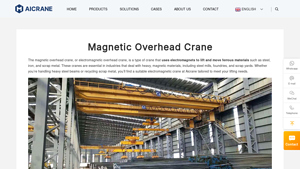
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for magnetic Crane
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, sourcing the right magnetic crane can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. With diverse applications ranging from recycling plants to steelmaking facilities, understanding the intricacies of magnetic cranes is essential for optimizing operations and enhancing productivity. This guide aims to demystify the magnetic crane market, providing insights into various types—including electromagnets and electro-permanent magnets—while exploring their specific applications and advantages across different industries.
Buyers will benefit from a thorough examination of key factors such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and the latest technological advancements that influence performance and reliability. With a focus on regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly Brazil and Vietnam—this comprehensive resource empowers stakeholders to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
By delving into case studies, expert recommendations, and best practices for integrating magnetic cranes into existing workflows, this guide serves as an invaluable tool for B2B buyers seeking to enhance their material handling capabilities. Whether you’re looking to upgrade your equipment or invest in new solutions, understanding the global market for magnetic cranes is the first step towards achieving operational excellence.
Understanding magnetic Crane Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Crane | Utilizes electric current to generate magnetic fields | Recycling plants, scrap yards | Pros: High lifting capacity; versatile. Cons: Requires reliable power supply. |
| Electro-Permanent Crane | Uses permanent magnets activated by electric pulses | Steel mills, manufacturing facilities | Pros: Energy-efficient; maintains grip without power. Cons: Initial cost can be high. |
| Charge Crane | Specialized for loading materials into furnaces | Steel production, foundries | Pros: High efficiency; designed for heavy loads. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Gantry Crane with Magnet | Combines gantry design with magnetic lifting capabilities | Outdoor applications, construction sites | Pros: Portable; flexible movement. Cons: May have lower load capacity compared to overhead cranes. |
| Magnetic Boom Lift Crane | Integrates magnetic lifting with boom lift functionality | Construction, heavy equipment handling | Pros: Ideal for tight spaces; versatile. Cons: May require additional training for operators. |
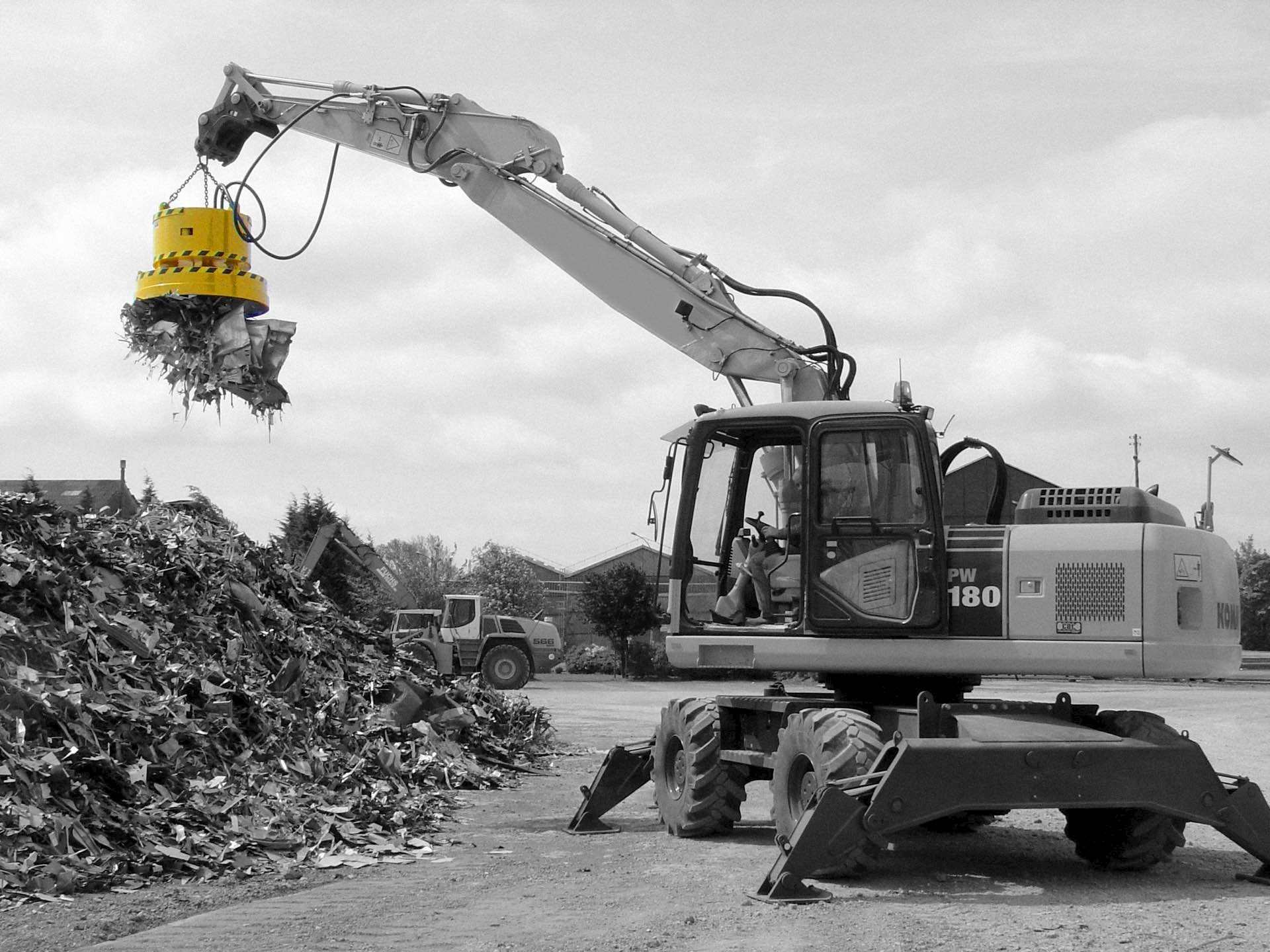
What Are the Characteristics of Electromagnetic Cranes?
