Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for farm electric vehicle
As the agricultural sector increasingly embraces sustainable practices, the demand for farm electric vehicles is surging. However, sourcing the right electric vehicles for agricultural applications poses significant challenges, particularly for international B2B buyers in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This comprehensive guide is designed to empower decision-makers by exploring the various types of electric farm vehicles, their applications, and the nuances of supplier vetting, pricing, and total cost of ownership.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into the advantages of electric utility vehicles, including their zero-emission capabilities, low operational costs, and adaptability to different agricultural environments. From compact models suited for vineyards and nurseries to robust off-road vehicles designed for rugged terrains, understanding the specifications and configurations available is crucial for optimizing farm operations.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and a thorough understanding of the electric farm vehicle landscape, this guide aims to facilitate informed purchasing decisions that align with sustainability goals and operational efficiency. Whether you are a farm manager in Germany or a procurement officer in Saudi Arabia, navigating the global market for electric farm vehicles has never been more accessible or essential.
Understanding farm electric vehicle Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Utility Vehicle (EUV) | Compact size, high load capacity, zero emissions | Farms, nurseries, greenhouses, vineyards | Pros: Eco-friendly, maneuverable; Cons: Limited range compared to traditional vehicles. |
| Off-Road Electric Utility Vehicle (EUTV) | Designed for rugged terrains, high towing capacity | Large estates, parks, challenging agricultural areas | Pros: Robust and durable; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Electric Agricultural Tractor | Specialized for fieldwork, larger than EUVs | Crop farming, large-scale agriculture | Pros: High efficiency for larger tasks; Cons: More expensive and requires more space. |
| Electric Cargo Transporter | Flatbed design, customizable configurations | Transporting goods and supplies across properties | Pros: Versatile and customizable; Cons: May lack advanced features of larger vehicles. |
| Electric Vineyard Utility Vehicle | Tailored for vineyard operations, compact and agile | Vineyards, orchards, horticultural applications | Pros: Ideal for tight spaces; Cons: Limited to specific agricultural tasks. |
What Are Electric Utility Vehicles (EUVs) and Their B2B Benefits?
Electric Utility Vehicles (EUVs) are compact, versatile vehicles designed for various agricultural tasks. Their zero-emission operation aligns with the increasing demand for sustainable farming practices. EUVs are particularly suitable for nurseries, greenhouses, and small farms where maneuverability is crucial. When purchasing, B2B buyers should consider factors such as load capacity, battery life, and the specific tasks they need the vehicle for, as these can significantly impact operational efficiency.
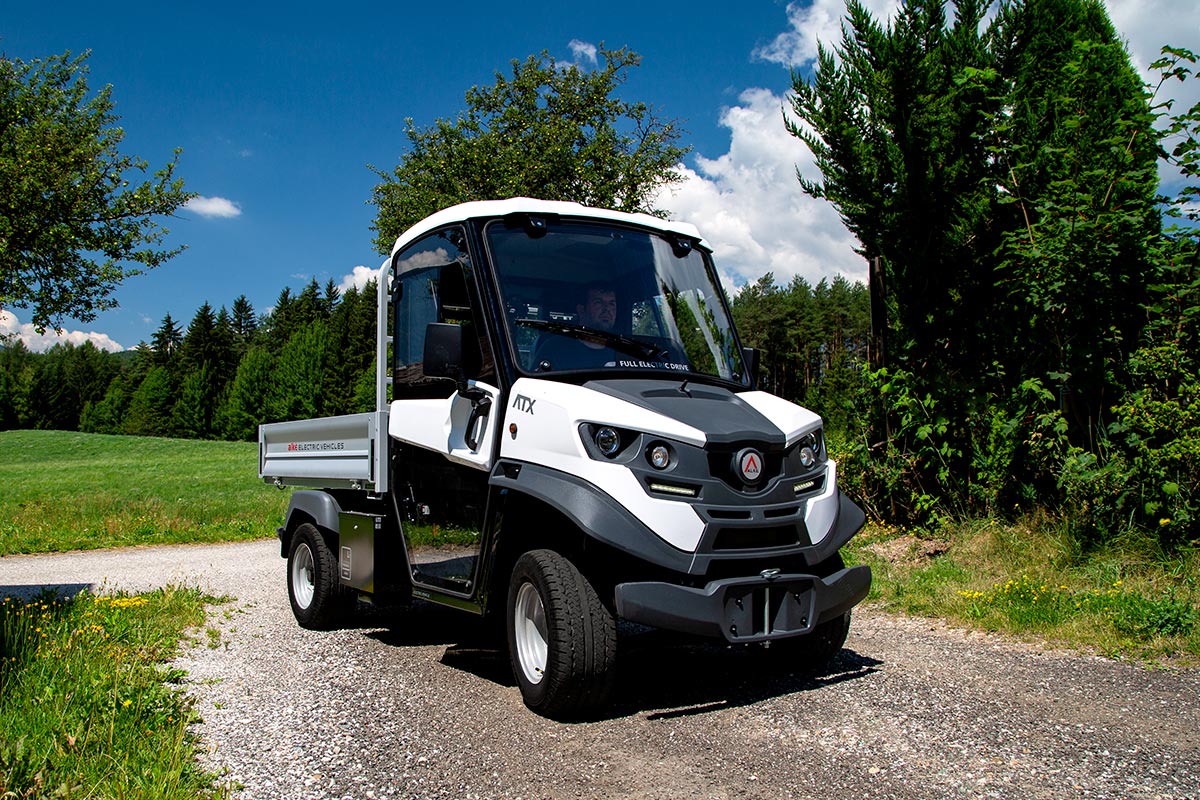
How Do Off-Road Electric Utility Vehicles (EUTVs) Meet Agricultural Demands?
