Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric car eec coc european
In an era where sustainability and innovation intersect, sourcing electric cars that meet EEC COC (Certificate of Conformity) standards for the European market presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you are operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, understanding the nuances of EEC certification is critical to ensure compliance and market success. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of electric vehicle certification, covering essential topics such as types of vehicles eligible for EEC COC, applications across various markets, effective supplier vetting processes, and an overview of associated costs.
Navigating the global market for electric vehicles can be daunting, especially when dealing with regulations that vary by region. This guide empowers B2B buyers by equipping them with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions. It provides actionable insights into the certification process, highlights key compliance requirements, and offers strategies for identifying reliable suppliers that can meet the specific demands of your target market. By understanding these elements, businesses can not only streamline their procurement processes but also enhance their competitive edge in the evolving landscape of electric mobility.
Understanding electric car eec coc european Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| EEC L1e Electric Scooters | Lightweight, max speed 25 km/h, typically two-wheeled | Urban commuting, last-mile delivery | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to maneuver. Cons: Limited speed and range. |
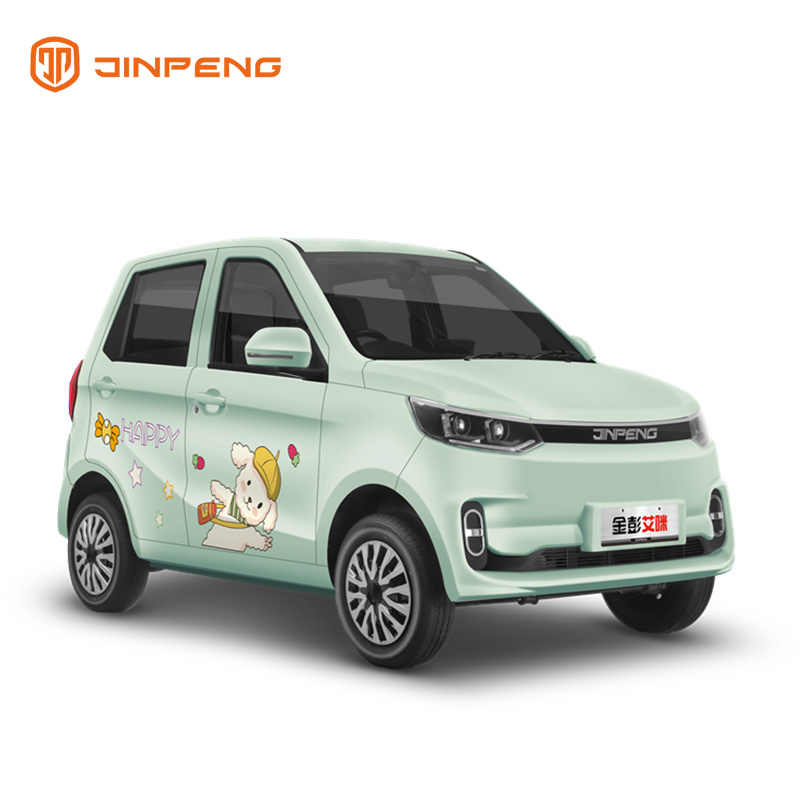
| EEC L6e Low-Speed Electric Cars | Compact, max speed 45 km/h, suitable for short distances | Neighborhood transport, tourism | Pros: No driver’s license required, eco-friendly. Cons: Limited to urban areas. |
| EEC L3e Three-Wheeled Vehicles | Enhanced stability, often designed for elderly users | Personal transport, mobility solutions | Pros: Easy access, stability. Cons: Less cargo space compared to four-wheeled options. |
| EEC L7e High-Powered Electric Cars | Higher power output, max speed up to 120 km/h | Commercial transport, premium services | Pros: Long-range, versatile. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| EEC L2e Electric Bicycles | Pedal-assisted, combines cycling with electric power | Eco-friendly transport, fitness markets | Pros: Promotes healthy living, easy to park. Cons: Requires physical effort. |
What are the Characteristics of EEC L1e Electric Scooters?
EEC L1e electric scooters are lightweight vehicles designed primarily for urban commuting. They have a maximum speed of 25 km/h, making them ideal for navigating through city traffic and congested areas. B2B buyers in sectors like last-mile delivery or urban transport can benefit from these scooters due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of use. However, their limited speed and range may not suit businesses requiring longer travel distances.
How Do EEC L6e Low-Speed Electric Cars Serve B2B Needs?
EEC L6e low-speed electric cars are compact vehicles that can reach speeds of up to 45 km/h, tailored for short-distance travel. They are particularly useful in neighborhoods and tourist areas where short, eco-friendly trips are common. Businesses in tourism, hospitality, and local transport can leverage these vehicles to enhance customer experience. While they are eco-friendly and do not require a driver’s license, their operational limitations may restrict their use in more extensive urban settings.
What Makes EEC L3e Three-Wheeled Vehicles Unique?
EEC L3e three-wheeled vehicles offer enhanced stability and are often designed with accessibility in mind, catering to elderly users or those with mobility challenges. These vehicles are suitable for personal transport and can be a valuable asset for businesses focusing on mobility solutions. Their ease of access is a significant advantage, though they may lack the cargo space that four-wheeled vehicles provide, which could be a consideration for businesses needing to transport goods.
