Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for engine-powered Crane
In the dynamic landscape of industrial machinery, sourcing the right engine-powered crane can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers. As global demand for efficient and safe lifting solutions increases, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the need for reliable and high-capacity cranes becomes paramount. This guide is designed to help international buyers navigate the complexities of selecting the ideal engine-powered crane for their specific operational needs, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions that align with their business goals.
This comprehensive resource covers various types of engine-powered cranes, including electric and hydraulic options, and their diverse applications across industries such as manufacturing, construction, and automotive repair. Additionally, we will delve into critical aspects of supplier vetting, cost considerations, and maintenance tips, all tailored to the unique challenges faced by businesses in different regions. By equipping buyers with actionable insights and best practices, this guide empowers them to enhance productivity, ensure safety, and optimize resource allocation in their operations.
Understanding the nuances of the engine-powered crane market will not only facilitate smarter investments but also foster long-term partnerships with suppliers who align with their operational standards. As you explore the sections ahead, you will gain the knowledge necessary to confidently select the right equipment that meets your organization’s demands while adhering to industry regulations and standards.
Understanding engine-powered Crane Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Engine Hoists | Utilizes hydraulic systems for lifting; foldable for storage. | Automotive repairs, machinery maintenance | Pros: High lifting capacity; compact design. Cons: Requires regular maintenance of hydraulic fluid. |
| Electric Floor Cranes | Powered by electricity; often features adjustable heights. | Manufacturing, assembly lines | Pros: Reduced manual effort; precise lifting control. Cons: Dependency on power supply; higher initial cost. |
| Counterbalanced Floor Cranes | Designed with a counterweight for stability; portable. | Construction sites, heavy equipment handling | Pros: Enhanced stability; versatile applications. Cons: Limited lifting height compared to others. |
| Portable Engine Cranes | Lightweight; easy to transport; ideal for small workshops. | Small-scale repairs, DIY projects | Pros: Highly portable; economical. Cons: Limited load capacity; may not suit heavy-duty tasks. |
| Jib Cranes | Fixed or mobile; allows lateral movement for precise positioning. | Warehousing, shipping, and logistics | Pros: Increases efficiency in tight spaces; versatile. Cons: Requires adequate space for setup; may need installation. |
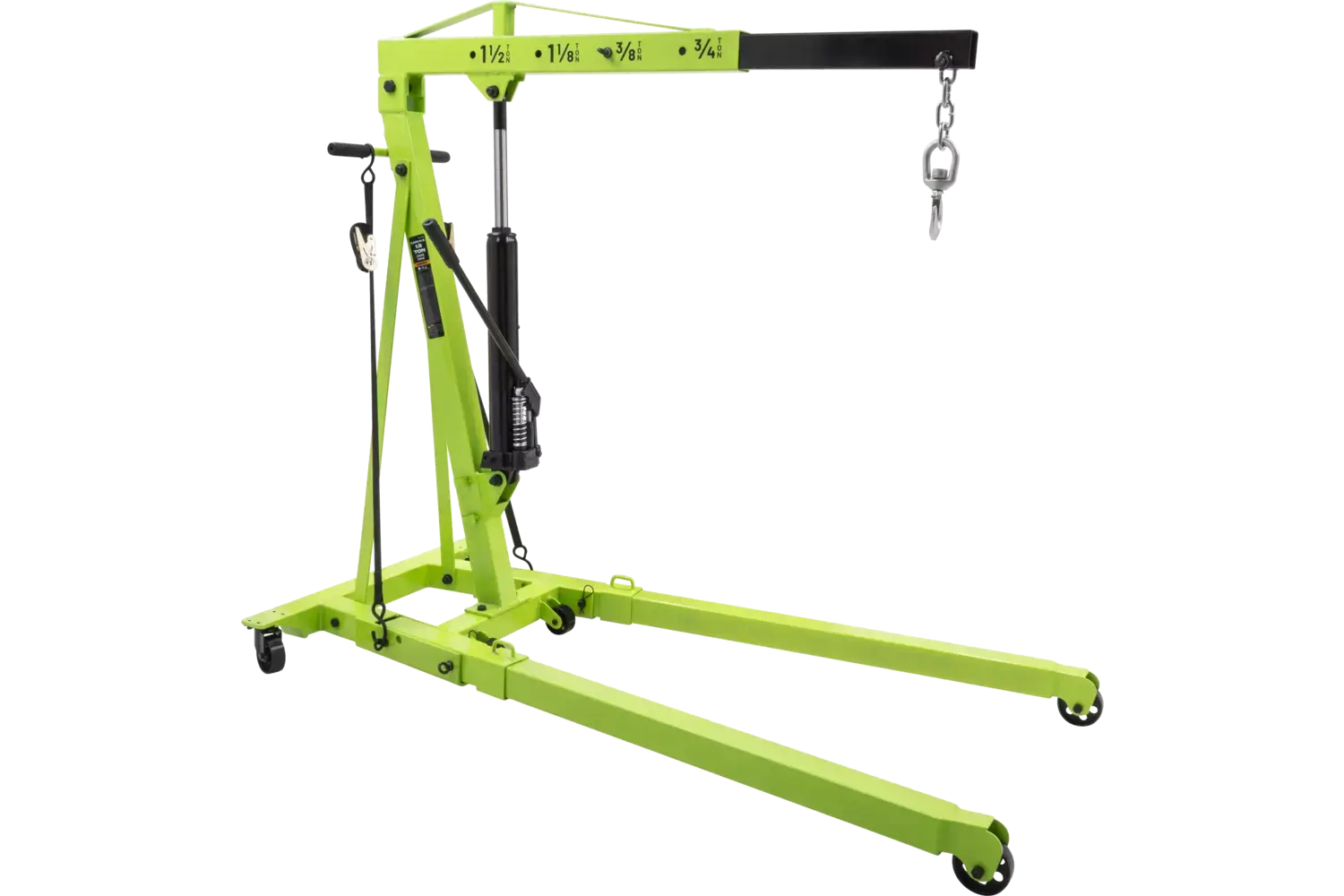
What Are the Characteristics of Hydraulic Engine Hoists?