Off-Road Electric Utility Vehicles (EUTVs) are engineered for rugged terrains, making them ideal for challenging agricultural environments. With a high towing capacity, they can handle heavy loads, making them suitable for large estates and parks. Buyers should evaluate the vehicle’s durability and battery performance, especially for operations involving steep gradients or unpaved roads. The initial investment may be higher, but the long-term benefits in efficiency and reduced emissions can justify the cost.
What Sets Electric Agricultural Tractors Apart for Large-Scale Farming?
Electric Agricultural Tractors are larger, specialized vehicles designed for extensive fieldwork. They offer high efficiency and can perform various tasks, making them essential for large-scale farming operations. B2B buyers should assess the tractor’s compatibility with existing equipment, its power output, and any necessary infrastructure for charging. While they come with a higher price tag, their ability to handle significant workloads can lead to substantial productivity gains.
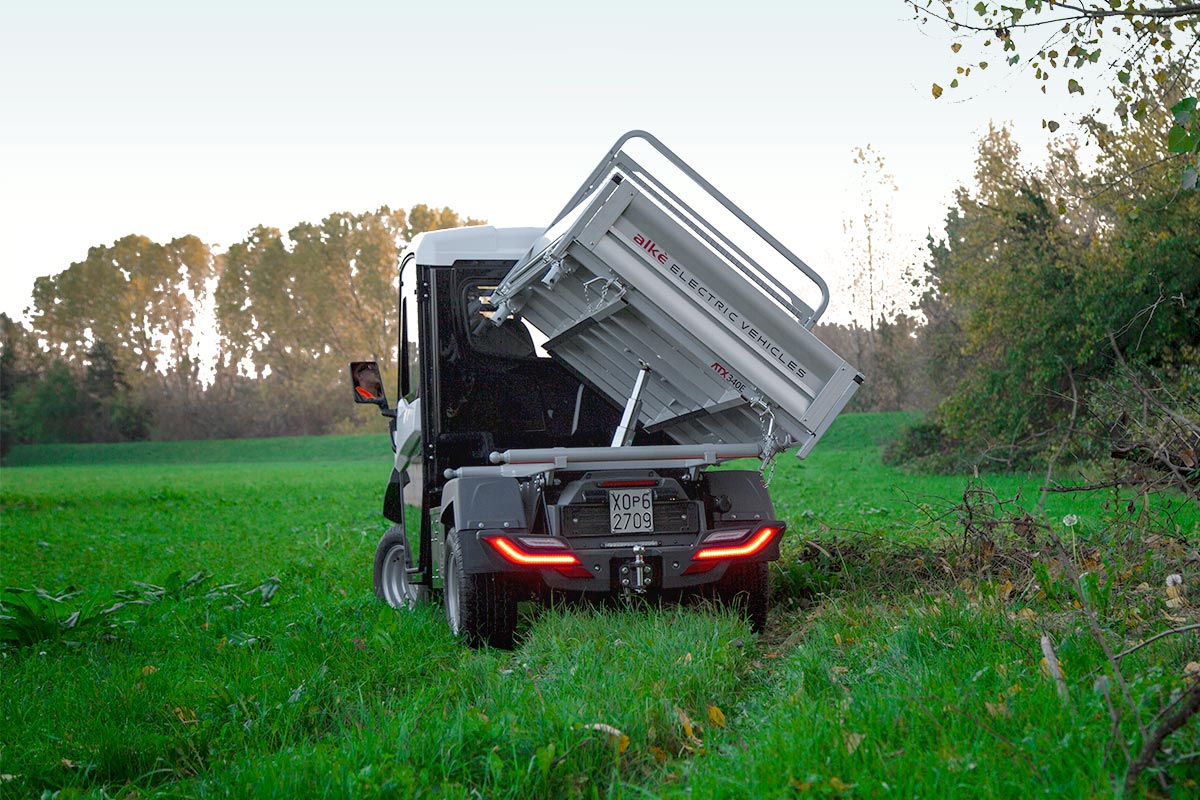
Why Choose Electric Cargo Transporters for Farm Operations?
Electric Cargo Transporters provide a flatbed design that can be customized for diverse applications, making them a flexible choice for transporting goods and supplies across agricultural properties. Their versatility allows for easy adaptation to specific tasks, which can enhance operational efficiency. Buyers should consider the vehicle’s load capacity and customization options to ensure it meets their logistical needs. While they may not have the advanced features of larger vehicles, their practicality makes them a valuable asset.
How Do Electric Vineyard Utility Vehicles Enhance Vineyard Management?
Electric Vineyard Utility Vehicles are specifically tailored for vineyard operations, offering compact design and agility that allow for easy navigation in tight spaces. They are particularly beneficial for transporting equipment and harvested goods within vineyards and orchards. B2B buyers should look for features like battery life and comfort options to improve operator conditions. Although their functionality is often niche, their efficiency in specialized tasks makes them a worthwhile investment for vineyard management.
Key Industrial Applications of farm electric vehicle
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of farm electric vehicle | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Transporting produce and equipment | Enhances efficiency and reduces operational costs | Load capacity, battery life, and terrain adaptability |
| Vineyards | Harvesting and transporting grapes | Increases productivity and minimizes damage to crops | Maneuverability in tight spaces and towing capacity |
| Greenhouses | Moving plants and supplies within facilities | Improves workflow and reduces labor costs | Compact design and ease of customization |
| Nurseries | Delivering seedlings and maintaining grounds | Supports sustainable practices and enhances plant care | Versatility in attachments and environmental impact |
| Public Parks | Maintenance and landscaping tasks | Reduces noise pollution and enhances visitor experience | Durability, battery range, and maintenance requirements |
How Are Farm Electric Vehicles Used in Agriculture?
