Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric cars zonder rijbewijs
In an era where mobility is increasingly defined by sustainability and accessibility, the market for electric cars zonder rijbewijs (license-free electric cars) is evolving rapidly. International B2B buyers face the challenge of navigating this emerging sector, where understanding the nuances of these vehicles is crucial. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, addressing the diverse types of electric cars without a driver’s license, their applications in various markets, and the essential factors to consider when sourcing these vehicles.
From the compact city-friendly models to more robust utility options, each vehicle type presents unique benefits tailored to specific consumer needs. This guide also delves into the intricacies of supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers can identify reliable manufacturers and distributors. Additionally, it provides insights into cost structures, financing options, and regulatory considerations across different regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—specifically in markets like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria.
By leveraging the information contained within this guide, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their business objectives and customer demands. Understanding the dynamics of the electric car zonder rijbewijs market not only enhances strategic sourcing but also positions businesses to capitalize on the growing trend towards eco-friendly transportation solutions.
Understanding electric cars zonder rijbewijs Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microcars | Compact size, limited top speed (typically 45 km/h), affordable | Urban deliveries, short-distance transport | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to maneuver in cities. Cons: Limited range and speed. |
| Electric City Cars | Designed for urban environments, higher speeds (up to 80 km/h) | Ride-sharing, rental services | Pros: More versatile than microcars, suitable for longer trips. Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Electric Cargo Vehicles | Larger storage capacity, designed for transporting goods | Last-mile delivery, logistics companies | Pros: Efficient for urban logistics, eco-friendly. Cons: Limited battery range affects long-distance use. |
| Electric Minivans | Family-oriented design, spacious interiors | Shuttle services, family transport | Pros: Comfortable for passengers, versatile seating. Cons: Higher maintenance costs. |
| Electric Bicycles | Pedal-assist feature, lightweight, eco-friendly | Delivery services, personal transport | Pros: Extremely cost-efficient, promotes sustainability. Cons: Not suitable for all weather conditions. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Microcars?
Microcars are small, nimble vehicles primarily designed for urban environments. They typically have a maximum speed of around 45 km/h and are often classified as vehicles that do not require a traditional driver’s license in many jurisdictions. For B2B buyers, microcars are ideal for businesses focused on short-distance transport and delivery within congested city centers. The lower purchase price and operational costs make them appealing, although the limited speed and range may restrict their use in broader applications.
How Do Electric City Cars Stand Out?
Electric city cars bridge the gap between microcars and conventional vehicles, offering higher speeds (up to 80 km/h) and greater versatility. They are well-suited for ride-sharing and rental services, allowing companies to cater to urban commuters looking for eco-friendly transport options. The initial investment is higher compared to microcars, but their enhanced capabilities can justify the cost for businesses aiming to expand their service offerings in urban markets.
What Advantages Do Electric Cargo Vehicles Provide?
Electric cargo vehicles are tailored for logistics and last-mile delivery. With larger storage capacities, they can efficiently transport goods while maintaining an environmentally friendly profile. Businesses in the logistics sector can benefit from reduced operational costs and improved sustainability. However, buyers should consider the limited battery range, which can impact long-distance deliveries and necessitate careful planning of routes.
Why Consider Electric Minivans for Family Transport?
Electric minivans offer spacious interiors and comfort, making them suitable for family-oriented services such as shuttle operations. Their design accommodates multiple passengers, making them ideal for companies that provide transport solutions for schools or events. While they offer versatility, potential buyers should weigh the higher maintenance costs against the benefits of enhanced passenger comfort and capacity.
How Do Electric Bicycles Fit Into the B2B Landscape?
Electric bicycles are an increasingly popular option for businesses focused on delivery and personal transport. Their pedal-assist feature allows for efficient travel over short distances while promoting eco-friendliness. They are particularly advantageous for companies aiming to reduce their carbon footprint. However, their usability can be limited by weather conditions, requiring businesses to consider seasonal impacts on operations.
Key Industrial Applications of electric cars zonder rijbewijs
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric cars zonder rijbewijs | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Mobility | Last-mile delivery solutions | Enhanced accessibility and reduced operational costs for deliveries | Battery efficiency, charging infrastructure, and vehicle size |
| Tourism and Leisure | Eco-friendly transportation for tourists | Attracts environmentally conscious customers and improves brand image | Vehicle design, comfort features, and local regulations |
| Public Transport | Shuttle services in urban areas | Reduces congestion and emissions, improving city livability | Fleet size, maintenance support, and service reliability |
| Healthcare | Patient transport services | Provides safe and reliable transport for patients with mobility issues | Accessibility features, safety standards, and operational costs |
| Education | Campus transportation for students | Promotes sustainable transport options and enhances campus mobility | Vehicle capacity, charging options, and maintenance services |
How Are Electric Cars Zonder Rijbewijs Used in Urban Mobility?
In urban mobility, electric cars zonder rijbewijs are increasingly utilized for last-mile delivery services. Businesses leverage these vehicles to navigate congested city streets, ensuring timely deliveries without the added expense of larger vehicles. The compact nature of these cars allows for easy maneuverability and parking in tight spaces, solving the problem of accessibility in urban environments. Buyers should consider battery efficiency and the availability of charging infrastructure to maximize operational efficiency.
What Role Do Electric Cars Zonder Rijbewijs Play in Tourism and Leisure?
