Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pedal electric vehicle
In today’s rapidly evolving transportation landscape, sourcing reliable and efficient pedal electric vehicles (PEVs) is increasingly critical for businesses looking to enhance their logistics and mobility solutions. With growing environmental concerns and urban congestion, international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly Germany and Brazil—face the challenge of identifying the right PEVs that align with both their operational needs and sustainability goals.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of pedal electric vehicles available, including cargo models, commuter bikes, and innovative hybrid designs, while exploring their various applications across different sectors. Additionally, it provides actionable insights on supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and the latest technological advancements shaping the market.
By equipping B2B buyers with essential knowledge and best practices, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions that not only meet their logistical requirements but also contribute to a greener future. Whether you are seeking to enhance your fleet for urban deliveries or promote sustainable commuting options for employees, understanding the nuances of the pedal electric vehicle market is vital for success in today’s competitive landscape.
Understanding pedal electric vehicle Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Cargo Bikes | Enhanced storage capacity, often with additional cargo racks | Delivery services, urban logistics | Pros: High load capacity, eco-friendly; Cons: Heavier, may require larger storage space. |
| Pedal-Assist Commuter Bikes | Lightweight, designed for daily commuting, often foldable | Employee transportation, bike-sharing | Pros: Easy to store, promotes health; Cons: Limited range compared to larger models. |
| Pedal Electric Trikes | Stability with three wheels, often suitable for all ages | Senior mobility, recreational use | Pros: Enhanced stability, accessible for seniors; Cons: Bulkier, less maneuverable in tight spaces. |
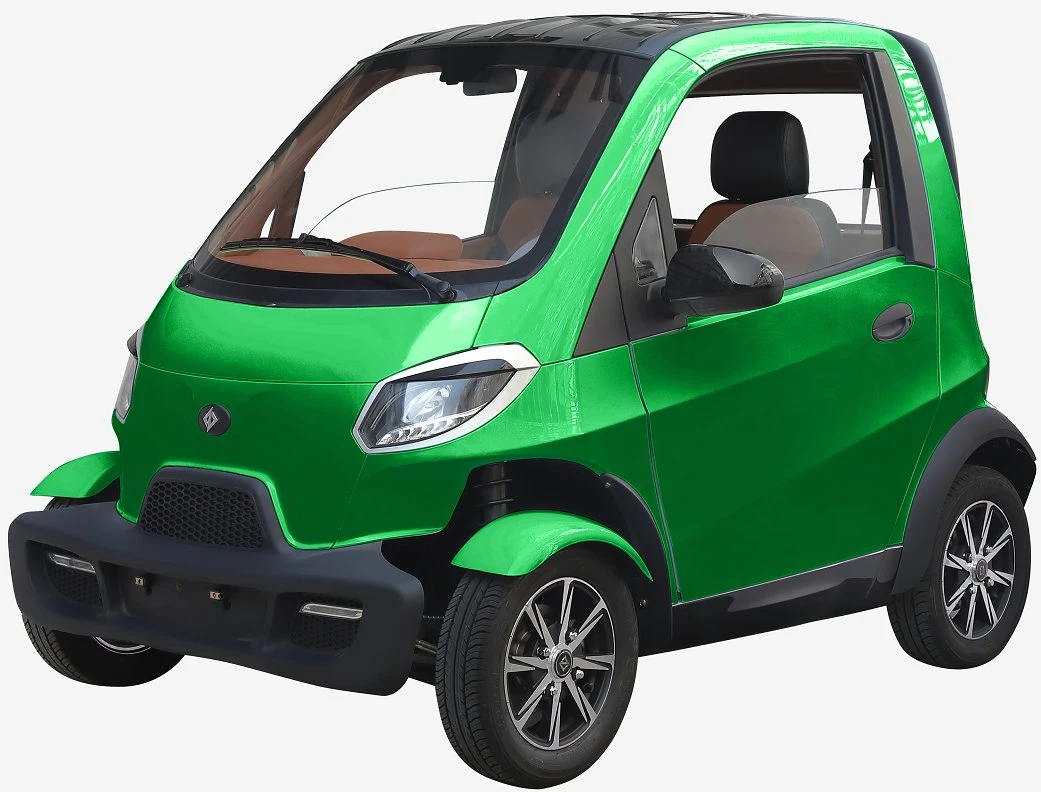
| Semi-Enclosed Velomobiles | Enclosed design for weather protection, car-like features | Urban commuting, short-distance travel | Pros: Comfort in various weather, unique appeal; Cons: Higher cost, may require more maintenance. |
| E-Bike Vans | Combination of bike and van features, often with passenger seating | Family transport, small group outings | Pros: Versatile use, can carry multiple passengers; Cons: Larger footprint, more complex maintenance. |
What Are Electric Cargo Bikes and Their B2B Applications?
Electric cargo bikes are designed to carry heavier loads than standard bicycles, often equipped with racks or storage compartments. Their primary applications include urban logistics and delivery services, making them ideal for businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint while enhancing delivery efficiency. When considering a purchase, businesses should evaluate the load capacity, battery life, and compatibility with existing logistics systems to ensure optimal integration.
How Do Pedal-Assist Commuter Bikes Benefit Businesses?
