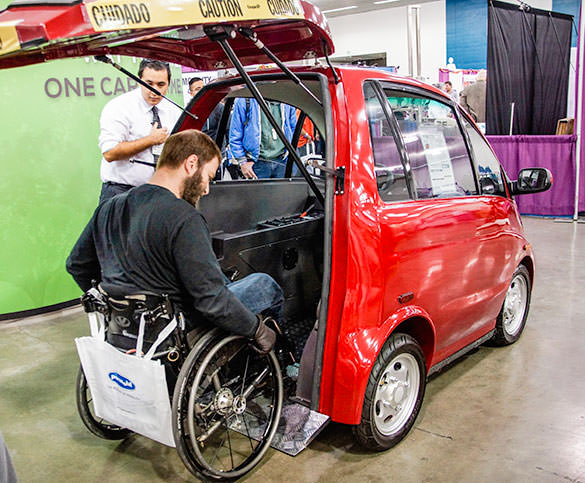
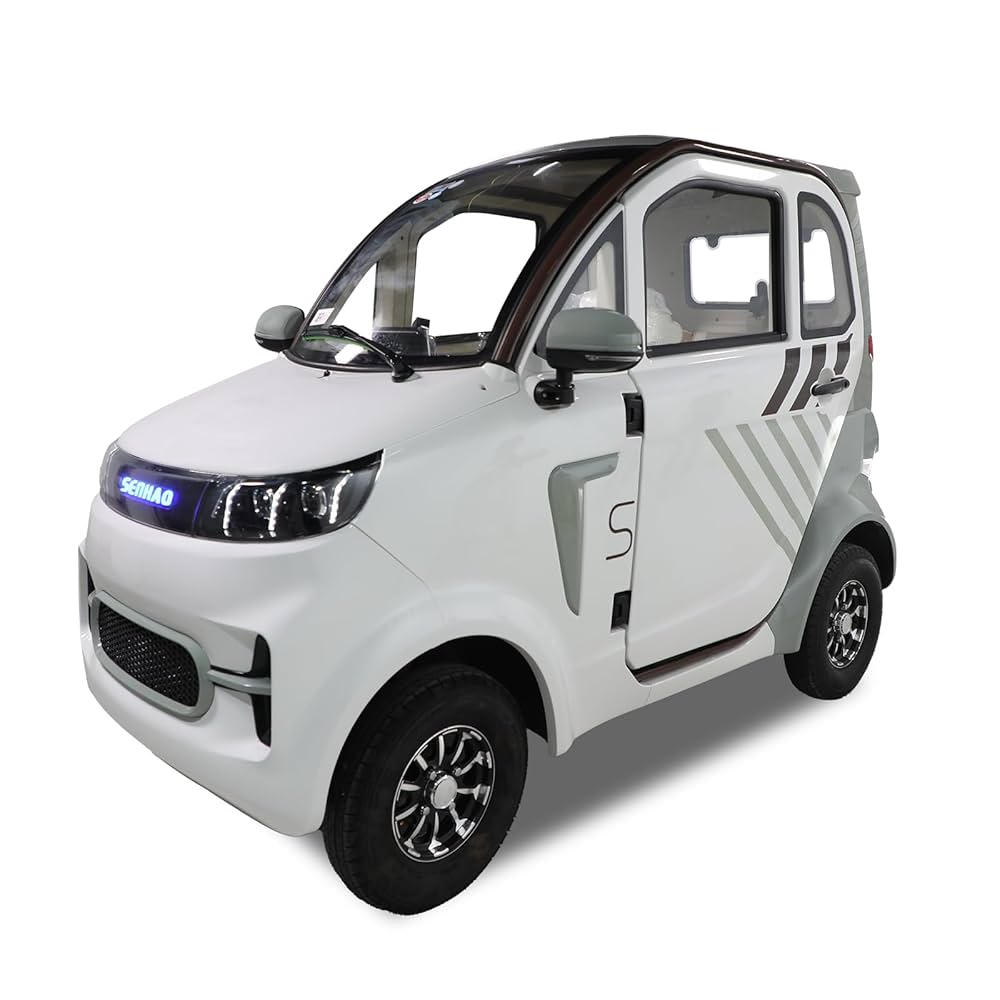
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for mobility electric car
As global interest in sustainable transportation surges, sourcing mobility electric cars presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. The complexities of navigating diverse market needs, regulatory environments, and technological advancements can be daunting. This comprehensive guide serves as a valuable resource for businesses, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, such as Nigeria and Saudi Arabia. It delves into various types of mobility electric vehicles, including compact city cars, solar-powered options, and innovative electric models designed for urban environments.
Throughout this guide, we address critical factors influencing purchasing decisions, such as supplier vetting, cost analysis, and the latest industry trends. By providing actionable insights and a thorough understanding of the mobility electric car landscape, we empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and sustainability commitments.
Whether your focus is on enhancing urban mobility solutions or investing in next-generation electric vehicles, this guide equips you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of the global market. Prepare to explore opportunities that not only meet current demands but also position your business for future growth in the evolving landscape of electric mobility.