Hydraulic engine hoists are designed to lift heavy loads using hydraulic pressure, making them suitable for automotive repairs and machinery maintenance. Their foldable design allows for easy storage, which is a crucial consideration for businesses with limited space. When purchasing, buyers should evaluate the lifting capacity and ensure regular maintenance of the hydraulic system to avoid potential failures.
How Do Electric Floor Cranes Enhance Operational Efficiency?
Electric floor cranes offer a significant advantage in environments where manual lifting is impractical. These cranes can adjust their height and provide precise control, making them ideal for manufacturing and assembly lines. Buyers should consider the power supply availability, as these cranes require electricity to operate. The initial investment is typically higher, but the reduction in manual labor can lead to long-term savings.
Why Choose Counterbalanced Floor Cranes for Construction Sites?
Counterbalanced floor cranes are engineered for stability, featuring a counterweight to balance heavy loads. They are portable and versatile, making them suitable for construction sites and heavy equipment handling. When considering a purchase, businesses should assess the crane’s lifting height and ensure it meets their operational needs while providing adequate safety features.
What Benefits Do Portable Engine Cranes Offer to Small Workshops?
Portable engine cranes are lightweight and designed for easy transport, making them an excellent choice for small workshops and DIY projects. They are typically more economical, catering to businesses that do not require heavy-duty lifting. However, buyers should be aware of their limited load capacity, as they may not be suitable for larger engines or heavy machinery.
How Do Jib Cranes Improve Logistics Operations?
Jib cranes are designed for both fixed and mobile applications, allowing for lateral movement and precise load positioning. They are particularly beneficial in warehousing and shipping operations, where efficiency is paramount. Businesses should consider the space available for installation and the crane’s lifting capacity to ensure it meets their logistical requirements effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of engine-powered Crane
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Engine-Powered Crane | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Lifting and positioning engines during assembly | Increases efficiency and reduces manual labor risks | Load capacity, portability, and compliance with safety standards |
| Construction | Hoisting heavy materials on-site | Enhances safety and speeds up construction timelines | Durability, ease of transport, and adaptability to various terrains |
| Oil & Gas | Moving equipment and machinery in remote locations | Minimizes downtime and improves operational efficiency | Weather resistance, fuel type, and maintenance support |
| Maintenance & Repair | Servicing heavy machinery and equipment | Improves service speed and reduces injury risks | Versatility, ease of use, and after-sales support |
| Warehousing & Logistics | Loading and unloading heavy items | Streamlines operations and increases productivity | Maneuverability, size, and compatibility with existing systems |
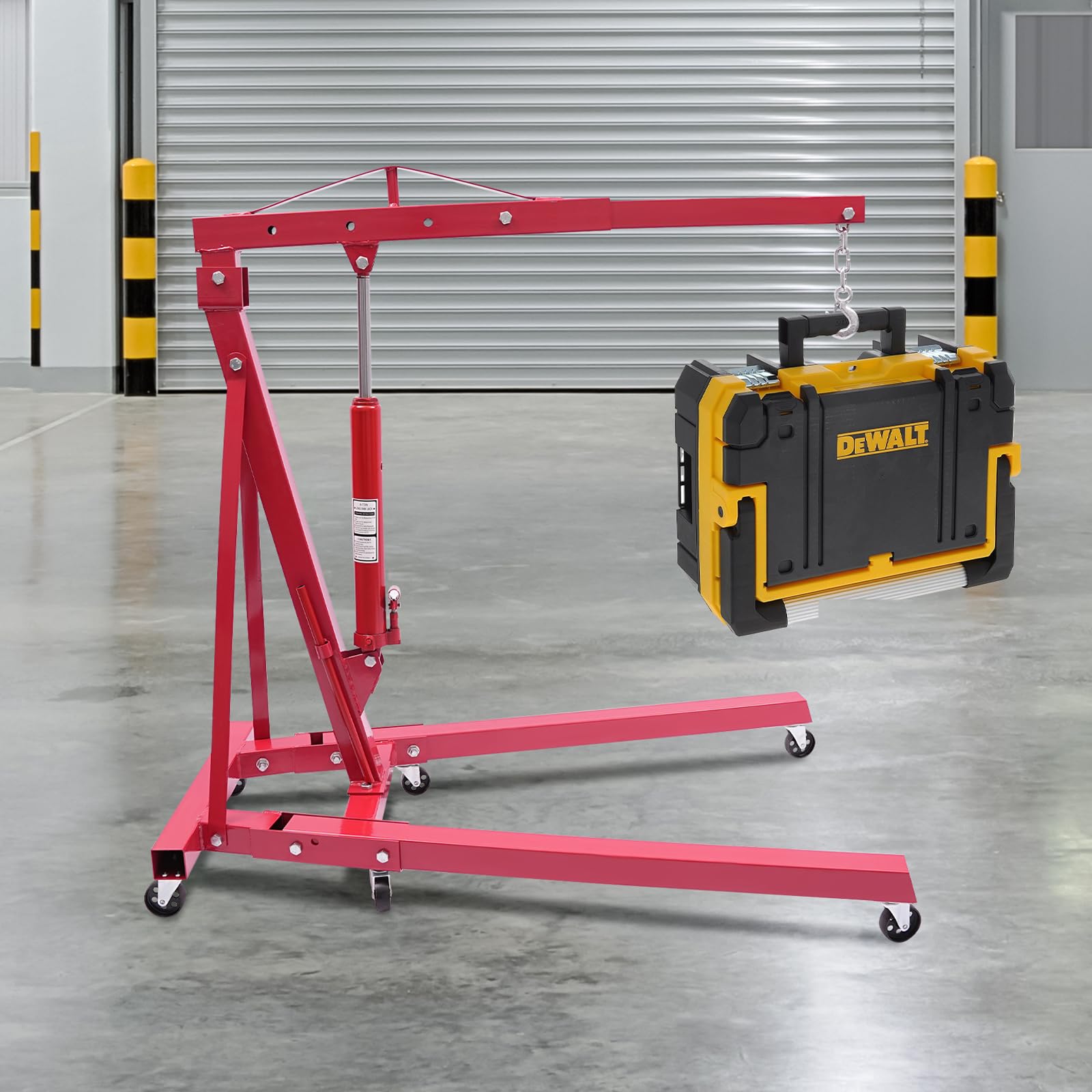
