Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric car inwheel motor
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicles (EVs), sourcing reliable electric car in-wheel motors presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. As the automotive industry shifts towards more innovative and efficient powertrain solutions, understanding the intricacies of in-wheel motor technology is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide delves into the diverse types of in-wheel motors available, their applications across various vehicle segments, and critical factors to consider during the supplier vetting process.
By exploring key aspects such as cost implications, performance metrics, and design flexibility, this resource empowers buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including markets like Germany and Brazil—to navigate the complexities of sourcing in-wheel motors effectively. With the increasing demand for sustainable transportation solutions, understanding the benefits and limitations of in-wheel motors can significantly influence product development and market positioning.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip B2B buyers with actionable insights and strategic knowledge, enabling them to confidently engage with suppliers and make choices that align with their operational goals and market demands. By leveraging this information, businesses can enhance their competitive edge in the global electric vehicle market, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable automotive future.
Understanding electric car inwheel motor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Drive Hub Motor | Integrated power electronics, no gears required | Passenger cars, light commercial vehicles | Pros: High efficiency, improved handling; Cons: Limited power output at high speeds. |
| Torque Vectoring Motor | Individual wheel torque control | Performance vehicles, advanced driver-assistance systems | Pros: Enhanced stability and traction; Cons: Increased complexity and cost. |
| Modular In-Wheel Motor | Customizable design with interchangeable parts | Electric buses, modular vehicles | Pros: Flexible manufacturing, easy upgrades; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Regenerative Hub Motor | Combines regenerative braking with in-wheel design | Urban delivery vehicles, taxis | Pros: Energy efficiency, reduced wear on brakes; Cons: Potential for increased unsprung weight. |
| Dual Motor System | Two motors per axle for enhanced performance | High-performance electric vehicles | Pros: Superior acceleration, improved control; Cons: Higher cost and complexity. |
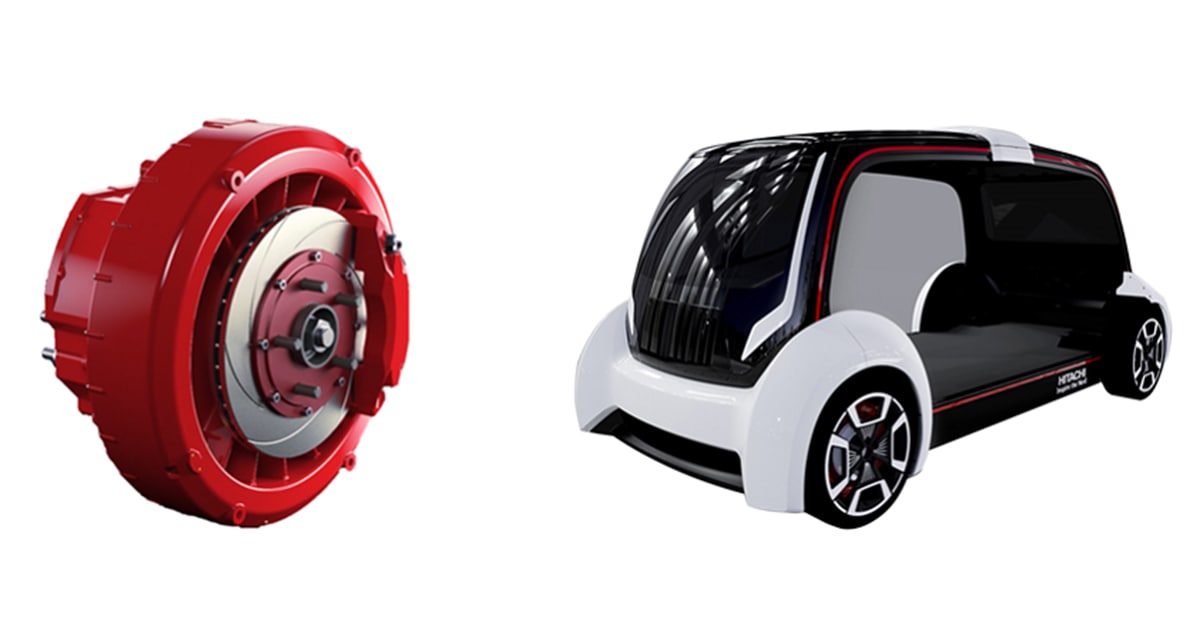
What are the Characteristics of Direct Drive Hub Motors?
Direct drive hub motors are characterized by their simplicity, integrating power electronics directly into the wheel assembly. This design eliminates the need for traditional mechanical linkages, reducing weight and enhancing efficiency. They are particularly suitable for passenger cars and light commercial vehicles, where space and weight savings are critical. B2B buyers should consider their operational efficiency and ease of integration into existing vehicle platforms, while being aware of potential limitations in high-speed performance.