Understanding mobility electric car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compact City Cars | Small, lightweight, often solar-assisted; designed for urban mobility. | Urban transportation, shared mobility services. | Pros: Cost-effective, easy parking. Cons: Limited range and capacity. |
| Personal Electric Vehicles (PEVs) | Designed for short trips; user-friendly, often customizable. | Last-mile delivery, personal use, and rentals. | Pros: Simplifies short-distance travel. Cons: May lack advanced features. |
| Multi-Purpose Electric Vehicles (MPEVs) | Versatile designs for both passengers and cargo; higher capacity. | Logistics, family transport, and small businesses. | Pros: High utility; versatile use. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Shared Mobility Solutions | Fleet vehicles designed for ride-sharing and mobility-as-a-service. | Ride-sharing platforms, corporate fleets. | Pros: Scalable; lower cost per trip. Cons: Maintenance and operational costs. |
| Autonomous Electric Vehicles (AEVs) | Equipped with advanced AI and sensor technology for self-driving. | Transportation services, logistics, public transit. | Pros: Reduced labor costs; increased efficiency. Cons: Regulatory hurdles and high tech costs. |
What Are Compact City Cars and Their B2B Relevance?
Compact city cars are designed for urban environments, focusing on efficiency and ease of use. Their small size allows for effortless maneuvering and parking in congested areas, making them ideal for businesses operating in cities with heavy traffic. B2B buyers should consider their affordability and low operational costs, especially for shared mobility services. However, the limited range and passenger capacity may not suit all operational needs.
How Do Personal Electric Vehicles (PEVs) Fit into the Market?
Personal electric vehicles (PEVs) cater to short-distance travel, emphasizing user-friendliness and customization. They are perfect for last-mile delivery services and urban rentals, providing a sustainable option for businesses focused on reducing their carbon footprint. B2B buyers should evaluate the simplicity and convenience these vehicles offer, but must also be aware that they may lack the advanced features found in larger electric vehicles.
What Benefits Do Multi-Purpose Electric Vehicles (MPEVs) Offer?
Multi-purpose electric vehicles (MPEVs) are designed for versatility, accommodating both passengers and cargo. They are particularly valuable for logistics companies and family transport services, as they provide a high utility rate. Buyers should consider the return on investment due to their multifunctional capabilities, though the higher initial costs may be a barrier for some businesses.
How Are Shared Mobility Solutions Changing the Landscape?
Shared mobility solutions are specifically designed for ride-sharing and mobility-as-a-service applications. These fleet vehicles enable businesses to scale their operations while reducing costs per trip. Buyers should assess the potential for high utilization rates, but must also factor in ongoing maintenance and operational costs that can impact profitability.
What Are the Implications of Autonomous Electric Vehicles (AEVs)?
Autonomous electric vehicles (AEVs) represent the forefront of technology in the mobility sector, equipped with AI and extensive sensor technology for self-driving capabilities. They offer significant advantages for transportation services and logistics, including reduced labor costs and increased operational efficiency. However, B2B buyers must navigate regulatory challenges and the high costs associated with advanced technology adoption.
Key Industrial Applications of mobility electric car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Mobility Electric Car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Transportation | Shared Mobility Services | Cost-effective, eco-friendly transport solutions | Local regulations, fleet management software, charging infrastructure |
| Logistics and Delivery | Last-Mile Delivery Solutions | Reduced operational costs, lower emissions | Battery range, vehicle size, cargo capacity |
| Tourism and Hospitality | Eco-Friendly Shuttle Services | Enhanced guest experience, sustainability branding | Vehicle customization, service frequency, local partnerships |
| Education and Institutions | Campus Mobility Solutions | Improved accessibility, reduced congestion | Safety features, vehicle capacity, maintenance support |
| Emergency Services | Rapid Response Vehicles | Quick deployment, enhanced operational efficiency | Reliability, vehicle durability, specialized equipment compatibility |
How Are Mobility Electric Cars Used in Urban Transportation Services?
Mobility electric cars are revolutionizing urban transportation, particularly through shared mobility services. Companies can deploy fleets of electric vehicles (EVs) for ride-hailing, car-sharing, or bike-sharing platforms, providing a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative to traditional transport. In regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, where urban congestion is a pressing issue, these vehicles can alleviate traffic and reduce emissions. Buyers should consider local regulations, the availability of charging infrastructure, and fleet management software to optimize operations.
What Role Do Mobility Electric Cars Play in Logistics and Delivery?
In logistics, mobility electric cars are increasingly utilized for last-mile delivery solutions. Businesses can leverage compact EVs to navigate urban environments efficiently, minimizing delivery times while reducing their carbon footprint. This is particularly relevant in South America, where urban areas face significant congestion challenges. Key requirements for buyers include ensuring adequate battery range for their delivery routes, vehicle size for cargo capacity, and the ability to integrate with existing logistics systems.
How Can Mobility Electric Cars Enhance Tourism and Hospitality Services?
Mobility electric cars serve as eco-friendly shuttle services for the tourism and hospitality sectors, providing guests with a sustainable transportation option while enhancing their overall experience. Hotels and resorts can offer electric shuttles for airport transfers or local excursions, promoting a green image that attracts environmentally conscious travelers. Buyers in this sector should focus on vehicle customization options, service frequency, and potential partnerships with local businesses to maximize impact.