Why Choose EEC L7e High-Powered Electric Cars for Commercial Use?
EEC L7e high-powered electric cars are designed for higher performance, with speeds reaching up to 120 km/h. This makes them suitable for various commercial applications, including premium transport services and logistics. Businesses looking for versatile, long-range electric vehicles can find these cars advantageous. However, the initial investment is typically higher, which may require careful financial planning for B2B buyers.
What are the Benefits of EEC L2e Electric Bicycles?
EEC L2e electric bicycles combine traditional cycling with electric assistance, promoting a healthy lifestyle while offering an eco-friendly transport solution. They are ideal for businesses in the fitness industry or those promoting sustainable commuting options. While they are easy to park and encourage physical activity, potential buyers should consider that they still require some physical effort to operate, which might not appeal to all users.
Key Industrial Applications of electric car eec coc european
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric car eec coc european | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Mobility | Last-mile delivery services using EEC certified electric vehicles | Reduces operational costs and carbon footprint while enhancing delivery speed | Ensure compliance with EEC standards and reliable sourcing of certified components |
| Tourism and Leisure | Electric mini-cars for sightseeing tours | Offers a unique and eco-friendly travel experience, attracting environmentally conscious tourists | Requires vehicles with EEC certification and suitable safety features for tourist safety |
| Public Transportation | Electric shuttles for public transport systems | Decreases urban congestion and pollution, enhancing the city’s appeal | Consider the integration with existing transport systems and EEC compliance for fleet vehicles |
| Logistics and Warehousing | Electric vehicles for warehouse operations | Increases efficiency in material handling and reduces noise pollution in urban areas | Focus on sourcing vehicles that meet EEC standards and have adequate battery life for operational demands |
| Healthcare | Electric vehicles for patient transport services | Provides a reliable, eco-friendly transport option for patients, enhancing service quality | Ensure vehicles meet EEC certification and have necessary medical transport features |
What are the key applications of EEC certified electric cars in urban mobility?
In urban mobility, EEC certified electric vehicles are increasingly being utilized for last-mile delivery services. These vehicles enable businesses to reduce operational costs while minimizing their carbon footprint. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing vehicles that comply with EEC standards ensures reliability and market acceptance. It’s crucial to maintain a consistent supply of certified components to avoid complications with vehicle certifications.
How can EEC certified electric vehicles enhance tourism and leisure industries?
The tourism sector benefits significantly from the integration of EEC certified electric mini-cars, which are ideal for sightseeing tours. These vehicles not only provide an eco-friendly travel option but also attract tourists who prioritize sustainability. For buyers in the Middle East and Europe, ensuring that these vehicles meet EEC certification is vital for safety and compliance. Additionally, features that enhance the tourist experience, such as comfort and accessibility, should be prioritized.
What role do electric shuttles play in public transportation systems?
EEC certified electric shuttles are becoming a staple in public transportation systems, offering a solution to urban congestion and pollution. They enhance the appeal of cities by providing a clean and efficient transport option. For international buyers, particularly in Europe, it is essential to consider how these vehicles can integrate with existing transport systems while ensuring EEC compliance. This includes evaluating the vehicles’ capacity, range, and ease of maintenance.
How are electric vehicles transforming logistics and warehousing?
In logistics and warehousing, EEC certified electric vehicles are revolutionizing material handling operations. They provide a quieter alternative to traditional vehicles, reducing noise pollution in urban settings. For businesses in logistics, especially in Brazil and Nigeria, sourcing EEC certified vehicles ensures compliance with international standards, which is crucial for operational efficiency and reputation. It is important to assess battery life and charging infrastructure to meet the demands of logistics operations.
Why are EEC certified electric vehicles important for healthcare services?
Healthcare services are increasingly relying on EEC certified electric vehicles for patient transport. These vehicles offer a dependable and eco-friendly option for transporting patients, which enhances the quality of care. Buyers in this sector must ensure that the vehicles not only meet EEC certification but also have the necessary features for medical transport. This includes safety measures, comfort, and accessibility to cater to diverse patient needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric car eec coc european’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating the Complexities of EEC Certification Requirements
The Problem: B2B buyers looking to import electric vehicles (EVs) face significant challenges in understanding and meeting the European Economic Community (EEC) certification requirements. The process can be convoluted and time-consuming, with numerous regulations governing components like the World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI), ISO certifications, and E-MARK certificates for individual parts. Buyers often feel overwhelmed, leading to delays in the import process and potential financial losses due to non-compliance.
The Solution: To effectively navigate EEC certification, buyers should adopt a systematic approach. Start by compiling a comprehensive checklist of all certification requirements, breaking down each component’s specifications and necessary documentation. Establish partnerships with reliable suppliers who can provide E-MARK certified parts, ensuring consistent sourcing to avoid complications during re-certification. Furthermore, consider hiring a compliance consultant with expertise in EEC regulations to facilitate the process. This proactive strategy not only streamlines certification but also mitigates risks associated with potential regulatory penalties.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Component Quality for Compliance
The Problem: A significant pain point for B2B buyers is ensuring that all components of their electric vehicles meet the stringent quality and safety standards required for EEC certification. Many buyers struggle with sourcing high-quality parts that are E-MARK certified, leading to concerns about product reliability and compliance. This issue is exacerbated in regions where access to certified suppliers is limited, increasing the risk of importing subpar components that could jeopardize compliance and brand reputation.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should prioritize establishing long-term relationships with certified component manufacturers. Conduct thorough due diligence to assess the quality assurance processes of potential suppliers. Implement a robust auditing system to periodically review supplier practices and ensure that components consistently meet EEC standards. Additionally, leverage technology by utilizing platforms that connect buyers with verified suppliers of certified parts. By building a reliable supply chain, buyers can enhance product quality while ensuring compliance with EEC regulations.
