Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for micro electric car concept
In today’s rapidly evolving automotive landscape, the micro electric car concept presents a promising solution for businesses seeking sustainable and efficient urban mobility options. As international B2B buyers navigate the challenges of sourcing compact vehicles that cater to the diverse needs of urban dwellers, understanding the nuances of micro electric cars becomes crucial. This guide delves into various aspects of the micro electric car market, including types of vehicles available, their applications in diverse environments, key supplier vetting criteria, and cost considerations.
The rise of micro electric vehicles is driven by an increasing demand for environmentally friendly transportation solutions that address urban congestion and reduce emissions. By providing insights into the best practices for evaluating suppliers, this guide empowers buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—countries like Brazil and Saudi Arabia—to make informed purchasing decisions. With a focus on the operational benefits of micro electric vehicles, from reduced parking space requirements to lower total cost of ownership, this resource equips businesses with the knowledge necessary to capitalize on this innovative automotive trend. In a market ripe for disruption, understanding the micro electric car concept can unlock significant opportunities for growth and sustainability.
Understanding micro electric car concept Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Commuter | Compact design, limited speed (up to 45 km/h), easy parking | Last-mile delivery, urban transport | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to maneuver. Cons: Limited speed and range. |
| Cargo Micro Electric Car | Larger cargo space, removable passenger seats | Delivery services, small businesses | Pros: Versatile for goods transport. Cons: Reduced passenger capacity. |
| Lifestyle Micro Car | Stylish design, often convertible or with unique aesthetics | Urban lifestyle markets, rentals | Pros: Appeals to young consumers, brand visibility. Cons: Higher cost. |
| Eco-Friendly Mini EV | Focus on sustainability, often made from recycled materials | Eco-conscious businesses, tourism | Pros: Low environmental impact. Cons: May have higher initial costs. |
| Shared Mobility Vehicle | Designed for ride-sharing, easy access, and robust safety features | Ride-sharing platforms, urban fleets | Pros: High demand in urban areas, scalability. Cons: Maintenance costs can add up. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Urban Commuter Micro Electric Cars?
Urban commuter micro electric cars are characterized by their compact size and low speed, typically capped at 45 km/h. These vehicles are designed for city driving, making them ideal for navigating congested urban environments. They offer significant advantages for businesses involved in last-mile delivery and urban transport, providing a cost-effective solution for short-distance travel. However, their limited speed and range can be drawbacks for buyers requiring longer travel capabilities.
How Do Cargo Micro Electric Cars Serve B2B Needs?
Cargo micro electric cars are tailored for businesses that need to transport goods within urban settings. They often feature a larger cargo area and removable passenger seats, allowing for flexible configurations based on specific needs. This versatility makes them suitable for delivery services and small businesses looking to optimize logistics. While they excel in cargo capacity, the trade-off is often reduced passenger space, which may not suit all businesses.
Why Choose Lifestyle Micro Cars for Urban Markets?
Lifestyle micro cars stand out due to their stylish designs and unique features, such as convertible options. They cater to urban lifestyle markets and are popular among younger consumers. These vehicles can also serve rental companies looking to attract customers with trendy options. Despite their appeal and potential for brand visibility, the higher cost may deter some buyers, making it essential to evaluate the target market’s willingness to pay a premium.
What Makes Eco-Friendly Mini EVs Attractive to Businesses?
Eco-friendly mini electric vehicles emphasize sustainability, often constructed from recycled materials. They attract eco-conscious businesses and tourism sectors that prioritize low environmental impact. These vehicles can enhance a company’s green image and appeal to environmentally aware consumers. However, potential buyers should consider the higher initial costs associated with these models, weighing them against long-term savings on fuel and maintenance.
How Do Shared Mobility Vehicles Fit into the B2B Landscape?
Shared mobility vehicles are specifically designed for ride-sharing applications, featuring easy access and robust safety features. They are highly relevant for ride-sharing platforms and urban fleets, where demand for efficient, scalable transportation solutions is growing. While they can generate substantial revenue in urban areas, businesses must account for ongoing maintenance costs, which can affect overall profitability.
Key Industrial Applications of micro electric car concept
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of micro electric car concept | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Mobility | Last-Mile Delivery Solutions | Reduces delivery costs and enhances efficiency in urban settings. | Lightweight design and compact size for maneuverability. |
| Tourism and Leisure | Eco-Friendly Sightseeing Tours | Attracts environmentally conscious tourists and reduces carbon footprint. | Custom branding options and range specifications for tours. |
| Retail and E-commerce | In-Store and Warehouse Logistics | Streamlines internal logistics and improves service speed. | Battery capacity and charging infrastructure compatibility. |
| Educational Institutions | Campus Transportation Solutions | Provides a sustainable transport option for students and staff. | Safety features and maintenance support for long-term use. |
| Shared Mobility | Car-Sharing Services | Offers an affordable, flexible transport solution for urban residents. | Fleet management systems and user-friendly interfaces. |
How Can Micro Electric Cars Enhance Urban Mobility for Last-Mile Delivery Solutions?
Micro electric cars like the Microlino can revolutionize last-mile delivery by providing a compact, efficient alternative to traditional delivery vehicles. Their small footprint allows them to navigate congested urban areas easily, reducing delivery times and operational costs. For B2B buyers in logistics, the lightweight design minimizes fuel consumption and maintenance costs, making them an attractive option for companies looking to enhance their urban delivery services.
