Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric truck legal for the road
In today’s rapidly evolving logistics landscape, sourcing electric trucks legal for the road presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. As companies strive to reduce their carbon footprint and meet stringent regulatory requirements, the demand for compliant, efficient electric vehicles has surged. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of the global market for electric trucks, detailing various types, applications, and the critical factors influencing purchasing decisions.
Buyers will find valuable insights into the specifications and features that distinguish street-legal electric trucks, such as safety standards and customization options tailored to specific business needs. Furthermore, we provide a thorough analysis of supplier vetting processes, ensuring that organizations can identify reliable manufacturers who meet local and international compliance standards. Cost considerations, including upfront investments and long-term savings through reduced operational expenses, are also examined to facilitate informed financial decisions.
This guide empowers B2B buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly Germany and Brazil—to navigate the complexities of sourcing electric trucks. By equipping businesses with actionable insights and expert recommendations, we aim to simplify the decision-making process, enabling organizations to invest in sustainable transportation solutions that drive efficiency and align with global sustainability goals.
Understanding electric truck legal for the road Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Speed Vehicle (LSV) | Limited to 25 mph, equipped with safety features like seatbelts and lights | Urban logistics, last-mile delivery | Pros: Cost-effective, eco-friendly; Cons: Speed limitations may affect efficiency |
| Electric Mini-Truck | Compact size, modular design for various cargo configurations | Facilities maintenance, small deliveries | Pros: Versatile, easy to maneuver; Cons: Limited payload capacity compared to larger trucks |
| Electric Utility Vehicle | Designed for heavy-duty tasks, often features specialized attachments | Construction, landscaping, municipal services | Pros: High durability, customizable; Cons: Higher initial investment, maintenance costs |
| Full-Size Electric Truck | Larger capacity, designed for long-distance hauling | Freight transport, large-scale deliveries | Pros: High payload, long-range; Cons: Higher operational costs, charging infrastructure needed |
| Electric Cargo Van | Enclosed cargo space, ideal for transporting goods securely | E-commerce, service industries | Pros: Enhanced security, weather protection; Cons: Limited to urban environments due to size |
What are the Characteristics of Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs)?
Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) are designed to operate safely in urban environments, typically limited to speeds of 25 mph. These vehicles often come equipped with essential safety features such as seatbelts, mirrors, and lights to meet regulatory standards. LSVs are particularly suitable for last-mile delivery and urban logistics, allowing businesses to navigate congested areas efficiently. B2B buyers should consider the cost-effectiveness and eco-friendliness of LSVs, although the speed limitation may impact overall delivery efficiency.
How Do Electric Mini-Trucks Serve B2B Needs?
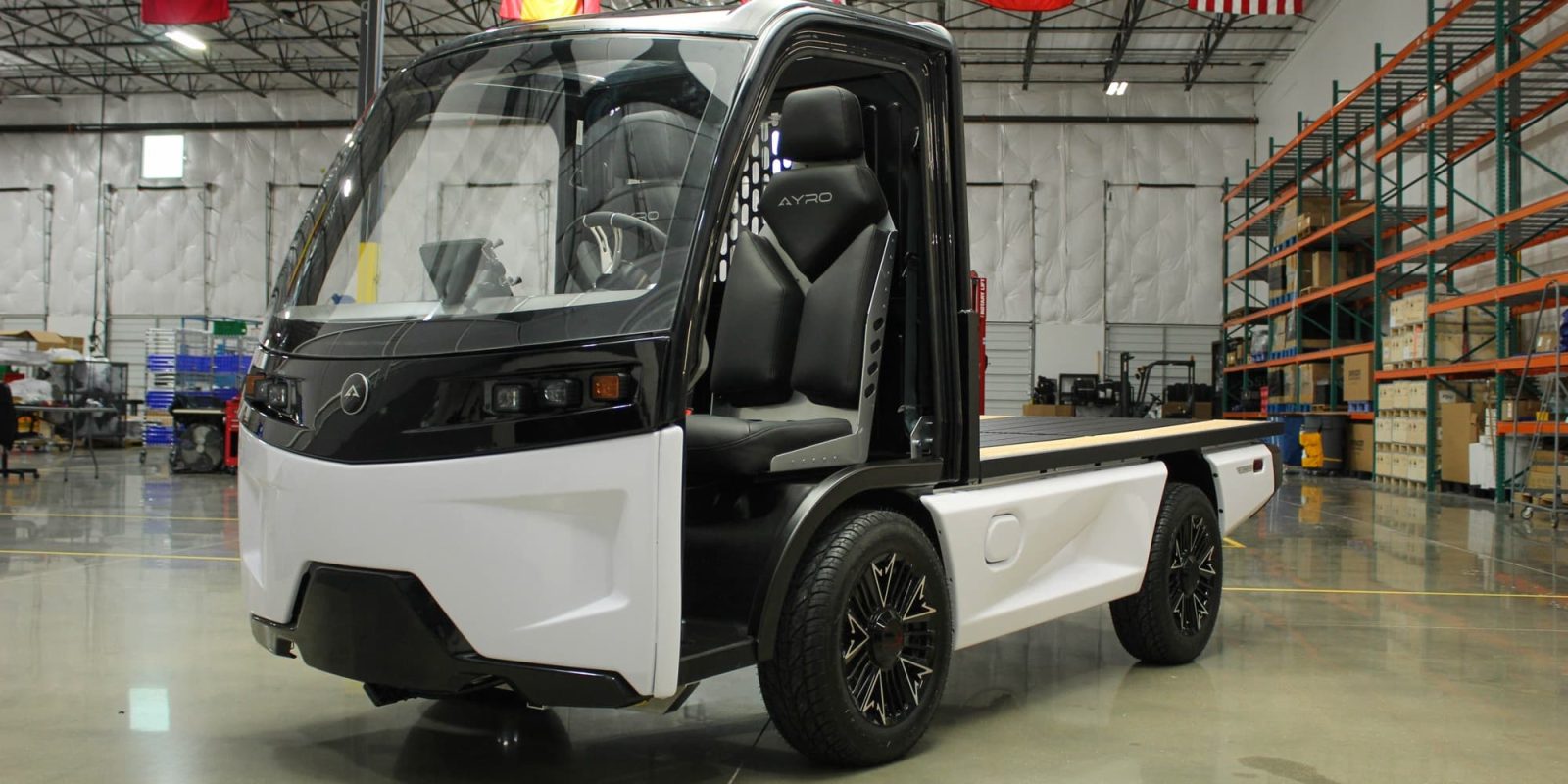
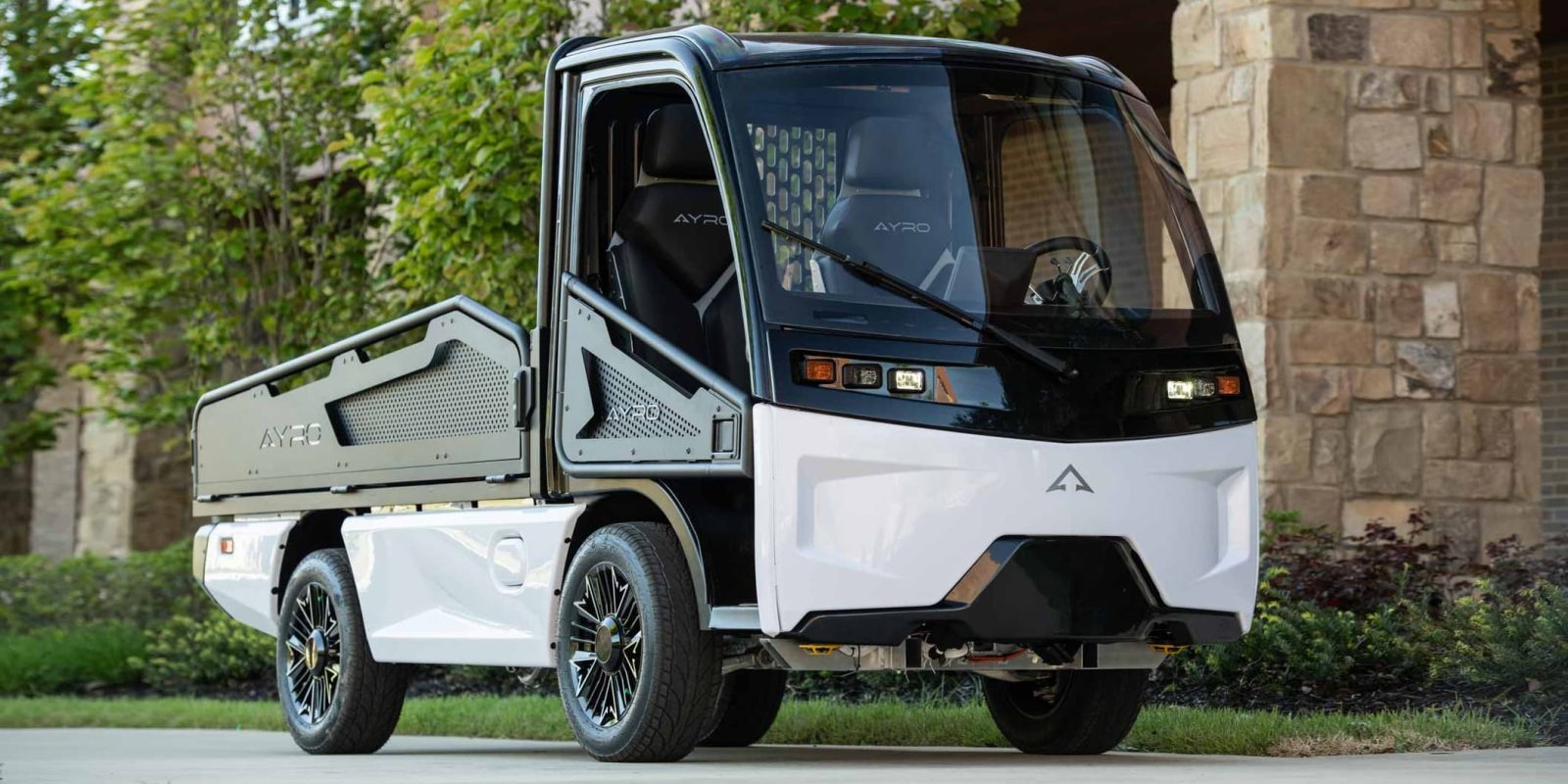
Electric mini-trucks, like the AYRO Vanish, offer a compact and modular design, making them highly versatile for various applications. Their small size allows for easy maneuverability in tight spaces, ideal for facilities maintenance and small deliveries. Buyers should evaluate the adaptability of these trucks for specific tasks, as their limited payload capacity can be a drawback for larger operations. However, their operational efficiency and reduced environmental impact make them a valuable addition to many fleets.
What Makes Electric Utility Vehicles Ideal for Heavy-Duty Tasks?
Electric utility vehicles are built for durability and can handle demanding tasks, often featuring specialized attachments for various applications. These vehicles are commonly used in construction, landscaping, and municipal services, where heavy lifting and rugged terrain are prevalent. B2B buyers should assess the initial investment against long-term savings from lower fuel and maintenance costs. While these vehicles may require a higher upfront expenditure, their robustness and versatility can justify the investment over time.
Why Choose Full-Size Electric Trucks for Freight Transport?
Full-size electric trucks are designed for long-distance hauling, offering substantial payload capacities. They are ideal for freight transport and large-scale deliveries, catering to businesses that require significant cargo space. Buyers should consider the operational costs, including charging infrastructure and maintenance. While full-size electric trucks present a higher initial investment, their efficiency in transporting large volumes over long distances can lead to cost savings in the long run.
How Do Electric Cargo Vans Enhance Delivery Security?
Electric cargo vans provide enclosed cargo spaces, making them ideal for securely transporting goods. They are particularly suited for e-commerce and service industries where product protection is paramount. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced security and weather protection against the potential limitations of maneuverability in urban environments. These vans can be a strategic investment for businesses focused on ensuring the safe delivery of goods to their customers.