In the agricultural sector, farm electric vehicles are primarily utilized for transporting produce and equipment across expansive fields. Their ability to operate without emissions makes them ideal for environmentally conscious operations, particularly in regions where sustainability is a growing concern. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should prioritize vehicles with a high load capacity and robust battery life to ensure they can complete daily tasks efficiently. Additionally, adaptability to various terrains is crucial for operations that involve challenging landscapes.
What Role Do Farm Electric Vehicles Play in Vineyards?
Vineyards increasingly rely on farm electric vehicles to streamline the harvesting process and transport grapes without causing damage. These vehicles are designed for maneuverability in narrow rows, allowing vineyard managers to optimize labor and enhance productivity. For international buyers, especially in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing vehicles with a good towing capacity and compact dimensions is essential. The ability to customize vehicles for specific vineyard tasks can further enhance operational efficiency.
How Are Farm Electric Vehicles Beneficial in Greenhouses?
In greenhouse settings, farm electric vehicles facilitate the movement of plants and supplies, significantly improving workflow. Their quiet operation is particularly advantageous in environments that require minimal disturbance. Buyers should consider vehicles that are compact and can be customized with various attachments, such as carts or watering units, to maximize functionality. As greenhouse operations expand globally, particularly in Europe, the focus on sustainable practices makes electric vehicles an attractive option.
Why Are Nurseries Adopting Farm Electric Vehicles?
Nurseries benefit from farm electric vehicles by using them to deliver seedlings and maintain grounds efficiently. These vehicles support sustainable practices by reducing emissions and noise, which is vital for plant health and customer satisfaction. International B2B buyers should look for versatile vehicles that can accommodate different attachments to cater to various nursery tasks. Additionally, understanding the environmental impact and sourcing vehicles that align with eco-friendly practices will resonate well with modern consumers.
What Advantages Do Farm Electric Vehicles Offer for Public Parks?
In public parks, farm electric vehicles are crucial for maintenance and landscaping tasks. Their low noise levels enhance the visitor experience while reducing pollution. Sourcing durable vehicles with a long battery range is essential for operations that cover large areas, particularly in regions with strict environmental regulations. Buyers should also consider the vehicle’s adaptability to different terrains and its ability to be equipped with various maintenance tools to meet diverse park management needs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘farm electric vehicle’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Range for Extensive Farm Operations
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of electric farm vehicles having a limited range, which can hinder productivity, especially on large agricultural properties. For instance, a vineyard manager may find that the vehicle runs out of charge before completing necessary tasks such as transporting supplies between distant fields or managing equipment across the estate. This not only disrupts workflow but also necessitates frequent recharging, leading to downtime and inefficiency.
The Solution: To address this issue, it’s crucial for buyers to select electric farm vehicles equipped with high-capacity batteries. When sourcing vehicles, look for models that offer options for extended battery life or quick charge systems. For instance, vehicles like the MAX-EV can be specified with battery packs that provide a range of up to 120 miles, making them suitable for extensive operations. Buyers should also consider investing in a robust charging infrastructure that includes fast chargers strategically placed around the property. By planning operations around charging schedules and selecting vehicles with efficient energy consumption, buyers can maximize the operational range and minimize downtime.
Scenario 2: Navigating Diverse Terrain with Electric Vehicles
The Problem: Many agricultural operations are characterized by diverse and challenging terrains, from steep hills to muddy fields. B2B buyers may encounter difficulties with electric vehicles that lack the necessary power and traction to operate effectively in these conditions. For example, a farm manager might purchase an electric utility vehicle only to discover that it struggles with steep slopes or off-road surfaces, leading to operational delays and increased maintenance costs.
The Solution: To overcome terrain challenges, buyers should prioritize electric farm vehicles designed specifically for off-road conditions. Look for vehicles with robust chassis and high towing capacities, such as those offered by Alke’, which can handle slopes up to 35%. When specifying vehicles, consider additional features like independent suspension systems and all-terrain tires that enhance traction and stability. It’s also beneficial to conduct field trials to assess vehicle performance in real-world conditions before finalizing a purchase. Ensuring that the chosen vehicle can navigate various terrains effectively will enhance productivity and reduce the risk of damage to the equipment.
Scenario 3: High Maintenance Costs and Environmental Regulations
The Problem: B2B buyers are increasingly pressured by rising maintenance costs and stringent environmental regulations. Traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles often require extensive maintenance and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, which can lead to compliance issues and affect a company’s sustainability goals. For instance, a greenhouse manager may find that their aging diesel-powered utility vehicles are not only costly to maintain but also fail to meet new environmental standards.
The Solution: Transitioning to electric farm vehicles can significantly reduce both maintenance costs and environmental impact. Buyers should look for vehicles that utilize advanced technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries and efficient electric motors, which require less maintenance than ICE vehicles. Moreover, selecting vehicles that are certified for low emissions helps in complying with environmental regulations. Engaging with manufacturers who provide comprehensive warranties and service packages can also mitigate long-term costs. For example, electric utility vehicles like the MAX-EV offer features that enhance durability and reduce wear and tear, ensuring a lower total cost of ownership. By investing in electric vehicles, buyers not only improve operational efficiency but also align their practices with sustainable agricultural standards.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for farm electric vehicle
What are the Key Materials Used in Farm Electric Vehicles?
When selecting materials for farm electric vehicles, several factors come into play, including performance, durability, cost, and suitability for specific agricultural applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of these vehicles, considering their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Perform in Farm Electric Vehicles?