Pedal-assist commuter bikes are lightweight and typically designed for daily commuting, often featuring foldable designs for easy storage. These bikes are suitable for employee transportation and bike-sharing programs, promoting sustainable commuting options. B2B buyers should consider the range, charging time, and potential for employee health benefits when evaluating options, as these factors can significantly influence employee satisfaction and productivity.
Why Choose Pedal Electric Trikes for Senior Mobility?
Pedal electric trikes offer enhanced stability with three wheels, making them particularly suitable for seniors or those requiring additional support. Their applications extend to recreational use and senior mobility, providing a safe and enjoyable riding experience. Buyers in the B2B sector should assess the trike’s weight capacity, ease of access, and comfort features to meet the needs of their target demographic effectively.
What Makes Semi-Enclosed Velomobiles Unique for Urban Commuting?
Semi-enclosed velomobiles combine the benefits of cycling with the comfort of a vehicle, providing weather protection and a car-like driving experience. These vehicles are particularly appealing for urban commuting and short-distance travel. B2B purchasers should weigh the higher initial investment against the potential for increased user engagement and satisfaction, as well as consider the maintenance requirements of these more complex vehicles.
How Can E-Bike Vans Serve Family Transport Needs?
E-bike vans integrate the features of a bicycle with those of a van, allowing for passenger seating and versatility in transport. They are ideal for family transport and small group outings, appealing to businesses focused on family-friendly services. When evaluating these vehicles, buyers should consider the balance between capacity, ease of use, and the potential for unique marketing opportunities in their region.
Key Industrial Applications of pedal electric vehicle
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of pedal electric vehicle | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Logistics | Last-mile delivery solutions | Reduces transportation costs and carbon footprint | Durability, battery life, and cargo capacity |
| Tourism and Recreation | Guided bike tours and rentals | Enhances customer experience and promotes eco-tourism | Customization options and service support |
| Municipal Services | Public transport alternatives | Alleviates traffic congestion and promotes sustainability | Compliance with local regulations and safety standards |
| Education and Training | Campus transportation for students and staff | Increases accessibility and reduces parking needs | Battery range and ease of use |
| Health and Wellness | Community health programs promoting active transport | Encourages physical activity and reduces healthcare costs | Ergonomics and safety features |
How Can Urban Logistics Benefit from Pedal Electric Vehicles?
In urban logistics, pedal electric vehicles are increasingly utilized for last-mile delivery solutions. These vehicles enable companies to efficiently transport goods within congested city areas while minimizing traffic delays and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By integrating pedal electric vehicles into their logistics operations, businesses can significantly lower transportation costs and enhance their sustainability profiles. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, it is crucial to assess the durability and battery life of these vehicles, as they may face varied terrains and conditions.
What Role Do Pedal Electric Vehicles Play in Tourism and Recreation?
In the tourism and recreation sector, pedal electric vehicles serve as an attractive option for guided bike tours and rentals. They not only enhance the customer experience by offering a unique and eco-friendly way to explore attractions but also promote sustainable tourism practices. Businesses looking to invest in this area should consider customization options to cater to diverse tourist preferences and ensure robust service support to maintain vehicle performance. This is especially relevant for buyers in Europe, where eco-tourism is gaining traction.
How Can Municipal Services Use Pedal Electric Vehicles for Public Transport?
Municipal services are leveraging pedal electric vehicles as public transport alternatives to alleviate traffic congestion and promote sustainable urban mobility. These vehicles can operate on bike lanes, providing a flexible and efficient means of transport for residents. For municipalities, compliance with local regulations and safety standards is paramount when sourcing these vehicles, ensuring they meet the operational requirements of their regions. This application is particularly relevant in densely populated urban areas in Europe and the Middle East.
Why Are Pedal Electric Vehicles Ideal for Education and Training?
In educational institutions, pedal electric vehicles can facilitate campus transportation for students and staff, enhancing accessibility while reducing the need for parking spaces. These vehicles support a culture of sustainability and health by encouraging active transport among the campus community. Buyers in this sector should prioritize battery range and user-friendliness when sourcing these vehicles, ensuring they meet the diverse needs of students and staff, particularly in regions where access to traditional transport may be limited.
How Do Pedal Electric Vehicles Contribute to Health and Wellness Initiatives?
Pedal electric vehicles play a vital role in community health programs that promote active transport. By providing an accessible means of transportation, these vehicles encourage physical activity and contribute to improved public health outcomes, potentially reducing healthcare costs for communities. Businesses and organizations should focus on ergonomics and safety features when sourcing these vehicles, ensuring they are suitable for a wide range of users and can effectively support health initiatives in various international markets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pedal electric vehicle’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Infrastructure Limitations for Pedal Electric Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America often face significant infrastructure challenges when integrating pedal electric vehicles (PEVs) into their operations. Inadequate bike lanes, poorly maintained roads, and a lack of charging stations can deter potential users from adopting these vehicles. This not only limits the utility of PEVs but also raises concerns about safety and reliability, making it difficult for businesses to justify the investment.