In the tourism sector, electric cars zonder rijbewijs serve as eco-friendly transportation options for tourists exploring cities. By offering these vehicles, businesses can attract environmentally conscious travelers looking for sustainable ways to navigate urban areas. This not only enhances the tourist experience but also boosts the brand image of the service provider. Buyers should focus on vehicle design and comfort features that cater to the needs of tourists, as well as compliance with local regulations regarding vehicle usage.
How Can Electric Cars Zonder Rijbewijs Enhance Public Transport Systems?
Electric cars zonder rijbewijs are ideal for shuttle services in urban areas, providing a sustainable alternative to traditional public transport. These vehicles help reduce congestion and emissions, contributing to a more livable city environment. By integrating them into public transport systems, cities can offer reliable and efficient transport options to residents and visitors alike. When sourcing these vehicles, businesses need to consider fleet size, maintenance support, and the reliability of service to ensure operational success.
In What Ways Do Electric Cars Zonder Rijbewijs Benefit Healthcare Services?
In healthcare, electric cars zonder rijbewijs are employed for patient transport services, ensuring safe and reliable transportation for individuals with mobility challenges. These vehicles are particularly beneficial in urban settings where traffic congestion can impede timely medical services. Buyers in this sector must prioritize accessibility features and compliance with safety standards, as well as evaluate operational costs to maintain a sustainable transport solution.
How Are Electric Cars Zonder Rijbewijs Used in Educational Institutions?
Educational institutions utilize electric cars zonder rijbewijs for campus transportation, providing students with a sustainable and convenient way to navigate large campuses. This not only promotes eco-friendly transport options but also enhances the overall mobility experience for students and staff. Buyers should assess vehicle capacity, charging options, and available maintenance services to ensure that the transport solution meets the specific needs of the educational environment.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric cars zonder rijbewijs’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance for Electric Cars Without a License
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face significant challenges in understanding and navigating the regulatory landscape surrounding electric cars zonder rijbewijs. Different countries have varying regulations regarding the use and sale of these vehicles, leading to potential legal liabilities and compliance issues. For instance, in some regions, these vehicles might be classified as low-speed vehicles, which could subject them to different safety and emission standards. This can create confusion for businesses looking to import, lease, or resell these vehicles, as they may inadvertently violate local laws.
The Solution:
To effectively navigate this regulatory maze, B2B buyers should conduct comprehensive research on the specific regulations governing electric cars zonder rijbewijs in their target markets. Collaborating with local legal experts or regulatory consultants can provide valuable insights. It is also beneficial to engage with industry associations that advocate for the interests of electric vehicle manufacturers and distributors. They can offer updates on regulatory changes and best practices for compliance. Establishing a robust compliance checklist that includes vehicle specifications, safety requirements, and documentation can streamline the process and mitigate risks.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Consumer Perceptions and Market Acceptance
The Problem:
Another pain point for B2B buyers is the challenge of changing consumer perceptions regarding electric cars zonder rijbewijs. Many potential customers may still associate these vehicles with lower quality or safety concerns compared to traditional cars. This skepticism can hinder sales and market penetration, especially in regions where electric vehicles are still gaining traction. For instance, buyers in regions like Africa or parts of South America might be more inclined to invest in conventional vehicles due to concerns about reliability and performance.
The Solution:
To overcome these perceptions, B2B buyers should focus on effective marketing strategies that highlight the advantages of electric cars zonder rijbewijs. This includes showcasing advanced safety features, the environmental benefits of electric vehicles, and cost savings associated with lower maintenance and fuel expenses. Creating educational campaigns that inform potential customers about the technology, performance, and real-life applications of these vehicles can help build trust. Additionally, providing testimonials and case studies from satisfied customers can reinforce credibility and encourage adoption.
Scenario 3: Addressing Range Anxiety and Charging Infrastructure Limitations
The Problem:
Range anxiety remains a critical issue for potential buyers of electric cars zonder rijbewijs. Many users fear that the limited range of these vehicles will not meet their daily transportation needs. Furthermore, inadequate charging infrastructure, especially in rural or developing areas, can exacerbate these concerns, making businesses hesitant to invest in electric vehicles for their fleets or as resale products.
The Solution:
To mitigate range anxiety, B2B buyers should emphasize the advancements in battery technology that have improved the range of electric cars zonder rijbewijs. They can also consider collaborating with charging network providers to enhance the charging infrastructure in their operational areas. Offering solutions such as mobile charging units or partnerships with local businesses to provide charging stations can significantly increase customer confidence. Furthermore, educating potential customers on efficient driving practices and planning routes can help them maximize their vehicle’s range, making electric cars a more viable option for everyday use.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric cars zonder rijbewijs
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Electric Cars zonder Rijbewijs?
In the production of electric cars zonder rijbewijs, the choice of materials significantly influences performance, durability, and overall market acceptance. Here, we analyze four common materials used in these vehicles, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Electric Cars zonder Rijbewijs?
Aluminum is a lightweight metal known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for electric vehicles (EVs) where weight reduction is crucial for efficiency. Its key properties include high corrosion resistance and good thermal conductivity, which help maintain battery performance and longevity.
Pros: Aluminum’s lightweight nature enhances vehicle efficiency and range, while its corrosion resistance minimizes maintenance costs. Additionally, it can be easily molded into complex shapes, facilitating innovative designs.
Cons: The primary drawback of aluminum is its relatively high cost compared to steel, which can impact the overall pricing of the vehicle. Manufacturing processes can also be more complex, requiring specialized techniques.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various media, including battery electrolytes, makes it suitable for components such as battery housings and structural frames.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should consider the availability of aluminum and potential import tariffs. Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential for ensuring quality and safety.