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for structural components. It generally exhibits good corrosion resistance when treated, and it can withstand high temperatures and pressures.
Pros & Cons: Steel’s primary advantage is its strength and ability to handle heavy loads, which is crucial for farm utility vehicles that require robust construction. However, it can be heavy, which may affect vehicle efficiency and battery life. Additionally, while steel is generally cost-effective, the need for protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance can increase manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application: Steel is ideal for parts that require high strength, such as chassis and frames. However, the weight factor may necessitate careful design considerations to ensure optimal performance in off-road conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe may prefer steel components that meet specific standards such as DIN EN 10025. In contrast, buyers in Africa and South America may focus on cost-effectiveness and availability of local suppliers.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Farm Electric Vehicles?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity. It can withstand moderate temperatures and is often used in parts that benefit from reduced weight.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum enhances vehicle efficiency and battery performance, making it an attractive option for electric vehicles. However, aluminum is generally more expensive than steel and may require specialized welding techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used for body panels and components that require a balance of strength and weight. Its corrosion resistance is particularly beneficial for vehicles operating in wet or humid environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East may prioritize aluminum for its heat resistance, while European buyers may look for compliance with standards like ASTM B209 for aluminum sheet and plate.
How Does Composite Material Enhance Farm Electric Vehicles?
Key Properties: Composites, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. They can be engineered to meet specific performance requirements, such as impact resistance.
Pros & Cons: Composites are lightweight and can significantly improve vehicle efficiency. However, they can be costly and may require specialized manufacturing processes. Additionally, repair of composite materials can be more challenging compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Composites are ideal for components that require high strength with minimal weight, such as body panels and interior components. Their corrosion resistance makes them suitable for vehicles operating in diverse environmental conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of composite materials and skilled labor for manufacturing and repairs, particularly in regions with less access to advanced manufacturing technologies.
What Advantages Does Plastic Offer in Farm Electric Vehicles?
Key Properties: Plastics are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can be molded into complex shapes. They are generally good insulators and can withstand a range of temperatures.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastics is their versatility and low weight, which can enhance vehicle efficiency. However, they may not offer the same level of strength as metals and can be more susceptible to UV degradation over time.
Impact on Application: Plastics are often used for non-structural components, such as dashboards, panels, and enclosures. Their lightweight nature can help reduce overall vehicle weight, improving battery performance.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific types of plastics used, as some may not meet local environmental regulations. For instance, European buyers may focus on compliance with REACH regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Farm Electric Vehicles
| Material | Typical Use Case for farm electric vehicle | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Chassis and structural components | High strength and durability | Heavy, may require corrosion coating | Medium |
| Aluminum | Body panels and lightweight components | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, requires specialized welding | High |
| Composite | Body panels and interior components | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Costly, difficult to repair | High |
| Plastic | Non-structural components (e.g., dashboards) | Lightweight, versatile | Lower strength, UV degradation | Low |
By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for farm electric vehicle
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Farm Electric Vehicles?
The manufacturing process of farm electric vehicles (FEVs) is a complex sequence of stages that ensures the final product is robust, efficient, and tailored for agricultural use. Here’s a breakdown of the main stages involved:
-
Material Preparation: The first stage involves selecting high-quality materials that can withstand the rigors of farm operations. Common materials include steel for the chassis, lithium-ion batteries for energy storage, and durable plastics for body components. Suppliers must ensure that all materials meet international standards and are sourced from reliable vendors.
-
Forming: This stage includes various techniques such as stamping, bending, and welding to shape the vehicle’s components. Advanced manufacturing technologies like CNC machining may be employed for precision parts. Proper forming techniques are crucial for ensuring the structural integrity of the vehicle, especially given the demanding environments they will operate in.
-
Assembly: Once individual components are formed, they are assembled into the vehicle. This stage often employs a combination of automated processes and manual labor. Key systems such as the electric drive, suspension, and braking are integrated during this phase. Quality control measures should be in place to ensure that all components fit together seamlessly and function as intended.
-
Finishing: After assembly, the vehicles undergo a finishing process that may include painting, coating, and final inspections. This stage not only enhances the vehicle’s aesthetic appeal but also provides protective layers against corrosion and environmental damage.
What Key Techniques Are Used in the Manufacturing of Farm Electric Vehicles?
Several key techniques enhance the manufacturing of farm electric vehicles:
-
Robotic Welding: This technique ensures consistent and high-quality welds, essential for the vehicle’s safety and longevity. Robotics can also increase production speed and reduce labor costs.
-
Battery Management Systems (BMS): Integrating advanced BMS is crucial for monitoring battery health, optimizing charging cycles, and ensuring safety during operation.
-
Modular Design: Many manufacturers adopt a modular approach, allowing for easy upgrades and repairs. This design flexibility is especially beneficial for B2B buyers who may require customized solutions for specific agricultural tasks.
What International Standards and Industry-Specific Certifications Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with relevant international standards and certifications. Here are some key standards to consider:
-
ISO 9001: This international standard specifies requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers adhering to ISO 9001 demonstrate a commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: While more common in the oil and gas industry, some manufacturers may utilize API standards for components related to hydraulic systems in FEVs.
What Are the Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) is integral to ensuring the reliability and safety of farm electric vehicles. Key QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components as they arrive at the manufacturing facility. Ensuring that materials meet specifications is vital for the entire production process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing stages, IPQC checks are performed to monitor processes and identify any deviations from the set standards. This can include visual inspections and functional tests at various assembly points.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the vehicle is fully assembled, FQC involves comprehensive testing of the entire unit. This includes functionality tests, safety checks, and performance evaluations to ensure the vehicle meets all operational requirements.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed in Quality Assurance?