What Role Do Micro Electric Cars Play in Eco-Friendly Sightseeing Tours?
In the tourism sector, micro electric cars serve as eco-friendly vehicles for sightseeing tours, appealing to environmentally conscious travelers. These vehicles offer a unique and intimate way to explore urban landscapes without contributing to air pollution. B2B buyers in tourism should consider the customization options available for branding, as well as the vehicle’s range and charging capabilities, to ensure they meet the demands of their tour schedules.
How Can Retail and E-commerce Benefit from Micro Electric Cars for Logistics?
Micro electric cars can streamline logistics within retail and e-commerce businesses by facilitating quick and efficient in-store and warehouse deliveries. Their compact design allows for easy navigation through narrow aisles and busy urban streets, improving service speed and customer satisfaction. Buyers in this sector should focus on battery capacity and compatibility with existing charging infrastructure to maximize operational efficiency and minimize downtime.
Why Are Micro Electric Cars Ideal for Campus Transportation Solutions in Educational Institutions?
Educational institutions can leverage micro electric cars for campus transportation, offering a sustainable and efficient way to move students and staff. These vehicles are not only environmentally friendly but also provide a cost-effective solution for managing campus logistics. B2B buyers in this sector should prioritize safety features and long-term maintenance support to ensure these vehicles meet the unique demands of a busy educational environment.
How Does Shared Mobility Benefit from the Adoption of Micro Electric Cars?
The shared mobility sector can significantly benefit from the adoption of micro electric cars, providing an affordable and flexible transportation solution for urban residents. These vehicles cater to the growing demand for car-sharing services, especially in densely populated areas. B2B buyers should consider fleet management systems and user-friendly interfaces to enhance the overall user experience and operational efficiency of their car-sharing services.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘micro electric car concept’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Urban Mobility Options for Businesses
The Problem: In many urban areas, traditional vehicles face restrictions due to congestion and environmental regulations. Businesses in sectors such as logistics and last-mile delivery struggle to navigate these limitations, often incurring additional costs or delays. For instance, a delivery service may find it challenging to meet customer demands while adhering to low-emission zone regulations, limiting their operational scope and increasing transportation expenses.
The Solution: B2B buyers can overcome this challenge by integrating micro electric cars into their fleets. These vehicles are designed to comply with urban mobility regulations, making them ideal for navigating restricted zones. When sourcing micro electric cars, businesses should look for models that offer compact dimensions, enabling them to park in tight spaces easily and reduce the time spent on deliveries. Additionally, investing in a mix of battery sizes can provide flexibility in range, accommodating different delivery routes. By leveraging micro electric cars, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency while aligning with sustainable practices.
Scenario 2: High Operational Costs of Traditional Vehicles
The Problem: Many companies are experiencing rising operational costs associated with fuel, maintenance, and insurance for traditional vehicles. In regions such as Africa and South America, where fuel prices can be volatile, the financial burden on businesses is significant. A logistics company, for example, may find that a large portion of their budget is consumed by fuel costs, leaving less room for investment in growth or other operational improvements.
The Solution: Transitioning to micro electric vehicles can significantly reduce overall operational costs. With lower charging costs compared to fuel expenses, companies can save money on energy consumption. Buyers should evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) for micro electric cars, considering not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing costs like insurance and maintenance, which are generally lower than those for conventional vehicles. Additionally, adopting fleet management software can optimize routes and charging schedules, further enhancing cost savings and operational efficiency.
Scenario 3: Concerns About Vehicle Safety and Reliability
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are hesitant to adopt micro electric cars due to concerns about safety and reliability, especially in regions with challenging road conditions or heavy traffic. Companies involved in transportation may worry that smaller vehicles lack the structural integrity or advanced safety features of conventional cars, potentially putting drivers and cargo at risk.
The Solution: Buyers should prioritize sourcing micro electric cars that come equipped with robust safety features, such as unibody safety cells and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Engaging with manufacturers that emphasize quality engineering and safety testing can provide peace of mind. It’s also essential to review customer feedback and independent safety ratings when considering various models. Companies can mitigate risk by conducting thorough field tests in real-world conditions before fully integrating these vehicles into their operations, ensuring they meet safety and reliability standards for their specific needs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for micro electric car concept
What Are the Key Materials for Micro Electric Cars?
When selecting materials for micro electric cars, it’s essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. The right material can enhance performance, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of micro electric vehicles: aluminum, high-strength steel, composite materials, and lithium-ion batteries.
How Does Aluminum Contribute to Micro Electric Car Performance?
Aluminum is widely used in micro electric cars due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 600°C and can withstand various environmental conditions.
Pros: Aluminum is durable, lightweight, and offers good thermal conductivity, which is beneficial for battery cooling. Its manufacturing processes, such as extrusion and die-casting, are well-established, leading to lower production costs.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost compared to other metals, and it can be more challenging to weld.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s lightweight properties improve energy efficiency and range, making it ideal for urban commuting.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is crucial, especially in regions like Europe where regulations are stringent. Buyers in Africa and South America may also prefer aluminum for its recyclability, aligning with sustainability goals.