Scenario 3: Managing the Role of an Authorized EU Representative
The Problem: For international buyers outside the EU, a critical requirement for EEC certification is the appointment of an authorized EU representative. This necessity can pose a logistical challenge, as buyers must identify a trustworthy representative who understands the complexities of EU regulations. Without a reliable representative, buyers risk delays in the certification process and potential rejection of their applications, leading to lost opportunities in the European market.
The Solution: To effectively manage this requirement, buyers should conduct a strategic search for an authorized EU representative who specializes in automotive regulations. Consider engaging a legal or compliance firm that has established connections within the EU market. These firms can provide not only representation but also guidance through the certification process, ensuring that all paperwork is correctly filed and that the buyer remains compliant with EU regulations. Additionally, fostering a collaborative relationship with the representative can facilitate smoother communication and expedite problem resolution, ultimately enhancing the buyer’s market entry strategy in Europe.
By addressing these common pain points with actionable solutions, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of EEC certification for electric vehicles more effectively, ensuring compliance and enhancing their competitiveness in international markets.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric car eec coc european
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Electric Cars for EEC COC Compliance?
When selecting materials for electric vehicles (EVs) that comply with EEC COC standards, it is essential to consider both performance and regulatory requirements. Below, we analyze four common materials used in electric cars, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight yet strong, with a good strength-to-weight ratio. It has excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which contributes to improved energy efficiency and range in electric vehicles. However, it can be more expensive than steel, and its manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized techniques like welding and casting.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is frequently used for body panels and structural components in electric vehicles. Its corrosion resistance is particularly beneficial in regions with high humidity or saline environments, such as coastal areas in Brazil or Nigeria.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet international standards such as ASTM B221 for extruded aluminum and ASTM B209 for rolled products. Understanding local preferences for lightweight materials can also influence purchasing decisions.
2. High-Strength Steel (HSS)
Key Properties: High-strength steel offers superior strength and durability while maintaining a relatively low weight. It is also highly resistant to deformation under stress.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of HSS is its cost-effectiveness compared to aluminum, providing a robust solution for structural components. However, it is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively affect the vehicle’s range and efficiency.
Impact on Application: HSS is commonly used in the chassis and safety structures of electric vehicles, where strength is paramount. Its ability to withstand high impact forces makes it ideal for safety-critical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A992 for structural steel is crucial. Buyers in regions like the Middle East may also need to consider the local climate’s impact on material performance, particularly regarding corrosion resistance.
3. Polycarbonate
Key Properties: Polycarbonate is a transparent thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and optical clarity. It can withstand a wide temperature range and is lightweight.
Pros & Cons: Polycarbonate’s primary advantage is its durability and ability to replace glass in applications like windows and light covers, reducing weight. However, it can be more prone to scratching and may require coatings for UV protection.
Impact on Application: This material is often used for light covers, windows, and interior components in electric vehicles, contributing to overall weight reduction and design flexibility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that polycarbonate products meet standards such as ASTM D635 for flammability. In regions with high UV exposure, such as Africa, UV-resistant coatings may be necessary to enhance longevity.
4. Lithium-Ion Battery Components
Key Properties: Lithium-ion batteries are characterized by high energy density, lightweight, and low self-discharge rates. They are crucial for electric vehicle performance.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of lithium-ion batteries is their ability to store significant amounts of energy in a compact form, which is essential for electric vehicle range. However, they can be expensive and have specific manufacturing and recycling challenges.
Impact on Application: Lithium-ion batteries are the primary energy source for electric vehicles, directly impacting range, charging times, and overall vehicle performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international safety and performance standards, such as IEC 62133, is critical. Buyers must also consider local regulations regarding battery disposal and recycling, especially in regions like South America where environmental regulations are evolving.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric car eec coc european | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels and structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | Medium |
| High-Strength Steel | Chassis and safety structures | Cost-effective and strong | Heavier than aluminum | Low |
| Polycarbonate | Light covers and windows | Durable and lightweight | Prone to scratching | Medium |
| Lithium-Ion Battery Components | Energy source for electric vehicles | High energy density | Expensive and recycling challenges | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers looking to navigate the complexities of material choices in electric vehicles, ensuring compliance with EEC COC standards while optimizing performance and cost.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric car eec coc european
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Electric Cars with EEC COC Certification?
The manufacturing process for electric cars that meet the EEC COC (Certificate of Conformity) certification involves several critical stages. These stages ensure that the vehicle not only meets the technical specifications set by European regulations but also adheres to the quality standards expected by international B2B buyers.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Electric Car Manufacturing?
The first stage involves selecting high-quality materials that comply with international standards. Common materials include:
- Body Structure: High-strength steel or aluminum for lightweight and structural integrity.
- Battery Components: Lithium-ion cells, which must meet strict safety and performance standards.
- Interior Materials: Eco-friendly plastics and textiles that are durable and safe.