The Solution: To overcome these infrastructure challenges, buyers should engage in dialogue with local government entities and community stakeholders to advocate for improved cycling infrastructure. By forming partnerships with local authorities, businesses can promote the development of dedicated bike lanes and the installation of charging stations specifically for PEVs. Additionally, conducting pilot projects that demonstrate the benefits of PEVs can help generate public interest and support. Buyers can also consider sourcing PEVs designed for rough terrains or those equipped with solar charging capabilities, which can minimize reliance on existing infrastructure and enhance operational flexibility.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Maintenance and Support for Pedal Electric Vehicles
The Problem: One of the primary concerns for businesses investing in pedal electric vehicles is the ongoing maintenance and support required to keep them operational. Many buyers worry about the availability of replacement parts and the accessibility of qualified service centers, especially in remote or underserved areas. This uncertainty can lead to extended downtimes, impacting logistics and overall productivity.
The Solution: B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing PEVs from manufacturers that offer comprehensive support packages, including warranties and readily available replacement parts. Conducting thorough research to identify manufacturers with established service networks is crucial. It’s advisable to build relationships with local service providers who can offer maintenance and repair services. Additionally, businesses can consider investing in training programs for their staff to perform basic maintenance tasks, which can significantly reduce downtime. Creating a maintenance schedule and keeping an inventory of essential spare parts can also ensure that operations remain uninterrupted.
Scenario 3: Addressing Range Anxiety and Battery Performance Concerns
The Problem: Range anxiety is a significant barrier for many businesses considering the adoption of pedal electric vehicles. In regions with vast distances between destinations or limited access to charging facilities, buyers may be concerned about the battery life and performance of PEVs. This apprehension can hinder investment decisions and limit the potential for widespread adoption within logistics and transportation sectors.
The Solution: To mitigate range anxiety, B2B buyers should thoroughly evaluate the battery specifications and range capabilities of the PEVs they are considering. Opting for models with higher battery capacities and those featuring regenerative braking systems can enhance overall efficiency. Buyers should also assess the feasibility of integrating charging solutions at key operational hubs to ensure vehicles are consistently charged and ready for use. Implementing route planning software that optimizes travel distances and includes charging station locations can further enhance efficiency. Providing training for staff on best practices for battery management can also extend the life of the batteries and improve performance, ensuring that businesses can maximize their investment in pedal electric vehicles.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pedal electric vehicle
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Pedal Electric Vehicles?
When selecting materials for pedal electric vehicles (PEVs), it’s crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and disadvantages, particularly from a B2B perspective. This analysis will cover aluminum, carbon fiber, steel, and plastics, focusing on their performance and suitability for international markets.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Pedal Electric Vehicles?
Aluminum is a lightweight metal known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, making it a popular choice for PEV frames and components. It has a high corrosion resistance, which is vital for vehicles exposed to various weather conditions. Aluminum can withstand temperatures up to 600°C and pressures of around 300 MPa, ensuring durability in diverse environments.
Pros: Aluminum is relatively easy to manufacture and can be extruded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs. It is also recyclable, aligning with sustainability goals.
Cons: While aluminum is durable, it can be more expensive than steel, impacting overall production costs. Additionally, it may not provide the same strength as steel in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum components are suitable for electric bike frames, battery casings, and wheels. However, buyers should consider the local availability and cost fluctuations in different regions.
International Considerations: Buyers in Africa and South America should be aware of local aluminum supply chains and recycling initiatives. In Europe, compliance with standards such as DIN EN 573 for aluminum alloys is essential.
What Advantages Does Carbon Fiber Offer for Pedal Electric Vehicles?
Carbon fiber is a composite material known for its exceptional strength and lightweight properties, making it ideal for high-performance PEVs. It can withstand temperatures of up to 200°C and has excellent fatigue resistance.
Pros: Carbon fiber components can significantly reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, enhancing performance and energy efficiency. The material also allows for greater design flexibility.
Cons: The primary drawback is the high manufacturing cost and complexity, which can limit its use to premium PEV models. Additionally, carbon fiber can be less impact-resistant compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Carbon fiber is often used in high-end bike frames, forks, and other critical components where weight savings are paramount.
International Considerations: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards like ISO 527 for tensile properties. In regions like Europe, sustainability certifications may also influence purchasing decisions.
How Does Steel Compare in the Context of Pedal Electric Vehicles?
Steel is a traditional material used in bicycle manufacturing, known for its strength and durability. It can handle high stress and is generally more affordable than aluminum and carbon fiber. Steel has a temperature rating of around 400°C and can withstand significant pressure.
Pros: Steel offers excellent impact resistance and is easy to weld, making it suitable for various applications. Its lower cost makes it an attractive option for mass production.
Cons: The primary disadvantage is its weight, which can negatively impact the overall efficiency of the vehicle. Additionally, steel is prone to corrosion if not adequately treated.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used for frames, handlebars, and other structural components.
International Considerations: Compliance with ASTM A500 standards is crucial for buyers in North America, while European buyers should refer to EN 10025 for structural steel.
What Role Do Plastics Play in Pedal Electric Vehicles?
Plastics, particularly engineering-grade polymers, are increasingly used in pedal electric vehicles for components like fenders, battery housings, and electrical enclosures. They are lightweight and can withstand various environmental conditions.
Pros: Plastics are generally cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs. They also offer good corrosion resistance.
Cons: While durable, plastics may not provide the same structural integrity as metals, particularly in high-stress applications. Their environmental impact during disposal is also a concern.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for non-structural components, such as body panels and interior fittings.
