Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for engine-driven Crane
As the demand for heavy lifting solutions continues to rise globally, international B2B buyers face a significant challenge in sourcing engine-driven cranes that meet their specific operational needs. With diverse applications ranging from construction and manufacturing to logistics and infrastructure development, selecting the right crane can be complex. This guide aims to simplify that process by providing a comprehensive overview of various types of engine-driven cranes, including hydraulic, truck-mounted, and all-terrain options.
Moreover, we will explore essential aspects such as supplier vetting, cost considerations, and maintenance requirements, empowering buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including markets like Vietnam and Germany—to make informed purchasing decisions. By delving into the intricacies of crane specifications, operational capabilities, and market trends, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the global market confidently. Whether you are expanding your fleet or entering new markets, understanding the nuances of engine-driven cranes will be pivotal in optimizing your logistics and operational efficiency.
Understanding engine-driven Crane Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Truck Cranes | Mobile, high lifting capacity, road transportable | Construction, heavy lifting | Pros: Versatile, high capacity; Cons: Maintenance costs can be high. |
| Carry-Deck Cranes | Compact design, ideal for tight spaces | Warehousing, manufacturing | Pros: Maneuverable, space-efficient; Cons: Limited lifting capacity. |
| Rough Terrain Cranes | Off-road capability, large tires for stability | Construction sites, outdoor projects | Pros: Excellent mobility on uneven terrain; Cons: Slower transport speed. |
| All-Terrain Cranes | Combination of road and off-road capabilities | Infrastructure projects, large events | Pros: Highly versatile, adaptable to various terrains; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Engine Hoists | Smaller, portable, typically lower capacity | Automotive repair, small workshops | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to store; Cons: Limited lifting capacity and range. |
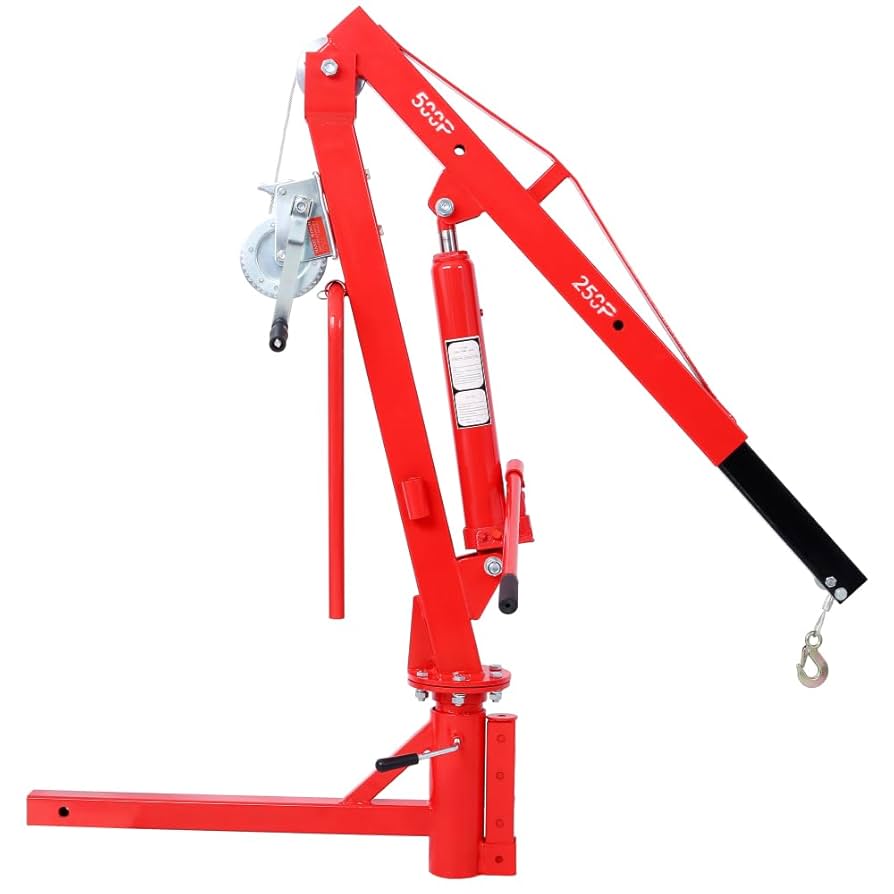
What Are the Key Characteristics of Hydraulic Truck Cranes?
Hydraulic truck cranes are known for their robust lifting capabilities and mobility, allowing them to travel on public roads. They typically feature a powerful hydraulic system that provides significant lifting force, making them ideal for construction and heavy lifting tasks. Buyers should consider the crane’s maximum capacity, boom length, and engine power when evaluating options, as these factors will impact performance on job sites.
How Do Carry-Deck Cranes Stand Out in Industrial Applications?
Carry-deck cranes are compact and designed for use in confined spaces, such as warehouses or manufacturing plants. Their low-profile design allows them to navigate tight corners while providing substantial lifting capabilities for light to moderate loads. B2B buyers should assess the crane’s pick-and-carry capacity, height, and maneuverability to ensure it meets their specific operational needs.
What Makes Rough Terrain Cranes Suitable for Challenging Environments?
Rough terrain cranes are specifically designed to operate on uneven ground, making them ideal for construction sites with challenging conditions. Equipped with large tires and a robust suspension system, these cranes can handle rough surfaces while providing excellent stability. Buyers should evaluate the crane’s lifting height, reach, and off-road capabilities to ensure it aligns with their project requirements.