How Do Torque Vectoring Motors Enhance Vehicle Performance?
Torque vectoring motors provide individual wheel torque control, allowing for superior handling and stability, particularly in performance vehicles and advanced driver-assistance systems. This technology enables precise distribution of torque based on driving conditions, improving traction and cornering capabilities. Buyers in the automotive sector should evaluate the added complexity and costs associated with this technology against the performance benefits it offers, especially in high-end vehicle markets.
What Makes Modular In-Wheel Motors a Flexible Choice?
Modular in-wheel motors offer a customizable design, allowing manufacturers to interchange components based on specific vehicle requirements. This flexibility is advantageous in applications such as electric buses and modular vehicles, where varying configurations may be needed. B2B buyers should assess the potential for future upgrades and adaptations, considering the initial investment costs against long-term operational benefits and production efficiencies.
Why Are Regenerative Hub Motors Important for Urban Vehicles?
Regenerative hub motors integrate regenerative braking systems with in-wheel designs, making them ideal for urban delivery vehicles and taxis. They enhance energy efficiency by converting kinetic energy back into usable power, which can significantly reduce operational costs. Buyers should consider the balance between energy savings and the potential increase in unsprung weight, which may affect ride comfort and handling.
What Benefits and Challenges Does a Dual Motor System Present?
A dual motor system features two motors per axle, providing enhanced performance and control for high-performance electric vehicles. This setup allows for superior acceleration and responsiveness, appealing to buyers in the luxury and sports vehicle markets. However, the complexity and higher costs associated with this technology may deter some manufacturers. B2B buyers must weigh the performance advantages against the financial implications and potential maintenance challenges.
Key Industrial Applications of electric car inwheel motor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric car inwheel motor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Integration in electric passenger vehicles | Enhanced vehicle performance and design flexibility | Quality certifications, supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness |
| Public Transportation | Use in electric buses and shuttles | Improved energy efficiency and reduced operational costs | Compliance with local regulations, maintenance support, scalability |
| Logistics and Delivery | Deployment in electric delivery vans and trucks | Increased payload capacity and reduced emissions | Customization options, lead times, warranty terms |
| Recreational Vehicles | Application in electric bicycles and scooters | Lightweight design and enhanced maneuverability | Compatibility with existing systems, pricing, and support services |
| Smart Urban Mobility | Utilization in shared mobility solutions like e-scooters | Cost reduction and improved urban mobility solutions | Integration capabilities, service availability, technology updates |
How is Electric Car In-Wheel Motor Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, in-wheel motors are integrated into electric passenger vehicles to provide direct drive capabilities. This technology eliminates the need for traditional drivetrains, reducing vehicle weight and enhancing performance metrics such as acceleration and handling. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and Europe, sourcing in-wheel motors requires attention to quality certifications and the reliability of suppliers to ensure that the components meet stringent automotive standards.
What Advantages Do In-Wheel Motors Offer for Public Transportation?
In the public transportation industry, electric buses and shuttles are increasingly utilizing in-wheel motors to improve energy efficiency and reduce operational costs. The ability to distribute power directly to each wheel allows for better torque management and enhanced stability, crucial for large vehicles. Buyers in this sector must consider local regulations and the need for maintenance support to ensure compliance and reliability in service.
How Can Logistics and Delivery Companies Benefit from In-Wheel Motors?
Logistics and delivery companies are deploying in-wheel motors in electric vans and trucks to increase payload capacity while simultaneously lowering emissions. The direct drive system provides a more efficient power transfer, which can lead to significant cost savings in fuel and maintenance. When sourcing these motors, businesses should focus on customization options that align with their vehicle specifications and operational demands, alongside lead times and warranty terms.
What Role Do In-Wheel Motors Play in Recreational Vehicles?
In recreational vehicles, such as electric bicycles and scooters, in-wheel motors offer a lightweight design that enhances maneuverability and performance. This application is particularly appealing in urban settings where space and weight are critical factors. Buyers should ensure that the in-wheel motors are compatible with existing systems and evaluate pricing and support services offered by manufacturers to maximize their investment.
How Do In-Wheel Motors Contribute to Smart Urban Mobility Solutions?
In the realm of smart urban mobility, in-wheel motors are pivotal for shared mobility solutions like e-scooters. These motors help reduce overall costs and improve the efficiency of urban transportation systems. For international buyers, especially in rapidly urbanizing regions, it is essential to assess the integration capabilities of these motors with existing platforms and the availability of ongoing service and technology updates to stay competitive in the market.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric car inwheel motor’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating the High Cost of In-Wheel Motors for Production
The Problem: As a B2B buyer, you may find the initial investment in in-wheel motor technology for electric vehicles daunting. Many manufacturers are deterred by the higher costs associated with producing vehicles equipped with multiple in-wheel motors compared to traditional motor systems. This financial burden can hinder your ability to innovate and compete in the market, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where budgets are often tight.
