Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric car coc eec
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicles, navigating the complexities of Electric Car Certificate of Conformity (EEC COC) is a critical challenge for international B2B buyers. As businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (including emerging markets like Vietnam and Brazil) seek to source compliant electric vehicles, understanding the EEC certification process becomes paramount. This guide aims to demystify the EEC COC requirements, detailing the types of vehicles eligible for certification, their applications, and the critical steps in supplier vetting.
Buyers will gain valuable insights into the compliance landscape, including essential documentation such as the World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI), ISO certifications, and E-MARK certificates for components. Moreover, this guide will cover cost considerations and strategies for sourcing high-quality electric vehicles that meet international standards. By leveraging this comprehensive resource, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring their investments align with both regulatory requirements and market demands.
Ultimately, this guide serves as a strategic tool for businesses looking to thrive in the global electric vehicle market, empowering them to navigate certification challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities in sustainable transportation. With the right knowledge, your business can not only comply with EEC regulations but also position itself as a leader in the burgeoning electric vehicle sector.
Understanding electric car coc eec Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| L6e Electric Vehicle | Limited speed (up to 45 km/h), compact design, typically 3-4 seats | Urban commuting, short-distance transport | Pros: Cost-effective, eco-friendly; Cons: Limited speed and range. |
| L7e Electric Vehicle | Higher speed capabilities (up to 70 km/h), more robust design | Delivery services, light cargo transport | Pros: Versatile, suitable for varied applications; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
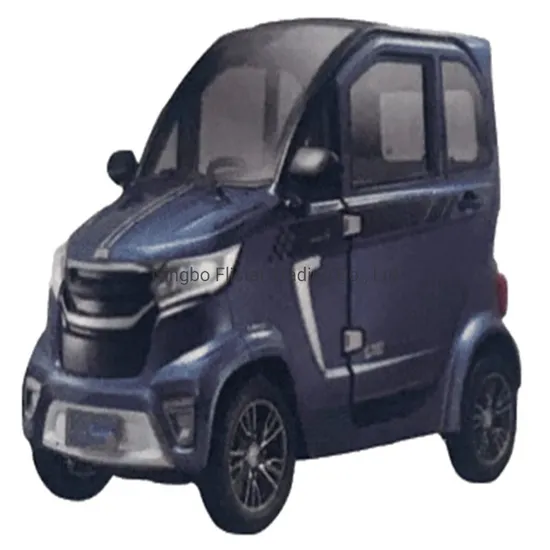
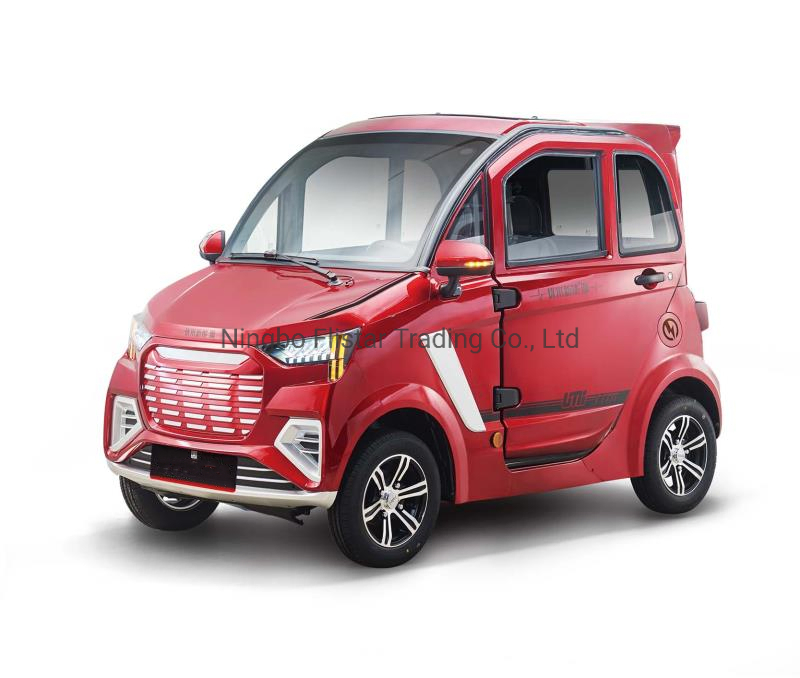
| EEC COC Mini Electric Car | Fully enclosed, designed for passenger comfort, often 2-4 seats | Personal use, small family transport | Pros: Safety features, comfortable; Cons: May have limited cargo capacity. |
| EEC COC Electric Cargo Vehicle | Designed for transporting goods, often with larger cargo space | Logistics, last-mile delivery | Pros: Efficient for urban deliveries; Cons: Limited passenger capacity. |
| Electric Pedal-Assisted Bicycle | Lightweight, compliant with specific EU standards, high maneuverability | Recreational, urban commuting | Pros: Promotes sustainability, easy to use; Cons: Not suitable for long distances. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of L6e Electric Vehicles?
