importing electric car low velocity models, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and associated tariffs. Engage with logistics providers experienced in automotive shipping to ensure safe and timely delivery. Understand the documentation required for customs clearance and plan for potential delays. Additionally, evaluate local infrastructure to ensure that the vehicles can be easily distributed once they arrive in your market. -
What international trade regulations should I be aware of when sourcing electric vehicles?
International trade regulations can vary widely based on your country of operation and the supplier’s location. Be aware of import tariffs, environmental standards, and safety regulations that may apply to electric vehicles in your region. It’s crucial to consult with trade experts or legal advisors to navigate these regulations effectively. Compliance with local laws ensures that your business avoids penalties and facilitates smoother operations. -
How can I determine the best market for electric car low velocity models in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
To determine the best market, conduct thorough market research focusing on demand for electric vehicles, infrastructure readiness, and local regulations. Analyze consumer preferences, existing competition, and potential partnerships with local distributors. Consider engaging with local automotive associations or attending trade shows to gain insights. Understanding regional trends and government incentives for electric vehicles can also inform your decision on market entry strategies.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Electric Car Low Velociti Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Cadillac – Elevated Velocity
Domain: cnbc.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: The Cadillac Elevated Velocity is an electric crossover concept car designed to enhance Cadillac’s all-electric luxury crossover segment. Key features include:
– Multiple user experience modes: ‘welcome mode’ with gull-wing doors and illuminated interior; ‘elevate mode’ for autonomous driving with a transformed interior; ‘velocity mode’ for an exhilarating driving experience.
– Exterior color insp…
2. Cadillac – CELESTIQ
Domain: cadillac.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Ultra-Luxury CELESTIQ, Custom-Commissioned, Hand-Built, Extraordinarily Rare, Starting at low-$400K, Advanced active, adaptive and automatic technologies, Active Air Suspension, Magnetic Ride Control, Active Rear Steering, Active Roll-Control, Adaptive All-Wheel-Drive, Active Aero Rear Spoiler, Active Aero Grille Shutters, Over 275 patented and patent-pending technologies, Industry-first four-zone…
3. GM Defense – Electric Military Concept Vehicle
Domain: gmdefensellc.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Electric Military Concept Vehicle (eISV) combines the nine-passenger Infantry Squad Vehicle (ISV) with GM’s battery electric solution. Key features include Silent Watch and Silent Extraction, low acoustic and thermal signatures, and mobile power generation. The vehicle seats up to five passengers, has a cargo box for mission packages, and includes a Roll Over Protection System (ROPS) made from 413…
4. Cadillac – Opulent Velocity
Domain: diehlcadillac.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Opulent Velocity is Cadillac’s future EV, emphasizing luxury and performance. It features advanced technology, sustainable materials, and a focus on electric powertrains. The design aims to blend elegance with cutting-edge innovation, catering to a premium market.
5. SkyQuest – Low Speed Electric Vehicle Market Insights
Domain: skyquestt.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Low Speed Electric Vehicle Market Size: USD 6.15 Billion in 2023, projected to grow to USD 9.43 Billion by 2032. Key segments include Application Type (Golf course, Hotels & resort), Vehicle Type (Golf cart, Commercial turf utility vehicle), Power Output (≤5 KW, 6-15 KW), Motor Type (AC Motor, DC Motor), Battery Type (Li-lon Battery, Lead Acid Battery). Report ID: SQMIG20X2008, Published Date: Nov…
6. Volkswagen – ID.3 vs Hyundai – Ioniq 5 Efficiency
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around the efficiency of electric vehicles (EVs) at different speeds, specifically mentioning the Volkswagen ID.3 and Hyundai Ioniq 5. Key points include that the Ioniq 5 has twice the range at 45 mph compared to 70 mph, and a significant drop in range at higher speeds (e.g., a 10% drop for every 5 mph increase). The conversation also touches on the impact of aerodynamics a…
7. Cadillac – Elevated Velocity EV Concept
Domain: evcentral.com.au
Introduction: Cadillac Elevated Velocity EV concept features:
– Designed to reboot Cadillac’s V-Series high-performance sub-brand.
– Appearance: resembles a jacked-up super sedan rather than a traditional SUV.
– Design cues expected to reappear in future models.
– Aerodynamic upper body for peak performance; off-road capabilities in the lower half.
– Classic long bonnet and gullwing doors for access to a s…
8. Cadillac – Opulent Velocity Electric Hypercar Concept
Domain: autos.yahoo.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Cadillac Opulent Velocity Electric Hypercar Concept
– Type: Hypercar
– Category: Electric vehicle
– Design: Low-slung, wide-stance coupe
– Heritage: Inspired by the Cadillac Cien concept from the early 2000s
– Features:
– Level 4 autonomous driving capabilities for fully hands-free experience
– Velocity Mode for manual driving with steering wheel and pedals
– HUD screen with augmented reali…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric car low velociti
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicles (EVs), the low-velocity segment presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers. Strategic sourcing is essential for companies looking to capitalize on this trend, allowing them to access innovative technologies and high-quality components that enhance performance and user experience. As demonstrated by Cadillac’s Elevated Velocity concept, the integration of luxury features and advanced driving modes can significantly differentiate products in a competitive marketplace.
By focusing on strategic partnerships and supply chain efficiencies, businesses can ensure they remain at the forefront of the low-velocity electric vehicle sector. This approach not only fosters innovation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable and high-performance vehicles.
As we look ahead, it is imperative for B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to actively engage with manufacturers and suppliers that prioritize quality, sustainability, and cutting-edge technology. By doing so, they can secure a competitive edge in their respective markets and contribute to the global transition towards electrification. The time to act is now—invest in strategic sourcing to drive your business forward in the electric vehicle revolution.