What Benefits Do Mobility Electric Cars Offer Educational Institutions?
Educational institutions can implement mobility electric cars as campus mobility solutions to improve accessibility and reduce congestion. By providing electric shuttles for students and staff, colleges and universities can foster a sustainable campus environment while enhancing transportation efficiency. Key considerations for buyers include safety features, vehicle capacity to accommodate student populations, and reliable maintenance support to ensure consistent service.
How Are Mobility Electric Cars Used in Emergency Services?
In emergency services, mobility electric cars can serve as rapid response vehicles, offering quick deployment capabilities in critical situations. Their low operational costs and reduced emissions also align with sustainability goals in public services. For international buyers, especially in regions with developing infrastructure, reliability and vehicle durability are paramount. Additionally, compatibility with specialized emergency equipment can determine the suitability of electric vehicles for specific applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘mobility electric car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles in Emerging Markets
The Problem: In many regions, particularly in Africa and parts of South America, the lack of adequate charging infrastructure poses a significant barrier to adopting mobility electric cars. B2B buyers in these regions may struggle with the uncertainty of how to support their electric vehicle (EV) fleet without sufficient charging stations. This can lead to operational inefficiencies, increased downtime, and concerns about vehicle range limitations that ultimately affect service delivery.
The Solution: B2B buyers should consider forming strategic partnerships with local governments and infrastructure developers to advocate for the establishment of charging stations. Engaging in community outreach can help identify high-traffic areas where charging stations would be beneficial. Additionally, exploring innovative solutions such as mobile charging units can help bridge the gap until permanent infrastructure is developed. Buyers can also invest in electric vehicles that support fast charging or that have swappable battery technology, allowing for quick turnaround times even in areas where infrastructure is currently lacking. By positioning themselves as advocates for infrastructure development, businesses can not only enhance their operational capabilities but also contribute to the broader adoption of electric mobility in their regions.
Scenario 2: High Initial Costs and Budget Constraints
The Problem: For many businesses, especially startups or small enterprises in the Middle East and Africa, the initial investment required to acquire mobility electric cars can be daunting. The perception of high upfront costs can deter potential buyers from transitioning to electric vehicles, despite the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance. This financial barrier can limit the potential for businesses to adopt sustainable practices that align with global trends.
The Solution: B2B buyers should explore financing options such as leasing or subscription services that reduce the burden of upfront costs. Many manufacturers now offer tailored financing solutions that allow businesses to pay for vehicles in manageable monthly installments. Additionally, buyers should investigate government incentives, grants, and subsidies available for electric vehicle purchases in their respective countries. Leveraging these financial aids can significantly lower the total cost of ownership. Furthermore, businesses can calculate total cost of ownership over the vehicle’s lifespan, including fuel savings and reduced maintenance costs, to present a compelling case for investment to stakeholders. By strategically managing finances and utilizing available resources, companies can make the transition to mobility electric cars more feasible.
Scenario 3: User Acceptance and Training for Electric Vehicle Technology
The Problem: As mobility electric cars integrate advanced technologies such as AI navigation, connectivity, and driver assistance systems, there can be a steep learning curve for users. B2B buyers may find that employees or customers are hesitant to embrace new technologies, leading to underutilization of the vehicle’s features and potential inefficiencies in operations. Resistance to change can stall the adoption of electric vehicles, impacting overall business performance.
The Solution: To facilitate user acceptance, B2B buyers should implement comprehensive training programs tailored to the specific technologies used in their electric vehicle fleets. This training should not only cover operational aspects but also emphasize the benefits of electric mobility, such as reduced emissions and lower operating costs. Companies can also create user-friendly manuals and quick-start guides to assist users in navigating the new technology. Offering incentives for early adopters within the organization can further encourage acceptance. Additionally, establishing a feedback loop where users can share their experiences can help refine training programs and improve overall satisfaction. By prioritizing user education and support, businesses can ensure a smoother transition to electric mobility and maximize the benefits of their investment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for mobility electric car
What Are the Key Materials Used in Mobility Electric Cars?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of mobility electric cars, selecting the right materials is crucial for enhancing performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the manufacturing of electric vehicles, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Contribute to Electric Vehicle Performance?
Aluminum is a lightweight metal with excellent strength-to-weight ratios, making it ideal for electric vehicle (EV) applications. It has a high corrosion resistance, which is vital for vehicles operating in diverse climates, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East. Aluminum can withstand temperatures ranging from -50°C to 150°C, ensuring reliability in extreme conditions.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight nature contributes to increased range and efficiency, while its recyclability aligns with sustainability goals.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex and costly, potentially impacting the overall vehicle price.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in the chassis and body panels, contributing to crashworthiness and safety.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial, especially in Europe. Buyers should also consider local sourcing to mitigate costs.
What Role Does Steel Play in Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Steel remains a staple in automotive manufacturing due to its strength and durability. It offers excellent resistance to wear and high pressures, making it suitable for structural components. Steel can also be treated for corrosion resistance, enhancing its longevity.
Pros: Steel is cost-effective and readily available, making it an attractive choice for manufacturers.