How is Engine-Powered Crane Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, engine-powered cranes are essential for lifting and positioning engines during assembly processes. These cranes provide a safe and efficient means to handle heavy engine components, which reduces the risk of worker injuries associated with manual lifting. Buyers in this sector should prioritize cranes with high load capacities and features that enhance stability and precision, ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
What Role Does Engine-Powered Crane Play in Construction?
Engine-powered cranes are invaluable on construction sites for hoisting heavy materials, such as steel beams and concrete blocks. Their ability to lift substantial weights significantly enhances safety by minimizing the risk of accidents related to manual handling. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing cranes that are durable and portable is crucial due to varying site conditions and the need for mobility across job sites.
How is Engine-Powered Crane Beneficial in Oil & Gas Operations?
In the oil and gas industry, engine-powered cranes facilitate the movement of heavy machinery and equipment, particularly in remote or offshore locations. These cranes help minimize operational downtime by enabling quick and efficient equipment relocation. Buyers should consider cranes that are weather-resistant and capable of operating in harsh environments, along with a reliable maintenance support system to ensure continuous operation.
Why is Engine-Powered Crane Important for Maintenance & Repair Services?
Engine-powered cranes are widely used in maintenance and repair services to lift and service heavy machinery and equipment. Their versatility allows for quick adjustments to various machinery types, improving service speed and reducing the risk of injuries. Buyers should focus on cranes that are easy to operate and come with robust after-sales support to ensure long-term reliability and performance.
How Does Engine-Powered Crane Enhance Operations in Warehousing & Logistics?
In warehousing and logistics, engine-powered cranes streamline the loading and unloading of heavy items, significantly improving operational efficiency. By automating these processes, businesses can reduce labor costs and enhance productivity. When sourcing cranes, it is essential to consider their maneuverability and size to ensure compatibility with existing warehouse systems and maximize space utilization.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘engine-powered Crane’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Maneuvering Heavy Loads in Tight Spaces
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in industries such as automotive or construction face the challenge of maneuvering heavy loads in confined workspaces. Engine-powered cranes, while powerful, can be cumbersome and difficult to navigate in tight areas. This can lead to inefficiencies, increased labor costs, and potential safety hazards if workers attempt to manually handle heavy equipment due to limited crane mobility.
The Solution: To effectively manage this issue, B2B buyers should consider sourcing engine-powered cranes specifically designed for tight spaces. Look for models that feature a compact design with foldable or telescopic legs, which allow for better positioning under low ground clearance vehicles or in narrow aisles. Prioritize cranes with smooth-rolling casters for enhanced maneuverability. Additionally, invest in training for operators to ensure they understand the crane’s capabilities and limitations. Proper training can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and enhance overall productivity.