The Solution: To effectively manage costs, consider strategic partnerships and bulk purchasing agreements with suppliers of in-wheel motors. Engage with manufacturers that offer modular designs, which can allow for more flexible configurations and potentially lower production costs. Additionally, conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis can illuminate the long-term savings associated with reduced vehicle weight and improved efficiency, which can offset the initial investment. Explore government incentives or grants available for electric vehicle innovations in your region, as these financial aids can significantly reduce overall expenditure.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Technical Limitations of In-Wheel Motors
The Problem: B2B buyers may encounter challenges related to the technical specifications and performance of in-wheel motors, particularly concerning torque and power output. The heavy nature of in-wheel motors often leads to increased unsprung weight, which can negatively affect the vehicle’s handling and comfort. This technical limitation can deter buyers from adopting this technology, especially when competing with more traditional electric vehicle designs.
The Solution: Addressing these technical limitations requires collaboration with engineering teams and in-wheel motor manufacturers to optimize the design. Consider investing in advanced simulation software to test various configurations and materials that can reduce weight while maintaining performance. Additionally, look into hybrid solutions that combine in-wheel motors with traditional drivetrain systems to balance power output and handling. Partnering with companies that specialize in automotive engineering can also provide insights into innovative braking solutions and weight management techniques that enhance vehicle dynamics.
Scenario 3: Managing Maintenance and Durability Concerns
The Problem: The durability of in-wheel motors is a common concern among B2B buyers, particularly in regions with rough terrain or extreme weather conditions. The exposure of in-wheel motors to shocks and stresses can lead to premature wear and higher maintenance costs, which can be a significant deterrent for companies looking to invest in this technology.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance concerns, it is essential to choose in-wheel motors that have been rigorously tested for durability and performance under various conditions. Work closely with suppliers who provide robust warranty options and after-sales support. Implement a regular maintenance schedule that includes inspections of the motors and associated components to identify potential issues before they escalate. Additionally, consider investing in training programs for your maintenance staff to ensure they are equipped to handle the specific requirements of in-wheel motor systems. This proactive approach not only extends the lifespan of your investment but also enhances overall vehicle reliability, making it more appealing to your customer base.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric car inwheel motor
What Are the Key Materials for Electric Car In-Wheel Motors?
In the development of electric car in-wheel motors, the selection of materials is critical for optimizing performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in this technology, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Do Steel Alloys Impact In-Wheel Motor Performance?
Steel alloys are frequently utilized in the structural components of in-wheel motors due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio and durability. Key properties include high tensile strength, good fatigue resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
Pros: Steel alloys are relatively inexpensive and widely available, making them a cost-effective choice for manufacturers. They also provide robust mechanical properties, ensuring longevity and reliability in demanding conditions.
Cons: On the downside, steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, and its weight can contribute to increased unsprung mass, potentially affecting vehicle handling. Manufacturing complexity may also increase due to the need for additional coatings or treatments to enhance corrosion resistance.
Impact on Application: Steel alloys are compatible with various media, including lubricants and cooling fluids, but require careful selection of coatings to prevent rust in humid environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 or DIN 17100 is crucial. Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East may prioritize corrosion-resistant treatments due to environmental factors.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in In-Wheel Motors?
Aluminum is another popular material for in-wheel motors, particularly for components where weight savings are essential. Key properties include excellent corrosion resistance, low density, and good thermal conductivity.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum contributes to improved vehicle efficiency and handling. It is also resistant to corrosion, which is advantageous in various climates.
Cons: However, aluminum can be more expensive than steel and may have lower strength, necessitating thicker sections or additional reinforcements. The manufacturing process can be more complex, requiring specialized techniques like die casting or extrusion.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, but its lower thermal conductivity compared to copper may limit its use in high-heat applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. In regions like South America, where cost sensitivity is high, the price of aluminum may be a deciding factor.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance In-Wheel Motor Design?
Composite materials, particularly carbon fiber and reinforced plastics, are increasingly being explored for in-wheel motor applications due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and design flexibility.
Pros: Composites offer significant weight savings and can be engineered for specific performance characteristics, making them ideal for high-performance applications. They also exhibit excellent fatigue resistance.
Cons: The primary drawback is the high cost of raw materials and manufacturing processes, which can be prohibitive for mass production. Additionally, composites may have limited thermal and electrical conductivity compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Composites are generally compatible with various media but require careful consideration of the environmental conditions to prevent degradation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific standards for composites, such as ASTM D3039 for tensile properties. In regions like Africa, where infrastructure for advanced composites may be limited, sourcing can be a challenge.
What Is the Importance of Copper in In-Wheel Motors?