L6e electric vehicles are designed for urban environments, offering a compact size that allows for easy navigation through tight spaces. They typically have a maximum speed of 45 km/h and are ideal for short-distance commuting or local errands. B2B buyers in sectors like urban transport or local service providers will find these vehicles cost-effective and eco-friendly, although their limited speed and range may not suit all operational needs.
How Do L7e Electric Vehicles Stand Out in the Market?
The L7e category of electric vehicles is characterized by its higher speed capabilities, reaching up to 70 km/h, making them suitable for a broader range of applications, including delivery services and light cargo transport. Their robust design allows for versatility in usage. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment costs against the potential for increased operational efficiency, especially in logistics and delivery sectors where speed is critical.
What Makes EEC COC Mini Electric Cars a Suitable Choice?
EEC COC mini electric cars are fully enclosed vehicles designed for passenger comfort, typically accommodating 2-4 individuals. They are particularly suited for personal use or small family transport in urban settings. B2B buyers in the tourism or rental sectors may find these vehicles appealing due to their safety features and comfort, but potential limitations in cargo capacity should be considered.
Why Are Electric Cargo Vehicles Essential for Logistics?
Electric cargo vehicles are specifically designed for transporting goods, featuring larger cargo spaces to accommodate various types of deliveries. They are particularly effective in last-mile delivery scenarios, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional delivery methods. B2B buyers in the logistics sector should evaluate the efficiency gains against the limited passenger capacity, ensuring that the vehicle aligns with their operational needs.
How Do Electric Pedal-Assisted Bicycles Fit into Urban Transportation?
Electric pedal-assisted bicycles provide a lightweight and maneuverable option for urban commuting and recreational use. They comply with specific EU standards, promoting sustainability in transportation. For B2B buyers in sectors such as tourism or urban mobility solutions, these bicycles can enhance service offerings. However, their suitability for longer distances may limit their appeal for certain applications.
Key Industrial Applications of electric car coc eec
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric car coc eec | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Mobility Solutions | Low-speed electric vehicles for urban commuting | Reduces traffic congestion and lowers emissions | Ensure compliance with local EEC regulations and sourcing E-MARK certified components. |
| Logistics and Delivery | Electric delivery vans for last-mile logistics | Cost-effective, eco-friendly transportation, and efficiency | Verify vehicle range and battery life to meet delivery demands; consider local charging infrastructure. |
| Tourism and Leisure | Electric mini-cars for tourist attractions | Enhances visitor experience while promoting sustainability | Assess vehicle design and comfort features suitable for tourist use; ensure compliance with safety standards. |
| Public Transportation | Electric shuttle buses for public transit systems | Provides a clean alternative for public transport | Focus on capacity and range requirements; consider partnerships with local governments for subsidies. |
| Industrial and Commercial Use | Electric utility vehicles for warehouses and factories | Increases operational efficiency and reduces carbon footprint | Evaluate charging capabilities and fleet management solutions; ensure compliance with EEC certification. |
How Do Electric Vehicles Transform Urban Mobility Solutions?
Low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) are increasingly utilized in urban mobility solutions, providing an eco-friendly alternative for city commuting. These vehicles help alleviate traffic congestion and significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, understanding local regulations regarding EEC certification is crucial. Buyers should ensure that the vehicles sourced comply with EU standards, focusing on the supply of certified components to maintain operational integrity.
What Role Do Electric Delivery Vans Play in Logistics and Delivery?
Electric delivery vans are revolutionizing the logistics sector, particularly for last-mile deliveries in urban areas. They offer a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution, contributing to lower operational costs and enhanced delivery efficiency. International B2B buyers must assess the vehicle’s range and battery life to ensure they meet the demands of their delivery routes. Additionally, considering the local charging infrastructure is vital for operational continuity and efficiency.
How Are Electric Mini-Cars Enhancing Tourism and Leisure Experiences?
Electric mini-cars are becoming popular in tourist attractions, providing visitors with a unique way to explore while minimizing environmental impact. These vehicles enhance the tourist experience by offering convenience and accessibility in busy areas. Buyers from tourist-heavy regions should focus on vehicle design, comfort, and safety features to ensure they meet the expectations of travelers. Compliance with EEC safety standards is also essential for maintaining a reputable service.
Why Are Electric Shuttle Buses Important for Public Transportation?
Electric shuttle buses are an innovative solution for public transportation systems, providing a sustainable alternative to traditional diesel buses. They help cities reduce their carbon footprint while improving air quality. B2B buyers in this sector should prioritize understanding the specific capacity and range requirements dictated by their local transit systems. Partnering with local governments can also facilitate access to subsidies and funding opportunities for electric vehicle integration.