International Considerations: Buyers should consider local regulations regarding plastic recycling and disposal, especially in Europe, where stringent environmental laws apply.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Pedal Electric Vehicles
| Material | Typical Use Case for pedal electric vehicle | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Frames, battery casings, wheels | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost than steel | Medium |
| Carbon Fiber | High-end bike frames, forks | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High manufacturing cost | High |
| Steel | Structural components, frames | Strong and impact-resistant | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Low |
| Plastics | Fenders, battery housings | Cost-effective and moldable | Lower structural integrity | Low |
This material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with performance, cost, and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pedal electric vehicle
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Pedal Electric Vehicles?
The manufacturing of pedal electric vehicles (PEVs) involves several critical stages, ensuring that each unit meets the required performance and safety standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared for Pedal Electric Vehicles?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. High-quality materials, including aluminum for frames, lithium-ion batteries, and composite materials for body parts, are sourced from reliable suppliers. The selection of these materials is crucial as they impact the vehicle’s weight, durability, and overall performance. Materials undergo rigorous inspection upon arrival at the manufacturing facility, where they are evaluated for compliance with international standards and specifications.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used?
The forming stage involves shaping the materials into components necessary for the PEV. Techniques such as extrusion, stamping, and CNC machining are commonly employed. For instance, aluminum frames are often extruded to achieve lightweight yet strong structures. The use of advanced technologies like 3D printing is also gaining traction, allowing for customized parts and rapid prototyping. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for B2B buyers looking for tailored solutions.
How Are Pedal Electric Vehicles Assembled?
The assembly process is a crucial phase where individual components come together to form the complete vehicle. This step typically involves skilled labor and automated systems to ensure precision. Key components such as the motor, battery, and control systems are integrated into the frame, with careful attention to wiring and connections. Assembly lines are designed to optimize efficiency, reducing lead times while maintaining high standards of quality.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used in Pedal Electric Vehicle Manufacturing?
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetic appeal and protective qualities of the PEV. Techniques such as powder coating and anodizing are employed to provide a durable finish that resists corrosion and wear. Quality checks are conducted throughout the finishing stage to ensure that the final product meets visual and functional standards.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Pedal Electric Vehicles?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the production of pedal electric vehicles, ensuring that every unit is safe, reliable, and compliant with regulations. The most relevant international standard for QA in manufacturing is ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has a systematic approach to managing quality, which is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable partners.
Which Industry-Specific Certifications Should B2B Buyers Look For?
In addition to ISO standards, pedal electric vehicles often need to meet industry-specific certifications such as CE marking in Europe, which indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For buyers in the Middle East or Africa, compliance with local regulations and standards is equally important. Understanding these certifications helps B2B buyers ensure that the products they procure meet the necessary legal and safety requirements.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in Pedal Electric Vehicle Production?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure adherence to specifications. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage inspects raw materials and components upon arrival. Ensuring that all materials meet quality standards before production begins minimizes the risk of defects.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing process, this stage involves regular inspections to verify that production processes are being followed correctly. This may include checking weld quality, component alignment, and electronic connections.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products leave the factory, they undergo a final inspection to ensure they meet all specifications. This may involve functional testing, performance evaluations, and visual inspections.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who maintain transparent quality control processes. Here are some actionable steps to verify supplier QC:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of manufacturing facilities can provide insights into a supplier’s QC practices. Buyers should inquire about the frequency and scope of these audits.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC checks. These reports should detail any defects found and corrective actions taken.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s quality assurance practices. This is particularly useful for B2B buyers who may lack the resources to perform in-depth inspections themselves.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential, especially when sourcing from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Each region may have different regulatory requirements and certification processes.
-
Regional Compliance: Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations that may affect product specifications, such as battery safety standards or emissions regulations.
-
Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality and compliance. Building relationships with suppliers and understanding their operational frameworks can help buyers navigate these differences effectively.
-
Documentation and Transparency: International buyers should ensure that suppliers provide clear documentation regarding compliance with both local and international standards. This transparency is crucial for building trust and ensuring product quality across borders.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for pedal electric vehicles are integral to producing high-quality, reliable products. By understanding these processes and actively engaging with suppliers, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and ensure they source the best products for their markets.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pedal electric vehicle’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed for B2B buyers looking to procure pedal electric vehicles (PEVs). As the demand for sustainable transportation solutions continues to rise, understanding the key factors in sourcing these vehicles is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This checklist will help you navigate the complexities of selecting the right supplier and product to meet your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for aligning your procurement with your business requirements. Consider factors such as vehicle capacity, battery life, range, and motor power. It’s also important to define any specific features needed for your target market, such as cargo space or passenger capacity.
- Consider the intended use: Will the vehicles be used for urban commuting, delivery, or recreational purposes?
- Assess regulatory compliance: Ensure that the specifications meet local regulations in your target market.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay informed about the latest trends and innovations in the pedal electric vehicle sector. Understanding current market dynamics can provide insights into what features or technologies may enhance your fleet’s performance.
- Look for technological advancements: Features such as smart connectivity, solar panels, or advanced battery technologies can differentiate products.
- Analyze competitor offerings: Study what competitors are using and how it impacts their efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s essential to thoroughly vet potential suppliers. This includes checking their reputation, financial stability, and customer service capabilities.
- Request comprehensive company profiles: Look for case studies and references from other B2B clients in your industry.