Key Industrial Applications of electric truck legal for the road
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric truck legal for the road | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logistics & Delivery | Last-Mile Delivery in Urban Areas | Reduced operational costs and improved sustainability | Compliance with local road regulations and charging infrastructure availability |
| Facilities Management | Maintenance and Service Operations | Increased efficiency and reduced carbon footprint | Customization options for cargo and tools, durability for varied terrains |
| Agriculture | Crop Transportation and Supply Chain | Enhanced logistics for perishable goods | Load capacity, battery life, and adaptability to rural settings |
| Hospitality & Events | On-Demand Shuttle Services for Guests | Improved guest experience and eco-friendly image | Passenger capacity, comfort features, and local service support |
| Construction & Renovation | Material Transport on Job Sites | Reduced emissions and lower fuel costs | Versatile cargo options and ability to navigate tight spaces |
How Are Electric Trucks Used in Last-Mile Delivery Scenarios?
In the logistics sector, electric trucks are increasingly being utilized for last-mile delivery, particularly in urban centers. These vehicles are designed to meet local regulations for low-speed vehicles, allowing businesses to navigate congested areas efficiently. They help reduce operational costs through lower fuel expenses and contribute to sustainability goals by minimizing emissions. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing trucks that comply with local regulations and have access to charging infrastructure is crucial.
What Role Do Electric Trucks Play in Facilities Management?
Electric trucks serve as versatile tools in facilities management, performing tasks such as maintenance and service operations. Their compact design and ability to carry substantial payloads make them ideal for navigating tight spaces in urban settings or large campuses. By utilizing electric trucks, businesses can enhance operational efficiency while reducing their carbon footprint. Buyers should consider customization options for tools and storage, as well as the vehicle’s durability to handle various terrains, especially in regions with diverse climates like the Middle East and Europe.
How Can Electric Trucks Enhance Agricultural Logistics?
In the agricultural sector, electric trucks are becoming essential for transporting crops and managing supply chains. Their ability to operate quietly and efficiently while carrying perishable goods allows farmers to maintain the integrity of their products. For buyers in rural areas of Africa or South America, it is vital to evaluate the truck’s load capacity and battery life to ensure it meets the demands of transporting goods over longer distances. Additionally, adaptability to different terrains is a significant consideration when sourcing these vehicles.
How Do Electric Trucks Improve Guest Services in Hospitality?
In the hospitality industry, electric trucks are being used for on-demand shuttle services, enhancing guest experiences while promoting an eco-friendly image. These vehicles can comfortably transport guests to various locations within resorts or urban hotels. For B2B buyers in Europe, especially in eco-conscious markets like Germany, sourcing trucks with adequate passenger capacity and comfort features is essential. Local service support for maintenance and charging infrastructure is another critical factor for ensuring smooth operations.
What Benefits Do Electric Trucks Bring to Construction Sites?
Electric trucks play a vital role in construction and renovation projects by facilitating the transport of materials on job sites. Their lower emissions and reduced fuel costs align with the industry’s growing focus on sustainability. Buyers should look for trucks that offer versatile cargo options and can maneuver in tight spaces, which are common in urban construction sites. Additionally, understanding the local availability of charging stations and maintenance services is crucial for operational efficiency, particularly in regions with developing infrastructure.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘electric truck legal for the road’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Compliance with Local Regulations
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the complex web of regulations governing electric trucks that are legal for road use. This is particularly challenging for companies operating across multiple regions—such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—where laws can differ significantly. Buyers may find themselves uncertain about the specific requirements for homologation, safety standards, and environmental regulations, leading to delays and potential fines. The fear of investing in a vehicle that may not be compliant can stall purchasing decisions and create frustration.
The Solution: To effectively navigate these compliance issues, B2B buyers should begin by conducting thorough research into the specific regulations for each target market. Partnering with local legal advisors or consultants who specialize in automotive regulations can provide invaluable insights. It is also crucial to work closely with manufacturers that offer vehicles certified for compliance in the required jurisdictions. For example, ensuring that the electric truck has passed homologation tests as per the local standards will give peace of mind. Moreover, investing in vehicles that come with comprehensive documentation about their compliance will streamline the verification process and facilitate smoother operations across different regions. Regular training for staff on regulatory changes will also keep companies ahead of potential pitfalls.
Scenario 2: Addressing Range Anxiety and Charging Infrastructure
The Problem: A significant concern for B2B buyers is range anxiety, particularly in logistics and delivery sectors where electric trucks are increasingly utilized. Buyers worry about the operational limitations imposed by battery range, especially in areas lacking adequate charging infrastructure. This can lead to productivity losses if vehicles cannot complete their routes or require unexpected downtime for charging. Additionally, the fear of not being able to recharge quickly enough to meet delivery schedules can deter companies from fully committing to electric trucks.
The Solution: To mitigate range anxiety, B2B buyers should perform a detailed analysis of their operational routes and assess the availability of charging stations along these paths. Investing in electric trucks that boast longer battery life and faster charging capabilities will also alleviate concerns. Furthermore, companies can explore partnerships with charging infrastructure providers to install dedicated charging stations at their facilities. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures that vehicles are always ready for use. Implementing a fleet management system that tracks battery usage and charging needs in real-time can further optimize routes and charging schedules, ultimately maximizing productivity.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is Competitive
The Problem: While electric trucks promise lower operational costs, B2B buyers often struggle to assess the total cost of ownership (TCO) accurately. This includes not only the initial purchase price but also ongoing maintenance, battery replacement, and potential downtime. Many buyers fear that the perceived savings on fuel and maintenance may not outweigh the higher upfront costs compared to traditional vehicles, especially in regions with less developed electric vehicle (EV) markets.
The Solution: B2B buyers should conduct a comprehensive TCO analysis before making a purchase. This involves calculating all relevant costs, including initial investment, financing options, expected lifespan of the vehicle, maintenance costs, and energy consumption. Engaging with manufacturers that provide clear TCO calculators or case studies can facilitate informed decision-making. Additionally, seeking out incentives or subsidies for electric vehicle purchases available in their region can significantly lower upfront costs. Companies should also consider the potential for reduced insurance premiums and tax benefits associated with environmentally friendly vehicles. By fully understanding and documenting the TCO, businesses can make a compelling case for the financial viability of electric trucks in their fleets.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric truck legal for the road
What Materials Are Commonly Used in Electric Trucks Legal for the Road?