What Are the Benefits of Electric Utility Vehicles in Industrial and Commercial Use?
Electric utility vehicles are transforming operations in warehouses and factories by enhancing efficiency and reducing carbon emissions. These vehicles are particularly beneficial for transporting goods within large facilities. For international buyers, evaluating the charging capabilities and fleet management solutions is essential to maximize operational efficiency. Ensuring that these vehicles meet EEC certification requirements is also critical for seamless integration into existing operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric car coc eec’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex EEC Certification Processes
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those new to the electric vehicle market, struggle with the intricate certification process required for electric cars to comply with EEC regulations. The ambiguity surrounding various terms like COC, WVTA, and type approval can create confusion, leading to delays in product launches and increased costs. Buyers often find it challenging to ensure that all components meet the mandatory E-MARK certification, which can cause setbacks if any part fails to comply.
The Solution: To effectively navigate the EEC certification process, B2B buyers should establish a clear checklist based on the latest regulations. This checklist should include obtaining a valid World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI), ensuring ISO certification is up-to-date, and sourcing components with current E-MARK certifications. Engaging a consulting firm with expertise in EEC compliance can also streamline the process, as they can provide insights and assist in the documentation required for certification. Additionally, building strong relationships with reliable component suppliers who consistently meet E-MARK standards will mitigate risks of delays or compliance issues.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Component Compliance for Electric Vehicles
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges ensuring that all components of their electric vehicles are compliant with EEC regulations. This is particularly problematic for manufacturers who wish to source parts from multiple suppliers. A failure to maintain compliance across components can jeopardize the entire vehicle’s EEC certification, leading to costly re-evaluations and potential market entry delays.
The Solution: To overcome this hurdle, buyers should implement a robust component sourcing strategy. This involves selecting suppliers who are not only compliant but also provide full transparency regarding the certification status of their components. Establishing long-term contracts with these suppliers can ensure consistency in quality and compliance. Furthermore, conducting regular audits of suppliers can help maintain standards and identify any potential compliance issues early in the production process. Leveraging a centralized database to track the certification status of all components used can also enhance oversight and facilitate smoother certification processes.
Scenario 3: Finding Authorized EU Representatives for EEC Certification
The Problem: For international buyers, especially those operating outside the EU, finding an authorized representative within the EU can be a significant obstacle. The requirement for an EU-based representative complicates the certification process and adds to the operational complexities, as buyers may not have established networks in the EU region.
The Solution: Buyers can address this challenge by researching and partnering with third-party firms that specialize in EEC certification and compliance. These firms often have established networks and can serve as authorized representatives, easing the burden on manufacturers. It’s beneficial to select a representative who has experience in the electric vehicle sector and understands the nuances of EEC regulations. Additionally, buyers should consider joining industry associations or forums focused on electric vehicles, as these platforms can provide valuable connections to potential representatives and insights into best practices for navigating certification challenges. By proactively addressing this requirement, B2B buyers can streamline their certification process and enhance their market readiness.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric car coc eec
What Are the Key Materials Used in Electric Car COC EEC Manufacturing?
When selecting materials for electric vehicles (EVs) that comply with EEC certification, it is crucial to consider properties such as durability, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with various applications. Here are four common materials used in the manufacturing of electric cars, along with their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Aluminum: A Lightweight Champion
Key Properties: Aluminum is known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. It typically withstands temperatures up to 600°C and is resistant to oxidation, making it ideal for various automotive applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which enhances vehicle efficiency and range. However, it can be more expensive than steel, and its manufacturing process may involve complex techniques like extrusion and casting, which could increase production costs.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in the chassis and body of electric vehicles, contributing to weight reduction and improved energy efficiency. It is compatible with various media, including battery systems, without significant risk of corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa and South America should ensure that suppliers adhere to international standards like ASTM and ISO for aluminum quality. Additionally, understanding local sourcing capabilities can help mitigate costs.
Steel: The Traditional Workhorse
Key Properties: Steel offers high tensile strength and durability, with temperature ratings typically ranging from -40°C to 600°C. It is also highly resistant to impact and wear.
Pros & Cons: While steel is generally more affordable than aluminum, its heavier weight can negatively impact vehicle efficiency. Furthermore, the manufacturing process can be less complex, making it easier to source and produce.
Impact on Application: Steel is often used in structural components and safety features of electric vehicles, ensuring robustness and longevity. Its compatibility with various coatings can enhance corrosion resistance, particularly in humid climates.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should be aware of the specific grades of steel required for EEC certification and ensure compliance with relevant standards such as EN and DIN.