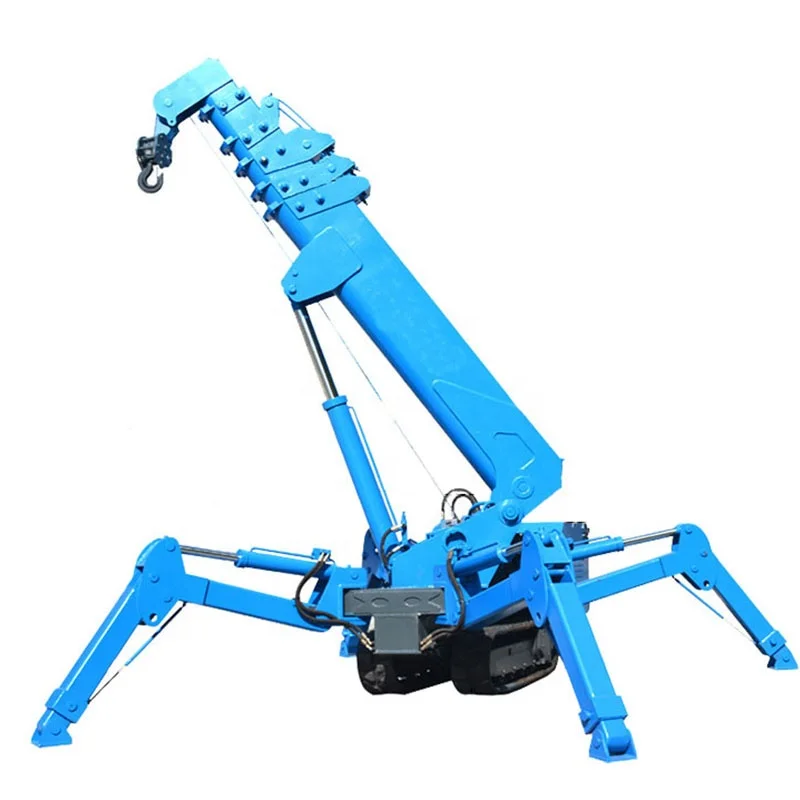
Why Choose All-Terrain Cranes for Diverse Job Sites?
All-terrain cranes combine the features of road and rough terrain cranes, providing exceptional versatility. They can easily transition between paved roads and rugged landscapes, making them suitable for various applications, including infrastructure projects and large events. Buyers should consider factors such as operating weight, fuel efficiency, and maintenance requirements to maximize their investment in an all-terrain crane.
What Are the Advantages of Engine Hoists for Smaller Tasks?
Engine hoists are smaller, portable lifting devices typically used in automotive repair and small workshops. They are cost-effective and easy to store, making them a practical choice for businesses with limited space. However, their lifting capacity is lower compared to larger cranes, so buyers should assess the weight of the loads they plan to lift to determine if an engine hoist meets their needs.
Key Industrial Applications of engine-driven Crane
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of engine-driven Crane | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Lifting and placing heavy materials on construction sites | Increases efficiency and reduces labor costs | Capacity, reach, and mobility for site conditions |
| Oil and Gas | Transporting equipment and materials to remote drilling sites | Enhances operational efficiency in challenging terrains | Durability, fuel efficiency, and load capacity |
| Manufacturing | Moving heavy machinery and components within factories | Streamlines production processes and minimizes downtime | Adaptability, control options, and maintenance support |
| Mining | Hauling heavy loads from extraction sites to processing areas | Improves productivity in challenging environments | Terrain adaptability, lifting capacity, and reliability |
| Logistics and Warehousing | Loading and unloading cargo from trucks and containers | Optimizes supply chain operations and reduces delays | Versatility, ease of transport, and safety features |
How are engine-driven cranes utilized in the construction industry?
In the construction sector, engine-driven cranes are vital for lifting and placing heavy materials, such as steel beams and concrete blocks. Their mobility allows them to navigate various terrains, making them suitable for both urban and remote construction sites. These cranes solve the problem of limited access to materials by enabling quick and efficient transport. Buyers should consider factors like lifting capacity, boom reach, and mobility options to ensure the crane meets site-specific requirements.
What role do engine-driven cranes play in the oil and gas sector?
Engine-driven cranes are indispensable in the oil and gas industry, particularly for transporting equipment and materials to remote drilling sites. Their robust design and powerful engines enable them to operate in challenging terrains, ensuring that essential supplies reach their destination on time. This capability enhances operational efficiency, minimizing downtime. Buyers must prioritize fuel efficiency, load capacity, and durability when sourcing cranes for this demanding environment.
How do engine-driven cranes improve manufacturing processes?
In manufacturing, engine-driven cranes facilitate the movement of heavy machinery and components within factories. By streamlining the handling of bulky items, these cranes reduce manual labor and enhance overall production efficiency. The ability to quickly reposition equipment minimizes downtime during assembly or maintenance. Buyers should focus on adaptability to various factory layouts, ease of control, and the availability of maintenance support when selecting cranes for manufacturing applications.
Why are engine-driven cranes essential in mining operations?
Mining operations often require moving heavy loads from extraction sites to processing areas, where engine-driven cranes excel. Their capacity to operate in rugged and uneven terrains significantly boosts productivity while ensuring the safe handling of materials. The cranes help address the challenges of transporting large volumes of ore and equipment. Buyers should evaluate terrain adaptability, lifting capacity, and reliability to ensure optimal performance in mining conditions.
How do engine-driven cranes optimize logistics and warehousing?