Suppliers must provide certifications for these materials, ensuring they meet relevant standards like ISO 9001 for quality management. B2B buyers should insist on transparency regarding the origin and certification of materials to avoid future compliance issues.
2. Forming: How Are Electric Car Components Shaped and Assembled?
The forming stage typically includes processes such as stamping, molding, and machining. This is where the vehicle parts are produced according to precise specifications:
- Stamping: This process is used for creating the car’s body panels from sheets of metal.
- Molding: Components such as battery casings and interior parts are often produced using injection molding techniques.
- Machining: Critical components, such as the motor and transmission, are machined to exact tolerances.
Quality control during this stage is crucial. B2B buyers should request documentation that outlines the production methods and any certifications of the machinery used, ensuring they align with industry standards.
3. Assembly: What Are the Best Practices for Assembling Electric Vehicles?
In the assembly stage, all components are brought together. This phase typically follows a systematic approach to minimize errors:
- Sub-Assembly: Major components like the powertrain and electrical systems are assembled separately before being integrated into the vehicle.
- Final Assembly: All sub-assemblies are combined, and systems are interconnected. This includes the integration of the battery, electric motor, and control systems.
During assembly, it’s essential to maintain a clean and organized workspace to prevent contamination and defects. B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly line’s layout and whether it follows lean manufacturing principles to optimize efficiency.
4. Finishing: How Is the Final Product Prepared for Market?
The finishing stage involves final inspections, painting, and detailing. Key steps include:
- Painting: High-quality paint processes are used to provide durability and aesthetic appeal, often employing environmentally friendly materials.
- Quality Checks: Each vehicle undergoes rigorous testing to ensure compliance with EEC standards. This includes checking for safety features, emissions, and overall performance.
For B2B buyers, understanding the finishing process can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality. Requesting samples or photographs of finished products can be beneficial to assess quality before bulk orders.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Electric Cars with EEC COC?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the production of electric vehicles to ensure compliance with EEC regulations and to meet buyer expectations.
International Standards: What Certifications Should Electric Vehicle Manufacturers Hold?
Manufacturers must adhere to various international and industry-specific standards:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes.
- CE Marking: This indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- E-MARK Certification: Required for vehicle components, ensuring they meet specific safety and performance criteria.
B2B buyers should verify that suppliers maintain these certifications and can provide documentation on their quality management systems.
Quality Control Checkpoints: How Are Quality Checks Conducted During Manufacturing?
Quality control is implemented at various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Incoming materials are inspected for compliance with specifications before they are accepted for use in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections are conducted during assembly to identify defects early and minimize waste.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection is performed on finished vehicles to ensure they meet all technical and regulatory requirements.
B2B buyers should request details about these checkpoints, including inspection reports and methodologies used.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should take proactive steps to ensure supplier quality control:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits can help verify compliance with quality standards. This includes reviewing production processes, quality control measures, and certifications.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing processes and product quality.
-
Documentation Review: Buyers should insist on access to quality control documentation, including inspection reports, test results, and compliance certifications.
By ensuring that suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures, B2B buyers can mitigate risks associated with non-compliance and maintain product integrity.
Conclusion: What Are the Benefits of Robust Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance?
Investing in robust manufacturing processes and comprehensive quality assurance not only ensures compliance with EEC COC certification but also enhances the overall product quality. For B2B buyers, understanding these processes is crucial in making informed purchasing decisions. It allows them to choose suppliers who prioritize quality, safety, and reliability, ultimately leading to successful long-term business relationships.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric car eec coc european’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for international B2B buyers looking to procure electric cars compliant with the EEC COC (Certificate of Conformity) for the European market. Understanding the certification process and the necessary steps to ensure compliance is crucial for successful procurement and market entry.
Step 1: Understand EEC Certification Requirements
Familiarize yourself with the EEC certification process, which is essential for any electric vehicle intended for sale in the European Union. This certification ensures that the vehicle meets EU safety and environmental standards. Key components include the World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI), ISO certification, and E-MARK certifications for individual components.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications required for the electric vehicle you wish to procure. This includes parameters such as battery capacity, motor power, maximum speed, and range. Defining these specifications upfront helps streamline the sourcing process and ensures that suppliers can meet your expectations.
- Consider market demands: Evaluate what features are popular in your target market, whether in Africa, South America, or Europe.
Step 3: Identify and Vet Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in EEC-certified electric vehicles. Check their experience, product offerings, and compliance with EU standards.
- Request documentation: Ask for their EEC certifications, quality control processes, and past client references to verify their credibility.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
It’s crucial to ensure that your selected suppliers hold valid certifications required for EEC compliance. This includes ISO certifications and E-MARK certificates for vehicle components.
- Check for updates: Regularly verify that their certifications are current and that they comply with the latest EU regulations.
Step 5: Evaluate Production Capabilities
Assess the production capabilities of potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your volume requirements and timelines. This includes evaluating their manufacturing processes, technology, and quality control measures.
- Site visits: If possible, conduct site visits to gain insights into their operations and quality assurance practices.
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Set up effective communication channels with your suppliers. Clear communication is vital for discussing specifications, timelines, and any potential issues that may arise during the procurement process.
- Use technology: Leverage tools like project management software or communication platforms to facilitate ongoing dialogue.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate the terms and conditions of the procurement agreement. This includes pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty provisions.