Composite Materials: The Future of Lightweight Solutions
Key Properties: Composites, often made from a combination of materials like carbon fiber and resin, provide excellent strength, lightweight properties, and corrosion resistance. They can withstand temperatures up to 300°C, depending on the resin used.
Pros & Cons: Composites offer significant weight savings and are highly customizable, but they can be expensive and complex to manufacture. The initial investment may be high, but the long-term benefits in efficiency can justify the cost.
Impact on Application: Composites are increasingly used in body panels and interior components, contributing to overall vehicle weight reduction. Their compatibility with electric systems makes them suitable for innovative designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the availability of composite materials in their regions and consider the implications of sourcing and manufacturing capabilities. Compliance with ASTM standards is essential for quality assurance.
Lithium-Ion Batteries: Powering the Future
Key Properties: Lithium-ion batteries are characterized by high energy density, lightweight, and long cycle life. They operate effectively within a temperature range of -20°C to 60°C.
Pros & Cons: These batteries provide high performance and efficiency, but they can be costly and require careful handling due to safety concerns. The recycling process for lithium-ion batteries is also complex, posing environmental challenges.
Impact on Application: Lithium-ion batteries are central to electric vehicle performance, directly affecting range and charging capabilities. Their compatibility with various electric systems makes them indispensable.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers must ensure compliance with safety and environmental regulations, particularly concerning battery disposal and recycling. Understanding local market dynamics can also aid in sourcing.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Electric Car COC EEC
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric car coc eec | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Chassis and body components | Lightweight, enhancing efficiency | Higher cost than steel | High |
| Steel | Structural components and safety features | Durable and cost-effective | Heavier, impacting efficiency | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Body panels and interior components | Significant weight savings | Expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | Power source for electric vehicles | High energy density and performance | Costly and requires careful handling | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers considering materials for electric vehicles under EEC certification. By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric car coc eec
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Electric Cars with EEC Certification?
The manufacturing process for electric cars that require EEC (European Economic Community) certification involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets stringent quality and safety standards. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Does Material Preparation Contribute to Quality Assurance?
Material preparation is the foundational step where raw materials are selected based on quality, sustainability, and compliance with international standards. This phase often involves sourcing components like batteries, electric motors, and body materials that comply with EEC requirements. Manufacturers typically adhere to ISO 9001 standards, which ensure that the materials used are reliable and traceable.
In this stage, suppliers must provide documentation of compliance with relevant standards, such as the E-MARK certification for components. This is particularly crucial for B2B buyers who need to verify that the materials used in production align with their own quality expectations and regulations in their markets.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Electric Car Manufacturing?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into components that will make up the vehicle. Techniques such as stamping, molding, and extrusion are commonly employed. Advanced technologies like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining and 3D printing are increasingly used to enhance precision and reduce waste.
During this stage, it is essential for manufacturers to maintain strict adherence to specifications and tolerances to ensure compatibility with other components. B2B buyers should inquire about the technologies used and the capabilities of the manufacturer to produce complex parts that meet their specific requirements.
How Is Assembly Conducted to Ensure Quality in Electric Vehicles?
The assembly stage is where various components come together to form the complete vehicle. This process often follows a well-structured workflow to minimize errors and enhance efficiency. Key assembly techniques include automated assembly lines, manual assembly, and quality checks at each phase.
Quality Control (QC) checkpoints are crucial during assembly. These may include In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) measures to ensure that each component fits correctly and functions as intended. B2B buyers should seek suppliers that implement rigorous assembly protocols and can provide documentation of their QC processes.
What Finishing Processes Are Important for EEC-Certified Electric Cars?
Finishing processes involve painting, coating, and final inspections. These steps not only enhance the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal but also protect it from environmental factors, ensuring longevity and reliability. Manufacturers often use environmentally friendly materials to comply with international regulations.
Final Quality Control (FQC) checks are conducted at this stage to confirm that the finished product meets all specifications and regulatory requirements. Buyers should verify that suppliers conduct thorough inspections and can provide certification of compliance with EEC standards.
What International Quality Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers need to be aware of the international quality standards that govern the manufacturing of electric vehicles, particularly those with EEC certification. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: Focuses on quality management systems and is crucial for ensuring consistent product quality.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- E-MARK Certification: Required for vehicle components to demonstrate compliance with EU regulations.
Understanding these standards can help buyers assess the credibility of potential suppliers and ensure they are meeting the necessary compliance requirements for their respective markets.
What Are the Common Quality Control Checkpoints in Electric Car Manufacturing?
Quality control is an integral part of the manufacturing process, particularly for electric cars that require EEC certification. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring production processes to detect any deviations from standards early on.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting comprehensive inspections of the finished product before it is shipped.
B2B buyers should look for suppliers that implement these checkpoints rigorously and can provide detailed reports on their quality control processes.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers can adopt several verification methods:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with standards.