In logistics and warehousing, engine-driven cranes are crucial for loading and unloading cargo from trucks and containers. Their efficiency in handling heavy loads optimizes supply chain operations and reduces delays in material movement. The versatility of these cranes allows them to adapt to different loading scenarios, enhancing warehouse productivity. When sourcing cranes for logistics, buyers should consider features like versatility, ease of transport, and safety mechanisms to protect workers and cargo.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘engine-driven Crane’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inefficiencies Due to Limited Crane Mobility
The Problem: In many industries, particularly construction and logistics, the mobility of equipment is crucial for operational efficiency. B2B buyers often find that traditional cranes are cumbersome and not easily transportable, leading to delays in job completion and increased costs. This issue is particularly pronounced in regions with challenging terrains or where sites are spread out. Buyers are frustrated by the inability to quickly move their cranes between job sites, which can significantly hinder productivity and increase labor costs.
The Solution: To address mobility challenges, B2B buyers should consider investing in engine-driven cranes specifically designed for versatility and ease of transport. Hydraulic truck-mounted cranes, for example, offer excellent lifting capabilities while being roadworthy. When sourcing these cranes, it’s essential to assess their specifications, including maximum travel speeds and weight capacities. Buyers should also inquire about the crane’s setup time and ease of operation, ensuring that it can be deployed quickly at various job sites. Partnering with a reputable supplier who understands the terrain and logistical challenges of the buyer’s specific operational environment can further enhance mobility solutions.
Scenario 2: Safety Concerns with Load Handling
The Problem: Safety is a paramount concern in any lifting operation. B2B buyers are often troubled by the potential risks associated with load handling, including accidents caused by equipment failure or improper operation. Many buyers express concern over the reliability of crane systems and the training required for operators. These fears can lead to hesitance in utilizing cranes for heavier loads, ultimately impacting project timelines and increasing labor expenses due to manual handling.
The Solution: To mitigate safety risks, buyers should prioritize sourcing engine-driven cranes equipped with advanced safety features such as anti-two block systems and overload protection. When selecting a crane, it’s essential to verify that it meets international safety standards and includes comprehensive operator training programs. Buyers should collaborate with suppliers who provide not only the equipment but also ongoing training and support for their operators. Regular maintenance checks and safety audits can further ensure that the cranes are in optimal working condition, minimizing the risk of accidents on site.
Scenario 3: High Operating Costs Due to Fuel Inefficiency
The Problem: Operating costs are a critical consideration for B2B buyers, especially in markets where profit margins are tight. Many buyers struggle with the high fuel consumption associated with engine-driven cranes, which can significantly inflate operational expenses over time. This is particularly problematic in regions where fuel costs are volatile, impacting budget forecasts and overall project profitability.
The Solution: Buyers should focus on acquiring engine-driven cranes that are designed for fuel efficiency. When evaluating options, it’s beneficial to look for models that incorporate advanced engine technology and lighter materials, which can reduce fuel consumption without sacrificing performance. Additionally, buyers should consider integrating telematics systems that monitor fuel usage and provide insights into operational efficiency. This data can help identify areas for improvement and optimize crane usage. Establishing a maintenance schedule to ensure that engines are running smoothly can also enhance fuel efficiency, ultimately leading to lower operating costs and improved profit margins.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for engine-driven Crane
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Engine-Driven Cranes?
When selecting materials for engine-driven cranes, several factors must be considered, including mechanical properties, environmental resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these cranes: steel, aluminum, composite materials, and cast iron.
How Does Steel Perform in Engine-Driven Cranes?
Steel is the most widely used material for engine-driven cranes due to its exceptional strength and durability. Key properties include high tensile strength, excellent fatigue resistance, and good weldability, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Steel can withstand high temperatures and pressures, which is crucial in demanding environments.
Pros: Steel’s durability and ability to handle heavy loads make it ideal for cranes that require high lifting capacities. Additionally, it is relatively cost-effective compared to other materials, especially in bulk.
Cons: However, steel is prone to corrosion, which can be a significant issue in humid or saline environments. This necessitates protective coatings or galvanization, increasing manufacturing complexity and costs.
For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 or DIN 17100 is essential. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America may need to consider local availability and cost fluctuations in steel.
What Advantages Does Aluminum Offer for Engine-Driven Cranes?
Aluminum is increasingly being used in crane construction due to its lightweight nature and corrosion resistance. Key properties include a lower density than steel, which allows for easier maneuverability and transport. Aluminum also has good thermal conductivity and resistance to oxidation.
Pros: The lightweight characteristic of aluminum reduces the overall weight of the crane, enhancing fuel efficiency and ease of handling. Its corrosion resistance is particularly beneficial in coastal or humid environments.
Cons: The main drawback is aluminum’s lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its application in heavy lifting scenarios. Additionally, aluminum can be more expensive than steel, impacting overall project budgets.
For international B2B buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 and JIS H4000 is crucial. Buyers in Europe may prefer aluminum due to its environmental benefits and recyclability.
How Do Composite Materials Impact Engine-Driven Crane Design?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass or carbon fiber, are gaining traction in specialized crane applications. These materials are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance.
Pros: Composites are significantly lighter than metals, which can enhance crane performance and reduce operational costs. They are also resistant to environmental degradation, making them suitable for harsh conditions.
Cons: However, composites can be more expensive to manufacture and may require specialized skills for assembly and repair. Their performance under extreme temperatures and loads can also be less predictable than metals.