Cons: Its weight can negatively affect the vehicle’s range and efficiency compared to lighter materials like aluminum.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used in the frame and suspension systems, providing robustness and stability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of varying steel grades and standards, such as JIS in Japan and EN in Europe, to ensure compliance with local regulations.
How Do Composites Enhance Electric Vehicle Design?
Composites, such as carbon fiber reinforced plastics, are increasingly being used in electric vehicles for their lightweight and high-strength properties. They offer excellent fatigue resistance and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Pros: Composites significantly reduce weight, improving energy efficiency and performance.
Cons: The high cost of materials and manufacturing processes can be a barrier for widespread adoption.
Impact on Application: Composites are often used in body panels and interior components, providing aesthetic appeal and functionality.
Considerations for International Buyers: Understanding the local market for composites and their certifications is essential, especially in regions with stringent environmental regulations.
What Are the Advantages of Using Lithium-Ion Batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries are the backbone of electric vehicles, providing high energy density and long cycle life. They perform well under a wide range of temperatures and have a relatively low self-discharge rate.
Pros: Their compact size and efficiency make them ideal for electric mobility solutions.
Cons: The sourcing of lithium can raise ethical and environmental concerns, particularly in regions where mining practices are under scrutiny.
Impact on Application: Lithium-ion batteries are crucial for the vehicle’s range and performance, directly affecting consumer acceptance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards for battery safety and recycling, as well as consider the supply chain implications of lithium sourcing.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Mobility Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for mobility electric car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Chassis and body panels | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Complex manufacturing process | Medium |
| Steel | Frame and suspension systems | Cost-effective, strong | Heavier, may reduce range | Low |
| Composites | Body panels and interior components | High strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Lithium-Ion | Powertrain and energy storage | High energy density, long cycle life | Ethical sourcing concerns | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers in the electric vehicle sector, enabling informed decisions that align with performance, cost, and compliance requirements across diverse markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for mobility electric car
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Mobility Electric Cars?
The manufacturing process for mobility electric cars is a sophisticated operation that encompasses several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets both quality and performance standards. Below are the main stages involved:
-
Material Preparation:
– The first stage involves sourcing and preparing materials, which typically include metals (like aluminum and steel), plastics, and advanced composites. Suppliers must provide materials that comply with international standards to ensure durability and safety.
– B2B buyers should seek suppliers that can demonstrate a robust supply chain and material certification processes, which guarantee the quality and sustainability of the materials used. -
Forming:
– This stage includes the shaping of raw materials into components using various techniques such as stamping, molding, and extrusion. Advanced manufacturing technologies like 3D printing are increasingly used to create complex parts that are lightweight yet strong.
– Buyers should inquire about the technologies employed by suppliers and the benefits they bring, such as reduced waste and improved design flexibility. -
Assembly:
– The assembly process involves integrating the various components into a cohesive vehicle. This can be done manually or through automated assembly lines, depending on the scale of production.
– Key techniques include robotic welding and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for material handling. B2B buyers should assess the assembly efficiency and flexibility of suppliers to adapt to changing production demands. -
Finishing:
– The final stage focuses on painting, coating, and quality checks to ensure the vehicle meets aesthetic and functional standards. This may include applying anti-corrosion treatments and final inspections.
– Buyers should look for suppliers that utilize eco-friendly finishing processes, which are increasingly important in global markets.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Mobility Electric Car Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of mobility electric cars, ensuring that every vehicle produced meets rigorous standards. Here are the critical components of QA:
-
What International Standards Govern Quality Assurance?
– Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential. ISO 9001 focuses on quality management systems and ensures that organizations consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
– Additionally, industry-specific standards like CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may apply, particularly concerning safety and environmental impact. -
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
– Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring production processes to identify and correct defects in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting thorough inspections of the finished product before it leaves the factory.
- Each checkpoint serves to minimize defects and ensure the final product is reliable.
-
Which Common Testing Methods Are Used?
– Common testing methods include functional testing, safety testing, and performance evaluations. These tests assess various parameters, such as battery efficiency, vehicle safety under crash conditions, and overall functionality.
– B2B buyers should ask suppliers about their testing protocols and any certifications they hold, as this can provide insights into the reliability of the vehicles produced.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control measures of potential suppliers is crucial in establishing trust and ensuring product quality. Here are several strategies:
-
Conducting Audits:
– Regular audits of suppliers can provide a comprehensive view of their quality control processes. Buyers should schedule these audits to evaluate compliance with industry standards and internal practices. -
Requesting Quality Reports:
– Suppliers should provide detailed reports on their quality assurance processes, including data on defect rates, testing results, and corrective actions taken in response to quality issues.
– These reports serve as documentation of the supplier’s commitment to quality and can be a deciding factor in supplier selection. -
Engaging Third-Party Inspections:
– Utilizing third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent organizations can assess the manufacturing processes and quality control measures without bias, providing unbiased evaluations.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges in ensuring quality control. Here are some nuances to consider:
-
Understanding Regional Standards:
– Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements and quality standards. Buyers must familiarize themselves with these standards to ensure compliance and avoid legal issues.
– For instance, European standards may be more stringent than those in other regions, which can affect product design and manufacturing processes. -
Cultural and Communication Barriers:
– Cultural differences can impact business practices and expectations regarding quality. Clear communication is essential to ensure all parties understand the quality requirements and standards.
– Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better understanding and adherence to quality expectations. -
Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations:
– The logistics of sourcing materials and transporting finished products across borders can affect quality. Buyers should evaluate suppliers’ capabilities in managing logistics efficiently while maintaining quality standards.
– It’s crucial to choose suppliers with robust logistics networks and contingency plans to handle potential disruptions.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for mobility electric cars is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on key stages of production, international standards, quality checkpoints, and verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. Additionally, being aware of the nuances in different regions will enable buyers to navigate the complexities of international trade effectively.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘mobility electric car’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring mobility electric cars. As the demand for sustainable and efficient urban transportation rises, understanding the key steps in the sourcing process can significantly enhance your decision-making. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of selecting the right electric vehicle that meets your operational needs and aligns with your sustainability goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for ensuring that the mobility electric car meets your operational requirements. Consider factors such as vehicle size, battery capacity, range, and charging options.
– Key details: Specify whether you need compact models for city commuting or larger vehicles for family transport.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Staying informed about the latest trends in electric mobility will provide insights into the most advanced technologies available. Innovations such as solar charging capabilities or AI-assisted driving can enhance efficiency and user experience.
– Key details: Look for suppliers that offer vehicles equipped with cutting-edge features, like advanced safety systems and user-friendly interfaces.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Assess their company profiles, product offerings, and previous client experiences to gauge reliability and performance.
– Key details: Request case studies or references from other businesses in your region or industry to understand how the supplier’s vehicles have performed in similar conditions.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Local Regulations
Ensure that the electric cars you are considering comply with local regulations and standards. Different regions may have varying requirements for electric vehicles, including safety standards and emissions regulations.
– Key details: Familiarize yourself with regional certifications that the vehicles must meet, which can influence your purchasing decision.
Step 5: Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Calculating the total cost of ownership will help you understand the long-term financial implications of your purchase. This includes not just the initial purchase price, but also maintenance, insurance, and operational costs like charging.
– Key details: Consider the potential savings from lower fuel costs and government incentives for electric vehicle purchases.
Step 6: Explore Financing and Leasing Options
Investigate various financing and leasing options available for mobility electric cars. Many suppliers offer flexible payment plans that can ease the upfront financial burden.
– Key details: Evaluate whether leasing may provide a better fit for your budget and operational flexibility compared to outright purchasing.
Step 7: Plan for Infrastructure and Support
Consider the necessary infrastructure to support your fleet of mobility electric cars. This includes charging stations, maintenance services, and driver training programs.
– Key details: Collaborate with suppliers to identify compatible charging solutions and ensure that your team is equipped to operate and maintain the vehicles effectively.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing mobility electric cars that not only meet their immediate needs but also contribute to sustainable urban transport solutions.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for mobility electric car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Mobility Electric Cars?
When sourcing mobility electric cars, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The raw materials used in manufacturing electric vehicles (EVs) include metals like aluminum and steel, plastics, and battery components such as lithium and cobalt. The fluctuations in material prices can significantly affect overall vehicle costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can include wages for assembly line workers, engineers, and administrative staff. In regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, the final pricing may be impacted.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facility operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the creation of molds and fixtures needed for production. These costs can be substantial, particularly for custom designs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC processes ensures that the vehicles meet safety and performance standards, which can add to costs but ultimately leads to higher customer satisfaction and reduced warranty claims.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and handling, can vary based on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer. Incoterms play a vital role in defining responsibilities for shipping and insurance.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a margin to cover profit and business sustainability. This margin can vary based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Mobility Electric Cars?
Several factors influence pricing in the mobility electric car sector:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders can lead to economies of scale, reducing the per-unit cost. Negotiating MOQ with suppliers can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, advanced technologies, or unique designs can raise costs. Buyers should assess whether these customizations align with their market needs.
-
Materials: The choice of materials impacts both cost and quality. Sustainable materials may offer long-term savings in maintenance but could increase initial costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Compliance with international safety and environmental standards can lead to higher upfront costs but may enhance marketability and reduce liability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer greater assurance of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is essential. Different Incoterms can shift costs and responsibilities, impacting the overall price.
What Strategies Can Buyers Use to Optimize Costs and Pricing?
B2B buyers should adopt specific strategies to enhance cost efficiency when sourcing mobility electric cars:
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume purchases to negotiate better pricing. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to favorable terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assess the TCO, which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. A slightly higher initial investment may lead to lower long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of additional costs such as tariffs, import duties, and local taxes that may apply when sourcing from different regions. Understanding these nuances can prevent unexpected financial burdens.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to identify competitive pricing and new suppliers. This can inform negotiation strategies and ensure that you are getting the best value.