Copper is essential in the electrical components of in-wheel motors due to its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. Key properties include high electrical conductivity, good thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion.
Pros: Copper’s superior conductivity enhances motor efficiency and performance, making it a preferred choice for wiring and connectors.
Cons: The main disadvantage is the high cost of copper, which can significantly impact the overall production cost. Additionally, copper is heavier than aluminum, which may affect the vehicle’s unsprung weight.
Impact on Application: Copper is compatible with various electrical media and is essential for effective heat dissipation in high-performance applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire is crucial. In Europe, buyers may also need to consider the implications of copper sourcing and recycling regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Car In-Wheel Motors
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric car inwheel motor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Alloys | Structural components | Cost-effective and durable | Prone to corrosion and heavier weight | Medium |
| Aluminum | Housing and lightweight components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and lower strength | High |
| Composites | High-performance components | Significant weight savings | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Copper | Electrical wiring and connectors | Excellent conductivity | High cost and adds weight | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with their specific operational and market needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric car inwheel motor
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Electric Car In-Wheel Motors?
The manufacturing process of electric car in-wheel motors is intricate and requires precision at every stage to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Here are the main stages involved:
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing in-wheel motors involves sourcing high-quality materials. Key components include magnetic steel for the rotor, copper for winding, and various alloys for the casing. Suppliers should ensure that materials meet international standards, such as ISO 9001, which emphasizes quality management systems. This stage often involves testing materials for strength, conductivity, and durability to guarantee they can withstand the rigors of automotive applications.
Forming and Machining
Once materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes. This can include stamping, forging, and casting to create components like the rotor and stator. Advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is often employed to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances. Techniques such as laser cutting and wire EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) are also common to ensure high accuracy. This stage is critical as even minor deviations can affect the motor’s performance.
Assembly
The assembly of in-wheel motors is a complex process that typically involves multiple sub-assemblies. Components such as the rotor, stator, and power electronics are integrated within the wheel hub. Automation plays a significant role here, with robotic arms performing repetitive tasks to enhance consistency. Additionally, manual inspections are conducted to ensure that all components fit together correctly and that there are no defects. The assembly stage also includes the installation of braking systems in collaboration with brake system specialists.
Finishing
The finishing stage involves several processes such as painting, coating, and insulation to protect the components from environmental factors. This is crucial for enhancing durability and performance. Additionally, the motors may undergo balancing to minimize vibrations during operation. Quality checks are performed at this stage to ensure that the final product meets the specified performance criteria.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential for In-Wheel Motors?
Quality control (QC) is paramount in manufacturing in-wheel motors to ensure safety and reliability. Here are some essential QC measures:
What Are the Relevant International Standards?
B2B buyers should be aware of the international standards that govern the manufacturing of electric car components. ISO 9001 is a key standard that outlines quality management principles, ensuring that manufacturers adhere to best practices. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE marking (which indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards) and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications may also be relevant depending on the application of the motors.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
The QC process typically includes several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet quality specifications before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, continuous monitoring is essential. This includes measuring tolerances during machining and inspecting assemblies for defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, finished motors undergo rigorous testing. This includes performance tests, such as checking torque output, efficiency, and thermal characteristics.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for In-Wheel Motors?
Several testing methods are commonly employed to validate the quality and performance of in-wheel motors:
-
Electrical Testing: This includes checking resistance, inductance, and insulation resistance to ensure proper functioning.
-
Mechanical Testing: This includes vibration analysis and thermal imaging to assess the motor’s performance under various conditions.
-
Environmental Testing: Motors may be subjected to temperature and humidity tests to evaluate their performance in different climates, which is particularly important for international buyers from diverse regions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is crucial. Here are some actionable steps:
What Audits and Reports Should Buyers Request?
Buyers should conduct audits of potential suppliers, focusing on their manufacturing processes and quality control systems. This includes reviewing their compliance with ISO standards and any industry-specific certifications. Requesting detailed quality reports can also provide insights into their QC processes and testing results.
How Important Are Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s manufacturing practices. These inspections can occur at various stages of production, offering peace of mind regarding the quality of the final product. Buyers should consider companies that specialize in automotive components for these inspections.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in QC and certification:
-
Regional Standards Compliance: Different regions may have specific standards that must be met. For example, European buyers may prioritize CE marking, while buyers in the Middle East may need to comply with local regulations.
-
Cultural and Logistical Considerations: When dealing with suppliers from different regions, understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate smoother negotiations and quality assurance processes.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should seek suppliers that provide transparency regarding their sourcing and manufacturing processes. This is particularly important in regions where regulatory enforcement may vary.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing in-wheel motors for electric vehicles, ensuring they select suppliers that meet their quality and performance expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric car inwheel motor’
Introduction
This sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in effectively procuring electric car in-wheel motors (IWMs). As the automotive industry shifts towards electrification, understanding the unique specifications, supplier capabilities, and market trends is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This checklist will help streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that you select the right technology and partner for your electric vehicle projects.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, it’s vital to clearly outline your technical requirements for the in-wheel motors. Consider factors such as power output, efficiency, weight, and integration capabilities with existing vehicle designs.