International buyers should consider the specific applications of composites and ensure compliance with standards like ASTM D3039. In regions with emerging markets, the initial investment in composites may be offset by long-term savings in maintenance.
What Role Does Cast Iron Play in Engine-Driven Cranes?
Cast iron is often used in crane components that require high wear resistance, such as gears and pulleys. Its key properties include excellent compressive strength and good machinability.
Pros: Cast iron components can withstand significant stress and are less likely to deform under heavy loads. This makes them ideal for high-impact applications.
Cons: However, cast iron is brittle and can fracture under tensile stress, limiting its use in structural components. Additionally, it is heavier than steel, which can reduce overall crane efficiency.
For B2B buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM A48 is necessary. Buyers from regions like the Middle East may find cast iron suitable for specific applications, but they must weigh its limitations against the operational requirements.
Summary of Material Selection for Engine-Driven Cranes
| Material | Typical Use Case for engine-driven Crane | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural framework and boom | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight cranes and components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength | High |
| Composite | Specialized applications and components | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher manufacturing costs | High |
| Cast Iron | Gears and pulleys | Excellent wear resistance | Brittle and heavy | Medium |
This material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, ensuring they make informed decisions based on application needs, compliance requirements, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for engine-driven Crane
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Engine-Driven Cranes?
The manufacturing of engine-driven cranes involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required performance and safety standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: Sourcing and Quality Control
Material preparation is the first crucial step in the manufacturing process. High-quality raw materials, such as steel and aluminum alloys, are sourced from reputable suppliers. These materials must meet specific mechanical properties and certifications. Prior to usage, suppliers typically conduct Incoming Quality Control (IQC) to verify the material specifications against industry standards. B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers maintain stringent quality checks during this stage, as the quality of raw materials directly impacts the crane’s performance and durability.
How Is Forming Achieved in Engine-Driven Crane Manufacturing?
The forming stage involves the transformation of raw materials into components that will make up the crane. Techniques such as cutting, welding, and machining are employed to create parts like the boom, chassis, and hydraulic systems. Advanced technologies like Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining are often used for precision cutting and shaping, ensuring that components fit together seamlessly during assembly.
B2B buyers should inquire about the manufacturing technologies utilized by suppliers to ensure that they are leveraging modern techniques that enhance accuracy and reduce waste.
What Happens During the Assembly Stage?
Assembly is where the individual components come together to form the complete crane. This process can be highly labor-intensive and may involve both manual labor and automated systems. During assembly, critical systems such as the hydraulic mechanisms, electrical systems, and engine mounts are integrated.
Quality Assurance checkpoints are essential during this phase, including In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), where operators inspect parts at various stages of assembly to catch any defects early. Buyers should ask suppliers about their assembly protocols and the qualifications of the personnel involved, as skilled labor is vital for quality craftsmanship.
How Is the Finishing Process Conducted?
The finishing stage focuses on enhancing the crane’s durability and aesthetics. This includes processes such as painting, coating, and surface treatment. Proper finishing not only improves the crane’s appearance but also protects it from environmental factors like corrosion and wear.
Manufacturers often employ techniques like powder coating or galvanization to ensure longevity. B2B buyers should confirm that their suppliers follow industry best practices for finishing to ensure that the cranes will withstand the rigors of their operational environments.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Standards for Engine-Driven Cranes?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for engine-driven cranes. Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers implement a robust quality management system. This standard focuses on consistent quality in design, development, production, installation, and service.
Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking in Europe and API (American Petroleum Institute) certification for cranes used in oil and gas applications further assure buyers of the product’s safety and reliability. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with relevant certifications, as these reflect adherence to quality and safety standards.
What Quality Control Checkpoints Are Essential in Crane Manufacturing?
Quality Control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that every aspect of the crane meets the required standards. The three primary QC checkpoints are:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint verifies the quality of raw materials upon arrival.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the assembly process, this ensures that any defects are identified and rectified before moving on to the next stage.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This is the final inspection before the product is shipped. It includes load testing, functionality checks, and safety inspections.
B2B buyers should ask suppliers for detailed reports on their QC processes, including any test results and certifications that validate the crane’s performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers should consider several verification strategies:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insights into the supplier’s adherence to quality standards and operational practices.
- Reports: Requesting detailed quality control reports can help buyers understand the QC processes and any issues encountered during manufacturing.
- Third-Party Inspection: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the crane’s quality and compliance with industry standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of the nuances in quality control and certification processes. Different regions may have varying regulations and standards that affect crane manufacturing and usage.
For instance, while CE marking is mandatory in Europe, other regions may have specific local certifications that need to be met. Buyers should conduct thorough research on the regulatory landscape of their respective regions and ensure that their suppliers are compliant with these standards.
Furthermore, understanding the local operational environment is crucial, as cranes may need to be adapted for different climatic conditions or specific applications. Buyers should engage in discussions with suppliers about the adaptability of their cranes to meet local requirements.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in the production of engine-driven cranes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and ensure the safety and efficiency of their lifting operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘engine-driven Crane’
When sourcing an engine-driven crane, a systematic approach is essential to ensure you acquire a machine that meets your operational needs while also aligning with your budget and project requirements. This checklist will guide you through the critical steps to consider in the procurement process.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before you begin your search, outline the specific technical requirements for the crane. Consider factors such as lifting capacity, boom length, and mobility type (e.g., truck-mounted or rough terrain). This clarity will help you filter options and avoid overspending on features that may not be necessary for your operations.
- Lifting Capacity: Assess the maximum weight you need to lift and ensure the crane can handle this load safely.