Why Is Steel Still a Preferred Choice for Certain Components?
Steel remains a staple material in automotive manufacturing due to its strength and durability. It is particularly favored for structural components where high tensile strength is required.
Pros: Steel is cost-effective and widely available, making it a practical choice for mass production. Its robustness ensures longevity and safety in various driving conditions.
Cons: The main limitation of steel is its weight, which can negatively affect the vehicle’s range and efficiency. Additionally, it is prone to corrosion if not adequately treated.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used in the chassis and body of electric cars zonder rijbewijs, where structural integrity is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local safety and environmental regulations. In regions with high humidity, such as parts of South America, corrosion-resistant coatings may be necessary.
What Role Does Composite Materials Play in Electric Vehicle Design?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced plastics, are increasingly used in electric cars due to their lightweight and high-strength characteristics.
Pros: Composites offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, significantly enhancing vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. They also provide excellent corrosion resistance and can be molded into intricate shapes.
Cons: The primary drawback is the high cost of production and the complexity of manufacturing processes, which can deter mass adoption.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for body panels and interior components, where weight savings directly translate to improved range.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the availability of composite materials and the need for specialized manufacturing processes. Compliance with international standards is crucial for ensuring quality.
How Does Plastic Contribute to the Electric Vehicle Ecosystem?
Plastics are widely used in electric cars for various components, including dashboards, panels, and insulation materials.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight, cost-effective, and can be produced in various colors and finishes. They also offer good insulation properties, which is beneficial for battery safety.
Cons: Plastics may not provide the same level of durability as metals and can degrade over time, especially under UV exposure.
Impact on Application: Plastic components are suitable for non-structural applications, contributing to overall weight reduction without compromising safety.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the environmental regulations regarding plastic use and recycling in their respective countries. Compliance with standards such as JIS is essential for ensuring product quality.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Cars zonder Rijbewijs
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric cars zonder rijbewijs | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Battery housings, structural frames | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Steel | Chassis, body components | Cost-effective, durable | Heavier, prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Composite | Body panels, interior components | High strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive, complex manufacturing | High |
| Plastic | Dashboards, panels, insulation materials | Lightweight, cost-effective | Less durable, UV degradation | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with critical insights into the materials used in electric cars zonder rijbewijs, aiding in informed decision-making for sourcing and compliance in diverse international markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric cars zonder rijbewijs
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Electric Cars Zonder Rijbewijs?
The manufacturing process for electric cars zonder rijbewijs, commonly referred to as microcars or voiturettes, involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both functional and regulatory standards. Understanding these stages provides B2B buyers with insights into the quality and reliability of the vehicles they are considering for purchase.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Electric Cars Zonder Rijbewijs?
The first step in manufacturing involves sourcing and preparing materials. High-quality materials such as lightweight metals (aluminum, magnesium) and advanced composites are favored for their strength-to-weight ratio, contributing to energy efficiency and performance. Battery components, including lithium-ion cells, are also sourced from specialized suppliers who meet stringent safety and quality standards.
2. Forming: How Are the Components Shaped and Prepared?
Once materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes. This includes stamping, extrusion, and molding to create the vehicle’s chassis, body panels, and other components. Advanced techniques such as hydroforming and injection molding are often employed to achieve complex shapes and optimize structural integrity.
3. Assembly: What Techniques Are Used to Assemble Electric Cars?
The assembly stage combines various components into a cohesive unit. This is typically done using automated assembly lines that employ robotics for precision and efficiency. Techniques such as spot welding and adhesive bonding are utilized to ensure a secure fit and enhance the vehicle’s durability.
4. Finishing: How Is the Final Product Prepared for Market?
Finishing processes include painting, surface treatment, and quality checks. State-of-the-art painting techniques not only improve aesthetics but also provide corrosion resistance. Final assembly checks ensure all components are correctly installed and functioning as intended.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented in Electric Car Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a pivotal aspect of the manufacturing process for electric cars zonder rijbewijs. It ensures that vehicles meet international and industry-specific standards, providing buyers with confidence in their purchases.
International Standards: Which Certifications Should Buyers Look For?
Manufacturers typically adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, ensuring consistent quality in products and services. Other relevant certifications may include CE marking, which indicates compliance with European safety standards, and API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications for automotive lubricants and components.
Quality Control Checkpoints: What Are the Key Quality Control Stages?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated at various stages of production:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet predefined specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process allows for immediate corrections and adjustments, minimizing defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished product to verify that it meets all design specifications and safety requirements.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Electric Car Production?
Testing methods are crucial for verifying the performance and safety of electric cars zonder rijbewijs. Common testing protocols include:
-
Safety Testing: Crash tests and electronic safety systems are evaluated to comply with regulatory requirements.
-
Performance Testing: Range, acceleration, and battery efficiency are assessed under various conditions to ensure reliability.
-
Durability Testing: Components undergo stress testing to evaluate their longevity and performance over time.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential. Here are actionable strategies:
1. Conducting Supplier Audits: What Should Buyers Look For?
Buyers should conduct regular audits of potential suppliers to evaluate their manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices. Audits should focus on compliance with international standards, the effectiveness of quality control measures, and the supplier’s history of product performance.
2. Requesting Quality Reports: What Information Should Buyers Expect?
Buyers can request detailed quality reports that outline the results of inspections and tests performed during manufacturing. These reports should include data on defect rates, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken.