- Be transparent: Clearly outline expectations to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth procurement process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing EEC-certified electric cars effectively, ensuring compliance and alignment with market needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric car eec coc european Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Electric Cars with EEC COC Certification?
When analyzing the cost structure for sourcing electric cars that meet EEC COC certification, several components come into play. These include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a significant factor, particularly for components such as batteries, motors, and body materials. High-quality materials that meet EU standards often come at a premium, which can affect overall pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the manufacturing location. Countries with higher wage standards may result in increased production costs, while lower-wage countries can offer more competitive pricing. However, it is essential to ensure that labor practices comply with international standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help keep overhead costs lower, impacting the final price.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for customized electric vehicles. This cost is often amortized over the production volume, meaning that larger orders can lead to lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with EEC standards necessitates a robust QC process. Costs associated with testing, certification, and inspections are crucial to maintaining quality and meeting regulatory requirements.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for shipping vehicles from the manufacturer to the buyer’s location can be significant, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and Incoterms can influence these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a profit margin into the pricing structure. This margin can vary based on market competition, demand, and the supplier’s positioning strategy.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect the Cost of Electric Cars?
Several factors influence pricing for electric cars intended for the European market:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Higher volumes usually lead to bulk pricing discounts, making it essential for buyers to assess their purchasing strategy.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customization requests can drive up costs. Buyers should be clear about their specifications to avoid unnecessary changes that could inflate the price.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the necessity for certifications (like ISO and E-MARK) can add to the cost. Buyers should weigh the benefits of high-quality components against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven quality and service, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects the allocation of costs and risks between buyers and suppliers. Understanding these terms can help buyers negotiate better deals and manage logistics more effectively.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing of Electric Cars?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage the power of negotiation by understanding the market landscape. Engage multiple suppliers to compare prices and offerings, which can lead to better terms.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also ongoing costs such as maintenance, charging infrastructure, and potential resale value. A lower upfront cost may not always equate to a better long-term investment.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Be aware of potential tariffs, import duties, and currency fluctuations that can affect overall costs when importing vehicles from other regions.
-
Seek Strategic Partnerships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, favorable terms, and priority service, which can be crucial in a competitive market.
-
Stay Informed About Regulatory Changes: Regulations regarding electric vehicles are evolving, particularly in the EU. Staying informed can help buyers anticipate changes that may impact costs or compliance requirements.
Conclusion
The sourcing of electric cars with EEC COC certification involves a complex interplay of costs and pricing influences. By understanding these elements and employing strategic buying practices, international buyers can optimize their sourcing efforts, ensuring they achieve both quality and value. It is important to note that the prices mentioned in any negotiations should be considered indicative and subject to change based on market conditions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric car eec coc european With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives for Electric Vehicle Solutions
In the rapidly evolving automotive landscape, especially concerning electric vehicles (EVs), it’s essential for B2B buyers to evaluate various solutions that meet their specific operational needs. The EEC COC (European Economic Community Certificate of Conformity) certification for electric cars ensures compliance with EU regulations, making them a popular choice in international markets. However, other viable alternatives exist, each offering distinct advantages and challenges. This section will compare the ‘Electric Car EEC COC European’ against two prominent alternatives: traditional internal combustion engine vehicles and electric bicycles.
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Car EEC COC European | Traditional Internal Combustion Engine Vehicle | Electric Bicycle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque, range up to 110 km | Variable, typically higher range and speed | Limited speed (25-45 km/h) and range (up to 100 km) |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | Generally lower upfront costs | Low initial cost, affordable maintenance |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires EEC certification, involves complex homologation processes | Simple to acquire, established supply chains | Minimal certification, easy to import and sell |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance needs due to fewer moving parts | Higher maintenance costs due to complex engines | Minimal maintenance, easier repairs |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting, short-distance travel | Long-distance travel, diverse applications | Short-distance commuting, urban transport |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Traditional Internal Combustion Engine Vehicles
Traditional vehicles powered by internal combustion engines (ICE) have been the standard mode of transport for decades. They typically offer a higher range and speed, making them suitable for long-distance travel and varied applications. However, they come with higher fuel and maintenance costs, and they contribute to environmental pollution. For buyers in regions where fuel infrastructure is robust, ICE vehicles may still be a practical choice. However, the increasing regulatory pressure on emissions and the shift toward greener technologies may diminish their long-term viability.
Electric Bicycles
Electric bicycles (e-bikes) present a compelling alternative, particularly for urban environments. They are generally more affordable, both in terms of initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs. E-bikes offer ease of mobility in congested areas, making them ideal for short-distance commutes. However, their performance is limited compared to electric cars, with lower speed and range. Additionally, the regulatory landscape for e-bikes is less stringent, facilitating quicker market entry. This makes them an attractive option for B2B buyers looking for cost-effective and eco-friendly transport solutions.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Electric Vehicle Solution
When selecting the appropriate electric vehicle solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific operational needs, budget constraints, and environmental goals. The ‘Electric Car EEC COC European’ offers a compliant, high-performance option suited for urban commuting and short-distance travel, particularly in regions with stringent vehicle regulations. In contrast, traditional ICE vehicles may appeal to those needing flexibility for longer trips, while electric bicycles represent a cost-effective and eco-friendly alternative for short-distance urban transport. Ultimately, the choice depends on balancing performance, cost, and regulatory requirements to align with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric car eec coc european
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Electric Cars Under EEC COC Certification?