- Boom Length and Reach: Determine the height and distance required for your lifting tasks to select a model that can meet these demands.
Step 2: Research Different Crane Types
Understand the various types of engine-driven cranes available in the market. This knowledge will help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs.
- Hydraulic vs. Electric: Hydraulic cranes are preferred for heavy-duty tasks, while electric cranes may be more suitable for lighter operations in confined spaces.
- Terrain Considerations: Choose between rough terrain cranes and all-terrain cranes based on the job site conditions you expect to encounter.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Vetting suppliers is crucial before making any commitments. A reputable supplier can significantly impact your experience and the quality of the crane you receive.
- Supplier Reputation: Look for reviews, testimonials, and case studies from other B2B buyers, particularly those in similar industries or regions.
- Certifications and Compliance: Ensure that the supplier adheres to international safety and quality standards, which is vital for operational reliability.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotations that outline pricing, delivery timelines, and warranties. A comprehensive quote allows for better comparison and negotiation.
- Breakdown of Costs: Ensure the quotation includes all associated costs, such as shipping, installation, and any optional features.
- Warranty and Support: Look for information on warranty terms and after-sales support to understand the supplier’s commitment to service.
Step 5: Conduct a Site Visit or Demonstration
If possible, visit the supplier’s facility to see the cranes in action or request a demonstration at your site. This step allows you to assess the equipment’s performance and suitability for your specific tasks.
- Operational Testing: Observe the crane’s lifting capabilities, maneuverability, and any specific features that are critical to your operations.
- Staff Training: Inquire about the supplier’s training programs for operators to ensure safe and efficient crane usage.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Purchase
Once you are satisfied with the supplier and the crane specifications, enter into negotiations. Be clear about your needs and any concerns you may have.
- Payment Terms: Discuss payment schedules, financing options, and any discounts for bulk purchases.
- Contract Clarity: Ensure the contract outlines all terms, including delivery schedules, maintenance responsibilities, and penalties for non-compliance.
Step 7: Plan for Installation and Training
After finalizing the purchase, organize for the crane’s installation and operator training. Proper setup and training are essential to maximize the crane’s performance and ensure safety on the job site.
- Installation Support: Confirm that the supplier provides installation services or guidelines for safe setup.
- Operator Certification: Arrange for training sessions to certify operators, ensuring they are skilled in using the crane effectively and safely.
By following this structured checklist, you can streamline the sourcing process for an engine-driven crane, ensuring that you make a well-informed investment that enhances your operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for engine-driven Crane Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Engine-Driven Crane Sourcing?
When sourcing engine-driven cranes, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials significantly impact the overall cost. High-strength steel and advanced hydraulic components will increase the price but enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled workers involved in manufacturing and assembly. Regions with higher labor costs can drive up pricing, while lower-cost regions may offer competitive rates.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and machinery required for crane production contribute to initial setup costs. Custom designs may necessitate additional tooling investments.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that cranes meet safety and performance standards. The costs associated with testing and certification can vary significantly based on regulatory requirements.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are crucial, especially for international buyers. These costs can fluctuate based on distance, mode of transport, and tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their expenses and risk, which can vary widely based on market competition and demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Engine-Driven Crane Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of engine-driven cranes, making it vital for buyers to consider them carefully:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers often offer lower prices for larger orders, making it beneficial for buyers with extensive needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized cranes tailored to specific applications can incur higher costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly affects both the performance and cost of the crane. Premium materials may enhance longevity but will also increase initial investment.
-
Quality and Certifications: Cranes that meet international safety and quality standards may come at a premium. However, investing in certified equipment can reduce long-term risks and liabilities.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capabilities, and customer service can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of reliability may charge more but offer better support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) is crucial for international transactions. These terms dictate who bears shipping costs and risks, affecting the total cost of acquisition.
What Are Some Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency in Crane Sourcing?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should adopt strategic approaches to enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engage in proactive negotiations with suppliers. Leverage market research to understand prevailing prices and be prepared to discuss terms that benefit both parties.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A lower upfront cost may result in higher long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes that can affect pricing. Establishing contracts in stable currencies can mitigate risks.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service terms. Regular communication and collaboration can enhance trust and facilitate smoother transactions.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for engine-driven cranes can vary significantly based on the aforementioned factors. Buyers are encouraged to obtain multiple quotes and conduct thorough due diligence to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing engine-driven Crane With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Engine-Driven Cranes in Heavy Lifting
When considering heavy lifting solutions, businesses often explore various technologies that can meet their operational needs. Engine-driven cranes are widely recognized for their power and versatility; however, evaluating alternatives can help buyers make informed decisions based on specific applications, budget constraints, and operational environments. Below, we compare engine-driven cranes with hydraulic cranes and electric-powered cranes to highlight their unique advantages and drawbacks.
| Comparison Aspect | Engine-Driven Crane | Hydraulic Crane | Electric-Powered Crane |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High capacity and mobility; suitable for rough terrains. | Excellent for heavy-duty lifting; versatile with various configurations. | Limited lifting capacity; best for indoor or light-duty tasks. |
| Cost | Generally higher initial investment; operational costs vary. | Moderate cost; rental options available for flexibility. | Lower purchase price; cost-effective for low-duty cycles. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific training for operators; setup can be complex. | Often straightforward to deploy; can be rented easily. | Quick setup; user-friendly controls. |
| Maintenance | Regular engine maintenance needed; potential for high downtime. | Lower maintenance needs; hydraulic systems are robust. | Minimal maintenance; primarily electrical components. |
| Best Use Case | Construction sites with varied terrain; heavy lifting needs. | Industrial settings, warehouses, and construction; suitable for heavy and precise lifts. | Workshops and factories; ideal for lighter loads and precision tasks. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Hydraulic Cranes?