Scenario 2: Maintenance Challenges and Downtime
The Problem: Engine-powered cranes are essential for lifting heavy machinery, but they often require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. B2B buyers frequently encounter issues related to hydraulic system failures, which can lead to unexpected downtime and costly repairs. This is particularly problematic in industries where efficiency and uptime are critical, such as manufacturing or logistics.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance issues, it is crucial for buyers to select high-quality engine-powered cranes with robust hydraulic systems and reliable components. Establish a regular maintenance schedule that includes routine checks of hydraulic fluid levels, inspecting hoses for wear, and ensuring that all moving parts are lubricated. Additionally, consider implementing a predictive maintenance strategy using IoT sensors that can monitor the crane’s performance in real-time. This proactive approach can help identify potential issues before they lead to breakdowns, thus minimizing downtime and extending the crane’s lifespan.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Operator Safety and Compliance
The Problem: Safety is a paramount concern for businesses using engine-powered cranes, especially when lifting heavy loads. Many buyers struggle with ensuring that their equipment meets safety standards and that operators are adequately trained to use the cranes safely. Non-compliance with safety regulations can result in severe penalties, workplace injuries, and damage to equipment.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing engine-powered cranes that comply with international safety standards, such as ASME and CE certifications. It is essential to verify that the cranes come with detailed operating manuals that include safety guidelines. Furthermore, investing in comprehensive training programs for operators can significantly enhance safety. This training should cover not only the operational aspects of the crane but also the identification of potential hazards and emergency procedures. Regular refresher courses can keep safety protocols top of mind and ensure that all personnel are equipped to operate the equipment safely. By fostering a culture of safety and compliance, businesses can protect their employees and assets while maintaining operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for engine-powered Crane
What Are the Common Materials Used in Engine-Powered Cranes?
When selecting materials for engine-powered cranes, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for specific applications. The following analysis focuses on four common materials: steel, aluminum, composite materials, and cast iron.
How Does Steel Perform in Engine-Powered Cranes?
Steel is the most widely used material in the construction of engine-powered cranes due to its high strength and durability. It typically offers excellent temperature and pressure ratings, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel cranes can withstand significant loads without deformation, which is crucial in industrial environments.
Pros: Steel is highly durable and can be manufactured to meet various specifications, including those set by international standards like ASTM and DIN. It is also relatively cost-effective compared to other materials, making it a popular choice among manufacturers.
Cons: The main drawback of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion, especially in humid or harsh environments. This necessitates protective coatings or treatments, which can increase manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various media, including oil and hydraulic fluids, makes it a versatile choice for cranes used in automotive and industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards is crucial. Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure that steel cranes meet local regulations regarding load capacities and safety features.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Engine-Powered Crane Design?
Aluminum is increasingly used in engine-powered cranes due to its lightweight nature and good corrosion resistance. This material is particularly beneficial in applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in mobile cranes.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight property, which enhances portability and ease of use. It also resists corrosion better than steel, reducing maintenance needs and extending the crane’s lifespan.
Cons: Aluminum is generally less strong than steel, which may limit its use in high-capacity cranes. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be more complex and costly.
Impact on Application: Aluminum cranes are suitable for environments where weight is a concern, such as construction sites with limited space. However, they may not be ideal for extremely heavy loads.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for aluminum cranes that comply with international standards, particularly in regions with stringent safety regulations, such as Europe.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Engine-Powered Cranes?
Composite materials are becoming popular in specialized applications due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion. These materials often combine fibers with a resin matrix, providing unique performance characteristics.
Pros: Composites offer excellent resistance to chemicals and environmental factors, making them ideal for cranes used in corrosive environments. Their lightweight nature also improves maneuverability.
Cons: The primary limitation of composite materials is their cost, which is generally higher than steel and aluminum. Additionally, they may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly useful in applications where exposure to harsh chemicals is a concern. However, their use may be limited by load capacity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that composite cranes meet relevant international safety and performance standards, especially in regions with diverse environmental conditions.
Why Is Cast Iron Still Relevant in Engine-Powered Cranes?
Cast iron is traditionally used in crane components due to its excellent wear resistance and ability to absorb vibrations. While not as common as steel or aluminum, it remains relevant in specific applications.
Pros: Cast iron is highly durable and can withstand heavy loads, making it suitable for stationary cranes. Its vibration-damping properties enhance operational stability.
Cons: The main disadvantage is its weight, which can limit mobility. Additionally, cast iron is more brittle than steel, making it susceptible to cracking under extreme stress.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is ideal for fixed installations where weight is less of a concern. However, its brittleness can be a limiting factor in dynamic applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that cast iron components meet local and international standards for safety and performance, particularly in regions with rigorous regulatory environments.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Engine-Powered Cranes
| Material | Typical Use Case for engine-powered Crane | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty industrial applications | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Mobile cranes in construction | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength compared to steel | High |
| Composite | Specialized applications in harsh environments | Excellent chemical resistance | Higher manufacturing cost | High |
| Cast Iron | Fixed installations | Excellent wear resistance | Heavy and brittle | Medium |
This material selection guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, ensuring they make informed decisions when sourcing engine-powered cranes tailored to their specific operational needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for engine-powered Crane
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Engine-Powered Cranes?
The manufacturing of engine-powered cranes involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets the highest standards of safety, durability, and efficiency. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing equipment.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation, where high-quality raw materials are selected. Engine-powered cranes typically use steel for their structural components due to its strength and durability. Advanced alloys may also be incorporated for specific parts that require enhanced resistance to wear and tear. Suppliers often conduct material inspections to ensure compliance with industry standards. B2B buyers should inquire about the origin of materials and any certifications that confirm their quality.
How Is the Forming Process Conducted?