What Role Does High-Strength Steel Play in Micro Electric Cars?
High-strength steel (HSS) is increasingly utilized in micro electric vehicles for its strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand high-pressure ratings and offers excellent structural integrity.
Pros: HSS provides superior crash protection, making it a preferred choice for safety-critical components. It is also cost-effective compared to aluminum.
Cons: While HSS is durable, it is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact energy efficiency.
Impact on Application: HSS is particularly suitable for the vehicle’s chassis and safety cell, enhancing passenger protection.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local safety standards and consider the availability of HSS in their region. In markets like Saudi Arabia, where high temperatures are prevalent, HSS’s resistance to deformation is a significant advantage.
How Do Composite Materials Enhance Micro Electric Vehicle Design?
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced plastics, are gaining traction in micro electric car design due to their lightweight and high-strength properties.
Pros: Composites offer exceptional strength while being significantly lighter than metals. They are also resistant to corrosion and can be molded into complex shapes.
Cons: The primary limitation is the high manufacturing cost and complexity involved in production, which can deter mass adoption.
Impact on Application: Composites can be used in body panels and interior components, enhancing aesthetic appeal and reducing overall vehicle weight.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must be aware of the specific manufacturing processes and quality standards required for composites. In Europe, adherence to environmental regulations regarding composite disposal is crucial.
What Is the Importance of Lithium-Ion Batteries in Micro Electric Cars?
Lithium-ion batteries are the heart of any electric vehicle, including micro electric cars, providing the necessary power for propulsion.
Pros: These batteries have high energy density and can be charged quickly, making them suitable for urban commuting. They also have a long life cycle and are becoming more cost-effective as technology advances.
Cons: The main drawback is their sensitivity to temperature extremes, which can affect performance and longevity.
Impact on Application: Lithium-ion batteries enable longer ranges and faster charging times, essential for urban mobility solutions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international battery standards, such as UN 38.3 for transport, is vital. Buyers in regions like Africa may need to consider the availability of charging infrastructure and battery recycling options.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Micro Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for micro electric car concept | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, chassis components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost than other metals | Medium |
| High-Strength Steel | Safety cell, chassis | Excellent crash protection | Heavier, impacting energy efficiency | Low |
| Composite Materials | Body panels, interior components | High strength-to-weight ratio | High manufacturing cost and complexity | High |
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | Powertrain, energy storage | High energy density and quick charging | Sensitive to temperature extremes | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of strategic material selection for micro electric cars, equipping B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for micro electric car concept
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Micro Electric Cars?
The manufacturing process for micro electric cars involves several key stages, each critical to producing a high-quality and efficient vehicle. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to collaborate with manufacturers in this innovative sector.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used?
The first step in manufacturing micro electric cars is material preparation. Manufacturers typically utilize lightweight materials such as aluminum and high-strength steel to enhance performance and safety. These materials contribute to the vehicle’s overall efficiency, allowing for better battery performance and range. The use of lithium-ion batteries is standard, given their energy density and efficiency. Suppliers must ensure that materials meet international standards for safety and durability, which is crucial for maintaining quality throughout production.
How Is the Forming Process Executed?
Following material preparation, the forming process takes place. This stage includes techniques such as stamping, extrusion, and bending to create the vehicle’s body and components. Advanced technologies like Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining are employed to ensure precision in forming parts that fit together seamlessly. For micro electric cars, forming techniques must be carefully monitored to maintain structural integrity while minimizing weight.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail?
The assembly stage is where various components come together to create the final product. This includes integrating the powertrain, battery systems, and electronic controls. Skilled labor is essential during this phase, as it requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure that every part functions correctly. Automation plays a significant role in assembly, reducing human error and increasing efficiency. Manufacturers often implement modular assembly techniques, allowing for easier upgrades and repairs in the future.
How Is the Finishing Process Completed?
The final stage in manufacturing is finishing, which encompasses painting, surface treatments, and quality checks. This process not only enhances the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal but also protects it from environmental factors. Manufacturers may utilize eco-friendly paints and coatings to align with sustainability practices, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should Micro Electric Car Manufacturers Follow?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, particularly in the automotive sector. For micro electric cars, adherence to international standards ensures that products meet safety, performance, and reliability benchmarks.
Which International Standards Are Relevant?
Manufacturers should comply with international standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that processes are efficient and customer-focused. Additionally, specific industry certifications like CE marking (Conformité Européenne) demonstrate compliance with European safety and environmental requirements, essential for B2B buyers in Europe.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage checks the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Ensuring that suppliers meet quality standards is crucial for the overall manufacturing process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC monitors various stages to catch defects early. This can include visual inspections and functional tests to ensure that components are assembled correctly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, FQC involves comprehensive testing of the completed vehicle. This includes performance tests, safety evaluations, and compliance checks with regulatory standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential to ensure reliability and safety.
What Are the Best Practices for Supplier Audits?
Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective methods for verifying quality control. Buyers should establish a clear audit framework that assesses the supplier’s adherence to international standards, production capabilities, and QA processes. Regular audits can help identify potential issues before they affect product quality.
How Important Are Quality Reports and Certifications?