– Torque and Power Requirements: Identify the torque specifications necessary for your vehicle’s performance.
– Size and Weight Constraints: Ensure that the motors fit within your vehicle’s design without compromising performance.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay informed about the latest advancements in in-wheel motor technology. Understanding market trends will help you identify leading suppliers and innovative solutions that can enhance your vehicle’s performance.
– Technological Developments: Look for innovations in efficiency and integration that can reduce costs and improve performance.
– Competitive Analysis: Analyze competitors who are utilizing IWMs and their results to inform your sourcing strategy.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
It’s crucial to thoroughly assess potential suppliers before making a commitment. Request detailed company profiles, including their manufacturing capabilities and technological expertise.
– Case Studies and References: Ask for references from clients in similar industries or regions to gauge supplier reliability.
– Quality Certifications: Ensure that suppliers possess relevant quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) that validate their production standards.
Step 4: Request Prototypes and Samples
Before finalizing your order, request prototypes or samples of the in-wheel motors. Testing these components will provide insights into their performance and integration with your vehicle.
– Performance Testing: Conduct tests to evaluate torque response, efficiency, and overall functionality.
– Compatibility Checks: Ensure that the IWMs integrate seamlessly with your vehicle’s design and other components.
Step 5: Understand Cost Structures and Payment Terms
Clarify the pricing structure and payment terms with your chosen supplier. Understanding the cost breakdown will help you budget effectively and avoid unexpected expenses.
– Total Cost of Ownership: Inquire about the long-term operational costs, including maintenance and potential savings from efficiency gains.
– Payment Flexibility: Discuss payment terms, including any options for bulk orders or long-term contracts.
Step 6: Assess Support and After-Sales Service
Evaluate the level of support and after-sales service offered by the supplier. Strong post-purchase support can significantly impact your project’s success.
– Technical Assistance: Ensure the supplier provides technical support for installation and troubleshooting.
– Warranty and Service Agreements: Confirm warranty terms and the availability of service agreements for long-term maintenance.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Agreements
Once you have selected a supplier, carefully review and finalize contracts. Ensure that all specifications, pricing, and delivery timelines are clearly defined.
– Legal Review: Consider having a legal expert review contracts to protect your interests.
– Contingency Plans: Include clauses for potential delays or issues in the supply chain to mitigate risks.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can strategically navigate the procurement process for electric car in-wheel motors, ensuring they select the right technology and partners for their electric vehicle initiatives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric car inwheel motor Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Electric Car In-Wheel Motors?
When sourcing in-wheel motors for electric vehicles, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. High-performance electric motors often utilize specialized magnetic steel and advanced composites, which are more expensive than standard materials. Additionally, the integration of power electronics and digital controls can further increase material costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for manufacturing in-wheel motors, particularly due to the complexity of the technology. Labor costs can vary widely based on geographic location, with regions like Europe generally having higher labor costs compared to parts of Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes and economies of scale can help mitigate these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially if custom molds or dies are required for specific designs. However, this cost can be amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the reliability and performance of in-wheel motors is critical. QC processes may involve testing and validation procedures, which contribute to overall costs but are necessary to meet regulatory standards and customer expectations.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can be significant, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties will affect the total logistics cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on the competitive landscape and the perceived value of their technology.
How Do Price Influencers Affect In-Wheel Motor Sourcing?
Several factors influence the pricing of in-wheel motors, which buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing often leads to lower per-unit costs. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can also impact pricing; negotiating favorable terms for larger volumes can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or specialized features can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the additional expenses incurred.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, UL) can enhance performance and reliability but will also increase costs. Buyers should assess whether these features align with their specific requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may charge a premium but offer greater assurance of quality.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) affects the responsibilities and costs associated with shipping. Understanding these terms can help buyers avoid unexpected expenses during transportation.
What Are the Best Negotiation and Cost-Efficiency Tips for Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiate Terms: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating better terms, including price breaks for larger volumes or extended payment terms that can improve cash flow.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the entire lifecycle costs, including maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential resale value. In-wheel motors may offer long-term savings through reduced running costs and greater efficiency.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations due to tariffs, taxes, and local market conditions. This understanding can aid in making informed decisions and identifying the most cost-effective suppliers.