The forming process involves shaping the prepared materials into the desired components of the crane. Techniques such as laser cutting, bending, and welding are commonly employed. For example, laser cutting allows for precise cuts that minimize waste and ensure accurate dimensions. Additionally, robotic welding is increasingly used to enhance the consistency and quality of welds. This automation not only boosts production efficiency but also reduces human error. Buyers should ask suppliers about the technologies used in forming processes to gauge the quality of craftsmanship.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
Once the individual components are formed, they undergo assembly. This stage is crucial, as it determines the crane’s overall functionality and safety. Experienced technicians assemble the components, often using jigs and fixtures to maintain accuracy. Hydraulic systems are integrated during this phase, which requires careful calibration to ensure optimal performance. B2B buyers should verify that the assembly team is trained and that they follow standard operating procedures to minimize the risk of defects.
How Are Finishing Techniques Applied?
The finishing process enhances the aesthetic appeal and longevity of the crane. Common techniques include powder coating and painting, which protect against corrosion and wear. Additionally, surface treatments may be applied to improve grip or reduce friction in moving parts. Buyers should inquire about the finishing processes used, as these can significantly affect the crane’s durability in harsh environments.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that each engine-powered crane meets international standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with relevant international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with these standards indicates that a manufacturer has established processes for continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards) and API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications are important for cranes used in specific sectors.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is divided into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection focuses on raw materials and components received from suppliers. It ensures that all materials meet specified standards before they enter the production line.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC monitors the production processes to catch defects early. This may involve routine checks and measurements to ensure components are being produced to specification.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, the crane undergoes a final inspection to ensure it meets all quality standards. This includes functional tests and safety checks before the product is shipped.
B2B buyers should request information about the QC processes from suppliers, including the frequency of inspections and the criteria used for acceptance.
How Can Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying the quality control measures of a supplier is essential for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing from international markets. Here are effective strategies:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers help ensure compliance with quality standards. Buyers can either perform these audits themselves or hire third-party services to assess the supplier’s quality management system.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality control processes, including results from previous inspections and any corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging a third-party inspection agency can offer an unbiased assessment of the cranes before purchase. This is particularly important for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where varying local regulations may impact the equipment’s compliance.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control in different regions is crucial. Specific certifications may be required based on local regulations, and compliance with international standards does not always guarantee acceptance in local markets.
In regions like Africa and the Middle East, buyers should be aware of additional certifications that may be mandatory, such as the Gulf Conformity Mark (G-mark) in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries. In contrast, European buyers must ensure compliance with the Machinery Directive, which mandates that all machinery sold in the EU meets specific safety and environmental standards.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that their investment in engine-powered cranes meets both operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘engine-powered Crane’
To facilitate the procurement of engine-powered cranes, this guide provides actionable steps for B2B buyers. The following checklist will help ensure you make informed decisions that meet your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical for selecting the right engine-powered crane. Consider factors such as load capacity, reach, and height requirements. Understand the types of materials and equipment you will be lifting, as well as the specific environments in which the crane will operate (e.g., construction sites, workshops).
Step 2: Assess Compliance and Safety Standards
Verify that the cranes you consider comply with relevant safety and industry standards. Look for certifications such as ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) or CE marking for products sold in Europe. Compliance ensures that the equipment is safe for use and meets necessary legal requirements, which can mitigate liability risks.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in similar industries or regions. Pay attention to their reputation for reliability and customer service, as these factors can significantly impact your procurement experience.
Step 4: Compare Pricing and Financing Options
Collect quotes from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures. Be aware of the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational costs, rather than just the initial purchase price. Additionally, inquire about financing options or leasing arrangements, which can provide flexibility in managing your budget.
Step 5: Examine Warranty and Support Services
A robust warranty and support service are essential when sourcing engine-powered cranes. Check the length and coverage of the warranty, as well as the availability of spare parts. Investigate the supplier’s technical support options to ensure you have access to assistance when needed, which can reduce downtime during operations.
Step 6: Conduct Site Assessments and Demonstrations
If possible, arrange site assessments or demonstrations of the cranes you are considering. This step is crucial for understanding how the crane will function in your specific environment and for verifying its suitability for your applications. Look for ease of operation, maneuverability, and safety features during these evaluations.
Step 7: Finalize Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, carefully review and negotiate the terms and conditions of the purchase agreement. Ensure that delivery schedules, installation services, and training for operators are clearly outlined. Pay attention to any clauses related to returns, damages, and liability to protect your interests.
By following these steps, you will be well-equipped to make a prudent purchase of an engine-powered crane that meets your operational requirements and enhances your productivity.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for engine-powered Crane Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Engine-Powered Crane Sourcing?
When sourcing engine-powered cranes, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-strength steel and durable components, while more expensive, ensure better performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages paid to workers during the manufacturing process. Skilled labor may command higher wages but contributes to better craftsmanship and reliability.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes all indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overheads.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for customized or specialized cranes. These costs are often amortized over larger production runs, making larger orders more economical.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes ensures that the cranes meet safety and performance standards. While this may increase upfront costs, it can reduce long-term liabilities and maintenance expenses.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary greatly depending on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer. Additionally, customs duties and taxes can significantly affect the total cost, especially for international shipments.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on market competition and the supplier’s business model.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Engine-Powered Crane Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of engine-powered cranes, which buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often offer discounts for bulk orders. Understanding the minimum order quantity (MOQ) can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized cranes designed for specific applications may incur higher costs due to the additional engineering and manufacturing processes involved.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Cranes made with higher-quality materials or those that meet specific certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) typically command higher prices but offer better reliability and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products due to their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery and responsibility for shipping costs can significantly impact the total cost. Incoterms dictate who bears the risk and cost during transportation, which can affect pricing negotiations.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in Crane Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are several tips to optimize sourcing costs:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Don’t hesitate to negotiate on price, especially for bulk orders. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts to secure larger contracts.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, operation, and potential downtime. Investing in higher-quality cranes may lead to lower TCO.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of the pricing dynamics in different regions. Local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and regional demand can impact costs significantly.