To ensure the quality and reliability of farm electric vehicles, manufacturers typically employ several testing methods:
-
Functional Testing: This involves testing the vehicle’s electric drive systems, braking systems, and other functional components to ensure they operate correctly under various conditions.
-
Durability Testing: Vehicles are subjected to rigorous testing that simulates real-world conditions, such as off-road terrains, load-bearing scenarios, and extreme weather conditions.
-
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Testing: Given the electrical components involved, ensuring that the vehicle meets EMC standards is crucial to prevent interference with other equipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are some strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC results, can help buyers assess the supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturer’s practices and adherence to international standards.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When dealing with suppliers from different regions, B2B buyers must be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certifications:
-
Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying requirements for certifications. For instance, while CE marking is critical in Europe, buyers in Africa or South America may have different regulatory requirements.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding the local business culture can influence negotiations and the implementation of quality control measures. Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication regarding quality standards.
-
Logistical Challenges: Transportation and logistics can impact the quality of the product upon arrival. Buyers should consider suppliers’ logistical capabilities to ensure that vehicles are delivered in optimal condition.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing farm electric vehicles, ensuring that they invest in reliable, high-quality products suited for their agricultural needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘farm electric vehicle’
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving agricultural sector, sourcing electric farm vehicles is essential for businesses aiming to enhance productivity and sustainability. This guide outlines a practical, step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers to ensure they make informed decisions when procuring these innovative vehicles. Each step emphasizes critical factors that contribute to the overall efficiency and ecological responsibility of farm operations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by clearly outlining your operational requirements, including load capacity, towing capabilities, and terrain adaptability. Consider the specific tasks the vehicle will perform, such as transporting materials or equipment across various landscapes. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for evaluating potential vehicles that align with your operational needs.
Step 2: Research Available Models
Conduct thorough research on the range of electric farm vehicles available on the market. Look for models that offer features such as compact dimensions for navigating tight spaces, robust chassis for durability, and efficient battery life. Assessing different models helps you identify which vehicles best meet your defined specifications and operational demands.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, it’s essential to vet potential suppliers meticulously. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and customer references, particularly from businesses in similar agricultural sectors or geographic regions. This evaluation will help you gauge the supplier’s reliability and their experience in delivering quality electric vehicles.
Step 4: Assess Environmental Impact and Compliance
Given the increasing focus on sustainability, ensure that the electric vehicles you consider are environmentally friendly and comply with local regulations. Look for vehicles that are 100% electric with zero emissions and evaluate the supplier’s adherence to ecological standards. This step is not only about compliance but also about enhancing your company’s green credentials.
Step 5: Analyze Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Calculate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) for each vehicle option, factoring in initial purchase price, maintenance costs, energy consumption, and potential savings from reduced fuel use. A thorough TCO analysis will provide a clearer picture of the long-term financial implications of your investment, helping you make a more sustainable economic choice.
Step 6: Request Demonstrations and Trials
Whenever possible, arrange for demonstrations or trial periods for the electric vehicles you are considering. This hands-on experience allows you to assess the vehicle’s performance in real-world conditions, ensuring it meets your expectations for usability and efficiency. Pay attention to factors such as ease of maneuverability and operator comfort during these trials.
Step 7: Review Warranty and Support Services
Finally, scrutinize the warranty and post-purchase support services offered by the supplier. A robust warranty can provide peace of mind, while reliable support services are crucial for minimizing downtime and ensuring your vehicles remain operational. Look for suppliers that offer comprehensive maintenance plans and responsive customer service.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for electric farm vehicles, ensuring they select the best options to meet their agricultural needs while promoting sustainability.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for farm electric vehicle Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Farm Electric Vehicles?
When considering the procurement of farm electric vehicles, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: This encompasses the raw materials used in manufacturing electric vehicles, such as lithium-ion batteries, steel for the chassis, and various electronic components. The quality of materials significantly influences the durability and performance of the vehicles.
-
Labor: Labor costs involve wages for skilled workers engaged in the assembly, quality control, and maintenance of electric vehicles. Skilled labor is often essential for the assembly of complex electronic systems and ensuring high-quality standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Investment in specialized tools and equipment is necessary for producing electric vehicles. This cost can vary based on the complexity of the vehicle design and the level of customization required.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that each vehicle meets safety and performance standards. This can involve testing components and systems, which adds to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs are critical, especially for international buyers. These costs can fluctuate based on distance, shipping methods, and import duties.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a profit margin to cover risks and ensure sustainability. Understanding the expected margin can provide insights into the pricing strategy of suppliers.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Farm Electric Vehicles?
Several factors influence the pricing of farm electric vehicles, particularly in a B2B context:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often offer discounts for bulk purchases. Understanding the MOQ can lead to significant savings for businesses planning to equip multiple vehicles.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customization options, such as the choice of battery capacity, towing capabilities, or additional features, can affect pricing. Tailoring vehicles to specific agricultural needs can incur additional costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO standards) may increase the initial cost but can enhance long-term reliability and performance, leading to lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to perceived reliability and service levels.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) can significantly affect the final cost to the buyer. Understanding these terms is essential for calculating the total landed cost of vehicles.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help Buyers Achieve Cost-Efficiency?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can leverage several strategies for effective negotiation:
-
Research Market Prices: Conducting thorough market research can help buyers understand the typical price range for farm electric vehicles. Knowledge of competitors’ pricing allows for better negotiation leverage.