-
Flexible Financing Options: Explore leasing or financing options that may reduce upfront costs and provide more predictable cash flow.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to fluctuations based on market conditions, currency exchange rates, and regional economic factors. Buyers should consult with suppliers for precise quotations tailored to specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing mobility electric car With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Mobility Electric Cars
As businesses navigate the evolving landscape of urban mobility, it is crucial to evaluate not only electric cars but also alternative solutions that can meet specific needs. The increasing emphasis on sustainability, cost-efficiency, and technological advancements has led to the emergence of various alternatives. This analysis compares mobility electric cars with two viable options: solar city cars and personal electric vehicles (NEVs), highlighting key aspects that influence purchasing decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Mobility Electric Car | Squad Solar City Car | Eli ZERO (Personal Electric Vehicle) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High speed and range; typically 150-300 km per charge | Limited speed (up to 70 km/h); solar-assisted range of 22-31 km/day | Compact, designed for short trips; range varies with battery capacity |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost, generally above €30,000 | Affordable starting price around €6,250 | Mid-range price point; varies based on configuration |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure; suitable for personal and fleet use | Minimal infrastructure needed; ideal for urban settings and sharing | Low barrier to entry; can be integrated into existing urban transport systems |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed; battery replacement every few years | Lower maintenance due to simpler design; solar panels require minimal upkeep | Minimal maintenance; battery management is straightforward |
| Best Use Case | Long-distance travel, fleet operations, urban commuting | Daily urban mobility, especially in congested areas | Short trips in urban settings, enhancing community engagement |
What Are the Pros and Cons of the Squad Solar City Car?
The Squad Solar City Car offers a unique approach to urban mobility, focusing on affordability and sustainability. Its solar panels allow for self-charging, making it an environmentally friendly option that reduces reliance on traditional charging stations. However, its limited speed and range may not suit every business need, particularly for those requiring longer travel distances. Additionally, the vehicle is designed primarily for urban environments, which may restrict its utility in rural areas.
How Does Eli ZERO Stand Out in Personal Mobility?
Eli ZERO reimagines personal transportation by offering a compact, zero-emission vehicle that promotes social engagement within communities. Its lightweight design and ease of maneuverability make it ideal for short urban trips. Nevertheless, its performance and range limitations may not satisfy businesses needing extensive travel capabilities. The vehicle’s focus on community interaction, however, can enhance customer experiences for businesses operating in densely populated areas.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Mobility Solution?
When selecting the appropriate mobility solution, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific operational needs, geographic location, and target market. Mobility electric cars are ideal for businesses requiring long-range capabilities and robust performance, while alternatives like the Squad Solar City Car and Eli ZERO provide cost-effective and sustainable options for urban mobility. Assessing the total cost of ownership, maintenance requirements, and user experience will enable businesses to make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives and sustainability goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for mobility electric car
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Mobility Electric Cars?
When considering mobility electric cars, understanding essential technical properties is crucial for B2B buyers. These specifications not only influence the performance and safety of the vehicles but also impact long-term operational costs and regulatory compliance.
1. Battery Capacity and Range
Battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), indicates how much energy the battery can store. This directly affects the vehicle’s range—the distance it can travel on a single charge. A higher capacity allows for longer trips, which is particularly important in regions with fewer charging stations. For B2B buyers, selecting vehicles with adequate range can enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
2. Charging Time and Compatibility
Charging time refers to how long it takes to recharge the vehicle’s battery. Different charging standards (e.g., Level 1, Level 2, DC fast charging) affect both the speed and convenience of recharging. B2B buyers must consider the existing infrastructure and the type of charging options available in their operational areas. Fast charging capabilities can minimize downtime, crucial for fleet operations.
3. Vehicle Weight and Materials
The weight of an electric vehicle significantly influences its efficiency and handling. Lighter materials, such as aluminum or advanced composites, reduce energy consumption and improve range. Understanding the material specifications helps B2B buyers assess durability, safety, and potential maintenance costs. Selecting vehicles with a robust yet lightweight design can lead to better performance in urban environments.
4. Safety Ratings and Features
Safety ratings, often derived from crash test results, provide insights into the vehicle’s protection capabilities. Features such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), multiple airbags, and crash structures are critical for ensuring passenger safety. For buyers, investing in vehicles with high safety ratings can reduce liability and enhance brand reputation.
5. Sensor Technology and Autonomous Capabilities
Modern mobility electric cars often come equipped with advanced sensor technologies, including LiDAR, cameras, and radar systems. These technologies enable features like lane-keeping assistance, adaptive cruise control, and even autonomous driving capabilities. Understanding these specifications is vital for businesses looking to invest in cutting-edge solutions that improve operational efficiency and customer experience.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Mobility Electric Cars?
Navigating the language of the mobility electric car industry is essential for effective communication and decision-making. Familiarity with key terms can streamline processes and enhance negotiations.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that manufactures products that may be marketed by another company. In the electric vehicle sector, OEMs design and produce vehicles or components, establishing brand identity. B2B buyers often engage directly with OEMs to ensure quality and compliance with industry standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of goods a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and capital investment. Negotiating favorable MOQs can lead to better pricing and reduced overhead costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price proposals from suppliers for specific products or services. This process helps businesses compare costs and quality before making purchasing decisions. A well-defined RFQ can lead to more accurate quotes and streamlined procurement processes.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps B2B buyers manage logistics, shipping costs, and risks associated with international trade.
5. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO represents the comprehensive assessment of costs associated with a vehicle over its entire lifecycle, including purchase price, financing, insurance, maintenance, and fuel. For B2B buyers, evaluating TCO is essential for making informed investment decisions that align with budget constraints and operational objectives.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can navigate the mobility electric car market more effectively, ensuring they make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and competitiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the mobility electric car Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Mobility Electric Car Market?
