Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for low speed electric car
In an era where sustainability and efficiency dominate the automotive landscape, navigating the global market for low-speed electric cars presents both opportunities and challenges for international B2B buyers. Sourcing low-speed electric vehicles (LSVs) that meet regional regulations and consumer expectations can be daunting, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide is designed to equip businesses with the essential knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions, addressing key considerations such as vehicle types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost analysis.
Low-speed electric cars are not just eco-friendly alternatives; they are versatile solutions suitable for urban environments, enabling efficient transportation in areas with heavy traffic and lower speed limits. By delving into the specifications, safety standards, and potential use cases of LSVs, this comprehensive guide empowers international buyers to identify the most appropriate vehicles for their specific needs.
Furthermore, we will explore the intricacies of supplier evaluation, ensuring that buyers can confidently select reputable manufacturers who comply with safety and performance regulations. As the demand for sustainable transportation continues to rise, understanding the landscape of low-speed electric cars will help businesses capitalize on emerging market trends and make strategic investments that enhance their operational efficiency and environmental responsibility.
Understanding low speed electric car Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Speed Vehicle (LSV) | Street-legal, max speed of 25 mph, under 3,000 lbs, safety standards | Urban transport, campus shuttles, resorts | Pros: Cost-effective, eco-friendly; Cons: Limited speed, range may not suit long distances |
| Neighborhood Electric Vehicle (NEV) | Similar to LSV but designed for residential areas, often more customizable | Residential communities, gated neighborhoods | Pros: Attractive design, social engagement; Cons: Limited to low-speed areas, potential regulatory hurdles |
| Electric Utility Vehicle (EUV) | Built for utility tasks, often includes cargo space and towing capabilities | Warehousing, agriculture, facility maintenance | Pros: Versatile for tasks, lower operational costs; Cons: May lack passenger comfort features |
| E-Shuttle | Designed for passenger transport, often features multiple seating options | Airports, large corporate campuses, events | Pros: Efficient people mover, can reduce traffic congestion; Cons: Higher initial investment, maintenance costs |
| Electric Golf Cart | Primarily for recreational use, lower speed than LSV, often lacks regulatory compliance | Golf courses, resorts, parks | Pros: Fun, easy to maneuver; Cons: Not street-legal, limited utility outside designated areas |
What are the characteristics and suitability of Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs)?
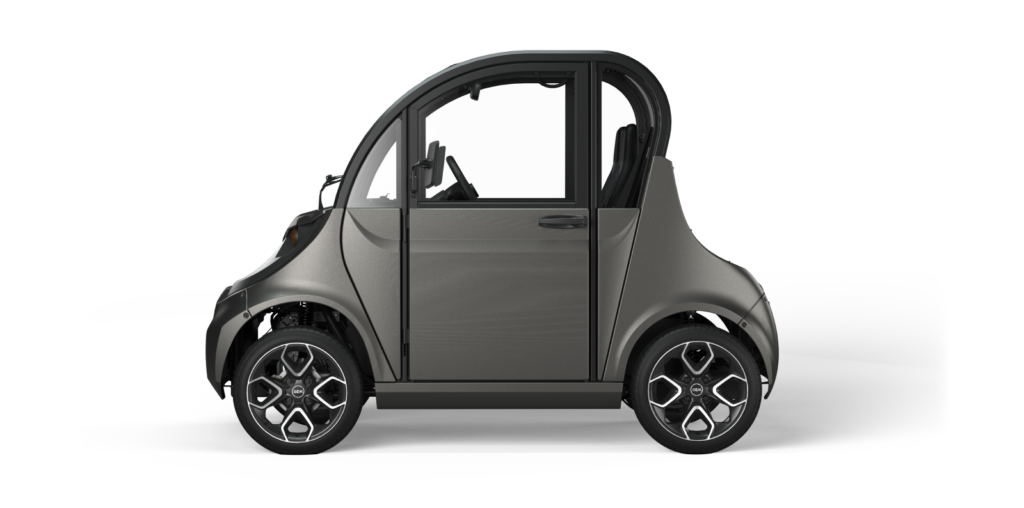
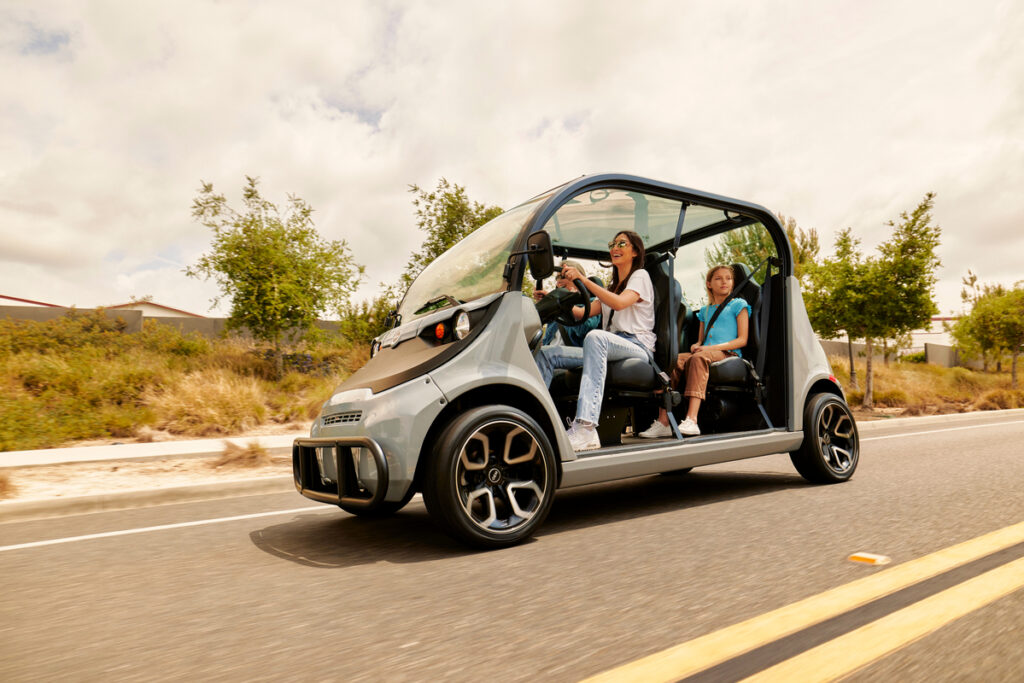
Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) are designed for urban environments, adhering to safety standards that allow them to operate legally on public roads with speed limits of 35 mph or less. Their lightweight construction and compact size make them ideal for short-distance travel, particularly in congested areas. For B2B buyers, LSVs are suitable for applications such as campus shuttles, resort transport, and urban delivery services, offering a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional vehicles. When considering purchasing, buyers should evaluate the vehicle’s range, battery life, and compliance with local regulations.