When selecting materials for electric trucks that are legal for road use, several factors come into play, including performance, durability, cost, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these vehicles: aluminum, high-strength steel, composites, and thermoplastics. Each material has unique properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly affect the performance and marketability of electric trucks.
How Does Aluminum Benefit Electric Truck Design?
Aluminum is widely used in the automotive industry due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating up to 600°F (315°C) and is highly resistant to oxidation, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros: Aluminum is lightweight, which enhances vehicle efficiency and range. It also offers good machinability, allowing for complex designs, and is recyclable, contributing to sustainability goals.
Cons: The primary drawbacks include higher material costs compared to steel and potential manufacturing complexities, especially in welding and joining processes.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s lightweight nature contributes to improved energy efficiency in electric trucks, making it ideal for applications requiring higher payload capacities.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe may prefer aluminum for its recyclability and compliance with stringent environmental regulations. However, they must consider the higher costs and ensure suppliers meet standards like ASTM or DIN.
What Role Does High-Strength Steel Play in Electric Truck Manufacturing?
High-strength steel (HSS) is another common material used in electric trucks, particularly for structural components. HSS can withstand significant stress and has a temperature rating that varies based on the specific alloy but can exceed 1,000°F (538°C) in some cases.
Pros: It offers superior durability and impact resistance, making it ideal for safety-critical applications. Additionally, it is generally more cost-effective than aluminum.
Cons: HSS is heavier than aluminum, which can negatively impact energy efficiency and range. It may also be more susceptible to corrosion unless properly treated.
Impact on Application: HSS is often used in the chassis and body panels to enhance safety and structural integrity, especially in urban environments where collisions may occur.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like South America and Africa should ensure that HSS used complies with local safety standards and regulations, such as ASTM A992 or JIS G3106.
How Do Composites Enhance Electric Truck Performance?
Composites, particularly fiber-reinforced plastics, are becoming increasingly popular in electric truck manufacturing due to their lightweight and high-strength properties. They can withstand temperatures up to 300°F (149°C) and offer excellent corrosion resistance.
Pros: Composites are lightweight, reducing overall vehicle weight and improving energy efficiency. They can be molded into complex shapes, providing design flexibility.
Cons: The primary limitation is the higher cost and complexity of manufacturing processes compared to metals. Additionally, composites may not be as easily recyclable.
Impact on Application: Composites are often used in body panels and interior components, enhancing aesthetics while contributing to weight savings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should be aware of the varying standards for composite materials and ensure compliance with regulations such as EN 13121.
Why Are Thermoplastics Important for Electric Truck Interiors?
Thermoplastics are increasingly utilized for interior components in electric trucks due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. They can withstand temperatures up to 200°F (93°C) and offer good chemical resistance.
Pros: Thermoplastics are lightweight, easy to mold, and can be produced at a lower cost than metals. They also provide good impact resistance.
Cons: While thermoplastics are durable, they may not offer the same structural integrity as metals, which can limit their use in load-bearing applications.
Impact on Application: Thermoplastics are ideal for dashboards, panels, and non-structural components, enhancing the vehicle’s overall design and user experience.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that thermoplastic materials meet local safety and environmental standards, including compliance with regulations like REACH in Europe.
Summary of Material Selection for Electric Trucks
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric truck legal for the road | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Body panels, chassis | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex joining | High |
| High-Strength Steel | Chassis, structural components | Durable, cost-effective | Heavier, corrosion susceptibility | Medium |
| Composites | Body panels, interior components | Lightweight, design flexibility | Higher cost, limited recyclability | High |
| Thermoplastics | Interior components, dashboards | Cost-effective, easy to mold | Limited structural integrity | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers in various international markets, helping them make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric truck legal for the road
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Electric Trucks Legal for the Road?
The manufacturing process of electric trucks designed for road use encompasses several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring the final product meets safety, performance, and environmental standards, especially for international markets.
How Does Material Preparation Impact Electric Truck Manufacturing?
Material preparation involves selecting and processing the appropriate materials, such as high-strength steel for the chassis and lightweight composites for the body. Suppliers often conduct thorough assessments to ensure that materials meet specific industry standards. This stage may also include sourcing environmentally friendly materials, aligning with global sustainability initiatives.
Advanced technologies, such as 3D printing, are increasingly used in material preparation to create prototypes and components efficiently. This innovation can reduce waste and speed up the design process, allowing manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands. The choice of materials significantly affects vehicle performance, durability, and overall cost, making it a critical consideration for B2B buyers.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Electric Truck Production?
In the forming stage, manufacturers employ various techniques to shape the prepared materials into desired components. Common methods include stamping, extrusion, and molding. For instance, stamping is often used for the chassis components, while injection molding is utilized for interior parts and dashboard assemblies.
This stage also requires precision engineering to ensure that all parts fit together seamlessly. Manufacturers may utilize computer numerical control (CNC) machines to achieve high levels of accuracy and repeatability. Effective forming techniques not only enhance product quality but also reduce assembly time, which is crucial for meeting delivery schedules.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Electric Truck Manufacturing?
The assembly stage is where all formed components come together to create the final product. This process typically involves both manual labor and automated systems to ensure efficiency and consistency. For electric trucks, assembly lines often integrate advanced robotics for tasks such as welding and component installation.
Quality control checkpoints are established throughout the assembly line to monitor the process. These checkpoints are crucial for identifying defects early, which can save costs and time. B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly process specifics, as a robust assembly operation can significantly influence the vehicle’s reliability and longevity.
What Finishing Techniques Are Employed in Electric Truck Production?
Finishing techniques are applied to enhance the vehicle’s appearance and protect it from environmental factors. Common finishing processes include painting, coating, and surface treatment. These processes not only provide aesthetic appeal but also contribute to corrosion resistance and overall durability.