Hydraulic cranes are formidable alternatives, especially in environments requiring heavy lifting. They are capable of handling substantial loads with precision and are often used in construction and industrial settings. The versatility of hydraulic cranes allows for various configurations, such as truck-mounted or all-terrain models, which enhance their usability in different environments. However, they can be costlier than electric options, and while rental services provide flexibility, they may not always be available in every region, particularly in less accessible markets.
How Do Electric-Powered Cranes Compare?
Electric-powered cranes offer an economical alternative for businesses focused on light-duty applications. Their lower purchase price makes them appealing, especially for companies with budget constraints. These cranes are user-friendly and require less maintenance than their engine-driven or hydraulic counterparts. However, their limited lifting capacity may restrict their use in heavy-duty scenarios. Additionally, electric cranes are best suited for indoor operations, which can limit their versatility in outdoor construction projects or rough terrains.
Making the Right Choice for Heavy Lifting Needs
In conclusion, selecting the right lifting solution depends on specific operational requirements, budget considerations, and the intended use case. Engine-driven cranes excel in mobility and heavy lifting capabilities, making them ideal for challenging environments. Hydraulic cranes provide robust performance for industrial applications, while electric-powered cranes serve well in controlled settings for lighter tasks. B2B buyers should assess their unique needs, including load specifications, site conditions, and operational budgets, to choose the most effective lifting solution that aligns with their business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for engine-driven Crane
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Engine-Driven Cranes?
Understanding the technical properties of engine-driven cranes is essential for B2B buyers, especially when making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Lifting Capacity
The lifting capacity indicates the maximum weight a crane can safely lift. For example, hydraulic cranes often range from 3,200 lbs to 10,000 lbs, depending on the model. This specification is vital for buyers to ensure that the crane meets the demands of their specific applications, whether for construction, logistics, or industrial maintenance. -
Moment Rating
This refers to the torque that the crane can handle, typically measured in foot-pounds (ft-lbs). A higher moment rating allows for greater stability and lifting efficiency. For instance, moment ratings can vary from 10,000 ft-lbs to 72,000 ft-lbs in different crane models. Understanding this property helps buyers select cranes that can operate effectively under varying load conditions without compromising safety. -
Boom Extension and Elevation Angles
The boom’s extension capability and elevation angles determine the crane’s reach and versatility. Many cranes offer powered elevation from -5 degrees to 75 degrees, with extensions that can range significantly. These features are crucial for tasks that require lifting materials to different heights or reaching into confined spaces, making them essential for buyers in sectors like construction and warehousing. -
Control Options
Different cranes come with various control systems such as proportional pendant, wireless, or manual controls. Advanced control options enhance precision and ease of use, which can lead to improved operational efficiency. Buyers should consider their workforce’s familiarity with different control systems to minimize training time and operational risks. -
Rotation Capability
The rotation capability, often specified in degrees (e.g., limited 365 degrees), indicates how far the crane can rotate while maintaining stability. This property is essential for tasks that require maneuvering loads around obstacles or in tight spaces, particularly in urban construction sites or industrial environments. -
Power Source
Engine-driven cranes may be powered by hydraulic systems or internal combustion engines. Understanding the power source is important for maintenance considerations and operational costs. Buyers should assess the availability of fuel types and the infrastructure required to support the crane’s operation in their specific region.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Engine-Driven Cranes?
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is important for buyers who seek high-quality parts and support for their cranes. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for buyers to understand pricing structures and inventory management. A high MOQ can affect cash flow and storage capabilities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing for specified goods or services. Knowing how to prepare an RFQ effectively can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is critical for managing shipping costs, risks, and insurance, especially for buyers in regions like Africa and South America. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. This term is crucial for planning and project timelines, helping buyers avoid delays in their operations. -
Certification Standards
These are industry-specific standards that products must meet to ensure safety and reliability. Buyers should be aware of relevant certification standards (like ISO or CE) to ensure compliance and quality assurance for their crane operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of acquiring engine-driven cranes more effectively, ensuring that they make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the engine-driven Crane Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the Engine-Driven Crane Sector?
The global engine-driven crane market is shaped by several key dynamics, driven primarily by infrastructure development, urbanization, and the increasing demand for efficient material handling solutions across various sectors. Emerging markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East are experiencing rapid growth in construction and industrial activities, leading to heightened demand for versatile cranes that can operate in diverse environments. In Europe, particularly in countries like Germany and Vietnam, there is a push towards advanced engineering and automation, resulting in the integration of IoT and smart technologies into crane operations.
Notably, the trend towards hydraulic cranes is becoming increasingly prevalent due to their ability to handle heavier loads with precision and ease. The introduction of telematics has also transformed crane operations, allowing for real-time monitoring of performance and maintenance needs, thus enhancing operational efficiency. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce has prompted logistics and warehouse operators to invest in mobile and compact cranes that can navigate tight spaces while providing reliable lifting capabilities.
International B2B buyers are advised to consider manufacturers that offer customizable solutions tailored to specific project requirements, as well as those that provide comprehensive after-sales support. Understanding local regulations and compliance standards is crucial for successful procurement, particularly in diverse markets where operational conditions may vary significantly.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Engine-Driven Crane Market?