Quality reports and certifications from recognized organizations provide additional assurance of a supplier’s commitment to quality. Buyers should request documentation of compliance with relevant standards and certifications to evaluate the supplier’s quality management practices thoroughly.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing process and quality control measures. These inspections can occur at various stages, from material sourcing to final product testing, ensuring that the manufacturer adheres to specified quality standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various regulations and certifications specific to their regions. Understanding these nuances can help facilitate smoother transactions and compliance.
How Do Regional Regulations Affect Manufacturing?
Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements that manufacturers must adhere to. For example, vehicles sold in Europe must meet stringent emissions and safety standards, while markets in Africa and South America may have different criteria. B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers are knowledgeable about these regulations and can provide compliant products.
What Should Buyers Know About Import Certifications?
Import certifications can vary significantly between regions. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the necessary documentation required to import micro electric cars into their countries. This may include emissions tests, safety certifications, and compliance with local laws regarding electric vehicles.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality and Compliance in Micro Electric Car Manufacturing
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is vital for B2B buyers in the micro electric car market. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, alongside robust quality control processes, buyers can ensure they source high-quality vehicles that meet international standards. Engaging in thorough supplier verification practices and staying informed about regional regulations will further enhance the buying process, paving the way for successful partnerships in this burgeoning industry.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘micro electric car concept’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in navigating the procurement process for micro electric car concepts. As urban mobility solutions gain traction globally, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of sourcing these vehicles is essential. This checklist outlines key steps to ensure that you select the right supplier and vehicle that meets your operational needs.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Establish clear technical requirements for the micro electric car concept you wish to procure. Consider aspects such as size, seating capacity, range, and speed limitations to ensure the vehicle aligns with intended use cases, especially in urban environments.
– Key considerations:
– Maximum range for daily use (e.g., 100 km).
– Speed requirements suitable for local regulations.
2. Research Market Trends and Regulatory Compliance
Stay informed about the latest trends in micro electric vehicles (EVs) and local regulations that may impact their use. Understanding zoning laws, emissions requirements, and potential subsidies in your target market can influence your purchasing decisions.
– Focus on:
– Emerging technologies like solar charging capabilities.
– Government incentives for electric vehicle adoption.
3. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct a thorough evaluation of potential suppliers to ensure they meet your quality and reliability standards. Request detailed company profiles, product specifications, and case studies from similar clients.
– Important factors:
– Supplier experience in the micro EV market.
– Customer testimonials and references.
4. Verify Certifications and Standards
Ensure that the vehicles meet international safety and quality certifications relevant to your market. Compliance with standards such as ISO, UNECE regulations, and local safety norms is critical for operational legitimacy.
– Check for:
– Safety certifications specific to electric vehicles.
– Environmental impact assessments if required.
5. Assess Cost of Ownership and Financing Options
Examine the total cost of ownership, including purchase price, maintenance, insurance, and charging infrastructure. Explore financing options available, such as leasing or financing through partnerships with local banks.
– Consider:
– Comparison of operating costs versus traditional vehicles.
– Potential savings from low maintenance and energy-efficient features.
6. Engage in Prototyping and Testing
Before finalizing a purchase, engage in prototyping and testing phases to evaluate the vehicle’s performance in real-world conditions. This step is crucial for understanding how the vehicle fits into your operational workflow.
– Test for:
– Handling and maneuverability in urban settings.
– Charging time and convenience.
7. Establish After-Sales Support and Warranty Terms
Verify the after-sales support provided by the supplier, including warranty terms, maintenance services, and parts availability. Strong support structures can significantly enhance the longevity and performance of your investment.
– Look for:
– Length and coverage of warranties.
– Availability of local service centers or support hotlines.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs while contributing to sustainable urban mobility solutions.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for micro electric car concept Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Micro Electric Cars?
When sourcing micro electric cars, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary components of the cost structure include:
- Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects costs. Lightweight materials like aluminum and advanced composites can increase initial expenses but may enhance performance and energy efficiency.
- Labor: Labor costs vary by region and production method. Automated manufacturing processes can reduce labor costs but may require significant upfront investment in machinery.
- Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility costs, and maintenance of production equipment. Efficient production lines can lower overhead per unit.
- Tooling: The costs associated with creating molds and tools for production can be substantial. Buyers should consider tooling costs in relation to expected production volume.
- Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes ensures product reliability and safety, which can increase initial costs but reduce long-term warranty claims and enhance brand reputation.
- Logistics: Transporting micro electric cars from manufacturing sites to markets involves freight costs, which can vary significantly based on distance and shipping method.
- Margin: Manufacturers typically apply a margin to cover risks and return on investment, which can vary based on market conditions and competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Micro Electric Car Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of micro electric cars:
- Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) that align with their market demand.
- Specifications/Customization: Custom features can increase costs. Buyers should assess the necessity of specific features versus standard offerings to optimize expenses.
- Materials: The selection of materials not only impacts durability and performance but also plays a significant role in the overall cost. Sustainable materials may attract a premium but can enhance brand appeal.
- Quality/Certifications: Compliance with international safety and environmental standards can increase costs, but these certifications are vital for market acceptance, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
- Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers with robust supply chains may offer more competitive pricing and better service.
- Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for cost management. Different Incoterms dictate who bears costs and risks at various stages of the shipping process, influencing the final price.
What Are the Best Tips for Buyers Negotiating Micro Electric Car Prices?