Automakers often use eco-friendly paints and coatings to align with global sustainability standards. Finishing is also the stage where final inspections occur, ensuring that the product meets all regulatory requirements before it is dispatched to customers. For B2B buyers, understanding the finishing processes can help assess the long-term value of the electric truck.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Standards for Electric Trucks?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the production of electric trucks, particularly for international markets. Manufacturers typically adhere to internationally recognized standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management systems, and other industry-specific standards such as CE marking in Europe or UL certification in North America.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Integrated into Manufacturing?
Quality control is integrated into the manufacturing process through various checkpoints, including Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
- IQC ensures that incoming materials meet specified requirements before production begins.
- IPQC involves monitoring the manufacturing process in real-time to catch defects as they occur.
- FQC is the final inspection stage, where the completed electric trucks undergo rigorous testing to confirm that they meet all performance and safety standards.
These checkpoints help maintain a consistent quality level, which is critical for building trust with B2B buyers.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Electric Trucks?
Testing methods vary depending on the components being evaluated. Common methods include:
- Crash Testing: To ensure compliance with safety regulations.
- Performance Testing: To assess speed, acceleration, and battery efficiency.
- Environmental Testing: To evaluate how the vehicle performs under extreme weather conditions.
B2B buyers should look for manufacturers that conduct comprehensive testing to ensure the reliability and safety of their electric trucks.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial to ensuring product reliability. Here are several methods to achieve this:
- Audits: Conducting onsite audits allows buyers to assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control systems firsthand.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into past performance and adherence to standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s capabilities.
B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should pay special attention to quality certifications and compliance with local regulations to avoid potential legal issues down the line.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Certification for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating the complexities of quality certification can be challenging for international buyers. Each region may have different requirements for electric trucks. For instance, while European countries often require CE marking, North American buyers may prioritize FMVSS compliance.
Understanding these nuances is essential for B2B buyers to ensure that their suppliers meet local and international safety and performance standards. Engaging with suppliers who have experience in international markets can help streamline this process and ensure compliance.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for electric trucks legal for the road are intricate and multi-faceted. By understanding these stages and standards, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure reliable and compliant vehicles for their operational needs. Investing time in assessing supplier capabilities, quality certifications, and manufacturing processes will ultimately lead to successful partnerships and sustainable business growth.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘electric truck legal for the road’
In the rapidly evolving landscape of electric vehicles, sourcing an electric truck that is legal for road use is a critical undertaking for businesses. This guide provides a practical checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the complexities of procuring street-legal electric trucks, ensuring compliance with local regulations and alignment with operational needs.
Step 1: Understand Local Regulations
Before proceeding with your purchase, familiarize yourself with the legal requirements governing electric trucks in your region. This includes understanding the classifications, such as Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs), and the specific safety and operational standards they must meet. Different countries and regions have varying regulations, so it’s essential to consult local transport authorities or legal experts to ensure compliance.
Step 2: Define Your Technical Specifications
Identify the specific requirements for your electric truck based on its intended use. Consider factors such as payload capacity, speed limits, range, and operational environment. For example, if you require a vehicle for last-mile delivery, prioritize features like compact design and maneuverability in urban settings.
- Payload Capacity: Ensure the truck can handle the weight of goods you plan to transport.
- Top Speed: Verify that the truck complies with local speed regulations for street-legal vehicles.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research on manufacturers and suppliers of electric trucks. Look for companies with a proven track record in producing street-legal vehicles. Request documentation such as certifications, customer testimonials, and case studies to gauge their reliability and quality.
- Supplier Certifications: Check for compliance with international safety standards and local regulations.
- Reputation: Seek feedback from other businesses in your industry that have purchased similar vehicles.
Step 4: Request Prototypes or Demonstrations
Whenever possible, arrange for test drives or demonstrations of the electric trucks you are considering. This step is vital to assess the vehicle’s performance, comfort, and suitability for your specific needs. Pay attention to handling, acceleration, and the ease of loading and unloading goods.
- Performance Assessment: Ensure that the truck meets your operational requirements in real-world conditions.
- User Experience: Evaluate the ergonomics and features that enhance driver comfort and safety.
Step 5: Consider Total Cost of Ownership
Beyond the initial purchase price, analyze the long-term costs associated with the electric truck. This includes maintenance, charging infrastructure, insurance, and potential government incentives for electric vehicle purchases. Understanding the total cost of ownership will help you make a more informed financial decision.
- Maintenance Costs: Research the expected upkeep costs specific to electric vehicles.
- Incentives: Investigate any available subsidies or tax breaks for purchasing electric trucks.
Step 6: Finalize Financing Options
Explore different financing options available for electric truck procurement. This may include leasing, loans, or grants specifically designed for green vehicles. A well-structured financing plan can ease the financial burden and enhance cash flow management for your business.
- Leasing vs. Buying: Assess the benefits of each option based on your company’s financial strategy and vehicle usage.
- Grants and Subsidies: Look into government programs that support electric vehicle purchases to reduce upfront costs.
Step 7: Plan for Charging Infrastructure
Develop a strategy for charging the electric trucks, considering both the location and the type of charging stations needed. Evaluate whether you will install charging stations at your facility or utilize public charging networks. A reliable charging plan is crucial for maximizing operational efficiency.
- Charging Type: Decide between Level 2 or DC fast chargers based on vehicle specifications and usage patterns.
- Location Assessment: Ensure that charging stations are conveniently located to minimize downtime during operations.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing electric trucks that are legal for road use, ensuring compliance with regulations while meeting operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric truck legal for the road Sourcing
When considering the sourcing of electric trucks legal for road use, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers. This analysis encompasses various cost components, price influencers, and actionable tips for negotiation and purchasing strategies.
What Are the Key Cost Components for Electric Trucks?
The cost structure of electric trucks includes several critical components:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as batteries, steel, and electronic components, significantly impacts pricing. Lithium-ion batteries, in particular, can represent a substantial portion of the overall cost due to their essential role in performance and range.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is often necessary for assembling electric drivetrains and advanced electronic systems, which can drive costs higher in regions with higher wage standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized tools and machinery for production can be significant. Customizations and unique designs may require additional tooling, affecting the overall cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes are essential for ensuring compliance with safety standards, particularly for street-legal vehicles. This aspect incurs additional costs but is critical for market entry.