-
Reviewing Quality Reports: Requesting access to quality reports and certifications that demonstrate adherence to international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to evaluate the manufacturer’s processes and products, ensuring unbiased assessments.
-
Feedback and References: Collecting feedback from other businesses that have worked with the supplier can provide insights into their reliability and quality.
What Are the Unique QC and Certification Challenges for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers face unique challenges regarding quality control and certification, particularly when dealing with suppliers in different regions. Variations in regulatory requirements, quality standards, and manufacturing practices can complicate the procurement process.
Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must ensure that the suppliers they engage with are familiar with local regulations and can provide products that comply with both international and regional standards. Establishing clear communication and expectations can mitigate risks and enhance collaboration between buyers and suppliers.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols associated with EEC-certified electric cars is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on key stages in manufacturing, international standards, and robust quality control practices, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric car coc eec’
In the rapidly evolving electric vehicle market, procuring EEC (European Economic Community) certified electric cars is crucial for international B2B buyers. This guide provides a practical checklist to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and maximizing market potential.
Step 1: Understand EEC Certification Requirements
Before initiating your procurement process, familiarize yourself with the EEC certification requirements. This certification is mandatory for electric vehicles sold in the EU and involves several components, including a World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI) and compliance with ISO standards. Understanding these requirements will help you assess potential suppliers effectively.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical specifications for the electric vehicles you intend to procure. Consider factors such as battery capacity, range, speed, and safety features. Detailed specifications not only streamline supplier evaluations but also ensure that the vehicles meet the needs of your target market.
Step 3: Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers who specialize in EEC-certified electric vehicles. Look for manufacturers with a strong track record in the industry, focusing on those with experience in exporting to your target regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. A well-established supplier can offer valuable insights and support throughout the procurement process.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
It is essential to verify that potential suppliers hold the necessary certifications for EEC compliance. Request documentation, including ISO certifications and E-MARK certificates for individual components. Ensuring that suppliers have these certifications helps mitigate risks related to compliance and product quality.
Step 5: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the manufacturing capabilities of your shortlisted suppliers. Inquire about their production capacity, technology used, and quality control processes. Suppliers with advanced manufacturing techniques and stringent quality checks are more likely to deliver reliable products that meet EEC standards.
Step 6: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Before finalizing your order, request samples of the electric vehicles. Conduct thorough testing to evaluate performance, safety, and compliance with EEC standards. This step not only confirms the quality of the products but also builds trust with your supplier by demonstrating your commitment to quality assurance.
Step 7: Establish Communication and Support Channels
Effective communication is vital for a successful partnership. Ensure that your supplier is responsive and provides ongoing support throughout the procurement process. Establish clear channels for communication regarding order status, delivery schedules, and any potential issues that may arise.
By following this step-by-step checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing EEC-certified electric vehicles, ensuring compliance while maximizing the potential for successful market entry.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric car coc eec Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Electric Car COC EEC Sourcing?
When sourcing electric cars that require EEC certification, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The main cost components include:
-
Materials: This encompasses the raw materials required for vehicle production, including metals, plastics, batteries, and electrical components. The choice of materials can significantly impact both cost and compliance with EEC standards.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and are influenced by local wage standards and the level of expertise required for manufacturing electric vehicles. Skilled labor is essential for ensuring quality production and adherence to EEC regulations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the manufacturing facility, utilities, equipment maintenance, and indirect labor. Efficient operations can help minimize these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Initial investments in specialized tooling and machinery are necessary for producing electric vehicles. This is a significant upfront cost that can be amortized over the production volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with EEC standards requires rigorous quality control processes. This may involve testing components and final products, which adds to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are critical, especially for international buyers. Factors like distance, shipping methods, and customs duties can vary significantly, impacting the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the margin expectations of your suppliers can help in negotiating better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Electric Car EEC Pricing?
Several factors influence the pricing of electric cars with EEC certification:
-
Volume/MOQ: The minimum order quantity (MOQ) can affect pricing. Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating bulk purchasing agreements can provide significant savings.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customizing vehicles to meet specific buyer needs can increase costs. Standard models tend to be cheaper, while bespoke features and specifications typically drive up the price.
-
Materials: The choice of components, especially batteries and electric motors, can greatly affect pricing. High-quality materials that comply with EEC standards may come at a premium.
-
Quality and Certifications: Vehicles that meet higher quality standards or additional certifications may carry higher costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced safety and reliability against the increased price.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of compliance and quality may charge more but offer greater assurance.
-
Incoterms: The agreed terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) can alter the total cost. Buyers should carefully evaluate these terms to understand who bears responsibility for shipping costs and risks.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Electric Car EEC Sourcing?