When negotiating prices for micro electric cars, international B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
- Emphasize Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the long-term savings associated with operating micro electric cars, including lower fuel and maintenance costs, to justify initial investments.
- Leverage Bulk Purchasing: Buyers should negotiate for discounts based on larger orders or long-term contracts, which can significantly lower unit prices.
- Request Detailed Quotes: Understanding the breakdown of costs can help buyers identify areas for potential savings, such as logistics or material costs.
- Explore Local Partnerships: Collaborating with local suppliers can reduce shipping costs and lead times, enhancing overall efficiency.
- Stay Informed About Market Trends: Awareness of market conditions and competitor pricing can provide leverage in negotiations, allowing buyers to make informed decisions.
What Should Buyers Know About Pricing Nuances in Different Regions?
Pricing dynamics can vary considerably by region:
- Africa and South America: Consideration of local economic conditions, import tariffs, and currency fluctuations is crucial. Buyers may need to factor in additional costs associated with infrastructure limitations.
- Middle East and Europe: Regulatory compliance and environmental standards are often stricter, which can influence pricing. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can meet these requirements to avoid penalties and enhance market acceptance.
Conclusion
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing influencers for micro electric cars is essential for B2B buyers. By leveraging negotiation strategies and being aware of regional pricing nuances, businesses can optimize their sourcing strategies and achieve better financial outcomes. Buyers should always seek indicative prices and be prepared for fluctuations based on market conditions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing micro electric car concept With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Urban Mobility
As cities evolve, the need for efficient and sustainable urban mobility solutions becomes increasingly paramount. The micro electric car concept presents an innovative way to address urban transportation challenges, but it’s essential for B2B buyers to consider various alternatives that may also meet their operational needs. This section compares the micro electric car concept against other viable solutions, helping businesses make informed decisions based on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Micro Electric Car Concept | E-Scooters | Public Transportation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Range: 228 km, Speed: 90 km/h | Range: 40-80 km, Speed: 25 km/h | Speed: Varies, Frequent service |
| Cost | Purchase: CHF 159/month | Purchase: CHF 300-1,200 | Monthly Pass: CHF 50-100 |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires minimal infrastructure | Requires minimal infrastructure | Dependent on city planning |
| Maintenance | Low (battery and tires) | Very low (tires, battery) | High (infrastructure upkeep) |
| Best Use Case | Urban commuting, second vehicle | Short trips, last-mile solutions | High-density areas, commuting |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
E-Scooters: A Flexible Solution for Short Distances
E-scooters have surged in popularity as an alternative mobility solution, particularly in urban environments. They are lightweight, easy to maneuver, and perfect for short distances, making them ideal for last-mile connectivity. However, e-scooters typically have a limited range of 40-80 km and a lower speed of around 25 km/h. While they require minimal infrastructure and maintenance, issues such as theft and regulation can pose challenges for fleet operators. E-scooters are best suited for businesses targeting quick urban commutes or addressing short-distance travel needs.
Public Transportation: A Tried-and-True Method
Public transportation remains one of the most reliable methods for urban mobility. Buses and subways can efficiently transport large numbers of people, reducing congestion and lowering individual carbon footprints. While the initial investment in infrastructure can be high and maintenance costs significant, public transport can be economically viable over time, especially in densely populated areas. However, public transport systems often face challenges such as delays and overcrowding, which can deter users. Businesses considering public transport solutions should evaluate the local transit landscape and potential partnerships with transit agencies.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Urban Mobility Solution
Selecting the appropriate urban mobility solution requires careful consideration of various factors, including operational needs, target demographics, and geographical constraints. The micro electric car concept offers a compelling option for businesses looking for efficient, eco-friendly transportation tailored for urban environments. However, alternatives like e-scooters and public transportation may also provide significant benefits depending on specific use cases. B2B buyers should conduct thorough assessments of each option’s performance, cost, and ease of implementation to determine the best fit for their unique requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for micro electric car concept
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Micro Electric Cars?
When considering the micro electric car concept, several technical properties are paramount. These specifications not only influence the vehicle’s performance and usability but also play a critical role in procurement and operational decisions for B2B buyers.
-
Battery Capacity (kWh)
Battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), indicates how much energy the battery can store, directly affecting the vehicle’s range. For instance, options like 5.5 kWh, 10.5 kWh, and 15 kWh batteries provide varying ranges (up to 228 km) and charging times. Understanding battery capacity is essential for B2B buyers as it influences operational costs, charging infrastructure needs, and customer satisfaction. -
Kerb Weight (kg)
The kerb weight of a micro electric car, such as 496 kg for the Microlino, affects handling, efficiency, and performance. A lighter vehicle generally consumes less energy, enhancing range and reducing operational costs. Buyers need to consider weight when evaluating fleet efficiency and compliance with local regulations, especially in urban areas. -
Maximum Speed (km/h)
The maximum speed is crucial for determining a vehicle’s suitability for various markets. For example, the Microlino has a max speed of 90 km/h, making it ideal for urban commuting while adhering to speed restrictions in low-emission zones. This specification is vital for B2B buyers targeting specific demographics, such as urban commuters or eco-conscious consumers. -
Charging Time (hours)
Charging time indicates how long it takes to fully recharge the battery. For instance, the Microlino can be charged in just four hours from a standard socket. Quick charging solutions are essential for businesses that require vehicle availability throughout the day, thus influencing fleet management strategies. -
Trunk Volume (liters)
The trunk volume, such as the Microlino’s 230 liters, defines the vehicle’s practicality for everyday use. A spacious trunk can accommodate various cargo needs, making the vehicle more appealing to businesses that require transport of goods. This property can significantly affect purchasing decisions, especially for urban delivery services.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand?