-
Logistics: Transportation of materials and finished products adds to the overall cost. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and customs regulations can influence logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a profit margin into their pricing, which can vary significantly based on market competition and demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Electric Trucks?
Several factors influence the pricing of electric trucks:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often secure better pricing due to economies of scale. Establishing a long-term partnership with a supplier may also yield favorable terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features, such as specialized cargo beds or advanced technology integrations, can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the necessity of these features against their budget.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials can affect not just the upfront cost but also the long-term durability and efficiency of the vehicle. Additionally, compliance with international quality standards can drive prices up.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their brand, while newer entrants might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international transactions, as they dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. These terms can significantly affect the total cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing electric trucks, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Open discussions about pricing can lead to better deals. Leverage volume commitments or long-term contracts to negotiate lower prices.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assess the TCO rather than just the purchase price. Consider factors like maintenance costs, fuel savings, and potential tax incentives for electric vehicles.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of potential tariffs, import duties, and currency fluctuations that can affect pricing. Engaging a local expert can help navigate these complexities.
-
Supplier Diversification: Avoid reliance on a single supplier. Exploring multiple options can provide leverage in negotiations and ensure competitive pricing.
Conclusion
Understanding the comprehensive cost and pricing analysis for electric trucks legal for road use is vital for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. By considering the various cost components, price influencers, and employing strategic negotiation techniques, businesses can secure favorable deals that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Keep in mind that prices fluctuate and should be viewed as indicative, with thorough research and supplier engagement being paramount for successful sourcing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing electric truck legal for the road With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Electric Trucks Legal for the Road
In the landscape of sustainable transportation solutions, electric trucks legal for road use present a compelling option for businesses seeking eco-friendly logistics. However, organizations may consider several alternatives that also aim to optimize efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Below, we compare electric trucks with two viable alternatives: electric vans and traditional diesel trucks.
| Comparison Aspect | Electric Truck Legal For The Road | Electric Van | Traditional Diesel Truck |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Top speed of 25 mph; payload up to 2,204 lbs | Similar speed; typically lower payload capacity | High speed and payload capacity, but less efficient in urban areas |
| Cost | Starting at $22,308 | Generally higher upfront cost, around $35,000 | Lower initial cost, but high fuel and maintenance expenses |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure; regulations for street use | Easier to implement in urban settings; fewer regulations | Widely accepted; existing infrastructure but may face urban access restrictions |
| Maintenance | Lower maintenance due to fewer moving parts | Similar low maintenance; may require specialized service | Higher maintenance costs; more frequent repairs needed |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for last-mile delivery in urban settings | Suitable for urban logistics and small deliveries | Best for long-distance transport and heavy-duty applications |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Vans?
Electric vans serve as a robust alternative to electric trucks, especially in urban environments. They typically offer similar performance in terms of speed and efficiency while providing ample cargo space. The downside, however, is that electric vans usually have a higher upfront cost compared to electric trucks and may have a lower payload capacity. Their implementation is often smoother due to less stringent regulations, making them a practical choice for businesses focused on last-mile delivery.
How Do Traditional Diesel Trucks Compare?
Traditional diesel trucks have long been the backbone of the logistics industry due to their high payload capacity and ability to cover long distances quickly. They are often less expensive to acquire upfront compared to electric options. However, they come with substantial ongoing costs related to fuel and maintenance, not to mention the environmental impact associated with diesel emissions. Additionally, many urban areas are beginning to impose restrictions on diesel vehicles, which could limit operational flexibility for businesses.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When evaluating the best transportation solution, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including operational requirements, budget constraints, and environmental goals. Electric trucks are particularly advantageous for businesses focused on reducing their carbon footprint and operating efficiently in urban settings. On the other hand, electric vans may be more appropriate for companies needing flexibility in logistics without the stringent regulations that come with electric trucks. Traditional diesel trucks may still hold value for businesses prioritizing heavy-duty applications and long-haul routes, despite their higher operational costs and environmental concerns.
Ultimately, the choice between electric trucks, electric vans, and traditional diesel trucks will depend on specific business needs, existing infrastructure, and strategic goals for sustainability and efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric truck legal for the road
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Electric Trucks Legal for the Road?
Understanding the technical properties of electric trucks that meet road regulations is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those engaged in logistics, delivery services, or municipal operations. Here are some key specifications to consider:
-
Payload Capacity
The payload capacity refers to the maximum weight an electric truck can safely carry, typically measured in pounds (lbs) or kilograms (kg). For instance, the Club Car Urban can handle up to 2,204 lbs. This property is essential for businesses as it directly impacts operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Knowing the payload capacity helps in planning deliveries and ensuring compliance with local regulations regarding weight limits on public roads. -
Top Speed
The top speed of electric trucks varies based on their classification (e.g., Low-Speed Vehicle or LSV). Many LSVs, like the AYRO Vanish, are limited to a maximum speed of 25 mph (40 km/h) to comply with safety standards. Understanding the top speed is vital for businesses that rely on timely deliveries in urban areas. It affects route planning and delivery schedules, especially in high-traffic environments. -
Battery Capacity and Range
Battery capacity, often measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), dictates how far an electric truck can travel on a single charge. A higher capacity translates to a longer range, allowing for more extended operations without recharging. For example, vehicles with larger battery packs may be more suitable for last-mile deliveries in remote areas. B2B buyers should assess the operational range to match their logistics needs, ensuring that vehicles can complete routes without downtime for charging. -
Homologation and Compliance
Homologation refers to the certification process that vehicles must undergo to meet specific safety and performance standards. In many regions, including North America and Europe, electric trucks must adhere to local regulations to be street-legal. Understanding homologation is essential for B2B buyers to ensure that the vehicles they purchase are compliant and safe for public road use, reducing the risk of legal complications. -
Chassis Material and Construction
The chassis material, often steel or aluminum, affects the durability, weight, and overall performance of the vehicle. A galvanized steel chassis, for instance, offers corrosion resistance and longevity, which is critical for commercial vehicles exposed to harsh conditions. For buyers, selecting vehicles with robust construction can lead to reduced maintenance costs and longer service life.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know When Purchasing Electric Trucks?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline the purchasing process and enhance negotiations. Here are several essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces components that are used in another company’s end product. In the context of electric trucks, knowing the OEM can help buyers understand the quality and reliability of the parts being used, which directly influences vehicle performance and longevity. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers as it can impact cash flow and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their operational needs without overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price proposals from suppliers for specific products or services. For buyers of electric trucks, issuing an RFQ can ensure competitive pricing and help in comparing different offerings based on specifications, delivery terms, and overall cost. -
Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. They clarify issues like shipping costs, insurance, and risk transfer. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to navigate logistics and ensure that all parties are aware of their obligations during the shipping process. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
TCO encompasses all costs associated with purchasing and operating a vehicle over its lifetime, including initial purchase price, maintenance, fuel (or charging), and resale value. For B2B buyers, calculating TCO helps in evaluating the long-term financial viability of electric trucks compared to traditional vehicles.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and regulatory requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the electric truck legal for the road Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers for Electric Trucks Legal for the Road?