How do Neighborhood Electric Vehicles (NEVs) stand out in the market?
Neighborhood Electric Vehicles (NEVs) share many characteristics with LSVs but are specifically tailored for residential use, often featuring customizable designs that enhance user experience. They are particularly suitable for gated communities and residential neighborhoods, where they can replace conventional vehicles for short trips. B2B buyers should consider the aesthetic appeal and social engagement potential of NEVs, as they can enhance community interactions. However, the limitations in speed and range, as well as potential regulatory challenges, should be carefully assessed.
What makes Electric Utility Vehicles (EUVs) a practical choice for businesses?
Electric Utility Vehicles (EUVs) are designed for operational efficiency, featuring cargo space and towing capabilities that make them suitable for various utility tasks. They are commonly used in warehousing, agriculture, and facility maintenance, where versatility and lower operational costs are essential. B2B buyers should prioritize features such as payload capacity, battery life, and maintenance costs when considering EUVs. While they provide utility advantages, buyers must also assess comfort levels for passengers if the vehicle will be used for transporting personnel.
Why are E-Shuttles increasingly popular for large venues?
E-Shuttles are specifically engineered for passenger transport, making them an efficient solution for airports, corporate campuses, and large events. They typically offer multiple seating options and can significantly reduce traffic congestion by providing an alternative to traditional buses or personal vehicles. For B2B buyers, the key considerations should include capacity, operational costs, and the vehicle’s ability to navigate specific environments. Although the initial investment may be higher, the long-term benefits of reduced congestion and enhanced passenger experience can justify the cost.
What are the benefits and limitations of Electric Golf Carts?
Electric Golf Carts are primarily designed for recreational use, often seen on golf courses and in resorts. They are easy to maneuver and provide a fun driving experience, making them attractive for leisure activities. However, they are not street-legal and are limited in utility outside designated areas. B2B buyers should weigh the fun and social aspects of these vehicles against their restrictions and consider whether they align with their operational needs. While they can enhance the guest experience in recreational settings, their limited functionality may not be suitable for all business applications.
Key Industrial Applications of low speed electric car
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Low Speed Electric Car | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Transportation | Last-Mile Delivery Solutions | Reduces operational costs and emissions | Compliance with local regulations and safety standards |
| Hospitality and Tourism | Shuttle Services for Resorts and Hotels | Enhances guest experience and accessibility | Customization options for branding and comfort features |
| Educational Institutions | Campus Transportation | Improves mobility for students and staff | Battery life and charging infrastructure availability |
| Industrial Parks and Warehouses | Internal Logistics and Transport | Increases efficiency in material handling | Payload capacity and durability for heavy use |
| Municipal Services | Community Maintenance and Patrol Vehicles | Cost-effective and environmentally friendly | Local service support and maintenance agreements |
How Are Low Speed Electric Cars Used in Urban Transportation?
In urban settings, low-speed electric cars are increasingly adopted for last-mile delivery solutions. These vehicles can navigate congested areas efficiently, reducing operational costs and emissions associated with traditional delivery methods. Businesses must ensure compliance with local regulations regarding vehicle specifications and safety standards, particularly in regions where electric vehicle adoption is still growing, such as parts of Africa and South America.
What Role Do Low Speed Electric Cars Play in Hospitality and Tourism?
In the hospitality sector, low-speed electric cars serve as shuttles for resorts and hotels, enhancing guest experience by providing convenient transportation options within expansive properties. These vehicles can be customized for branding purposes, making them an attractive choice for businesses looking to improve service and accessibility. Buyers should consider comfort features and the capacity to accommodate varying guest needs, especially in tourist-heavy regions in the Middle East and Europe.
Why Are Low Speed Electric Cars Valuable for Educational Institutions?
Educational institutions utilize low-speed electric cars for campus transportation, facilitating mobility for students and staff across large grounds. This application addresses the challenge of accessibility and promotes sustainable transport solutions. Buyers from educational sectors should evaluate the battery life and availability of charging infrastructure to ensure uninterrupted service, particularly in developing regions where such facilities may be limited.