Navigating the micro electric vehicle market requires familiarity with specific trade terminology that can influence procurement and operational strategies.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that manufactures products or components that are used in another company’s end product. In the micro electric car market, understanding OEM relationships is crucial for ensuring quality components and compliance with industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ can help in budgeting and inventory management, particularly when evaluating suppliers for fleet purchases. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to invite suppliers to bid on specific products or services. In the context of micro electric vehicles, issuing an RFQ can help businesses compare pricing and specifications from multiple manufacturers, ensuring a competitive procurement process. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers involved in importing micro electric vehicles, as they define responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO refers to the total costs associated with owning a vehicle over its entire lifespan, including purchase price, maintenance, insurance, and fuel costs. For B2B buyers, calculating TCO is vital for assessing the economic viability of investing in micro electric vehicles compared to traditional options.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies empowers B2B buyers in making informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the micro electric car concept Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Shaping the Micro Electric Car Concept Sector?
The micro electric car sector is witnessing transformative growth, driven by urbanization, environmental concerns, and technological advancements. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should note that urban congestion is prompting cities to explore alternative mobility solutions. Micro electric vehicles (EVs) are emerging as a practical response, offering compactness and efficiency for densely populated areas. These vehicles often cater to a dual market: they serve as a first car for individuals in urban settings and as a second vehicle for families needing a cost-effective, eco-friendly alternative.
Emerging trends include advancements in battery technology, which are crucial for improving range and charging times. The rise of smart technology integration, such as vehicle connectivity and autonomous features, is also reshaping consumer expectations. B2B buyers should consider sourcing vehicles equipped with these technologies to meet market demand. Additionally, the growing emphasis on sustainability is pushing manufacturers to adopt innovative sourcing strategies, favoring local suppliers and eco-friendly materials.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influence the Micro Electric Car Concept Sector?
Sustainability is a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the micro electric car sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, from raw material extraction to vehicle assembly, is under scrutiny. Buyers should prioritize manufacturers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing carbon footprints through sustainable practices. This includes utilizing renewable energy in production and implementing waste reduction strategies.
Ethical sourcing of materials is equally important. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and environmentally friendly extraction methods not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances brand reputation. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) can serve as indicators of a company’s commitment to sustainability. Furthermore, sourcing components made from recycled materials or bio-based alternatives can significantly contribute to the overall eco-friendliness of micro electric cars.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Micro Electric Cars Relevant to B2B Buyers?