- Assess their production capacity: Ensure they can meet your order volume and delivery timelines.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications and Standards
Ensuring that your suppliers adhere to relevant industry standards and certifications can safeguard your investment. This step is particularly important for compliance with safety and environmental regulations.
- Check for international certifications: Look for ISO certifications or compliance with local regulations, especially in markets like Europe where standards are stringent.
- Evaluate sustainability practices: Assess their commitment to sustainability, which can enhance your brand’s image and appeal to eco-conscious consumers.
Step 5: Request Samples and Conduct Trials
Before finalizing any orders, request samples or conduct trials of the pedal electric vehicles. This allows you to evaluate the quality and performance of the products firsthand.
- Assess usability and comfort: Ensure that the vehicles meet user expectations in terms of ride comfort and ease of use.
- Test under real conditions: Conduct trials in environments similar to where the vehicles will be used to gauge performance.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier and product, it’s time to negotiate terms and conditions. This includes pricing, payment terms, warranty, and after-sales support.
- Clarify payment options: Explore financing options or payment plans that can benefit your cash flow.
- Ensure clear warranty terms: Understand what is covered under warranty and the process for claims, as this can affect long-term maintenance costs.
Step 7: Plan for After-Sales Support and Maintenance
Finally, consider the after-sales support and maintenance options available from your supplier. Reliable support is essential for minimizing downtime and ensuring the longevity of your fleet.
- Inquire about service networks: Ensure the supplier has a robust service network in your operational regions.
- Assess training options: Consider whether the supplier offers training for your staff on maintenance and operation to enhance efficiency.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for pedal electric vehicles, ensuring they make informed and strategic purchasing decisions.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pedal electric vehicle Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Pedal Electric Vehicles?
When sourcing pedal electric vehicles (PEVs), it’s vital for international B2B buyers to understand the underlying cost structure. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials significantly influence the overall cost. High-grade aluminum or carbon fiber frames, lithium-ion batteries, and advanced electronic components can elevate costs but enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely based on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can impact quality. Skilled labor, particularly in assembly and quality control, is crucial for maintaining high standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, rent, equipment maintenance, and other operational costs associated with the production facility. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, impacting the final pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, particularly for custom or specialized components. These costs are typically amortized over production runs, making larger orders more cost-effective.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes is essential to ensure product reliability and compliance with international standards. Effective QC can reduce return rates and enhance brand reputation, justifying higher upfront costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and insurance, vary significantly based on the destination and the mode of transport. Understanding the logistics involved can prevent unexpected expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will build in a profit margin that reflects their operational costs and market position. This can vary based on the supplier’s brand strength and market demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Pedal Electric Vehicle Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of pedal electric vehicles:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchasing often leads to lower unit costs. Buyers should negotiate terms that allow for larger orders to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized features, such as unique designs or specific components, can increase costs. Buyers should assess whether these specifications provide sufficient value to justify the additional expense.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials typically come at a premium but can lead to lower maintenance costs and longer product lifespans. Certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may also affect pricing, as they require adherence to specific manufacturing standards.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, lead times, and reliability can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their products due to perceived quality and service levels.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can significantly affect total costs. Buyers should understand the implications of terms like FOB (Free on Board) versus CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) to manage risk and expenses effectively.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Negotiating Pedal Electric Vehicle Prices?
Navigating the procurement of pedal electric vehicles requires strategic negotiation and awareness of total cost implications:
-
Negotiate Terms and Conditions: Leverage volume and long-term relationships to negotiate better pricing and payment terms. Many suppliers are open to flexibility for larger orders.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also operational costs, maintenance, and potential resale value. A higher initial investment in quality may yield lower TCO over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Markets: Familiarize yourself with regional pricing differences. Factors like local tariffs, taxes, and currency fluctuations can impact overall costs. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these nuances is critical.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that quotes include a breakdown of all costs. This transparency aids in identifying areas for potential savings and facilitates easier comparisons between suppliers.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on supplier negotiations, market conditions, and changes in material costs. Buyers should conduct thorough research and engage in direct discussions with suppliers for accurate pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pedal electric vehicle With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Pedal Electric Vehicles
In the rapidly evolving landscape of urban mobility, pedal electric vehicles (PEVs) have emerged as a sustainable option for transportation. However, businesses and municipalities may explore various alternatives that also address mobility challenges, environmental concerns, and cost-effectiveness. This section evaluates PEVs against other viable solutions, such as traditional bicycles and electric scooters, to provide B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of their options.
Comparison of Pedal Electric Vehicles with Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Pedal Electric Vehicle | Traditional Bicycle | Electric Scooter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Top speed of 25 km/h, 40 km range | Varies by rider; limited speed and range | Typically 25 km/h, range of 20-40 km |
| Cost | $2,350 – $4,820 (varies by model) | $300 – $1,200 (varies by quality) | $300 – $1,500 (varies by model) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires some assembly; charging infrastructure needed | Minimal setup; no charging needed | Simple to use; charging infrastructure required |
| Maintenance | Moderate; battery and motor care needed | Low; mainly tire and brake maintenance | Moderate; battery and tire maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting, short trips, cargo | Casual commuting, fitness | Quick urban trips, short distances |
Pros and Cons of Each Alternative
Traditional Bicycle
Traditional bicycles are a cost-effective mode of transport, ideal for individuals seeking fitness benefits alongside commuting. They require minimal maintenance and do not rely on charging infrastructure, making them suitable for areas with limited access to electricity. However, their performance is heavily dependent on the rider’s physical ability, limiting speed and range compared to pedal electric vehicles. This makes them less practical for longer commutes or for transporting goods.