-
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing strong partnerships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to innovations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
It is essential to note that prices for in-wheel motors can vary significantly based on multiple factors, including specifications, supplier negotiations, and market conditions. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric car inwheel motor With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Electric Car In-Wheel Motors
As the electric vehicle (EV) market evolves, various technologies aim to enhance vehicle performance, efficiency, and design. Among these, electric in-wheel motors stand out for their innovative approach to power delivery. However, other viable alternatives exist, each with unique advantages and limitations. This analysis provides a comparative overview of electric car in-wheel motors against two notable alternatives: traditional centralized motors and advanced e-axle systems.
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Car In-Wheel Motor | Traditional Centralized Motor | Advanced E-Axle System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque response, torque vectoring; individual wheel control enhances handling | Good torque but less responsive; requires complex drivetrain | Improved efficiency and torque management; integrates motor, transmission, and differential |
| Cost | Higher due to manufacturing complexity; involves multiple motors per vehicle | Generally lower; simpler design with fewer components | Competitive; lower than multiple in-wheel motors but higher than centralized motor systems |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex integration; requires redesign of vehicle architecture | Straightforward; widely understood and implemented | Moderate; combines benefits of both centralized motors and in-wheel designs but requires specialized knowledge |
| Maintenance | Potentially higher; motors exposed to road conditions and wear | Lower; centralized location protects from environmental factors | Moderate; centralized location simplifies some aspects but may require specific expertise |
| Best Use Case | High-performance vehicles, luxury models requiring advanced handling | Mass-market vehicles, cost-sensitive segments | Commercial vehicles, hybrids, and performance-focused models |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Traditional Centralized Motors?
Traditional centralized motors have been the backbone of vehicle design for decades. Their simplicity and cost-effectiveness make them ideal for mass production. The centralized design allows for easier maintenance and a more robust power delivery system, minimizing the complexity of integration. However, the reliance on a single motor means that performance can be limited, especially in terms of torque response and handling characteristics. Additionally, the drivetrain components such as gearboxes and differentials can introduce inefficiencies and increase weight, impacting overall vehicle performance.
How Do Advanced E-Axle Systems Compare?
Advanced e-axle systems are becoming increasingly popular due to their integration of the motor, transmission, and differential into a single unit. This design offers significant advantages in terms of efficiency and weight reduction, making them suitable for a variety of applications from commercial vehicles to performance-oriented models. E-axles can deliver enhanced torque management and are easier to manufacture than multiple in-wheel motors. However, they still require a certain level of complexity in design and integration, which may pose challenges for some manufacturers.
Conclusion: Which Electric Vehicle Powertrain Solution is Right for Your Business?
Choosing the right powertrain solution for electric vehicles depends on various factors, including performance requirements, cost constraints, and design flexibility. For B2B buyers, it is essential to consider the specific needs of the target market. If high performance and advanced handling are priorities, in-wheel motors might be the best fit despite their higher costs and complexity. Conversely, if cost-efficiency and ease of maintenance are critical, traditional centralized motors or advanced e-axle systems may be more appropriate. Assessing these elements will ensure that your investment aligns with your strategic goals and meets market demands effectively.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric car inwheel motor
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Car In-Wheel Motors?
When evaluating in-wheel motors for electric vehicles (EVs), several critical technical properties are essential for B2B buyers to consider. Understanding these specifications can help facilitate informed purchasing decisions and ensure compatibility with specific vehicle designs.
1. Power Output
Power output is a measure of the motor’s ability to deliver energy, typically expressed in kilowatts (kW). This specification is crucial for determining the performance capabilities of the vehicle, including acceleration and top speed. Higher power output can result in improved vehicle responsiveness, making it a vital consideration for manufacturers targeting performance-oriented markets.
2. Torque Rating
Torque rating, measured in Newton-meters (Nm), indicates the rotational force the motor can produce. In-wheel motors benefit from direct torque delivery to the wheels, enhancing traction and stability. For B2B buyers, a higher torque rating can translate to better handling and performance, particularly in challenging driving conditions.
3. Efficiency
Efficiency, typically expressed as a percentage, reflects how well the motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Higher efficiency ratings lead to reduced energy consumption and longer driving ranges. This property is particularly important for buyers focused on sustainability and operational cost reductions, as it directly impacts the total cost of ownership.
4. Weight
The weight of the in-wheel motor affects the overall vehicle dynamics and performance. Heavier motors can contribute to unsprung weight, impacting ride quality and handling. Buyers should seek a balance between motor power and weight, as lighter motors can enhance efficiency and driving comfort.
5. Integration Capability
In-wheel motors often come with integrated power electronics and control systems, which simplify installation and reduce the need for additional components. This feature is beneficial for manufacturers looking to streamline production processes and minimize costs. Understanding integration capabilities can help buyers select motors that fit seamlessly into their vehicle designs.