3. Utilizing Third-Party Inspections: How Can Buyers Ensure Objectivity?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These organizations can verify compliance with international standards and provide certifications that enhance buyer confidence.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
For B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is critical. Buyers should be aware of:
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements that affect vehicle compliance. Understanding these can aid in selecting suppliers that meet local market needs.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should seek suppliers that provide clear visibility into their supply chain, ensuring that all components are sourced from reputable manufacturers.
-
Cultural Considerations: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers and understanding cultural differences can facilitate better communication and adherence to quality standards.
Conclusion: How Can Buyers Leverage Manufacturing Insights for Better Decision-Making?
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for electric cars zonder rijbewijs, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business needs. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to international standards and maintain robust quality control practices will ultimately lead to safer, more reliable vehicles for their customers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric cars zonder rijbewijs’
Introduction
This guide aims to assist B2B buyers in the procurement of electric cars zonder rijbewijs (license-free electric cars). As the market for these vehicles expands, understanding the essential steps for sourcing can help ensure that you make informed decisions that align with your operational needs and budget considerations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, it’s vital to clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider factors such as battery capacity, range, charging time, and vehicle dimensions.
– Battery and Range: Ensure the vehicle meets the operational range required for your intended use, especially in regions with varying infrastructure.
– Charging Requirements: Assess the charging infrastructure available in your area to ensure compatibility with the vehicle’s charging system.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Regulations
Understanding the current market trends and regulatory environment is crucial. Research the legal requirements for electric cars zonder rijbewijs in your target markets, including any potential subsidies or incentives.
– Local Regulations: Different countries have specific regulations governing the use of license-free vehicles. Make sure your chosen models comply with these laws.
– Market Trends: Stay informed about technological advancements and competitor offerings to ensure you select vehicles that meet modern consumer expectations.
Step 3: Identify and Evaluate Potential Suppliers
A thorough evaluation of suppliers is critical to ensure quality and reliability. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in producing electric vehicles.
– Supplier Background: Investigate the supplier’s history, production capabilities, and customer reviews.
– Certifications and Compliance: Verify that the suppliers adhere to international safety and environmental standards, which can impact market acceptance.
Step 4: Request Proposals and Conduct Comparisons
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed proposals that include pricing, warranties, and after-sales service.
– Pricing Structures: Compare not only the upfront costs but also the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and energy consumption.
– Warranty and Support: Evaluate the warranty terms and the availability of technical support and spare parts.
Step 5: Test Drive and Inspect Vehicles
Before finalizing any purchase, arrange for a test drive and a thorough inspection of the vehicles. This step ensures that the vehicles meet your performance expectations and quality standards.
– Performance Testing: Assess acceleration, braking, and handling characteristics to ensure they align with your requirements.
– Quality Check: Look for signs of build quality and reliability, including the materials used and the overall finish.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Purchase
Once satisfied with the vehicles and supplier, proceed to negotiate the terms of purchase. This includes pricing, delivery timelines, and payment conditions.
– Flexible Payment Options: Inquire about leasing options or installment plans that could ease budget constraints.
– Delivery and Training: Discuss logistics for delivery and whether training for your team on vehicle operation and maintenance will be provided.
Step 7: Plan for After-Sales Support and Maintenance
After purchase, establish a plan for after-sales support and maintenance. This ensures the longevity and optimal performance of your fleet.
– Scheduled Maintenance: Determine a maintenance schedule that aligns with manufacturer recommendations.
– Support Access: Ensure you have access to a reliable support system for any issues that may arise post-purchase.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed, strategic decisions when sourcing electric cars zonder rijbewijs, ensuring they meet their operational needs while adhering to market standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric cars zonder rijbewijs Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Electric Cars zonder Rijbewijs?
When sourcing electric cars zonder rijbewijs, understanding the cost structure is vital for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials such as batteries, electric motors, and chassis significantly influences pricing. Lithium-ion batteries, which are essential for electric vehicles, can constitute a large portion of the total material costs. Sourcing high-quality components may raise initial costs but can enhance long-term reliability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on geographic location and the complexity of the assembly processes. Regions with advanced manufacturing capabilities may offer skilled labor at higher rates, impacting overall costs. However, investing in skilled labor can reduce defects and improve production efficiency.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead costs, making it crucial for suppliers to adopt lean manufacturing principles.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific vehicle designs can entail significant upfront investments. Buyers should consider whether suppliers have the necessary tooling already or if new investments are required, as this can affect the overall pricing structure.
-
Quality Control (QC): Maintaining high standards through rigorous QC processes incurs costs but is essential for ensuring safety and compliance with regulations. Buyers should evaluate the QC procedures of suppliers to ensure they meet industry standards.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, can vary widely based on the origin of the vehicles and the destination. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and any customs duties or tariffs also play a critical role.
-
Margin: Suppliers will factor in their profit margin, which can fluctuate based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of their products.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Total Cost of Electric Cars zonder Rijbewijs?
Several key influencers can affect pricing, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often result in lower unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs with suppliers to achieve better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or unique specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials can impact both cost and quality. Buyers should consider the certifications required for their markets, as compliance can affect sourcing decisions.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but their reliability can justify the higher costs.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for budgeting. Terms like CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight) or FOB (Free on Board) can significantly affect total costs depending on the responsibilities for shipping and insurance.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs When Sourcing Electric Cars zonder Rijbewijs?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-effectiveness:
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations with suppliers regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Establishing a good relationship can lead to favorable terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the TCO rather than just the purchase price. Evaluate long-term costs such as maintenance, energy consumption, and resale value to make informed decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes that can affect pricing. Conduct thorough market research to understand regional pricing trends and dynamics.