-
Highlight Long-Term Partnerships: Emphasizing the potential for long-term collaboration can encourage suppliers to offer more favorable pricing or terms.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership: When discussing pricing, focus on TCO rather than just the upfront cost. Highlight the benefits of lower maintenance, fuel savings, and longer lifespan of electric vehicles compared to traditional options.
-
Flexibility on Specifications: Being open to slightly altering specifications or features can lead to significant cost reductions.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Engaging with local manufacturers can reduce shipping costs and lead to faster delivery times, enhancing overall efficiency.
What Should International Buyers Keep in Mind Regarding Pricing Nuances?
Buyers from diverse regions should be aware of the following nuances:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rates can impact costs significantly. It’s advisable to negotiate prices in stable currencies or consider hedging options.
-
Import Duties and Taxes: Understanding local regulations regarding import duties can help buyers budget effectively and avoid unexpected costs.
-
Cultural Factors: Relationship-building is often crucial in many regions. Establishing a rapport with suppliers can lead to better deals and terms.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that any vehicle meets local regulations and standards, as non-compliance can lead to additional costs or delays.
Conclusion
When sourcing farm electric vehicles, a comprehensive understanding of the cost structure, pricing influencers, and effective negotiation strategies is essential for achieving the best value. International buyers should conduct thorough research and consider all cost components to make informed purchasing decisions. While prices can vary widely based on numerous factors, focusing on long-term value and operational efficiency can lead to sustainable agricultural practices and enhanced profitability.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing farm electric vehicle With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Farm Electric Vehicles
In the evolving landscape of agricultural technology, B2B buyers must evaluate various solutions that can enhance operational efficiency while promoting sustainability. Farm electric vehicles (FEVs) are increasingly recognized for their zero-emission performance, but alternative solutions also exist that may suit different operational needs and budgets. This analysis compares FEVs with traditional diesel-powered tractors and biofuel vehicles, providing insights into their respective advantages and disadvantages.
| Comparison Aspect | Farm Electric Vehicle | Diesel-Powered Tractor | Biofuel Vehicle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High torque, quiet operation, suitable for off-road | High power output, versatile, suitable for heavy-duty tasks | Moderate power, dependent on biofuel quality |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower operating costs | Lower initial cost, higher fuel and maintenance costs | Moderate initial cost, fluctuating fuel prices |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires charging infrastructure, may need training | Widely available and understood, minimal training required | Requires sourcing of biofuels, may need infrastructure |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to fewer moving parts | Higher maintenance needs due to engine complexity | Moderate maintenance, dependent on fuel system |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for small to medium farms, vineyards, and greenhouses | Best for large-scale operations needing heavy lifting | Suitable for operations seeking sustainable fuel alternatives |
Pros and Cons of Diesel-Powered Tractors
Diesel-powered tractors have long been the backbone of agricultural operations, known for their robust power and versatility. They excel in heavy-duty tasks and can operate in a variety of conditions, making them suitable for large farms and diverse agricultural practices. However, they come with higher operational costs due to fuel consumption and maintenance needs, alongside environmental concerns due to emissions. For B2B buyers focused on immediate power needs and established infrastructure, diesel tractors remain a viable option, albeit one that may not align with sustainability goals.
Exploring Biofuel Vehicles as an Alternative
Biofuel vehicles represent a bridge between traditional fossil fuels and renewable energy sources. They utilize biofuels derived from organic materials, reducing greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional diesel. While they offer a more sustainable option, the performance can be variable based on biofuel quality and availability. Additionally, sourcing biofuels may require investments in infrastructure. For agricultural operations looking to enhance sustainability without a complete shift to electric, biofuel vehicles can provide an effective compromise.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Agricultural Solution
When selecting the appropriate solution for agricultural operations, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific needs, including farm size, operational tasks, budget constraints, and sustainability goals. Farm electric vehicles offer significant benefits in terms of environmental impact and long-term operating costs but may require initial investments in infrastructure. Diesel tractors remain practical for large-scale, heavy-duty operations, while biofuel vehicles present an alternative for those seeking a more sustainable fuel source. By aligning the chosen solution with operational goals and environmental commitments, buyers can optimize their agricultural practices for the future.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for farm electric vehicle
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Farm Electric Vehicles?
When considering the purchase of electric vehicles for agricultural purposes, understanding their technical properties is crucial. Here are several critical specifications that buyers should evaluate:
-
Load Capacity
– Definition: This refers to the maximum weight that the vehicle can safely transport, often measured in kilograms (kg) or pounds (lb).
– Importance: A higher load capacity allows for more efficient transport of goods, reducing the number of trips needed and optimizing labor costs on farms. -
Towing Capacity
– Definition: This is the maximum weight that the vehicle can tow, which is vital for hauling trailers or other equipment.
– Importance: In agriculture, towing capacity is essential for operations that require moving heavy loads, such as farm machinery or harvested crops, thereby enhancing operational efficiency. -
Battery Range
– Definition: The distance a vehicle can travel on a single charge, usually expressed in miles or kilometers.
– Importance: A longer battery range is critical for farms with vast areas to cover, ensuring that vehicles can complete their tasks without frequent recharging interruptions. -
Charging Time
– Definition: The duration required to fully charge the vehicle’s battery, typically measured in hours.
– Importance: Shorter charging times increase vehicle availability and reduce downtime, allowing farms to maintain productivity throughout the day. -
Terrain Capability
– Definition: This specification indicates the vehicle’s ability to operate on various types of terrain, including off-road conditions.
– Importance: Vehicles designed for rugged terrain can be used in diverse agricultural settings, from vineyards to hilly farms, making them versatile investments. -
Eco-Friendliness
– Definition: This term refers to the vehicle’s emissions and overall environmental impact.