Electromagnetic cranes are designed to handle ferrous materials efficiently by generating a magnetic field through electric current. These cranes are widely used in recycling plants and scrap yards due to their ability to lift and transport heavy metals like steel and iron. When considering an electromagnetic crane, B2B buyers should evaluate their power supply reliability, as these cranes require a constant current to function effectively. Additionally, the lifting capacity and operational speed are critical factors for optimizing productivity in material handling.
How Do Electro-Permanent Cranes Stand Out?
Electro-permanent cranes utilize permanent magnets that can be activated and deactivated with electric pulses. This design allows them to maintain their magnetic grip without continuous power, making them energy-efficient. They are particularly suitable for steel mills and manufacturing facilities where consistent performance is essential. Buyers should consider the initial investment cost, as electro-permanent cranes can be pricier than other options. However, the long-term savings on energy costs can offset this expense, making them an attractive choice for organizations focused on sustainability.
What Are the Unique Features of Charge Cranes?
Charge cranes are specifically designed for the steel production industry, where they load scrap or ore into furnaces. These cranes can be either floor-mounted or overhead, depending on the facility’s layout and requirements. Their high efficiency and capability to handle significant loads make them indispensable in foundries and steel mills. Buyers should assess the crane’s compatibility with their existing infrastructure and the specific load requirements of their operations to ensure optimal performance.
Why Choose Gantry Cranes with Magnet Features?
Gantry cranes equipped with magnetic lifting capabilities are ideal for outdoor applications and construction sites. Their portable design allows for flexible movement and easy setup, making them suitable for tasks that require lifting and transporting heavy loads without overhead structures. However, buyers should note that while gantry cranes are budget-friendly and versatile, they may not match the load capacity of traditional overhead cranes. Evaluating the specific lifting needs and site conditions is crucial for making the right investment.
How Do Magnetic Boom Lift Cranes Enhance Material Handling?
Magnetic boom lift cranes combine the functionality of a boom lift with magnetic lifting capabilities, making them particularly useful in construction and heavy equipment handling. Their design allows for operation in tight spaces, providing a versatile solution for various material handling tasks. However, organizations considering this type of crane should ensure that their operators are adequately trained to handle the unique challenges posed by this equipment. Understanding the operational requirements and potential limitations will help maximize the benefits of using a magnetic boom lift crane.
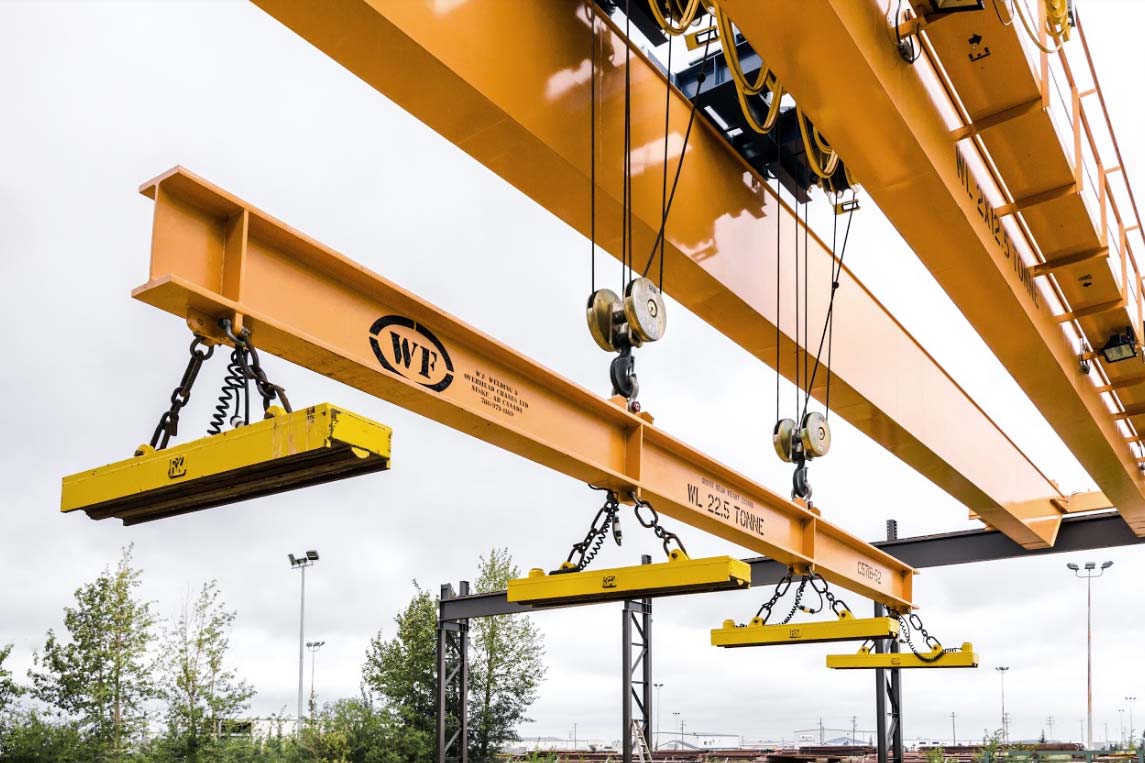
Key Industrial Applications of magnetic Crane
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Magnetic Crane | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Manufacturing | Handling of Scrap Metal and Raw Materials | Increases efficiency in material handling, reducing labor costs and time delays | Reliability of power supply, compatibility with existing systems, and load capacity requirements |
| Recycling and Waste Management | Sorting and Moving Recyclable Metals | Enhances recycling rates and operational efficiency, leading to increased profitability | Customization options for different material types, durability, and maintenance support |
| Construction and Heavy Industry | Lifting and Positioning Steel Beams and Components | Streamlines construction processes and improves safety by minimizing manual handling | Load weight specifications, environmental resistance, and operator training requirements |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Transporting Steel Parts and Components | Reduces production downtime and improves logistics efficiency | Integration with automated systems, safety features, and compliance with industry standards |
| Shipbuilding | Lifting Heavy Metal Plates and Structures | Speeds up production timelines and enhances safety in heavy lifting operations | Magnet strength, power source requirements, and adaptability to various ship designs |
How is Magnetic Crane Used in Steel Manufacturing?