How Do Low Speed Electric Cars Enhance Efficiency in Industrial Parks and Warehouses?
In industrial parks and warehouses, low-speed electric cars are effective for internal logistics and transport, aiding in the movement of goods and personnel. Their compact design allows for maneuverability in tight spaces, increasing operational efficiency. Businesses must consider payload capacity and vehicle durability to withstand frequent use, especially in regions with varying climatic conditions, such as Brazil and Saudi Arabia.
What Benefits Do Municipal Services Gain from Low Speed Electric Cars?
Municipal services leverage low-speed electric cars for community maintenance and patrol duties, providing a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional vehicles. These cars can navigate urban environments easily, making them suitable for various municipal applications. When sourcing, municipalities should prioritize local service support and maintenance agreements to ensure long-term operational reliability, particularly in emerging markets with growing urban populations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘low speed electric car’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Regulatory Compliance for Low-Speed Electric Cars
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with understanding the regulatory landscape surrounding low-speed electric cars (LSEVs). Each region, whether in Africa, South America, or Europe, has specific regulations regarding vehicle specifications, safety standards, and road usage. For instance, a buyer looking to operate LSEVs for urban transportation may find it challenging to navigate the complexities of local laws, leading to potential legal liabilities and financial penalties.
The Solution: To effectively navigate these regulatory waters, B2B buyers should prioritize engaging with local automotive regulatory bodies and legal consultants who specialize in transportation laws. Before purchasing LSEVs, conduct thorough research on the specific regulations in the target market, focusing on vehicle classifications, required safety features, and permissible roadways. Additionally, consider partnering with manufacturers that have experience in your region and can provide vehicles compliant with local laws. Leverage resources such as government websites and industry associations to stay updated on any regulatory changes that could affect operations.
Scenario 2: Addressing Limited Range and Battery Life Concerns
The Problem: A common concern among B2B buyers is the limited range of low-speed electric cars, which can be a significant drawback in regions with vast urban sprawl or inadequate charging infrastructure. Businesses that rely on these vehicles for deliveries or shuttle services may find themselves facing operational inefficiencies, especially if vehicles frequently run out of charge before completing their routes.
The Solution: To mitigate range anxiety, buyers should carefully evaluate the battery specifications and charging capabilities of potential LSEVs before procurement. Opt for models that offer extended battery life and faster charging options, as these features are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency. Additionally, consider investing in a network of charging stations within your operational area. This could involve partnerships with local businesses or municipalities to establish charging infrastructure in strategic locations. Implementing route planning software that optimizes travel distances and charging stops can further enhance the vehicle’s utility.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Safety Features Meet User Expectations
The Problem: Safety is a paramount concern for organizations looking to incorporate low-speed electric cars into their fleets. Many B2B buyers worry about the adequacy of safety features, especially when these vehicles are used in environments with heavy pedestrian traffic, such as urban centers or college campuses. Without proper safety measures, companies risk accidents that could lead to liability issues and damage to their reputation.
The Solution: B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing low-speed electric cars that not only meet but exceed standard safety requirements. Look for vehicles equipped with comprehensive safety features such as robust occupant protection systems, backup cameras, and advanced braking systems. It’s also beneficial to conduct a comparative analysis of various manufacturers’ safety ratings and performance in real-world scenarios. Implementing driver safety training programs can further enhance safety by ensuring that operators are well-versed in the unique handling characteristics of LSEVs. Regular maintenance checks and safety audits should also be scheduled to ensure that vehicles remain in optimal condition for safe operation.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for low speed electric car
What Are the Key Materials Used in Low-Speed Electric Cars?
Low-speed electric cars (LSEVs) require a careful selection of materials to ensure safety, performance, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of LSEVs, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Aluminum is a popular choice for the chassis and body panels of low-speed electric cars due to its lightweight nature and excellent corrosion resistance. With a temperature rating that can withstand extreme conditions, aluminum contributes to the overall efficiency of electric vehicles by reducing weight and improving range.
Pros: Aluminum is durable and offers good strength-to-weight ratios, enhancing vehicle performance. It is also relatively easy to manufacture and can be recycled, aligning with sustainability goals.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which can be higher than steel. Additionally, aluminum may require specialized welding techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance makes it suitable for various environmental conditions, especially in coastal areas. However, international buyers must consider the availability of skilled labor for aluminum fabrication.
Steel: Strength and Versatility
Steel is widely used in the structural components of low-speed electric vehicles due to its strength and affordability. It can withstand significant stress, making it ideal for safety-critical applications such as the frame and suspension systems.
Pros: Steel is cost-effective and readily available, making it a practical choice for manufacturers. Its durability ensures a long lifespan, which is a critical factor for B2B buyers looking for reliable products.
Cons: The primary disadvantage of steel is its weight, which can negatively impact the vehicle’s range and efficiency. Additionally, steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Steel’s versatility allows for various applications within LSEVs, but buyers in humid or saline environments should prioritize corrosion-resistant coatings or treatments.
Composite Materials: Lightweight and Strong
Composite materials, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, are increasingly used in low-speed electric cars for body panels and interior components. These materials offer a unique combination of lightweight properties and high strength.