-
Supplier Evaluation: Conduct due diligence on potential suppliers, looking for those with strong performance histories, relevant certifications, and customer testimonials to mitigate risks.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for electric cars zonder rijbewijs can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier practices, and regional economic factors. The figures mentioned are indicative and should be verified with suppliers for accuracy in specific procurement scenarios.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric cars zonder rijbewijs With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Personal Mobility
In the rapidly evolving landscape of personal mobility, businesses are presented with various options to meet their transportation needs. Electric cars zonder rijbewijs, or electric cars that can be driven without a traditional driver’s license, are gaining traction for their convenience and accessibility. However, alternative solutions such as electric scooters and traditional scooters (mopeds) also provide viable options for urban mobility. This analysis will compare these alternatives based on key performance indicators relevant to B2B buyers.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Cars Zonder Rijbewijs | Electric Scooters | Traditional Scooters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate speed (up to 45 km/h); suitable for urban commuting | High maneuverability; speed varies by model (up to 25-30 km/h) | Moderate speed (up to 45 km/h); good for city use |
| Cost | Generally higher purchase price (€10,000 – €15,000) | Lower initial cost (€300 – €1,500) | Moderate cost (€1,000 – €3,000) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires parking space and charging infrastructure | Very easy to park; minimal charging needs | Requires parking space; fuel considerations |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance; battery replacement necessary | Low maintenance; fewer moving parts | Moderate maintenance; engine upkeep required |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for short urban commutes and local deliveries | Great for quick trips, last-mile connectivity | Suitable for urban commuting where speed is essential |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Electric Scooters
Electric scooters are an increasingly popular choice for urban mobility, especially among younger demographics and businesses focusing on last-mile delivery solutions. Their lightweight design allows for easy maneuverability in congested areas, and they often come at a fraction of the cost of electric cars zonder rijbewijs. However, the limited speed and range may restrict their use for longer commutes or more extensive transportation needs. Additionally, they require less maintenance due to fewer mechanical parts, making them cost-effective in the long run.
Traditional Scooters
Traditional scooters offer a balance between speed and cost, making them a practical alternative for urban transportation. With speeds comparable to electric cars zonder rijbewijs, they provide a similar commuting experience while typically costing less upfront. However, traditional scooters require regular maintenance, including oil changes and engine checks, which can add to the total cost of ownership. Furthermore, fuel costs can be a concern, particularly as global fuel prices fluctuate. They are best suited for users who prioritize speed and flexibility in urban environments.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Mobility Solution
When selecting the appropriate mobility solution for a business, it’s essential to consider specific operational needs, budget constraints, and the typical use case. Electric cars zonder rijbewijs offer a robust alternative for those needing a vehicle that combines convenience with the ability to transport goods or passengers. In contrast, electric and traditional scooters may serve businesses focused on short trips or last-mile logistics. Ultimately, B2B buyers should weigh factors such as total cost of ownership, maintenance requirements, and the intended application to make an informed decision that aligns with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric cars zonder rijbewijs
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Electric Cars Zonder Rijbewijs?
When evaluating electric cars zonder rijbewijs (license-free electric cars), it is crucial to understand specific technical properties that influence performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some essential specifications:
-
Battery Capacity (kWh)
– Definition: This measures the total amount of energy the battery can store. A higher capacity typically translates to a longer range.
– B2B Importance: For businesses, understanding battery capacity is vital for determining the vehicle’s operational range and suitability for specific applications, such as urban deliveries or personal transport. -
Range (WLTP)
– Definition: The Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure (WLTP) range indicates how far the vehicle can travel on a single charge under standardized conditions.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the range helps businesses assess the practicality of the vehicle for their needs, ensuring that it can cover daily distances without requiring frequent recharges, thus optimizing operational efficiency. -
Charging Time (Fast Charging)
– Definition: This refers to the time required to charge the vehicle’s battery from a low state to a significant level (typically 20% to 80%).
– B2B Importance: Shorter charging times can enhance fleet productivity by reducing downtime. Businesses can evaluate which models offer the fastest charging solutions that align with their operational schedules. -
Motor Power (kW)
– Definition: The power output of the electric motor, usually expressed in kilowatts (kW). It indicates the vehicle’s performance capabilities, including acceleration and handling.
– B2B Importance: Understanding motor power is essential for businesses that require vehicles for specific tasks, such as transporting goods or navigating hilly terrains. Higher power outputs can also indicate better performance under load. -
Safety Ratings
– Definition: Ratings provided by safety organizations that evaluate vehicle crashworthiness and safety features.
– B2B Importance: Safety ratings are critical for businesses concerned about liability and employee safety. High ratings can also enhance brand reputation when offering transportation solutions to customers.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know for Electric Cars Zonder Rijbewijs?
Understanding common trade terminology is essential for navigating the procurement and negotiation processes in the electric vehicle market. Here are key terms to be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Buyers should consider OEMs when looking for reliable components or vehicles, as they typically guarantee quality and compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchases effectively and negotiate better terms, especially if they are looking to stock vehicles for resale or fleet purposes. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing information for specific products.