The electric truck market is witnessing a transformative phase driven by several global factors. Increasing urbanization and the demand for sustainable logistics solutions are propelling the adoption of electric trucks, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. B2B buyers are increasingly focusing on last-mile delivery solutions that can navigate urban settings efficiently, which is where electric trucks excel due to their compact design and low operational costs.
Moreover, regulatory frameworks are evolving to support electric vehicle (EV) adoption. Governments are implementing stricter emissions regulations and providing incentives for electric vehicle purchases, creating a favorable environment for electric truck manufacturers. Emerging technologies, such as enhanced battery efficiency and smart fleet management systems, are also reshaping sourcing trends, making electric trucks more appealing for commercial use.
The market dynamics are further influenced by the growing emphasis on fleet electrification. Companies are looking to reduce their carbon footprint and operational costs, leading to increased investments in electric trucks as a viable alternative to traditional diesel vehicles. With a diverse range of applications—from delivery services to utility work—international B2B buyers are presented with unique opportunities to customize their electric truck fleets to meet specific operational needs.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Electric Truck Sector?
Sustainability is at the forefront of the electric truck market, influencing both procurement strategies and product development. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing environmentally friendly vehicles as part of their corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. The environmental impact of electric trucks is significantly lower than that of their internal combustion counterparts, primarily due to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and lower energy consumption.
Ethical sourcing practices are also becoming crucial, as buyers demand transparency in the supply chain. This includes the sourcing of sustainable materials, such as recycled metals and eco-friendly components, which are essential for the production of electric trucks. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and adherence to the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) standards are increasingly sought after by companies aiming to validate their sustainability claims.
Furthermore, the use of green certifications and materials not only enhances a company’s brand image but also aligns with the growing consumer preference for sustainable products. As B2B buyers invest in electric trucks, they are encouraged to engage with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical and sustainable practices, thereby fostering a circular economy within the industry.
How Has the Electric Truck Market Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the electric truck market reflects significant technological advancements and shifts in consumer preferences. Initially, electric vehicles were viewed as niche products due to limitations in battery technology and range. However, with recent innovations in battery efficiency and charging infrastructure, electric trucks have become more viable for commercial applications.
The introduction of regulatory measures aimed at reducing emissions has further accelerated the market’s growth. Countries across Europe and North America have set ambitious targets for electrification, pushing manufacturers to develop street-legal electric trucks that cater to diverse commercial needs.
As a result, electric trucks have transitioned from being a novelty to becoming essential components of logistics and transportation sectors. Today, they are recognized for their efficiency, lower total cost of ownership, and capability to meet stringent environmental standards, making them an attractive option for international B2B buyers looking to modernize their fleets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric truck legal for the road
-
How do I ensure the electric truck I purchase meets legal requirements for my region?
To ensure compliance with local regulations, familiarize yourself with the specific vehicle classification and safety standards applicable in your region. For instance, in the U.S., electric trucks must meet the Low-Speed Vehicle (LSV) standards if they are to be street-legal. Conduct thorough research on homologation processes, which include testing vehicles for safety and performance criteria set by governing bodies. Collaborating with reputable manufacturers who understand local regulations can also simplify this process and ensure you acquire a compliant vehicle. -
What is the best electric truck for last-mile delivery in urban environments?
The ideal electric truck for last-mile delivery in urban settings is one that combines compact design, agility, and sufficient payload capacity. Models like the Club Car Urban and AYRO Vanish are designed for maneuverability in tight spaces while offering customizable cargo options. Look for features such as a top speed suitable for urban traffic laws, a durable build to handle various weather conditions, and extended battery life for longer operational hours. Evaluating these factors will help you select a truck that enhances your delivery efficiency. -
What customization options are available for electric trucks?
Customization options for electric trucks can vary significantly by manufacturer. Common customizations include different bed sizes, cargo configurations (like enclosed boxes or flatbeds), and features such as climate control systems, enhanced safety packages, and specialized tires for varied terrain. Additionally, some manufacturers offer bespoke solutions based on your specific operational needs, which can improve efficiency and functionality. Engaging with suppliers during the design phase can help you tailor a truck that meets your unique business requirements. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for electric trucks?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for electric trucks can differ depending on the manufacturer and your location. Typically, manufacturers may set MOQs to ensure production efficiency and cost-effectiveness. For B2B buyers, it is advisable to negotiate MOQs, especially if you are a small or mid-sized enterprise. Some manufacturers may offer flexibility or tiered pricing based on order size, which can help you manage initial costs while scaling your fleet over time. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing electric trucks internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases of electric trucks can vary widely based on the supplier, contract terms, and your creditworthiness. Common payment methods include bank transfers, letters of credit, and installment payments. It’s essential to clarify these terms upfront and ensure they align with your financial capabilities. Additionally, consider discussing options for partial payments upon delivery or performance milestones to mitigate risks associated with large capital expenditures. -
How can I verify the quality assurance (QA) practices of electric truck manufacturers?