Pros: Composites can significantly reduce vehicle weight, enhancing performance and energy efficiency. They also allow for complex shapes and designs, which can improve aesthetics and aerodynamics.
Cons: The manufacturing process for composites can be complex and costly, making them less accessible for some manufacturers. Additionally, repair and recycling can be challenging compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly advantageous in regions with strict weight regulations. However, international buyers must ensure compliance with local standards for materials used in vehicle construction.
Plastic: Cost-Effective and Flexible
Plastics are commonly used in low-speed electric vehicles for components such as dashboards, interior trims, and light housings. Their versatility and cost-effectiveness make them a popular choice among manufacturers.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight and can be molded into various shapes, allowing for design flexibility. They are also resistant to corrosion and can be produced at a lower cost than metals.
Cons: Plastics may not offer the same level of durability as metals, particularly in high-stress applications. They can also degrade over time when exposed to UV light unless treated.
Impact on Application: For international buyers, the choice of plastic must consider local regulations regarding recyclability and environmental impact. Compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN is crucial.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Low-Speed Electric Cars
| Material | Typical Use Case for low speed electric car | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Chassis and body panels | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Steel | Structural components | Cost-effective and durable | Heavier weight can impact efficiency | Low |
| Composite | Body panels and interior components | Lightweight and design flexibility | Complex and costly manufacturing | High |
| Plastic | Dashboards and interior trims | Cost-effective and versatile | Less durable in high-stress areas | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials used in low-speed electric cars, emphasizing their properties, advantages, and considerations for international markets. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with regional standards and operational needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for low speed electric car
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Low Speed Electric Cars?
The manufacturing process for low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs) involves several critical stages, each crucial for ensuring the final product meets safety, performance, and quality standards. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess potential suppliers effectively.
1. Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in LSEVs?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. The primary materials used in the production of LSEVs include:
- Body Materials: Typically, manufacturers use lightweight metals like aluminum or high-strength steel to create the vehicle’s frame and body. These materials help maintain a lower weight, essential for electric vehicle efficiency.
- Battery Components: Lithium-ion batteries are common in LSEVs due to their high energy density and lightweight properties. Manufacturers need to ensure these batteries meet international safety and performance standards.
- Interior and Exterior Components: Plastics and composites are often used for aesthetic and functional parts, including dashboards, seats, and panels. These materials are selected for their durability and resistance to environmental factors.
2. Forming: How Are Low Speed Electric Cars Shaped?
The forming stage involves various techniques to shape the prepared materials into components of the LSEV. Key techniques include:
- Stamping: This is commonly used for creating body panels. Large presses stamp flat sheets of metal into the desired shapes, ensuring consistency and precision.
- Injection Molding: This technique is used for producing plastic components. It allows for intricate designs and reduces waste by utilizing materials efficiently.
- Welding and Joining: Advanced welding techniques, such as laser welding, are employed to assemble the vehicle’s frame. This ensures strong joints that can withstand the stresses of driving.
3. Assembly: What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
The assembly stage is where the vehicle comes together. This typically includes:
- Chassis Assembly: The frame is built first, incorporating the suspension system, wheels, and braking systems. Precision is key here to ensure all components fit and function correctly.
- Electrical System Integration: The vehicle’s electric powertrain, including motors and battery packs, is installed. Manufacturers must ensure proper connections and insulation to avoid electrical failures.
- Final Assembly: This includes installing interior components, such as seating and dashboard systems, as well as exterior elements like lights and mirrors. Each component must meet stringent quality checks during this phase.
4. Finishing: How Are Low Speed Electric Cars Finished?
The finishing stage enhances the vehicle’s aesthetics and protects it from environmental factors. Key processes include:
- Painting and Coating: High-quality paints and protective coatings are applied to the vehicle’s exterior. This not only improves appearance but also adds layers of protection against corrosion and wear.
- Quality Inspections: Final inspections are conducted to ensure that all components meet the required specifications and safety standards before the vehicle is deemed ready for delivery.
What Quality Assurance Processes Are Commonly Used in LSEVs?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical part of the manufacturing process, especially for low-speed electric vehicles. Implementing robust QA processes helps ensure that vehicles meet international safety and performance standards.
Relevant International Standards: What Should B2B Buyers Know?
Manufacturers of LSEVs often adhere to various international standards, including:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for ensuring consistent product quality across all manufacturing stages.
- CE Marking: For vehicles sold in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements.
- FMVSS (Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards): In the U.S., LSEVs must meet specific safety standards outlined by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA).
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before being used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During assembly, regular inspections are conducted to identify any defects or deviations from standards. This can include visual inspections and functional tests.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, a comprehensive inspection is performed on the finished vehicle. This includes functionality tests, safety checks, and compliance with standards.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used for Low Speed Electric Cars?
Testing is essential to confirm that LSEVs operate safely and effectively. Common testing methods include:
- Durability Testing: Vehicles undergo stress tests to evaluate their performance under various conditions, including extreme temperatures and rough terrains.
- Safety Testing: Crash tests and rollover simulations are conducted to ensure occupant safety. Compliance with safety standards is crucial for market acceptance.
- Battery Performance Testing: This involves assessing the battery’s range, charging efficiency, and lifecycle. Battery tests are particularly important given the reliance on electric powertrains.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Here are several methods:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits can provide insights into a supplier’s quality management practices, production capabilities, and adherence to international standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand a supplier’s performance history and any issues encountered during production.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures and product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers should be aware of specific nuances regarding quality control, especially when sourcing from regions with varying standards:
- Regional Standards: Different regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, may have unique regulatory requirements. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local standards.