The importance of sustainability in the engine-driven crane sector cannot be overstated. As global awareness of environmental impact increases, B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices. This includes the use of environmentally friendly materials in crane production, adherence to emissions regulations, and the implementation of energy-efficient technologies. Buyers are increasingly seeking out cranes that utilize alternative fuels or hybrid systems to reduce carbon footprints.
Ethical sourcing practices are equally critical. Buyers are encouraged to engage with manufacturers who maintain transparent supply chains and ensure fair labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and OHSAS 18001 (Occupational Health and Safety) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical standards.
Moreover, the industry is witnessing a growing trend towards the adoption of recycled materials in crane manufacturing. This not only reduces waste but also aligns with the circular economy model that many businesses are striving to implement. For B2B buyers, partnering with suppliers who prioritize sustainability can enhance brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious clients.
What Is the Historical Context of Engine-Driven Cranes Relevant to Today’s B2B Market?
The evolution of engine-driven cranes can be traced back to the early 20th century when mechanization began to revolutionize construction and manufacturing processes. Initially powered by steam, cranes transitioned to internal combustion engines, significantly enhancing their lifting capacities and operational efficiency. The introduction of hydraulic systems in the mid-20th century marked a pivotal shift, allowing cranes to perform intricate maneuvers and lift heavier loads.
As technology progressed, the development of electric and hybrid cranes emerged, reflecting a growing emphasis on sustainability. These innovations have not only improved performance but also catered to the increasing regulatory requirements surrounding emissions and energy consumption. Today, the engine-driven crane sector is characterized by advanced engineering, with smart technologies paving the way for greater automation and efficiency.
For international B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is essential, as it informs current trends and innovations that can impact purchasing decisions. Recognizing the trajectory of crane technology can help buyers anticipate future developments and align their procurement strategies accordingly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of engine-driven Crane
-
How do I choose the right engine-driven crane for my project?
Selecting the right engine-driven crane involves assessing your project’s specific requirements, including load capacity, reach, and operational environment. Consider factors such as the weight of the materials to be lifted, the height and distance you need to reach, and whether the crane will be used in confined spaces or on rough terrain. Additionally, evaluating the crane’s hydraulic system and control options, such as proportional or wireless controls, can enhance operational efficiency and safety. Consulting with a knowledgeable supplier can provide tailored recommendations based on your needs. -
What are the key features to look for in an engine-driven crane?
When evaluating engine-driven cranes, prioritize features such as lifting capacity, boom length, and rotation capabilities. Look for cranes with a robust hydraulic system that ensures smooth and powerful lifting operations. Other important features include anti-two block systems for safety, various control options (manual vs. powered), and compact designs for maneuverability in tight spaces. Additionally, consider the crane’s versatility for different applications, such as construction, maintenance, or material handling, to ensure it meets your operational needs. -
What customization options are available for engine-driven cranes?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for engine-driven cranes to meet specific operational requirements. Customizations can include modifications to load capacity, boom length, control systems, and additional safety features. Some suppliers may also provide tailored solutions for unique applications or challenging environments. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers to explore available options and ensure that the crane aligns with your project specifications. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for engine-driven cranes?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for engine-driven cranes varies by manufacturer and supplier. Typically, larger companies may have higher MOQs due to production costs and inventory management. However, some suppliers may accommodate smaller orders, especially for specialized or custom cranes. It’s advisable to communicate your needs directly with suppliers to negotiate MOQs that suit your purchasing strategy, especially if you’re looking to test a product before committing to larger orders. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing an engine-driven crane?
Payment terms for engine-driven cranes can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the size of the order. Common terms include a deposit upfront (usually ranging from 20% to 50% of the total cost), with the balance due upon delivery or prior to shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing options or installment plans for larger purchases. Always clarify the payment terms before finalizing your order to avoid misunderstandings and ensure that they align with your budget and cash flow. -
How can I vet suppliers for engine-driven cranes?
To vet suppliers for engine-driven cranes, start by researching their reputation within the industry. Check for customer reviews, case studies, and references from previous clients. Evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, certifications, and adherence to international quality standards. Additionally, assess their after-sales support, warranty policies, and responsiveness to inquiries. Attending industry trade shows or connecting with other B2B buyers can also provide valuable insights into reliable suppliers. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing engine-driven cranes?
Importing engine-driven cranes involves several logistics considerations, including shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Ensure that the supplier provides detailed shipping information, including freight costs and estimated delivery times. Familiarize yourself with local customs requirements, import duties, and taxes that may apply to heavy machinery. Partnering with a logistics provider experienced in heavy equipment can help navigate these complexities and ensure a smooth delivery process. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from suppliers?