To optimize costs and ensure successful sourcing of EEC-certified electric cars, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing, terms, and potential discounts for larger orders. Clear communication can lead to better pricing structures and favorable terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the entire lifecycle cost of the vehicles, including maintenance, insurance, and potential resale value. This holistic view can inform better purchasing decisions.
-
Research Local Market Conditions: Understanding the specific market dynamics in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can provide insights into pricing strategies and supplier competitiveness.
-
Seek Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify competitive pricing. This practice also allows buyers to compare different offerings and quality levels.
-
Consider Long-term Partnerships: Establishing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved service, and consistent quality over time.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices associated with EEC-certified electric cars can vary widely based on numerous factors. The information provided here is indicative and should be verified with suppliers to obtain accurate quotes tailored to specific requirements and market conditions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric car coc eec With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Electric Car COC EEC Solutions
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicles (EVs), businesses are increasingly faced with a variety of transportation solutions. Understanding the alternatives to Electric Car COC EEC certifications can aid international B2B buyers in making informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market regulations. This analysis compares Electric Car COC EEC against two viable alternatives: Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles (HFCVs) and Traditional Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles.
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Car Coc Eec | Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles (HFCVs) | Traditional Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency; suitable for urban areas | Long range; quick refueling | Established technology; widely available |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost; potential savings on fuel | High initial cost; lower long-term fuel costs | Low initial cost; fluctuating fuel prices |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires EEC certification; manageable for compliance | Infrastructure still developing; limited refueling stations | No special certification; readily available infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; fewer moving parts | Moderate maintenance; fuel cell specifics | Higher maintenance; more moving parts and wear |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting and short-distance travel | Long-distance travel; fleets | General use; established markets in various sectors |
Understanding the Pros and Cons of Each Alternative
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles (HFCVs)
HFCVs operate using hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, resulting in zero emissions. They are particularly advantageous for long-distance travel, as they can be refueled quickly, similar to traditional gas vehicles. However, the initial investment for HFCVs is significantly higher than for electric vehicles, and the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is still in its infancy, limiting their immediate practicality in many regions.
Traditional Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles
ICE vehicles have been the mainstay of the automotive industry for over a century. Their advantages include lower upfront costs and a well-established refueling infrastructure. However, they face increasing scrutiny due to their environmental impact, as they emit greenhouse gases and contribute to pollution. As regulatory pressures mount globally, the long-term viability of ICE vehicles is being questioned, particularly in urban environments where emissions regulations are becoming stricter.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
Choosing the right transportation solution requires a careful assessment of your specific business needs, market dynamics, and regulatory environment. Electric Car COC EEC solutions are particularly advantageous for urban applications where efficiency and environmental considerations are paramount. Conversely, if your operations require longer travel distances or involve fleets, HFCVs may be more suitable despite their higher initial costs. Traditional ICE vehicles may still serve a role in certain markets, but their future is uncertain as sustainability becomes a priority.
Ultimately, B2B buyers should weigh the initial costs, operational efficiencies, and compliance requirements of each option against their strategic goals. Embracing innovative technologies such as electric or hydrogen-powered vehicles can enhance sustainability efforts while aligning with global trends toward greener transportation solutions.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric car coc eec
What Are the Key Technical Properties for Electric Car CoC EEC Certification?
In the realm of electric vehicles (EVs) and their certification, understanding essential technical properties is critical for B2B buyers. Here are some of the most significant specifications that manufacturers and importers need to be aware of:
-
World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI)
The WMI is a unique identifier assigned to vehicle manufacturers, forming the first three characters of the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). This specification is crucial for ensuring traceability and compliance with international regulations. For B2B buyers, verifying a manufacturer’s WMI can help assess reliability and adherence to quality standards, which is vital for long-term partnerships. -
ISO Certification
ISO certifications, particularly ISO 9001, signify that a company meets international quality management standards. For electric car manufacturers, this certification assures B2B buyers of consistent quality in production processes. It is essential for establishing trust and ensuring that products meet both safety and performance standards throughout their lifecycle. -
E-MARK Certification for Components
E-MARK certification is mandatory for specific vehicle components such as lights, tires, and brakes. Each component must be sourced from suppliers who maintain their E-MARK certification. This specification is particularly important for B2B buyers as it guarantees that all parts comply with EU regulations, reducing the risk of compliance issues and enhancing vehicle safety. -
Electric Motor and Battery Specifications
Key performance indicators such as power output (measured in kilowatts), battery capacity (measured in amp-hours), and range (measured in kilometers) are critical for electric vehicles. These specifications not only affect vehicle performance but also impact operational costs and customer satisfaction. B2B buyers must assess these metrics to ensure the vehicles meet market demands and customer expectations. -
Safety Standards Compliance
Compliance with international safety standards, including the EN15194 for electric bicycles and similar standards for electric vehicles, is mandatory. This encompasses mechanical safety, electrical safety, and electromagnetic compatibility. For B2B buyers, understanding these standards helps in selecting compliant products that avoid legal liabilities and enhance marketability. -
Environmental Compliance
Adherence to environmental standards, such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), is increasingly important. It ensures that the manufacturing processes do not involve harmful materials, which is a growing concern among consumers and regulators alike. B2B buyers should prioritize manufacturers who demonstrate environmental responsibility, as this can significantly influence brand reputation and sales.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Electric Car CoC EEC Transactions?