- Certification Requirements: Certifications may vary by region, affecting the ability to market and sell LSEVs. Buyers should verify that suppliers possess the necessary certifications for their target markets.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in manufacturing practices and quality expectations can help buyers navigate supplier relationships more effectively.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms for low-speed electric cars is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they partner with reliable suppliers that meet their quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘low speed electric car’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers interested in sourcing low-speed electric cars (LSEVs). With the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions in urban areas, understanding the procurement process is essential. This checklist outlines the critical steps to ensure you select the right vehicles that meet your specific operational needs while adhering to regulatory standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly define the technical specifications of the low-speed electric car you require. Consider factors such as maximum speed, range, weight capacity, and number of passengers. Understanding these specifications will help you narrow down your options and ensure the vehicles meet your operational requirements.
- Consider Local Regulations: Research local regulations regarding LSEVs, including maximum speed limits and any specific safety features mandated in your region.
- Identify Use Cases: Determine how the vehicles will be used—whether for short urban trips, shuttle services, or utility tasks—to guide your specifications.
Step 2: Assess Supplier Compliance with Safety Standards
Safety is paramount when sourcing low-speed electric cars. Ensure that potential suppliers comply with relevant safety standards, such as those set by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the U.S. or equivalent bodies in your target market.
- Request Documentation: Ask suppliers for safety certification documents and compliance records to verify their adherence to safety regulations.
- Inspect Safety Features: Evaluate the safety features included in the vehicles, such as seat belts, lights, and braking systems, to ensure they meet or exceed required standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from previous clients, particularly those in similar industries or geographic regions.
- Review Reputation: Check online reviews and industry ratings to gauge supplier reliability and customer satisfaction.
- Conduct Site Visits: If possible, visit the supplier’s facilities to inspect their production processes and quality control measures.
Step 4: Consider Total Cost of Ownership
Beyond the initial purchase price, assess the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, charging infrastructure, and insurance costs. Understanding these expenses is crucial for budgeting and long-term financial planning.
- Calculate Maintenance Costs: Inquire about the average maintenance costs and warranty coverage for the vehicles.
- Evaluate Charging Solutions: Consider the cost of setting up charging stations and the electricity costs associated with operating LSEVs.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, negotiate the terms and conditions of your purchase. This includes pricing, delivery schedules, and after-sales support.
- Seek Volume Discounts: If you plan to purchase multiple units, negotiate for bulk discounts to reduce overall costs.
- Clarify Support Services: Ensure that the supplier provides adequate support services, including training for drivers and maintenance personnel.
Step 6: Plan for Implementation and Training
After finalizing your order, develop a comprehensive implementation plan that includes driver training and vehicle integration into your existing fleet.
- Organize Training Sessions: Schedule training for drivers and staff to ensure safe and efficient operation of the new vehicles.
- Monitor Performance: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor the vehicles’ performance and make adjustments as necessary.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing low-speed electric cars, ensuring they select vehicles that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for low speed electric car Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Low-Speed Electric Car Manufacturing?
When sourcing low-speed electric cars (LSVs), understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-quality batteries, electric motors, and lightweight materials such as aluminum can increase initial costs but may enhance performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is essential for assembly, particularly for electrical components and safety features that meet federal standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility maintenance, and indirect labor costs. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead costs, ultimately benefiting the buyer.
-
Tooling: Investment in specialized tools and molds for production can be substantial. Buyers should consider this in their total cost calculations, especially when customizing designs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes are necessary to ensure compliance with safety standards. This adds to the cost but is crucial for maintaining brand reputation and ensuring user safety.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary greatly depending on the distance and method of transport. Buyers should also factor in customs duties and taxes for international shipments.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a markup to cover their costs and generate profit. Understanding the manufacturer’s pricing strategy can aid in negotiations.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Low-Speed Electric Vehicle Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of low-speed electric cars:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Establishing a relationship with manufacturers can yield favorable terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customizing features, such as battery capacity or safety enhancements, can increase costs. Buyers must balance their needs against budget constraints.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Premium materials and certifications can enhance vehicle safety and efficiency, but they also elevate costs. Buyers should evaluate the long-term benefits of investing in higher-quality components.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established manufacturers may offer better quality assurance but might come with a higher price tag.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery (e.g., FOB, CIF) can impact the overall cost. Buyers should ensure they are clear on who bears the risk and cost during shipping.
What Are the Best Negotiation Strategies for B2B Buyers?
To optimize costs in sourcing low-speed electric cars, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If possible, consolidate orders to meet minimum volume requirements, which can lead to significant savings.
-
Highlight Long-Term Partnerships: Emphasizing potential long-term relationships can encourage suppliers to offer better pricing or terms.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Gathering quotes from various manufacturers can provide insights into market pricing and help in negotiating better deals.
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also maintenance, insurance, and operational costs. A higher initial investment may lead to lower TCO over time.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Different regions may have varying import duties, taxes, and market conditions that can affect pricing. Conducting thorough market research can equip buyers with valuable negotiation leverage.
Conclusion: What Should B2B Buyers Keep in Mind?