– Importance: With increasing global emphasis on sustainability, electric vehicles with zero emissions can enhance a farm’s reputation and compliance with environmental regulations.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Electric Farm Vehicle Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can help buyers navigate the procurement process effectively. Here are key trade terms relevant to electric farm vehicles:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure that they are getting quality components and support for their electric vehicles. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ can help businesses plan their purchases and manage inventory effectively, especially when scaling operations. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing and availability for a specific product or service.
– Importance: An RFQ enables buyers to gather competitive pricing, ensuring they make informed financial decisions when purchasing electric vehicles. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including delivery and payment terms.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks associated with acquiring electric farm vehicles from overseas. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
– Definition: The comprehensive assessment of all costs associated with owning a vehicle over its entire life cycle.
– Importance: Evaluating TCO helps businesses make informed decisions by considering not just the purchase price but also maintenance, fuel savings, and depreciation. -
LSV (Low-Speed Vehicle)
– Definition: A vehicle designed for limited speed, often used in specific agricultural or urban environments.
– Importance: Understanding LSV classifications can help buyers select vehicles that comply with local regulations while serving their operational needs effectively.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can enhance their purchasing strategy for electric farm vehicles, ensuring they make informed and cost-effective decisions.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the farm electric vehicle Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Global Farm Electric Vehicle Market?
The farm electric vehicle (FEV) sector is experiencing significant transformation, driven by global demand for sustainable agricultural practices and advancements in electric mobility technology. Key market dynamics include a growing emphasis on reducing carbon footprints and enhancing operational efficiencies. International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly seeking compact, versatile electric utility vehicles that can operate effectively in diverse agricultural environments.
Emerging technologies such as cloud connectivity and real-time data analytics are revolutionizing how these vehicles are utilized. Cloud-connected vehicles allow for fleet management optimization, enabling operators to track vehicle performance, battery status, and location. This tech-savvy approach not only boosts productivity but also enhances decision-making processes in agricultural management. Additionally, the trend towards customization is gaining traction, with manufacturers offering a wide range of configurations and accessories that cater to specific agricultural needs, from vineyards to nurseries.
The shift from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to electric alternatives is particularly pronounced in regions where environmental regulations are tightening. For instance, countries in Europe are leading the charge with strict emissions targets, while emerging markets in Africa and South America are increasingly recognizing the long-term cost benefits of adopting electric vehicles. As fuel prices rise and maintenance costs for ICE vehicles become less favorable, the FEV sector is poised for continued growth.
How Is Sustainability Influencing B2B Sourcing for Farm Electric Vehicles?
Sustainability is at the forefront of sourcing decisions in the farm electric vehicle market. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing environmentally friendly solutions that align with their corporate social responsibility goals. Electric vehicles, with their zero-emission profiles, are an attractive option for agricultural businesses aiming to reduce their environmental impact.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are scrutinizing the sourcing of materials used in electric vehicles, such as lithium-ion batteries, to ensure they are ethically sourced and produced. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and adherence to responsible mining practices are becoming critical factors in procurement decisions.
Moreover, manufacturers are also focusing on creating vehicles that are not only efficient but also recyclable. This includes using sustainable materials and implementing take-back programs for end-of-life vehicles. Buyers who invest in sustainable solutions can enhance their market reputation, attract environmentally conscious consumers, and potentially benefit from government incentives aimed at promoting green technologies.
What Is the Historical Context of Farm Electric Vehicles?
The evolution of farm electric vehicles can be traced back to the early 21st century when the agricultural sector began to explore alternatives to traditional diesel-powered machinery. Initially, electric utility vehicles were seen as niche products, primarily used in specialized applications like greenhouses and small-scale farms. However, as advancements in battery technology and electric drivetrain systems emerged, the capabilities of these vehicles expanded significantly.
By the mid-2010s, the global push for sustainability began to reshape the landscape of agricultural practices. Farmers and agricultural businesses started adopting electric vehicles not only for their environmental benefits but also for their operational efficiencies. Today, electric farm vehicles are recognized as integral tools for modern agriculture, providing a versatile, cost-effective, and eco-friendly solution to meet the demands of a rapidly evolving industry.
This historical context highlights the growing acceptance and integration of electric vehicles within the agricultural sector, paving the way for future innovations and increased adoption across global markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of farm electric vehicle
-
How do I choose the right electric vehicle for my farm’s specific needs?
Selecting the right electric vehicle for your farm involves evaluating the terrain, load requirements, and the specific tasks you need the vehicle to perform. Consider factors such as towing capacity, battery life, and whether the vehicle can navigate narrow trails or steep inclines. Additionally, assess the vehicle’s adaptability to different agricultural tasks, such as transporting goods, equipment, or personnel. Engaging with suppliers who offer customization options can also help you tailor the vehicle to your operational needs. -
What features should I look for in a farm electric vehicle?
Key features to look for include a robust design for off-road capabilities, high towing capacity, and ample load capacity. Additionally, prioritize zero-emission technology for environmental compliance, a long-lasting battery with efficient charging options, and compact dimensions for maneuverability in tight spaces. Optional features like enclosed cabins for comfort, customizable accessories, and cloud connectivity for real-time vehicle monitoring can also enhance efficiency and productivity on your farm. -
What are the typical payment terms when sourcing electric farm vehicles?
Payment terms can vary by supplier but generally include options such as upfront payments, deposits with the balance due upon delivery, or installment plans. Some suppliers may offer financing options to help manage cash flow. It is crucial to clarify payment terms before finalizing any agreement, ensuring they align with your budget and procurement schedule. Always request a detailed invoice outlining all costs, including shipping and taxes, to avoid any surprises. -
How do I vet suppliers of electric farm vehicles effectively?
To vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation in the industry, including customer reviews and case studies. Request references from previous clients to gauge their experience with the supplier. Additionally, check for certifications or compliance with international standards, particularly if you are importing vehicles. Engage in direct conversations with potential suppliers to assess their responsiveness, expertise, and willingness to customize vehicles to meet your specific needs. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for electric farm vehicles?
MOQs can differ significantly among suppliers, often depending on production capabilities and the specific vehicle model. Some manufacturers may offer flexible MOQs for first-time buyers, while others may require bulk orders for better pricing. It is advisable to discuss your requirements with suppliers to determine if they can accommodate smaller orders or if they have specific MOQ guidelines. This can help you plan your procurement strategy more effectively. -
Are electric farm vehicles suitable for use in extreme weather conditions?
Many electric farm vehicles are designed to operate efficiently in various weather conditions, including extreme heat and cold. When sourcing, look for vehicles equipped with features such as insulated cabins and robust suspension systems. Additionally, inquire about the vehicle’s battery performance in different temperatures, as this can affect operational efficiency. Supplier specifications should provide insights into how their vehicles handle challenging climates, ensuring they meet your operational demands. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing electric farm vehicles?
When importing electric farm vehicles, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and local regulations regarding vehicle compliance. Collaborate with a logistics provider experienced in international trade to navigate these complexities. Ensure that you have all necessary documentation ready, including import permits and vehicle specifications. Understanding the timeline for delivery and potential delays is also crucial to align with your operational schedules. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for electric farm vehicles purchased internationally?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed product specifications and certifications from suppliers. Consider arranging for third-party inspections before shipment to verify compliance with your standards. Establish clear communication regarding warranty terms and service agreements, as these can affect long-term satisfaction with your purchase. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s after-sales support, including parts availability and maintenance services, to ensure ongoing vehicle performance and reliability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Farm Electric Vehicle Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Alke – Best Electric Farm Utility Vehicles
Domain: alke.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Best Electric farm utility Vehicles | Alke’ includes: ATX 340E Off road vehicles, ATX 330E Electric Vehicles, ATX 320E Small Electric Pick-up, ATX 310E, ATX ED electric vehicles – Double cab, Atex explosion proof vehicles, Waste Collection Electric Ambulance, Off Road Utility Vehicles, Electric Van, Snow blade, Electric vehicles with loading bed, Electric Ambulance, Airport vehicles, Refrigerated …
2. Facebook – Key Insights on Battery Performance
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Facebook – Key Insights on Battery Performance, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. 8760 Solar – Electric Farm Vehicles
Domain: 8760solar.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Electric farm vehicles are powered by batteries lasting up to 14 hours. They include drones, crop-picking robots, tractors, mowers, and forklifts. Electric vehicles address labor shortages and rising operational costs while increasing sustainability. The average price of gasoline is $4.37, while the electric gallon equivalent is $1.39, saving $2.98 per gallon. Potential annual savings by switching…
4. Wuzheng – Electric Three-Wheeled Farm Trucks
Domain: electrek.co
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Electric three-wheeled farm trucks from Wuzheng, China, are designed for affordability, versatility, and efficiency. They are used for transporting harvests, fertilizers, tools, and crops across fields, especially in rural areas with narrow and unpaved roads. Key features include a lower bed for easier loading, tailgates and side gates for conversion into flat-bed trucks, and tilting beds for dump…
5. EPower Trucks – Electric Utility Vehicles
Domain: epowertrucks.co.uk
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: EP AMP XL Road Legal Utility Vehicle: Power: Electric, Carrying Capacity: 400kg, Range: 50 – 70 miles, Speed: 24 mph, Towing Off Road: 150kg; Alke ATX 310 E Electric Compact Utility Vehicle: Power: Electric, Carrying Capacity: 620kg, Range: 45 miles, Towing Capacity: 2,000kg, Turning Radius: 2,600mm; Alke ATX 320 E Electric Compact Utility Vehicle: Power: Electric, Carrying Capacity: 635kg, Range:…
6. CEFC – Electric and Energy Efficient Farm Vehicles
Domain: cefc.com.au
Introduction: Electric and Energy Efficient Farm Vehicles are designed to reduce reliance on non-renewable energy sources, particularly diesel, in agricultural operations. Key features include: 1. Transition towards battery electric, fuel cell, or modern efficient vehicles. 2. Enhanced fuel efficiency and emissions reduction through replacement of aged vehicle fleets. 3. Co-benefits include reduced fossil fuel …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for farm electric vehicle
In the evolving landscape of agriculture, the adoption of electric farm vehicles presents a transformative opportunity for businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These vehicles not only enhance operational efficiency but also align with the growing demand for sustainable practices in farming. By strategically sourcing electric utility vehicles, companies can significantly reduce their environmental footprint while improving productivity.
Investing in electric farm vehicles, such as compact utility trucks and off-road capable models, allows agricultural enterprises to navigate narrow trails and challenging terrains without the emissions associated with traditional diesel-powered machinery. The long-term benefits, including lower maintenance costs and fuel savings, contribute to an attractive total cost of ownership, making these vehicles a smart financial choice.
As the agricultural sector continues to prioritize sustainability and efficiency, now is the time for international B2B buyers to explore the diverse offerings available in the electric vehicle market. Embrace this shift towards greener operations, and secure your competitive edge in the global marketplace. Connect with suppliers today to discuss tailored solutions that meet your specific operational needs and contribute to a more sustainable future in agriculture.