When navigating the landscape of electric vehicles (EVs) compliant with the EEC COC (Certificate of Conformity) certification in Europe, several technical specifications are critical for B2B buyers. Understanding these specifications not only ensures compliance but also aids in making informed purchasing decisions.
1. World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI)
The WMI is a unique code assigned to each vehicle manufacturer, critical for identification in the automotive industry. It consists of the first three characters of the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) and is essential for traceability and compliance. For B2B buyers, verifying the WMI helps ensure that they are sourcing vehicles from legitimate manufacturers, reducing the risk of counterfeit products.
2. ISO Certification
ISO certifications indicate that a manufacturer adheres to international quality management standards. Buyers should verify the ISO certification scope and expiration dates to ensure continuous compliance and reliability. This certification is crucial for maintaining quality assurance and can significantly impact the long-term performance and marketability of the vehicles.
3. E-MARK Certification for Components
E-MARK certification is mandatory for various components such as lights, tires, and safety features. Each component must have its E-MARK certification, which confirms it meets EU safety and environmental standards. For B2B buyers, sourcing vehicles with certified components ensures they are purchasing safe and compliant products, minimizing liability and enhancing customer trust.
4. Battery Specifications
The type and specifications of the battery are vital for the performance of electric vehicles. Key parameters include battery capacity (measured in Ah), voltage (V), and type (e.g., Lithium-ion, Lead-Acid). Understanding these specifications helps buyers evaluate the range, charging time, and overall efficiency of the vehicle, aligning with their operational needs.
5. Power System and Motor Specifications
The power system, including motor type and power output (measured in kW), directly affects vehicle performance. For instance, a higher kW rating typically means better acceleration and climbing ability. Buyers must assess these specifications to ensure the vehicle meets their operational requirements and performance expectations.
6. Brake and Suspension Systems
The type of brake system (e.g., disc brakes) and suspension design significantly influence vehicle safety and comfort. Understanding these systems helps buyers ensure that vehicles can handle various road conditions and provide a smooth ride, which is especially important for urban and rural markets.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Electric Vehicle Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for B2B buyers in the electric vehicle sector. Below are some common terms that are frequently encountered.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of electric vehicles, it’s crucial for buyers to identify OEMs to ensure they are sourcing high-quality components from reputable manufacturers.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory costs and meet their production needs without overcommitting financially.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and other details for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, crafting an effective RFQ can help in obtaining competitive pricing and terms, streamlining the purchasing process.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, ensuring smoother cross-border transactions.
5. Homologation
Homologation is the process of certifying that a vehicle meets the regulatory standards of a specific market. This term is particularly relevant for B2B buyers looking to ensure that vehicles comply with local regulations before importation and sale.
By understanding these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the electric vehicle market with greater confidence, ensuring compliance, safety, and quality in their purchasing decisions.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric car eec coc european Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Electric Car EEC COC European Sector?
The electric vehicle (EV) sector, particularly in the context of the European Economic Community (EEC) Certificate of Conformity (COC), is experiencing significant growth, driven by both regulatory changes and consumer demand for sustainable transport solutions. International B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several key trends shaping the market. Firstly, the European Union’s stringent emissions regulations are pushing manufacturers to adopt electric technologies, thus increasing the demand for compliant vehicles. Buyers should be aware that vehicles must meet specific EEC certification standards, including component certifications and safety protocols, which can vary by member state.
Moreover, advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure are enhancing the appeal of electric cars. With innovations such as fast-charging solutions and improved battery life, the range anxiety that has historically hindered EV adoption is diminishing. Additionally, the shift towards shared mobility solutions, especially in urban areas, is creating new opportunities for electric mini-cars and neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs). Buyers looking to source electric vehicles should focus on manufacturers that not only comply with EEC regulations but also demonstrate commitment to innovation and quality.
Another emerging trend is the increasing emphasis on localization in supply chains. International buyers should consider partnering with local suppliers for components that require EEC certification, as this can streamline the certification process and reduce potential compliance risks. By understanding these dynamics, B2B buyers can better navigate the complexities of sourcing electric vehicles in the European market.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Electric Car EEC COC European Sector?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of the electric vehicle industry, with an increasing emphasis on ethical sourcing and environmental impact. For B2B buyers in the electric car sector, understanding the significance of sustainable practices is crucial. The production of electric vehicles involves various materials, including lithium for batteries and rare earth elements for motors, which can have substantial environmental footprints. As a result, ethical sourcing of these materials is essential to minimize negative impacts and enhance brand reputation.
Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to recognized sustainability certifications and practices. This includes sourcing components that carry ‘green’ certifications, such as those indicating compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Additionally, supporting suppliers that utilize recycled materials or engage in fair labor practices not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also appeals to the growing consumer base that values corporate responsibility.
Furthermore, the push for a circular economy in the automotive sector is gaining traction. This involves designing vehicles and components with end-of-life recyclability in mind, which can significantly reduce waste. B2B buyers can benefit by aligning with manufacturers who are committed to this philosophy, ultimately leading to a more sustainable and ethical supply chain.
What Is the Evolution of the Electric Car EEC COC European Sector?