-
Leverage Local Suppliers: Whenever possible, consider sourcing from local manufacturers to reduce logistics costs and lead times. Local suppliers may also have better knowledge of regional compliance and certification requirements.
-
Conduct Market Research: Stay informed about current market trends and pricing benchmarks. This knowledge can empower you during negotiations and help you identify the best suppliers.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices referenced in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always consult multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate and competitive pricing tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing engine-powered Crane With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Engine-Powered Cranes for Lifting Solutions
In the industrial sector, selecting the right lifting solution is crucial for optimizing efficiency and safety. While engine-powered cranes are a popular choice for heavy lifting tasks, there are several viable alternatives that can also meet various operational needs. This section compares engine-powered cranes with two alternatives: hydraulic floor cranes and electric hoists. By examining key aspects such as performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases, businesses can make informed decisions tailored to their specific requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Engine-Powered Crane | Hydraulic Floor Crane | Electric Hoist |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High load capacity (up to 6,000 lbs) | Moderate load capacity (up to 2,500 lbs) | High speed and precision lifting (varies by model) |
| Cost | $500 – $11,300 | $500 – $3,000 | $1,000 – $5,000 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires setup and space | Simple to use, often portable | Requires electrical source, easy installation |
| Maintenance | Moderate (engine upkeep) | Low (minimal moving parts) | Moderate (electrical checks needed) |
| Best Use Case | Heavy industrial applications | Automotive repair and assembly | Warehousing and assembly line tasks |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Hydraulic Floor Cranes?
Hydraulic floor cranes are favored for their simplicity and effectiveness in lifting moderate loads, typically up to 2,500 lbs. They are often portable, making them suitable for automotive repair shops where space may be limited. The low maintenance requirement is a significant advantage, as they consist of fewer moving parts compared to engine-powered cranes. However, their performance is limited compared to engine-powered cranes, making them less suitable for heavy industrial applications. For businesses focused on versatility in smaller lifting tasks, hydraulic floor cranes present an excellent solution.
How Do Electric Hoists Compare as an Alternative?
Electric hoists are another efficient lifting solution that excels in speed and precision. They are particularly beneficial in environments such as warehouses and assembly lines where quick lifting and lowering of loads is necessary. With varying capacities, electric hoists can handle significant weights while minimizing manual labor. However, they require access to an electrical source, which can pose limitations in remote or outdoor locations. Maintenance is also essential, as regular electrical checks are necessary to ensure safe operation. For businesses needing high-speed lifting capabilities, electric hoists are an effective alternative.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Lifting Solution?
When selecting the appropriate lifting equipment, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational requirements, including load capacity, workspace constraints, and budget. Engine-powered cranes are ideal for heavy-duty tasks but may not be necessary for lighter applications. Hydraulic floor cranes offer a practical solution for automotive and light industrial work, while electric hoists provide rapid lifting capabilities suitable for fast-paced environments. By carefully evaluating these alternatives, buyers can choose the most suitable solution that aligns with their operational needs and enhances productivity.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for engine-powered Crane
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Engine-Powered Cranes?
When considering the purchase of engine-powered cranes, understanding their technical properties is crucial for making informed decisions. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Load Capacity
This specification indicates the maximum weight the crane can lift safely. Load capacities typically range from 500 lbs to 6,000 lbs, depending on the crane model. For B2B buyers, selecting a crane with an appropriate load capacity ensures that it can handle the intended lifting tasks without risking equipment failure or safety hazards. -
Boom Height Adjustment
The boom height refers to the vertical reach of the crane. Most cranes feature adjustable booms, allowing users to raise or lower the load as needed. This property is vital for accessing different working heights, especially in construction or automotive applications. Ensuring that the crane meets the required boom height for specific tasks can enhance operational efficiency. -
Material Grade and Construction
The materials used in the crane’s construction, such as steel or aluminum, impact its durability and strength. Higher-grade materials can withstand greater stress and environmental challenges, which is crucial for cranes used in harsh conditions. B2B buyers should assess the material quality to ensure longevity and reliability in demanding work environments. -
Hydraulic System Specifications
Engine-powered cranes often utilize hydraulic systems for lifting mechanisms. Key specifications include the hydraulic pump’s capacity and the cylinder’s stroke length. A robust hydraulic system ensures smooth operation and quick lifting times, enhancing productivity. Buyers should evaluate these specifications to ensure they meet operational needs. -
Foldability and Portability
Many cranes are designed with foldable components for easy storage and transport. This feature is particularly beneficial for businesses operating in multiple locations or those with limited storage space. B2B buyers should consider whether the crane’s design allows for convenient mobility, which can save time and reduce logistical challenges. -
Safety Features
Safety mechanisms such as overload protection, locking casters, and emergency stop buttons are essential for minimizing workplace accidents. Understanding the safety features included with the crane is vital for compliance with occupational safety standards and protecting workers.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Engine-Powered Cranes?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline the purchasing process and improve communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of cranes, an OEM may provide replacement parts or entire cranes. Understanding OEM relationships can be crucial for ensuring quality and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ helps in budgeting and inventory planning. It can also affect pricing; larger orders may result in lower per-unit costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document soliciting price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. In the context of engine-powered cranes, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare offers and negotiate better terms, ensuring they receive competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers, especially when importing cranes from different countries. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. For buyers, understanding lead times is essential for planning and project scheduling, particularly in industries where timing is critical. -
Warranty and Service Agreements
Warranties provide assurance regarding the quality and reliability of the crane, covering repairs or replacements within a specified period. B2B buyers should pay attention to warranty terms and available service agreements, which can safeguard their investment and ensure operational continuity.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions when investing in engine-powered cranes, enhancing both safety and efficiency in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the engine-powered Crane Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Engine-Powered Crane Market?