6. Durability and Environmental Resistance
Durability refers to the motor’s ability to withstand operational stresses, such as shocks and vibrations. Environmental resistance encompasses the motor’s capability to perform under various temperature and humidity conditions. For B2B buyers, selecting motors with high durability and environmental resistance ensures long-term reliability and reduced maintenance costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Electric Car In-Wheel Motors?
Understanding industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are several important trade terms relevant to in-wheel motors:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces components that are used in another company’s end products. In the context of in-wheel motors, OEMs are responsible for designing and manufacturing these components, ensuring they meet specific performance and regulatory standards. Buyers often engage with OEMs to secure quality parts that align with their vehicle specifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to evaluate their purchasing strategy, especially for new models where demand may be uncertain. Negotiating favorable MOQs can help manage inventory costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price proposals from suppliers for specific products or services. For in-wheel motors, an RFQ typically outlines technical specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines. This process helps buyers compare suppliers and make informed procurement decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. They cover aspects such as delivery points, risk transfer, and cost allocation. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers involved in cross-border transactions of in-wheel motors, as they clarify obligations and help avoid disputes.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. Understanding lead times is critical for B2B buyers to manage production schedules and meet market demands. Effective communication with suppliers regarding lead times can optimize inventory management.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing in-wheel motors for electric vehicles more effectively, ensuring they make strategic decisions that align with their business goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric car inwheel motor Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Impacting the Electric Car In-Wheel Motor Sector?
The electric car in-wheel motor sector is undergoing a transformative phase driven by several global trends. As electric vehicles (EVs) gain traction, the demand for innovative technologies that enhance performance and efficiency is rising. Key drivers include the push for sustainability, government incentives for electric mobility, and advancements in battery technology. In regions like Europe, particularly Germany, there is a strong regulatory framework supporting EV adoption, while in Africa and South America, the focus is on cost-effective solutions that can be adapted to local markets.
Current B2B tech trends include the integration of advanced power electronics and digital controls in in-wheel motors, which allow for greater efficiency and performance. Moreover, the trend towards modular manufacturing processes is appealing to international buyers, enabling customization and scalability in production. As vehicle designs evolve to capitalize on the benefits of in-wheel motors—such as improved torque response and reduced weight—companies are also exploring partnerships with technology providers to enhance their product offerings.
Emerging markets are witnessing a growing interest in electric mobility solutions, with local manufacturers beginning to invest in in-wheel motor technologies. This presents significant sourcing opportunities for international buyers looking to diversify their supply chains and tap into innovative solutions that cater to regional needs.
How Can B2B Buyers Prioritize Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Electric Car In-Wheel Motor Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming critical considerations for B2B buyers in the electric car in-wheel motor sector. The environmental impact of sourcing materials and manufacturing processes is under increasing scrutiny, especially as the automotive industry strives to reduce its carbon footprint. Buyers should seek suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices, such as utilizing recycled materials and renewable energy sources in production.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated, particularly in regions where labor practices and resource extraction may pose risks. B2B buyers should conduct thorough due diligence on their suppliers’ practices and seek certifications that validate their commitment to ethical sourcing. Green certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management, can serve as indicators of a supplier’s dedication to sustainability.
Moreover, as consumer demand for environmentally friendly products continues to grow, aligning with suppliers who share a commitment to sustainability can enhance a brand’s reputation and marketability. By investing in ethically sourced materials and sustainable manufacturing processes, B2B buyers can contribute to the broader goal of achieving a greener automotive industry.
What Is the Brief Evolution of In-Wheel Motor Technology in the Electric Vehicle Sector?
In-wheel motor technology has its roots in early automotive innovations, dating back to the Lohner-Porsche hybrid of 1900, which featured electric motors embedded in the wheel hubs. However, it wasn’t until recent advancements in materials and manufacturing processes that in-wheel motors gained renewed interest, particularly within the electric vehicle sector.
The evolution of this technology has been marked by significant milestones, including the development of more compact and efficient electric motors, improved power electronics, and better integration with vehicle design. Today’s in-wheel motors offer advantages such as enhanced torque response, reduced weight, and the elimination of traditional driveline components, which have made them a viable option for modern electric vehicles.
As manufacturers continue to innovate, the potential for in-wheel motors to reshape vehicle design and performance remains significant, making it a focal point for B2B buyers looking to stay ahead in the competitive electric vehicle market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric car inwheel motor
-
How do I determine the right specifications for in-wheel motors for my electric vehicle project?
To identify the right specifications, assess your vehicle’s design, intended use, and performance requirements. Key factors include motor power output, torque, weight, and size constraints. Additionally, consider the integration of components such as power electronics and braking systems. Collaborate with manufacturers to customize motor specifications that align with your vehicle’s unique requirements and operational goals. -
What are the advantages of sourcing in-wheel motors from international suppliers?