The mobility electric car sector is experiencing rapid transformation driven by several global factors. Increasing environmental concerns are pushing governments and consumers toward sustainable transportation solutions, particularly in emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The push for reduced carbon emissions is prompting regulatory frameworks that favor electric vehicles (EVs), with nations like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia committing to ambitious EV adoption targets.
Technological advancements in battery technology and electric drivetrains are also reshaping the market. Innovations such as swappable batteries, as seen in vehicles like the Squad Solar City Car, are enhancing convenience and reducing downtime for users. Furthermore, the rise of Mobility as a Service (MaaS) platforms is altering traditional vehicle ownership models, making electric cars more accessible to businesses and consumers alike.
International B2B buyers should be aware of the growing trend towards integration of AI and smart technologies in EVs, such as those offered by AFEELA, which emphasize user-centric experiences. This integration not only enhances the functionality of vehicles but also creates new revenue streams through software and data services. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for businesses looking to invest in or source from the evolving electric mobility landscape.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Your B2B Strategy in the Mobility Electric Car Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a core principle in the sourcing strategies of international B2B buyers in the mobility electric car sector. The environmental impact of traditional automotive manufacturing practices is prompting businesses to seek suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices. This includes the use of ethically sourced materials, such as recycled metals and eco-friendly composites, which are increasingly favored in the production of electric vehicles.
Moreover, the importance of transparent supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly demanding visibility into their suppliers’ sourcing practices to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and social responsibility standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems or materials certified by organizations like Cradle to Cradle can significantly enhance a company’s reputation and appeal in the marketplace.
By aligning with suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, businesses can not only mitigate risks associated with environmental compliance but also capitalize on the growing consumer preference for green products. This alignment can lead to stronger partnerships and enhance market competitiveness in the mobility electric car sector.
What Is the Evolution of the Mobility Electric Car Sector?
The mobility electric car sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, electric vehicles were limited in range and performance, often perceived as impractical alternatives to conventional vehicles. However, technological advancements in battery efficiency, electric drivetrains, and charging infrastructure have dramatically improved the feasibility of electric mobility.
The introduction of regulatory incentives and environmental awareness has further accelerated this evolution. Countries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are now investing heavily in EV infrastructure and technology, reflecting a global shift towards sustainable transportation solutions. As this sector continues to mature, businesses that adapt to these changes and prioritize innovation will be well-positioned to thrive in the competitive landscape of mobility electric cars.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of mobility electric car
-
How do I solve the challenges of sourcing mobility electric cars internationally?
Sourcing mobility electric cars from international suppliers can be streamlined by conducting thorough market research to identify reputable manufacturers. Utilize platforms like trade shows, online marketplaces, and industry forums to connect with potential suppliers. Establish clear communication regarding specifications, compliance with local regulations, and after-sales support. Consider utilizing third-party logistics providers familiar with international trade to facilitate the shipping and customs processes, ensuring a smoother transaction and timely delivery. -
What are the best electric vehicles for urban mobility in developing markets?
When selecting electric vehicles for urban mobility in developing markets, consider options like compact electric cars and micro-mobility solutions such as e-scooters and e-bikes. Vehicles like the Squad Solar City Car and Eli ZERO offer affordability, sustainability, and efficiency, making them ideal for congested urban environments. Ensure the selected models comply with local regulations and have the necessary features to address the specific mobility needs of the region. -
What customization options are typically available for electric vehicles?
Most manufacturers offer various customization options, including color choices, interior features, and technology upgrades. Businesses can request adaptations to suit local market preferences, such as language options in user interfaces or specific safety features required by local regulations. It’s essential to discuss customization possibilities during negotiations to ensure the final product meets your business’s operational needs and customer expectations. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for purchasing mobility electric cars?
The MOQ varies by manufacturer and is often influenced by the type of vehicle and production capabilities. Generally, larger orders may lead to better pricing and favorable terms. For businesses looking to enter the market, establishing a relationship with the supplier may allow flexibility in MOQ, especially for initial orders or pilot programs. Discuss this upfront to understand the supplier’s policies and negotiate accordingly. -
What are the payment terms typically offered by suppliers of mobility electric cars?
Payment terms can range from upfront payments to installment plans, often influenced by the size of the order and the relationship with the supplier. Many suppliers may require a deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due prior to shipment. It’s important to discuss and agree on payment terms that align with your cash flow and operational needs. Always ensure the terms are documented in the purchase agreement to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for electric vehicles sourced internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and compliance certifications from the manufacturer. Implement a quality control process that includes pre-shipment inspections, where third-party inspectors can verify that vehicles meet agreed-upon standards. Establish clear KPIs for performance and reliability, and consider arranging for a trial period to evaluate the vehicles’ performance in real-world conditions before finalizing large orders. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing mobility electric cars?
Logistics for importing electric vehicles include understanding the shipping methods, customs regulations, and tariffs applicable in your country. Evaluate the supplier’s ability to manage logistics or consider using a freight forwarder with experience in automotive imports. Ensure that the vehicles are shipped in compliance with safety standards, and factor in additional costs such as insurance, port fees, and inland transportation when budgeting for your purchase. -
What are the key regulations to consider when purchasing mobility electric cars for international markets?