The engine-powered crane sector is witnessing significant growth driven by various global factors. The surge in construction and infrastructure development, particularly in emerging markets such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East, is a primary catalyst. Countries like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia are ramping up their investments in large-scale projects, necessitating efficient lifting solutions. Additionally, the increasing demand for automation and advanced technology is shaping sourcing trends. The integration of IoT and AI in crane operations enhances safety, efficiency, and predictive maintenance, which are critical for international B2B buyers.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a focal point in procurement strategies. As environmental regulations tighten, companies are prioritizing eco-friendly cranes that minimize emissions and energy consumption. This shift is also reflected in the growing popularity of electric-powered options, which are seen as cleaner alternatives to traditional engine-powered models. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that offer innovative solutions, such as telematics for remote monitoring, which can significantly reduce operational downtime and enhance productivity.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of Engine-Powered Cranes?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the engine-powered crane industry. The environmental impact of industrial equipment, including emissions and resource consumption, is under scrutiny. Companies are now expected to demonstrate commitment to sustainability through their supply chain practices. This includes sourcing materials from suppliers with recognized green certifications and those that adhere to ethical labor practices.
In addition, the demand for ‘green’ cranes is on the rise. This encompasses cranes designed to reduce energy consumption, utilize recyclable materials, and employ manufacturing processes that lessen environmental harm. By investing in sustainable cranes, B2B buyers not only comply with regulations but also enhance their corporate image, appealing to environmentally conscious clients and stakeholders. Furthermore, suppliers who can prove their commitment to sustainability often gain a competitive edge, making them more attractive partners in a global market increasingly focused on ethical practices.
What Is the Evolution of Engine-Powered Cranes in the B2B Landscape?
The evolution of engine-powered cranes has been marked by significant technological advancements and shifts in market demand. Initially designed for simple lifting tasks, these cranes have transformed into sophisticated machines that incorporate hydraulics, electronics, and smart technology. The introduction of hydraulic systems in the mid-20th century revolutionized lifting capabilities, allowing for more efficient and safer operations.
In recent years, there has been a notable shift towards electric and hybrid models, responding to growing environmental concerns. This evolution is not just about improved functionality; it reflects a broader industry trend towards automation and data-driven decision-making. As international buyers increasingly prioritize efficiency, safety, and sustainability, understanding the historical context of these changes can provide valuable insights into making informed purchasing decisions in today’s dynamic market.
In conclusion, the engine-powered crane sector is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, sustainability concerns, and changing market dynamics. For B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets, staying attuned to these trends is essential for making strategic sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of engine-powered Crane
-
How do I select the right engine-powered crane for my business needs?
Selecting the right engine-powered crane involves assessing your specific operational requirements. Consider factors such as load capacity, boom height, and portability. Evaluate the types of tasks you’ll perform—whether lifting engines, heavy machinery, or other equipment. Research different models from reputable manufacturers, focusing on durability, ease of use, and maintenance needs. If your operations are in challenging environments (like construction sites), prioritize cranes designed for stability and safety. Lastly, consult with suppliers to ensure compatibility with your operational setup. -
What is the typical load capacity range for engine-powered cranes?
Engine-powered cranes typically have a load capacity ranging from 500 lbs to over 6,000 lbs, depending on the model and manufacturer. For lighter tasks, smaller cranes with capacities around 1,000 to 2,500 lbs may suffice, while heavier operations may require cranes that can lift up to 6,000 lbs or more. When determining capacity, factor in the weight of the objects you plan to lift and any additional equipment needed for lifting. Always choose a crane with a capacity exceeding your maximum load to ensure safety and efficiency. -
What are the common payment terms for international orders of engine-powered cranes?
Payment terms for international orders can vary significantly by supplier and region. Common terms include upfront payment, a deposit followed by the balance upon delivery, or payment via letters of credit. Ensure you clarify the terms before finalizing your order, as they can impact your cash flow. Additionally, consider currency fluctuations and transaction fees, especially when dealing with suppliers from different continents. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also facilitate smoother negotiations regarding payment terms. -
How do I vet suppliers of engine-powered cranes for reliability?