The evolution of the electric car sector, particularly regarding EEC certification, has been shaped by technological advancements and regulatory developments. The introduction of the EEC certification framework was a pivotal moment, as it established a standardized approach for vehicle compliance across Europe. Initially, the focus was primarily on traditional combustion engines; however, as awareness of climate change increased, the emphasis shifted towards electric and hybrid vehicles.
Since the implementation of the new standard 168/2013, which detailed the requirements for EEC certification, manufacturers have been compelled to adopt more rigorous testing and compliance measures. This has not only enhanced the safety and reliability of electric vehicles but has also fostered innovation in design and technology. As the market continues to mature, international B2B buyers can expect to see more sophisticated electric vehicle offerings that meet both regulatory standards and consumer expectations for sustainability and performance. Understanding this evolution is crucial for buyers looking to make informed sourcing decisions in a rapidly changing marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric car eec coc european
-
How do I ensure compliance with EEC certification for electric vehicles?
To ensure compliance with EEC certification, first, familiarize yourself with the mandatory requirements, including obtaining a World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI) and ISO certification. All components must have E-MARK certification, which verifies their compliance with EU safety standards. It’s essential to engage an authorized representative based in the EU to facilitate the certification process. Regular audits and updates to your documentation will help maintain compliance and avoid penalties. -
What are the key features to look for in an electric car for the European market?
When sourcing electric cars for the European market, prioritize models that meet EEC certification standards, ensuring they have appropriate technical specifications such as maximum speed and range. Look for features that enhance safety and comfort, like advanced braking systems, ergonomic seating, and reliable battery capacity. Additionally, consider the vehicle’s ability to comply with local regulations regarding emissions and safety to ensure market acceptance. -
What payment terms should I negotiate when sourcing electric vehicles?
When negotiating payment terms, it’s common to consider options such as T/T (Telegraphic Transfer) or L/C (Letter of Credit). Determine the payment schedule that aligns with your cash flow needs, such as partial payments upon order confirmation and the remainder upon delivery. Ensure that the terms also protect you against supplier defaults, potentially including an escrow arrangement or performance bonds for larger orders. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for electric cars?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the model of the electric vehicle. Typically, manufacturers may set MOQs ranging from 5 to 50 units for electric cars, especially for specialized models like EEC-certified vehicles. Before placing an order, inquire about the MOQ and whether there are flexible options for first-time buyers or sample orders to test market demand. -
How can I vet suppliers of EEC-certified electric vehicles?
Vetting suppliers involves several key steps: check their EEC certification status and ensure they have a track record of compliance with EU regulations. Request references from previous clients and verify their production capabilities and quality assurance processes. It’s also advisable to conduct factory visits or third-party audits to assess their manufacturing practices and adherence to international standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric vehicles?
Logistics for importing electric vehicles include understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Ensure your supplier can provide all necessary documentation for customs clearance, including the EEC certification and bill of lading. It’s crucial to partner with a logistics provider experienced in handling automotive imports, as they can navigate complex regulations and ensure timely delivery. -
What customization options are available for electric vehicles in the B2B market?
Customization options can vary by manufacturer but typically include features such as color, interior design, battery capacity, and technological enhancements like infotainment systems. Discuss your specific needs with the supplier to explore available modifications that align with your target market preferences. Customization can also extend to branding opportunities, allowing you to incorporate your company’s logo and design elements. -
How do I assess the quality assurance (QA) processes of electric vehicle manufacturers?