In the steel manufacturing sector, magnetic cranes are pivotal for efficiently handling scrap metal and raw materials. These cranes streamline operations by swiftly moving heavy ferrous materials from one location to another, significantly reducing labor costs and minimizing the risk of workplace injuries. Buyers in this sector should consider the reliability of the power supply, ensuring that the cranes can handle the constant operation and demanding environments typical of steel mills. Compatibility with existing systems and the required load capacity are also critical factors.
What Role Does Magnetic Crane Play in Recycling and Waste Management?
Magnetic cranes are vital in recycling facilities, where they are employed to sort and transport recyclable metals. By automating the lifting and sorting processes, these cranes enhance recycling rates and operational efficiency, ultimately boosting profitability. International buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, should focus on customization options that cater to different types of recyclable materials, as well as the durability of the cranes given the often harsh working conditions in waste management environments.
How Do Magnetic Cranes Enhance Construction Processes?
In the construction and heavy industry sectors, magnetic cranes are used for lifting and positioning steel beams and components. This application not only streamlines construction processes but also improves safety by minimizing the need for manual handling of heavy materials. Buyers should ensure that the cranes meet specific load weight specifications and are resistant to environmental factors, particularly in outdoor construction sites. Additionally, operator training requirements should be factored in to maximize safety and efficiency.
How are Magnetic Cranes Applied in Automotive Manufacturing?
Magnetic cranes are extensively used in automotive manufacturing to transport steel parts and components throughout the production line. This application reduces production downtime and enhances logistics efficiency, which is critical in a sector where timely delivery is paramount. Buyers should look for cranes that can integrate seamlessly with automated systems, ensuring that safety features are in place to protect workers and equipment. Compliance with industry standards is also a key consideration in sourcing these cranes.
What is the Importance of Magnetic Cranes in Shipbuilding?
In the shipbuilding industry, magnetic cranes are employed for lifting heavy metal plates and structures, which is essential for speeding up production timelines. These cranes significantly enhance safety during heavy lifting operations, as they can handle substantial weights with ease. Buyers in this sector should pay attention to the strength of the magnets used and the power source requirements, as well as the adaptability of the cranes to various ship designs. Such considerations will ensure that the cranes meet the rigorous demands of shipbuilding projects.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘magnetic Crane’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Lifting Heavy Ferrous Materials Efficiently
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in industries like recycling, steelmaking, or manufacturing face the challenge of efficiently moving heavy ferrous materials. Traditional cranes may require multiple operators and complex rigging setups, which can slow down operations and increase labor costs. Additionally, there is always the risk of human error during the lifting process, which can lead to accidents, equipment damage, or material loss, further complicating logistics and impacting the bottom line.
The Solution: To enhance efficiency and safety, investing in a high-capacity magnetic crane specifically designed for heavy lifting is essential. Buyers should look for cranes equipped with powerful electromagnets or electro-permanent magnets, which can easily lift and transport large volumes of ferrous materials without the need for complex rigging. When sourcing a magnetic crane, it’s crucial to specify the maximum weight capacity needed for your operations and ensure that the crane’s magnet strength aligns with your materials’ weights. Additionally, incorporating automation features can help minimize human error, further improving safety and operational efficiency. Collaborating with a reputable manufacturer who provides tailored solutions and robust after-sales support can significantly enhance the overall effectiveness of your lifting operations.
Scenario 2: Frequent Equipment Maintenance and Downtime
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with unexpected maintenance issues and equipment downtime associated with magnetic cranes, which can severely disrupt production schedules. Factors such as wear and tear on electrical components, magnet malfunctions, or inadequate power supply can lead to prolonged periods where the crane is out of service. This unplanned downtime not only impacts productivity but can also lead to financial losses and strained client relationships.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance challenges, it is vital to choose magnetic cranes with durable components designed for the specific operational environment, such as those found in steel mills or recycling facilities. Buyers should seek cranes that feature advanced monitoring systems to track performance metrics and predict maintenance needs before they become critical. Establishing a routine maintenance schedule with a qualified technician can ensure that all components, particularly electrical connections and magnets, are regularly inspected and serviced. Furthermore, opting for cranes with readily available spare parts and robust warranty options can provide peace of mind and reduce the risk of extended downtime.