Electric Scooter
Electric scooters offer a convenient and straightforward solution for urban mobility, particularly in congested areas. Their compact design allows for easy maneuvering and parking, while the electric motor provides a boost that can help users travel longer distances with less physical exertion. However, they generally have a shorter range than pedal electric vehicles and require regular charging, which can be a challenge in areas lacking adequate infrastructure. Additionally, they may not be as versatile for carrying cargo or passengers.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between pedal electric vehicles and their alternatives, B2B buyers should consider their specific use cases, budget constraints, and infrastructure availability. Pedal electric vehicles excel in performance and cargo capacity, making them suitable for businesses focused on sustainable commuting and delivery solutions. In contrast, traditional bicycles can be the go-to for cost-sensitive buyers prioritizing fitness, while electric scooters provide a quick, convenient option for urban travel. Ultimately, the choice will depend on the target market’s needs, local conditions, and long-term goals for mobility solutions.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pedal electric vehicle
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Pedal Electric Vehicles?
Understanding the technical specifications of pedal electric vehicles (PEVs) is crucial for B2B buyers looking to invest in this rapidly evolving sector. Here are some of the critical specifications that influence performance, usability, and marketability:
-
Battery Capacity (Ah and Wh)
– Definition: Measured in amp-hours (Ah) and watt-hours (Wh), battery capacity indicates how much energy the battery can store. A higher capacity typically translates to longer range.
– B2B Importance: Buyers must assess battery capacity to ensure the vehicle meets operational needs, especially in regions where charging infrastructure may be limited. For instance, a vehicle with a 30-Ah battery can provide approximately 40 miles of range, making it suitable for urban commuting. -
Motor Power (Wattage)
– Definition: The power output of the electric motor, usually specified in watts (W), affects acceleration and top speed. Common ratings range from 250W to 750W.
– B2B Importance: Motor power determines the vehicle’s ability to handle various terrains and load capacities. Buyers should match motor power to intended use—higher wattage is beneficial for hilly or rugged environments. -
Weight Capacity (kg and lbs)
– Definition: The maximum weight the vehicle can safely carry, including passengers and cargo, is crucial for safety and performance.
– B2B Importance: Understanding weight capacity helps buyers choose vehicles that can accommodate their operational requirements. For example, a vehicle with a 160 kg (353 lbs) capacity is ideal for family transport or delivery services. -
Frame Material and Durability
– Definition: The construction material of the vehicle frame (e.g., aluminum, steel, carbon fiber) affects durability, weight, and cost.
– B2B Importance: Buyers must consider the environmental conditions in which the PEV will operate. For example, aluminum frames are lightweight and corrosion-resistant, making them suitable for coastal regions. -
Range per Charge (km or miles)
– Definition: The distance a PEV can travel on a single charge, often influenced by battery capacity, motor efficiency, and terrain.
– B2B Importance: Range is a critical factor for fleet operators or delivery services, as it affects operational efficiency and downtime for charging. A vehicle with a 65 km (40 miles) range may be adequate for urban routes but insufficient for long-distance applications.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Pedal Electric Vehicle Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B environment. Here are some commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers sourcing components or vehicles, as it impacts quality, pricing, and warranty support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: MOQ considerations can affect purchasing decisions, especially for smaller businesses or startups that may not need large volumes. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document issued by a buyer to request pricing and terms from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Importance: Utilizing RFQs helps buyers compare costs and negotiate better terms with multiple suppliers, leading to informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers for the delivery of goods under sales contracts.
– Importance: Knowing Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, crucial for international transactions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Importance: Buyers must consider lead times to plan inventory and operations effectively, especially in industries with tight delivery schedules.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing pedal electric vehicles, ensuring they choose products that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pedal electric vehicle Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Pedal Electric Vehicle Sector?