The micro electric car concept has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from niche products to viable urban mobility solutions. Initially, micro cars were seen as novelty items, often lacking the performance and safety features of traditional vehicles. However, advancements in battery technology and vehicle design have propelled these vehicles into mainstream markets.
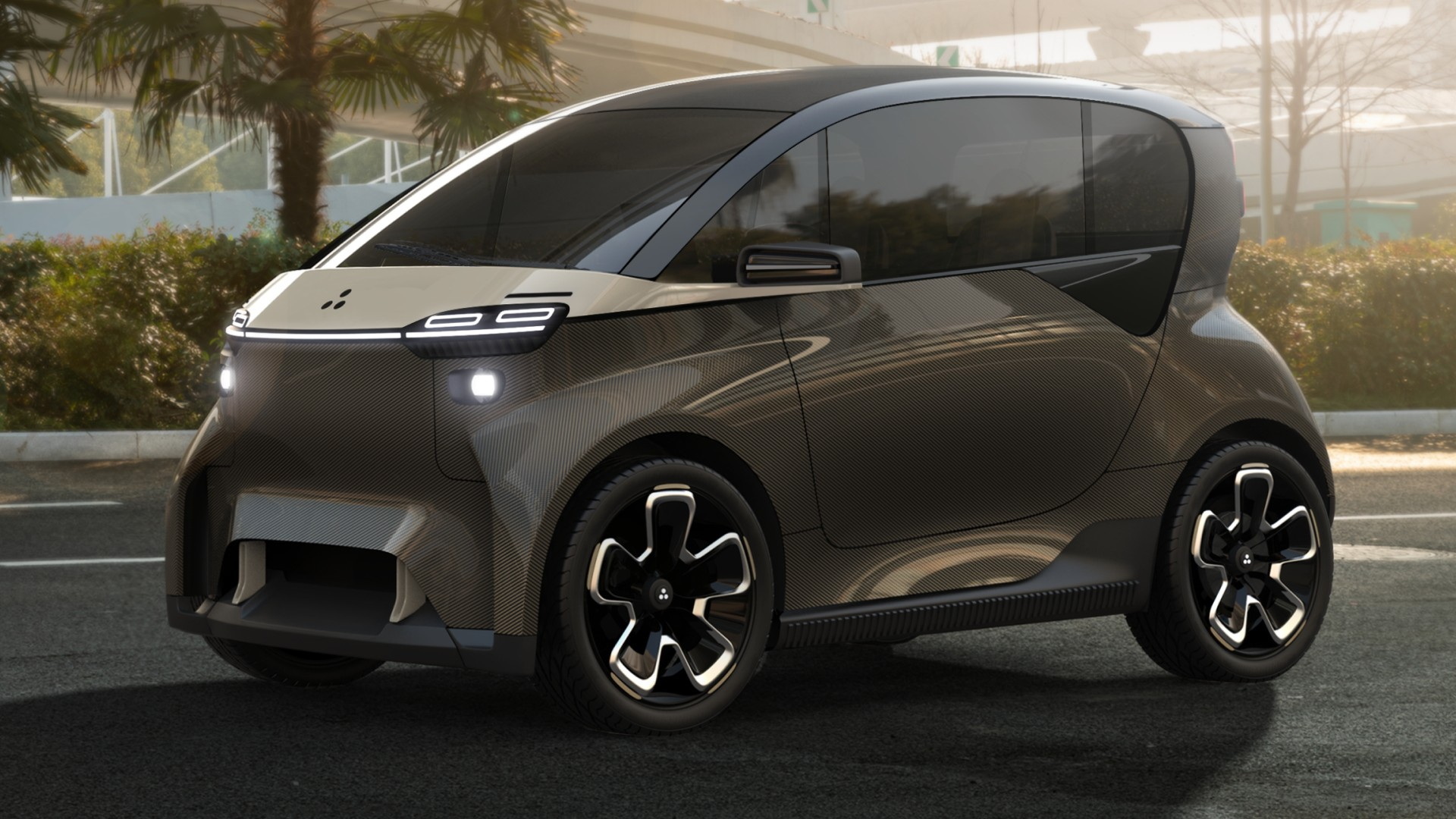
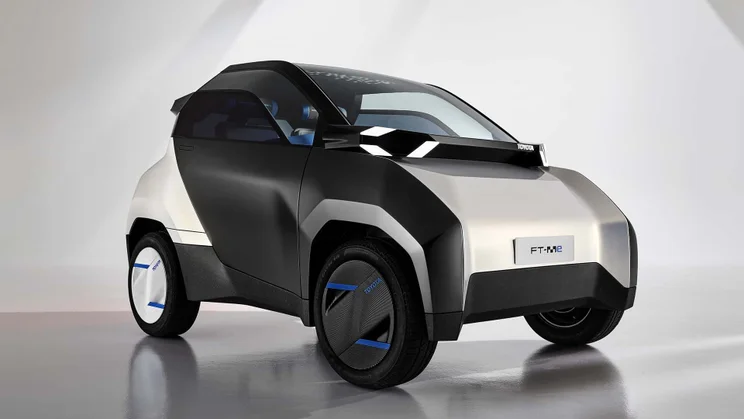
The introduction of models like the Microlino and Toyota’s FT-Me concept reflects a growing recognition of the unique needs of urban consumers. These vehicles combine compact design with enhanced safety features and efficiency, making them attractive for both individual and commercial use. As the market continues to mature, B2B buyers should be aware of the rapid innovation cycles and the importance of aligning with manufacturers who are at the forefront of these developments. Understanding the historical context of micro electric cars can provide valuable insights into future trends and opportunities in this dynamic sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of micro electric car concept
-
How do I assess the quality of micro electric cars from suppliers?
To evaluate the quality of micro electric cars, start by requesting detailed specifications, including safety features, battery life, and performance metrics. Conduct on-site visits to manufacturing facilities to observe production processes and quality control measures. Additionally, review certifications and compliance with international safety standards. Ask for customer testimonials and case studies to gauge the supplier’s reliability. Finally, consider third-party assessments or industry awards to further substantiate the supplier’s credibility. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing micro electric cars in B2B transactions?
Payment terms can vary significantly by supplier, but common practices include a deposit (often 20-30%) upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipping or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment terms for larger orders. It’s crucial to discuss and negotiate these terms upfront to ensure they align with your cash flow and budgeting strategies. Always review the payment structure in the context of the total cost of ownership, including shipping and duty fees. -
What customization options are available for micro electric cars?
Customization options can include color, branding, and interior features tailored to your specific needs. Some manufacturers may offer modular designs that allow for adjustments in seating capacity or cargo space. It’s essential to clarify the extent of customization available and any associated costs or lead times. Discuss your requirements early in the sourcing process to ensure the supplier can meet your expectations without significant delays. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for micro electric cars?
MOQs for micro electric cars typically depend on the supplier and the specific model. Some manufacturers may allow small orders (e.g., 10-50 units) to accommodate startups or smaller businesses, while others may set higher minimums to justify production runs. When negotiating, consider potential future demand to avoid being locked into excessive inventory. Always confirm the MOQ in writing before proceeding with an order to prevent misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure compliance with international trade regulations for micro electric cars?
To ensure compliance, familiarize yourself with import/export regulations in your target markets, including emissions standards and safety requirements. Work with legal advisors or trade compliance experts to navigate tariffs, duties, and documentation necessary for international shipping. Additionally, verify that your supplier adheres to compliance standards in their country and can provide the necessary certifications for your market. Regular audits and updates on regulations can help maintain compliance. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing micro electric cars?