Scenario 3: Limited Versatility in Lifting Applications
The Problem: Many businesses encounter limitations with their existing lifting equipment, which may not be versatile enough to handle a wide range of ferrous materials or adapt to different operational needs. This lack of flexibility can lead to inefficiencies, as companies may need to invest in multiple cranes or equipment types to meet diverse lifting requirements, complicating inventory management and operational workflows.
The Solution: To address versatility concerns, buyers should consider acquiring magnetic cranes that can be customized or retrofitted for various lifting applications. This could involve selecting cranes with adjustable magnet configurations or those designed to be compatible with additional lifting attachments. When sourcing these cranes, it’s essential to discuss your specific operational needs with manufacturers, who can offer tailored solutions that enhance versatility. Investing in modular magnetic cranes that can be easily adapted for different materials—such as transitioning from scrap metal to larger steel components—can streamline operations and reduce the need for multiple machines. Additionally, providing training for operators on using the crane’s features effectively can maximize its potential across diverse applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for magnetic Crane
What Are the Common Materials Used in Magnetic Cranes?
When selecting materials for magnetic cranes, several factors come into play, including the operational environment, load requirements, and specific application needs. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of magnetic cranes, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international buyers.
Steel: The Backbone of Magnetic Crane Construction
Key Properties: Steel is renowned for its high tensile strength and durability. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 500°C (932°F) and can withstand significant pressure. Corrosion resistance can be enhanced through galvanization or coating.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its robustness and ability to handle heavy loads, making it ideal for industrial applications. However, it can be heavy and may require additional structural support. The cost of steel can vary widely based on quality and market conditions, and manufacturing complexity can increase with the need for specialized treatments.
Impact on Application: Steel is suitable for environments where heavy ferrous materials are handled, such as scrap yards and steel mills. Its compatibility with various loading conditions makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM A36 or JIS G3101 is crucial. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider local availability and pricing fluctuations.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Key Properties: Aluminum offers a lower density compared to steel, making it lightweight and easier to handle. It has excellent corrosion resistance, especially when anodized, and can perform well in temperatures up to 200°C (392°F).
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which can reduce operational costs related to energy and structural support. However, it has lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-load applications. The cost of aluminum is generally higher than that of steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly useful in environments where corrosion is a significant concern, such as coastal areas or chemical plants. Its lightweight nature allows for easier maneuverability in applications requiring frequent movement.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. In regions with high humidity, the corrosion resistance of aluminum makes it a preferred choice.
Composite Materials: The Future of Crane Technology
Key Properties: Composites, often made from a combination of materials like fiberglass and resin, offer a unique blend of strength and lightweight properties. They can withstand temperatures of up to 120°C (248°F) and are inherently resistant to corrosion.
Pros & Cons: Composites provide excellent strength-to-weight ratios and are resistant to environmental degradation. However, they can be more expensive to manufacture and may require specialized fabrication techniques. Their performance under extreme loads is still being evaluated in some applications.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for specialized applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aerospace or advanced manufacturing environments. Their resistance to corrosion makes them ideal for harsh environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with standards such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties. The availability of composite materials may vary significantly by region, impacting procurement strategies.
Copper: Essential for Electromagnetic Components
Key Properties: Copper is an excellent conductor of electricity, with high thermal and electrical conductivity. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 200°C (392°F) and is resistant to corrosion in various environments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, making it essential for the electromagnetic components of cranes. However, it is heavy and can be expensive compared to other materials. Its mechanical strength is lower than that of steel.
Impact on Application: Copper is critical in applications requiring efficient electromagnetic performance, such as in the coils of electromagnets used in magnetic cranes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM B170 is necessary. Buyers should also consider the fluctuating prices of copper on the global market, which can impact overall project costs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Magnetic Cranes
| Material | Typical Use Case for Magnetic Crane | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy lifting in scrap yards | High tensile strength and durability | Heavy; requires structural support | Medium |
| Aluminum | Corrosive environments | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength | High |
| Composite | Specialized applications | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| Copper | Electromagnetic components | Superior electrical conductivity | Heavy and expensive | Medium |
This guide serves as a strategic resource for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on material properties, application suitability, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for magnetic Crane
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Magnetic Cranes?
The manufacturing of magnetic cranes involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets industry standards and operational requirements. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The initial step involves sourcing high-quality materials such as steel, copper, and specialized magnetic components. Suppliers should be vetted for quality compliance, and materials should undergo inspection for defects before entering the production line. This phase is crucial, as the quality of raw materials directly impacts the performance and durability of the magnetic crane.
-
Forming: In this stage, materials are shaped into the necessary components. Techniques such as forging, casting, and machining are commonly employed to create parts like the crane frame, magnet housing, and lifting hooks. Advanced technologies, including CNC machining, can ensure precise tolerances and enhance the structural integrity of the components.
-
Assembly: The assembly process involves integrating all individual components into a functioning magnetic crane. This includes the installation of the magnet system, electrical wiring, and control systems. Skilled technicians utilize standardized assembly procedures to ensure consistency and quality. It is essential that all parts fit correctly to prevent operational failures during lifting tasks.
-
Finishing: The finishing stage includes surface treatments such as painting, coating, or galvanizing to protect against corrosion and wear. Quality checks are performed to ensure that all components are free from defects and that protective coatings meet specified thickness and adhesion standards. This stage is vital for enhancing the crane’s lifespan, especially in harsh environments such as recycling plants and steel mills.