– Relevance: Issuing an RFQ can help buyers compare prices and terms from different suppliers, ensuring they secure the best deal for their desired electric vehicles. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for understanding shipping responsibilities and costs, which is particularly important for international buyers importing electric vehicles. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
– Definition: The purchase price of an asset plus the costs of operation, maintenance, and depreciation over its useful life.
– Relevance: TCO calculations help businesses evaluate the long-term financial implications of investing in electric cars zonder rijbewijs, leading to more informed purchasing decisions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, optimize their procurement strategies, and enhance their operational efficiencies in the growing electric vehicle market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric cars zonder rijbewijs Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics in the Electric Cars Zonder Rijbewijs Sector?
The market for electric cars zonder rijbewijs (license-free electric vehicles) is gaining traction globally, driven by increasing urbanization, changing consumer preferences, and environmental concerns. In regions like Africa and South America, where transportation infrastructure may be less developed, these vehicles offer a practical and accessible alternative for short-distance travel. The Middle East and Europe are also witnessing a surge in demand, particularly among younger demographics who view these vehicles as a safer and more affordable option compared to traditional cars or scooters.
Key trends shaping this market include the integration of advanced technology, such as smart connectivity features and enhanced battery systems, which improve performance and user experience. Additionally, the rise of subscription models and leasing options is making these vehicles more financially accessible for businesses and consumers alike. As B2B buyers evaluate sourcing opportunities, understanding local regulations and consumer behavior is crucial, as these factors can vary significantly across regions.
Moreover, the push towards electrification in the automotive sector is prompting manufacturers to innovate and adapt their offerings. For international B2B buyers, this means opportunities to partner with suppliers who are agile and responsive to market changes, ensuring a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving landscape.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence the Electric Cars Zonder Rijbewijs Market?
Sustainability is a cornerstone of the electric vehicles market, including electric cars zonder rijbewijs. The environmental impact of these vehicles is significantly lower than traditional combustion engine cars, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality in urban areas. However, the sourcing of materials and components remains a critical consideration. B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who adhere to ethical sourcing practices, ensuring that raw materials—particularly lithium and cobalt used in batteries—are sourced responsibly and sustainably.
The importance of transparency in the supply chain cannot be overstated. Buyers should seek partners who can provide documentation on the origins of their materials, as well as certifications that demonstrate adherence to environmental and social governance (ESG) standards. Investing in ‘green’ certifications not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products. As the market evolves, B2B buyers who prioritize ethical sourcing will likely gain a competitive advantage and foster long-term relationships with environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Evolution of Electric Cars Zonder Rijbewijs and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of electric cars zonder rijbewijs can be traced back to their initial conception as small, low-speed vehicles. Originally viewed as a niche market, advancements in battery technology and increasing environmental awareness have transformed these vehicles into viable alternatives for urban mobility. Historically, they were primarily targeted at specific demographics, such as teenagers or individuals with driving restrictions, but the market is now expanding to include a broader audience.
This evolution is particularly relevant for B2B buyers, as it signals a shift in market dynamics and consumer acceptance. The increased functionality and improved safety features of modern electric cars zonder rijbewijs make them appealing not only for personal use but also for commercial applications, such as last-mile delivery services. Understanding this evolution allows B2B buyers to anticipate market needs and make informed sourcing decisions that align with emerging trends and consumer preferences. As the market continues to mature, the potential for innovation and collaboration in this sector remains significant.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric cars zonder rijbewijs
-
How do I choose the right supplier for electric cars zonder rijbewijs?
Selecting the right supplier involves evaluating their reputation, product quality, and compliance with international standards. Start by researching potential suppliers through trade shows, online directories, and industry reviews. Request samples to assess the vehicle’s performance and reliability. Additionally, ensure that the supplier can provide necessary certifications and warranties. Establish clear communication to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to accommodate your specific needs, such as customization options and delivery timelines. -
What are the key features to look for in electric cars zonder rijbewijs?
When sourcing electric cars zonder rijbewijs, focus on key features such as battery capacity, range, charging time, and safety standards. Evaluate the vehicle’s performance metrics, including acceleration and top speed, to ensure it meets your target market’s expectations. Additionally, consider the vehicle’s design, comfort, and technological integrations, such as connectivity options. Understanding these features will help you match the vehicles to your customers’ preferences and regulatory requirements in different regions. -
What are the typical payment terms for international purchases of electric cars zonder rijbewijs?
Payment terms can vary significantly between suppliers, but typical arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and balance payments upon delivery. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide a balance of security and cash flow. Consider using letters of credit or escrow services to ensure both parties are protected during the transaction. Be clear about any additional costs such as shipping, customs duties, and taxes to avoid unexpected expenses. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for electric cars zonder rijbewijs?
MOQs for electric cars zonder rijbewijs can differ based on the supplier and the model. Generally, manufacturers may have a MOQ ranging from 10 to 50 units to cover production costs. However, some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or smaller businesses. Discuss your needs openly with potential suppliers, as they may be willing to accommodate smaller orders, especially if you can demonstrate a commitment to future purchases. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for electric cars zonder rijbewijs?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed product specifications and certifications from suppliers. It’s beneficial to conduct factory visits or audits to observe their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Implement a thorough inspection process upon receiving the vehicles, checking for compliance with your specifications and safety standards. Establish a clear return policy for defective units and maintain open lines of communication with the supplier for ongoing support. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing electric cars zonder rijbewijs?