Regulations vary significantly by country and region, covering aspects like safety standards, emissions requirements, and vehicle classification. Research local laws to ensure the electric vehicles you intend to purchase comply with these regulations. In some regions, additional requirements such as battery disposal and recycling regulations may apply. Engaging with local legal experts or industry associations can provide valuable insights into compliance and help mitigate potential legal issues.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Mobility Electric Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. AFEELA – Electric Vehicle
Domain: shm-afeela.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: AFEELA 1 is an electric vehicle (EV) developed by Sony Honda Mobility. It features a refundable $200 reservation fee for securing a unit. The vehicle offers an in-cabin demo experience at AFEELA Studios, showcasing its advanced features without the need for driving. Key highlights include:
– AFEELA Intelligent Drive with smart navigation powered by AI, equipped with 40 sensors (18 cameras, 1 LiDAR…
2. Eli – ZERO Personal Vehicle
Domain: eli.world
Introduction: Eli ZERO is a next generation personal vehicle designed for daily short trips. It is a zero-emission vehicle that aims to enhance social engagements and improve personal transportation in urban environments.
3. Aptera – Solar Electric Vehicle
Domain: aptera.us
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Aptera is a solar electric vehicle designed to be highly efficient, requiring no charging for most daily use. Key specifications include:
– Integrated solar cells generating approximately 700 watts
– Up to 40 miles of free solar-powered driving per day
– 400 miles of range per full charge
– Acceleration from 0-60 mph in less than 6 seconds
The vehicle is currently in testing and validation, a…
4. Zeekr – Key Vehicles
Domain: zeekr.eu
Introduction: {“vehicles”:[{“model”:”Zeekr 001″,”type”:”Luxury Shooting Brake”,”cruising_range_km”:”620 Km (WLTP)”,”acceleration_0_100″:”3.8 s”,”charging_time”:”30 min (10-80%)”},{“model”:”Zeekr X”,”type”:”Luxury Urban SUV”,”cruising_range_km”:”446 Km (WLTP)”,”acceleration_0_100″:”3.8 s”,”charging_time”:”29 min (10-80%)”},{“model”:”Zeekr 7X”,”type”:”Next Generation SUV”,”cruising_range_km”:”615 Km (WLTP)”,”acce…
5. Fotona Mobility – Key Product Details
Domain: solaremobility.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Key Product Details:
1. **Brand**: Fotona Mobility
2. **Warranty**: 2-year minimum warranty
3. **Power Options**: Electric motors rated at 250W, 300W, 350W, 500W, and 800W with 36V and 48V options.
4. **Display**: LCD or LED display for speed and battery level monitoring.
5. **Types of Scooters**:
– **Moto 800W**: 4-wheeled, 800W engine, suitable for slopes, multiple battery options, up to 110k…
6. EV Rider – Transport AF+ Folding Electric Scooter
Domain: electricwheelchairsusa.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: EV Rider Mobility Scooters are designed for seniors, elderly, disabled individuals, and even kids. They offer a variety of models including luxurious and transportable options. Key products include: 1. EV Rider Transport AF+ Folding Electric Scooter – $2,250.00 (was $2,599.00) 2. EV Rider Transport Plus Folding Mobility Scooter – $1,695.00 (was $1,998.00) 3. EV Rider Gypsy Q2 Folding Mobility Scoo…
7. Rivian – ALSO E-Mobility Solutions
Domain: rivianforums.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Rivian is launching a new electric micromobility company named “ALSO” that will focus on e-bikes, scooters, and other small electric vehicles. The flagship product is expected to be released by 2026 and aims to provide alternative transportation options for city-dwellers.
8. DR Automobiles – Electric Vehicles
Domain: drautomobiles.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Electric mobility – DR Automobiles offers a range of electric vehicles that are designed for safety, efficiency, and environmental sustainability. Key features include:
1. **Zero-Emission Vehicles**: DR electric cars are purely electric, eliminating the need for an internal combustion engine, providing a silent and agile driving experience.
2. **Battery Efficiency**: Equipped with intelligent bat…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for mobility electric car
In the rapidly evolving landscape of mobility electric cars, strategic sourcing remains essential for international B2B buyers seeking competitive advantage. By leveraging innovative technologies, such as solar energy integration and advanced AI navigation systems, companies can enhance their offerings while reducing costs and environmental impact. The emergence of compact, efficient vehicles tailored for urban environments, like the Squad Solar City Car and Eli ZERO, highlights the shift towards sustainable transportation solutions that cater to diverse consumer needs.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to embrace electric mobility, the demand for reliable supply chains and partnerships will only grow. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that emphasize safety, durability, and sustainability, ensuring that their investments align with global trends and regulatory frameworks.
Looking ahead, the potential for growth in the electric vehicle sector is immense. Companies are encouraged to explore collaborative opportunities and invest in forward-thinking technologies that promise to redefine urban mobility. Engage with industry leaders, share insights, and capitalize on the momentum of this transformative era in transportation. Together, we can pave the way for a cleaner, more efficient future in mobility.