How Do Quality Assurance Practices Enhance the Manufacturing of Magnetic Cranes?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of magnetic cranes, ensuring that each unit meets international and industry-specific standards. Key QA practices include adherence to international standards like ISO 9001, as well as industry-specific certifications such as CE and API.
-
International Standards Compliance: ISO 9001 outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) that organizations must follow to ensure consistent quality in products and services. Manufacturers of magnetic cranes should implement a QMS that encompasses all production stages, from material sourcing to final assembly.
-
Industry-Specific Certifications: Certifications such as CE mark indicate compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. For B2B buyers, especially those from Europe, verifying these certifications is crucial for ensuring that the equipment meets local regulations.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Magnetic Crane Manufacturing?
To maintain high standards of quality, manufacturers implement several quality control (QC) checkpoints throughout the production process. These checkpoints typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials and components are inspected upon delivery. This includes verifying material certifications and conducting physical inspections to ensure compliance with specifications. Non-conforming materials are rejected or quarantined for further evaluation.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the assembly and forming processes. This can involve measuring component dimensions, checking for proper assembly, and ensuring that all systems function as intended. Real-time adjustments can be made to rectify any issues, minimizing waste and improving efficiency.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the completed crane undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it operates correctly and safely. This includes load testing, magnetic performance testing, and electrical system evaluations. FQC ensures that the crane meets operational specifications before it is shipped to the customer.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance for Magnetic Cranes?
Several testing methods are employed to assess the quality and performance of magnetic cranes. These include:
-
Load Testing: This method verifies the crane’s ability to lift specified weights safely. Testing is conducted under controlled conditions to ensure that the crane can handle its rated capacity without failure.
-
Magnetic Field Testing: This test measures the strength and uniformity of the magnetic field generated by the crane’s electromagnet. Ensuring optimal magnetic performance is critical for effective material handling.
-
Electrical Testing: Electrical systems, including wiring and controls, undergo testing to verify functionality and safety. This includes insulation resistance tests and functional checks of the control systems.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is essential. Here are effective strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturing processes and quality assurance systems in place. This firsthand assessment can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide detailed quality reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. These documents should outline any non-conformities and corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased review of the supplier’s operations and quality control practices. This is particularly useful for buyers unfamiliar with local standards and practices.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate various quality control and certification nuances when sourcing magnetic cranes. Factors to consider include:
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have specific regulations that impact the design and manufacturing of cranes. Buyers should be familiar with local standards, such as those enforced by the European Union or the American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
-
Supplier Certification: Buyers should prioritize suppliers with recognized certifications, as these indicate a commitment to quality and compliance with international standards. Certifications should be verified for authenticity.
-
Cultural and Logistical Considerations: Understanding cultural differences and logistical challenges is crucial when dealing with suppliers in various regions. Clear communication regarding quality expectations and delivery timelines can mitigate risks.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing magnetic cranes, ensuring they acquire reliable, high-quality equipment tailored to their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘magnetic Crane’
To assist international B2B buyers in procuring a magnetic crane, this guide provides a comprehensive checklist of actionable steps. Each step is designed to ensure that you make informed decisions, securing the right equipment for your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is essential before initiating the procurement process. Consider factors such as the types of materials you will be lifting, the weight capacity required, and the operational environment (e.g., indoor vs. outdoor use). This will help you identify the specific features needed in a magnetic crane, such as the type of magnet (electromagnetic or electro-permanent) and power supply specifications.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Researching the market will give you insights into available options and help you understand pricing trends. Utilize online platforms, industry reports, and trade shows to gather information on different manufacturers and models. Pay attention to user reviews and feedback to gauge the performance and reliability of various magnetic cranes.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to perform a thorough evaluation. Request company profiles, certifications, and case studies to assess their credibility and experience in manufacturing magnetic cranes. Additionally, seek references from clients in similar industries or regions to ensure they have a proven track record of delivering quality products.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Standards
Ensure that the magnetic cranes you are considering comply with relevant industry standards and safety regulations. Look for certifications from recognized bodies that confirm adherence to quality and safety protocols. This is particularly important in sectors such as steelmaking and recycling, where operational safety is paramount.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you have narrowed down your list of potential suppliers, request detailed quotations that outline pricing, terms, and conditions. Compare the cost against the specifications and features offered to ensure you’re getting the best value for your investment. Be sure to clarify any additional costs such as shipping, installation, and after-sales support.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
After-sales service can be a critical factor in your decision-making process. Inquire about warranty terms and the availability of technical support or maintenance services. A reliable supplier should provide comprehensive support to address any operational issues that may arise post-purchase, ensuring minimal downtime.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, it’s time to finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure that all terms, including delivery timelines, payment terms, and service agreements, are clearly outlined and agreed upon. A well-drafted contract will protect both parties and facilitate a smoother transaction process.
Following this checklist will empower you to make informed decisions when sourcing a magnetic crane, ensuring that you select the right equipment for your operational needs while maximizing value and minimizing risk.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for magnetic Crane Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Magnetic Cranes?