Logistics involves multiple considerations, including shipping methods, customs clearance, and local transportation. Determine the best shipping options based on cost and delivery timelines, and ensure the supplier provides necessary shipping documentation. Familiarize yourself with import regulations in your country, including tariffs and taxes. Partnering with a logistics provider experienced in automotive imports can streamline the process and mitigate potential delays. -
How do I handle customization requests for electric cars zonder rijbewijs?
When seeking customization, clearly outline your requirements to potential suppliers. Discuss options for modifications such as color, branding, and additional features that may appeal to your market. Some manufacturers may have standard customization packages, while others can accommodate bespoke requests. Ensure that customization does not compromise compliance with safety and regulatory standards. Establish timelines and costs associated with customization to align expectations. -
What are the emerging trends in the electric car zonder rijbewijs market?
The electric car zonder rijbewijs market is evolving with trends such as increased battery efficiency, improved charging infrastructure, and a focus on sustainability. Innovations in design and technology, such as smart connectivity and enhanced safety features, are becoming standard. Additionally, the growing demand for urban mobility solutions is driving interest in compact and affordable electric vehicles. Staying informed on these trends can help you better position your offerings and meet the changing needs of your customers.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Electric Cars Zonder Rijbewijs Manufacturers & Suppliers List
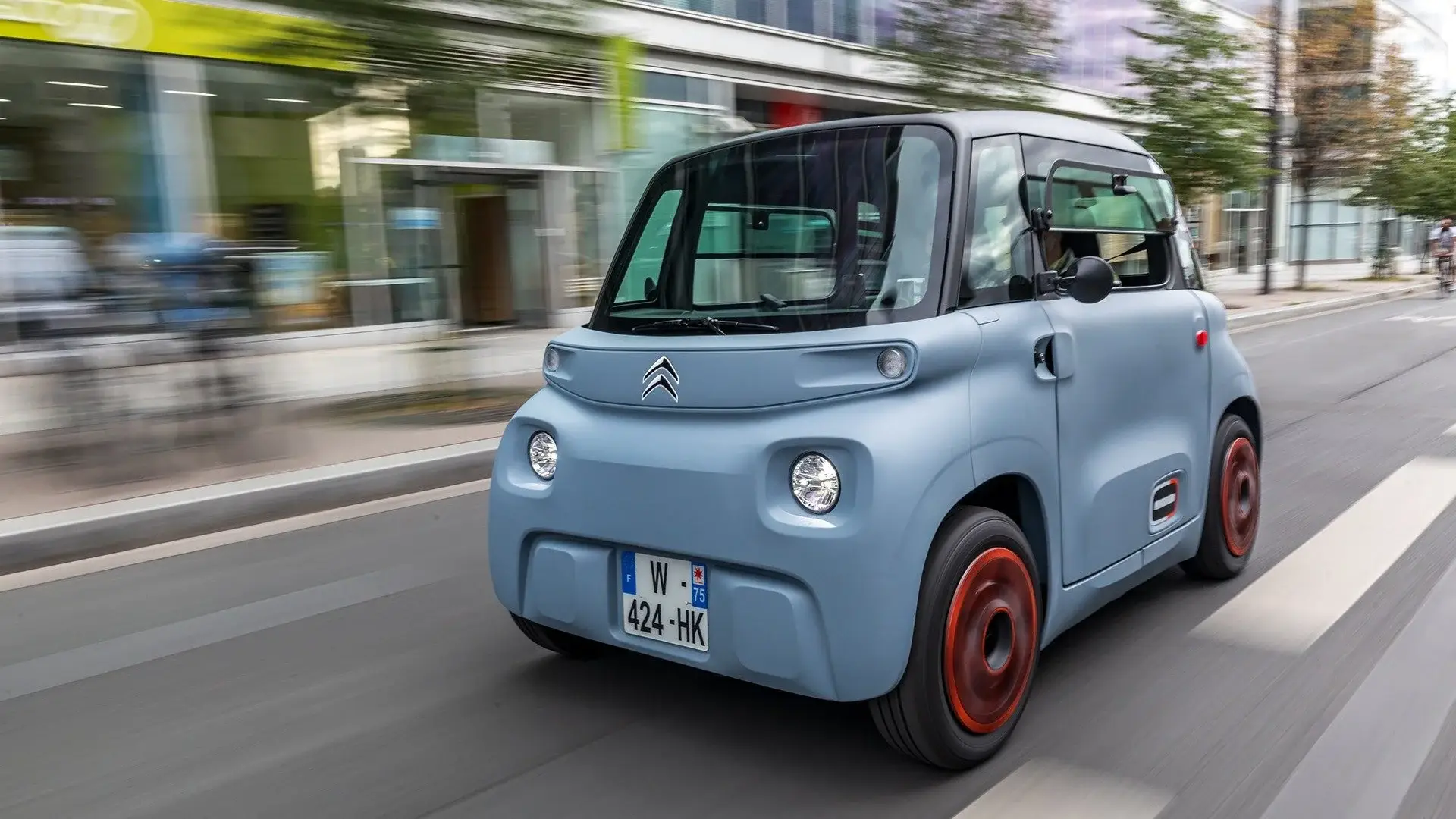
1. Citroën – Ami Electric Car
Domain: citroen.nl
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Citroën Ami: Elektrische kleine auto. Prijs vanaf € 8.490. APR 5,25%, EAR 6,23%, met een looptijd van 36 maanden. Compact, elektrisch, rijbewijsvrij vanaf 16 jaar. Unieke eigenschappen: eenvoudig te besturen, gemakkelijk aan te passen, panoramisch glazen dak. Interieur: 3,9 inch digitaal display, automatische versnellingsbak, 1 USB-oplaadpoort. Laadoplossingen: geïntegreerde oplaadkabel voor stand…
2. Mobilize – Duo Electric Micro-City Car
Domain: mobilize.co.nl
Introduction: Mobilize Duo is a 100% electric micro-city car available in two versions: DUO 45 Neo (max speed 45 km/h, no driver’s license required for 16+) and DUO 80 Pro/Evo (max speed 80 km/h, requires a driver’s license B). It features a range of up to 161 km, can be charged via a regular outlet in 5.5 hours, and has a compact design with two upward-opening wing doors for easy access. The car includes a com…
3. Autovisie – Elektrische Voertuigen zonder Rijbewijs
Domain: autovisie.nl
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Rijden zonder autorijbewijs in kleine elektrische auto’s zoals scootmobiel auto’s en brommobielen is mogelijk. Deze voertuigen kunnen tot 45 km/u rijden en zijn ideaal voor stadsritten en korte afstanden. Voordelen zijn onder andere gratis parkeren in drukke steden, lage gebruikskosten, en bescherming tegen weer en wind. De For Motion Dike Mini Auto is een voorbeeld van een scootmobiel auto, ontwo…
4. Scootmobielcentrum – Nieuwe 45 km Auto