While sourcing low-speed electric cars, it’s essential to analyze the comprehensive cost structure and price influencers. Buyers should focus on negotiating favorable terms and understanding the long-term implications of their purchasing decisions. By paying attention to the nuances of international sourcing, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their strategic goals. Always remember to request indicative pricing to avoid unexpected costs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing low speed electric car With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Low-Speed Electric Cars
In the pursuit of sustainable and efficient urban mobility, low-speed electric cars (LSEVs) have emerged as a popular choice. However, businesses seeking transportation solutions should consider various alternatives that may also meet their operational requirements. This analysis compares low-speed electric cars with golf carts and bicycles, focusing on key aspects relevant to B2B buyers.
| Comparison Aspect | Low Speed Electric Car | Golf Cart | Bicycle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Max speed: 25 mph; suitable for short urban trips | Max speed: 15 mph; designed for golf courses, limited on roads | Varies; can exceed 20 mph with e-bikes; highly versatile |
| Cost | $15,240 – $21,240 (varies by model) | $5,000 – $15,000 (depends on customization) | $500 – $3,000 (depends on type and features) |
| Ease of Implementation | Street-legal; requires licensing and insurance; more complex setup | Easier to implement for private use; less regulation | Minimal regulation; easy to deploy, no licensing needed |
| Maintenance | Moderate; requires regular servicing and battery checks | Low; simple mechanics, but battery maintenance needed | Low; occasional tire and brake maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Urban environments; short-distance travel; community transport | Golf courses, resorts, and private communities | Short trips, personal commuting, and eco-friendly transport |
Understanding Golf Carts as an Alternative
Golf carts are primarily designed for use on golf courses and private communities. They typically have a lower maximum speed of around 15 mph and are not street-legal in many jurisdictions. While they are more affordable than low-speed electric cars, their limited functionality restricts their application primarily to recreational or private settings. Businesses operating in gated communities or large resorts may find golf carts an effective solution for local transport, but their limited speed and range may not be suitable for broader urban applications.
Evaluating Bicycles: A Cost-Effective Option
Bicycles, including electric bikes (e-bikes), offer a highly flexible transportation alternative. With costs ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars, they are significantly more affordable than low-speed electric cars. Bicycles have minimal regulatory requirements and can be used in various environments, making them an excellent choice for short commutes and eco-friendly travel. However, they may not be ideal for transporting multiple passengers or goods, which limits their applicability for businesses needing to transport larger groups or equipment.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
Selecting the appropriate transportation solution depends on various factors, including budget, operational needs, and the specific environment in which the vehicles will be used. Low-speed electric cars provide a balance of speed, capacity, and compliance with regulations, making them suitable for urban settings and community transport. On the other hand, golf carts and bicycles offer distinct advantages in terms of cost and simplicity, albeit with limitations in performance and versatility. B2B buyers should assess their unique requirements carefully, considering both immediate needs and long-term operational goals, to make the most informed decision.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for low speed electric car
What are the Key Technical Properties of Low-Speed Electric Cars?
When assessing low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs), several critical specifications are essential for B2B buyers to understand. These properties not only affect the vehicle’s performance but also influence purchasing decisions, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
1. Maximum Speed and Weight Rating
Low-speed electric cars are designed with a maximum speed of 25 mph (40 km/h) and a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) of less than 3,000 lbs (1,361 kg). This specification is crucial because it determines where the vehicle can legally operate. For instance, LSEVs can be used on roads with speed limits of 35 mph or lower, making them suitable for urban environments and short-distance travel.
2. Battery Capacity and Range
Battery capacity, typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), defines how far a vehicle can travel on a single charge. Many LSEVs offer ranges from 60 to 100 miles, which is ideal for local commuting and community transport. Understanding battery specifications is vital for B2B buyers to ensure that the vehicle meets operational needs without frequent recharging, thereby optimizing fleet management.
3. Charging Time and Type
Charging time and compatibility with charging infrastructure are critical considerations. LSEVs may support standard AC charging or rapid DC charging options. A vehicle that can charge quickly and is compatible with existing charging stations will reduce downtime and enhance fleet productivity, making it an attractive option for businesses.
4. Safety Features Compliance
LSEVs must meet specific safety standards set by regulatory bodies such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the U.S. Required features include headlights, turn signals, seat belts, and backup cameras. Compliance with safety standards not only ensures legal operation but also enhances the vehicle’s marketability and protects the buyer from potential liability issues.
5. Materials and Construction Quality
The materials used in the construction of LSEVs, such as high-strength steel and advanced composites, affect durability, weight, and maintenance costs. A vehicle built with high-quality materials will typically have a longer lifespan and lower total cost of ownership, which is a critical consideration for B2B buyers looking to invest in a fleet.
What are Common Trade Terms in the Low-Speed Electric Vehicle Industry?
Understanding the terminology used in the low-speed electric vehicle market can greatly enhance communication between buyers and suppliers, ensuring clarity and efficiency in transactions.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of LSEVs, OEMs supply critical components like batteries, motors, and safety systems. Buyers should consider the reputation and reliability of OEMs to ensure quality and compatibility.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for B2B buyers to understand as it can impact inventory management and cash flow. Negotiating favorable MOQs can help businesses scale their purchases according to demand.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. For low-speed electric vehicles, an RFQ can help buyers compare prices, terms, and conditions from different manufacturers, facilitating informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify shipping, insurance, and freight costs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border purchases of LSEVs to avoid unexpected costs and ensure smooth logistics.
5. TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with owning a vehicle over its entire life cycle, including purchase price, maintenance, insurance, and depreciation. B2B buyers should analyze TCO to make informed financial decisions and select vehicles that provide the best value over time.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when considering investments in low-speed electric vehicles, ensuring they meet both operational needs and compliance requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the low speed electric car Sector
What Are the Global Drivers for the Low-Speed Electric Car Market?
The low-speed electric vehicle (LSEV) market is gaining momentum due to several global drivers. Urbanization trends, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, are pushing the need for efficient, cost-effective transportation solutions. Many cities are grappling with traffic congestion and pollution, making LSEVs an attractive alternative. With their compact size and low operational costs, these vehicles are ideal for short-distance travel, particularly in densely populated urban areas.
Emerging technologies are reshaping the LSEV landscape, with advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure driving innovation. International B2B buyers are increasingly seeking vehicles that not only meet regulatory requirements but also offer enhanced features such as improved safety standards and longer battery life. Additionally, government incentives aimed at promoting electric mobility are emerging in various countries, making LSEVs a financially viable option for businesses looking to invest in sustainable transport solutions.
What Are the Current and Emerging B2B Sourcing Trends in the Low-Speed Electric Car Sector?
B2B sourcing trends in the LSEV sector are increasingly focused on partnerships with manufacturers who prioritize innovation and sustainability. Buyers are looking for suppliers that can offer customizable vehicles that cater to specific business needs, whether for urban transport, tourism, or last-mile delivery. The trend towards electric mobility is accompanied by a demand for transparency in the supply chain, prompting buyers to collaborate with manufacturers who adhere to ethical sourcing practices.
Additionally, the importance of after-sales support and service agreements is growing, as businesses seek to minimize downtime and maximize the lifespan of their fleet. As the market matures, international B2B buyers are also exploring opportunities for joint ventures and collaborations to tap into local knowledge and distribution networks, particularly in emerging markets like Brazil and Saudi Arabia.
How Do Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Low-Speed Electric Car Market?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the low-speed electric vehicle market, with businesses increasingly focused on minimizing their environmental impact. The production of LSEVs involves sourcing materials that have a reduced carbon footprint, such as recycled metals and sustainable composites. Ethical sourcing is also becoming crucial, as buyers demand transparency regarding the origin of materials used in vehicle manufacturing.
Green certifications are gaining traction, providing assurance that vehicles meet environmental standards. Suppliers with certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and STeP (Sustainable Textile and Leather Production) are becoming preferred partners for international buyers. By choosing ethically sourced materials, businesses not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also enhance their brand reputation among environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Low-Speed Electric Cars?
The concept of low-speed electric vehicles has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, these vehicles were primarily used in niche markets such as golf courses and gated communities. However, as urbanization and environmental concerns have intensified, the demand for street-legal LSEVs has surged.
In the early 2000s, regulatory changes in various countries, particularly in the U.S., recognized low-speed vehicles as a legitimate category of transportation, paving the way for broader acceptance. Today, innovations in battery technology and design are enhancing the appeal of LSEVs, making them suitable for a wider range of applications, from commercial use to personal mobility. As the market continues to evolve, B2B buyers are presented with an expanding array of options that combine efficiency, sustainability, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of low speed electric car
-
How do I determine the appropriate low-speed electric vehicle (LSEV) for my business needs?
To select the right LSEV, assess your specific operational requirements, such as passenger capacity, cargo needs, and typical travel distances. Consider the vehicle’s range, speed, and compliance with local regulations. Additionally, evaluate the terrain where the vehicle will be used, as some models may perform better on uneven surfaces. Engaging with suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and customization options will help ensure the vehicle aligns with your business model. -
What are the key safety standards for low-speed electric vehicles?
Low-speed electric vehicles must comply with safety standards set by local regulatory bodies, such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the U.S. Key requirements typically include functioning headlamps, turn signals, tail lights, and safety belts. Furthermore, vehicles should have a backup camera and a VIN (Vehicle Identification Number). Ensure that suppliers provide documentation proving compliance with these standards, especially if you plan to operate in different countries with varying regulations. -
How can I assess the reliability of potential suppliers for low-speed electric vehicles?
To vet suppliers, start by reviewing their industry reputation and experience in the LSEV market. Request references from past clients and check for customer reviews. Additionally, inquire about their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards. A thorough site visit to the supplier’s facility can also provide insights into their operational standards and capabilities. -
What customization options are typically available for low-speed electric vehicles?
Many manufacturers offer customization options such as seating configurations, color choices, and additional features like climate control, enhanced safety systems, or specialized cargo areas. Discuss your specific needs with suppliers, and ask for examples of previous customizations they have completed. This ensures that the vehicle not only meets regulatory standards but also aligns with your brand and operational requirements. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for low-speed electric vehicles?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly by supplier and the specific vehicle model. Generally, manufacturers may have MOQs ranging from 1 to 50 units, depending on production capabilities and inventory. It is advisable to negotiate MOQs, especially if you are a smaller buyer. In some cases, suppliers may be willing to accommodate lower quantities for initial orders or pilot programs. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing low-speed electric vehicles internationally?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include a deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due prior to shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans, particularly for larger orders. Always clarify payment methods, currencies accepted, and any associated fees before finalizing agreements to ensure transparency. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for low-speed electric vehicles?