To vet suppliers effectively, start by researching their reputation in the industry. Look for reviews, testimonials, and case studies from other businesses that have purchased from them. Verify their certifications and compliance with international safety and quality standards, such as ISO and ASME. Request references and reach out to previous clients to inquire about their experiences. Additionally, assess the supplier’s experience in your region, especially in terms of logistics and support services, to ensure they can meet your specific needs. -
What customization options are available for engine-powered cranes?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for engine-powered cranes to meet specific operational needs. Customizations can include variations in load capacity, boom length, and hydraulic power systems. Additionally, options for different wheel configurations or materials can enhance performance in specific environments. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available modifications. This can help ensure the crane aligns with your operational processes, enhancing efficiency and safety during use. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for engine-powered cranes?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for engine-powered cranes can vary based on the manufacturer and the type of crane. Some suppliers may have MOQs as low as one unit, while others may require orders of several units to maintain cost-effectiveness. When sourcing, inquire about MOQs to understand how they align with your purchasing strategy. If you’re exploring bulk purchases, consider negotiating with suppliers for better pricing or terms based on your anticipated needs. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for my engine-powered crane purchase?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and quality certifications from your supplier. Most reputable manufacturers provide warranties or guarantees on their products, which can serve as an assurance of quality. Conduct thorough inspections upon delivery to verify that the cranes meet your ordered specifications and safety standards. Additionally, consider establishing a quality control process that includes periodic checks during operation to maintain safety and performance standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing engine-powered cranes?
When importing engine-powered cranes, it’s crucial to understand logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and local transportation. Evaluate different shipping options (air freight vs. sea freight) based on cost and urgency. Familiarize yourself with import duties and taxes specific to your country, which can significantly affect the overall cost. Additionally, ensure your supplier can provide necessary documentation, such as bills of lading and customs declarations, to facilitate a smooth import process. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can further streamline operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Engine-Powered Crane Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Carlyle Tools – Engine Crane
Domain: carlyletools.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: {“name”:”Engine Crane”,”price”:”$829.99″,”features”:[“Rapid rise hydraulic jack for quick elevation without a load”,”Low-profile base for access under vehicles with low ground clearance”,”Foldable legs for convenient storage”,”Chain and swivel hook assembly for easier positioning”],”benefits”:[“Versatile tool for lifting and positioning engines”,”Practical addition to any professional or DIY garag…
2. Sunex Tools – Engine Cranes & Stands
Domain: sunextools.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Engine Cranes & Stands by SUNEX Tools include durable engine slings, traverse bars, and options with a 2-ton capacity designed for safe and efficient engine lifting. Key products include: 2 Ton Foldable Engine Crane (5222), 1000 lb Deluxe Geared Engine Stand (8300GB), 1 Ton Engine Stand (8400), Engine Transverse Bar with Arm Support (5207), 3/4 Ton Engine Sling (5208A), and Oil Drip Pan for Engine…
3. Crane Depot – Floor Cranes
Domain: cranedepot.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Floor cranes are industrial lifting devices used for loading, unloading, and transporting heavy parts and equipment. They are available in various types, including portable and floor-mounted options. The selection includes electric-powered and hydraulic floor cranes. Key features include:
– Capacity options: 2,000 lb, 4,000 lb, 6,000 lb
– Price range: List prices from $680.00 to $3,015.00 with d…
4. Vestil – Engine Hoists & Floor Cranes
Domain: vestil.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Category: Engine Hoists & Floor Cranes
Vestil’s Engine Hoists & Floor Cranes provide a versatile solution for lifting and positioning heavy equipment with precision and ease. Their durable design and adjustable features ensure safety and efficiency across a variety of industrial tasks. By investing in these tools, you enhance productivity and reduce physical strain on workers.
Key Products:
– Pow…
5. Astro Crane – Tower Cranes
Domain: astrocrane.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Tower cranes are typically powered by electricity from generators or a city grid. They consist of four electric motors, including an articulated lifting motor for vertical motion and a distribution motor for movement along the jib. A typical tower crane is powered by 200 kW (208 V or 800 amps). Electricity is often supplied from generator sets powered by a diesel engine and an alternator. Tower cr…
6. Stratus – SAE-EC4400 Engine Crane
Domain: stratusautoequip.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Stratus SAE-EC4400 Engine Crane
– Price: $816.00
– Lifting Capacity: 4,400 lbs
– Shipping Weight: 154 lbs
– Shipping Size: 38″L * 23″W * 8″H
– Warranty: 5 Year Structural, 3 Year Hydraulic, 2 Year Electrical
– Free Shipping to all 48 lower states (with $425 surcharge for OR, WA, ID, MT, ND, SD, ME)
– Available for pickup with a $100 in-store discount
– Ships within 1 to 2 business days
– Designed …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for engine-powered Crane
In the competitive landscape of industrial equipment, strategic sourcing of engine-powered cranes emerges as a crucial factor for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring safety. By selecting high-quality cranes, such as those featuring hydraulic systems and adjustable capacities, businesses can enhance their productivity while minimizing the risk of workplace injuries. Understanding the specific needs of your operations—whether for lifting heavy engines or facilitating complex manufacturing tasks—will guide you toward the most suitable equipment.
Moreover, as international markets continue to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for reliable and versatile lifting solutions is set to grow. Investing in durable and efficient engine-powered cranes not only strengthens your supply chain but also positions your business for long-term success in a rapidly changing environment.
As you consider your sourcing options, prioritize partnerships with reputable suppliers who understand your unique challenges and can provide tailored solutions. Embrace this opportunity to elevate your operations and drive innovation. The future of your business depends on the choices you make today—choose wisely and invest in quality.