When sourcing magnetic cranes, buyers must consider several critical cost components that contribute to the overall price. The primary elements include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in manufacturing magnetic cranes significantly influence costs. High-grade steel and advanced magnetic systems (such as electromagnets or electro-permanent magnets) command higher prices but provide better performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can impact the pricing structure. Skilled labor is often required for assembling and testing cranes, especially for custom designs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and factory rent. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific crane designs can add to initial costs. However, investing in quality tooling can lead to better precision and reduced production times in the long run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous quality control measures ensure that cranes meet safety and performance standards. Investing in comprehensive QC processes can lead to higher upfront costs but ultimately reduces the risk of defects and operational failures.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs must be factored into the total cost. International shipping, particularly to regions like Africa or South America, may involve significant logistics expenses due to distance and customs procedures.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their costs and risks. This margin can vary depending on the supplier’s market position, reputation, and the level of service provided.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Magnetic Crane Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of magnetic cranes, affecting how buyers negotiate and manage their budgets:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Suppliers often provide better pricing for higher volumes, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs carefully.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom cranes designed for specific applications or with unique features may incur higher costs. Clear communication of requirements can help suppliers provide accurate quotes.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Cranes built with certified materials that meet international safety and performance standards may cost more upfront but offer better reliability and lower maintenance costs over time.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and location can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their expertise and reliability, while newer or less reputable suppliers may offer lower prices but with potential quality risks.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects logistics costs and responsibilities. Understanding terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can help buyers manage costs effectively.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Magnetic Crane Sourcing?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of pricing can lead to more cost-effective sourcing:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating terms, particularly for bulk orders. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service agreements.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also factors like maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime. A higher-quality crane may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to lower TCO.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences due to local market conditions, tariffs, and currency fluctuations. Conducting market research can provide insight into fair pricing.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Always ask for itemized quotes that break down costs. This transparency allows for better comparison between suppliers and helps identify areas for potential savings.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keeping abreast of industry trends and technological advancements can provide leverage during negotiations and help in making informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for magnetic cranes can vary widely based on the factors discussed. It’s essential for buyers to seek updated quotes from multiple suppliers and consider all cost components to make informed sourcing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing magnetic Crane With Other Solutions
When considering lifting solutions for ferrous materials, it’s essential to evaluate alternatives to magnetic cranes to find the most suitable option for specific operational needs. Each solution has its unique characteristics that can influence performance, cost, and usability in different environments, particularly in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
| Comparison Aspect | Magnetic Crane | Charge Crane | Gantry Crane |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency in lifting ferrous materials; quick operation | Excellent for loading/unloading in steel mills; handles heavy loads | Versatile for various lifting tasks; adaptable to different environments |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing electricity costs | Higher upfront costs due to complexity | Generally lower cost; budget-friendly for smaller operations |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires installation of electrical systems; moderate complexity | Complex installation; needs specific infrastructure | Easy to install; can be moved or adjusted as needed |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular checks on electrical systems and magnets needed | High; frequent maintenance on electrical and mechanical systems | Low; requires less frequent checks; simpler mechanics |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for recycling and scrap yards | Best for steelmaking and heavy industrial applications | Suitable for workshops and areas needing mobility |
What are the Pros and Cons of Charge Cranes?
Charge cranes are critical in steel production, designed to efficiently load scrap or ore into furnaces. They excel in environments requiring the handling of heavy materials, often reaching capacities of 150 tons or more. However, their complexity can lead to higher initial costs and significant maintenance demands. They also require specialized infrastructure, making them less adaptable than other solutions in less industrialized settings.
How Do Gantry Cranes Compare?
Gantry cranes offer a flexible and cost-effective solution for various lifting tasks. Their design allows for mobility, making them suitable for workshops or job sites where overhead systems are impractical. While they are generally less expensive and easier to implement than magnetic or charge cranes, they may not provide the same lifting capacity for heavy materials, especially in high-volume operations.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Lifting Solution?
Choosing the right lifting solution involves assessing the specific operational needs, budget constraints, and the materials being handled. Magnetic cranes are exceptional for ferrous materials and high-efficiency operations, especially in recycling contexts. Charge cranes are optimal for heavy-duty applications in steelmaking but come with higher costs and maintenance. Gantry cranes serve well in versatile applications where mobility and cost are prioritized. Understanding these alternatives allows B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and environmental conditions.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for magnetic Crane
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Magnetic Cranes?
When considering the procurement of magnetic cranes, understanding their essential technical properties is critical for ensuring optimal performance and safety in operations. Here are some of the key specifications that B2B buyers should prioritize:
1. Lifting Capacity
The lifting capacity of a magnetic crane is the maximum weight it can safely lift and transport. This specification is crucial because it directly affects operational efficiency and safety. Buyers must match the crane’s capacity to the typical loads they will handle, which often includes ferrous materials like steel and iron. A mismatch can lead to equipment failure or accidents.
2. Magnet Type
Magnetic cranes typically utilize either electromagnets or electro-permanent magnets. Electromagnets are activated by an electric current and are suitable for dynamic lifting operations, while electro-permanent magnets provide a strong hold without continuous power, making them energy-efficient. Understanding the type of magnet is essential for buyers to assess the crane’s suitability for specific applications, particularly in recycling and metal handling industries.
3. Power Supply Requirements
Magnetic cranes require a reliable power source to operate effectively. The specifications often include voltage and current ratings, which are vital for ensuring compatibility with existing electrical systems. Buyers should consider the implications of power supply on operational costs and downtime, especially in regions with unstable power sources.
4. Control System
The control system of a magnetic crane dictates how the operator engages and disengages the magnet. Modern cranes often come with sophisticated control systems that allow for precise movements and safety features. Understanding the control system is vital for ensuring ease of use and minimizing the risk of accidents during operation.
5. Safety Features
Safety is paramount in any industrial setting. Magnetic cranes should be equipped with features such as overload protection, emergency stop functions, and safety interlocks. These specifications are essential for compliance with industry safety standards and for protecting both personnel and equipment.