To ensure quality, request detailed QA protocols from the supplier, including their testing processes and certifications. It’s beneficial to establish a written agreement that outlines quality standards and inspection rights upon delivery. Consider conducting inspections at the supplier’s facility before shipment and upon arrival to confirm that vehicles meet agreed-upon specifications and standards. -
What logistics considerations should I take into account when importing low-speed electric vehicles?
Logistics for importing LSEVs involve several factors, including shipping methods, customs regulations, and transportation routes. Consult with freight forwarders who specialize in vehicle transport to understand potential challenges and costs. Ensure that all necessary documentation, such as import permits and compliance certificates, is prepared in advance to facilitate a smooth import process. Additionally, consider local infrastructure and distribution channels for efficient delivery to end-users.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Low Speed Electric Car Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Gemcar – e2: Nimble EV
Domain: gemcar.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) are street-legal, four-wheeled vehicles with a top speed of 25 mph and a gross vehicle weight rating of less than 3,000 lbs. They are typically electric and must adhere to federal safety standards. Key models include:
– e2: Nimble EV with up to 97 miles of range, seats 1-2, starting at $15,240 MSRP.
– e4: Popular and versatile EV with up to 91 miles of range, seats 1-4,…
2. Vantage – Electric Low-Speed Vehicles
Domain: vantagevehicle.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Vantage’s electric low-speed vehicles (LSVs) provide eco-friendly transport solutions for various businesses and facilities. Key features include:
– Zero emissions, contributing to cleaner air and reduced environmental impact.
– Street-legal design, allowing operation in urban and industrial environments (up to 25 mph).
– Powered by 100% lithium electric charging systems, requiring no specializ…
3. Marshell – EEC Approved DS-A2-2 Electric Vehicle
Domain: marshell.net
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: EEC Approved Electric Low Speed Vehicle, Model: DS-A2-2, Max Speed: 40 km/h, Climbing Capacity: 30%, Controller: 48V 400A
4. Reddit – Affordable Medium Speed Electric Vehicle
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Small, durable, relatively comfortable, inexpensive electric vehicle; capable of reaching speeds up to 35 mph; ideally seats 4; classified as medium speed vehicles (MSV); currently limited options available.
5. Westward Industries – MAX-EV LSV Electric Utility Vehicle
Domain: westwardindustries.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: MAX-EV LSV Electric Utility Vehicle
– Type: Low Speed Electric Utility Vehicle (LSV)
– Seating Capacity: 2 and 4-seater options
– Drivetrain: Electric drivetrain with permanent magnetic advanced motor
– Battery Options: Standard lithium-ion batteries ranging from 8kWh to 24kWh
– Estimated Range: 35-45 miles (8kWh), up to 120 miles (20kWh)
– Max Speed: 25 mph (on-road), 52 mph (for higher models)
-…
6. Eli Zero – All-Electric Two-Seater
Domain: electrek.co
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Eli Zero: All-electric two-seater, expected to enter US market soon, pre-order program launching, designed to comply with LSV regulations, pricing not announced but costs around €14,000 in Europe (approx. US $15,000). Wink Motors: Four LSV models (Sprout, Sprout Solar, Mark 1, Mark 2 Solar), prices under US $10,000 for budget models, around US $12,000 for premium models, four-seaters, fireproof Li…
7. Moto Electric Vehicles – Low Speed Electric Vehicles
Domain: motoelectricvehicles.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Moto Electric Vehicles offers a range of Low Speed Vehicles (LSVs) that are electric and street legal, designed for speed-controlled communities with speed limits of 25-35 mph. The vehicles are equipped with safety features similar to conventional automobiles, including safety belts, parking brakes, rearview mirrors, headlights, taillights, and turn signals. They provide options for customization …
8. Raymond West – Low-Speed Electric Vehicles
Domain: raymondwest.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Low-Speed Electric Vehicles from ICON® EV ECO family, including EPIC Carts, Cruise Car Inc, and utility vehicles. Key offerings include: 2-Seater Golf Carts (EPIC Cart E20), 4-Seater Golf Carts (variety of options), 6-Seater Golf Carts (EPIC Cart E60 for hotels and resorts), I20 Series (2-Seater), I40 Series (4-Seater), I60 & I80 Series (6 to 8-Seater), utility carts, and passenger vehicles. Featu…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for low speed electric car
As the global demand for sustainable transportation solutions continues to rise, low-speed electric vehicles (LSVs) present a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers. These vehicles, designed for urban environments, not only comply with safety standards but also cater to the growing need for efficient, cost-effective, and eco-friendly transportation options. Sourcing LSVs strategically can help businesses capitalize on urban mobility trends while enhancing their sustainability initiatives.
In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the potential for LSV adoption is significant. With their ability to navigate congested areas and fulfill short-distance travel needs, LSVs can serve various sectors, including tourism, hospitality, and community services. Buyers should focus on partnerships with reputable manufacturers that offer innovative designs, robust safety features, and flexible financing options to maximize their investment.
Looking ahead, the market for low-speed electric vehicles is poised for growth, driven by urbanization and evolving transportation policies. Now is the time for international buyers to engage in strategic sourcing initiatives that not only align with their business objectives but also contribute to a greener future. Embrace the opportunity to lead in this emerging sector and secure your place in the evolving landscape of urban mobility.