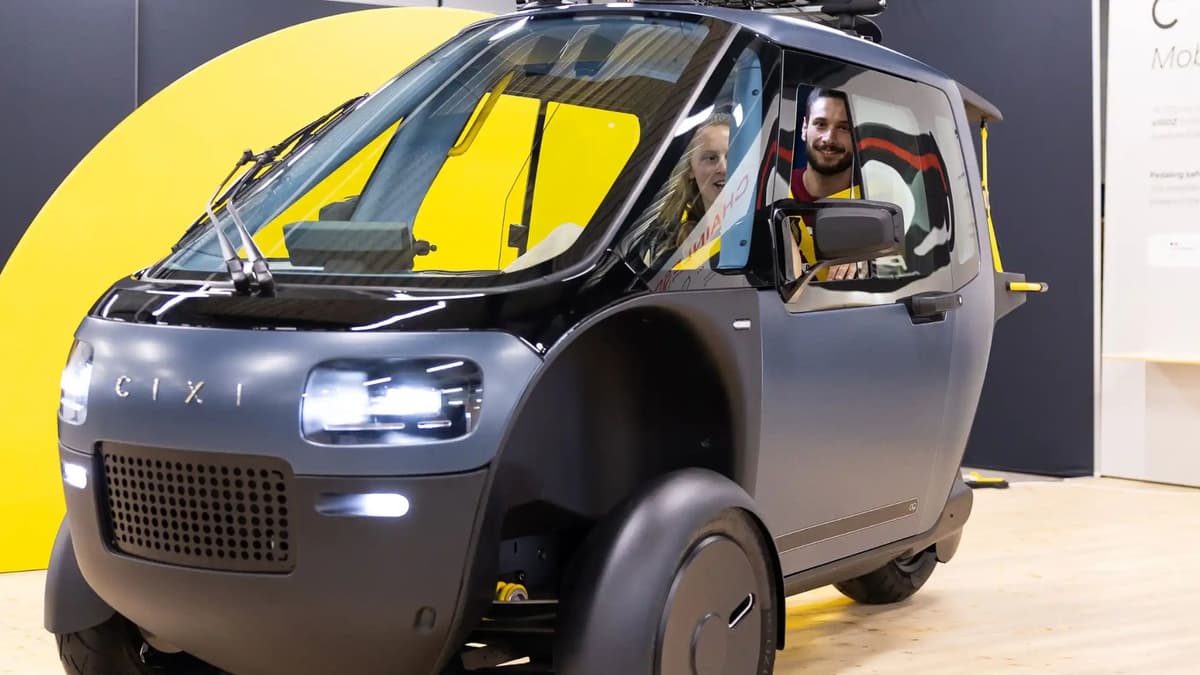
The pedal electric vehicle (PEV) market is experiencing significant growth, driven by a confluence of global factors. Increased urbanization, rising fuel prices, and growing concerns about climate change have amplified the demand for sustainable transport solutions. The global shift towards reducing carbon footprints is particularly pronounced in regions such as Europe and parts of Africa and South America, where government incentives and infrastructure improvements support the adoption of electric mobility. Notably, countries like Germany are leading the way in innovation, with products such as the Hopper—a hybrid vehicle combining bike and car features—setting new benchmarks for design and functionality.
Emerging B2B technology trends include the integration of smart features like IoT capabilities in electric bikes and enhanced battery technology, which increases range and efficiency. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce has led manufacturers to explore direct-to-consumer sales models, streamlining the supply chain and enhancing customer engagement. For B2B buyers, understanding these market dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions that align with consumer preferences and regulatory standards.
How Is Sustainability Impacting Sourcing Trends in the Pedal Electric Vehicle Sector?
Sustainability is a paramount concern in the pedal electric vehicle sector, influencing sourcing decisions at every level. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, as well as the lifecycle of the vehicles, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing practices and sustainability. This includes using recycled materials, minimizing waste, and ensuring that manufacturing processes are energy-efficient.
Moreover, ‘green’ certifications have gained traction, serving as essential indicators of a product’s environmental impact. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) or the Energy Star label are becoming crucial for B2B buyers looking to align their procurement strategies with sustainability goals. This trend is particularly relevant in regions like Europe, where regulatory frameworks are stringent and consumers are more environmentally conscious.
How Has the Pedal Electric Vehicle Sector Evolved Over Time?
The pedal electric vehicle sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, e-bikes were viewed primarily as niche products, catering to specific demographics such as commuters and recreational users. However, advancements in battery technology, coupled with increased urban congestion and the need for eco-friendly transportation options, have propelled PEVs into the mainstream.
In the early 2000s, the introduction of lithium-ion batteries revolutionized the industry, allowing for lighter, more efficient designs. Today, innovative models like the Hopper exemplify the modern PEV’s blend of functionality and sustainability, appealing to a broader audience. As the sector continues to mature, it is poised to play a vital role in reshaping urban mobility across continents, making it a focal point for B2B buyers seeking long-term partnerships and sustainable solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pedal electric vehicle
-
1. How do I choose the right pedal electric vehicle for my business needs?
Selecting the appropriate pedal electric vehicle (PEV) involves evaluating your specific operational requirements. Consider factors such as the terrain where the vehicles will be used, the average load they need to carry, and the expected range on a single charge. Additionally, assess the vehicle’s capacity for customization, as this can greatly enhance functionality for your business. Research the manufacturer’s reputation and customer service capabilities, especially in your region, to ensure ongoing support and maintenance. -
2. What are the common customization options available for pedal electric vehicles?
Customization options for pedal electric vehicles often include adding cargo racks, specialized seating, and upgraded battery capacities. Some manufacturers allow for color and branding choices, which can enhance your business’s visibility. Additionally, you may find options for integrating technology such as GPS tracking, mobile device chargers, or specialized lighting systems. Always discuss customization possibilities with suppliers to ensure they meet your operational needs and comply with local regulations. -
3. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for pedal electric vehicles?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for pedal electric vehicles can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer and the specific model. Generally, larger manufacturers might have higher MOQs, ranging from 10 to 50 units, while smaller producers may accept smaller orders. It’s essential to communicate your needs clearly during the negotiation process. Consider factors such as your budget and expected demand when determining how many vehicles to order. -
4. How do I verify the credibility of a pedal electric vehicle supplier?
Verifying the credibility of a supplier involves several steps. Start by checking their business credentials, including registration and certifications. Look for customer reviews and case studies to gauge their reliability and service quality. Additionally, inquire about their experience in your specific market, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Request references from other B2B clients, and consider visiting their facility if feasible. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing pedal electric vehicles?