Sourcing in-wheel motors from international suppliers can provide access to advanced technology, competitive pricing, and diverse manufacturing capabilities. Suppliers from regions like Europe and Asia often have established expertise in electric vehicle components, leading to innovative designs and improved efficiency. Furthermore, international partnerships can enhance supply chain flexibility and open new market opportunities for your business. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for in-wheel motors?
Minimum order quantities for in-wheel motors can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific motor design. Generally, MOQs may range from 50 to several hundred units. When negotiating with suppliers, consider discussing your project’s scale and potential for future orders to secure more favorable terms. Smaller initial orders may also be possible for prototyping or pilot projects. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing in-wheel motors?
Payment terms for in-wheel motor purchases can vary based on supplier policies and the scale of the order. Common terms include a deposit (typically 30-50%) upon order confirmation, with the balance due prior to shipping or upon delivery. It is crucial to clarify terms regarding currency, payment methods, and any potential discounts for early payment or bulk orders during contract negotiations. -
How can I ensure the quality of in-wheel motors from international suppliers?
To ensure quality, conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Request certifications, such as ISO 9001, and inquire about their quality control processes. Implement a quality assurance plan that includes product inspections, performance testing, and adherence to international standards. Establish clear communication regarding quality expectations and consider third-party inspections for added assurance. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing in-wheel motors?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Evaluate whether air freight or sea freight is more suitable based on urgency and budget. Familiarize yourself with import duties and tariffs that may apply. Collaborate with logistics providers experienced in international shipping to streamline the process and ensure timely delivery. -
What customization options are available for in-wheel motors?
Many suppliers offer customization options to meet specific requirements, including motor size, power output, and integrated electronics. Customization may also extend to features such as torque vectoring capabilities and thermal management systems. Engage with manufacturers early in the design process to discuss your needs and explore available modifications that enhance your vehicle’s performance. -
How do I vet potential suppliers of in-wheel motors effectively?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry reputation, experience, and previous client testimonials. Conduct background checks to verify their financial stability and operational capacity. Request samples and evaluate their product quality firsthand. Additionally, engage in direct communication to assess their responsiveness and willingness to collaborate on your specific needs. This comprehensive approach will help you identify reliable partners for your sourcing needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 4 Electric Car Inwheel Motor Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Protean Solutions – ProteanDrive
Domain: proteanelectric.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Protean Solutions specializes in in-wheel motor technology for passenger cars, light commercial vehicles, and future transport solutions. Their key product, ProteanDrive, features integrated power electronics and digital control, enabling direct drive without the need for gears. Benefits of their in-wheel motors include improved torque response, enhanced handling, faster acceleration, reduced char…
2. Nissan – In-Wheel Motor Technology
Domain: nissan-global.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: The in-wheel motor is a type of electric vehicle (EV) drive system that installs motors adjacent to each driving wheel, allowing for direct power to the wheels. This design enhances accelerator responsiveness and aligns the vehicle’s behavior with the driver’s steering inputs, providing a more intuitive driving experience. Unlike conventional EVs, which use a single motor and drive shaft, the in-w…
3. Protean Electric – PD18 In-Wheel Motor
Domain: emobility-engineering.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: The Protean Electric PD18 in-wheel motor is designed for retrofitting to existing vehicles, allowing for improved packaging and energy storage. It features a unique rotor-stator relationship where the stator is surrounded by the rotor, and incorporates a disc brake developed with Alcon. The motor integrates all necessary power electronics, requiring only connections for high-voltage cables, coolin…
4. Endless Sphere – QSMotors 12kW Hub Motors
Domain: endless-sphere.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: QSMotors hub motors with a nominal power of 12kw, suitable for installation in the rear of front-wheel drive gas-powered vehicles to create a hybrid system. The hub motors are designed to be held by a single shaft for easier installation. They can reach speeds of 100-120 km/h with standard 17-inch tires.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric car inwheel motor
In the evolving landscape of electric vehicles, the adoption of in-wheel motor technology presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers. This innovative approach not only enhances vehicle efficiency through reduced weight and improved torque distribution but also fosters creative freedom in vehicle design. By strategically sourcing in-wheel motors, companies can capitalize on the benefits of lower operational costs and increased range, while also addressing the challenges of manufacturing and integration.
As the demand for electric vehicles grows across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, particularly in markets like Germany and Brazil, sourcing in-wheel motors can position businesses at the forefront of this automotive revolution. It is crucial for buyers to engage with reputable suppliers who understand the nuances of this technology and can offer scalable solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Looking ahead, the landscape for in-wheel motors is poised for growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing consumer demand for sustainable transport solutions. International buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships that not only enhance their product offerings but also contribute to a greener future. Embrace this opportunity to lead the charge in the electric vehicle market by investing in innovative in-wheel motor solutions.