Navigating the B2B landscape for electric vehicles involves familiarizing oneself with specific trade terminology. Here are some key terms to consider:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts or vehicles that are sold under another company’s brand name. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for B2B buyers as it influences product quality and warranty terms. Establishing partnerships with reputable OEMs can enhance supply chain reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers to understand as it impacts inventory management and cash flow. Negotiating favorable MOQs can help buyers optimize their purchasing strategies and minimize excess stock. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. This term is important for buyers looking to streamline procurement processes. A well-structured RFQ can lead to better pricing and service agreements. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B buyers to mitigate risks and clarify obligations in cross-border transactions. -
Type Approval
This term refers to the process of certifying that a vehicle meets specified regulations and standards. For B2B buyers, understanding type approval is key to ensuring that vehicles can be legally sold and operated in target markets, thereby avoiding costly compliance issues. -
Homologation
Homologation is the process of certifying that a vehicle complies with all regulatory requirements for a specific market. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects the vehicle’s market entry strategy and overall compliance with local laws.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms not only aids B2B buyers in making informed purchasing decisions but also strengthens their negotiation power and strategic planning in the electric vehicle market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric car coc eec Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Electric Car COC EEC Sector?
The electric vehicle (EV) market, particularly in the context of the Electric Car Certificate of Conformity (COC) EEC, is witnessing rapid growth driven by several global factors. The push for sustainable transportation solutions is a major driver, as governments worldwide are implementing stringent emissions regulations and incentives for electric mobility. For international B2B buyers, particularly from emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic sourcing decisions.
Emerging technologies such as advanced battery systems, vehicle-to-grid integration, and AI-driven fleet management are reshaping the landscape. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce is increasing demand for electric delivery vehicles, prompting manufacturers to innovate and adapt quickly. Buyers must also consider the regulatory landscape, especially concerning EEC certification, which is mandatory for vehicles sold in the EU. This certification ensures that vehicles meet safety and environmental standards, making compliance a key focus for manufacturers and buyers alike.
Furthermore, market dynamics are influenced by shifting consumer preferences towards electric vehicles, driven by greater awareness of environmental issues. As a result, sourcing trends are leaning towards suppliers who can offer certified vehicles with robust quality assurance processes. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with manufacturers who not only meet certification requirements but also demonstrate a commitment to innovation and sustainability.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Electric Car COC EEC Sector?
In today’s market, sustainability is no longer optional; it is a critical component of B2B sourcing strategies. For the electric car COC EEC sector, this means prioritizing suppliers who adhere to ethical sourcing practices and environmental stewardship. The production of electric vehicles has a significant environmental footprint, particularly concerning battery production and raw material extraction. Buyers should seek manufacturers who implement sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing waste throughout the production process.
Ethical supply chains are becoming increasingly important, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where the mining of lithium and cobalt for batteries poses environmental and social challenges. Buyers should conduct due diligence to ensure that their suppliers are compliant with international labor standards and that they source materials responsibly. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and fair trade certifications can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, obtaining green certifications for electric vehicles, such as CE and E-MARK, not only enhances product credibility but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. By aligning sourcing strategies with sustainability goals, B2B buyers can enhance their market position and contribute positively to environmental conservation.
What Is the Historical Context of Electric Car COC EEC Certification?
The evolution of electric vehicle certification, particularly the COC EEC, has been shaped by increasing regulatory scrutiny and the growing importance of environmental sustainability. The introduction of the EEC certification in the early 2010s marked a significant step towards standardizing safety and environmental compliance for electric vehicles in the European market. This initiative aimed to harmonize regulations across member states, facilitating smoother trade and ensuring that consumers have access to safe and eco-friendly vehicles.
Over the years, the standards have evolved to address advancements in technology and changing market demands. The implementation of the new standard 168/2013 in 2016, for example, introduced more detailed classifications and requirements for vehicle manufacturers. As the market continues to expand, particularly in emerging economies, the relevance of COC EEC certification will likely grow, prompting manufacturers and international buyers to stay informed about compliance requirements and market trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric car coc eec
-
How do I ensure compliance with EEC certification for electric vehicles?