Logistics play a critical role in the timely delivery of micro electric cars. Consider factors such as shipping methods, transit times, and costs associated with customs clearance. Assess the supplier’s ability to handle logistics efficiently, including their experience with international shipping and familiarity with local regulations. Additionally, plan for potential delays by maintaining open communication with your supplier and logistics partners. -
How do I conduct effective supplier vetting for micro electric car manufacturers?
Effective supplier vetting involves several steps: research potential suppliers’ market reputation, check their financial stability, and request references from previous clients. Conduct site visits to assess manufacturing capabilities and quality control practices. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or Global Sources to verify supplier credentials and read reviews. Additionally, consider requesting samples or trial orders to evaluate product quality firsthand before committing to larger purchases. -
What after-sales support should I expect when sourcing micro electric cars?
After-sales support can vary by supplier but typically includes warranty coverage, maintenance services, and customer service for troubleshooting. Clarify the terms of warranties, including duration and what components are covered. Inquire about training for your staff on vehicle operation and maintenance. A reliable supplier should provide ongoing support, including access to spare parts and technical assistance, ensuring your fleet remains operational and efficient.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Micro Electric Car Concept Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Microlino – Compact Electric Car
Domain: microlino-car.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Microlino Car details:
– Space for 2 adults and 3 beer crates.
– Fully charged in 4 hours on a standard household socket.
– Fits in any parking space, allowing cross-parking and easy exit onto the sidewalk.
– Trunk volume: 230 liters, accommodating shopping bags, 1 large suitcase, 2 pieces of hand luggage, or 3 beer crates.
– Maximum range: 228 km.
– Maximum speed: 90 km/h.
– Kerb weight: 4…
2. Pinterest – Micro Car Concepts
Domain: pinterest.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Micro car concepts, including various designs and models such as Fiat’s Centoventi, which previews a modular electric Panda, Citroën’s ME Concept, a boxy all-terrain EV with retro aesthetics, and Uniti’s plan to create the iPhone of EVs. Related interests include modern military vehicles, autonomous trucks, compact electric cars, and futuristic vehicle designs.
3. Opel – Rocks-e, AIXAM – e City GTO, Microlino – Key Product
Domain: go-e.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Opel Rocks-e: Purchase price: from €7,990, Top speed: 45 km/h, Range: up to 75 km, Max charging power: 2.3 kW, Battery capacity: 5.5 kWh. AIXAM e City GTO: Purchase price: from €17,990, Top speed: 45 km/h, Range: up to 113 km, Max charging power: 2.3 kW, Battery capacity: 5.5 kWh. Microlino: Purchase price: from €19,990, Top speed: 90 km/h, Range: up to 228 km (WLTP), Max charging power: 2.2 kW, B…
4. Eli – $11,900 Electric Micro Car
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Eli launches its $11,900 electric micro ‘car’ in the US.
5. Toyota – FT-Me Concept
Domain: newsroom.toyota.eu
Introduction: Toyota FT-Me Concept, a compact battery electric vehicle designed for urban environments. Measures less than 2.5 meters in length, occupies half a parking space. Features premium styling with a bi-tone black and white design. Accessible for entry-level driving licenses, usable by individuals as young as 14 in some markets. Offers customisable options for diverse users, including teenagers and prof…
6. Volkswagen – ID. EVERY1
Domain: volkswagen-newsroom.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: The ID. EVERY1 is an entry-level electric model from Volkswagen, designed to provide mobility for everyone. It is part of the ID. family of electric vehicles and aims to be accessible in terms of pricing and functionality.
7. Telo Trucks – TELO MT1 All-Electric Mini Truck
Domain: telotrucks.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: {“model”:”TELO MT1″,”type”:”All-Electric Mini Truck”,”dimensions”:{“length”:”152 in”,”width”:”73 in”,”height”:”67 in”},”bed_size”:{“length”:”60-96 in”,”width”:”56 in”,”depth”:”18 in”},”seating_capacity”:”2, 5, or 8 seats”,”performance”:{“acceleration_0_60″:”6.0 s”,”power”:”300 hp”,”payload_capacity”:”2000 lbs”,”towing_capacity”:”6600 lbs”},”battery”:{“standard_range”:”260 mi”,”long_range”:”350 mi”…
8. Facebook – AI-Driven Generative Design Solutions
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – AI-Driven Generative Design Solutions, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for micro electric car concept
As the micro electric car market continues to evolve, strategic sourcing becomes increasingly essential for international buyers seeking to capitalize on this burgeoning segment. The compact design and eco-friendly attributes of micro electric vehicles (EVs) position them as optimal solutions for urban mobility, particularly in regions facing space constraints and environmental regulations. By leveraging local suppliers and sustainable production practices, companies can not only enhance their supply chain resilience but also align with global sustainability goals.
The Microlino and Toyota’s FT-Me exemplify innovative approaches to urban transportation, offering unique features that cater to diverse consumer needs, from efficient charging options to versatile interiors. These vehicles present a significant opportunity for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to meet the growing demand for affordable, sustainable mobility solutions.
As we look ahead, international B2B buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships that enhance their offerings in the micro electric vehicle space. By investing in strategic sourcing now, companies can position themselves at the forefront of a transformative automotive landscape, driving both economic and environmental benefits.