To verify the quality assurance practices of electric truck manufacturers, request documentation of their QA processes, certifications, and compliance with international standards (like ISO 9001). Conducting factory visits or audits can provide insights into their production methods and quality controls. Additionally, seeking references or reviews from other B2B buyers can help gauge the reliability and performance of the vehicles produced by the manufacturer. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric trucks?
When importing electric trucks, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Ensure that your supplier provides detailed information on packaging and transport to minimize damage during transit. Understanding local import duties and taxes is crucial, as these can significantly impact overall costs. Collaborating with a logistics partner experienced in automotive imports can streamline the process and ensure compliance with all regulations. -
How do I assess the total cost of ownership (TCO) for electric trucks?
To assess the total cost of ownership (TCO) for electric trucks, consider not only the initial purchase price but also long-term operational costs, including maintenance, insurance, and energy consumption. Evaluate potential savings from reduced fuel costs and any government incentives for electric vehicle purchases. Additionally, factor in depreciation and resale value to get a comprehensive view of the financial implications over the truck’s lifespan. Utilizing TCO calculators can also provide valuable insights for informed decision-making.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Electric Truck Legal For The Road Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Club Car – Urban LSV
Domain: clubcar.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Product Name: Club Car Urban
Type: LSV (Low-Speed Vehicle) / Electric Truck
MSRP: Starting at $25,680 (LSV)
Capacity: Up to 1,400 lbs (LSV) / Up to 2,204 lbs (XR)
Speed: Street-legal up to 25 mph (LSV)
Features:
– 3-point seatbelts
– Mirrors
– Tail lights
– Brake lights
– Turn signals
– Horn
– In-dash storage compartment
– Backup camera system
– All-season road tires
– Premium instrument cluster
…
2. GEM – eL XD Electric Utility Vehicle
Domain: gemcar.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: GEM eL XD Electric Utility Vehicle
– Payload Capacity: 1,415 lbs
– Towing Capacity: 1,250 lbs
– Seating: 1-2 passengers
– Range: Up to 78 miles between charges (varies by model, battery, payload, and terrain)
– Dimensions: Length 146 in (371 cm), Width 55.5 in (141 cm), Height 73 in (186 cm)
– Bed Dimensions: 70 in (178 cm) long, 48 in (122 cm) wide
– Turning Radius: 194 in (493 cm)
– Wheelbase: 1…
3. Eli Zero – All-Electric Two-Seater
Domain: electrek.co
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Eli Zero: All-electric two-seater, expected to enter US market soon, pre-order program launching, designed to comply with LSV regulations, estimated price around $15,000. Wink Motors: Four models (Sprout, Sprout Solar, Mark 1, Mark 2 Solar), prices under $10,000 for budget models, around $12,000 for premium models, four-seaters, fireproof lithium iron phosphate batteries, air conditioning, solar v…
4. TELO – All-Electric Mini Truck
Domain: telotrucks.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: {‘name’: ‘TELO MT1’, ‘type’: ‘All-Electric Mini Truck’, ‘dimensions’: {‘length’: ‘152 in’, ‘width’: ’73 in’, ‘height’: ’67 in’}, ‘bed_size’: ’60-96 in × 56 in × 18 in’, ‘seating_options’: [‘2 seats’, ‘5 seats’, ‘8 seats’], ‘performance’: {‘acceleration_0_60’: ‘6.0 s’, ‘power’: ‘300 hp’, ‘drivetrain’: ‘2WD’, ‘payload’: ‘2,000 lbs’, ‘towing’: ‘6,600 lbs’}, ‘battery’: {‘standard_range’: ‘260 mi’, ‘lo…
5. Maison Law – California Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs)
Domain: maisonlaw.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: California Low-Speed Vehicles (LSVs) are small, usually electric vehicles designed to travel at lower speeds than regular automobiles. Key details include:
– Range: Approximately 30 miles on a charge.
– Weight: Gross vehicle weight rating of 3,000 pounds or less.
– Speed: Maximum speed of 25 mph; can only travel on streets with a speed limit of 35 mph or less, unless local authorities state other…
6. Landline Media – Electric Truck Weight Increase
Domain: landline.media
Introduction: New Michigan law allows electric trucks to weigh up to 82,000 pounds, an increase from the previous limit of 80,000 pounds. The law permits electric truck tractors to exceed axle loading and weight load maximums by up to 2,000 pounds, while maintaining a gross weight limit of 82,000 pounds for electric truck tractors or combinations with semitrailers. This change aligns Michigan’s regulations with…
7. Moto Electric Vehicles – Street Legal Golf Carts & Electric Shuttles
Domain: motoelectricvehicles.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Moto Electric Vehicles offers a variety of street legal golf carts and electric shuttles, including:
1. **MotoEV Electro Neighborhood Buddy** – 6 Passenger (Back to Back) Highriser Street Legal Golf Cart
2. **MotoEV Electro Bubble Buddy** – 5 Passenger EMS Responder Electric Shuttle
3. **MotoEV Electro Transit Buddy** – 15 Passenger Shuttle
4. **MotoEV Electro Transit Buddy 15 Passenger XE** – Ha…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric truck legal for the road
In the evolving landscape of electric trucks that are legal for road use, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for businesses aiming to leverage this technology. Key takeaways highlight the importance of understanding vehicle homologation processes, which ensure compliance with safety and performance standards. This is particularly relevant for international buyers who must navigate diverse regulations across regions, including stringent requirements in Europe and emerging markets in Africa and South America.
Investing in electric trucks not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances operational efficiency, particularly in last-mile delivery scenarios. The versatility of models, like the Club Car Urban and AYRO Vanish, illustrates the potential for customization to meet specific business needs, from urban logistics to agricultural applications.
As we look to the future, the demand for electric trucks will only grow, driven by increasing regulatory support and market acceptance. International B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers to explore tailored solutions that fit their operational requirements. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, businesses can position themselves at the forefront of the electric vehicle revolution, unlocking new opportunities for growth and sustainability.