To ensure compliance with EEC certification, start by familiarizing yourself with the four mandatory conditions: obtain a unique World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI), secure an ISO certificate relevant to your production scope, ensure that all components possess E-MARK certification, and appoint an authorized EU representative. Regular audits and timely updates to your certifications are crucial. Additionally, maintain consistent sourcing of E-MARK certified components to avoid complications with your EEC certificate. -
What is the best way to vet suppliers for electric car EEC certification?
When vetting suppliers for electric cars with EEC certification, prioritize manufacturers with a proven track record in compliance and quality assurance. Request documentation of their certifications, including EEC and ISO certificates. Conduct thorough background checks, seek references, and consider visiting the manufacturing facility if possible. Engaging with suppliers that have experience exporting to your target market can also enhance reliability and reduce potential trade barriers. -
What customization options are available for electric vehicles?
Customization options for electric vehicles often include modifications in design, features, and specifications to meet specific market needs. Buyers can request changes to battery capacity, motor performance, color, interior features, and additional safety equipment. Discuss your requirements with the supplier early in the negotiation process to ensure they can accommodate your needs while adhering to EEC regulations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for EEC-certified electric vehicles?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly between suppliers and are often influenced by production capacity and the type of vehicle. Generally, MOQs for EEC-certified electric vehicles range from 10 to 100 units. It is advisable to discuss MOQs directly with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that suit your business model and market demand, especially if you are looking to enter a new region. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing electric vehicles internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include upfront deposits (typically 30-50% of the total order value) with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer more flexible terms, such as net 30 or net 60 days after delivery. It’s crucial to clarify payment terms before finalizing contracts to ensure alignment with your financial policies and mitigate risks. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for imported electric vehicles?
To ensure quality assurance for imported electric vehicles, establish a comprehensive QA process that includes pre-shipment inspections and compliance testing to EEC standards. Work with third-party inspection services to assess product quality before shipment. Additionally, consider implementing a warranty clause in your contract that allows for returns or replacements if vehicles do not meet specified standards upon arrival. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing electric vehicles?
Logistics for importing electric vehicles involve several key considerations, including shipping methods, customs clearance, and local regulations. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling vehicle imports to navigate these complexities. Understand the tariffs and duties applicable to electric vehicles in your destination country, and ensure that all necessary documentation, including EEC certification, is in order to avoid delays during customs clearance. -
How do I handle after-sales support for electric vehicles?
After-sales support is critical for maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty. Establish a clear plan for servicing, spare parts availability, and customer support channels. Collaborate with your supplier to understand the warranty terms and service obligations. Consider setting up a local service network or partnership with service centers to provide efficient support and maintenance for customers in your market, ensuring compliance with local regulations and enhancing your brand reputation.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 3 Electric Car Coc Eec Manufacturers & Suppliers List
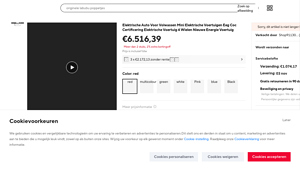
1. AliExpress – Electric Car for Adults
Domain: aliexpress.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: This company, AliExpress – Electric Car for Adults, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Miou Truck – X8 Model
Domain: mioutruck.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: {“Vehicle Model”:”X8″,”Body size”:”2580*1365*1650mm”,”Wheelbase”:”1680mm”,”Min Ground Clearance”:”215mm”,”Seats”:”Front 2+ Rear 2″,”Motor Type”:”60/72V 2000W/3000W/4000W”,”Battery Type”:”Lead-Acid”,”Battery Capacity”:”60V/72V 80AH/100AH/110AH”,”Charger Type”:”60V15A”,”Charger Time”:”6H”,”Charging Voltage”:”110V-220V”,”Transmission system”:”Automatic”,”Front & Rear Brake”:”front disc/rear disc”,”Ti…
3. Facebook – Mini Electric Car
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: mini electric car, top China manufacturer, EECL7ECOC certification, OEM/ODM
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric car coc eec
The landscape of electric vehicle (EV) certification, particularly EEC (European Economic Community) certification, presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers. As global demand for electric vehicles continues to rise, understanding the nuances of EEC certification is crucial for ensuring compliance and market entry in Europe. Key takeaways include the importance of securing a unique World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI), obtaining ISO certifications, and ensuring that all vehicle components are E-MARK certified.
Strategic sourcing plays a vital role in this process, enabling businesses to establish reliable supply chains for certified components while maintaining adherence to EU regulations. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also enhances product credibility in competitive markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Looking ahead, the EV market is set to expand rapidly, driven by increasing environmental awareness and government incentives for sustainable transport solutions. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with certified suppliers and leverage strategic partnerships to navigate this evolving landscape effectively. By doing so, they can position themselves advantageously in a burgeoning market, ensuring compliance and fostering long-term success.