Domain: scootmobielcentrum.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Nieuwe 45 km auto kopen of leasen – rij zonder rijbewijs. Kenmerken: geen autorijbewijs nodig, maximale snelheid van 45 km/u, geen APK-keuring, lage onderhoudskosten, standaard uitgerust met parkeercamera, elektrische ramen, bluetooth audio, led verlichting, centrale deurvergrendeling, volledig elektrisch. Modellen: Move E4, For Motion Dike, MOVE Vigorous 8, For Motion Brik, Move E3, Killerbee E-C…
5. Ligier – Elektrische Brommobielen
Domain: ligier.be
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: – Product: Elektrische brommobielen (citycars) van Ligier
– Prijs: Vanaf €12.995, afhankelijk van het batterijpakket
– Actieradius:
– 12,42 kWh accu: tot 192 km
– 8,28 kWh accu: tot 123 km
– 4,14 kWh accu: tot 63 km
– Oplaadtijd:
– 4 kWh accu: ongeveer 2 uur 30 minuten op een standaard stopcontact
– 12 kWh accu: ongeveer 6 uur 15 minuten op een standaard stopcontact
– Voordelen:
– S…
6. Fast Furious Scooters – Elektrische Brommobielen
Domain: fastfuriousscooters.nl
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Brommobiel kopen? Nieuw, elektrische & 100% rijbewijsvrij. Verschillende modellen beschikbaar: MOVE E3, MOVE E4, MOVE CityCar, MOVE Vigorous 8, MOVE Vigorous 1500, Killerbee Sunshine Q2. Prijzen variëren van €6.299,95 tot €9.999,95. Lease opties beschikbaar vanaf €146,47 p/m. Geschikt voor 2 personen, maximum snelheid 45 km/u. Geen rijbewijs nodig voor bepaalde modellen. Elektrische brommobielen z…
7. Mini Auto – Rijbewijsvrije Modellen
Domain: brommobielaanbod.nl
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Mini auto kopen of leasen? 100% rijbewijsvrije modellen. Mini auto biedt een compacte, elektrische en toegankelijke manier om zelfstandig en comfortabel te reizen. Modellen: For Motion Dike Scooter Auto, Move E4 Scootmobiel Auto, Move E3 Overdekte Driewieler, Move Vigorous 8, Move CityCar, Killerbee E-Car Microcar. Aanbiedingen: MOVE Vigorous 1500 InnerCity II €6,299.95, MOVE Vigorous 1500 S-line …
8. IVA Citycar – 25km Auto
Domain: riminicars.nl
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: {“Merk”:”IVA Citycar Brommobiel”,”Type”:”25km Auto”,”Aantal_deuren”:2,”Transmissie”:”Automaat”,”Tellerstand”:”1 KM”,”Bouwjaar”:”15-12-2023″,”Brandstof”:”Elektrisch”,”Prijs”:”€ 7.250,-“,”Kleur”:”overig”,”BTW/MARGE”:”BTW”,”Vermogen”:”0 PK”,”Carrosserie”:”Hatchback”,”Onderhoudsboekje”:”aanwezig? dealer”,”Bijtelling”:”0 %”}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric cars zonder rijbewijs
The growing popularity of electric cars zonder rijbewijs, particularly in emerging markets, presents significant opportunities for B2B buyers. These vehicles, often seen as safer alternatives to traditional scooters, cater to a diverse demographic, including young drivers and urban commuters. Strategic sourcing is essential, allowing buyers to identify reliable manufacturers and models that meet regional compliance and safety standards.
Furthermore, the competitive pricing and advanced features of electric brommobielen make them an attractive investment for businesses looking to expand their fleet or offer innovative transportation solutions. As the global market for electric vehicles continues to evolve, aligning with established suppliers can enhance supply chain efficiency and mitigate risks associated with fluctuating demand.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should actively explore partnerships with manufacturers of electric cars zonder rijbewijs. By doing so, they can leverage the growing trend of eco-friendly transportation, ultimately contributing to sustainability goals while addressing local mobility challenges. Now is the time to engage with suppliers and harness the potential of this burgeoning market.