6. Operating Environment
The environment in which a magnetic crane operates can significantly impact its performance. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive substances should be considered. Buyers need to ensure that the crane is designed to withstand the specific conditions of their operational environment, which is especially relevant in outdoor or harsh industrial settings.
What Are the Common Trade Terms Related to Magnetic Cranes?
Familiarity with industry jargon and trade terminology is critical for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms that buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of magnetic cranes, buyers may work with OEMs to source specialized components that meet specific operational needs. Understanding OEM relationships can help ensure quality and compatibility.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and upfront investment. Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their purchases and manage cash flow effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This process is essential for comparing costs and securing the best deal on magnetic cranes. A well-prepared RFQ can streamline procurement and ensure that all necessary specifications are clearly communicated.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, which delineate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms is crucial for negotiating contracts and managing shipping logistics, particularly for international purchases of magnetic cranes.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to its delivery. This term is critical for B2B buyers to understand as it impacts project timelines and operational planning. Buyers should consider lead times when assessing suppliers to ensure they can meet their production schedules.
6. Warranty
A warranty is a promise made by the manufacturer regarding the quality and reliability of the product. In the case of magnetic cranes, warranties can cover defects and performance issues. Understanding warranty terms is important for buyers to protect their investments and ensure long-term reliability in their operations.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and ensure safety in their material handling processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the magnetic Crane Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers in the Magnetic Crane Sector?
The magnetic crane sector is experiencing significant growth, driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for efficient material handling in industries such as construction, steelmaking, and recycling is a primary driver. As urbanization accelerates in regions like Africa and South America, there is a heightened need for effective lifting solutions that can handle heavy ferrous materials. Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce has led to an uptick in logistics and warehousing operations, necessitating advanced lifting equipment like magnetic cranes to streamline operations.
Emerging technologies such as automation and IoT (Internet of Things) are also reshaping the market dynamics. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking cranes equipped with smart technology that enhances operational efficiency and reduces labor costs. For instance, cranes integrated with real-time monitoring systems can optimize load handling and improve safety measures. Additionally, the rise of electric and hybrid cranes is gaining traction due to their lower operational costs and reduced environmental impact, appealing to eco-conscious buyers across Europe and the Middle East.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing Trends in the Magnetic Crane Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the magnetic crane sector. As businesses increasingly focus on their environmental footprint, the demand for ethically sourced materials and sustainable manufacturing practices is on the rise. This shift is particularly evident in regions like Europe, where stringent regulations around emissions and waste management are in place.
Buyers are prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials in crane construction or obtaining green certifications. For instance, cranes designed with energy-efficient electromagnets not only reduce energy consumption but also minimize overall operational costs. Additionally, ethical sourcing practices ensure a transparent supply chain, which is vital for maintaining brand integrity and customer trust.
Investing in magnetic cranes that adhere to sustainability standards can also enhance a company’s reputation and marketability. As global consumers become more eco-conscious, aligning with sustainable practices can provide a competitive edge, especially in emerging markets where responsible sourcing is gaining traction.
What Is the Evolution of Magnetic Crane Technology and Its Impact on B2B Buyers?
The evolution of magnetic crane technology has significantly influenced the operational landscape for B2B buyers. Originally, cranes relied on simple mechanical hooks for lifting, which limited their efficiency and application scope. With advancements in electromagnet technology, magnetic cranes have emerged as essential tools for industries that require the handling of heavy ferrous materials, such as steel and scrap metal.
From basic designs, today’s magnetic cranes are equipped with sophisticated control systems that allow for precise load management and enhanced safety features. This technological evolution not only increases productivity but also reduces the risk of accidents, making them a preferred choice for businesses focusing on operational excellence.
Furthermore, the historical shift towards automation and digitalization in manufacturing and logistics sectors has elevated the importance of integrating magnetic cranes with smart technologies. B2B buyers are now more inclined to invest in advanced magnetic cranes that promise long-term value through improved efficiency and reduced operational costs, thereby transforming their material handling processes.
This comprehensive overview of the magnetic crane sector aims to equip international B2B buyers with actionable insights to navigate the evolving landscape, focusing on key trends, sustainability, and technological advancements that shape their sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of magnetic Crane
-
How do I select the right magnetic crane for my operations?
Choosing the right magnetic crane depends on several factors, including the type of materials you’ll be handling, load capacity, and operational environment. Assess your specific needs, such as the weight and dimensions of the ferrous materials, frequency of use, and available space. Consult with manufacturers to understand the various types of magnetic systems—like electro-permanent or electromagnets—and their suitability for your applications. Additionally, consider customization options to ensure the crane meets your operational requirements efficiently. -
What are the key features to look for in a magnetic crane?
When sourcing a magnetic crane, prioritize features such as load capacity, magnet type, safety mechanisms, and control options. Look for cranes equipped with robust electromagnets for heavy loads and adjustable settings for different material sizes. Safety features like emergency shut-offs and overload protection are critical. Furthermore, consider cranes with user-friendly control interfaces and remote operation capabilities, which can enhance operational efficiency and safety in various industrial environments. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing a magnetic crane?
Payment terms for magnetic cranes can vary significantly based on the supplier, order size, and region. Typically, manufacturers may require a deposit (often 30-50%) upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipment or upon delivery. International buyers should confirm the payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, letter of credit) and be aware of any additional fees related to currency conversion or international transactions. Always negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and budget. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for magnetic cranes?