To assess the QA processes, request detailed documentation of the manufacturer’s quality management system, including ISO certifications and testing protocols for their vehicles. Inquire about their inspection procedures at various production stages, from component sourcing to final assembly. Engaging with third-party testing labs for independent verification of vehicle performance and safety can also provide additional assurance of quality before making a purchase.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Electric Car Eec Coc European Manufacturers & Suppliers List
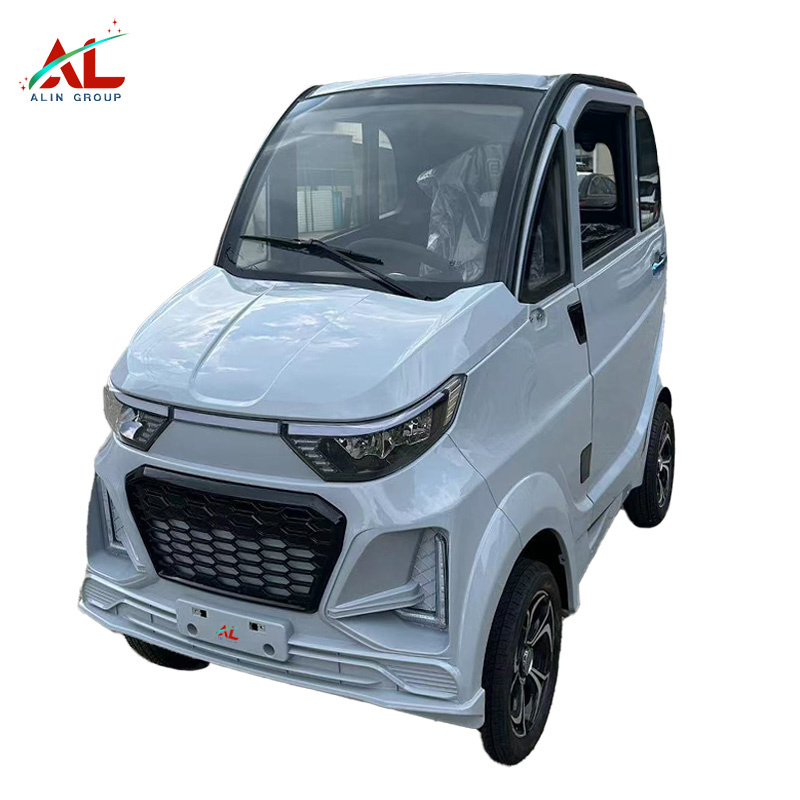
1. Runhorse – EEC COC Electric Mini Car J2
Domain: runhorseev.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
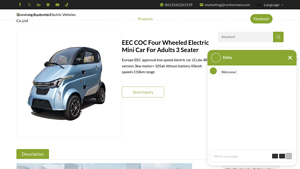
Introduction: Product Name: EEC COC Four Wheeled Electric Mini Car for Adults 3 Seater
Manufacturer: Runhorse Electric Vehicles
Model: J2
Motor: 3kw
Battery: 105ah lithium battery
Top Speed: 45 km/h
Range: 110 km on a single charge
Certification: EEC and COC certified
Design: Mid-steering, compact size, 2-seater
Use: Suitable for commuting, errands, and city exploration
Features: Environmentally friendly, easy …
2. Tesla – Model S Specifications
Domain: teslamotorsclub.com
Introduction: Tesla Model S
– Maximum permissible mass: 2590 kg
– Mass in running order: 2175 kg
– Max payload: 415 kg
– Not certified for towing
– Maximum continuous rated power: 69 kW
– Number of seating positions: 2 front, 3 rear (optional rear facing seats not included in certification)
3. Runhorse – J2-P Electric Scooter
Domain: diplomatie.gouv.ne
Introduction: {“Model”:”Runhorse J2-P”,”Charging Time”:”6 Hours”,”Steering Mode”:”Middle Handlebar”,”Color Options”:”White/Red/Blue”,”Certificate”:”EEC L6e”,”Multimedia”:”MP5 + Rearview Camera”,”Max Distance”:”100km”,”Mini Ground Clearance”:”160mm”,”Seater”:”1″,”Dimensions (L*W*H)”:”2890*1180*1780 mm”,”Max Speed”:”52 km/h”,”Transport Package”:”Iron Shelf”,”Trademark”:”Runhorse”,”Origin”:”Shandong, China”,”HS Co…
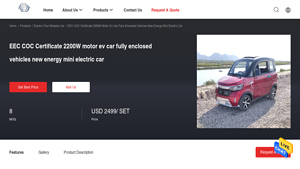
4. Automatic Electric Car – EEC COC Certificate 2200W Motor EV
Domain: automaticelectriccar.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: {“Product Name”: “EEC COC Certificate 2200W Motor EV Car”, “Type”: “Fully Enclosed Mini Electric Car”, “Dimensions”: “2605*1295*1610MM”, “Motor Power”: “2.2 KW”, “Maximum Speed”: “45KM/H”, “Voltage”: “60V”, “Curb Weight”: “341kg (Without Batteries Weight)”, “Charging Time”: “6-8 hours”, “Seating Capacity”: “3 seats (1 driver, 2 passengers)”, “Battery”: “Lead-acid battery 60V 58AH”, “Driving Range”…
5. Shandong Yunlong – EEC L6e Electric Mini Car
Domain: bev-cars.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Product Name: EEC L6e Electric Car Mini Car
Manufacturer: Shandong Yunlong Eco Technologies Co., Ltd.
Certificates: CE, EEC, Coc
Speed: 45 km/h
Battery: 60V 58AH Lead-Acid Battery
Endurance Mileage: 80 km
Motor: 1500W high-speed motor, rear-wheel drive
Brake System: Four Wheel Disc Brakes, hydraulic shock absorption
Tires: Thicken and widen vacuum tires
Interior: Luxurious with multimedia, heater,…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric car eec coc european
What Are the Key Benefits of Strategic Sourcing for EEC COC Electric Cars?
In the rapidly evolving electric vehicle market, strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with EEC COC regulations while optimizing costs and enhancing supply chain efficiency. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East, understanding the nuances of EEC certification is crucial. This certification not only facilitates entry into the European market but also underscores a commitment to quality and safety standards.
How Can Buyers Prepare for the Future of Electric Vehicle Sourcing?
As the demand for electric vehicles grows, so does the complexity of sourcing compliant components. Buyers must prioritize partnerships with manufacturers who have robust E-MARK certifications and a reliable supply chain for essential parts. This strategic approach mitigates risks associated with certification complications and ensures a seamless entry into the competitive European market.
What Steps Should Buyers Take to Position Themselves for Success?
Looking ahead, B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who demonstrate a proactive approach to compliance and innovation. Investing in strategic sourcing now will position companies to capitalize on the expanding electric vehicle market. By aligning with trusted manufacturers, buyers can enhance their product offerings and meet the increasing consumer demand for environmentally friendly transportation solutions.
In conclusion, embracing strategic sourcing for EEC COC electric vehicles not only ensures regulatory compliance but also fosters long-term business growth. International buyers should act decisively to secure their place in this dynamic market and drive the transition towards sustainable mobility.