Reputable suppliers of engine-driven cranes should have robust quality assurance measures in place. This includes adherence to industry standards, regular inspections during the manufacturing process, and comprehensive testing of the cranes before delivery. Suppliers should also provide documentation of compliance with safety and performance standards. Request information on their quality control processes and warranty policies to ensure you are purchasing a reliable and durable product that meets your operational needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 Engine-Driven Crane Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Liftmoore – Hydraulic Powered Cranes
Domain: liftmoore.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic Powered Cranes by Liftmoore, Inc. offer a range of models with varying capacities and moment ratings. Key specifications include:
– Max Capacity: Ranges from 3,200 lbs to 10,000 lbs
– Moment Rating: Ranges from 10,000 ft.-lbs to 72,000 ft.-lbs
– Control Options: Proportional Pendant, Proportional Wireless (WP Control System)
– Rotation: 365 Degrees
– Boom Elevation: Power -5 Deg. to…
2. Vestil – Engine Hoists & Floor Cranes
Domain: industrialproshop.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: This company, Vestil – Engine Hoists & Floor Cranes, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Gingerich Crane – Hydraulic Carry-Deck Cranes
Domain: gingerichcrane.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Hydraulic Cranes offered by R. Gingerich Crane include: 1. Carry-Deck Cranes: – Broderson IC80 (9-ton): Capacity on Outriggers: 18,000 lbs, Pick and Carry Capacity: 11,700 lbs, Height: 7′ 3″, Width: 6′ 6″, Maximum Tip Height: 46′, Maximum Horizontal Reach: 40′. – Broderson IC200 (15-ton): Capacity on Outriggers: 30,000 lbs, Pick and Carry Capacity: 17,000 lbs, Height: 7′ 11″, Width: 7′ 10.5″, …
4. Ruger Industries – Truck Mounted Cranes
Domain: davidround.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Ruger Industries truck mounted cranes provide up to 6,000 lbs. of portable lifting capacity. Features include: 360° boom rotation, adjustable brake to control rotation, and mounted on Timken tapered roller bearings for easy rotation under maximum loads. Available models include: TM-1/4 (500 lbs capacity, 42-1/2″ boom length, 50-1/2″ overall height), TM-1/2 (1,000 lbs capacity, 48″ boom length, 60″…
5. Tico Crane – Hydraulic Pump & PTO for Ford F350
Domain: steelsoldiers.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Tico crane for sale with hydraulic pump and PTO for a 1991 5-speed Ford F350. Questions raised include compatibility of the PTO with a Deuce vehicle, attachment method to the pump (via a small drive shaft), types of PTO needed, cost estimates (around $300 for stock PTO, $500 for transfer case PTO), and engagement methods (mechanical lever or pull knob). Discussion includes options for self-contain…
6. BHS – Power Drive Gantry Crane
Domain: na.bhs1.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {‘name’: ‘Power Drive Gantry Crane’, ‘sku’: ‘PGC-PDC’, ‘capacity_options’: [{‘capacity’: ‘4,000 lb / 1814 kg’, ‘type’: ‘2 Ton’}, {‘capacity’: ‘6,000 lb / 2722 kg’, ‘type’: ‘3 Ton’}], ‘features’: [‘Safe and easy vertical extraction for most standard lift truck batteries’, ‘Modular design for easy system expansion’, ‘Variety of standard heights, beam spans, and capacities available’, ‘Variable frequ…
7. Reddit – New Engine Crane
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This company, Reddit – New Engine Crane, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. Digga – Drilling Augers for Truck Cranes and Telehandlers
Domain: diggausa.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Digga’s range of drilling augers for truck cranes and telehandlers includes high-quality, cost-effective solutions designed for optimal performance. Key features include:
– Manufactured and assembled by Digga using high-grade materials and strict quality control.
– Fitted with Digga/Eaton bell motors with integrated pressure relief valve.
– Innovative gearbox design allows for maximum drilling …
9. Mining Dump Truck – RT100 100T Model
Domain: mining-dumptruck.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: {“Model Number”:”RT100″,”Lifting Capacity”:”100T”,”Driving Type”:”4×4″,”Dead Weight In Travel State”:”76830 Kg”,”Engine Model”:”QSL8.9″,”Min.rated Working Radius”:”3m”,”Base Boom Length”:”12.4m”,”Overall Length”:”14900 mm”,”Overall Width”:”3500 mm”,”Overall Height”:”3990 mm”,”1st Axle Weight”:”41710 kg”,”2nd Axle Weight”:”35120 kg”,”Engine Rated Output”:”224/2100 KW/(r/min)”,”Engine Rated Torque”:…
10. Attachment Co – Truck Crane Auger Drive 7000TC
Domain: attachmentco.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Truck Crane Auger Drive for Trucks with up to 14GPM. Model: 7000TC (5000-14) Auger Drive. Torque: 5000 ft-lbs. Suitable for S5 Augers (2.5″ Hex) with diameters ranging from 6 in. to 36 in. Torque Range: 1547 – 5,029 ft-lb. Oil Pressure Range: 1160 – 3771 psi. Oil Flow Range: 4-14 gpm. Speed Range: 9-30 rpm. Unit Height: 31 in. Unit Diameter: 12 in. Unit Weight: 243 lbs. Hitch Options: Single Pin H…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for engine-driven Crane
As the demand for engine-driven cranes continues to rise across various sectors, strategic sourcing emerges as a vital component for international B2B buyers. By carefully evaluating suppliers, understanding the technical specifications such as lifting capacities and operational efficiencies, and aligning with manufacturers that offer tailored solutions, businesses can enhance their operational capabilities. The hydraulic-powered and truck-mounted cranes stand out for their versatility and mobility, making them essential tools for construction and industrial applications.
Investing in quality cranes not only ensures reliability and safety but also contributes to long-term cost savings and productivity improvements. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with reputable manufacturers that provide robust support and maintenance services, ensuring optimal performance throughout the equipment’s lifecycle.
Looking ahead, the landscape for engine-driven cranes is evolving, with technological advancements paving the way for smarter, more efficient models. International buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are encouraged to seize the opportunity to innovate their operations. Engage with industry leaders and explore the latest offerings to position your business for success in an increasingly competitive market. Embrace the future of lifting solutions and elevate your operations today.