The MOQ for magnetic cranes can vary widely among manufacturers. Some suppliers may offer single units, while others might require bulk orders to optimize production costs. For international buyers, it’s essential to inquire about MOQs during the supplier vetting process, as lower MOQs can facilitate trial runs or initial assessments of the crane’s performance in your operations. Additionally, consider the potential for discounts on larger orders, which can reduce overall procurement costs. -
How do I ensure quality assurance when sourcing a magnetic crane?
To ensure quality assurance, conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific compliance documents to verify their manufacturing standards. It’s also beneficial to ask for references or case studies from previous clients. Additionally, consider arranging for a factory visit or requesting a pre-shipment inspection to evaluate the crane’s quality and performance before finalizing the purchase. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing a magnetic crane?
Logistics play a crucial role in importing magnetic cranes. Consider factors such as shipping methods (ocean vs. air freight), customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to ensure proper packaging and compliance with import regulations. Additionally, factor in transportation costs, insurance, and potential duties or tariffs that may apply upon arrival in your country. Planning for these logistics can help avoid unexpected delays or expenses. -
How can I customize a magnetic crane to meet my specific needs?
Customization options for magnetic cranes are typically available through most manufacturers. Discuss your specific requirements with the supplier, including load capacity, magnet strength, and operational features. Many manufacturers offer tailored solutions, such as specialized magnet configurations or integration with existing systems. Be clear about your operational environment and any unique challenges you face, as this will help the manufacturer provide a more effective solution suited to your needs. -
What are the common applications of magnetic cranes in different industries?
Magnetic cranes are widely used in various industries, particularly in recycling, steelmaking, and manufacturing. They are essential in scrap yards for efficiently moving ferrous materials, in steel mills for handling raw materials and liquid metal, and in manufacturing facilities for transporting heavy metal parts. Understanding the specific applications within your industry can guide you in selecting the right type of magnetic crane that enhances productivity and safety in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Magnetic Crane Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. The Horseshoe Crab – Ship to Shore Magnetic Crane
Domain: thehorseshoecrab.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Ship to Shore Magnetic Crane
Price: $55.50 USD
Compatibility: Works with the magnetic container ship and magnetic truck.
Shipping Information: Non-personalized orders processed within 24 – 48 hours; personalized orders within 48 – 72 hours. Shipping via UPS or USPS. Customer responsible for claims on lost or damaged packages.
2. TeacherGeek – Electromagnet Crane 2.0
Domain: teachergeek.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Electromagnet Crane Activity – Not for sale, replaced by Electromagnet Crane 2.0. Mission: Design and build a crane to sort magnetic materials for recycling. Educational Goals: Utilize design and engineering process, encourage creativity, learn about electromagnetism, apply scientific method, innovate crane design. Recommended for ages 7-11. Two choices: Without Labs (self-directed) or With Labs (…
3. WF Steel & Crane – Magnet Cranes
Domain: wfsteelandcrane.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Magnet Cranes from WF Steel & Crane utilize electro-magnets for remote and controlled lifting. They enhance safety and efficiency in handling various materials including plates, beams, scrap materials, rebar, and castings. The cranes feature sealed coils encased in cast iron for durability in harsh environments. They can lift single or multiple items and allow for rotation of products for easy sta…
4. School Specialty – STEM/Engineering Activity
Domain: schoolspecialty.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, School Specialty – STEM/Engineering Activity, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. AIC Crane Lifting Solutions – Magnetic Overhead Cranes
Domain: aicraneliftingsolution.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Magnetic Overhead Crane – Lifting Magnetic Materials Efficiently. Types: AQ-QC Type with Electromagnetic Chuck, AQ-QCL Type with Electromagnetic Hanging Beam. Applications: Steel plants, scrap yards, steel mills, metal processing, recycling, warehouse operations. Specifications: AQ-QC Capacity: 10-50 tons, Span: 10.5~31.5m, Lifting height: 6~18m, Lifting speed: 7.8-13.3m/min, Trolley speed: 31.3-4…
6. LittleBits – Magnet Crane Model
Domain: littlebits.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: This company, LittleBits – Magnet Crane Model, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. iStock – Magnetic Crane Illustrations
Domain: istockphoto.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: This company, iStock – Magnetic Crane Illustrations, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for magnetic Crane
Why is Strategic Sourcing Essential for Magnetic Crane Procurement?
In the evolving landscape of industrial operations, strategic sourcing is pivotal for optimizing the procurement of magnetic cranes. These specialized cranes not only enhance efficiency in handling ferrous materials but also contribute significantly to operational safety and productivity across various sectors, such as steelmaking and recycling. By partnering with reputable manufacturers and suppliers, international buyers can ensure access to high-quality equipment tailored to their specific needs, ultimately reducing operational costs and minimizing downtime.
How Can International Buyers Benefit from Investing in Magnetic Cranes?
Investing in magnetic cranes offers considerable advantages, particularly for industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These regions are witnessing rapid industrialization and urbanization, leading to an increasing demand for effective materials handling solutions. By leveraging advanced magnetic crane technology, businesses can streamline their processes, improve material flow, and enhance overall productivity.
What’s Next for B2B Buyers in the Magnetic Crane Market?
Looking forward, the magnetic crane market is poised for growth, driven by innovations in magnet technology and automation. Buyers are encouraged to stay informed about industry advancements and explore partnerships with leading suppliers to capitalize on emerging opportunities. Engaging in strategic sourcing not only secures competitive pricing but also ensures alignment with sustainability goals and compliance with global standards. Take action now—evaluate your current material handling solutions and consider integrating magnetic cranes to elevate your operational capabilities.