Payment terms for sourcing pedal electric vehicles typically vary by supplier but may include options like upfront payments, deposits, and installment plans. Some suppliers may offer financing options or payment through letters of credit, particularly for larger orders. Ensure that the payment terms are clearly defined in the contract to avoid any misunderstandings. Negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs and operational timeline. -
6. What quality assurance measures should I look for in pedal electric vehicles?
Quality assurance measures are crucial for ensuring the reliability and safety of pedal electric vehicles. Look for suppliers who adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Inquire about their testing processes for durability, battery performance, and safety features. Request documentation regarding warranties and service agreements to understand the level of support you can expect post-purchase. Comprehensive QA processes will minimize potential issues down the line. -
7. How is logistics managed when importing pedal electric vehicles?
Logistics for importing pedal electric vehicles involves coordination between suppliers, shipping companies, and customs authorities. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, including freight terms (FOB, CIF, etc.) and estimated delivery times. Ensure that the supplier provides necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices and shipping manifests. It’s advisable to work with a logistics partner experienced in international trade to navigate potential challenges and ensure timely delivery. -
8. What are the regulatory considerations for using pedal electric vehicles in different countries?
Regulatory considerations for pedal electric vehicles can differ significantly across countries and regions. Familiarize yourself with local laws regarding vehicle classification, safety standards, and usage in bike lanes or on public roads. In some regions, you may need to register the vehicles or obtain specific permits. Consult with local authorities or legal experts to ensure compliance with all regulations to avoid fines or operational disruptions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Pedal Electric Vehicle Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Pedal Electric – Premium E-Bike H/T
Domain: pedalelectric.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Electric Pedal Bike: Premium E-Bike
– Free Shipping: Lower 48 States with Code: LDFREESHIP
– Models:
1. H/T
– Price: $2,350
– Color Options: Onyx Black, Bone White
– Range: 40-60 miles
– Motor: 1 x 750W
– Battery: 768Wh
– Speed: 28 MPH (Class 3), 20 MPH (Class 2)
2. CORE 2.0
– Price: $2,650
– Color Options: Onyx Black, Olive Green
– Range: 30-50 mil…
2. Hopper Mobility – The Hopper
Domain: newatlas.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: The Hopper is a pedal-electric, semi-enclosed three-wheeler manufactured by Hamburg-based startup Hopper Mobility. It measures 212 cm long by 115 cm wide (6 ft, 11 in by 3 ft, 9 in) and features two 20-inch bicycle tires in the front and a 10-inch scooter tire in the rear. The vehicle is powered by a 250-watt rear hub motor, allowing a top speed of 25 km/h (16 mph) and a range of approximately 65 …
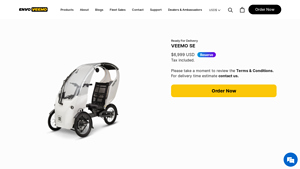
3. Veemo SE – Urban Mobility Redefined
Domain: veemo.ca
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Veemo SE”, “price”: “$6,999 USD”, “description”: “A semi-enclosed, pedal-electric vehicle designed for urban mobility, combining the comfort and stability of a car with the efficiency of a bicycle, offering weather protection and suitability for bike lanes.”, “max_speed”: “32km/h (25km/h for EU)”, “max_torque”: “80Nm”, “transmission”: “Shimano Altus 9 Speed”, “battery”: “48V15Ah”, “suspe…
4. Motoring Electric – One-Pedal Driving System
Domain: motoringelectric.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: One-pedal driving allows electric car owners to operate the vehicle using only the accelerator pedal, utilizing regenerative braking to slow down the car. This system converts the electric motor into a generator when the driver lifts off the accelerator, slowing the vehicle and recharging the battery simultaneously. While it enhances driving ease and can slightly extend range, it may not be suitab…
5. VinFast – One-Pedal Driving Feature
Domain: ewingvinfastofplano.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: One-pedal driving feature in VinFast VF8 and VF9 allows driving with just the accelerator, minimizing brake pedal use. The electric motor slows the vehicle when the throttle is released, utilizing regenerative braking to recover energy. Regenerative braking can be adjusted via a 15.6-inch infotainment display, with options from low to high and a Creep Mode for gradual movement. Brake lights activa…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pedal electric vehicle
In the evolving landscape of transportation, pedal electric vehicles (PEVs) are emerging as a pivotal solution for sustainable commuting and last-mile connectivity. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the diverse offerings—from premium crafted electric bikes to innovative hybrid models like the Hopper—can provide a competitive edge. The strategic sourcing of these vehicles not only enhances fleet efficiency but also aligns with global sustainability goals, addressing the urgent need for eco-friendly transport alternatives.
Investing in PEVs allows businesses to tap into a growing market driven by consumer demand for environmentally responsible choices. As manufacturers innovate with features such as electric pedal-by-wire systems and integrated cargo solutions, buyers should leverage these advancements to meet specific regional needs and preferences.
Looking ahead, the potential for pedal electric vehicles is vast, with opportunities for collaboration across various sectors. International buyers are encouraged to engage with manufacturers, explore financing options, and adapt to this transformative shift in mobility. By positioning themselves strategically within this market, businesses can lead the charge towards a greener, more sustainable future in transportation.